JKBOSE 9th Class Science Solutions Chapter 8 Is Matter Around Us Pure ?
JKBOSE 9th Class Science Solutions Chapter 8 Is Matter Around Us Pure ?
JKBOSE 9th Class Science Solutions Chapter 8 Is Matter Around Us Pure ?
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 9th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 9th Science Is Matter Around Us Pure ? Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ Pure Substance. It consists particles of only one kind and has a definite set of properties. Pure substances include elements and compounds.
◆ An Element is a pure substance which is made up of only one kind of particles (atoms). It can neither be built up nor broken down into two or more simpler substances by any known physical or chemical methods, e.g., copper, silver etc.
◆ A compound is a pure substance which is obtained by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass, e.g., water, ammonia etc.
◆ Mixture. It is a material obtained by mixing two or more substances in any proportion without any chemical change taking place.
◆ Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
◆ The properties of a mixture lie between those of its components whereas properties of a compound are different from those of its constituents.
◆ Mixtures can be separated into pure substances by using suitable separation techniques.
◆ Solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances whose composition can be changed within certain fixed limits.
◆ Binary solution is a solution having two components.
◆ Components of a binary solution Solute are called solute and solvent.
◆ Solute is the minor component of solution whereas solvent is the major component of a solution.
◆ Concentration of a solution is the amount of solute present per unit volume or per unit mass of solvent or solution.
◆ A saturated solution is one which does not dissolve any more of the solute at a given temperature and pressure.
◆ Colloids are heterogeneous mixtures in which the particles have size more than 100 nm. These particles are called colloidal particles and constitute the dispersed phase whereas the medium in which colloidal particles are dispersed constitute dispersion (Le) stufoc to smulo medium.
◆ Suspensions. Materials which are insoluble in a solvent and have particles that are visible to naked eyes form suspensions.
◆ In suspensions, the particle size is more than 100 nm and are heterogeneous.
◆ Physical Change. It is a temporary change in which only the physical properties of substances change and it can be reversed.
◆ Chemical Change. It is a permanent change in which the chemical properties of substances change and there is change in composition and cannot be reversed.
◆ Filtration. The process of separation of an insoluble solid component of a mixture from a liquid component is called filtration.
◆ Evaporation. It is the slow process of conversion of liquid into gaseous state (vapour) at a temperature below its boiling point.
◆ Distillation. It is the process of conversion of liquid into gaseous state by heating it to the boiling point and condensing the vapour to get pure liquid.
◆ Fractional distillation. It is the process of separating two miscible liquids having different boiling points by distillation using a fractionating column.
◆ Chromatography. It is the process of separation of dissolved components of a mixture by adsorbing on a suitable substance (called adsorbent).
IMPORTANT TERMS/FACTS TO MEMORIES

TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. What is meant by a pure substance ?
Ans.— It is a material containing particles of only one kind having a definite set of properties. Pure substances include elements and compounds.
Q. 2. List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Ans.—
| Homogeneous mixture | Heterogeneous mixture |
| It consists of a single phase. | It consists of two or more phases. |
|
It has a uniform composition in the throughout.
|
It does not have a uniform composition thoughout. |
| It has the same properties throughout the bulk. | It does not have same properties throughout the bulk. |
| There are no visible boundaries between its components. | There are visible separation between its components. |
| Examples : Sodium chloride dissolved in O water, ethyl alcohol dissolved in water. | Examples : Air, gun powder, iron filings, sand and sulphur. |
Q. 3. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
Ans.— Same as Q. No. 2 on TBQ Page 120.
Q. 4. How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other ?
Ans.—
| Property | True Solution | Colloidal solution | Suspension |
| Nature | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous | Heterogeneous |
| Particle size | Less than 1 nm | 1 to 100 nm | More than 100 nm |
| Diffusion | Diffusion rapidly | Diffusion slowly | Don’t Diffusion |
| Filtrability | Paritcles can pass through ordinary filter paper as well as semi – permeable membrane | Paritcles can pass through ordinary filter paper but not through demi – per – meable membrane | Particles can ‘ t through filter paper as well as semi – permeable mem – brane |
| Appearance | Clear and transparent | Generally clear and transparent | Opaque |
| Tyndall | Dont’ show | Show | May or may not shoe |
| Visibility | Particles are not visible | Particles can be seen only with ultra – microscope | Particles can be seen with naked eye or microscope. |
Q. 5. To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of hond water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Ans.— Mass of sodium chloride (solution) = 36 g
Mass of water (solvent) = 100 g
Total mass of solution = 100 + 36 = 136 g
Mass percentage of solution = Mass of solute / Mass of solution × 100
= 36 / 136 × 100
= 26.47
Q. 6. How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25°C), which are miscible with each other ?
Ans.— By Distillation.
Q. 7. Name the technique to separate :
(i) Butter from curd
(ii) Salt from sea water
(iii) Comphor from salt.
Ans.— (i) By centrifugation.
(ii) By evaporation.
(iii) By sublimation.
Q. 8. What types of mixture are separated by the technique of crystallisation ?
Ans.— The mixtures in which the substance is soluble in a suitable hot solvent whereas 1 the impurities are insoluble.
Q. 9. Classify the following as chemical or physical changes :
(a) cutting of trees, (b) melting of butter in a pan, (c) rusting of almirah, (d) boiling of water to form steam (e) passing of electric current through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases. (f) dissolving common salt in water (g) making a fruit salad with raw fruits. (h) burning of paper and wood.
Ans.—(a) Chemical change, (b) Physical change, (c) Chemical change, (d) Physical change, (e) Chemical change, (f) Physical change, (g) Physical change, (h) Chemical change.
Q. 10. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Ans.— Some examples are
Water — pure substance
Milk — Mixture
LPG — Mixture
Bread — Mixture
Kerosene oil — Mixture
Air — Mixture
paper — Mixture
Ink — Mixture
Curd — Mixture
Wood — Mixture
Ice — Pure substance
Soda water — Mixture
Ice cream — Mixture
Butter — Mixture
Vanaspati — Mixture
Lemon juice — Mixture
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following ?
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water. (b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride. (c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car. (d) Different pigments from an extract of flower petals. (e) Butter from curd (f) Oil from water, (g) Tea leaves from tea, (h) Iron pins from sand, (i) Wheat grains from husk, (j) Fine mud particles suspended in water.
Ans.— (a) Evaporation, (b) Sublimation, (c) Filtration, (d) Chromatography, (e) Centrifugation, (f) Separating funnel, (g) Filtration, (h) Magnetic separation, (i) Gravity separation, (j) Centrifugation
Q. 2. Write the steps you would use for making solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Ans.— Step 1. Boil some solvent (water) in a pan.
Step 2. Put some solute (tea leaves) in a t in a tea pot.
Step 3. Pour the boiling water into the tea pot and let it soak for a few minutes to form a solution.
Step 4. Stir the solution in the tea pot.
Step 5. Take some solute (sugar) into a cup.
Step 6. Filter the above solution obtained in step 4 using strainer and take this solution (filtrate) in the cup. Pour two tea-spoons of milk into the cup and stir it with a spoon. This gives us tea which is ready for drinking. The is left on the strainer because these are insoluble whereas sugar and milk are soluble solutes.
Q. 3. Explain the following giving examples :
(a) saturated solution
(b) pure substance
(c) colloid
(d) suspension.
Ans.—(a) Saturated Solution. A solution in which no more of the solute can be dissolved at the given temperature is said to be saturated at that temperature. For example, 50 g of NaCl added to 100 ml of water.
(b) Pure substance. A pure substance is made of only one type of atoms or molecules. Pure substances have the same colour, taste, texture at the given temperature and pressure. Pure substance has a fixed melting or boiling point at the constant pressure. Pure substance includes elements and compounds. For example, hydrogen gas, sodium chloride, water etc.
(c) Colloid. A substance is said to be in the colloidal state if its particle size lies between win muretu 1 to 100 nm. The colloidal solution is heterogeneous and consist of two phases i.e. dispersed phase or colloidal particles and dispersion medium in which colloidal particles are suspended e.g. colloidal solution of starch in water.
(d) Suspension. It is a heterogeneous mixture in which the particles of the solute don’t dissolve but remain suspended throughout the bulk of the material and the size of particles is more than 10-7m. The particles can be seen with naked eye.
Q. 4. Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture :
soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea.
Ans.— Soda Water — Homogeneous mixture
Wood — Homogeneous mixture
Air — Homogeneous mixture
Soil — Homogeneous mixture
Vineger — Homogeneous mixture
Filtered tea — Homogeneous mixture.
Q. 5. How would you confirm that a colourless liquid given to you is pure water ?
Ans.— Determine the boiling point of the given liquid. If its boiling point is 100°C at 1 atmosphere pressure it is pure water and if boiling point is above 100°C, it is impure water.
Q. 6. Which of the following materials fall in the category of a” pure substance ” ?
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxid
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air
Ans.— (a) Ice
(b) Iron
(c) Hydrochloric acid
(d) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
Q. 7. Identify the solutions among the following mixtures :
(a) soil
(b) sea water
(c) air
(d) coal
(e) soda water
Ans.— (b),(c) and (e).
Q. 8. Which of the following will ” Tyndall effect” ?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution.
Ans.—(b) and (d) because these are colloidal solutions.
Q. 9. Which of the following are chemical changes ?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) freezing of water
(g) Burning of candle.
Ans.— (a) growth of a plant
(b) Rusting if iron
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Burning of a candle.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Give important characteristics of a mixture.
Ans.— The important characteristics of a mixure are :
1. In a mixture, the components, elements or compounds are present in no fixed ratio.
2. A mixture is formed from its components as a result of physical change.
3. The properties of a mixture lie between those of its constituents.
4. A mixture may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
5. The constituents of a mixture can be separated by physical methods only.
6. The formation of a mixture from its constituents does not involve any energy change.
Q. 2. Give important differences between a compound and a mixture.
Or
Give five differences between Compound and Mixture.
Ans.—
| Compound | Mixture |
| A compound is formed from its constituent elements as a result of chemical reaction. | A mixture is obtained from its (elements, compounds) components as a result of physical change. |
| A compound is always homogeneous in nature. | The mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. |
| In a compound the elements are present in a fixed ratio by weight. | In a mixture the components can be present in any ratio. |
| The components of a compound can’t be separated by physical methods but can be separated by chemical methods only. | The components of a mixture can be separated by physical methods only. |
| The formation properties of a compound are different from that of its elements. | The properties of a mixture lie between those of its components. |
| The formation of a compound from its elements is accompanied by energy changes. | The formation of a mixture from its constituents is not accompanied by energy changes. |
Q. 3. State briefly how would you separate or name the process use to separate :
(i) Common salt from a solution of common salt and water.
(ii) Alcohol from a mixture of alcohol and water.
(iii) Sulphur from a mixture of carbon particles and powdered roll sulphur.
(iv) The coloured dyes in black ink.
Ans.— (i) The solution containing common salt in water is concentrated and is then cooled. The crystals of common salt are formed which can be separated by filtration.
(ii) Alcohol can be separated from water by fractional distillation as the two liquids differ in their boiling points.
(iii) The mixture is treated with carbon disulphide which dissolves powdered sulphur in it. It is filtered to separate carbon particles. The filtrate upon concentration and cooling gives crystals of sulphur which can be separated by the process of filtration.
(iv) The coloured dyes in black ink can be separated by the process of paper chromatography.
Q. 4. Explain the following :
(a) Fractional crystallisation (b) Sublimation (c) Filtration.
Ans.— (a) Fractional Crystallisation. The process of separation of components of a mixture having different solubilities in the same solvent by crystallisation is called fractional crystallisation. This method is used for the separation of components of a mixture which are soluble in the same solvent on heating but have different solubilities. For example, a mixture of potassium nitrate and sodium chloride can be separated by this method. This can be explained as follows :
The mixture is dissolved in water. The solid is concentrated to the crystallisation point. On cooling the crystals of less soluble component i.e., sodium chloride appear first. These are separated. On further cooling the crystals of more soluble component i.e., of potassium nitrate will appear. The pure crystals can be obtained by recrystallisation from the same solvent i.e. water.
(b) Sublimation. This method is used for the separation of the components of a mixture in which one component undergoes sublimation whereas other does not. For example, a mixture of ammonium chloride and common salt can be separated by this method. For this purpose take the mixture of ammonium chloride and common salt in a china dish. Cover it with an inverted funnel and its open end is closed with cotton wool. The walls of china dish are kept cooled. On heating, ammonium chloride sublimes and condenses on the cooler parts whereas common Salt is left behind. The fine powder of ammonium chloride deposited on the funnel is scrapped with the help of a knife. Similarly, the mixture of iodine and sand can be separated by this method in which iodine sublimes whereas sand does not.

(c) Filtration. In this method, the mixutre is dissolved in a suitable solvent in which one component dissolves whereas other does not.

For example, a mixture of charcoal and sulphur can be separated by this method. The mixture is treated with carbon disulphide which dissloves sulphur whereas charcoal is left behind. The insoluble charcoal is separated by filtration and is dried. From the filtrate, sulphur can be obtained by evaporating carbon disulphide.
Q. 5. Explain the process of :
(i) Distillation, (ii) Evaporation.
Ans.—(i) Distillation. The process of converting a liquid into gaseous state by heating to boiling point and condensing the vapour to get the pure liquid is called distillation.
This method is used when the solid is non-volatile and liquid does not have a high boiling point.
For example, salt can be separated from sea water by this method. For this purpose the apparatus is fitted as shown below :

The mixture of solid and liquid is taken in a distillation flask. On heating vapour of liquid (water) are produced. These are condensed in water condenser and collected in a receiver. The non-volatile sodium chloride is left behind.
Similarly, a mixture of methyl alcohol and iodine can be separated by this method.
(ii) Evaporation. Evaporation is a process of changing a liquid into its gaseous state by heating it at a temperature below its boiling point. For example, common salt can be obtained from a mixture of common salt and water by evaporation.
The mixture is heated in a china dish using sand bath when water vaporises whereas common salt is left behind.
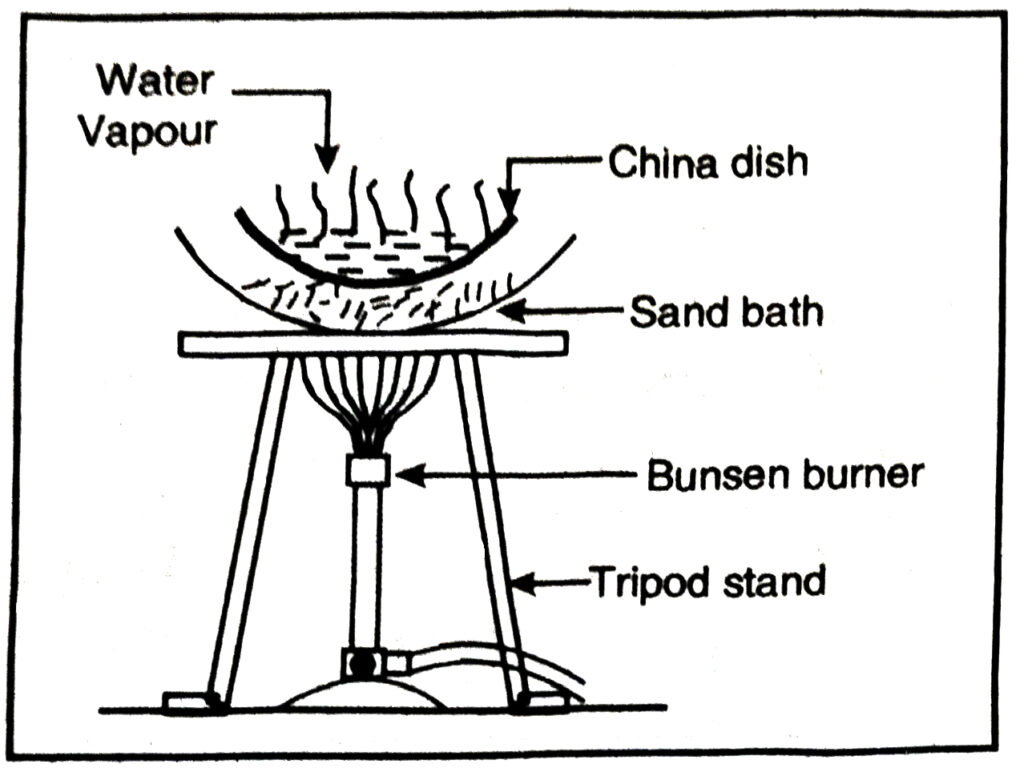
Q. 6. How will you separate gas – gas mixtures ?
Ans.— The gas – gas mixtures can be separated by the following method :
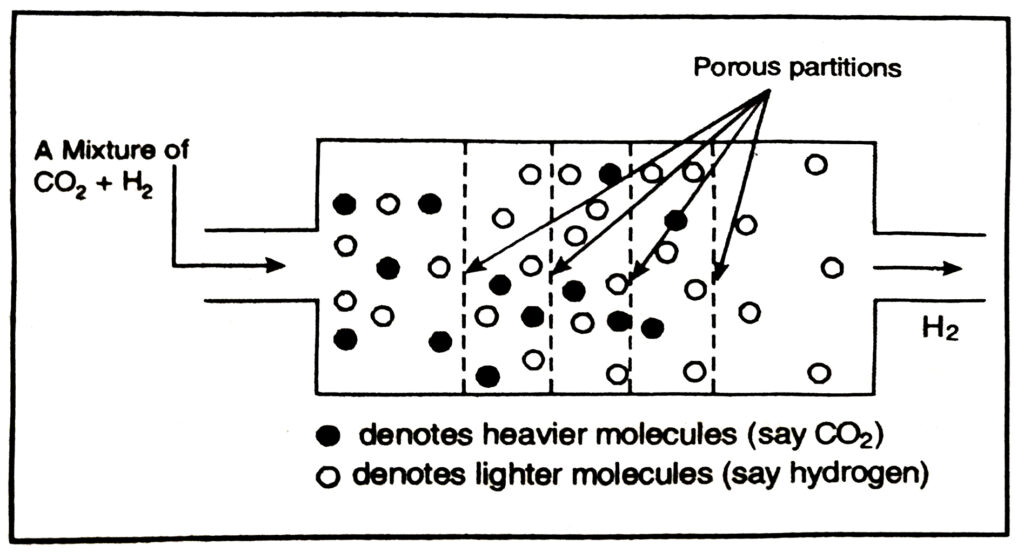
Fractional evaporation of mixture of liquefied gases. The mixture of two gases is liquefied by applying high pressure and then allowing it to expand. For example, when air is liquefied example, a under high pressure and allowing it stand, both oxygen and nitrogen get liquefied. The above liquid mixture is maintained at a temperature of -196°C (b.pt of liquid N₂), nitrogen boils off. For mixture of carbon
dioxide and hydrogen can be separated by passing through porous partitions as shown below.
In this case, H₂ being lighter diffuses at a faster rate as compared to CO₂.
Q. 7. What is chromatography ? Why is it regarded as superior method of purification ?
Ans.— Chromatography. The process of separation of different components of a mixture by adsorbing them over a suitable material (called adsorbent) is called chromatography. Originally, this technique was used to separate coloured mixtures but now-a-days this method can be used for colourless as well as coloured substances.
The main advantages of this technique are :
(i) It can be applied to separate the mixture even if very small amount of mixture of the substances is available.
(ii) The components of a mixture don’t get wasted during separation.
(iii) It also helps in estimating the constituents of a mixture apart from separation.
Q. 8. What is the principle of chromatographic separation ? Name the different types of chromatography commonly used.
Ans.— Chromatography is based upon the distribution of the mixture of the components between the two phases i.e. a stationary phase and a moving phase. The moving phase consists of mixture of the substances to be separated. The moving phase is applied over a solid or liquid i.e., a stationary phase. The stationary phase separates the components of the mixture by the phenomenon of either partition, adsorption or ion exchange. The different chromatographic techniques are :
(a) Column chromatography
(b) Thin layer chromatography
(c) Ion exchange chromatography
(d) Paper chromatography.
Q. 9. What are the various types of colloidal solutions based upon the physical states of dispersed phase and dispersion medium ? Give one example in each case.
Ans.— These are of eight types :
| Dispersed Phase | Dispersion Medium | Type or name of colloidal solution | Examples |
| Solid | Solid | Solid sol | some coloured glasses |
| Liquid | Solid | Gel | Cheese, butter |
| Gas | Solid | Solid foam | Sponge, rubber foam |
| Solid | Liquid | Sol | Mud, milk of magnesia |
| Liquid | Liquid | Emulsion | Milk, hair cream |
| Gas | Liquid | Foam | Froth, whipped cream |
| Solid | Gas | Solid aerosol | Smoke |
| Liquid | Gas | Liquid aerosol | Fog, mist |
Q. 10. Define concentration of a solution. How is concentration of a solution expressed ?
Ans.— Concentration of a solution. It indicates the amount of solute dissolved per unit mass or volume of solvent or solution.
The concentration of a solution can be expressed as
(i) Mass percentage of a solution = Mass of Solute / Mass of Solution × 100(ii) Mass of volume percentage of a solution = Mass Solute / Volume of solution × 100
Q. 11. What is paper chromatography? How will you separate the coloured constituents present in a mixture of ink and water ?
Ans.— The process of separation of different dissolved components of a mixture by adsorbing them on a suitable material (called adsorbent) is called chromatography. The adsorbent can be solid or liquid. For example, alumina, magnesium oxide, special filter que most rotalli yd betonqos el sidstoes paper.
The components of a mixture are generally dissolved in a solvent like water, alcohol etc.
If a filter paper is used as an adsorbent for the separation of a components of a mixture, this technique is called paper chromatography.
The process of separation of coloured constituents present in a mixture of ink and water is described ahead :
(i) Take a special filter paper about 25 cm long and 4 cm broad and stick it to a glass nerod at its one end with the help of gum as shown given ahead. Mark a line at a distance of 3 cm from the lower end with the help of pencil. Put a drop of ink at the centre of this line with the help of a fine capillary.
(ii) Dip this end in water taken in a beaker upto 2 cm.
(iii) Suspend this filter paper in a tall cylinder and allow it to stand undisturbed for one hour. The water rises up the filter paper and reaches the ink drop, dissolves its components and rise upwards along with water. The different components of ink are adsorbed upto different extents on the filter paper, therefore, they travel different distances on the filter paper.
(iv) After one hour, the filter paper is taken out and dried. Different bands of colours corresponding to the components of ink are produced on the filter paper. This filter paper is called chromatograph.

Q. 12. Briefly describe simple methods of separating the following mixtures :
(a) Powdered chalk and sugar
(b) Nitre and common salt
(c) Iron and copper filings
(d) Ammonium chloride, sand and common salt
(e) Ammonia and hydrogen.
Ans.— (a) Powdered chalk and sugar can be separated by using water which dissolves sugar and chalk is insoluble. It is separated by filtration. From sugar solution, sugar is obtained by evaporating water.bedoel vierne
(b) Nitre and common salt. The mixture can be separated by fractional crystallisation from the solutions in water because they have different solubilities in water.
(c) Iron and copper filings can be separated by using a magnet when iron filings cling to magnet whereas copper filings don’t.
(d) Ammonium chloride, sand and common salt. Ammonium chloride is separated by sublimation. Sand and common salt are separated by using water when sand remains insoluble and is separated by filtration. From aqueous solution, sodium chloride can be separated by evaporation.
(e) Ammonia and hydrogen can be separated by diffusion through porous pot. Ammonia and hydrogen have different rates of diffusion due to different densities.
Q. 13. How will you separate liquid-liquid mixture or immiscible liquids ?
Ans.— The liquid-liquid mixtures can be separated by using :
1. Separating funnel
2. Fractional distillation.
1. Separation of liquid-liquid mixture by using separating funnel. This method is used when the two liquids are immiscible. For example, a mixture of carbon disulphide and water can be separated by this method.
The mixture is taken in a separating funnel. The funnel is allowed to stand for sometime. On standing, the liquid having higher density forms the lower layer whereas the liquid having lower density forms the upper layer. The two liquids are taken out from the separating funnel in separate conical flask.
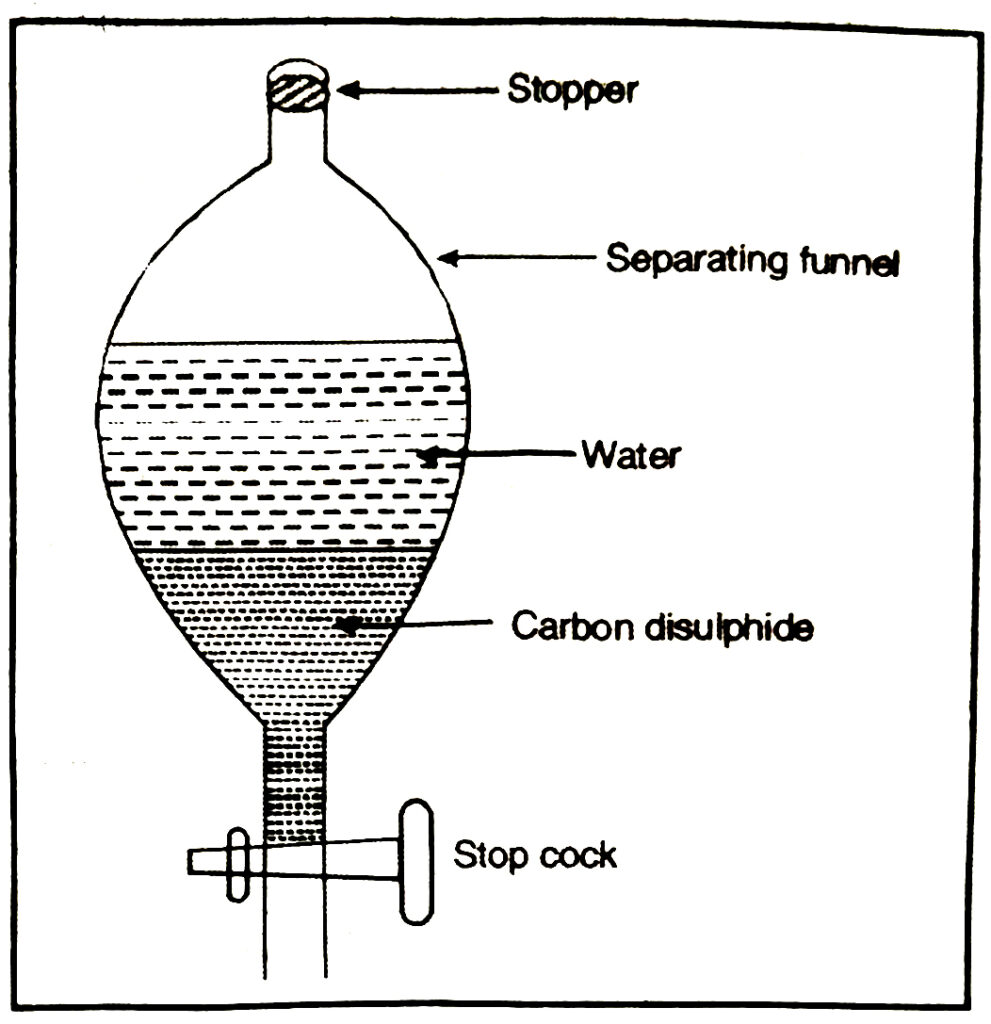
2. Separation of liquid-liquid mixture using fractional distillation. The process of separating the mixture of two immiscible liquids by using distillation carried out with the help of a long fractionating column is called fractional distillation. For example, a mixture of ethyl alcohol and water can be separated by this method. The apparatus is fitted as shown below :

The mixture of ethyl alcohol and water is heated in a distillation flask fitted with a fractionating column. On heating the vapour of liquid having lower boiling point are produced first and condensed in the water condenser and collected in a receiver. When the temperature of thermometer begins to rise, the vapour of other liquid are produced and these are condensed and collected in a separate receiver.
Homogeneous mixture. e.g. Brass is a homogeneous mixture of copper and zinc.
Heterogeneous mixture. e.g. common salt and sand.
Q. 14. How will you separate the solid-liquid mixtures ?
Ans.— The solid-liquid mixtures can be separated by the following methods :
1. By sedimentation and decantation. In this method, the mixture is allowed to stand when the solid particles settle down as sediment whereas clear liquid is left behind which is poured out carefully. This process is called decantation e.g. mixture of sand and water can be separated by this method. By this method, the complete separation is not possible.
2. By filtration. In this method, the mixture can be separated by using filter paper when the insoluble solid is left on the filter paper whereas the clear liquid passes out from the filter paper and is collected. For example, a mixture of chalk and water can be separated by this method.

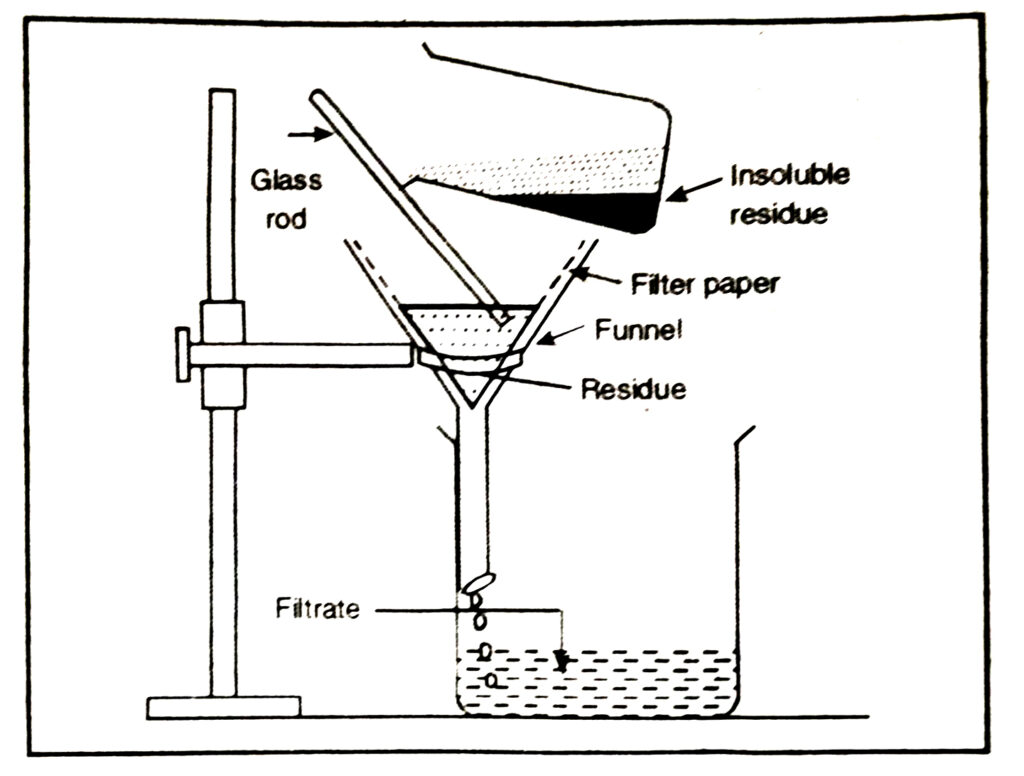
Q. 15. Compare the following sentences with appropriate terms such as evaporation, filtration, distillation, fractional distillation, sublimation, separating funnel.
(a) Ammonium chloride is separated from a mixture of sodium chloride and ammonium chloride by the process of ……….. .
(b) When sodium hydroxide is added to ferric chloride solution, a reddish brown precipitate is formed. The precipitate is separated from the mixture by the process of …………. .
(c) Benzene and water are ………….. liquids and can be separated by …………. .
(d) Pure iodine can be obtained by the process of …………nesliga
(e) Greasy spots can be removed from clothes by …….. .
Ans.— (a) Sublimation (b) Filtration (c) Immiscible, separating funnel (d) Sublimation (e) Petrol.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Give three characteristics of a pure substance.
Ans.— 1. It is homogeneous.
2. It has a definite set of properties.
3. A pure substance cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any known physical method.
Q. 2. Give three characteristics of a mixture.
Ans.— 1. The components of a mixture are present in any ratio.
2. It can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
3. The mixture can be separated with its constituents by physical or mechanical methods only.
Q. 3. Give reasons to show that ammonia is a compound.
Ans.— (i) The properties of ammonia are different from those of its components i.e. nitrogen and hydrogen.
(ii) When ammonia is formed from nitrogen and hydrogen, energy is given out.
(iii) In ammonia, N and H are present in fixed ratio of 14: 3 by mass.
Q. 4. Give two points of evidence that sodium chloride is a compound.
Ans.— Sodium chloride is a compound because :
(i) in sodium chloride, sodium and chlorine are combined chemically in a fixed ratio by mass.
(ii) the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine is accompanied loss of energy.
Q. 5. Give three reasons why air is considered a mixture and not a compound.
Ans.— In air :
(i) the components are not present in any fixed ratio.
(i) the properties of air are average of the properties of its components.
(ii) the components can be separated by physical methods.
Q. 6. Name the technique which could be used to separate
(i) Iodine crystals from sand (ii) Petrol from crude oil.
Ans.— (i) Iodine crystals can be separated from sand by sublimation.
(ii) Petrol can be separated from crude oil by fractional distillation.
Q. 7. How will you separate :
(i) Pure water from sea water ?
(ii) Kerosene oil from a mixture of kerosene oil and petrol ?
Ans.— (i) It can be obtained by the process of distillation. When sea water is distilled, water distils, and vapour are condensed in a receiver whereas common salt is left behind in the retort.
(ii) Kerosene oil can be separated from a mixture of kerosene oil and petrol by fractional distillation when petrol distils off first and then kerosene oil distils off.
Q. 8. (i) Name the kind of change of state when naphthalene changes into gaseous state.
(ii) Name one element which undergoes similar change as in (i).
(iii) Name a common substance which exists in all the three states of matter.
Ans.— (i) Sublimation (ii) Ammonium chloride (iii) Water.
Q. 9. Define electrophoresis.
Ans.— Electrophoresis is the process of migration of colloidal particles towards oppositely charged electrode under the influence of an electric field. The electrophoresis is due to the charge present on the colloidal particles.
Q. 10. Explain Brownian movement.
Ans.— Brownian movement. When colloidal solutions are viewed with the help of ultra-microscope, it is observed that colloidal particles follow zig-zig path. This is called Brownian movement. This effect is due to the unequal impacts of the particles of dispersion medium with colloidal particles.
Q. 11. Explain Tyndall effect.
Ans.—Tyndall effect. If a bright, narrow and convergent beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution and is viewed at right angles with the help of a microscope, the path of light becomes, visible and a bright cone of light called Tyndall cone is produced. This luminosity of path of a beam of light in a colloidal solution is called Tyndall effect.

Q. 12. Choose the appropriate word (s) and complete the sentences (i) to (iv) given below.
(i) In a refinery, petrol is obtained from crude oil by the process of ……… .
(ii) Grass stains are removed from the clothing by using ………. as solvent.
(iii) Common salt is obtained from sea water by the process of ……. .
(iv) When caustic soda solution is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate, a blue precipitate of copper hydroxide is obtained. The copper hydroxide can be separated from the mixture by the process of……….. .
Ans.— (i) Fractional distillation (ii) methylated spirit (iii) evaporation (iv) filtration.
Q. 13. Can a mixture of chloroform (b.pt. 61°C) and carbon tetrachloride (b.pt. 77°C) be satisfactorily separated by the process you use for separating the various fractions of petroleum ?
Ans.— Yes, a mixture of chloroform and carbon tetrachloride can be separated by using fractional distillation as used for the separation of various fractions of petroleum. The heating should be carried out slowly on a sand bath and vapours are condensed in a Liebig condenser and collected in separate receivers.
Q. 14. Name a mixture used :
(i) by all living beings
(ii) in the construction of buildings
(iii) as a food.
Ans.— (i) Air (ii) Cement (iii) Milk.
Q. 15. Which of the following statements are correct and which are incorrect ?
(i) Milk is a mixture.
(ii) Smoke is a mixture of solids and gases.
(iii) Ice cream is a mixture.
(iv) Mercury is a solid
(v) Thums up is a homogeneous mixture.
Ans.— (i) True
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) True
Q. 16. Define physical change and chemical change.
Ans.— Physical Change. It is a temporary change in which only the physical properties of substances change and it can be easily reversed.
Examples : Glowing of an electric bulb, evaporation of water.
Chemical Change. It is a permanent change in which the chemical properties of substances change and there is a change in composition and cannot be reversed.
Examples : Baking of a cake, Drying of a paint etc.
Q. 17. Define colloidal solution.
Ans.— It is a heterogeneous mixture or solution in which the particles having size 1 to 100 nm and are suspended in a suitable solvent or dispersion medium. For example, starch solution.
Q. 18. Define dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Ans.— Dispersed phase. In the colloidal solution colloidal particles constitute dispersed phase.
Dispersion medium. In the colloidal solutions the medium in which colloidal particles are dispersed in, is called dispersion medium.
e.g. in the colloidal solution of starch in water, starch particles constitutes dispersed phase and water constitutes dispersion medium.
Q. 19. Define crystallisation. Give its importance.
Ans.— It is a process in which a pure solid in the form of crystals is separated by cooling its hot saturated solution in a suitable solvent.
Importance :
1. For the purification of salt obtained from sea water.
2. To get crystals of alum from impure samples.
Q. 20. While diluting a solution of salt in water, Anu by mistake added acetone (boiling point, 56°C). What technique would you suggest her to get back acetone ? Justify your choice.
Ans.— Acetone can be separated from mixture by distillation because it h because it has lesser boiling point than water and it will come out ut first.ogomon & ei qu’ eroudi
Q. 21. (i) Some reduced iron filings and powdered roll sulphur are well mixed and heated in a test tube. Describe all what you observe.
(ii) Name the grey mass which is formed in test tube at the end of reaction.
(iii) Would you call the above reaction : exothermic or endothermic ?
Ans.— (i) When iron filings and powdered roll sulphur are well mixed and heated in a test tube, iron (II) sulphide is produced
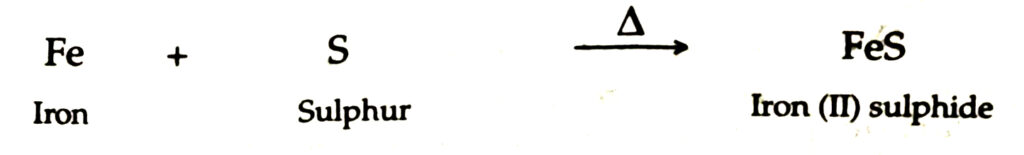
(ii) Grey mass of iron (II) sulphide is produced.
(iii) The above reaction is endothermic, because heat energy is absorbed.
Q. 22. What are exothermic and endothermic reactions ?
Ans.— Exothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is evolved. e.g. burning of candle.
Endothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed e.g. decomposition of calcium carbonate to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Q. 23. What are the advantages of crystallisation over evaporation ?
Ans.— 1. Some solids decompose on heating to dryness.
2. Some solids like sugar may get charred on heating.
3. Some impurities may be present in the solution on dissolving the impure solid in a solvent.
Q. 24. Define chromatography and give its importance.
Ans.— It is the technique of separating those solutes from solution which are adsorbed on the same adsorbent but upto different extents.
Importance : 1. To isolate the compounds from natural sources.
2. For the separation, purification and identification of the constituents of a mixture (coloured as well as colourless).
Q. 25. Define distillation and give its importance.
Ans.— The conversion of a liquid into the vapour and condensing the vapours back into liquid is known as distillation.
Importance :
1. To separate two miscible liquids which boil without decomposition and have sufficient differences in their boiling points (more than 30°C).
2. To separate a volatile component of a solution from a non-volatile component.
Q. 26. solution of acetone in water contains 5 ml is 50 ml of its aqueous solution. Calculate the volume percentage of the solution.
Ans.— Volume of solute = 8 ml
Volume of solution = 50 ml
Volume percentage of solution = 5/10 × 100 = 10
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Define aqueous solution.
Ans.— It is a solution in which water acts as a solvent.
Q. 2. Define concentration of a solution.
Ans.— It indicates the exact amount of solute dissolved in an exact amount of solvent or solution.
Q. 3. How will you check the purity of a substance ?
Ans.— A pure substance has a fixed melting and boiling points at a given pressure.
O. 4. What is solvent ?
Ans.— It is the component of a solution which is present in large amount and in which solute is dissolved and has the same physical state as solution.
Q. 5. Define ternary solution.
Ans.— A solution having three components is called a ternary solution.
Q. 6. What is an alcoholic solution ?
Ans.— A solution in which alcohol is the solvent is called alcoholic solution.
Q. 7. Define unsaturated solution.
Ans.—A solution in which more of solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is said to be unsaturated solution.
Q. 8. What is a non-aqueous solution ?
Ans.— It is a solution in which solvent is other than water.
Q. 9. Define emulsion.
Ans.— Emulsion. It is a colloidal solution of two immiscible liquids e.g. milk, face cream etc.
Q. 10. What liquid would you select to remove sulphur from crucible ?
Ans.— Carbon disulphide is suitable for removing sulphur from crucible because sulphur is soluble in it.
Q. 11. What process would you use to separate and then collect alcohol (b.pt. 78°C) from a mixture of alcohol and water ?
Ans.— Fractional distillation.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the Correct Answer :
1. A pure substance can be :
(A) Element
(B) Compound
(C) Mixture
(D) both (A) and (B).
Ans.— (D) both (A) and (B).
2. Tyndall effect is shown by :
(A) True solution
(B) Pure liquids
(C) Suspension
(D) Colloidal solution.
Ans.— (D) Colloidal solution.
3. Which is not a compound :
(A) Air
(B) Water
(C) Ice
(D) Ice cream.
Ans.— (A) Air
4. A mixture of Carbon monoxide and Carbon dioxide can be separated by :
(A) Diffusion through a porous pot
(B) Evaporation
(C) Centrifugation
(D) None.
Ans.— (A) Diffusion through a porous pot
5. Mixtures are of :
(A) Two types of
(B) One type
(C) Pure substance
(D) None.
Ans.— (A) Two types of
6. Which represents a chemical change ?
(A) Freezing of water
(B) Digestion of food
(C) Mixing of iron fillings and sand
(D) None of these.
Ans.— (B) Digestion of food
7. Which is a pure substance ?
(A) Air
(B) Milk
(C) Brick
(D) Mercury.
Ans.— (D) Mercury.
8. Which represents a mixture ?
(A) Ice
(B) Ice cream
(C) Diamond
(D) Graphite.
Ans.— (B) Ice cream
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here