Describe the structure, reproduction and nature of bacteriophage (virus).
Q. Describe the structure, reproduction and nature of bacteriophage (virus).
Ans. The virus which attacks on bacteria and completes its life cycle inside the bacterial cell is called bacterial virus or bacteriophage virus. It is the eater of bacterial cell. The phenomenon of attacking on bacterial cell and completing its life cycle inside the cell was first observed by F. Jwort and D. Herelle in 1917. The bacteriophage viruses are hypothetical ultramicroscopic organisms. One of the bacteriophage virus which attacks on Escherichia Coli bacteria is known as coliphage virus.
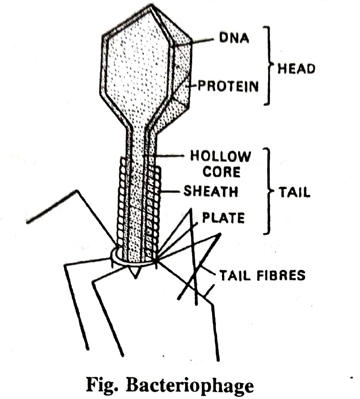
Structure: The bacteriophage virus is a sperm-shaped and has a hexagonal broad head and a tail like appendage. The hexagonal head is externally covered by a protein sheath, called head protein. Inside the sheath nucleic acid in the form of DNA is found. The tail like appendage is hollow and is known as core. The margin of core consists of protein sheath. The lower most part of tail is called end plate which is provided with six fibre like structures, called tail fibres. In the middle of tail fibres there are two spike like bodies. The virus makes its movement with the help of these fibres.
There are several types of bacteriophage virus designated as T1, T2, T4, T6, T7, T4, phase (bacteriophage) is the most complex virus, which infects the bacterium Escherichia coli. T4 virus consists of a head and a tail. The head is elongated and provided with protein sheath. The tail consists of a distal hexagonal core through which DNA passes on its way into the host cell.
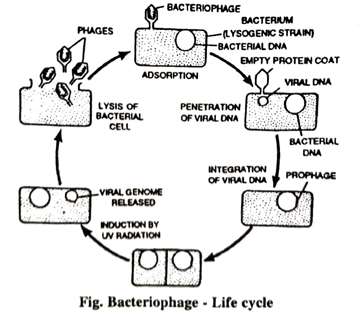
Life cycle (Multiplication or reproduction): A multiplication cycle has been developed to explain the phase attack on the bacterial cell and to produce more bacterial viruses. The virus attacks on the bacterial cell through tall part and the DNA migrates into the bacteria leaving hollow coat on the outer surface of the bacterial cell. DNA inside the cell starts multiplication in which both cell constituents are utilized on synthesis of new bacterial viruses. Thus within a few minutes the organism bursts and 100 or 200 new bacteriophages are liberated which are again capable of lying on new bacterial cells.
Nature of bacteriophage: The modern studies reveals, the following facts to explain the nature of bacteriophage :
1. The bacteriophage viruses are crystalline particles of definite shapes and sizes which can infect the new host cell.
2. They have the characters of growth and multiplication.
3. They are not capable to survive in non-living tissues.
4. They have two essential constituents -protein and nucleic acid (Nucleoprotein).
5. They are highly resistant to sunlight, temperatures, acids, alkalies and other salts.
6. They have capacity of transmission from unhealthy to healthy cells.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here