JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ When electric current flows through a wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. The direction of magnetic field produced is given by right hand cork screw rule or right hand thumb rule.
◆ Direction of magnetic field produced due to the current passing in a solenoid is given by clock rule.
◆ A compass placed near a current carrying conductor experiences a force. The direction in which the magnetic needle placed in the field of the coil deflects, is given by a SNOW rule or Ampere SWIMMING rule.
◆ Electromagnets are used for lifting heavy loads. It is also used in many electronics and electric appliances.
◆ D.C. motor converts direct current into mechanical energy.
◆ Electric generator converts mechanical energy into alternating current.
◆ Electromagnets are much stronger than permanent magnets.
◆ Fleming’s left hand rule. Stretch first finger, central finger and thumb of your left hand in mutually perpendicular directions, then if first finger points towards field (magnetic), central finger towards current, then the thumb points towards motion.
◆ Fleming’s right hand rule. Stretch first finger, central finger and thumb of your right hand in mutually perpendicular directions, then if first finger points towards field (magnetic), thumb denotes the direction of motion, then the central finger will point towards the direction of induced current.
◆ The direction of magnetic field at a point is given by the direction which a unit north pole placed at that point would move.
◆ Lines of force are closer together where the magnetic field is stronger and wider apart where the magnetic field is weaker.
TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Ans. A compass needle is a small bar magnet with one end as north and the other end as south pole. It is a well known fact that similar poles repel each other and dissimilar poles attract each other. When N-pole of a bar magnet is brought near the compass, the north pole of compass gets repelled while its S-pole is attracted so that compass needle gets deflected.
Q. 2. Draw magnetic lines around a bar magnet.
Ans. Place a bar magnet in the middle of a sheet of paper fixed on drawing board by using adhesive tape. Mark the boundary of the magnet with a pencil. Place compass near north pole of the magnet when south pole of the compass will point towards north pole of the magnet. Mark the two points a, b at the two ends of the needle. Move the needle to a new position such that Spole of compass needle is at b [position previously held by N-pole]. Repeat this till you reach south pole of the magnet (Fig. 4.1). Now Join the marked points on a paper by a smooth line which gives one magnetic line of force as shown in Fig. 4.2. Repeat this procedure taking different starting points.
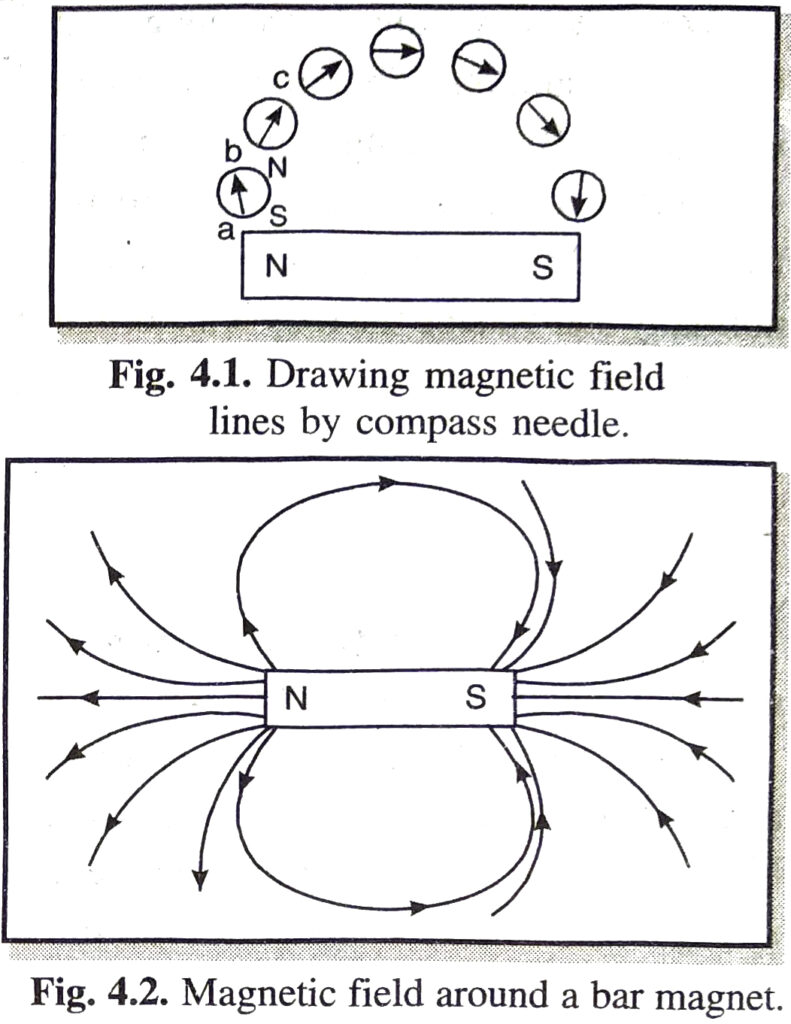
Q. 3. List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Ans. Properties (characteristics) of magnetic lines of force :
- These are the closed curves passing through the magnet. Outside the magnet lines of force start from north pole of the magnet and end at the south pole and inside the magnet, the direction of magnetic lines are from south pole to north pole.
- The two magnetic lines of force never intersect each other.
- They have a tendency to contract lengthwise which explains the attraction between opposite poles.
- The tangent at any point of the magnetic lines of force gives the direction of the field at that point.
- They exert lateral pressure upon each other, which explains repulsion between like poles.
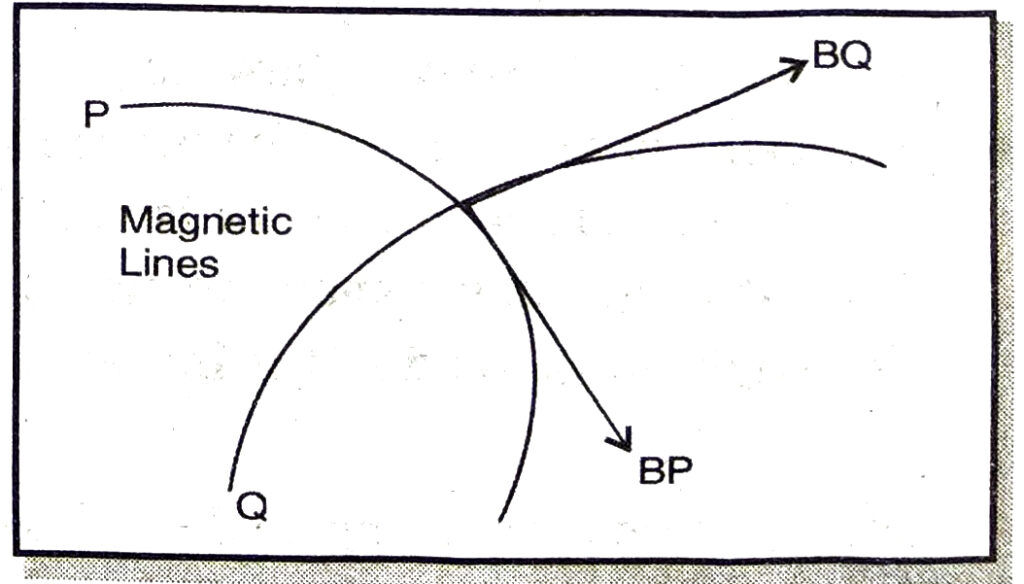
Q. 4. Why two magnetic lines of forces never intersect each other?
Ans. No two magnetic lines of force cross each other because, if they did so, then at the point of intersection; the compass needle would point towards two directions at the same time, which is not possible. Hence two magnetic lines never intersect each other.
Q. 5. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply right hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Ans. The direction of the magnetic field inside and outside loop is as shown in Fig. By applying right hand rule we find that the direction of magnetic field inside the loop is downward normally and outside the loop it is normal to the plane of paper.

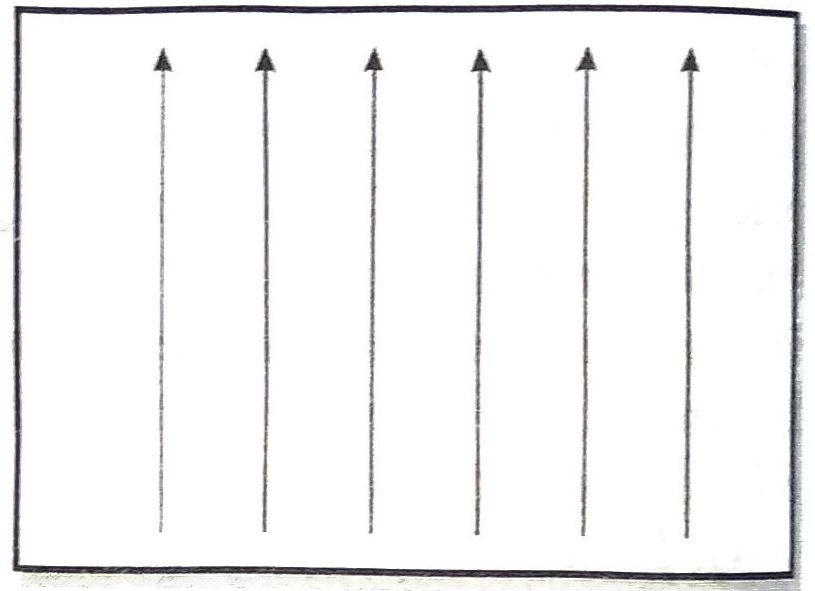
Q. 6. The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Ans. Uniform magnetic field is shown by equidistant and parallel lines as shown in Fig. If the parallel lines are close to each other, the field is strong. The stronger the field, the closer are the lines.
Q. 7. Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current
(a) is zero; (b) decreases as we move towards end; (c) increases as we move towards end; (d) is same at all the points.
Ans. (d) is correct. The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid is same at all the points.
Q. 8. Which of the following property of proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field ? [There may be more than one correct answer].
(a) mass; (b) speed; (c) velocity; (d) momentum.
Ans. (c) Velocity and (d) Momentum.
Q. 9. In activity shown, how do you think the displacement of rod AB will be affected :
(i) if the current in rod AB is increased;
(ii) a stronger horse shoe magnet is used;
(iii) length of the rod AB is increased.

Ans. (i) Since force acting on the rod is directly proportional to the current passing through it. Therefore, the displacement will be increased when current is increased.
(ii) Stronger the magnet, more will be the force and hence the displacement.
(iii) Force is also directly proportional to the length of the rod. Hence rod will be displaced more if the length is increased.
Q. 10. A positively charged particle emitted from a nucleus alpha particle projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is :
(a) towards south
(b) towards east
(c) downward
(d) upward.
Ans. (d) upward
Q. 11. State Fleming’s left hand rule.
Or
What is Fleming’s left hand rule for the direction of force on current carrying conductor ?
Ans. Fleming’s left hand rule. It states, “Stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the first finger points in the direction of magnetic field and central (second) finger points towards the direction of current then thumb points towards the direction of motion” as shown in Fig.

Q. 12. What is the principle of an electric motor ?
Ans. Principle of Electric motor. Electric motor is based upon the principle that when a current carrying coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque which rotates the coil.
Q. 13. What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor ?
Ans. The split rings act as a commutator in D.C. motor i.e., it reverses the direction of current through the circuit after every half cycle.
Q. 14. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Ans. There are mainly two methods to induce current in a coil.
1. By relative motion between coil and a magnet.

When the magnet is stationary [at rest as in Fig. (a)], no induced current is produced,
When magnet is moving with its N-pole towards the coil, deflection in galvanometer is as shown in Fig. (b). Direction of the current gets reversed when N-pole is withdrawn from inside the coil (going away from coil) as shown in Fig. (c). Faster the magnet.moves, more is the deflection and hence current in galvanometer.
Deflection produced in the galvanometer needle by the current is same when N-pole was moving down [Fig. (b)] or when south pole is out of the coil [Fig. (e)].
Current and hence deflection in the galvanometer needle will be again produced if magnet is kept at rest and coil is moved.
2. By changing current in the neighbouring circuit.
Take a nonconducting cylindrical tube (say of card board). Wind two set of coils I and II on it as shown. Connect a battery and a key to the ends of coil I and a galvanometer to the ends of coil II. When plug is inserted in key K, there will be an instantaneous deflection in galvanometer even though there is no cell in this circuit. Now take out the plug from key K. An instantaneous large deflection in opposite direction to previous deflection will be produced in galvanometer. Thus current has been induced in coil II due to increase or decrease of current in the coil I.

Q. 15. State the principle of electric generator.
Ans. Principle of Electric Generator. Electric generator is based upon Fleming’s right hand rule.
Fleming’s right hand rule. Stretch the thumb, fore-finger, control (middle) finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other. If fore-finger indicates the direction of magnetic field, the thumb shows the direction of motion of the conductor, the central (middle) finger will show the direction of induced current.

Q. 16. Name some sources of direct current.
Ans. Sources of direct current are: (i) Cell (ii) Battery (iii) D.C. generator.
Q. 17. Which sources produce alternating current ?
Ans. Alternating current is produced by A.C. generators. There are hydro-generator and thermal generators.
Q. 18. Choose the correct option:
A rectangular coil of copper wire is rotated in magnetic field. The direction of induced current changes once in each :
(a) two revolutions;
(b) one revolution;
(c) half revolution;
(d) one-fourth revolution.
Ans. (c) half revolution.
Q. 19. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Or
Write the two safety measures commonly used in electric circuit appliances.
Ans. Common Safety Measures used in Electric Circuits. Two most common safety measures used are:
1. A safety fuse of proper rating connected in a circuit prevents damage to the electric appliances and also the circuit due to overloading or short circuiting.
2. Earth wire prevents possible electric shock when live wire incidently touches the body of appliance.
Q. 20. An electric oven of 2kW power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect ? Explain.

A current of 9.09 A will flow in the circuit. Since the current rating of circuit is 5 A, the fuse (of 5 A) rating if inserted in the circuit will burn up. If no fuse is placed in the circuit, there may be a fire.
Q. 21. What precautions should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits ?
Ans. Precautions to avoid overloading.
1. Wires used for carrying current should be of proper current rating. Whereas wire of low current rating may be used for lighting electric bulbs, tubes, T.V. etc., and wires of higher current rating should be used for A.C., heating appliances etc.
2. There should be a separate circuit for heating appliance.
3. PVC of good quality should be used for insulating wires.
4. Each circuit should have a fuse of proper rating.
5. After every 3-4 years wires should be replaced by new wires of proper rating.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long wire? The field consists of:
(a) straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) concentric circle centred on the wire.
Ans. (d); concentric circles centred on the wire
Q. 2. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is :
(a) the process of charging a body.
(b) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(d) the process of rotating the coil of an electric motor.
Ans. (c) producing induced current in a coil due to relativemotion between a magnet and the coil.
Q. 3. The device used for producing electric current is called :
(a) generator;
(b) galvanometer;
(c) ammeter;
(d) motor.
Ans. (a) generator.
Q. 4. The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that:
(a) AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has a permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate higher voltage. higher voltage.
(c) AC generator will generate
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Ans. (d) AC generator has slip rings while DC generator has a commutator.
Q. 5. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit.
(a) reduces substantially;
(b) does not change;
(c) increases heavily;
(d) vary continuously.
Ans. (c) increases heavily.
Q. 6. State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electric energy.
(b) An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(d) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire.
Ans. (a) is false. It converts electric energy to mechanical energy.
(b) is true.
(c) is true.
(d) is false. Green is usually earth wire.
Q. 7. List three sources of magnetic field.
Ans. Sources of Magnetic field are:
1. Magnet.
2. Current carrying conductor.
3. Current carrying solenoid.
Q. 8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine north and south poles of current carrying solenoid with the help of bar magnet ? Explain.
Ans. Solenoid. It consists of a coil of a number of turns of insulated copper wire closely wound in the shape of a cylinder. Magnetic field around a current carrying solenoid is shown in Fig. (a).
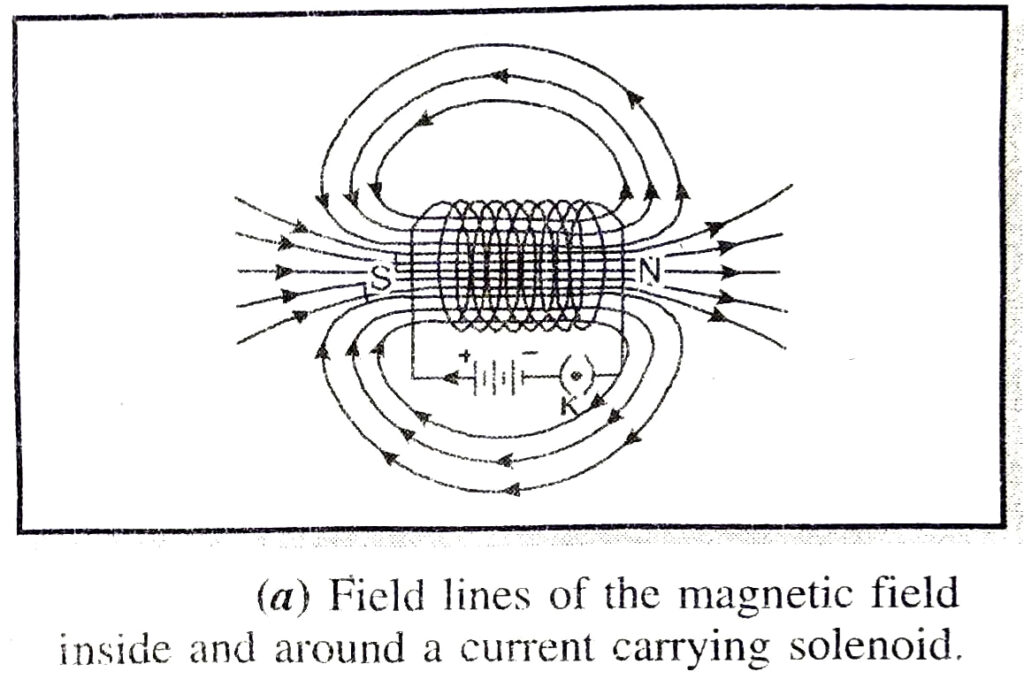
These magnetic lines due to current carrying solenoid appear to be similar to that of a bar magnet shown in Fig. (b).

One end [right end] of solenoid behaves like north pole and the other end [left end] behaves like south pole. Magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This means that the field is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
A soft iron rod when placed inside the solenoid behaves, like an electromagnet.
Q. 9. When is, the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field, the largest ?
Ans. When the current carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field the force experienced by a current carrying conductor is largest.
Q. 10. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam moving horizontally with back towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of the magnetic field ?
Ans. The magnetic field will be acting in vertically downward direction in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule. [Direction of the current should be considered in a direction opposite to the direction in which the electrons flow].
Q. 11. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in electric motor ?
Or
Explain principle and working of an electric motor. Draw a labelled diagram.
Ans. Electric motor. It is a device which is used to convert electric energy into mechanical energy.
Principle, “When a current carrying coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque which rotates the coil.”
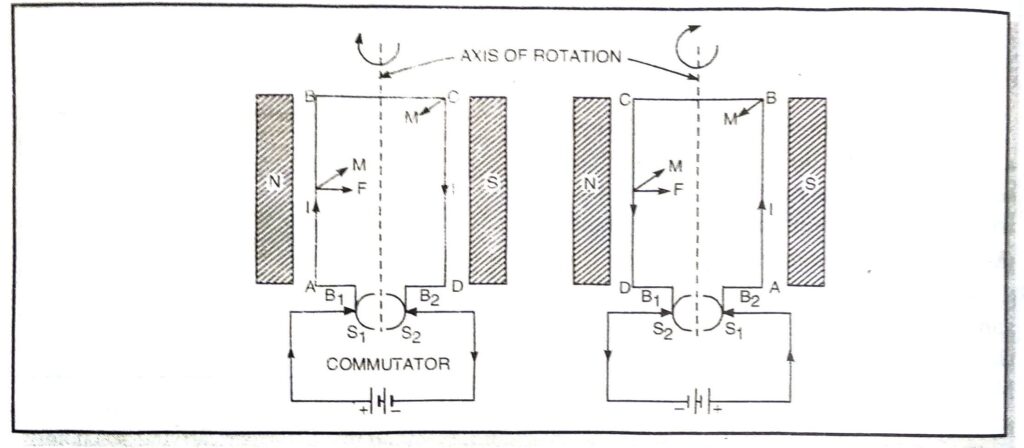
Fig. I indicates direction of current; F the direction field and M the direction of motion
Working. A direct current from a battery is passed through armature. The current flows in the coil along ABCD as shown in Fig. (a). The limb AB of the coil experience downward and CD of the coil experience upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule. These two equal and opposite forces constitute a couple tending to rotate the coil in clockwise direction. After half the rotation, brush B₁ has contact with S₂ and brush B₂ with S₁. The direction of the current gets reversed. The current now flows along DCBA instead of along ABCD. Limb DC experiences downward and BA experiences an upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule.
The process repeats itself and motion of armature becomes continuous after some time.
Functions of Split rings. They help in reversing the direction of current in the coil after every half rotation.
Q. 12. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Ans. Electric motor are used in battery operated toys, in tape recorder, in car fans, mixers, grinders, computers and variety of other electric appliances.
Q. 13. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(i) pushed into the coil;
(ii) withdrawn from inside the coil;
(iii) held stationary in the coil ?
Ans. (i) When the bar is pushed into the coil, there will be momentary deflection of galvanometer in one direction. This is so because when magnet is brought near the coil, magnetic lines linked with the coil increases, so that induced emf is produced which induces current in the coil.
(ii) Faster, we push the magnet, more will be the deflection.
(iii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn, there will again be momentary galvanometer deflection but in a direction opposite to that when magnet was pushed in. This time also current is induced in the coil.
(iv) When the magnet is held stationary inside the coil, there will be no deflection in galvanometer. It is because no emf is induced and hence no current is induced in the coil.
Q. 14. Two circular coils A and B placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in coil B ? Give reason.
Ans. If the current in the coil is changed (switched on or switched off), then an electric current is induced in coil B.
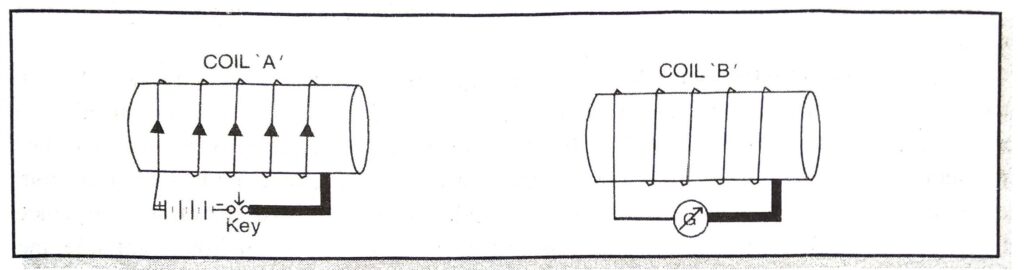
It is because when, plug in the key is introduced, current flows through the coil ‘A’ so that magnetic field is produced all round it. These magnetic lines produced in the coil ‘A’ will pass through the coil ‘B’ with the result induced emf and hence induced current is produced in the coil ‘B’ which is indicated by deflection of the galvanometer. Now when plug is removed from the key (switched off) the magnetic lines of force linked with the coil ‘B’ again change (decreases). This time again current is induced in the coil ‘B’.
Q. 15. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Ans. Electric short-circuit occurs when :
(i) live wire incidently touches neutral or earth-wire.
(ii) insulation around the current carrying wires is weak.
(iii) insulation gets hardened by the excessive use.
(iv) current passed through wire is more than its rating.
Q. 16. What is the function of earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances ?
Ans. Earth wire. It is used as a safety measure especially for electric appliance having metallic body. The metallic body of appliances like electric press, fans, toasters, refrigerators etc. are connected to earth wire which provides an easy path for current to go to the earth in case live wire touches the body of appliance incidently. The user will not suffer a severe electric shock in the event of touching a defective appliance.
Q. 17. State two properties of magnetic field lines.
Ans. 1. Magnetic field start from north and end at south.
2. They never intersect each other.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Give magnetic field due to solenoid. On what factors the strength of the field depends ?
Or
What is solenoid ? How does a solenoid behave like a bar magnet ?
Ans. Solenoid. A solenoid is a long circular coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire.
Magnetic field due to solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces magnetic field around it as shown in Fig. Magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The magnetic lines enter from one end of the solenoid and leave at the other end. If we look from left end, the current appears to be passing in the solenoid in clockwise direction and hence it acts as a south pole according to clock rule. If the solenoid is viewed from right side, the current appears to be in anticlockwise direction. Hence, right hand side face of the solenoid behaves as if this were a north pole.
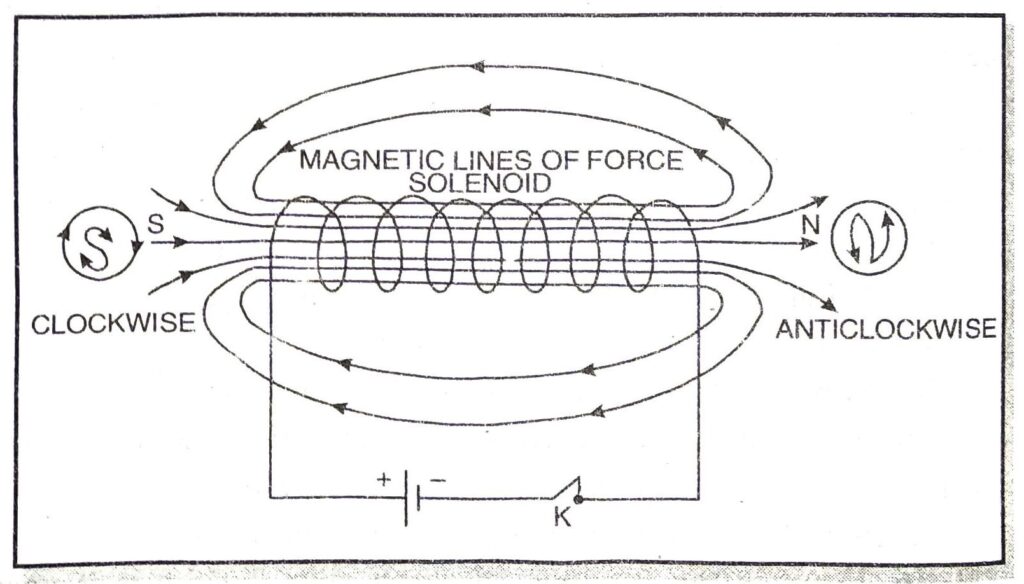
Since the current flows in the various turns of the solenoid in the same direction, the magnetic field produced by each turn of the solenoid adds up, giving a very strong resultant field inside the solenoid. Hence, a solenoid may be used in making electromagnets.
The strength of the magnetic field produced depends upon the following three factors :
(i) Number of turns. The more the number of turns, the stronger will be the magnetic field produced.
(ii) Strength of the current in the solenoid. Larger the current, stronger will be the magnetic field produced.
(iii) Nature of core of solenoid. The strength of the field depends upon the core on which the coil is wound. For air core, field is very weak whereas for soft iron-core, the field very strong.
Q: 2. What is Oersted Experiment? What is the effect needle ?
Ans. Oersted Experiment. Hans Oersted, in 1820, observed that a current-carrying wire deflects a magnetic needle placed near it. Since a magnetic needle can be deflected by a magnetic field, so he concluded that current flowing in a wire produce magnetic field around it which gives rise to mechanical force.
In his experiment, Oersted placed a wire between points X and Y parallel and above a magnetic needle as shown in the fig. He passed current through the wire in the direction from X to Y (i.e. from S-pole to N-pole of the magnetic needle) and observed that the N-pole of the magnetic needle gets deflected westward. On reversing the direction of flow of current the N-pole of the magnetic needle got deflected towards east. From this he concluded that every

conductor carrying current in surrounded by a magnetic field. The direction of deflection of magnetic needle can be remembered by SNOW rule which is stated as.” If the current flows through a wire from S-pole to N-pole when wire is placed over the magnetic needle, then the N-pole of the magnetic needle gets deflected towards the west direction.”
Effect of a Bar magnet on a compass needle. A compass needle is in fact a short and thin magnet pivoted at its centre on a vertical axis. When a bar magnet is brought near it the compass needle being free to move gets deflected due to attraction between dislike poles and repulsion between like poles of the bar magnet and compass needle.
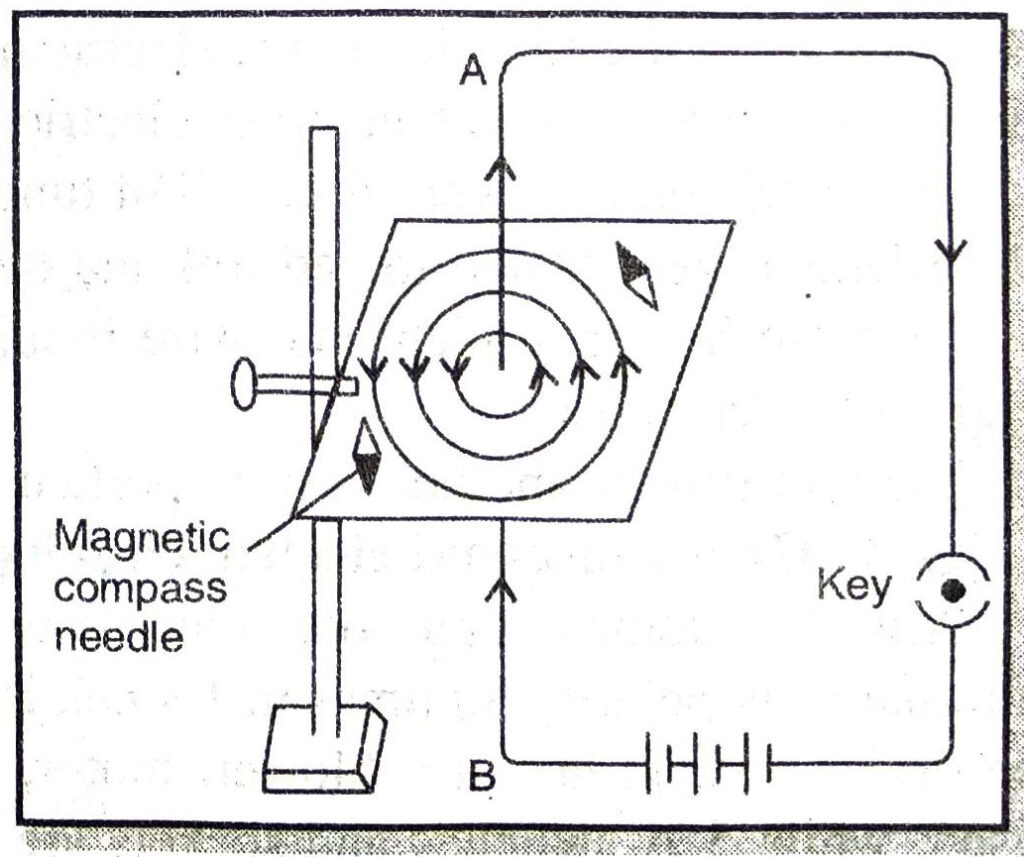
Q. 3. How will you prove that current carrying conductor produces the magnetic field? Draw the diagram.
Ans. Magnetic field due to a straight current carrying conductor. Take a rectangular cardboard sheet. Make a small hole in its middle. Fix this sheet horizontally in a wooden stand. Now pass a straight copper wire AB vertically through the hole. Now sprinkle some iron filings on the cardboard sheet. Connect the ends A and B of the wire to the terminals of a battery through a key. Insert the plug in the key to allow current to flow through the wire AB. Gently tap the cardboard when iron filings arrange themselves in concentric circlesaround the wire representing magnetic lines of force. To find the direction of the field produced, place a small magnetic compass on the sheet and note the direction in which N-pole of the compass points. If the current is flowing in upward direction in the wire, the direction of magnetic force is anticlockwise. And in case the current in the wire flows in the downward direction, then the direction of magnetic field will be clockwise. The direction of magnetic field due to current can also be determined by applying right hand thumb rule.
Q. 4. What is an electromagnet? Upon what factors its strength depends ?
Ans. Electromagnet. The combination of soft iron core and a current carrying insulated copper wire wound over it is called an electromagnet.
Very strong electromagnets can be produced by winding an insulated copper wire on a soft iron core. When current is passed through a solenoid, a magnetic field is produced. Now if a soft iron core is placed inside the solenoid, the strength of the magnetic field becomes very large. The reason for increase in magnetic field is due to the fact that iron gets magnetised by induction.

A simple electromagnet is as shown in Fig. To make an electromagnet, a soft iron core is placed inside a solenoid having large turns of insulated copper wire. The two ends of the solenoid are connected to a battery and a key.
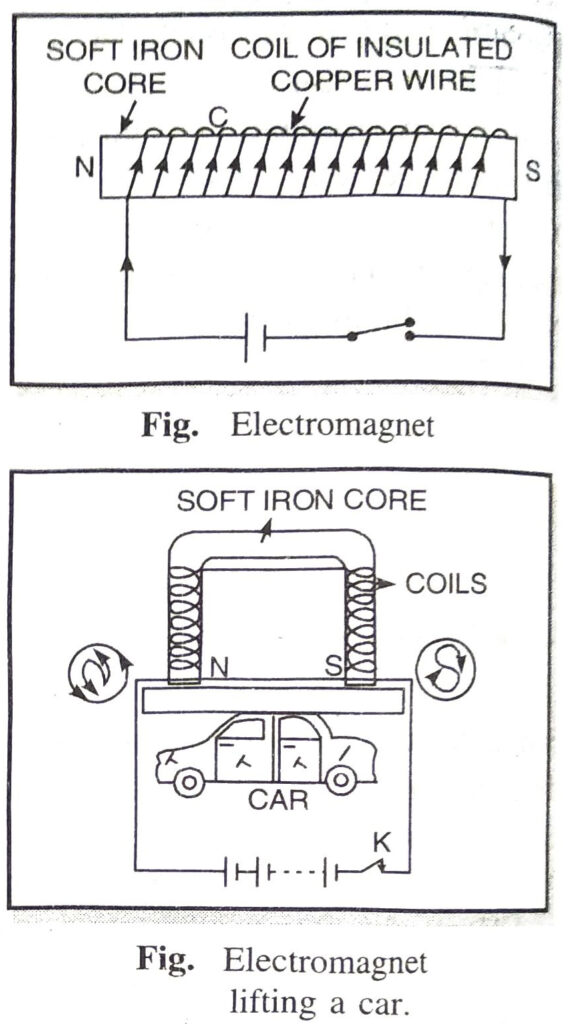
Strength of electromagnet depends upon
(i) Number of turns. Strength of electromagnets is directly proportional to the number of turns.
(ii) Current flowing. More the current flowing through the wire, stronger is the electromagnet.
(iii) Length of the air gap. Lesser the length of air gap between poles, stronger is the electromagnet.
Air gap between the poles of a U-shaped electromagnet is small, hence it is very strong magnet.
Q. 5. Give practical applications of heating effect of electric current.
Ans. A large number of electric appliances are based upon heating effect of electric current. Some of these are electric lamps, electric iron, toaster, electric kettle, room heater, hot plates, immersion rod, geyser, hair drier, electric blanket, cooking range etc. ,
In electric bulbs, a very thin coil of tungsten is used as a filament. When current is passed the filament gets heated to red hot and then white hot when it emits light.
In room heater, a nichrome wire mounted on porcelain rod is used. In immersion rod, carbon heater is used.
Electric fuse is another very important application of heating effect of current.
Q. 6. Give household electric circuits.
Ans. For domestic purposes electricity supplied to us is at 220 V and A.C. The current alternates its polarity 50 times in 1 s i.e., its frequency is 50 Hz., where heavy currents are to be drawn e.g., in hot air blower, motor, geyser, etc., 15 A switches and 15 A sockets are used, while 5 A switches and sockets are used for bulbs, tubes, radio, C.T.V., refrigerator, fans etc. The main supply is delivered to houses using a three-core wiring called live, neutral and the earth. The live wire is red (or brown) in colour and brings current. It is dangerous to touch live wire with bare hands. Neutral is black (or light blue) coloured wire and is used as return wire. The third wire, green (or yellow green) in colour is earth-wire. Earth wire may be connected to a pole or a metal plate sunk deep in the earth. It is a safety measure and does not in any way affect the supply. Earth wire is usually connected to the body of the electric appliances. If at any time, the live wire incidentally touches the frame of the electric appliance, the earth wire sends the current from the body of the appliances to the earth.

Q. 7. What is the function of safety fuse? How it connected in circuit ?
Ans. Functions of Safety fuse. Usually the wires chosen for electric circuits are such that these allow a certain maximum current to pass through them without excessive heating of the circuits. If, however, incidentally there is a short-circuiting or over-loading, the current exceeds this maximum permissible value. The wires may get over-heated and catch a fire. The most important safety device used these days is safety fuse.
Safety Fuse. Fuse is piece of wire of a material with a low melting point. Good fuse wire is always made of pure tin but alloy made of tin and copper or tin and lead (63% tin and 37% lead) is generally used.
Fuse is Always connected to live wire
When current of value more than maximum permissible limit is passed through the circuit, the fuse wire melts due to excessive heating. This way the circuit is broken to ensure safety of the circuit. It is due to this fact that the fuse is usually called safety fuse. The thickness, length and material of the fuse wire depends upon the maximum current permitted through the circuit. For proper protection, a fuse of proper value is a must. Fuse of improper rating is a curse instead of being a safety device.

Q. 8. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes ?
Ans. Principle. Electric generators are based on the principle that an induced current is produced in a conductor whenever there is change in magnetic lines of force linked with it. The direction of induced current is given by Fleming’s right hand rule.
Construction. A simple A.C. generator consists of the following important parts :
(i) Armature. It consists of a coil ABCD having a large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound over a soft iron core. The coil is called armature. The armature is mounted on an axle which can be rotated by force exerted by falling water, wind or steam.
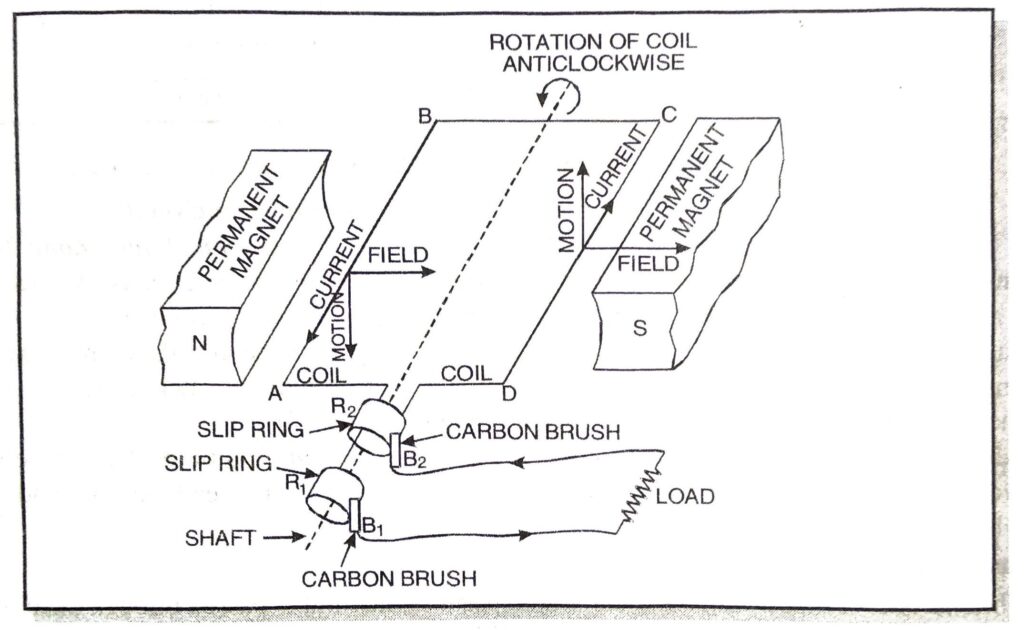
Fig. (a) A.C Dynamo/Alternator
(ii) Field Magnets. The coil is held between the concave pole pieces of a strong magnet called the field magnets. In small dynamos, the magnetic field is provided by a permanent magnet.
(iii) Split Rings. These consist of two hollow metallic rings R₁ and R₂ mounted on the axle of the rectangular coil ABCD. Ends of the arms AB and CD of the coil are connected to the rings R₁ and R₂ respectively.
(iv) Current from B₁, B₂ is taken out to load connected across two brushes.
Working. Let the coil be initially in horizontal position as shown in Fig (a). Let the coil be rotated in anticlockwise direction between the pole pieces N and S of a magnet.
At an instant, let the arm AB move down and arm CD move up as shown in the figure. The arm AB cut the magnetic lines of force near N-pole of the magnet, arm CD cut the lines near S pole of the magnet. Due to the change in the magnetic field cutting the coil, an induced current is produced in AB and DC. Using Fleming’s right hand rule to sides AB and DC of the coil, we observe that the current flows in the direction B to A and D to C. Thus effective current flows along DCBA [Fig. (a)]. “
After half rotation, sides AB and DC of the coil will interchange their positions. AB will come towards right and DC towards left. Now AB starts moving up and DC downwards. The direction of induced current in each side is reversed after half a revolution. Due to the change in the direction of induced current in the coil is reversed after half revolution, hence positive or negative polarity of the two ends is also changed.

SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What is Ampere’s swimming rule ?
Ans. Ampere’s Swimming Rule. Imagine a person swimming along the wire in the direction of the current so that current enters the foot and leaves the head, the face towards the compass with hands spread normal to the body then the north pole of the compass needle will be deflected towards his left hand.

Q. 2. What are the methods of demagnetising a permanent magnet ?
Ans. Methods of demagnetising a permanent magnet.
1. Magnets can be demagnetised by:
(i) keeping them without keepers over a long time. The slow self-demagnetisation will demagnetise the magnets.
(ii) dropping it from a height.
(iii) rough handling.
(iv) heating the magnet.
(v) hammering the magnet.
2. Magnet can also be demagnetised by placing it within a solenoid and passing A.C. through it. [Fig.]

Q. 3. Compare a permanent magnet and an electromagnet,
Ans. Comparison of Permanent magnet with Electromagnet
| Permanent Magnet | Electromagnet |
|
|
Q. 4. What are electric generators or dynamos? What is the principle of each ?
Ans. Electric Generators or Dynamos. Electric generators are devices used to produce electric currents. They convert mechanical energy into electric energy. The direction of the current produced in dynamos is in accordance with Fleming’s right hand rule.
Principle of Electric Generators. Electric generators are based upon the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a coil placed in the magnetic field is rotated then the current is induced in the coil. In dynamos, a rectangular coil having straight sides is made to rotate rapidly in the magnetic field due to poles of a horse-shoe magnet when the coil cuts the magnetic lines of force due to which a current is produced in the dynamo coil.
Q. 5. What are hazards of electricity ?
Ans. Hazards of Electricity. Electricity is the most important source of energy. Proper use of electricity is a boon while improper use is very dangerous and may prove to be fatal. There are number of hazards caused by improper use of electricity.
1. If by accident a person touches a live wire, he gets a very severe shock which may prove fatal.
2. Loose connections, defective switches and sockets can cause sparking which may lead to fire.
3. Short circuiting due to damaged wires or overloading of circuits can cause fires.
Q. 6. What are essential precautions to be used while using electricity ?
Ans. The following precautions should be observed while using electricity :
1. Turn off all switches including main switch whenever sparking or fire is noticed.
2. All connections must be tight. Wires must be covered with proper insulation of proper thickness. All joints must be covered with insulating tape of a good quality. Defective switches should be immediately replaced.
3. Fuses should always be connected to live wire. The earth wire must be connected to the body of electric appliance.
4. Fuse must be of proper rating and should always be connected to live wire.
5. Whenever repairs are needed, switch off main switch. If however, repairs need a direct handling of live wire, rubber gloves, rubber shoes and a plier with insulated handle should be used.
6. If inspite of all the precautions, a person gets a shock due to accidental touching a live wire, one should try to provide such a person with support of some non-conducting material like wood, plastic or rubber. Never try to pull away person by your hand.
7. Always put on dry rubber shoes while repairing the circuit.
Q. 7. What are bifurcated circuits ?
Ans. A large number of pairs of wires start from the main switch and are taken to different rooms. Each distribution circuit is provided with a separate fuse so that if a fault occurs in one circuit, only the corresponding fuse blows off but the other circuit remains unaffected. All the distribution circuits are put in parallel. In house, we can have a large number of circuits but the minimum number of circuits required are two, one 5 A circuit with 5 A fuse. 5 A circuit is used for smaller loads e.g., electric bulbs, T.V., tube lights, fans etc. The 15 A circuit is called power circuit connecting air-conditioner, geyser, motor, etc. The wiring of 5 A circuit may be by a single copper wire with proper insulation. In 15 A circuit, 3 to 7 wires with top class insulation cable are usually used.
Q. 8. What is meant by over-loading ?
Ans. Over-loading. Overloading means to draw large current from the mains. This happens when many appliances are connected with single socket simultaneously. The supply wires as well the wires used in household wiring has a specific rating. The rating of 15 A means that if a current upto 15A is passed through the circuit, there is no likely damage feared to the circuit. But if a current more than maximum allowed limit is passed, there may be excessive heating of the wires and it may damage the wiring.
Q. 9. What is meant by short-circuiting?
Ans. Short-circuiting. An electric circuit is said to be short-circuited if a live wire touches neutral wire or earth wire, a large current flows through the circuit due to almost zero resistance of the circuit. This results in increase of temperature and hence heating of wires which may cause fire or damaging the appliance.
To save the circuit from damage due to over-loading or short-circuiting, a fuse of proper rating is put in each circuit.
Q. 10. What is the necessity of earthing an electric appliance ?
Ans. In order to work an electric apparatus, we require two wires, one live wire and the other neutral wire. Due to wear and tear or due to excessive heating, sometimes live wire touches the body of the apparatus we may get shock when we incidently touch the apparatus. To avoid the risk of electric shock, the metal body of the electric appliance is earthed. The one end of the earth point is buried deep in the earth.

Q. 11. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Ans. Electric short-circuit occurs when :
(i) live wire incidently touches neutral or earth-wire.
(ii) insulation around the current carrying wires is weak.
(iii) insulation gets hardened by the excessive use.
(iv) current passed through wire is more than its rating.
Q. 12. What is Magnetic field ? What do you mean by Field lines?
Ans. Magnetic field. Magnetic field at a point is defined as the force experienced by an isolated unit north pole placed at that point. The S.I. unit of field is Tesla. Field lines. These lines are also called magnetic lines of force which is a curve or line along which an isolated unit north pole would move, if free to do so (to move), in the given magnetic field and tangent to it at any point, gives the direction of of intensity at that point.

Q. 13. Write down basic laws of magnetism. Write down the uses of magnet.
Ans. Laws of Magnetism. There are two basic laws of magnetism. These are :
1. Like poles (North-North, South-South) repal each other.
2. Unlike poles (North-South) attract each other.
Uses of Magnet.
1. Magnets are used to make a tight seal on the doors of refrigeators and freezers.
2. Magnets are used to store data in computers and scanning machines which doctors use to see inside patient’s bodies.
3. Magnets power speakers in stereos, earphones and televisions.
4. Magnets are used in electric bell, magnetic compass.
5. Magnets are used in cranes to separate magnetic and non-magnetic substances from their mixture.
Q. 14. Explain the working of an electric motor and give its applications.
Ans. Electric motor. It is a device which is used to convert electric energy into mechanical energy.
Principle, “When a current carrying coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque which rotates the coil.”

Fig. I indicates direction of current; F the direction field and M the direction of motion
Working. A direct current from a battery is passed through armature. The current flows in the coil along ABCD as shown in Fig. (a). The limb AB of the coil experience downward and CD of the coil experience upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule. These two equal and opposite forces constitute a couple tending to rotate the coil in clockwise direction. After half the rotation, brush B₁ has contact with S₂ and brush B₂ with S₁. The direction of the current gets reversed. The current now flows along DCBA instead of along ABCD. Limb DC experiences downward and BA experiences an upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule.
The process repeats itself and motion of armature becomes continuous after some time.
Functions of Split rings. They help in reversing the direction of current in the coil after every half rotation.
Applications of Electric Motor. The applications of electric motor mainly include blowers, fans, machines tools, pumps, turbines, power tools, alternators, compressors, rolling mills, ships, movers, paper mills, heating ventilating and cooling (HVAC) equipment and home appliances.
Q. 15. What is the pattern of magnetic field pattern due to current carrying conductor.
Ans. The direction of magnetic field produced around a straight current carrying conductor is given by right hand thumb rule and by right hand cork screw rule.
Right hand thumb rule is stated as : Imagine that the wire is grasped in the right hand so that the thumb points along the wire in the direction of current, the curling fingers will then point in the direction of magnetic field [Fig. (a) and (b)].
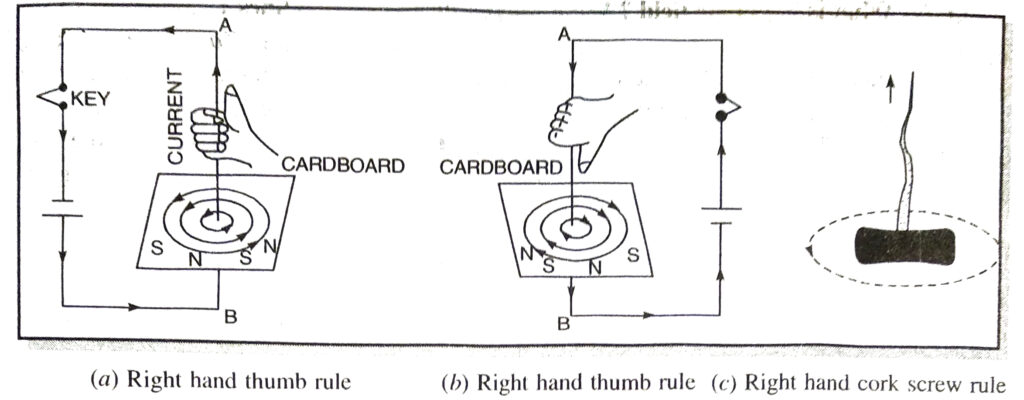
Right Hand Cork-Screw Rule. Imagine a right handed cork-screw to be lying with its direction coinciding with the conductor carrying current and to be revolved so that it travels in the direction in which thumb rotates gives the direction of lines of force [Fig. (c)].
Q. 16. What is Right-hand thumb rule ?
Ans. Right-hand thumb rule. Refer Q. 15 above.
Q. 17. What is the pattern of magnetic field due to a circular coil carrying current ?
Or
Explain the nature of magnetic field produced due to curent in a circular loop of wire.
Ans. Magnetic field due to circular Conductor. When a current is passed through a circular coil in clockwise direction, the magnetic field will be as shown in figure (a). Here the current is passing clockwise when looked from front side. At the points where the conductor passes through horizontal plane (say cardboard), the lines of force are almost circular, their direction being given by right hand grip rule. Near the central region, the lines are quite straight and at right angles to the plane of the coil.
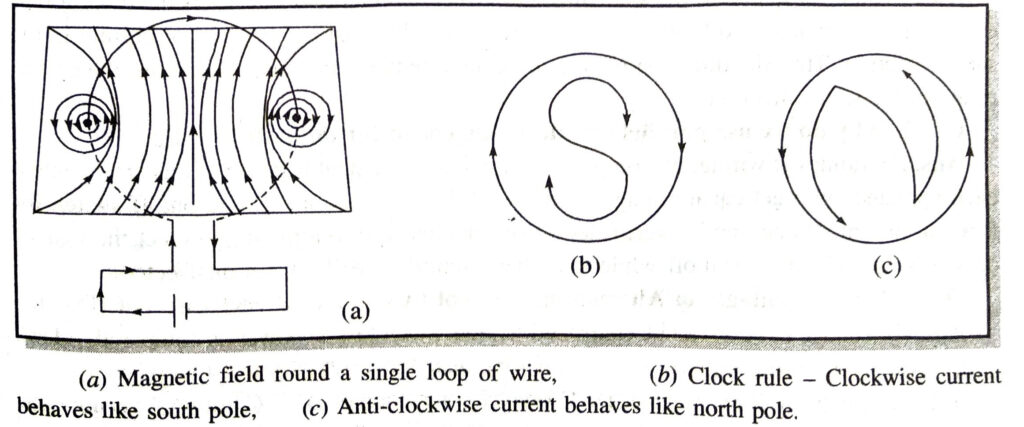
Further, it is clear from the figure that all the lines enter at the nearer face and leave at the farther face. Evidently, the lines of force due to the current flowing in circular loop closely resembles those produced by a magnetized circular disc of steel of same boundary as that of the coil, so that one face of it is north and other a south pole. The polarity of any face of coil can be determined by remembering a simple rule known as clock rule. If the current round any face of the coil flows in an anticlockwise direction it behaves like a north pole and if the current is in clockwise direction, the face acts as a south pole [Fig. (b), Fig. (c)].
Q. 18. Name five devices where permanent magnets are used ?
Ans. D.C. motor used in toys, tape recorders, galvanometer, A.C. dynamo, electric energy meters etc.
Q. 19. How can we increase the strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying circular coil.
Ans. (i) By increasing the current flowing through the coil.
(ii) By increasing the number of turns of the coil.
(iii) By decreasing the radius of the coil.
Q. 20. A current-carrying straight conductor is placed in East-West direction. What will be the direction of the force experienced by this conductor due to earth’s magnetic field? How is this force affected on :
(a) reversing the direction of flow of current.
(b) doubling the magnitude of the current ?
Ans. The direction of the force will be vertically downward due to earth’s horizontal magnetic field.
(a) On reversing the direction of flow of current, the direction of force will be vertically upward.
(b) If the magnitude of current is doubled, the force will be doubled but the direction of force will remain the same.
Q. 21. What is the role of the split rings in an electric motor ?
Ans. In an electric motor, the split ring acts as a commutator and reverses the direction of current in the armature (coil) after every half rotation. This ensures the flow of current in the same direction. Thus the direction of rotating couple remains unchanged making the coil to rotate in the same direction.
Q. 22. Why do we use parallel circuit arrangement for domestic wiring ?
Ans. For domestic wiring, we use parallel circuit arrangement because in this arrangement each appliance will get equal voltage (potential difference) and a separate on/off switch for flow of current. If one line is overloaded or one appliance develops some defect the fuse of only this line will be blown off while the other circuit/line will remain unaffected.
Q. 23. Give advantages of Alternating Current (A.C.) over Direct Current (D.C.).
Ans. (i) Voltage of A.C. can be controlled without much loss to power as compared to D.C.
(ii) A.C. can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
(iii) A.C. can be easily converted into D.C. whereas conversion of D.C. into A.C. is not easy.
(iv) The cost of generation of A.C. is much less than cost of generation of D.C.
Q. 24. What is the difference between Alternating Current (A.C.) and Direct Current (D.C.) ?
Ans. Difference between Alternating Current and Direct Current.

VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Does a stationary charge has magnetic field around it?
Ans. No. There is no magnetic field around a stationary charged particle.
Q. 2. What happens if a current carrying conductor is placed in magnetic field ?
Ans. It experiences a force given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
Q. 3. What is a dynamo ?
Ans. Dynamo. It is a device which converts mechanical energy into electric energy.
Q. 4. On what principle is an a.c. motor based ?
Ans. It is based upon Fleming’s left hand rule.
Q. 5. What is an electric motor ?
Ans. Electric motor. It is a device which converts electric energy into mechanical energy.
Q. 6. What type of field is around stationary charge ?
Ans. Around stationary charge only electric field is produced whereas magnetic field is produced only around a moving charge.
Q. 7. List three sources of magnetic field ?
Ans. Electromagnet, load stone, solenoid, bar magnet.
Q. 8. What do you mean by solenoid ?
Ans. Solenoid. It is a long circular coil having large number of close turns of insulated copper wire which produces magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it.
Q. 9. What is a fuse?
Ans. Fuse. It is a safety device which is introduced in electric circuit to prevent damage to the circuit due to over-loading or short circuiting.
Q. 10. Define A.C. and D.C.
Ans. Direction of A.C. changes after every half cycle whereas in D.C., the direction of current remains the same.
Q. 11. Name the scientist who established a relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Ans. H.C. Oersted.
Q. 12. Name the Physical quantity whose S.I. unit is weber/m².
Ans. Magnetic field.
Q. 13. In which part of a bar magnet, the magnetic field lines are more denser ?
Ans. At the poles of a magnet.
Q. 14. How is the strength of the magnetic field at a point near a wire related to the strength of the electric current flowing in the wire.
Ans. The strength of the magnetic field is directly proportional to the strength of the current.
Q. 15. How does the strength of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of a wire depend on :
(a) radius of the coil (b) number of turns of the coil.
Ans. (a) Strength of magnetic field (B) 
(b) Strength of magnetic field (B) ∝ Number of turns of the coil (N).
Q. 16. Name any two devices which uses electric motor as an essential component in their working.
Ans. (i) Water pump (ii) Electric fan.
Q. 17. What is electromagnetic induction ?
Ans. Electromagnetic Induction. It is the process in which change of magnetic field in a coil/conductor induces electric current or emf in the neighbouring coil/conductor.
Q. 18. In which situation do we use Fleming’s right hand rule ?
Ans. To find the direction of Induced current.
Q. 19. What frequency of A.C. current is used in our country?
Ans. 50 He (Hz).
Q. 20. Draw a clean and well labelled diagram of an electric motor.
Ans. Electric motor. It is a device which is used to convert electric energy into mechanical energy.
Principle, “When a current carrying coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque which rotates the coil.”

Fig. I indicates direction of current; F the direction field and M the direction of motion
Working. A direct current from a battery is passed through armature. The current flows in the coil along ABCD as shown in Fig. (a). The limb AB of the coil experience downward and CD of the coil experience upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule. These two equal and opposite forces constitute a couple tending to rotate the coil in clockwise direction. After half the rotation, brush B₁ has contact with S₂ and brush B₂ with S₁. The direction of the current gets reversed. The current now flows along DCBA instead of along ABCD. Limb DC experiences downward and BA experiences an upward force in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule.
The process repeats itself and motion of armature becomes continuous after some time.
Functions of Split rings. They help in reversing the direction of current in the coil after every half rotation.
Q. 21. Name the types of current with graphic sketches.
Ans. Types of current. There are two types of current :
1. Direct current (D.C.)

2. Alternating current (A.C)

MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Which one of the following is based upon electromagnetic induction ?
(A) Galvanometer
(B) Transformer
(C) X-rays
(D) Voltmeter.
Ans. (B) Transformer
2. A charge is stationary at a place, its magnetic field will :
(A) be parallel to charge
(B) perpendicular to charge
(C) be absent since no magnetic field
(D) is produced around stationary charge.
Ans. (C) be absent since no magnetic field
3. When soft iron bar is introduced inside a current carrying solenoid, the magnetic field inside the solenoid will :
(A) increase
(B) decrease
(C) be zero
(D) remain unaffected.
Ans. (A) increase
4. An electric motor transfers :
(A) electric energy into mechanical energy
(B) mechanical energy to electric energy
(C) chemical energy to electric energy
(D) electric energy to sound energy.
Ans. (A) electric energy into mechanical energy
5. Material of the core of strong electromagnet is :
(A) soft iron
(B) steel
(C) copper
(D) laminated steel strips.
Ans. (A) soft iron
6. The commercial unit of electric energy is :
(A) watt
(B) kilowatt
(C) kilowatt hour
(D) kilovolt.
Ans. (C) kilowatt hour
7. Magnetic lines of force inside current carrying solenoid are:
(A) parallel inside the solenoid and circular at the ends.
(B) circular but intersect each other
(C) along the axis and are parallel to each other.
(D) perpendicular to axis and equidistant from each other.
Ans. (C) along the axis and are parallel to each other.
8. The direction of induced current is given by :
(A) Ampere’s swimming rule.
(B) Fleming’s left hand rule.
(C) Fleming’s right hand rule.
(D) Maxwell’s cork screw rule.
Ans. (C) Fleming’s right hand rule.
9. Magnetic field lines
(A) Intersect at 90° to one another
(B) Intersect at 45° to each other
(C) Do not intersect each other
(D) Cross each other at an angle 60° to one another.
Ans. (C) Do not intersect each other
10. In electric motor, the direction of current in the coil changes once in each
(A) two rotations
(B) half rotation
(C) one rotation
(D) one-fourth rotation.
Ans. (B) half rotation
11. An electric generator converts
(A) electric energy into mechanical energy
(B) mechanical energy into heat energy
(C) electric energy into chemical energy
(D) mechanical energy into electric energy.
Ans. (D) mechanical energy into electric energy.
12. A magnet attracts
(A) Plastic
(B) Any metal
(C) Aluminium
(D) Iron and steel.
Ans. (D) Iron and steel.
13. Device used for producing electric current is called
(A) Generator
(B) Galvanometer
(C) Ammeter
(D) Motor.
Ans. (A) Generator
14. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
(A) reduces substantially
(B) does not change
(C) increases rapidly
(D) varies continuously.
Ans. (C) increases rapidly
15. When an electric current flows in a wire, it produces
(A) an electric field
(B) magnetic field
(C) Neither electric nor magnetic field
(D) both electric and magnetic field.
Ans. (D) both electric and magnetic field.
16. The direction of magnetic field produced on passing electric current in a conductor is determined by :
(A) Maxwell’s Left hand rule
(B) Fleming’s right hand rule
(C) Fleming’s left hand rule
(D) Faraday’s Law.
Ans. (A) Maxwell’s Left hand rule
17. The direction of the force produced in a current carrying coil placed in a strong magnetic field is determined by :
(A) Maxwell’s right hand rule
(B) Fleming’s right hand rule
(C) Fleming’s left hand rule
(D) Faraday’s Law.
Ans. (C) Fleming’s left hand rule
18. What is the colour of neutral wire in a domestic electric circuit?
(A) Black
(B) Red
(C) Green
(D) No speeific colour.
Ans. (A) Black
19. When a current carrying wire and Neutral wire come in contact so that heavy current begins to flow, this arrangement is called :
(A) Overloading
(B) Short-Circuit
(C) Earthing
(D) All the above
Ans. (B) Short-Circuit
20. Connecting metallic frame of high power electrical appliances with the earth wire of domestic circuit is called :
(A) Over-loading
(B) Short-circuit
(C) Earthing
(D) All of these.
Ans. (C) Earthing
21. Which of the following is source of direct current ?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Button cell
(C) Lead battery
(D) All of these.
Ans. (A) Dry cell
22. Similar magnetic poles :
(A) Attract
(B) Repel
(C) Both attract and repel
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Repel
23. Magnetic field lines are :
(A) Straight lines
(B) Curved
(C) Closed curves
(D) Triangular.
Ans. (C) Closed curves
24. A convenient way of finding the direction of magnetic field associated with current carrying conductor is :
(A) Fleming’s Right hand Rule
(B) Right hand thumb Rule
(C) Fleming’s Left hand Rule
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Right hand thumb Rule
25. When a coil is kept stationary relative to the magnet, the galvanometer gives deflection :
(A) Maximum
(B) Zero
(C) Constant
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Zero
26. The direction of induced current is given by :
(A) Fleming’s right-hand rule
(B) Fleming’s left-hand rule
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of the above.
Ans. (A) Fleming’s right-hand rule
27. Filament of a bulb is made of :
(A) Aluminium
(B) Silver
(C) Tin
(D) Tungsten.
Ans. (D) Tungsten.
28. The magnetic lines of force is a quantity that has :
(A) only direction
(B) only magnitude
(C) both directions as well as magnitude
(D) none of these.
Ans. (C) both directions as well as magnitude
29. Fleming’s left-hand rule is applied to find the direction of:
(A) Magnetic lines of force
(B) Induced current
(C) Force on a current carrying conductor
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Force on a current carrying conductor
30. A live wire in a domestic circuit is of:
(A) Red colour
(B) Green colour
(C) Black colour
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Red colour
31. The magnetic field inside long straight solenoid carrying current :
(A) is zero
(B) decreases as we move towards its ends
(C) increases as we move towards its ends
(D) is the same at all points.
Ans. (D) is the same at all points.
32. An induced emf is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The magnitude of induced emf does not depend on :
(A) The no. of turns in the coil
(B) The strength of the coil
(C) The speed with which magnet is moved
(D) The resistivity of the material of the coil.
Ans. (C) The speed with which magnet is moved
33. Current carrying conductor is :
(A) Permanent magnet
(B) Temporary magnet
(C) Neutral magnet
(D) None of these.
Ans. (D) None of these.
34. A dynamo :
(A) Crests mechanical energy
(B) Creates electrical energy
(C) Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
(D) Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Ans. (D) Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
35. Which among the following produces strong magnetic field ?
(A) Permanent magnet
(B) Neutral magnet
(C) Bar magnet
(D) Electromagnet.
Ans. (D) Electromagnet.
36. When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, then :
(A) Speed of particle is changed
(B) Speed of particle remains unchanged
(C) Direction of particle remains unchanged
(D) Acceleration of the particle remains unchanged.
Ans. (A) Speed of particle is changed
37. A magnet has two poles, choose the poles:
(A) East-West
(B) North-South
(C) East-North
(D) West-South.
Ans. (B) North-South
38. Which is the S.I. unit of magnetic field ?
(A) Newton
(B) Ampere
(C) Tesla
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Tesla
39. The device used for producing current is called:
(A) Generator
(B) Voltmeter
(C) Ammeter
(D) Galvanometer.
Ans. (A) Generator
40. Inside a solenoid the magnetic field :
(A) Decreases along the axis
(B) Increases along the axis
(C) Is zero
(D) Is uniform.
Ans. (D) Is uniform.
41. A.C. is converted into D.C. by a :
(A) Generator
(B) Rectifier
(C) Motor
(D) Dynamo.
Ans. (B) Rectifier
42. A magnetic field outside the solenoid is :
(A) Uniform
(B) Non-uniform
(C) Neither of both
(D) Both (A) and (B).
Ans. (D) Both (A) and (B).
43. The path followed by unit North pole in a magnetic field is known as:
(A) Magnetic lines of force
(B) Magnetic field
(C) Magnetic current
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Magnetic lines of force
44. Earth’s magnetic field has a horizontal component except at :
(A) Equator
(B) Magnetic Poles of Earth
(C) A latitude of 60°
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Magnetic Poles of Earth
45. In Fleming’s left-hand rule thumb indicates :
(A) Current
(B) Field
(C) Direction of force
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Direction of force
46. One way device is :
(A) A.C.
(B) D.C.
(C) A.C. and D.C.
(D) None of these.
Ans. (D) None of these.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here