JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 7 Periodic Classification of Elements
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 7 Periodic Classification of Elements
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Periodic Classification of Elements Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ Periodic classification is the systematic study of the properties of the elements.
◆ Periodic table. It is a chart in which the various elements have been arranged in such a manner that elements having similar physical and chemical properties occur in the same vertical column (group).
◆ Dobereiner’s triads. It is a group of three elements having similar chemical properties in which the atomic weight of the middle element is the average of the other two elements.
◆ Newland’s Law of Octaves. It states that when the elements are arranged in the ascending order of their increasing atomic weights, every eighth element has properties similar to the first element like the eighth note of an octave of music.
◆ Mendeleev’s Periodic law. It states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses. It was given by Mosley.
◆ Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. It is a table obtained by arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic masses of the elements.
◆ Modern Periodic law. It states that physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
◆ Groups are the vertical columns in the periodic table. There are eighteen groups. These are group 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18.
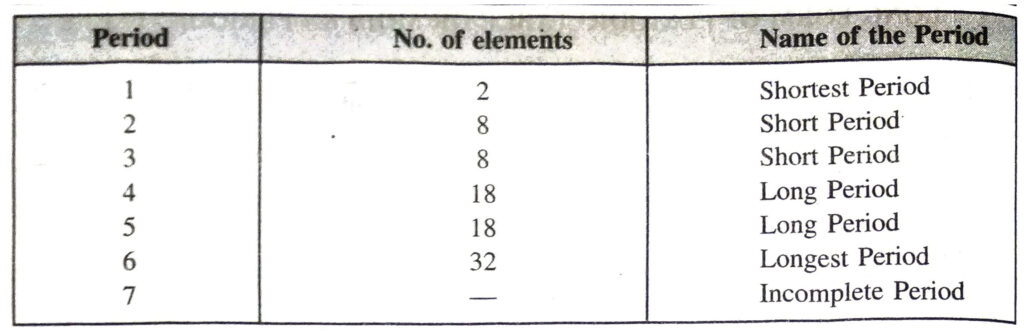
◆ Periods are the horizontal rows in the periodic table. There are seven periods.
◆ Modern Periodic Table or Long form of the Periodic Table. It is a table or chart in which the various elements have been arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers in such a manner that the elements having similar properties fall in the same vertical column or group.
◆ Periodicity is the repetition of the similar properties of the elements placed in a group and separated by definite intervals of atomic numbers (8, 8, 18, 18, 32).
◆ Groups. Some important groups are :
(a) Alkali metals are the elements present in group 1 of the Long form of the Periodic Table.
(b) Alkaline earth metals are the elements present in group 2 of the Long form of the Periodic Table.
(c) Noble Gases are the element in group 18 of the Periodic Table.
(d) Halogens are the elements present in group 17 of the Periodic Table.
◆ Periods
(a) First period is a short period consisting of only 2 elements.
(b) Second and third periods are short periods and consist of 8 elements each.
(c) Fourth and fifth periods are long periods and consist of 18 elements each.
(d) Sixth period is a long period and consists of 32 elements.
(e) Seventh period is incomplete (25 elements).
The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
◆ Groups. Elements of groups 1 and 2 are called alkali metals and alkaline earths respectively.
(a) Elements of groups 3 to 12 are called transition elements.
(b) Elements of group 17 starting from fluorine are called halogens.
(c) Elements of group 18 starting from helium are called noble gases. These elements are chemically less reactive.
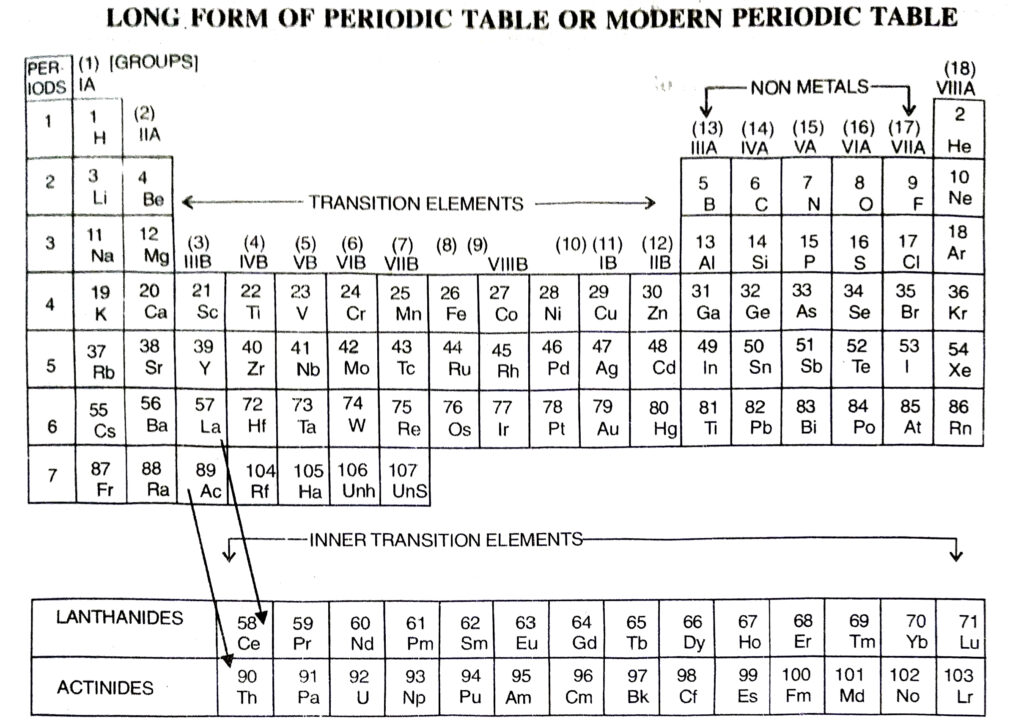
◆ Lanthanides. Fourteen elements starting from lanthanum having atomic numbers 58 to 71 are called lanthanides.
◆ Actinides. Fourteen elements starting from actinium having atomic numbers 90 to 103 are called actinides.
◆ Lanthanides and actinides are placed separately at the bottom in the periodic table.
◆ Metalloids. Elements which behave both as metals and non-metals are called metalloids.
◆ Periodic properties. These are the properties of an element which are related to the electronic configuration of its atom and change periodically down a group and along a period.
◆ Atomic radius or Atomic size is the distance from the centre of the nucleus of the atom up to the outermost shell of electrons.
◆ Valency is the combining capacity of the element and is equal to either the number of valence electrons or eight minus the number of valence electrons (For normal elements).
IMPORTANT TERMS AND FACTS TO MEMORISE
⇒ Units of valency: No
⇒ Valency of a normal element = No. of electrons in the valence shell of an atom (if number of electrons is 1 to 4)
or Eight-number of electrons in the valence shell of an atom (if no. of electrons is 4 to 8).
⇒ Units of atomic radius Å or pm.
TBQ TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic table ?
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Ans. (c).
Q. 2. Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCI₂, which is a solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the periodic table as :
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Ans. (b)
Q. 3. Which element has :
(a) two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons ?
(b) the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2 ?
(c) a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell ?
(d) a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell ?
(e) twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell ?
Ans. (a) Neon
(b) Magnesium
(c) Silicon
(d) Boron
(e) Carbon.
Q. 4. (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as Boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as Fluorine have in common?
Ans. (a) All elements of this column have 3 electrons in their valence shell like Boron. (b) All elements of this column have 7 electrons in their valence shell like fluorine.
Q. 5. An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this element ?
(b) To which of the following element would it be chemically similar ? (atomic numbers are given in parenthesis).
N (7), F (9), P (15), Ar (18).
Ans. (a) 17
(b) F (9) (2, 7)
Q. 6. The position of three elements A, B and C in the periodic table are as shown below :
Group 16 Group 17
…………. …………..
………….. A
………….. …………..
B C
(a) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B.
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A ?
Ans. (a) A is non-metal.
(b) C is less reactive than A.
(c) C has smaller size than B.
(d) Anion, A–.
Q. 7. Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong group 15 of the periodic table. Write the electronic configurations of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative ? Why?
Ans.
K L M
N1 has electronic configuration 2 5
P15 has electronic configuration 2 8 5
Nitrogen is more electronegative than Phosphorus due to smaller size.
Q. 8. How does the electronic configurations of an atom relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table ?
Ans. By knowing the electronic configuration of an element, we can know its period number from the number of shells present in its atom and from number of electrons in the valence shell of its atoms we can know its group number. e.g. let us consider the case of sodium atom.
Atomic number of sodium = 11
Its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 1
∴ Number of shells = 3 (K) (L) (M)
∴ Sodium belongs to 3rd period.
Also sodium atom has one electron in its valence shell.
∴ It is present in first group.
∴ Sodium lies in the first group and third period of Modern Periodic Table.
Q. 9. In the Modern Periodic Table, calcium (atomic number 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21 and 38. Which of these have physical and chemical properties resembling calcium ?
Ans. Elements with atomic numbers 12 and 38 because they have two electrons in their valence shells like calcium (2, 8, 8, 2).
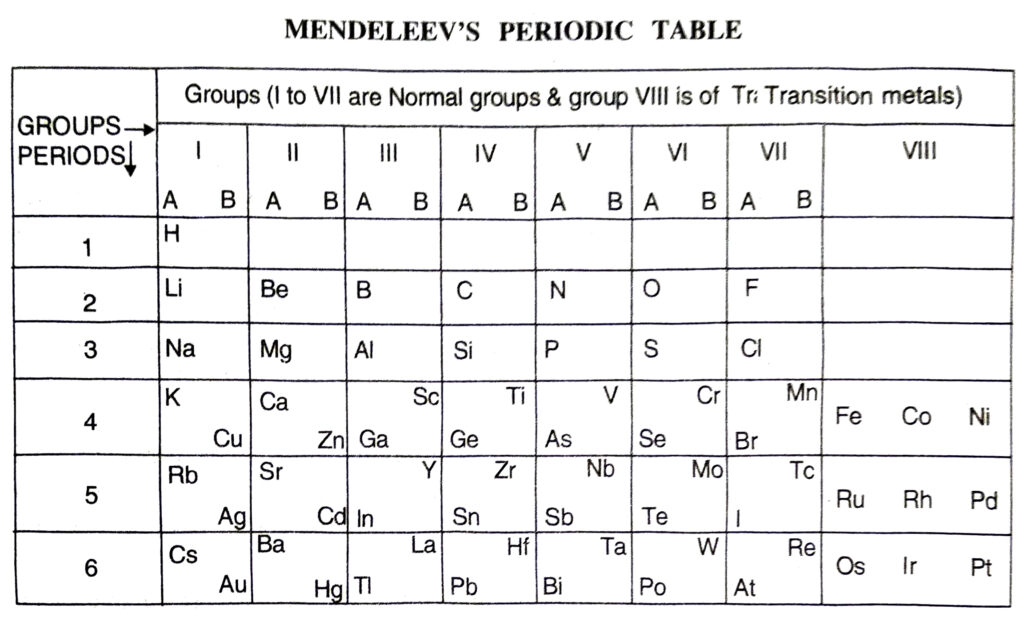
Q. 10. Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s Periodic table and the Modern Periodic table.
Or
Differentiate between Mendeleev’s periodic table and Modern periodic table.
Ans. Similarities :
1. In both the elements are arranged in groups and periods.
2. In both similar elements are placed in same group.
3. Both the classification make the study of elements simple and systematic. Differences:
| Mendeleev’s Periodic Table |
Modern Periodic Table |
- The elements are arranged in order of increasing mass numbers.
- It has 8 vertical columns called groups.
- Groups excess group VIII have been divided into sub groups A and B.
- Noble gases are not included in this table.
|
- The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers.
- It contains eighteen vertical columns called groups.
- Each group is an independent group.
- Noble gases are included in this periodic table.
|
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. (a) What was Dobereiner’s basis of classifying elements ?
(b) What is the basis of classification of elements according to Mendeleev ?
Ans. (a) Dobereiner gave a classification in which the elements were arranged in a group of three elements called triads. The arrangement was such that the atomic masses of the middle elements were almost the average of the atomic masses of the first and third elements.
(b) Mendeleev based his classification of Law called Mendeleev’s Periodic Law. The law may be stated as :
Physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic weights or atomic masses.
Q. 2. Discuss salient features of long form of periodic table.
Ans. (i) It is based upon Modern Periodic law.
(ii) It has 18 vertical columns called groups.
(iii) There are seven horizontal rows called periods. .
(v) Noble gases has been assigned group 18.
(iv) Metals and non-metals have been separated
Q. 3. Define valency of an atom. How does it vary in a group and in a period of periodic table ?
Or
What happens to valency of elements :
(a) in a group
(b) along a period.
Explain with reasons.
Ans. It is the combining capacity of an atom of the element and it is equal to number of electrons lost or gained or contributed for sharing by an atom of the element to complete its octet.
As we move from top to bottom in a group, valency remains same e.g., group 1 elements have a valency of 1.
As we move from left to right along a period, valency increases from 1 to 4 and decreases from 4 to zero.
Q. 4. State Mendeleev’s periodic law. Describe two anomalies of Mendeleev’s periodic classification of elements.
Ans. It states that properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses.
Anomalies
(a) Cobalt with atomic mass (58.9) is placed before nickel having atomic mass 58.7.
(b) Elements with similar properties are placed in different groups. For example, copper has been placed in group I B and mercury in group II B.
Q. 5. Give a brief discussion of the Mendeleev’s classification of the elements.
Ans. Mendeleev’s classification of the elements is based upon the Mendeleev’s periodic law. In this table the vertical columns are called Groups and horizontal rows are known as Periods. These are briefly discussed as follows:
1. Groups. These are the vertical rows. There are in all eight groups. The elements present in first seven groups are called Normal Elements. The elements present in group VIII are called the Transition Elements. Each group (I to VII) has been further divided into subgroups which are called A and B. The inert gas or noble gas elements (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe) were not known at that time. Therefore, they were not shown in the table. All the elements placed in a group have the same valency. All the elements present in a sub-group have the similar properties. For example, group I-B includes element Cu (Copper), Ag (Silver) and Au (Gold). They have similar properties. Group VII has three columns.
2. Periods. These are the horizontal rows called periods. There were in all six periods in the original periodic table. The seventh period was added later on and this is not shown in the periodic table. The properties of the elements present in a period change systematically. For example, in every period, the first element is a typical metal. As we move from left to right, the metallic character gradually decreases and non-metallic character increases. For example, in period 2, the first element Li (Lithium) is a metal while the last element F (Fluorine) is a non-metal. The Mendeleev’s Periodic Table is shown below :
Q. 6. Discuss some major merits of the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
Ans. Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
Mendeleev’s periodic table was the first proper systematic classification of the elements. The important merits of the table are listed as follows:
1. Systematic study of elements. With the classification of elements into groups and periods, their study became quite systematic.
2. Correction of atomic masses. The periodic table helped in correcting the atomic masses of some of the elements because the elements were arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses.
3. Prediction of new elements. At the time Mendeleev gave the periodic table, only 63 elements were known. While arranging these elements in groups and periods, certain gaps were left. These gaps represented some undiscovered elements. But the properties of these unknown elements could be predicted from their positions in the respective groups. This helped, later on, to discover these elements.
Q. 7. Point out the major defects in the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
Or
What are the limitations of Mendeleev’s periodic table ?
Ans. Defects in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
The Mendeleev’s periodic table was quite helpful in the classification of the elements. But it had certain defects also. These are discussed as follows:
1. Position of hydrogen. The position of hydrogen is doubtful.
2. Position of isotopes. The periodic table is based on the basis of the atomic masses of the elements. This means that the elements with different atomic masses must be given separate places in the table. As a result of it, the isotopes of an element must be allotted separate positions. For example, there are three isotopes for hydrogen and they must be given three separate places in the table. But only one position for hydrogen has been given.
3. Wrong order of atomic masses of some elements. In the table, the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses. In this table there are some anomalies. For example, Co (Cobalt) with atomic mass 58-9 should be placed after Ni (Nickel) with atomic mass 58.7. But it has been placed before nickel.
4. Elements with similar properties placed in different groups. In the periodic table, it has been found that the elements with similar properties are placed in different groups. For example, copper and mercury have many common properties. But copper has been placed in group I B and mercury in group II B.
5. No similarity in the elements placed in sub-groups. The elements present in different sub-groups of the same group are expected to have common properties. But these are quite different. For example, elements in group I A are very soft and reactive metals but elements in group IB are hard and less reactive in nature.
6. No explanation for the cause of periodicity. This table does not explain cause of periodicity.
Q. 8. Give a brief description of Long Form of Periodic Table.
Or
Write down the brief description of groups and periods in Modern Periodic Table.
Ans. The Long form of periodic table has been formed by arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic numbers. It is based upon Modern periodic law which states that the properties of the elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers. Just as in case of the Mendeleev’s table, this periodic table has also been divided into Periods and Groups.
(a) Groups
These are the vertical columns. In all, there are eighteen groups in the table. The details of the groups are as ahead :
Group 1. The elements present in group 1A or 1 are called Alkali Metals.
Group 2. The elements which are present in group IIA or 2 are called Alkaline Earth Metals.
Groups 13 to Group 18. There are in all six groups. The Groups 13 to 16 are named after the first element present in the family. For example, Group IIIA or 13 is called Boron Family because first member is boron. Group 17 consists of a family called Halogen Family. The group 18 is also called zero group because the elements have zero valency. These elements are all gases. They have very little tendency to take part in chemical combination. These are also called Noble Gases.
Group 3 to Group 12. There are in all ten groups. These are all metals and are called Transition elements. When we go down each group, the metallic character further increases. Group 3 also includes fourteen elements belonging to Lanthanide family. These are called Lanthanides because they start after Lanthanum (La) with Z = 57. These are present in the 6th period as shown in the table. It (group 3) also includes another fourteen elements called Actinides. These are present in 7th period. These are so called as they come after Actinium (Ac) with Z = 89. These are placed at the bottom of the table for convenience.
(b) Periods
Periods are the horizontal rows which are present in the Long Form of Periodic Table. There are in all seven periods. The seventh period is still incomplete. The number of elements which are included in each period are given ahead :
Q. 9. What is periodicity ? What is the cause of periodicity?
Ans. It is the repetition of the similar properties of the elements placed in a group and separated by definite gaps of atomic numbers (8, 8, 18, 18, 32).
Cause of Periodicity. The properties of the elements, particularly the chemical properties, are linked with number of electrons present in the outermost shell of their atoms which is also called Valence shell. Elements with similar valence shell electronic configurations are expected to have similar properties.
It may be noted that all the elements which are present in a group having similar outer electronic configuration and the same valence shell electronic arrangement gets repeated after definite gaps of atomic numbers (8, 8, 18, 18, 32) therefore, the elements placed in a group show similar properties.
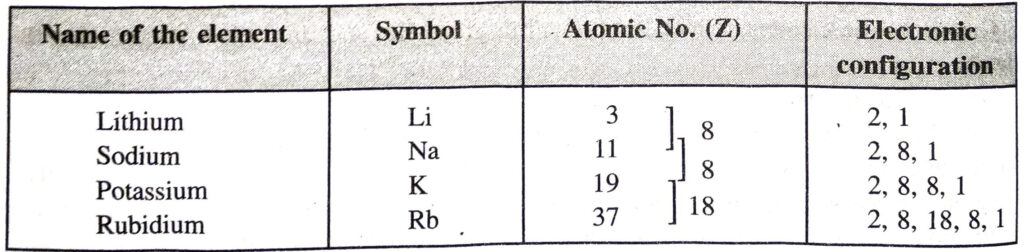
Example. Let us write the electronic distribution of the first four members of the alkali metals present in group I.
All the four elements have one electron each in the valence shell of their atoms. They have, therefore, similar properties.
Q. 10. What is atomic radius? How do the atomic radii of the elements change in a group ?
Ans. Atomic radius. The atomic radius of an element is related to the atomic size and may be defined as the distance between the centre of the nucleus of an atom and the outermost shell of electrons.
Variation of atomic radii in a group. In a group, the atomic radii of the elements increase as we move down the group. The atomic radii of the alkali metals of group 1 are shown in the table. The last element Francium (Fr) is radioactive and unstable. Therefore, its atomic radius has not been determined.
Explanation. In a group, as we move downwards there is a regular addition of one new shell. For example,
| Element |
Atomic no. (Z) |
Electronic configuration |
No. of shells |
Atomic radius (pm) |
|
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Rubidium
Cesium
|
3
11
19
37
55
|
2,1
2, 8, 1
2, 8, 8,1
2, 8, 18, 8, 1
2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1
|
Two shells
Three shells
Four shells
Five shells
Six shells
|
123
154
202
216
235
|
Since the number of electron shells increases, the size of the elements increases down a group.
Q. 11. Why is Long Form of Periodic Table regarded better than Mendeleev’s Periodic Table ?
Or
Give two achievements of modern periodic table.
Or
Give the merits of modern periodic table.
Or
How could Modern Periodic Table remove various anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table ?
Ans. Long Form of Periodic Table is regarded better than the Mendeleev’s periodic table due to the following reasons :
1. It is based upon atomic number which is considered better than the atomic mass because the properties of the elements are related to the atomic number.
2. It explains why the elements placed in a group show similar properties but Mendeleev’s Periodic Table gives no explanation for the same.
3. All groups in the Periodic Table are independent groups and there are no sub-groups as in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
4. Many defects in the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table have been removed.
5. There is no confusion regarding the position of isotopes because all the isotopes of an element have the same atomic number.
6. The periodic table is more systematic than the Mendeleev’s table and is easy to remember.
Q. 12. The following table shows the position of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F in the periodic table.
|
→
Groups
↓ Periods
|
1 |
2 |
3 to 12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
| 2 |
A |
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
C |
| 3 |
|
D |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
E |
Using the above table answer the following questions :
(a) Which element will form only covalent compounds ?
(b) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(c) Which element is non-metal with valency of 3 ?
(d) Out of D and E, which one has a bigger atomic radius and why?
Ans. (a) E (b) D (c) B (d) D.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What is Newland’s Law of Octaves ?
Or
Describe Newland’s Law of Octaves.
Ans. It states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses, every eighth element has the same properties as the first element. This means that the properties of the eighth element were the same as those of the first element and properties of the ninth element were the same as those of the second element and so on.
Thus Li, Na and K have gap of seven elements and they show similar properties. Similarly Be, Mg and Ca also have gap of seven elements. These elements have also similar properties.
Q. 2. Define Modern periodic law. Why was it necessary to change the basis of classification from atomic masses to atomic numbers ?
Ans. Modern Periodic Law. The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. It was necessary to change the basis of classification from atomic masses to atomic numbers because atomic number and not atomic mass is the fundamental property of an element.
Q. 3. How are the various groups of the Modern Periodic Table designated according to IUPAC system and old system ?
Ans. The designations of various groups of the Modern periodic table are:
Old IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIII IB IIB IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 0 system
IUPAC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8, 9, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 system
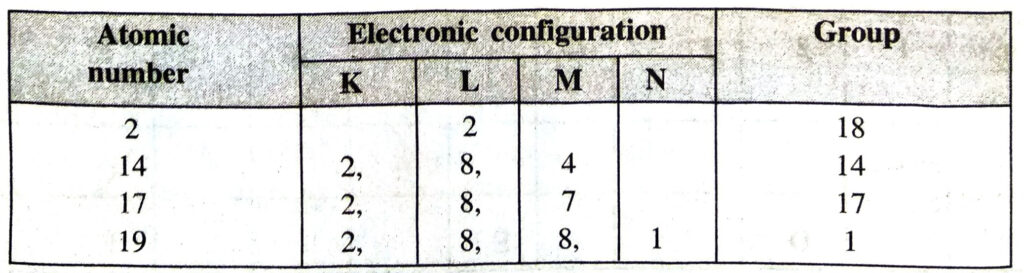
Q. 4. Write down the electronic configuration of elements with atomic numbers 2, 14, 17, 19. Indicate the group of the periodic table to which they belong.
Ans. The information is being given in a tabular form.
Q. 5. Why are group 1 elements called alkali metals ?
Ans. The members of group 1 are called alkali metals because all of them are water soluble. They react with water to form soluble hydroxides. The soluble hydroxides of the metals are called alkalies.
2M + 2H₂O → 2MOH + H₂
(Alkali metal atom) (Water soluble hydroxide)
Q. 6. (i) Name the members of the alkaline earth family.
(ii) To which group do they belong ?
(iii) Which member is radioactive in nature ?
(iv) Which member is the least reactive?
Ans. (i) The members of the alkaline earth family are: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra.
(ii) They belong to group 2.
(iii) The radioactive member in them is Radium (Ra).
(iv) The least reactive member of the family is Beryllium (Be).
Q. 7. Nitrogen (atomic no. 7) and phosphorus (atomic no. 15) belong to group 15 of the periodic table. Write the electronic configuration of the two elements in terms of K, L, M shells. Predict whether these are metallic or non-metallic.
Ans.
K L M
N7 2 5
P15 2 8 5
N is non-metal because it has more than 3 electrons in its outermost shell.
Similarly, P is a non-metal.
Q. 8. Fill in the blanks :
(a) Oxygen and sulphur belong to same …….……… .
(b) The elements of group 17 are called …….……… .
(c) The valency of the members of noble gas family is …….……… .
(d) Along a period, the metallic character of the elements …….……… .
Ans. (a) group (b) halogens (c) zero (d) decreases.
Q. 9. Why does the reactivity of non-metals decreases down a group ?
Ans. In a group, containing non-metals, the reactivity decreases down the group. For example, in the halogens present in group 17, the first member fluorine (F) is the maximum reactive while iodine (I) is the least reactive in nature.
Explanation. In non-metals, the atoms of the elements have tendency to gain electrons and not to lose electrons. By gaining electrons, the atoms achieve a noble gas configuration or stable electronic configuration. As we move down the group, the atomic size increases. Therefore, the nucleus of the atom experiences less attraction towards the coming electron. In other words, the electrons accepting tendency of the element decreases down the group. The reactivity of the elements also decreases down the group.
Q. 10. What are noble gas elements ? Why are they so called ?
Ans. Noble gas elements are the elements present in group 18 of the periodic table which is also called zero group. It means that the valency of the elements is zero. Actually, whereas the first member helium has two electrons in its only shell, the atoms of the remaining elements (Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and Radon) have eight electrons in their outermost shells. They do not have any tendency to combine with atoms of other elements. Hence, they show zero valency. These are also called noble gases because they do not take part in chemical combination.
Q. 11. How does the reactivity of the metals vary in a group ?
Ans. In a group, containing metals, the reactivity increases down the group. For example, in the metals of group 1 (Alkali metals), Lithium reacts with water very slowly. Sodium is more reactive and potassium is still more reactive than sodium.
Explanation. Down every group, the size of the atom increases. Therefore, the release of the electrons from the valence shell of the atom becomes easier. Since the reactivity of element is directly related to the release of the electrons from the valence shell of its atom, the reactivity of the metals increases down a group.
Q. 12. How is metallic character of an element defined ? How does the metallic character of the elements change in a group ?
Ans. Metallic character of an element may be expressed in terms of its tendency to lose electrons and to form positive ion.
M (Element) → M+ + e–
In a group the metallic character increases downwards. For example, among the elements of group 2, Beryllium (Be) is the least metallic. At the same time, radium (Ra) which is the last element is maximum metallic in nature.
Explanation. As we down a group, the size of the atom increases. Therefore, the electrons present in the outermost shell experience less attraction towards the nucleus. The release of the electrons from the atom becomes easier. Therefore, the tendency to form positive ions also increases and the metallic character of the elements increases down the group.
Q. 13. The metallic character of the elements in a period decreases from left to the right. Justify.
Ans. Explanation. The metallic character of an element is expressed in terms of tendency to release electrons. In a period, the electron releasing tendency of the elements gradually decreases. Therefore, the metallic character of the elements gradually decreases. For example in third period, Na, Mg, Al-Metals
Si-Metalloid
P, S, Cl-Non-metals.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q 1. State Mendeleev’s Periodic law.
Ans. It states that the properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic weights.
Q. 2. Write two limitations of Mendeleev’s classification.
Ans. (a) Position of hydrogen is uncertain.
(b) Elements with similar properties are placed in different group.
Q. 3. Name the families to which the first and the last element in each period belong.
Ans. The first element belongs to alkali metals (group IA) and the last belongs to noble gases (group VIII A or zero).
Q. 4. Name the group to which the element with electronic configuration 2, 8, 3 belongs.
Ans. It belongs to the group IIIA or 13.
Q. 5. What is the relation between Na and Al ?
Ans. Both of them belong to the third period.
Q. 6. What is the valency of nitrogen?
Ans. Three (3). It is calculated as 8 number of valence electrons i.e. 8-5 = 3.
Q. 7. Out of Li and Na, which is more reactive ?
Ans. Na is more reactive than Li.
Q. 8. Which group of elements was missing from the Mendeleev’s original periodic table?
Ans. The zero group consisting of noble gases was missing from the original periodic table given by Mendeleev.
Q. 9. An element is present in a group IIA of the periodic table. Predict its two properties.
Ans. It has two electrons in the valence shell. It is of metallic nature.
Q. 10. Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his periodic table of elements ?
Ans. Because the elements corresponding to these gaps were not known at the time Mendeleev gave the table. They were discovered later on.
Q. 11. What is the main characteristic of the last element in a period? What is the name of the family to which it belongs ?
Ans. The last element in a period has a complete outermost shell. It has either two or eight electrons in the outermost shell. It belongs to the noble gas family.
Q. 12. Name two elements with filled outermost shells.
Ans. Helium (2), Beryllium (2,2).
Q. 13. Give the example of an element discovered after Mendeleev gave the Periodic table.
Ans. Gallium.
Q. 14. An element of group 14 has an atomic number 14. Examine if this element will have metallic properties or not.
Ans. The element in group 14 of the periodic table has 4 electrons in its outermost shell. It will have non-metallic properties.
Q. 15. Three element X, Y and Z have different number of electrons in the valence shells of their atoms. State whether these elements belong to the same group or same period in the periodic table.
Ans. The elements do not belong to the same group because in a group all the elements present have same number of valence electrons. However, these elements can belong to the same period.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Which of the following has the largest atomic radius?
(A) K
(B) Li
(C) Na
(D) Rb.
Ans. (D) Rb.
2. The law of Triads was given by :
(A) Newlands
(B) Mendeleev
(C) Moseley
(D) Dobereiner.
Ans. (D) Dobereiner.
3. Modern Periodic Table has :
(A) 8 Groups
(B) 18 Groups
(C) 7 Groups
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) 18 Groups
4. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, the properties of elements are a periodic function of their :
(A) Atomic size
(B) Atomic mass
(C) Ionisation energy
(D) Atomic number.
Ans. (B) Atomic mass
5. Number of periods in modern periodic table is :
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8.
Ans. (C) 7
6. Number of groups and periods respectively present in modern periodic table are?
(A) 16, 7
(B) 6, 16
(C) 18, 7
(D) 18, 6.
Ans. (C) 18, 7
7. Which of the following is least reactive alkali metal?
(A) Li
(B) K
(C) Na
(D) Rb.
Ans. (A) Li
8. As we move down the group the atomic size :
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) remains constant
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) increases
9. How many elements were known when Mendeleev grouped his periodic table ?
(A) 36
(B) 56
(C) 115
(D) 63.
Ans. (D) 63.
10. Modern periodic table was given by :
(A) Mendeleev
(B) Moseley
(C) Newlands
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Moseley
11. Elements of the same group of periodic table have same :
(A) atomic size
(B) electronic arrangement
(C) same number of electrons in the outermost shell
(D) same number of neutrons.
Ans. (C) same number of electrons in the outermost shell
12. Halogens lie in the modern periodic table in :
(A) Group 17
(B) Group 7
(C) Group 16
(D) Group 18.
Ans. (A) Group 17
13. Modern Periodic table is based upon :
(A) Modern Periodic law
(B) Mendeleev’s Periodic Law
(C) Atomic weight
(D) None.
Ans. (A) Modern Periodic law
14. The element with atomic number 11 resembles with the element having atomic number :
(A) 10
(B) 19
(C) 24
(D) 35.
Ans. (B) 19
15. Number of elements present in the third period of the periodic table is :
(A) 3
(B) 8
(C) 18
(D) 32.
Ans. (B) 8
16. An atom of the element whose first shell is en complete and has no other shell, the atom is :
(A) Sodium
(B) Helium
(C) Chlorine
(D) Hydrogen.
Ans. (B) Helium
17. Which among the following is not the noble gas ?
(A) He
Ans. (D) N.
18. The properties of an element are periodic function of their atomic mass. Who said this?
(A) Newland
(B) Dobereiner
(C) Mendeleev
(D) None of the above.
Ans. (B) Dobereiner
19. Which pair of atomic numbers represents elements in the same group ?
(A) 11, 19
(B) 6, 12
(C) 4, 16
(D) 8, 17.
Ans. (A) 11, 19
20. When we go down the group in a periodic table :
(A) Only Physical properties show variation
(B) Only Chemical properties show variation
(C) Both Physical and Chemical properties show variation
(D) Properties remain same.
Ans. (C) Both Physical and Chemical properties show variation
21. Which among the following is most reactive halogen ?
(A) F
(B) Cl
(C) Br
(D) I.
Ans. (A) F
22. Electronic configuration of Mg is :
(A) 2, 8, 1
(B) 2, 8, 8
(C) 2, 8, 2
(D) 2, 8, 5.
Ans. (C) 2, 8, 2
23. Which of the following is known as shortest period?
(A) 1st period
(B) Second period
(C) Fifth period
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Fifth period