PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
PSEB 10th Class Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
→ Control and coordination are the functions of the nervous system and hormones in our bodies.
→ The responses of the nervous system can be classified as a reflex action, voluntary action, or involuntary action.
→ The nervous system uses electrical impulses to transmit messages.
→ The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system that responds to stimuli by electrical impulses.
→ The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
→ The brain is the highest coordinating centre of the body.
→ The nervous system gets information from our sense organs and acts through our muscles.
→ In many animals and some plants, there are some movements not connected with growth.
→ Some movements, in response to the environment, are carefully controlled. Each kind of change in the environment evokes an appropriate movement in response.
→ Living organisms must use systems providing control and coordination.
→ Specialized tissues are used to provide these control and coordination activities.
→ All information from our environment is detected by the specialized tips of some nerve cells.
→ We have generally five sense organs such as the eye, the ear, the nose, the tongue, and the skin.
→ The information is acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell.
→ It sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse.
→ The nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons.
→ ‘Reflex’ is a word we use very commonly when we talk about some sudden action in response to something in the environment.
→ Thinking is a complex activity, so it is bound to involve a complicated interaction of many nerve impulses from many neurons.
→ The thinking tissue in our body consists of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. It sits in the forward end of the skull.
→ Nerves from all over the body meet in a bundle in the spinal cord on their way to the brain.
→ Nerves supply information to various organs of the body.
→ The reflex arcs have evolved in animals because the thinking process of the brain is not fast enough.
→ Brain and reflex arcs receive information from all parts of the body.
→ In fact, many animals have very little or none of the complex neuron networks needed for thinking.
→ The spinal cord is made up of nerves that supply information to think about.
→ The brain and spinal cord constitute the central nervous system.
→ The brain also has to send messages to muscles.
→ The brain allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking.
→ The brain has three major parts or regions, namely the fore-brain, mid-brain, and hind-brain.
→ The fore-brain is the main thinking part of the brain. It has regions that receive sensory impulses of hearing, smell, sight, and so on.
→ Many involuntary actions are controlled by the mid-brain and hind-brain.
→ All the involuntary actions including blood pressure, salivation, and vomiting are controlled by the medulla in the hind-brain.
→ The vertebral column or backbone protects the spinal cord.
→ The plants also use electrical-chemical means to convey the information from cell to cell.
→ Some tendrils are sensitive to touch.
→ Light and gravity change the directions of growing parts of the plant.
→ The directional or tropic movements can be either towards the stimulus or away from it.
→ The stimulated cells release a chemical compound, this compound would diffuse all around the original cell.
→ Hormones are used by multicellular organisms for control and coordination, show a great deal of diversity.
→ Different plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development, and responses to the environment.
→ A hormone called auxin, synthesized at the shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer.
→ The plant hormones are gibberellins which, like auxins, help in the growth of the stem.
→ Adrenaline is a hormone secreted by the adrenal (kidney) gland in humans. It affects the heart, respiration, digestion, skeleton muscles in humans and other organisms.
→ Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make the thyroxine hormone.
→ Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth.
→ In case of iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goiter.
→ Growth hormone is one of the hormones secreted by the pituitary. As its name indicates, growth hormone regulates the growth and development of the body.
→ There is the secretion of testosterone in males and estrogen in females.
→ Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels.
→ Neuron: The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is called a neuron.
→ Sensory organ: The organs which sense the changes in the surrounding environment and pass on the information to the central nervous system are called sensory organs.
→ Hormone: The special chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands (ductless glands) and transported by the blood to control the body functions.
→ Phototropism: The movement of plants towards light is called phototropism.
→ Geotropism: The movement of plant roots due to the earth’s gravity is called geotropism.
→ Chemotropism: The movement of plant parts or plants due to the chemical stimulus is called chemotropism.
→ Phytohormones: These are the hormones secreted by plants to perform various functions.
→ Nastic movements: When the stimulus does not produce any movement in plants.
→ Phytochrome: These are special pigments that respond to the photoperiod.
→ Ganglion: The group of cell bodies of nerve cells is called a ganglion.
→ Reflex action: The involuntary actions towards emergency situations.
→ Reflex arc: The path through which the signal travels during reflex action is called the reflex arc.
→ Spinal cord: Nerves from all over the body meet to form a bundle/cord on their way to connect with the hindbrain is called the spinal cord.
→ Central nervous system: The brain and nerve cord together constitute the central nervous system.
→ Motor neurons: The neurons which carry the responses to the concerned organs.
→ Sensory neurons: The neurons which carry the message from sensory organs to the brain.
→ Nerve impulse: The conduction of chemical or electric signals by nerve cells is called nerve impulse.
→ Voluntary action: These are the actions that need thinking. They are performed knowingly, i.e., controlled by conscious thought. Example. Speaking to a friend, writing a letter, etc.
→ Involuntary action: These are not under the control of the will of an individual. They are automatic responses to a stimulus that is not under the voluntary control of the brain. Example. Touching a hot plate unknowingly.
→ Endocrine glands secrete the hormones directly into the blood.
→ Exocrine glands are glands with ducts that pour their secretion at the site of action.
→ Insulin is the hormone produced by β-cells of islets of Langerhans which controls sugar metabolism.
Science Guide for Class 10 PSEB Control and Coordination InText Questions and Answers
Question 1. What is the difference between reflex action and walking?
Answer:
Differences between reflex action and walking:
| Reflex Action | Walking |
| 1. It is an inborn action and present in an individual right from birth. | 1. Walking is acquired through learning. |
| 2. It is controlled by spinal cord. | 2. It is controlled by hind brain. |
| 3. It cannot be changed. | 3. It can be changed. |
| 4. It is involuntary action. | 4. To start with it is voluntary and later on it becomes involuntary. |
| 5. Response is given by muscles and glands. | 5. Response is given by muscles. |
Question 2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
Synapse is a junction between terminal ends of one axon and dendrites of adjacent neuron. There is a gap between the two called synaptic cleft. As the electrical impulse reaches the terminal knobs, they release chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals cross the gap and start a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of next neuron. Synapse ensures that nerve impulse travels in one direction only.
Question 3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Cerebellum part of hind brain maintains posture and equilibrium.
Question 4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (Incense stick)?
Answer:
Sensory information regarding smell is received by olfactory lobes of brain. As the air passes through the nasal chambers, the olfactory epithelial cells get stimulated and convey the information as electrical impulses to brain which have the power of interpretation.
Question 5. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:
Thinking centres are located in brain. Brain is the co-ordinating centre. Brain and spinal cord in coordination with each other control all voluntary and involuntary actions. The spinal reflexes are produced in the spinal cord but the message of reflex action taken also goes to brain where the thinking process occurs. Some reflex arcs involve the brain rather than the spinal cord only.
Question 6. WTiat are plant hormones? Name any two.
Answer:
Plant hormones. These are chemical compounds secreted by plants which diffuse all around the other cells and regulate the activities. Plant hormones help to co-ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
Examples : Auxins and Cytokinin.
Question 7. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
Sensitive plant show seismonastic movements. It is due to turgidity of cells. The movement of a shoot is a tropic movement.
| Movement of the leaves of sensitive plant | Movement of shoot towards light |
| 1. It is a nastic movement which does not depend on the direction of stimulus. | 1. It is a tropic movement. |
| 2. The stimulus is touch. | 2. The stimulus is light. |
| 3. It is caused by sudden loss of water from the swelling present at the base of the leaves. | 3. It is caused by the unequal growth on the two sides of the shoot. |
| 4. It is not a growth movement. | 4. It is a growth movement. |
Question 8. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer:
IAA = Indole-3-Acetic Acid.
Question 9. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
Auxins synthesised in the tip helps the cells to grow longer. Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or support by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. It is due to accumulation of auxins.
Question 10. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer:
Experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism
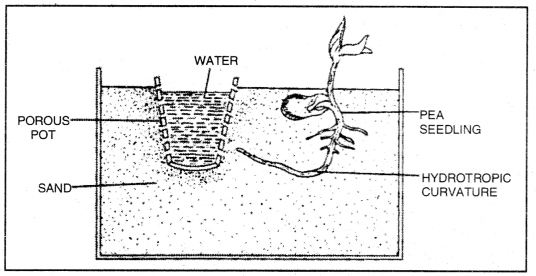
Demonstration of hydrotropism
- Take a porous pot and fill it with water.
- Keep a few freshly germinated pea seedlings in a dried sand.
- As the water is not available in sand the root growing will bend towards porous pot filled with water.
- You wall observe a hydrotropic curvature of the root as it grows towards water.
- This bending of root show the movement as a response towards water.
Question 11. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
Chemical coordination. It is brought about by chemical messengers called hormones. They are secreted by endocrine glands (ductless glands). The hormones are carried by the blood to the site of action (target organs). The hormones are consumed during their action. Hormones provide wide ranging changes.
Question 12. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:
Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone. Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. It is required for growth. In case of deficiency of thyroxine, a disorder called goitre is caused. Thus, the use of iodised salt is advisable .to prevent iodine deficiency disorders in the body.
Question 13. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into blood?
Answer:
Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal gland during emergencies. It prepares the body to respond effectively. Following actions occur :
- Heartbeats faster so as to pump the blood to muscles that need more energy.
- The blood supply to the digestive system and skin is reduced due to the contraction of muscles around these organs. This helps in diverting blood supply to muscles.
- Breathing becomes fast.
Question 14. Why are some patients with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Insulin hormone is secreted by Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. This hormone helps in regulating sugar levels in the blood. Its deficiency results in high sugar levels and causes many harmful effects. To bring the sugar level to normal in such diabetic patients, insulin injections are given.
PSEB 10th Class Science Guide Control and Coordination Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1. Which of the following is plant hormone?
(A) Insulin
(B) Thyroxin
(C) Oestrogen
(D) Cytokinin.
Answer:
(D) Cytokinin.
Question 2. The gap between two neurons is called :
(A) Dendrite
(B) Synapse
(C) Axon
(D) Impulse.
Answer:
(B) Synapse.
Question 3. The brain is responsible for :
(A) Thinking
(B) Regulating the heart beat
(C) Balancing
(D) All of above.
Answer:
(D) All of above.
Question 4. What is the function of receptors in the body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:
Receptors. They are meant for receiving and detecting the information from environment. They are located in sense organs. They receive the information detected by tips of dendrites and convey them as electrical impulses.
If receptors do not detect the information, there will not be any co-ordination. It may lead to accidents. Body response will not be there.
Question 5. Draw a labelled diagram of neuron and explain its function.
Or
Draw the structure of neuron and label the following on it.
Nucleus, Dendrite, Cell body and Axon.
Answer:
Functions of Neuron (Nerve cell).
- Nerve cells are specialised for conducting information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another part.
- Dendrites acquire the information.
- Axon conducts information as electrical impulse.
- Terminal arborization pass the information as chemical stimulus at synapse for onward transmission.
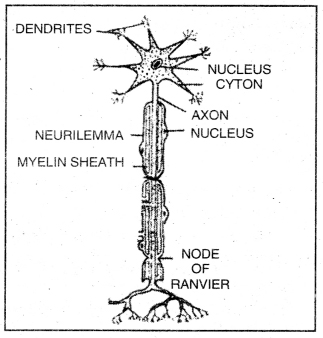
A Nerve Cell
Question 6. How does phototropism Occur in planes?
Answer:
Phototropism.
It is an established fact that plants bend towards light when they are exposed to it from one side of long axis. The aerial parts are positively phototropic and the roots and other underground parts bend away from light. These movements are due to interaction of light and auxins. The unilateral growth causes bending of stem as tip grows more rapidly.
Question 7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury?
Answer:
- Spinal cord mainly controls reflex actions in the body. Spinal cord is made up of nerves which supply information to think about. Thus these actions will get disrupted in case of injury to spinal cord.
- Sensation and movement are restricted.
Question 8. How does chemical co-ordination occur in plants?
Answer:
Chemical coordination in plants
- Plants do’not have well organised nervous and muscular system, still they respond to stimuli and co-ordinate in the best possible way.
- Different kinds of stimuli trigger the release of chemicals called plant hormones or phytohormones.
- These phytohormones help to coordinate growth development and responses to the environment.
- Auxins stimulate the cells to grow longer on one side of shoot in response to light thus it bends way.
- Gibberellins help in growth of stem.
- Cytokinins promote cell division.
- Abscisic acid inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
Question 9. What is the need for a system of control and co-ordination in an organism?
Answer:
Control and Co-ordination in the body is of two types i.e. nervous control and hormonal control. Nervous control is rapid. It takes place through electrical signals called nerve impulses. The hormonal control is through chemical messengers called hormones secreted by endocrine (ductless) glands and carried by blood to the target organs.
Question 10. How are involuntary actions different from reflex action?
Answer:
Reflex action is sudden and quick response to input (stimulus). It saves from many accidents. It is controlled by spiral cord. The involuntary actions are controlled by midbrain and hind brain. These are the actions in which thinking does not have any control. These actions are blood pressure, salivation and cycling.
Question 11. Compare and contrast the nervous and hormonal mechanism for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
Differences between endocrine system and nervous system
| Endocrine System | Nervous System |
| 1. The action of endocrine system is often very diverse, affecting many cells and sometimes several organs found in different parts of the body. | 1. The action of nervous system is limited to a few muscle fibres or gland cells of an organ or organ system. |
| 2. The system is not directly connected to organs or tissues under its control. | 2. The system is directly connected to tissues or organs under its control. |
| 3. It exerts its control through hormones or chemical regulators poured into circulatory system. | 3. Nervous system exerts its control through chemical stimulants poured directly over the tissues or organs. |
| 4. The information is transmitted slowly. | 4. The information is transmitted almost instantaneously. |
| 5. The system takes time to produce response. It, therefore, regulates those processes where the response is not immediately required. | 5. It controls process where an immediate response is required. |
| 6. The effect is long lasting. | 6. The effect is short lived. |
Question 12. What is the difference between the manner is which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our leg.
Answer:
Movement of human leg is under the control of nervous system. It is under the
direction of motor area which, controls voluntary muscles of leg. The sensitive plant “Touch me not,” moves its leaves in response to touch but without any regulation by nervous tissue.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is not a plant hormone?
(A) GA3
(B) Ethylene
(C) Phytochrome
(D) Auxins.
Answer:
(C) Phytochrome
Question 2. Cytokinins stimulate the cell for:
(A) Turgor
(B) Elongation
(C) Cell division
(D) Wall thickening
Answer:
(C) Cell division
Question 3. Movement in the leaf of the Touch-me-not (Mimosa) plant is:
(A) Epinasty
(B) Hyponasty
(C) Nyctinasty
(D) Seismonasty.
Answer:
(D) Seismonasty.
Question 4. Hydrotropism is response towards:
(A) light
(B) touch
(C) gravity
(D) water.
Answer:
(D) water.
Question 5. The reflex action is :
(A) blinking of eyelid
(B) swallowing of food bolus
(C) sneezing and coughing
(D) All the above.
Answer:
(D) All the above.
Question 6. Nerve fibres transmit the nerve message by means of :
(A) chemical
(B) physical
(C) electrochemical
(D) electrical.
Answer:
(C) electrochemical
Question 7. Brain and spinal cord act as :
(A) Receptors
(B) Effectors
(C) Modulators
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(A) Receptors
Question 8. Which of the following is not a structure in the hind brain?
(A) Medulla oblongata
(B) Thalamus
(C) Cerebellum
(D) Pons.
Answer:
(B) Thalamus
Question 9. Which one of the following endocrine gland produces two distinct hormones?
(A) Adrenal
(B) Thymus
(C) Testis
(D) Pineal.
Answer:
(A) Adrenal
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Are movements in living organi-sms a characteristic of life?
Answer:
No.
Question 2. Movements in plants are due to result of which kind of action?
Answer:
Growth.
Question 3. Crying, respiration and voluntary movements are linked to which category.
Answer:
Involuntary actions.
Question 4. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Answer:
Neuron.
Question 5. What is the function of dendrites?
Answer:
Dendrites acquire the information.
Question 6. Name the structure of neuron which conduct impulse.
Answer:
Axon.
Question 7. Name the sites where electrical impulses are conducted into hemical impulses.
Answer:
Synapse.
Question 8. What is a neuron?
Answer:
Neuron: It is a structural and functional unit of nervous system. It is the largest cell of the body.
It has three components i.e.
- cell body
- dendrites
- axon.
Question 9. What is synaptic cleft?
Answer:
The gap between dendrites of one neuron and axon of the next neuron is called synaptic cleft.
Question 10. Mention the receptors for light and sound in animals.
Answer:
- Receptors for light. Photore-ceptors (Eyes)
- Receptors for sound. Phonoreeeptors (Ears)
Question 11. What is reflex action?
Answer:
Reflex action: It is sudden spontaneous, mechanical, involuntary response to a stimulus by voluntary organs.
Question 12. Give two examples of reflex action.
Answer:
- Closing of eyes in response to bright light.
- Withdrawal of hand in case touched a hot plate.
Question 13. Which organ is involved in reflex action?
Answer:
Spinal cord.
Question 14. Name three parts of neurons in complex reflex arc.
Answer:
A complex reflex arc is composed of afferent, connector and efferent neurons.
Question 15. Name the main constituents of central nervous system.
Answer:
Brain and spinal cord.
Question 16. What are the components of peripheral nervous system?
Answer:
Cranial (cerebral) nerves and spinal nerves originating from brain and spinal cord respectively.
Question 17. Name the three main parts of brain.
Answer:
Fore brain, Mid brain and Hind brain.
Question 18. List three involuntary actions.
Answer:
Circulation of blood, secretion of saliva and movement of food in the alimentary canal.
Question 19. Involuntary actions are cont-rolled by which part of brain.
Answer:
Medulla.
Question 20. Cycling, walking along a straight path and picking up of pencil are controlled by which part of brain.
Answer:
Cerebellum of hind brain.
Question 21. Name the part of brain which control balancing and voluntary movements of body.
Answer:
Cerebellum of hind brain.
Question 22. What is the function of cerebro spinal fluid?
Answer:
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) acts as a shock absorber.
Question 23. Name the structure which protects spinal cord.
Answer:
Vertebral column.
Question 24. How does plant cell change its shape?
Answer:
Change in the water content of plant cell.
Question 25. What is the function of tendril.
Answer:
Tendril helps in climbing along a support.
Question 26. Name the hormone which help in cell division.
Answer:
Cytokinin.
Question 27. Name the hormone secreted by adrenal gland.
Answer:
Adrenaline.
Question 28. Where is thyroxine hormone secreted?
Answer:
Thyroid gland.
Question 29. Name the hormone which plays role in metabolism of carbo-hydrates, proteins and fats.
Answer:
Thyroxine hormone.
Question 30. Name the gland which secreted growth hormone.
Answer:
Pituitay gland.
Question 31. Name the hormones which play role in maturity during adolescence in boys and girls.
Answer:
Testosterone in boys and estrogen in girls.
Question 32. Where is insulin secreted?
Answer:
Pancreas.
Question 33. In addition to nervous system, which other system plays role in coordination.
Answer:
Endocrine system which secretes chemical messengers called hormone.
Question 34. Name the hormone which helps in chemical co-ordination in plants.
Answer:
Phytohormone (plant hormones).
Question 35. What is the main element of thyroxine hormone?
Answer:
Iodine.
Question 36. What is the main function of the vasopressin hormone?
Answer:
Regulates water content in the blood.
Question 37. Write the function of hormone ‘thyroxine’ in our body.
Answer:
It regulates metabolism of carbo-hydrates, fats and proteins.
Question 38. Which two systems of body work together for control and coordination of body parts?
Answer:
Nervous system and Hormonal system (endocrine glands).
Question 39. Which organ secretes a hormone when the blood sugar rises. Name a digestive enzyme released by this organ.
Answer:
- Pancreas releases insulin hormone.
- Trypsin enzyme.
Question 40. Define endocrine glands.
Answer:
These glands are ductless glands which secrete chemical messengers called hormones carried by blood to target organs.
Question 41. Name the hormone which inc-reases blood pressure and rate of heart beat.
Answer:
Adrenaline.
Question 42. Name the female sex hormones.
Answer:
- Progesterone
- Oesterogen
- Estardiol.
Question 43. Name the following :
(i) The cause of diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
Deficiency of insulin
(ii) The two portions of adrenal gland.
Answer:
Adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
(iii) The gland which function actively in emergency situations.
Answer:
Adrenal medulla
(iv) The hormone of pituitary that helps in child birth.
Answer:
Oxytocin
(v) The endocrine gland located on the top of kidneys.
Answer:
Adrenal gland
(vi) The gland which secretes insulin.
Answer:
Pancreas.
Question 44. Name the following :
(i) The hormone which prepares the body to meet any emergency situation.
Answer:
Adrenaline
(ii) An example of the disease caused due to insufficient secretion of hormone.
Answer:
Cretinism
(iii) The gland, which produces the so called ‘emergency hormone’.
Answer:
Adrenal gland
(iv) Carrier of hormones from the gland to target organ.
Answer:
Blood
(v) The hormone which controls (i.e. reduces) the level of sugar in blood, and the gland which secretes it.
Answer:
Insulin, Pancreas.
Question 45. Name the three kinds of neuron.
Answer:
- Motor neuron
- Sensory neuron
- Relaying neuron.
Question 46. What happens when bright light is focussed on eyes?
Answer:
Eyes get closed in response to light so as to protect the eyes.
Question 47. Where are receptors located in the body?
Answer:
Sense organs.
Question 48. What is the function of gustatory receptors?
Answer:
To taste the food.
Question 49. Name the organs concerned with sense of smell.
Answer:
Olfactoreceptor.
Question 50. Which part of plant bends towards light?
Answer:
Shoot apex.
Question 51. Name the largest cell present in human body.
Answer:
Neuron.
Question 52. What are the three basic regions of the brain?
Answer:
- Fore brain
- Mid brain
- Hind brain.
Question 53. Which part of the brain controls the heart?
Answer:
Medulla oblongata.
Question 54. Name the following :
(i) Structural and functional units of the nervous system.
Answer:
Neurons
(ii) Two type of peripheral nerves.
Answer:
Cranial and spinal nerves
(iii) Most important part of the nervous system.
Answer:
Brain
(iv) Three divisions of human brain.
Answer:
Fore brain, mid brain and hind brain
(v) Largest part of the brain.
Answer:
Cerebrum
(vi) Two types of matter present in brain and spinal cord.
Answer:
White matter and grey matter.
Question 55. How many hormones are secreted by pituitary gland?
Answer:
13 Types of hormones are secreted by pituitary gland.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are hormones? Why are they called chemical messengers? What are the general properties of hormones?
Answer:
Hormones: They are informational molecules secreted by the endocrine cells in one part of the body in response to changes in external or internal environment, and carried by blood to another part where they stimulate or inhibit specific physiological processes for the good of the body as a whole.
In other words, the hormones are chemical messengers that regulate the biological processes in the organisms as they carry the information in the form of chemicals.
General properties of hormones
- The hormones themselves do not create biochemical processes. They only modify the existing metabolic processes and change the rate of action.
- Hormonal actions are usually long lasting than those produced by nerve impulses.
- They are effective in minute quantities.
- They are secreted in response to specific stimuli.
- They are secreted independent of one another.
Question 2. What is phototropism?
Answer:
Phototropism is the growth movement in response to unidirectional stimulus of light. It is observed in plant stem, root, leaves. Stem is positively phototropic.
Question 3. Write differences between nastic and tropic movements.
Answer:
| Nastic Movements | Tropic Movements | |
| 1. Growth | growth independent movements | growth dependent movements |
| 2.Time of Action | immediate | slow |
| 3. Response to Stimulus | Non-directional | directional |
| 4. Reason for action | change in turgor | cell division |
| 5. Alternate name | nastics | tropism |
| 6. Examples | folding of leaves of touch me- not(Mimosa), opening and closing of stomata | phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism, chemotropism |
Question 4. Why is pituitary gland called master endocrine gland?
Answer:
Pituitary gland is a small pea-shaped endocrine gland situated inferior to hypothalamus. It is called master endocrine gland because its secretion control and regulates the secretions of all other endocrine glands.
Question 5. Name one disorder each in case of less (hypo) or excess (hyper) secretion of insulin and thyroxine.
Answer:
| Name of hormone | Disorder due to hvposecietion | Disorder due to hypersecretion |
| Insulin | Diabetes | Hyperglycemia |
| Thyroxine | Myxedema | Exophthalmic goitre |
Question 6. List four uses of auxins.
Answer:
Functions of IAA
- IAA brings about cell elongation.
- It initiates the formation and growth of roots and stem if applied to the cutting of stem.
- Application of auxins causes formation of seedless fruits.
- It has an inhibitory effect on abscission of leaves and fruits, which lead to leaf fall and fruit drop.
- The parthenocarpy can be induced by application of auxins.
- Respiration rate increases with auxins.
Question 7. What are the physiological effects of gibberellins?
Answer:
Physiological effects of gibberellins :
- Gibberellins promote cell-division.
- Gibberellins promote cell-elongation.
- Gibberellins lead to increase in the length of internodes.
- Gibberellins induce parthenocarpy in many cases e.g. tomato.
- Gibberellins promote flowering in some plants like Chrysanthemum.
- Gibberellins prevent senescence in leaves.
Question 8. What are the functions of cytokinins?
Answer:
Functions of cytokinins
- It promotes cell division by activating DNA synthesis.
- It promotes the growth of lateral buds by neutralising the auxin.
- It is reported that cytokinin activates protein synthesis in buds by incorporation of labelled amino acid.
- It is also found to be effective in removing the apical dominance.
Question 9. Write short notes on abscisic acid and ethylene.
Or
Write functions of abscisic acid.
Answer:
Abscisic acid (ABA)
- Abscisic acid (ABA) is a growth regulator found widespread in plants. It is a growth inhibitor.
- Abscisic acid causes the inhibition of mitosis in the vascular cambium.
- As the winter approaches, the ABA brings about the dormancy of axillary buds.
- Abscisic acid also induces the dormancy in seeds.
- It causes ageing in leaves. It is also called ‘stress hormone’.
Question 10. Write functions of Ethylene.
Answer:
Ethylene:
Ethylene is synthesized in the plants from amino acid methionine. Ethylene produces the effect on the growth of vegetative and reproductive parts of the plant.
Ethylene is the only gaseous phytohormone. It is basically a growth inhibitor and brings about the following functions in the plant body.
- Ethylene inhibits root growth and development of lateral buds.
- Ethylene inhibits the elongation of stem and stimulates its transverse expansion.
- The changes which occur during the ripening of fruit are also attributed to the effect of ethylene.
- Ethylene also accelerates the process of ageing in plant organs.
Question 11. What is chemotropism?
Answer:
Directional movement of a plant/ or its parts in response to chemicals is called chemotropism e.g. growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule is a chemotropic movement due to which fertilization of flower takes place.
Question 12. Give examples of geotropism.
Answer:
- 1.Roots move in the direction of gravity (positive geotropism).
- Shoots move (up) against direction of gravity (negative geotropism).
Question 13. What is the type of phenomenon shown in the figure? Define the same.
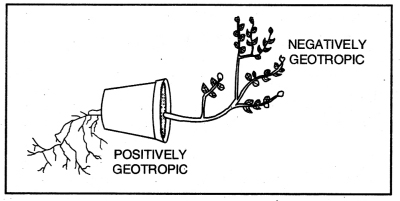
Answer:
- Geotropism:
- Geotropism. It is a type of growth movements induced by stimulus of gravity.
Question 14. Differentiate between hormones and enzymes.
Answer:
Differences between hormones and enzymes
| Hormones | Enzymes |
| 1. They are produced by glands which lack ducts (endocrines). | 1. They are generally produced by glands which bear the ducts (exocrine). |
| 2. They may be steroids, amines or protein in chemical nature, | 2. They are always proteinic in nature. |
| 3. They are consumed during metabolism. | 3. They act as catalysts and are produced in the same quantity at the end of reaction. |
Question 15. Briefly explain the autonomic nervous system.
Answer:
- Autonomic nervous system: The autonomic nervous system coordinates the activities of viscera through the regulation of their smooth muscles and glands by its nerves.
- The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body to face an emergency by accelerating heart beat and breathing rate; dilating the bronchioles to facilitate gas exchange; and sending blood to the organs which need it most such as heart, brain and skeletal muscle for “fight or flight”. It releases neurotransmitters adrenaline and noradrenaline into the synapses (adrenergic).
- The parasympathetic nervous system acts when body is relaxing after an emergency. It restores heart beat and respiratory rate to normal and restarts digestion. It releases acetylcholine into the synapses (cholinergic).
Question 16. List different parts of the human nervous system.
Answer:

Question 17. Define ‘nerve impulse’. Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse?
(i) towards the cell body?
(ii) away from the cell body?
Answer:
Nerve impulse: The information passing through neurons in the form of electrical and chemical signals is called nerve impulse. Neurofibrils in the neuron help to conduct impulses.
Neuron is structural and functional unit of nervous system.
- Dendrite carries the impulse to cell body.
- Axon carries impulse away from cell body.
Question 18. Name the five major senses of man.
Answer:
Five major senses of man
- Sense of hearing.
- Sense of smell.
- Sense of touch.
- Sense of taste.
- Sense of vision or sight.
Question 19. Write short note on meninges present around brain. Name the fluid present in the spaces in between meninges. Mention its function.
Answer:
Meninges (Sing. Meninx.) The protective membranes present around brain. They are as follows :
- Duramater: It is outer, thick, non-vascular membrane present inner to bones of cranium.
- Piamater: It is inner, thin, vascular membrane present closely around brain.
- Arachnoid membrane: It is the middle membrane.
- Cerebrospinal fluid is present in between the meninges. It protects brain from mechanical shock.
Question 20. Label the parts of human brain.

Answer:
A. Cerebrum
B. Cerebellum
C. Medulla oblongata.
Question 21. What is a gland? Name the two types of glands.
Answer:
Definition: A cell, a tissue, or an organ which secretes certain useful chemical compounds required for particular function is called a gland.
Types: Animals have two types of glands: exocrine and endocrine.
Question 22. How does our body maintain blood sugar level?
Answer:
The timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanisms.
When the sugar levels in blood rise, they are detected by the cells of the pancreas which respond by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
Question 23. Why is pancreas a dual gland?
Answer:
Pancreas is a dual gland because it acts as both endocrine and exocrine gland. As endocrine it secretes hormones like insulin, glucagon. As an exocrine gland, it releases enzymes like trypsin, lipase, amylase etc. Such types of glands are also called heterocrine glands.
Question 24. List the functions of testosterone and estrogen.
Answer:
- Functions of testosterone: Develops male reproductive organs and secondary sexual characters in males.
- Functions of estrogen: Develops female genital organs and secondary sexual characters in females.
Question 25. Name the hormones which stimulate the testis.
Answer:
- Follicular Stimulating Hormone (FSH). It stimulates the production of sperms in the testis.
- Interstitial Stimulating Hormone (ISH). It stimulates the interstitial cells of the testis and produce a male sex hormone known as ‘testosterone’.
The FSH and ISH are secreted by pituitary gland.
Question 26. List some of the functions of adrenal glands.
Answer:
Functions of adrenal glands
- Prepare the body for emergencies.
- Regulate the kidney in maintaining salt and water balance.
- Control blood pressure and pulse rate.
- Control concentration of sodium, potassium and sugar in the body.
- Control some sexual characteristics.
- Influence breakdown of tissue proteins into amino acids.
Question 27. Write a note on turgor movements.
Or
Mechanism of movements shown by Mimosa pudica, if touched.
Answer:
Turgor movements. Mimosa pudica (Touch-me-not) shows typical seismonastic type of movements. It is a paratonic variation type of movement which is brought about in response to external stimulus of touch. Leaf of Mimosa pudica is a compound leaf. It shows pulvini of primary and secondary order of petioles and sub-petioles. It gives a very quick response to a shock stimulus.
Question 28. How do phototropism differ from geotropism?
Answer:
Differences between phototropism and geotropism
| Phototropism | Geotropism |
| 1. Response of parts of plants in the form of growth movement to the stimulus of light is called phototropism. | 1. It applies to growth movements induced by stimulus of force of gravity. |
| 2. Stem and aerial parts bend towards light source. | 2. Stem and aerial parts move away from force of gravity. |
| 3. Roots and other underground parts move away from source of light. | 3. Roots and other underground parts move towards the force of gravity. |
Question 29. List the major endocrine glands and state their position in the human body.
Answer:
The major endocrine glands in the human body are:
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid gland
- Thymus gland
- Islets of Langerhans present in Pancreas
- Adrenal gland
- Testis
- Ovary
- Pineal Gland.
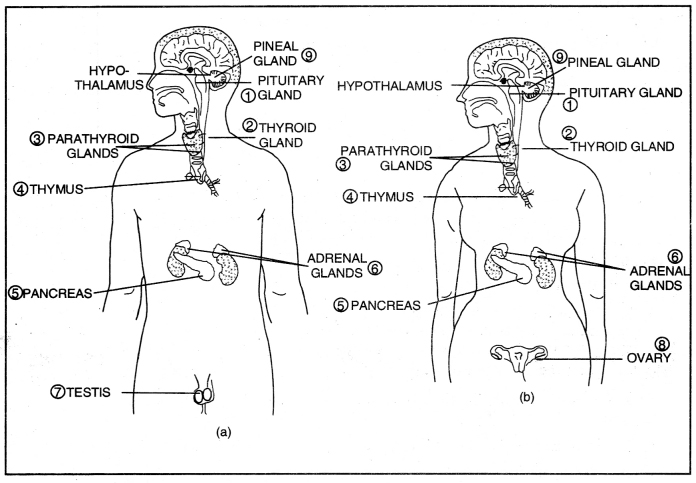
Endocrine glands in human (a) male (b) female
Question 30. Nervous and hormonal system together perform the function of control and co-ordination in human beings.” Justify the statement.
Answer:
Nervous and hormonal system. Both nerves and hormones transmit information between different parts in the animal body, in the same manner (chemical communication). Both coordinate and regulate physiological activities of the organisms. Moreover, there is a considerable coordination between the two. Synthesis and release of some hormones are regulated by nerves. On the other hand, hormones may also influence the activation of nerves. Because of their interrelationship, the nervous and the endocrine system are now together referred to as the neuroendocrine system.
Question 31. What are the general functions of ‘hormones’?
Answer:
Functions of Hormones
- Hormones stimulate the tissue activity.
- Hormones regulate growth and reproduction.
- Hormones control metabolism.
- Hormones synthesize, store and utilize substances like glucose.
- Hormones conserve water and minerals.
Question 32. Label 1 and 2 in the figure given below:
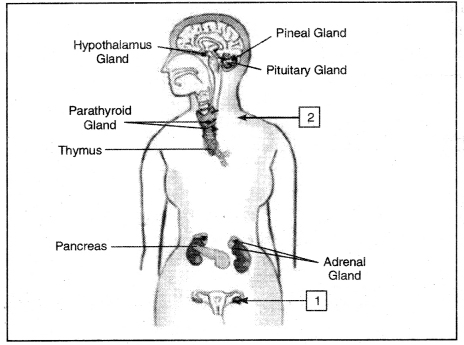
Answer:
1. Ovary
2. Neck showing location of Thyroid.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Draw a well labeled diagram of the human brain and mention the functions of its various parts.
Answer:
Human brain is divided into three parts- Fore brain, mid brain and hind brain.
1. The Fore Brain: It is the largest part of the brain. It consists of the following parts :
(a) Olfactory lobes: They are concerned with sense of smell.
(b) Cerebrum: It is the most important and largest part of the fore brain. It is divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres called corpus callosum.
The functions of cerebrum are :
- It analyses the sensory signals in the association areas and thinking of a proper response.
- It sends response signals (motor signals) to the muscles through the motor areas.
- It stores memory of different experiences and uses this memory to generate proper responses.
- It is the seat of understanding language, memory, knowledge and logical thinking.

Section of human brain
(c) Thalamus: It is situated underneath (below) the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate the incoming sensory signals to the cerebrum and outgoing motor signals from it.
- It controls many of the body’s important activities and feelings’ such as hunger, thirst, temperature regulation, sleep, emotional behaviour and sexual activity.
- It produces and secretes hormones that control the functioning of the pituitary gland situated just below it. It also controls the function of internal body organs by means of the autonomic nervous system.
2. The Mid Brain: It consists of crura cerebri and optic lobes. It is the topmost structure of the brain stem :
- It has centres relating to pain, temperature and touch.
- It controls many involuntary actions of the body.
- It has a collection of cells that control functioning of eyes and ears.
3. The Hind Brain: It consists of the pons, cerebellum and medulla oblongata :
(a) Pons. It is a bulging structure situated below the mid brain. It consists of large bundles of nerve fibres that interconnect different regions of the brain.
(b) Cerebellum. It is located at the lower back side of the brain under the cerebrum. Its functions are as follows :
- Maintaining the posture and balance of the body by controlling the muscles.
- It also controls the voluntary actions of the body by controlling motor signals coming from the cerebrum.
(c) Medulla oblongata. It is long stalk-like lowermost portion of the brain stem.. At the lower side it is connected with the spinal cord. It controls many involuntary actions such as salivation, vomiting, blood pressure, respiration and heart beat.
Question 2. Describe the structure of spinal cord.
Answer:
The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum where it is continuous with the medulla. It is a vital link between the brain and the body, and from the body to the brain. The spinal cord is 40 to 50 cm long and 1 cm to 1.5 cm in diameter. Two consecutive rows of nerve roots emerge on each of its sides. These nerve roots join distally to form 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal cord is a cylindrical structure of nervous tissue composed of white and grey matter, is uniformly organized. The spinal nerve contains motor and sensory nerve fibres to and from all parts of the body.
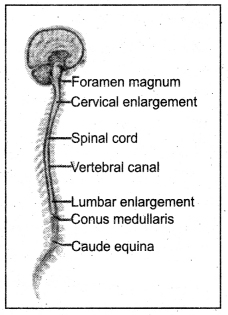
Spinal Cord
Although the spinal cord constitutes only about 2% of the central nervous system (CNS), its functions are vital.
Knowledge of spinal cord functional anatomy makes it possible to diagnose the nature and location of cord damage and many cord diseases.
Question 3. What is reflex action? Explain giving an example. What is reflex arc?
Answer:
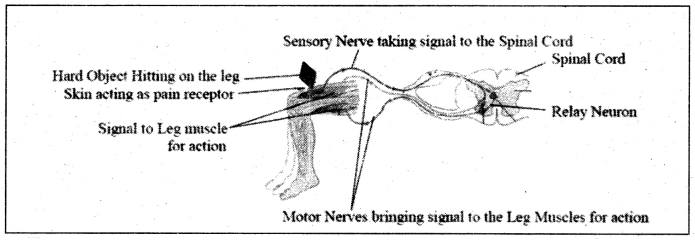
Reflex action is a quick action in response without involvement of the thought process. It is controlled through the spinal cord in which transfer of impulse takes place from sensory neuron to the motor neuron. The path through which the signal travels during reflex action is called the reflex arc. As the reflex arc is a shorter route reflex action takes place in a fraction of a second. For example, if a person accidentally hits something on the leg, the pain receptors in the skin receive the pain and generate an electric signal. This impulse is sent by the sensory neuron to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord the impulse is transferred quickly to the motor neuron, which relays it to the leg muscles for quick action.

Question 4. List the components of nervous system. What is a synapse? Explain what are its kinds.
Answer:
- Nervous system: It consists of central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and autonomic nervous system.
- Central nervous system: It consists of brain and spinal cord. It is the main controlling centre of the body.
- Peripheral nervous system: It consists of cranial and spinal nerves.
- Autonomic nervous system consists of a special set of peripheral nerves that innervate organs like heart, lungs, digestive tract.
Autonomic nervous system can be divided into two divisions :
(a) Sympathetic nervous system.
(b) Parasympathetic nervous system.
Synapse: Synapse is the close proximity of the axon of one neuron and the dendrite or cvton of another neuron with a gap. In a synapse, the transmitting cell is called the presynaptic cell, and the receiving cell is termed the postsynaptic cell. A narrow gap, called synaptic cleft, separates the presynaptic cell from the postsynaptic cell. Hence, an action potential occurring in the membrane of the presynaptic cell cannot be directly transmitted to the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
Question 5. What are phytohormones? Classify the main groups.
Answer:
Growth regulators: Growth is regulated not only by environmental factors like light and temperature but also by certain chemical substances within the plants. These substances are known as plant hormones, growth hormones, phytohormones or growth regulators. A plant hormone can be defined as a chemical substance, which is capable of translocation and regulating one or more physiological reactions, when present in low concentrations.
- Auxins
- Gibberellins
- Cytokinins
- Ethylene.
- Abscisic acid (ABA).
On the basis of their effect, phytohormones can be divided into two groups :
(а) Growth promoters: These stimulate the plant growth e.g. auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins and ethylene.
(b) Growth inhibitors: These inhibit or retard plant growth e.g. ABA.
Question 6. Explain the following :
(i) Hydrotropism (ii) Thigmotropism (iii) Chemotropism.
Or
Explain briefly the various types of plant movements.
Answer:
Movements: Movements of plant parts can mostly be classified as growth movements and turgor movements. The growth movements are autonomic. The movements induced by external stimuli are called paratonic. Tropic movements can be of various types depending on the nature of external stimulus e.g. geotropism, thigmotropism, thermotropism, hydrotropism, chemotropism and phototropism.
Nastic movements are in the bifacial organ. Seismonastic movements are observed in Mimosa pudica.
- Phototropism: Movements towards stimulus of light.
- Geotropism: Movements towards stimulus of force of gravity.
- Hydrotropism: The term hydrotropism is applied to growth movements in response to external stimulus of water. Roots, normally or positively hydrotropic (i.e., they bend towards the source of water).
- Thigmotropism: Thigmotropism is the tropic movement in the plants due to the stimulus of touch, tactile, mechanical or rubbing.
- Chemotropism: When chemical substances are the external stimuli, the growth movement is termed as chemotropism. The best example is the growth of pollen tube through stigma and style towards the embryo sac with the stimulus of chemical substances present in the carpel.
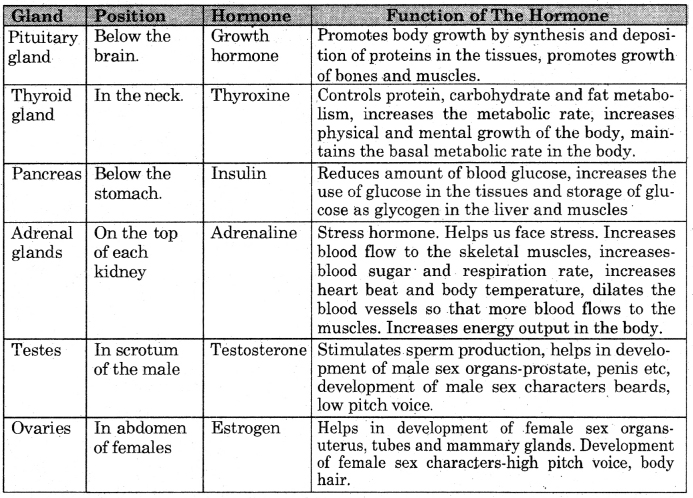
Question 7. Describe various endocrine glands.
Answer:
Endocrine glands and their secretions
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here