JKBOSE 9th Class Mathematics Solutions Chapter 4 Logarithms
JKBOSE 9th Class Mathematics Solutions Chapter 4 Logarithms
JKBOSE 9th Class Mathematics Solutions Chapter 4 Logarithms
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 9th Class Mathematics Solutions
J&K class 9th Mathematics Logarithms Textbook Questions and Answers
Rational Numbers As Exponents :
(i) If m is a positive integer and x and y are rational numbers such that x = y, then y1/m = x.
y1/m is called the mth root of y and is written as m√y.
Using this meaning we define xm for a positive rational exponent m. If m= 0 then x0 = 1.
(ii) If x = r/s is a non-zero rational number, then {r/s}-m = {s/r}m
Rational Numbers As Exponents When Exponent is Any Positive Rational Number
If x is a positive rational number and m = p/q is a positive rational Pexponent then we define xp/q as:
(i) the qth root of xp i.e.
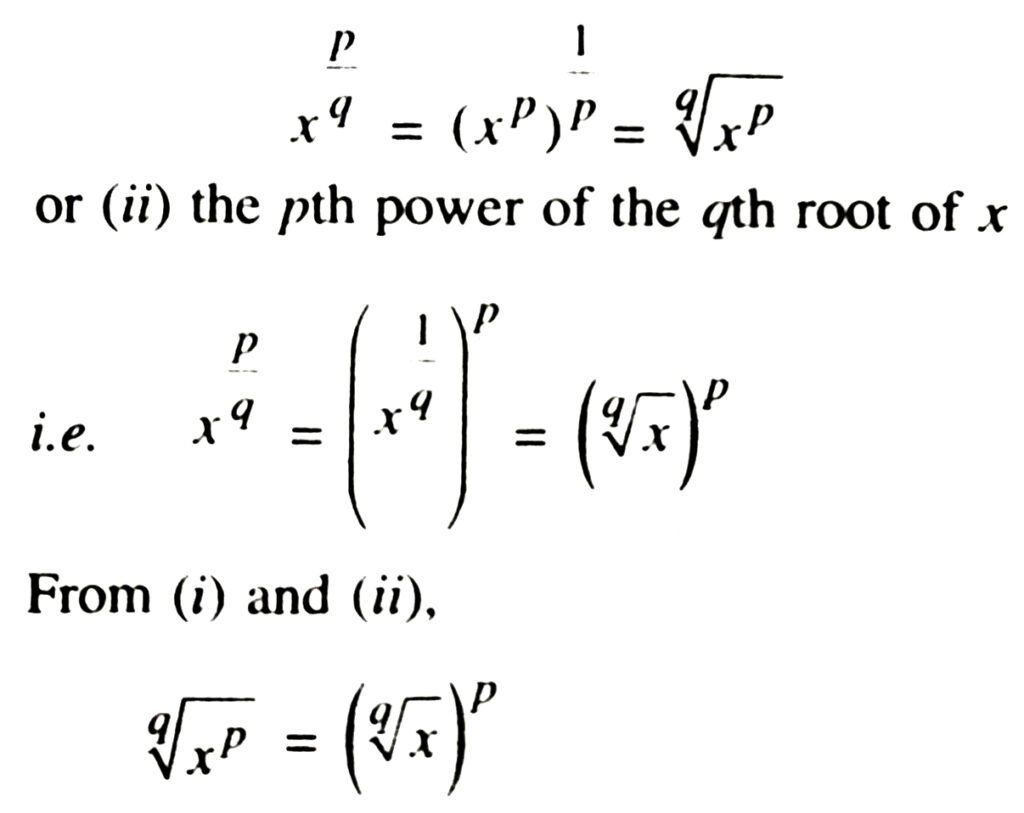

TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.1
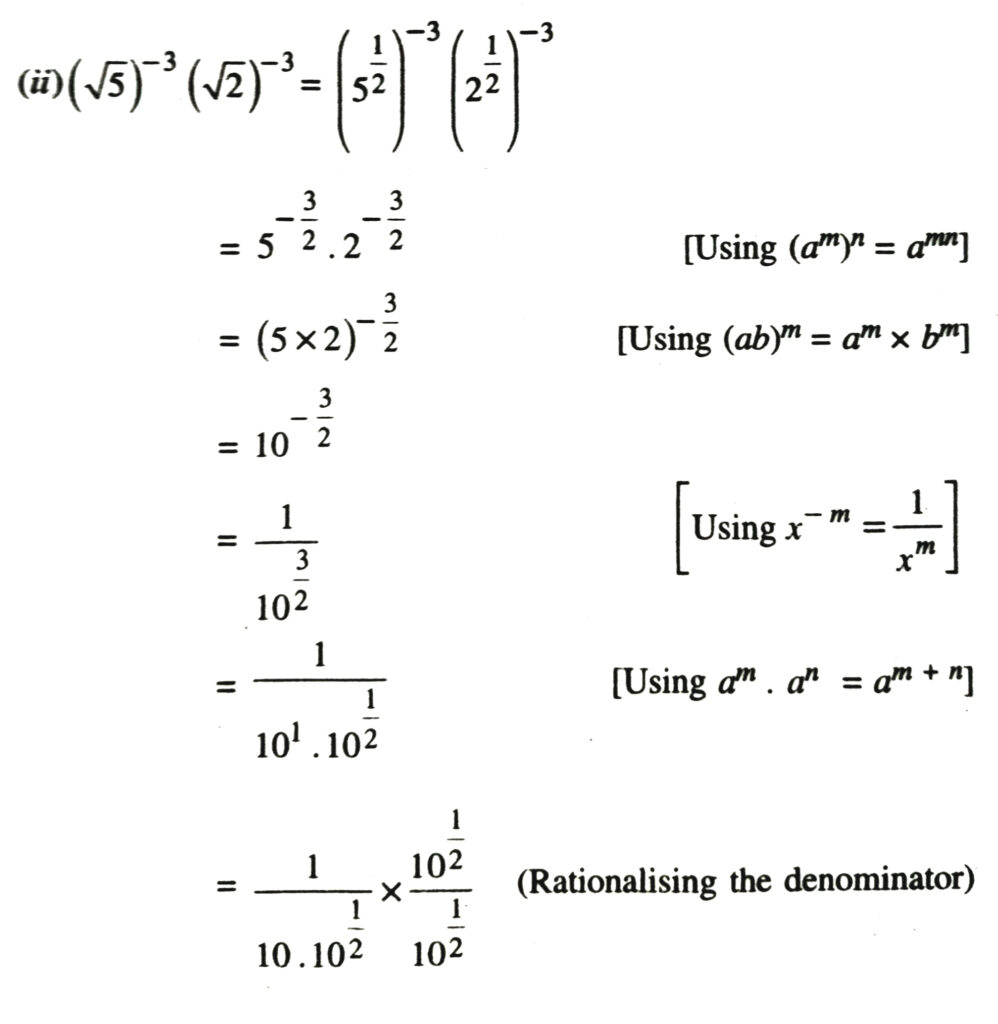
1. Simplify each of the following removing redical signs nagative indices wherever they occur :

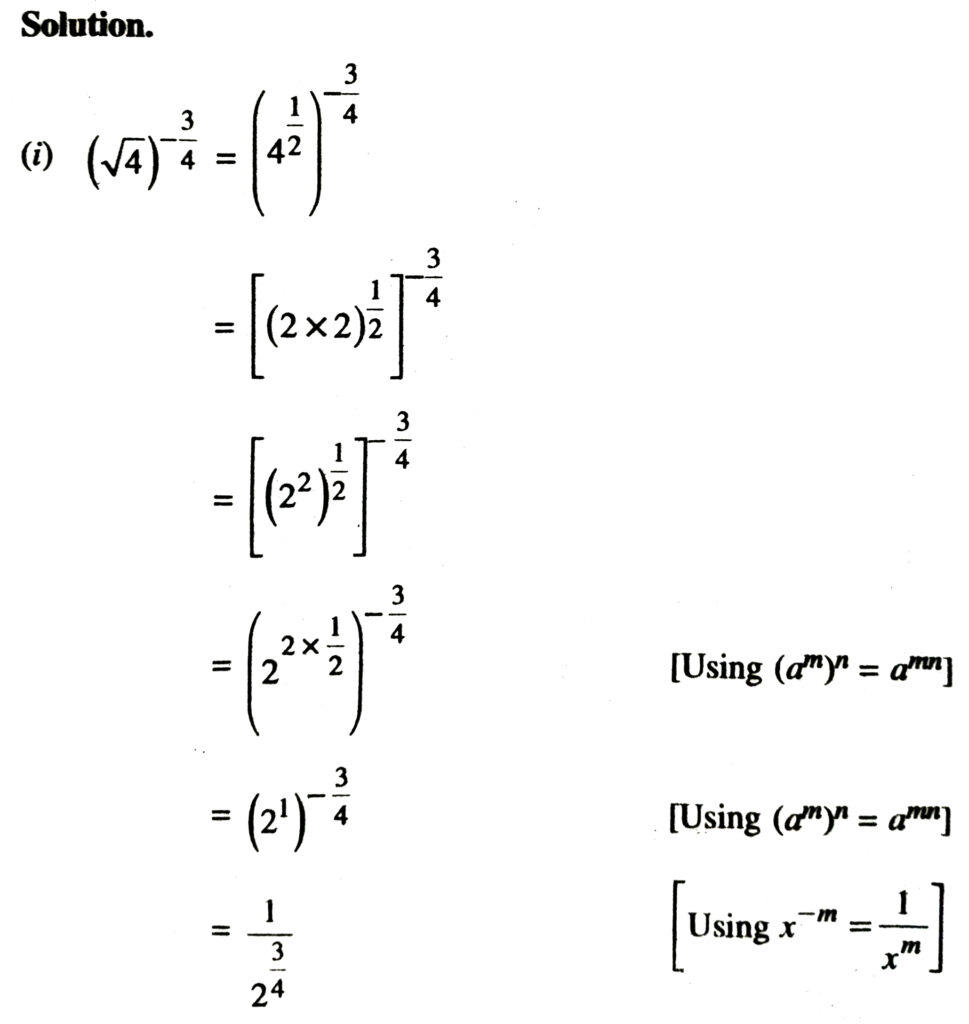

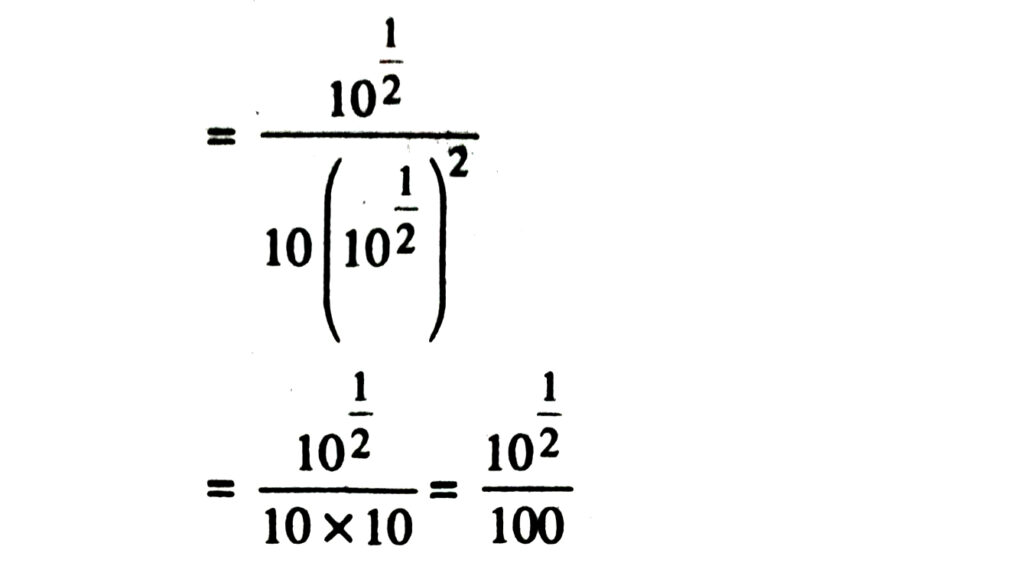
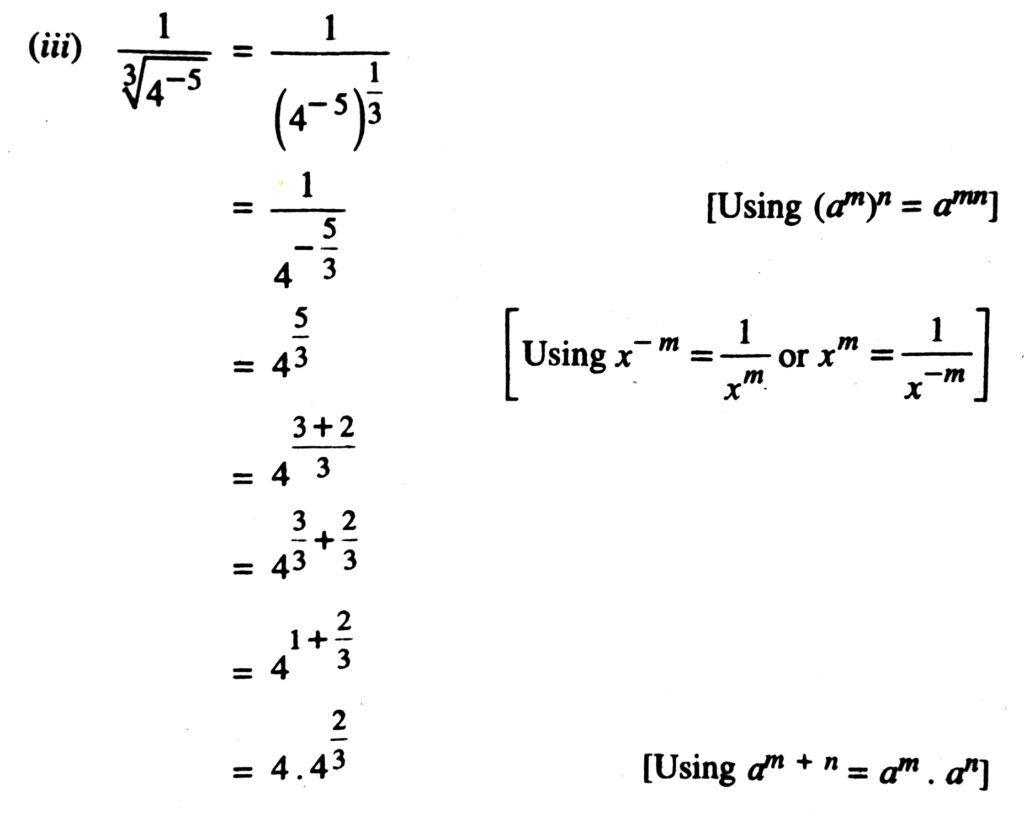
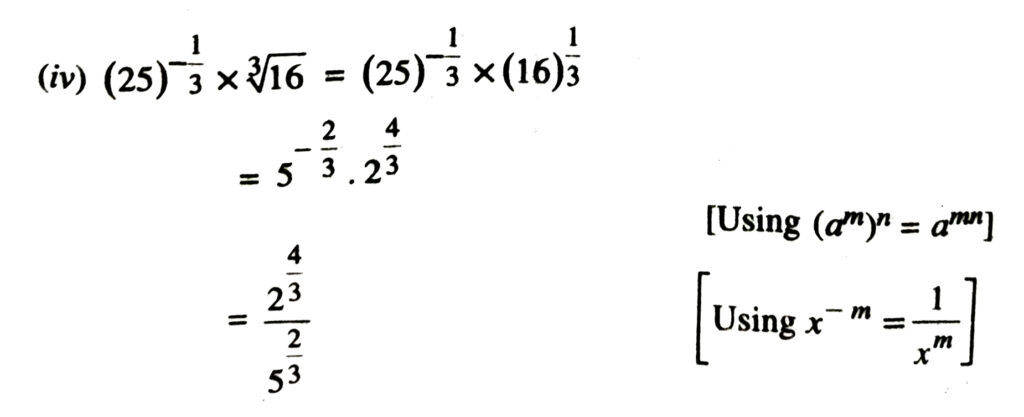
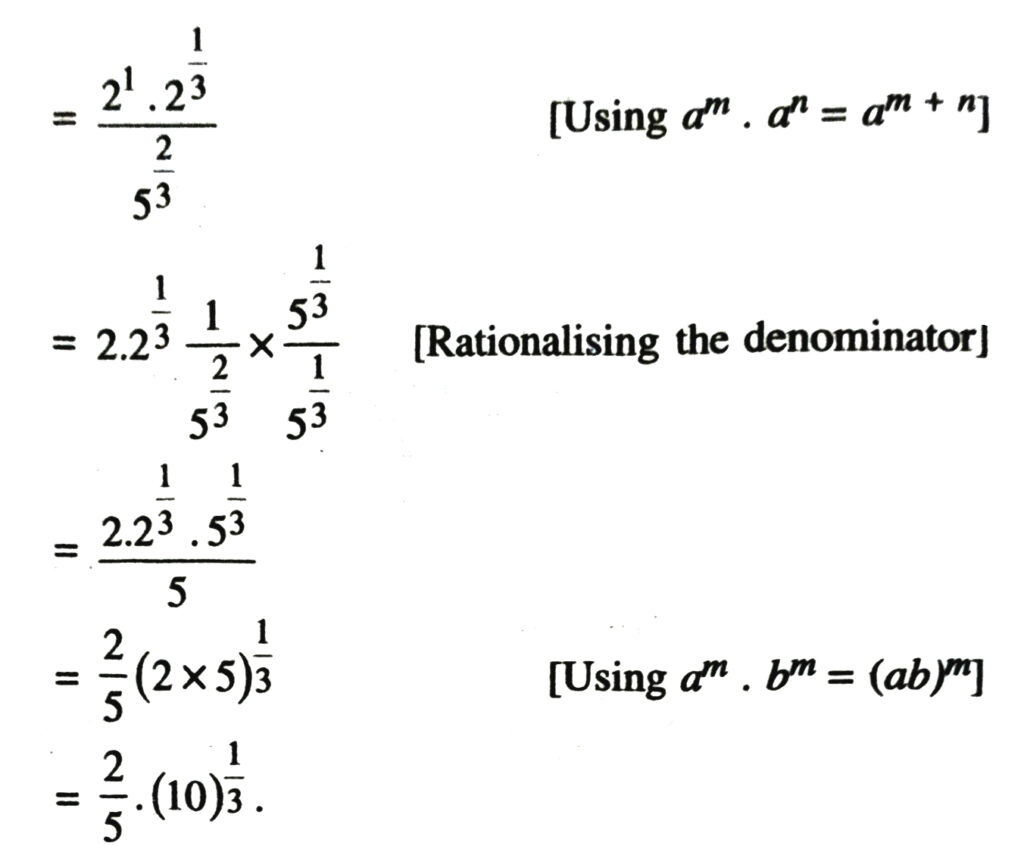
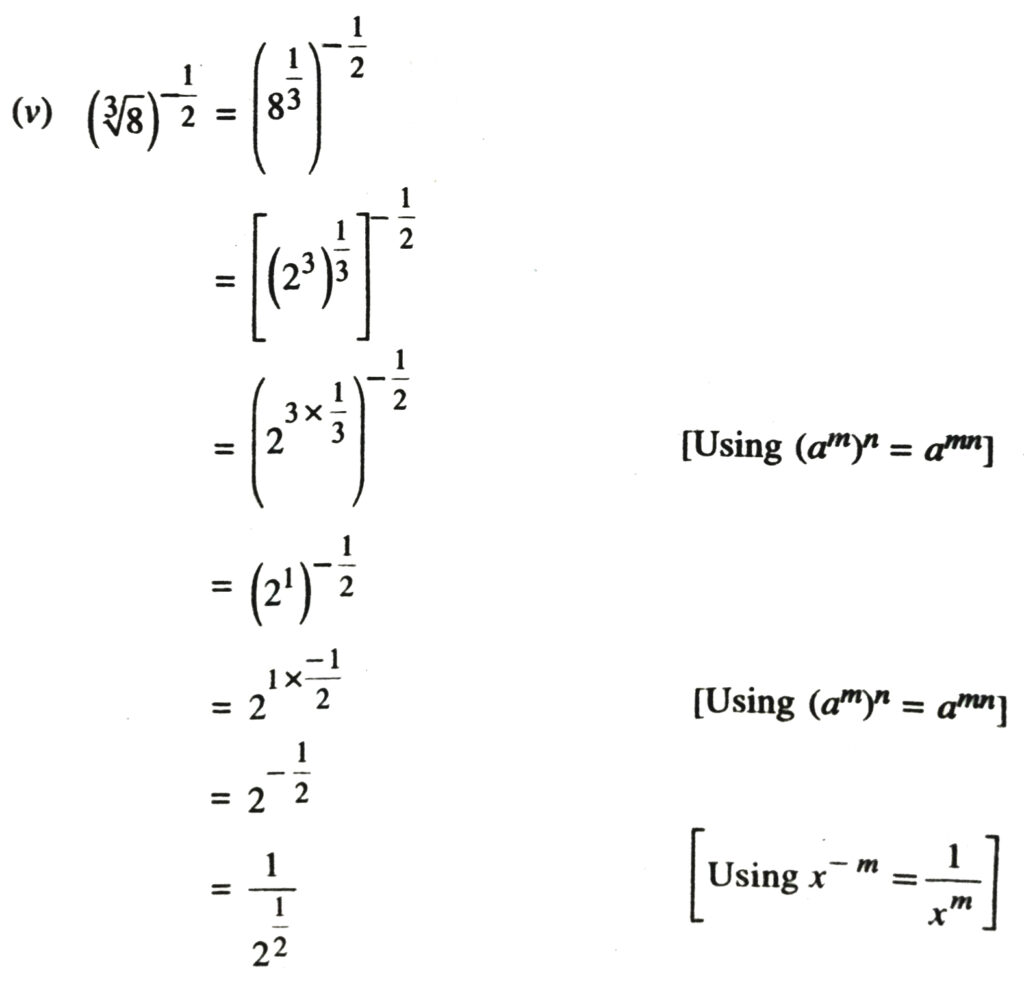
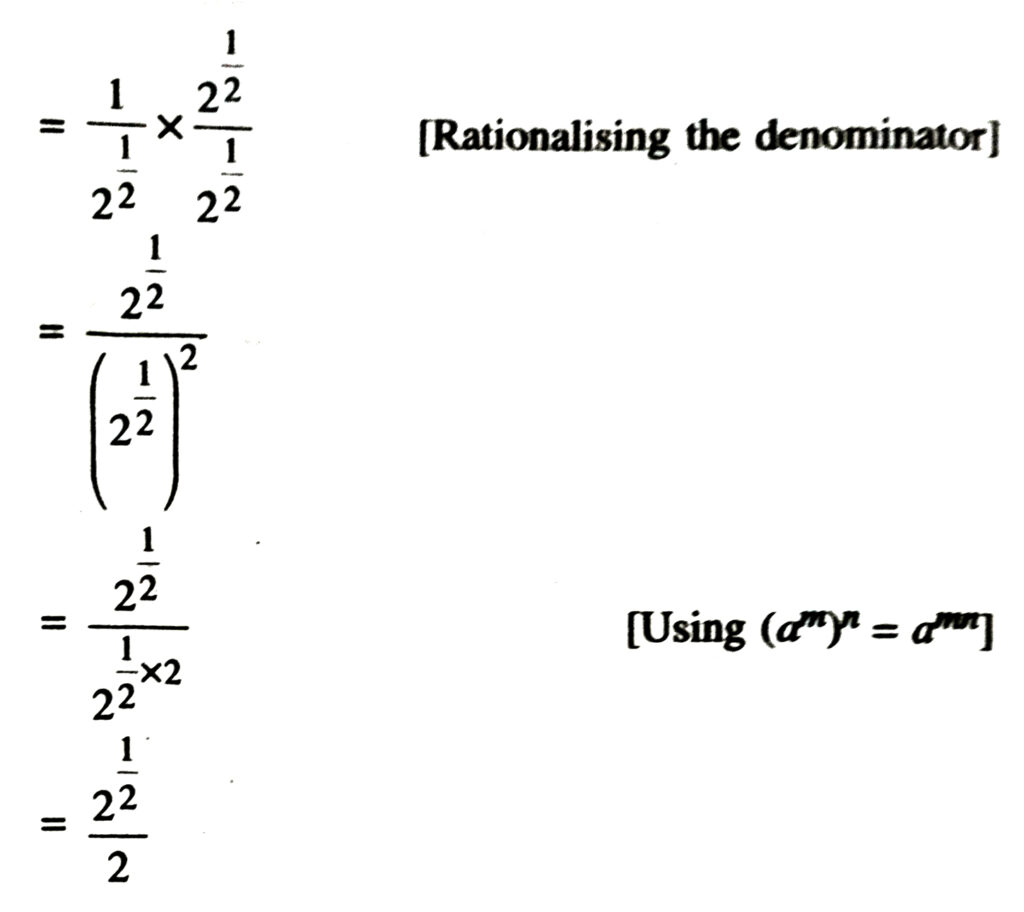
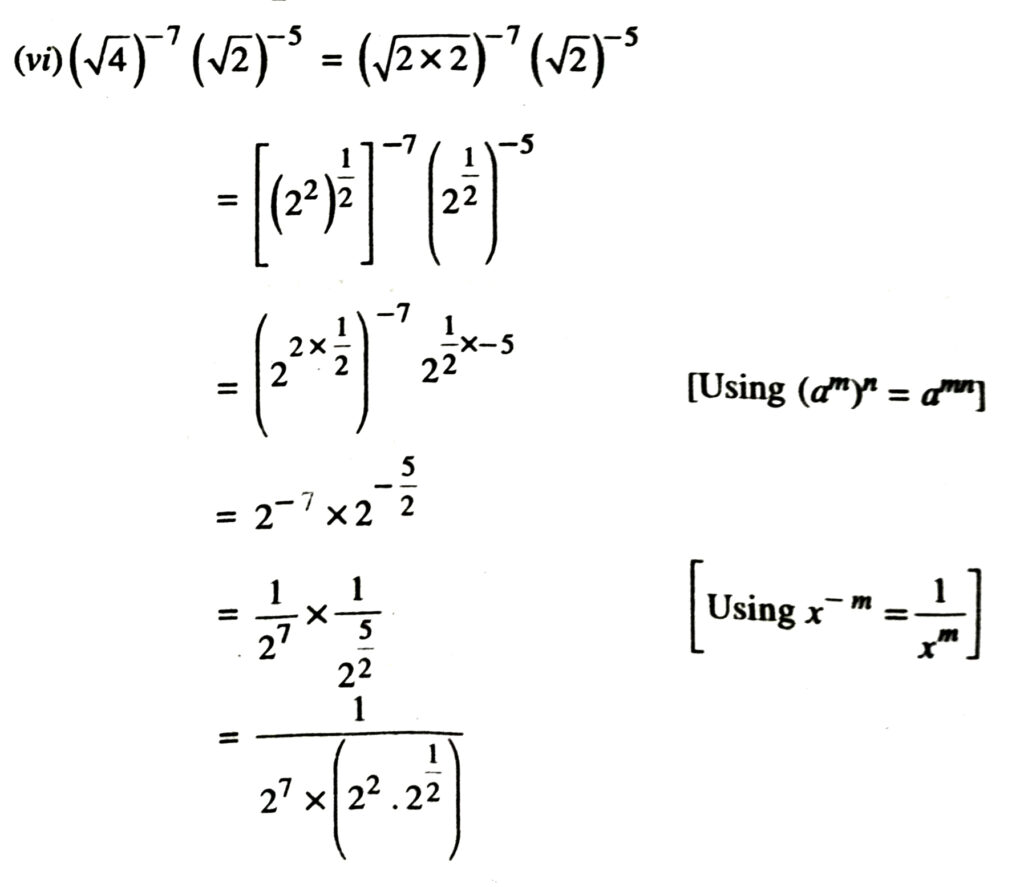
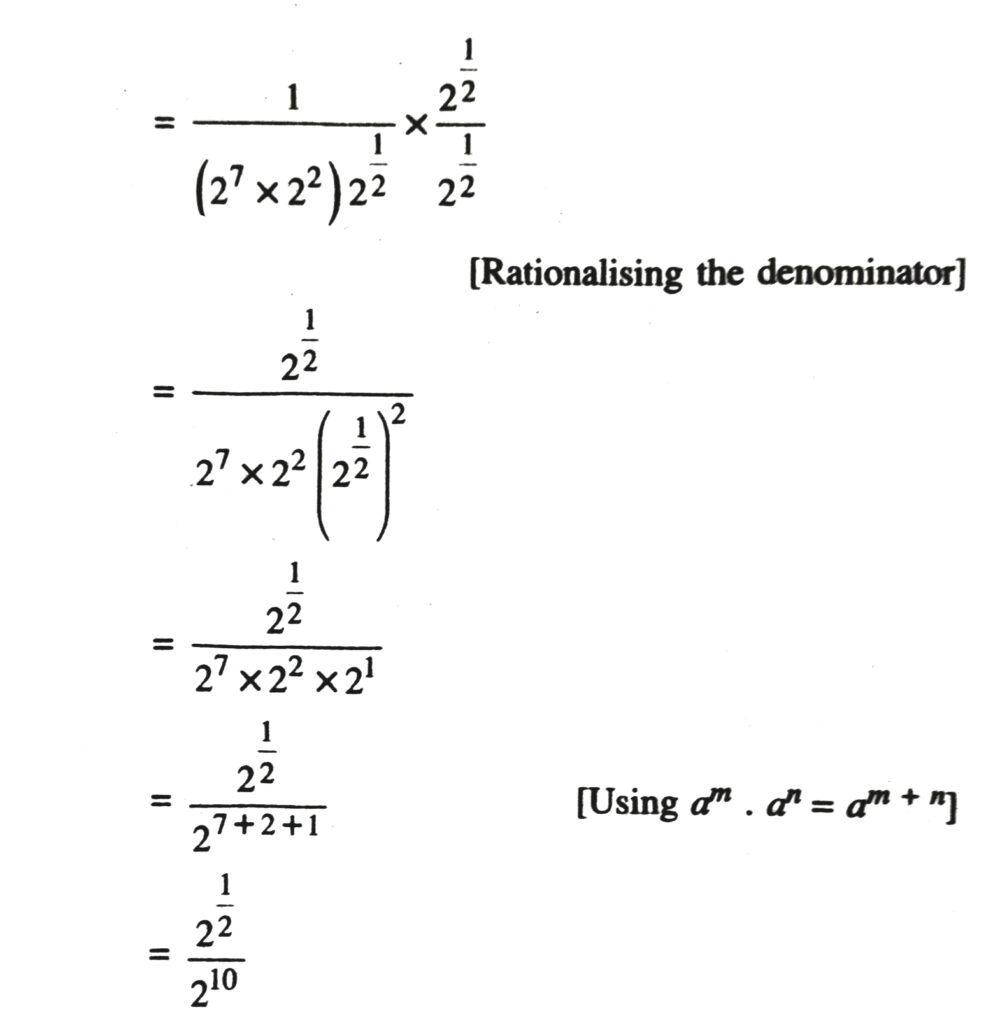
2. Assuming that x, y, z are positive real numbers, simplify each of the following :
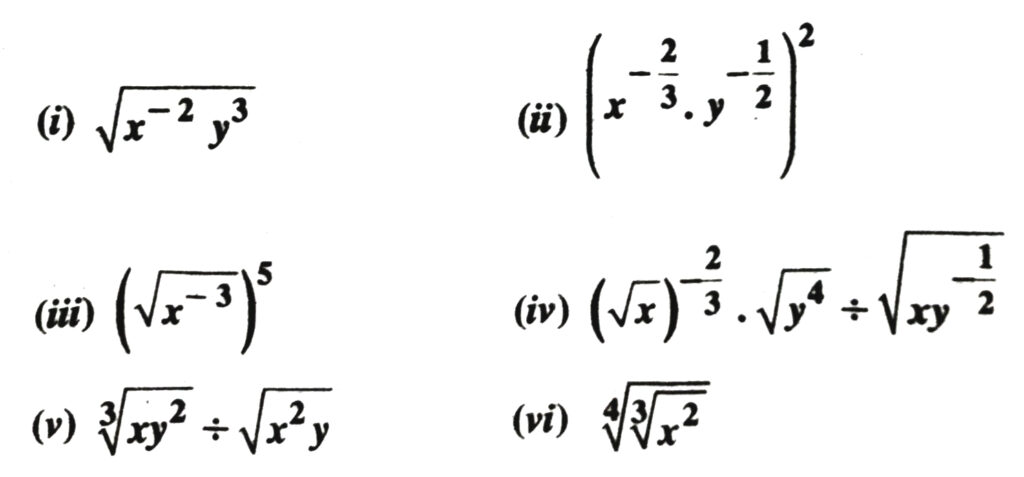
Solution.
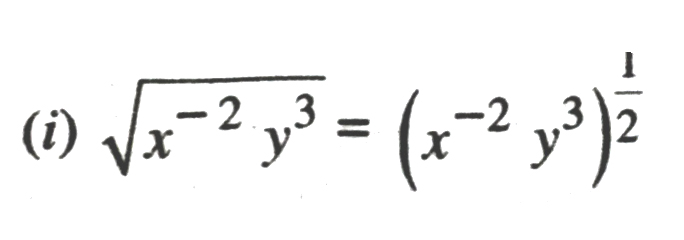
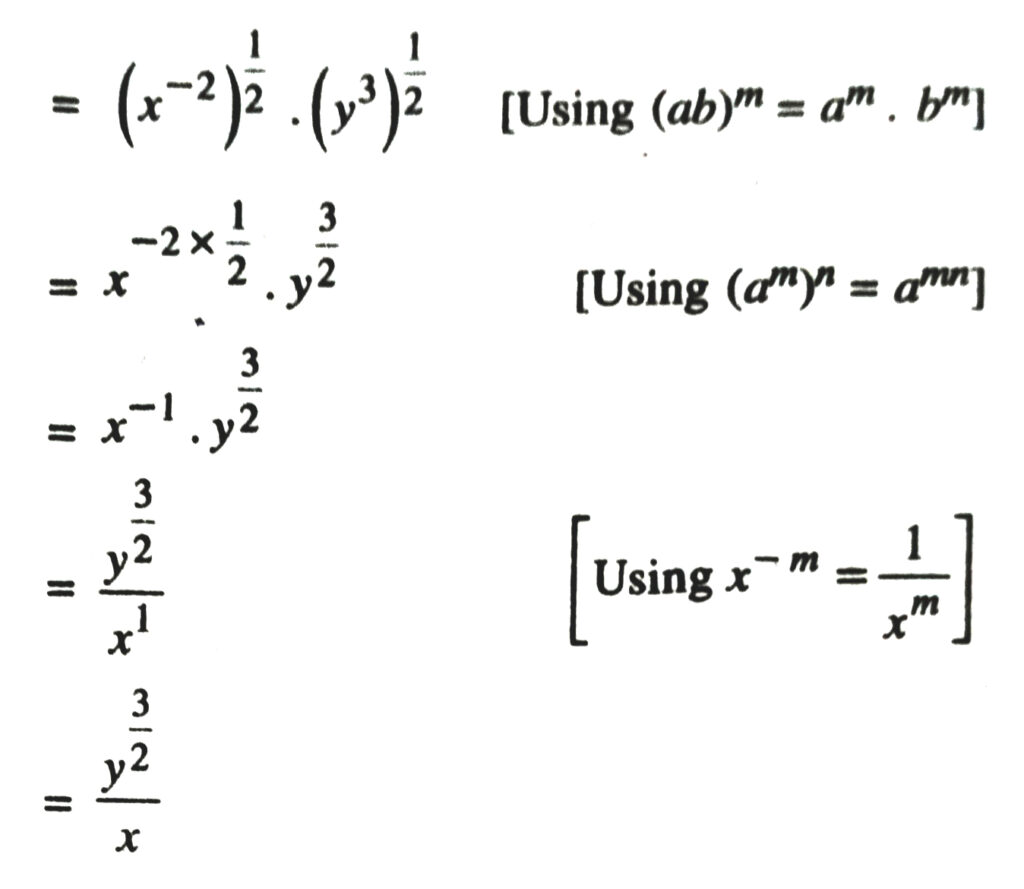
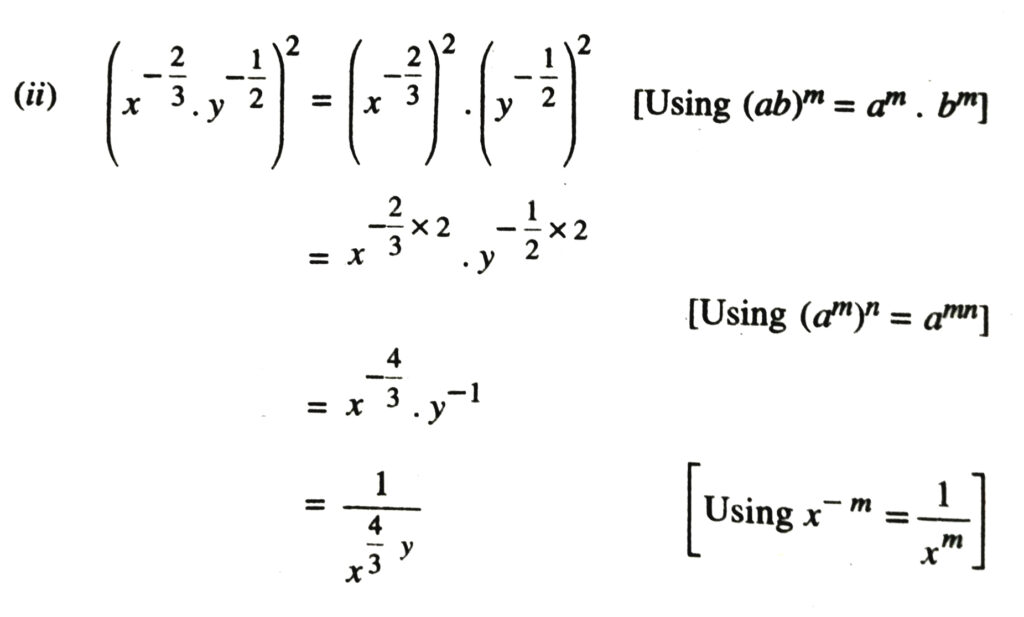
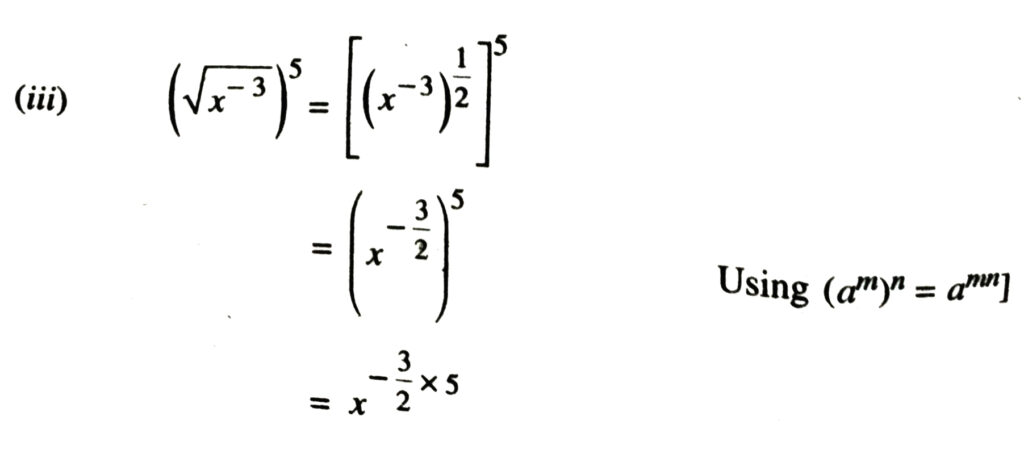
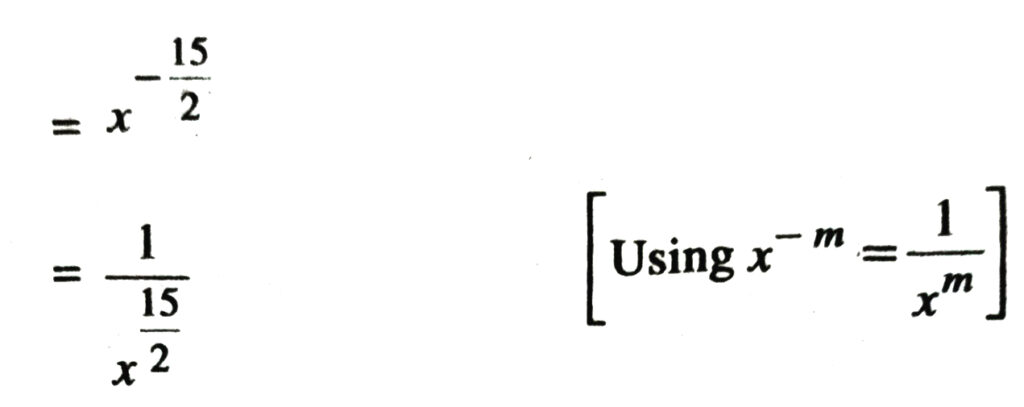
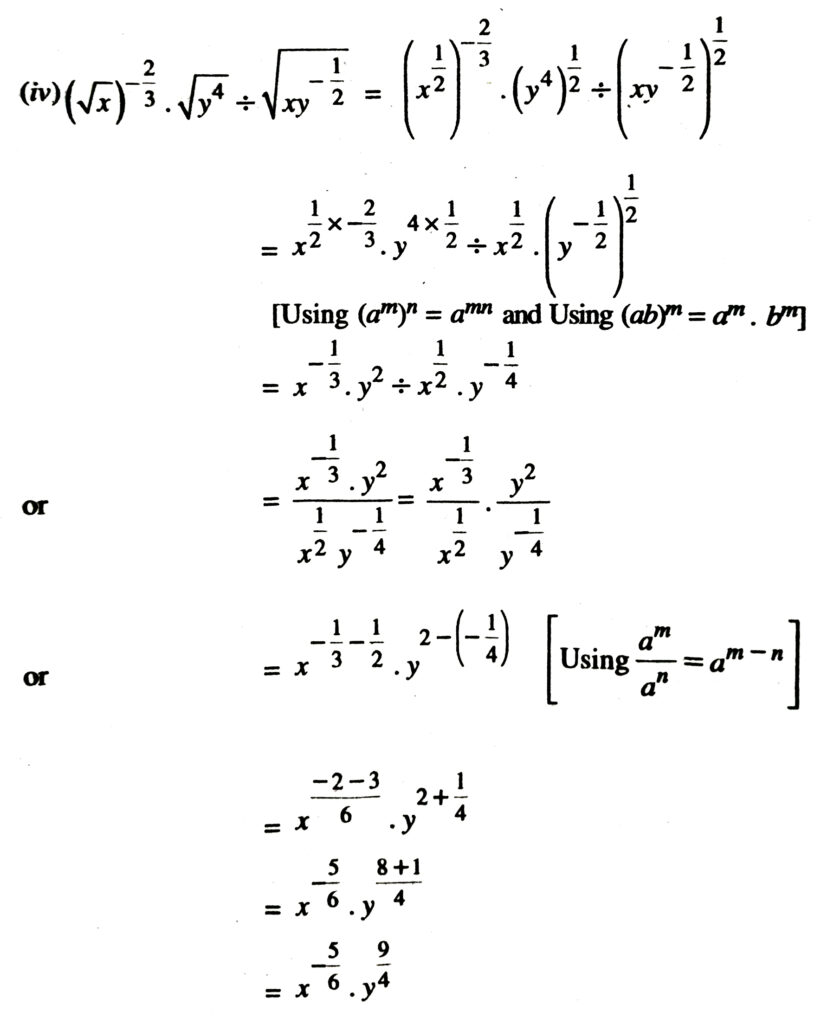
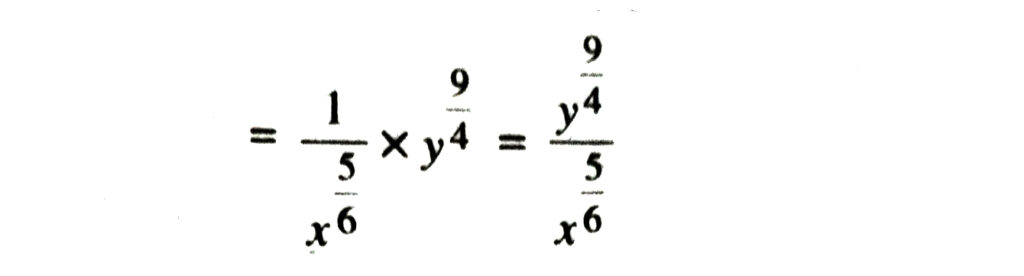
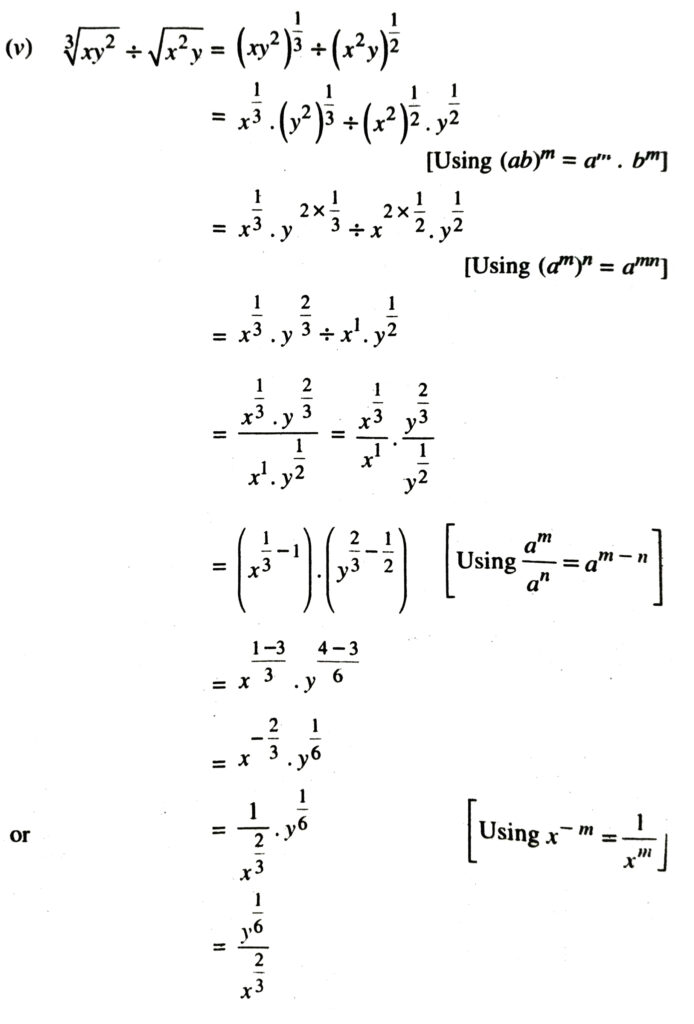
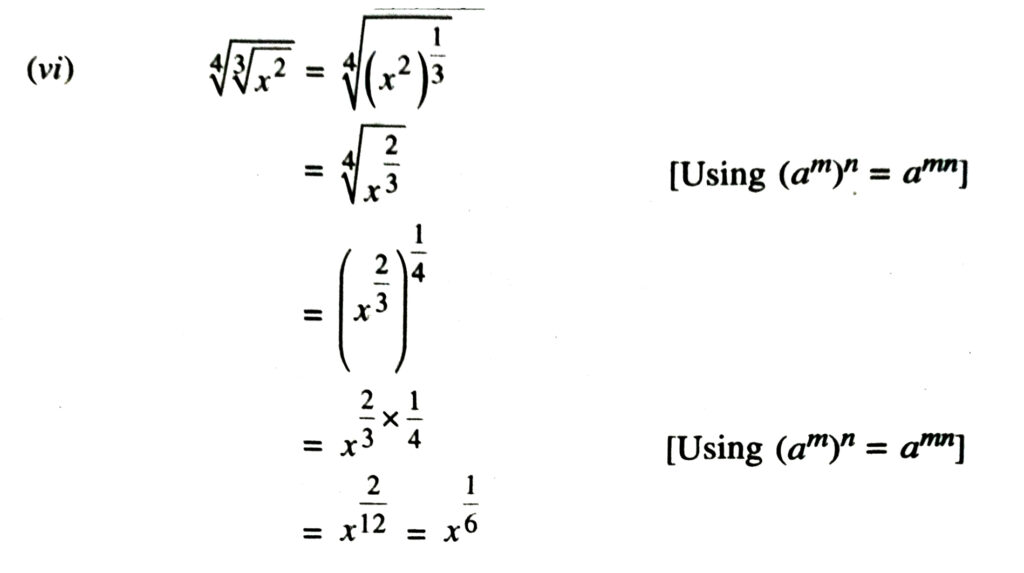
3. Assuming that x, y, z are positive real numbers and exponents are all rational numbers, show that :
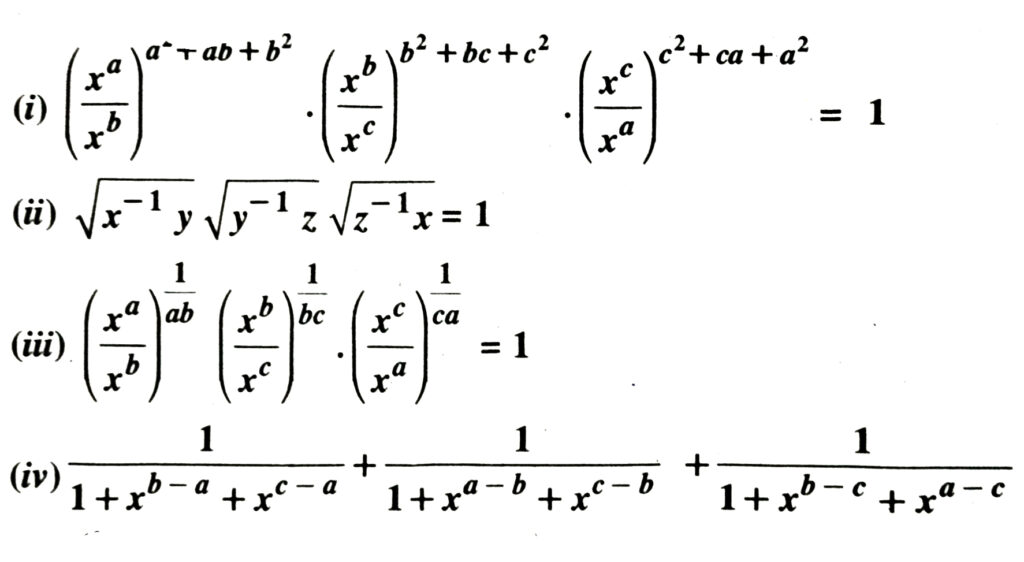
Solution.
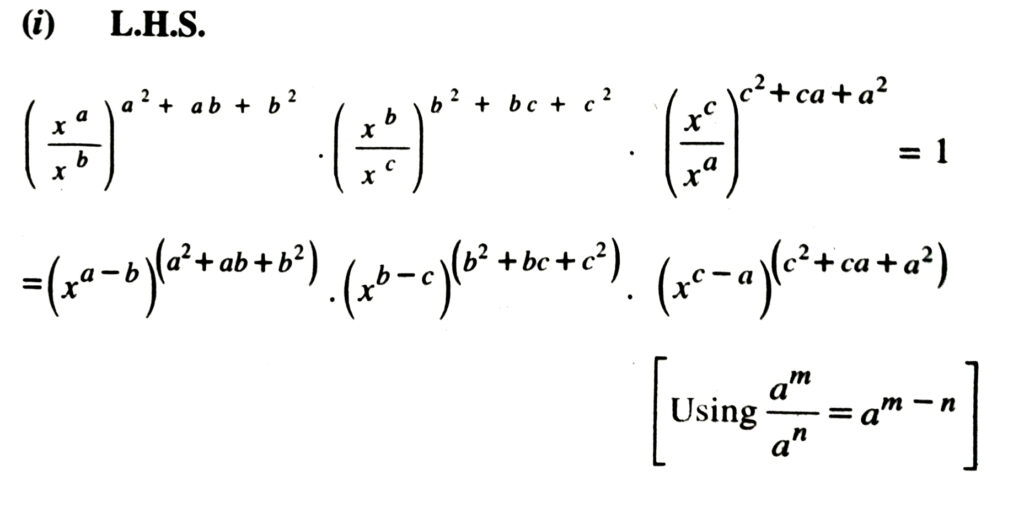

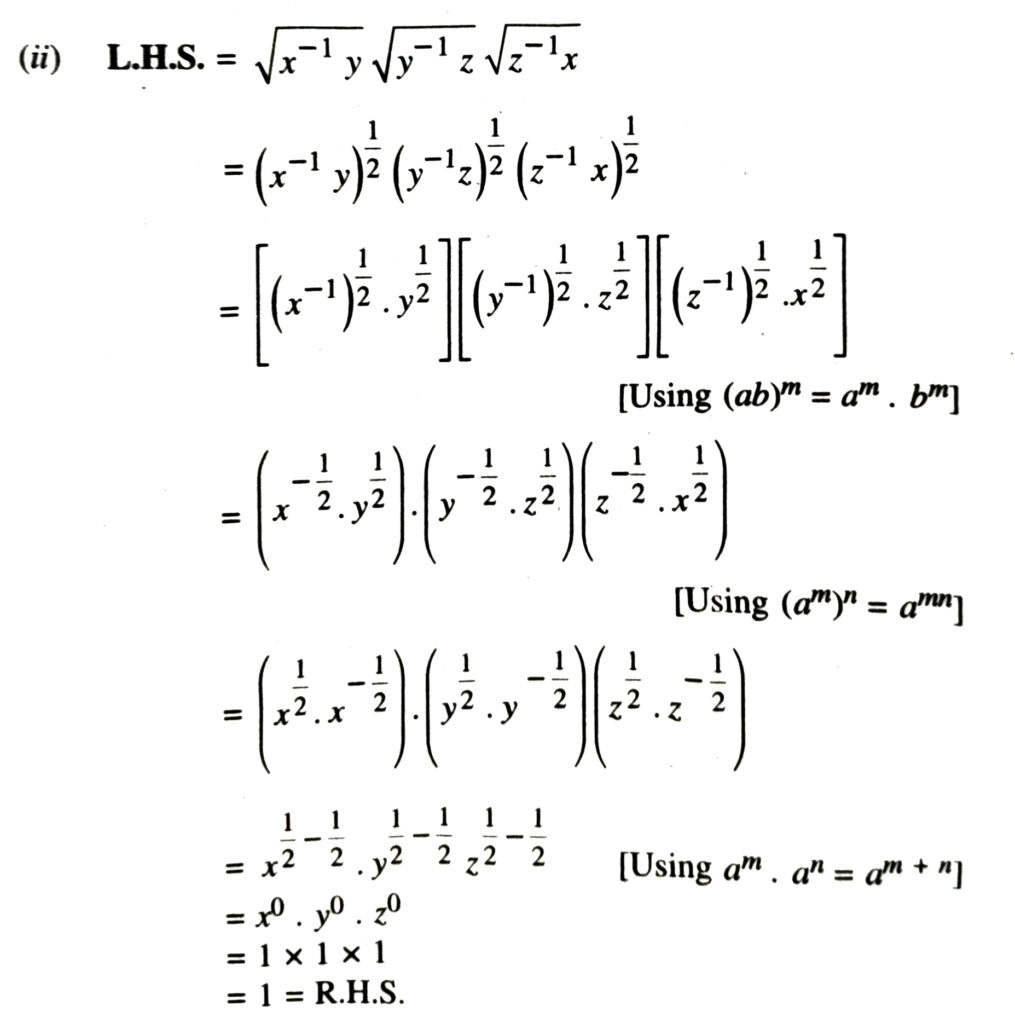

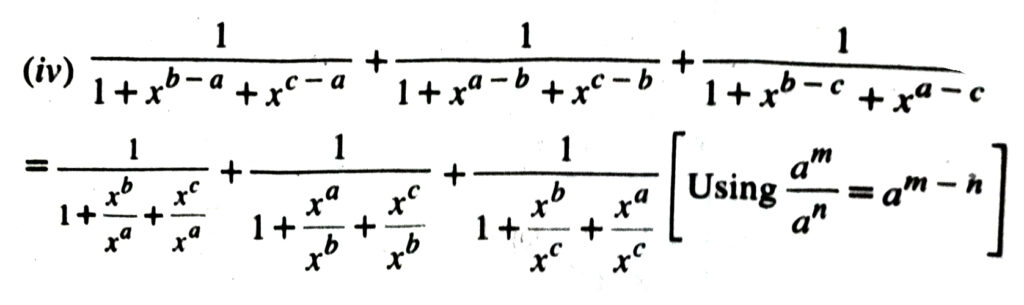
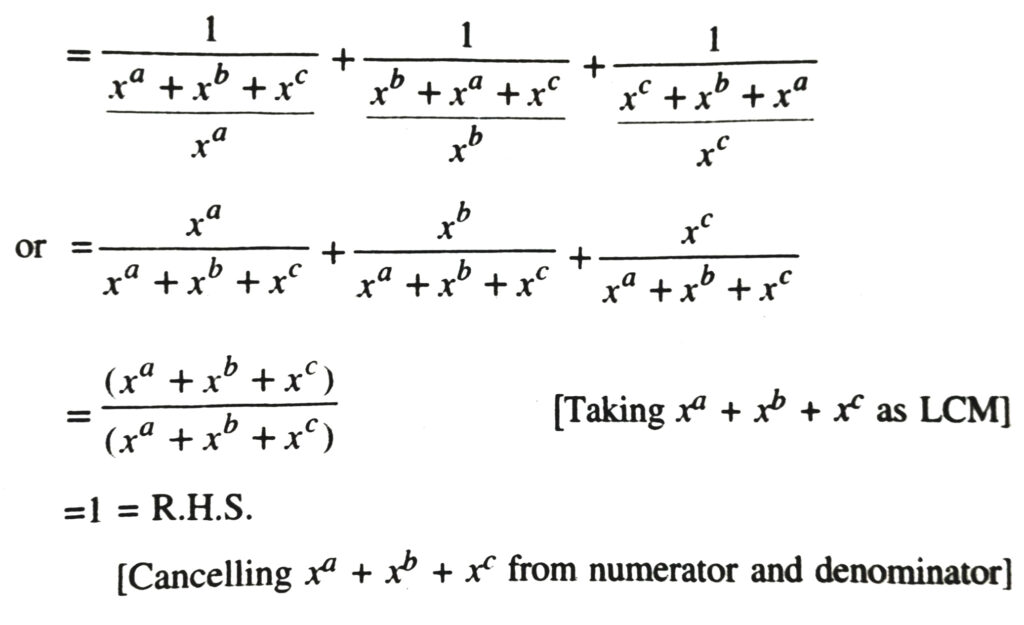
Definition of Logarithms
For a positive real number a and a rational number m Let am = b where b is a real number. In other words the mth power of base a is b. Another way of stating the same fact is logarithm of b to base a is m. We write it as logab = m “log” being the abbreviation of the word “logarithm”. 1
Note : log101 = 0 since 10⁰ = 1
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.2
1. Write the following in the form of logarithms :
(i) 25 = 32 (ii) 10³ = 1000 (iii) 34 = 81 (iv) 54 = 625 (v) 10-1 = 0.1 (vi) 7² = 49
Solution.— (i) 25= 32 Here a = 2, m = 5 and b = 32 the 5th power of base 2 is 32.
In form of logarithms, the logarithm of 32 to base 2 is 5.
Thus we have log232 = 5.
(ii) 10³ = 1000 Here a = 10, m = 3 and b = 1000. The 3rd power of base 10 is 1000.
In form of logarithms; the logarithm of 1000 to the base 10 is 3.
Thus we have log101000 = 3
(iii) 34 = 81, here a = 3, m = 4 and b = 81, the 4th power of base 3 is 81.
In the form of logarithms; the logarithm of 81 to the base 3 is 4.
Thus we have log381 = 4.
(iv) 54 625, here a = 5, m = 4 and b = 625, the 4th power of the base 5 is 625.
In the form of logarithms; the logarithm of 625 to the base 5 is 4.
Thus we have log5625 = 4.
(v) 10-1 = 0.1, here a = 10, m = – 1 and b = 0.1, the – 1 power of the base 10 is 0.1.
In the form of logarithms; the logarithm of 0.1 to the base 10 is -1.
Thus we have log10 (0.1) = − 1
(vi) 7² = 49. Here a = 7, m = 2 and b = 49.
The 2nd power of the base 7 is 49.
In the form of logarithms; the logarithm of 49 to the base 7 is 2.
Thus we have log7 49 = 2.
2. Express each of the following in exponential form :
(i) log525 = 2
(ii) log3 243 = 5
(iii) log101000 = 3
(iv) log2 64 = 6
(v) log4 64 = 3
Solution.— (i) log525 = -2; Here b = 25, a = 5 and m = 2
We write loga b = m in exponential form, as am = b
So we write log525 = 2 in exponential form as 52 = 25
(ii) log3243 = 5; Here b = 243, a = 3 and m = 5
We write logab = m in exponential form; as am = b
So we write log3243 = 5 in exponential form as 35 = 243
(iii) log101000 = 3; Here a = 10, m = 3 and b= 1000 in exponential form we write logab = m as am
So we write log101000 = 3 in the exponential form as 103 = 1000
(iv) log264 = 6; Here a = 2, m = 6 and b = 64
We write logab = m in exponential form; as am = b
So we write log264 = 6 in exponential form as 26 = 64.
(v) log464 = 3; Here a = 4, m = 3 and b = 64
We write log4b = m in exponential form as am = b
So write log464 = 3 in the exponential form as 43 = 64
Laws of Logarithms

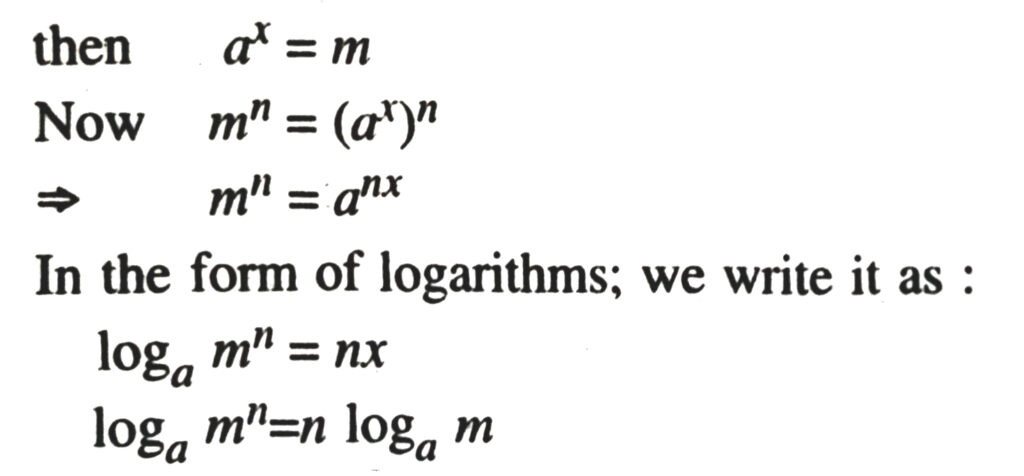
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.3
In each of the following, assume that the base a = 10 wherever, it has not been indicated :
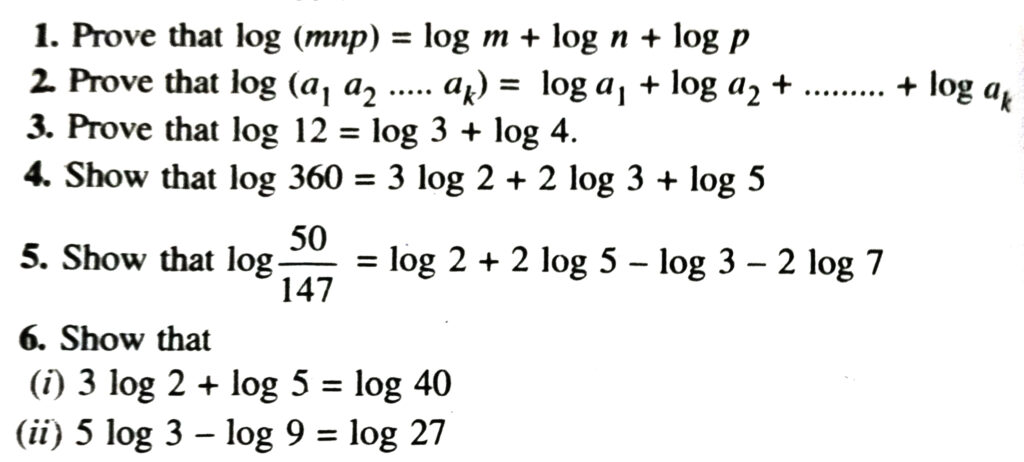
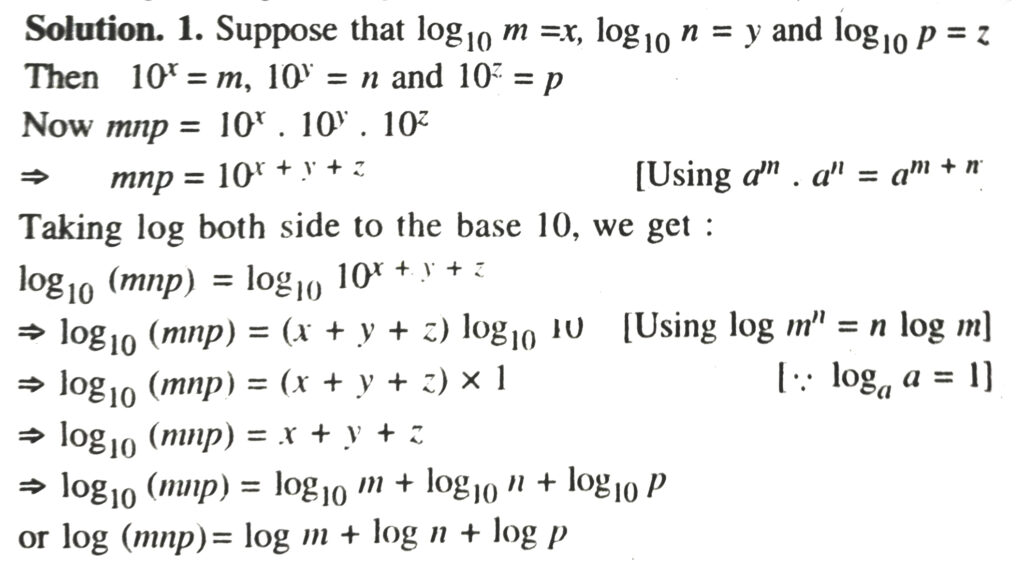
2. Suppose that
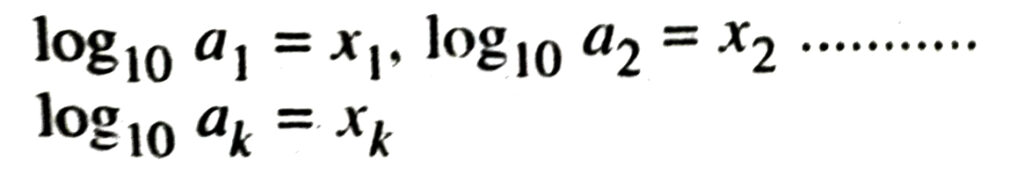
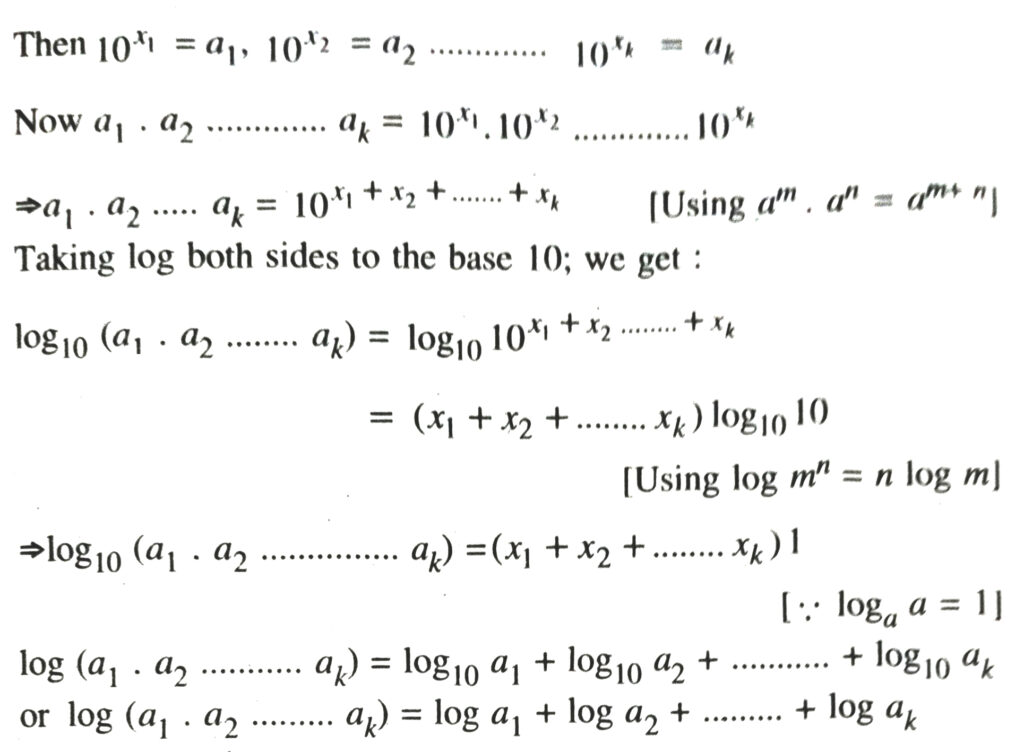
3. We can write
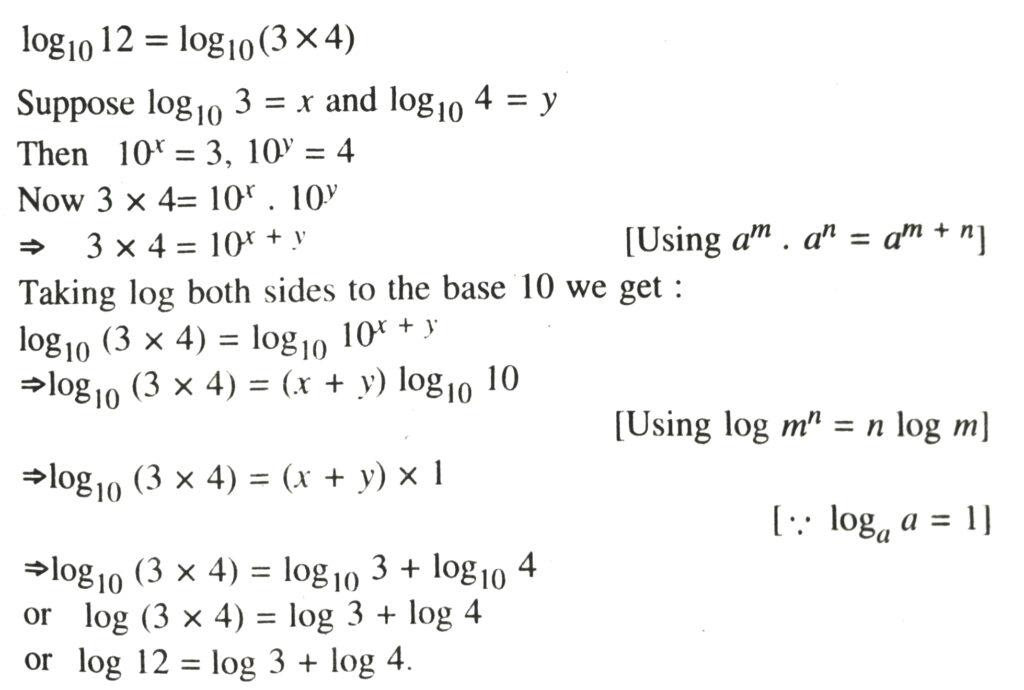
4. We can write
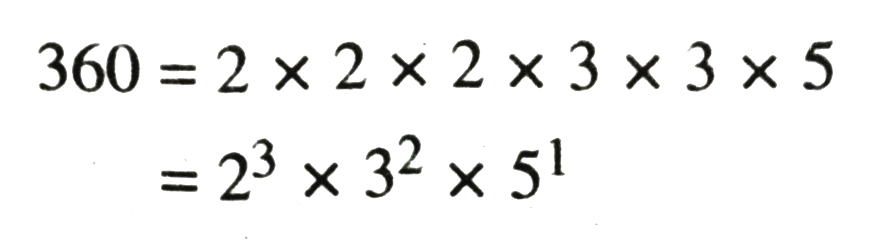
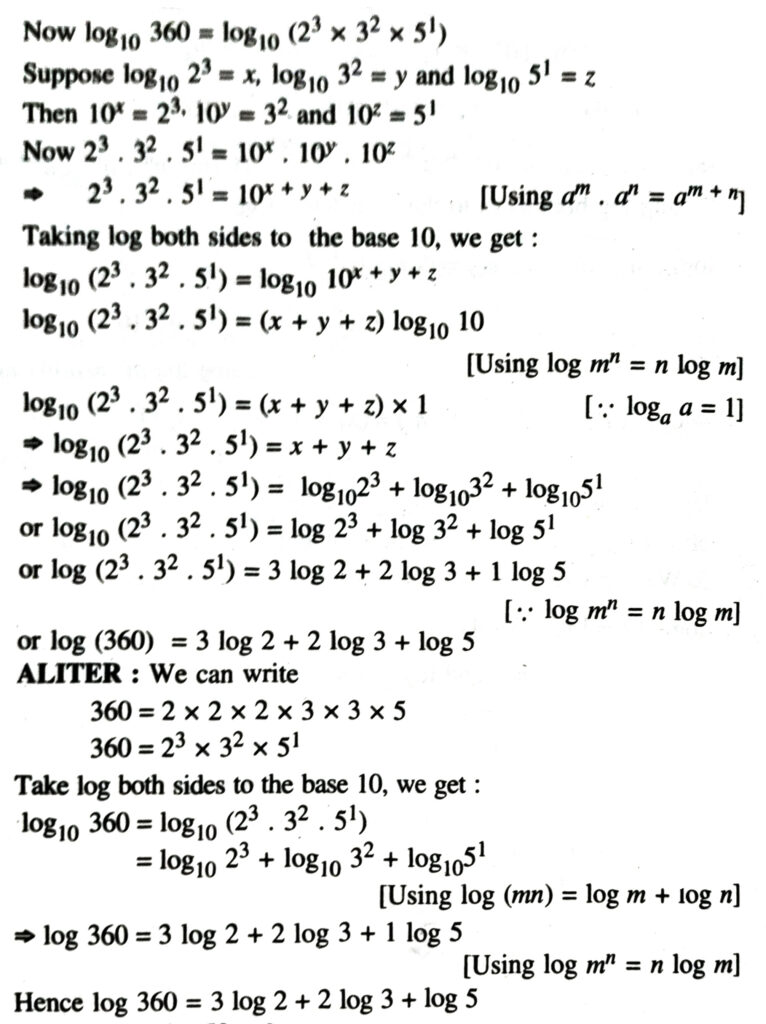
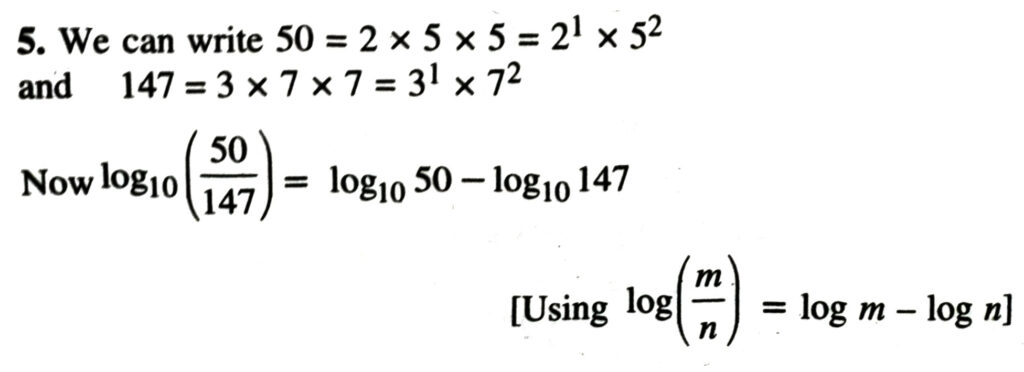
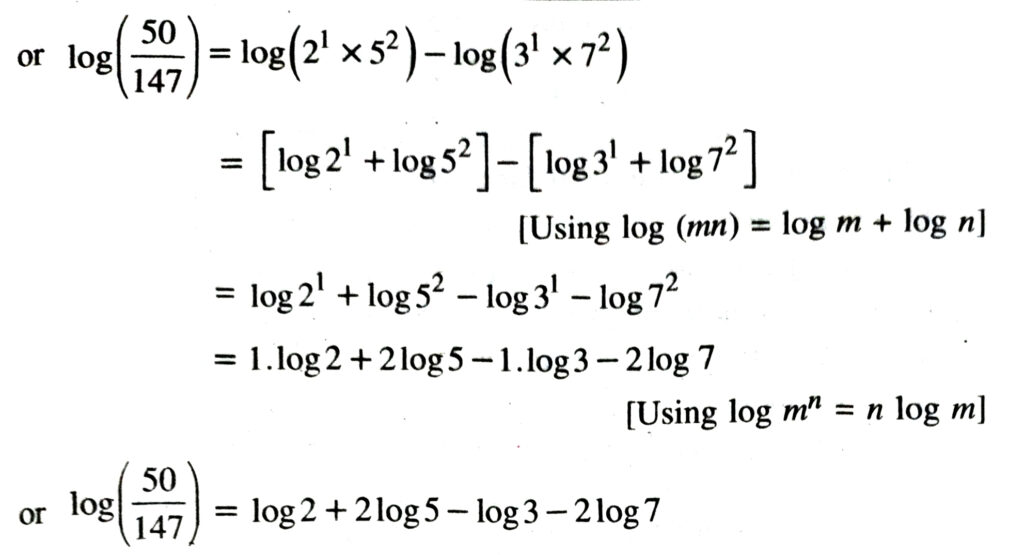

Standard Form of Decimal
Any positive decimal can be wirtten in the form
n = m × 10P
where p is an integer (positive, zero or negative) and 1 ≤ m < 10.
This is called the standard form of n.
Working Rule saiety
1. Move the decimal point to the left or to the right, as may be necessary, to bring one non-zero digit to the left of decimal point.
2. (a) If we move p places to the left; multiply by 10P.
(b) If we move p places to the right, multiply by 10-P.
(c) If we donot move the decimal point at all, multiply by 10⁰.
(d) Write the new decimal obtained by the power of 10 (of step 2) to obtain the standard form of the given decimal.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.4
1. Write each of the following in standard form :
(i) 3.12 (ii) 31.23 (iii) 312.3 (iv) 3123 (v) 312300 (vi) 0.3123 (vii) .03123.
Solution.— As we know that any positive decimal n is in its standard form if we express it as n = m × 10P.
where p is an integer (positive, zero or negative) and 1 ≤ m < 10.
Now;


2. Write the following numbers in decimal form, without powers of 10 as factors :
(i) 5.6 × 10³
(ii) 1.436 × 10-¹
(iii) 2.4 x 10-²
(iv) 9.632 × 10⁵
(v) 1.2056 × 10²
(vi) 1.2056 × 10-².
Solution.—

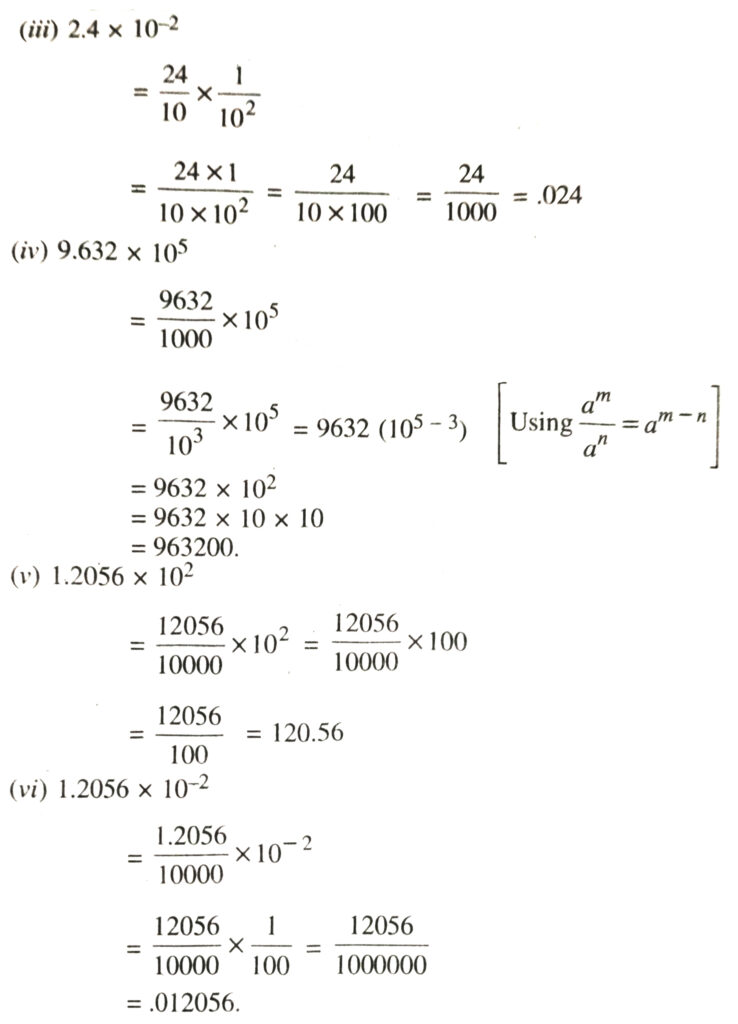
Characteristic and Mantissa
Consider the standard form of n
n = m × 10P where 1 ≤ n < 10.
Taking logarithms to the base 10 and using the laws of logarithms.
log n = log (m × 10P)
= log m + log 10P
= log m + p log 10
= log m + p.
or log n = p + log m
Here p is an integer and called Characteristic of log n.
As 1 ≤ m < 10, so 0 ≤ log m < 1
log m is called mantissa of log n.
Step to find log n
1. Put n in the standard form, say
n = mx 10P, 1 ≤ m < 10
2. Read off the characteristic p of log n from this expression (exponent of 10).
3. Look up log m from the tables
For example for log (6.234), we look in row 62 under column 3. We find 7945.
So 7945 + 3 = 7948
Hence log (6.234) = 0.7948.
4. Write log n = p + log m.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.5
1. Use logarithm tables to find the logarithms of the following numbers :
(i) 1270
(ii) 12.70
(iii) 431.5
(iv) 11.23
(v) 0.1257
(vi) 0.0012
(vii) 0.00001379.




Finding n when log n is given
If log n = t, we sometime say = antilog t
we write log n as
log n = p + log m
We first take antilog of mantissa; log m in antilog table. Let the number corresponding to log m be k i.e. antilog (log m) = k. Since the characteristic of log n is p. So the standard form of n is given by n = k × 10P
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4:6
1. Using tables, find the logarithm of each of the following numbers :
(i) 4.8
(ii) 7
(iii) 3.17
(iv) 3.172
(v) .235
(vi) .2354


2. Find log x, if x equals
(i) .0768
(ii) .0025
(iii) .0087
(iv) .00954
(v) .0056
(vi) .0287



3. Find the antilogarithm of each of the following :
(i) 0.752
(ii) .301
(iii) .5428
(iv) 2.752
(v) 1.301
(vi) 2.5428


4. Each of the following numbers is logarithm of some number. Express each in the form p + log in, where p is the characteristic and log m the mantissa and find the number.
(i) 1.2086
(ii) – 1.2084
(iii) – 2.4325
(iv) – 3.6432
(v) 2.5674
(vi) – 0.62.



Use of logarithms in numerical calculation
As we know that logarithm is a rule to shorten lengthy and difficult calculations; in this section we shall use logarithms in numerical calculation.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.7
(Use logarithmic tables)
1. Find the value of
(i) 6.45 × 981.4
(ii) 0.0064 × 1.507


2. Evaluate :
(i) 2.632/.0045
(ii) 0.54 ÷ 216.3

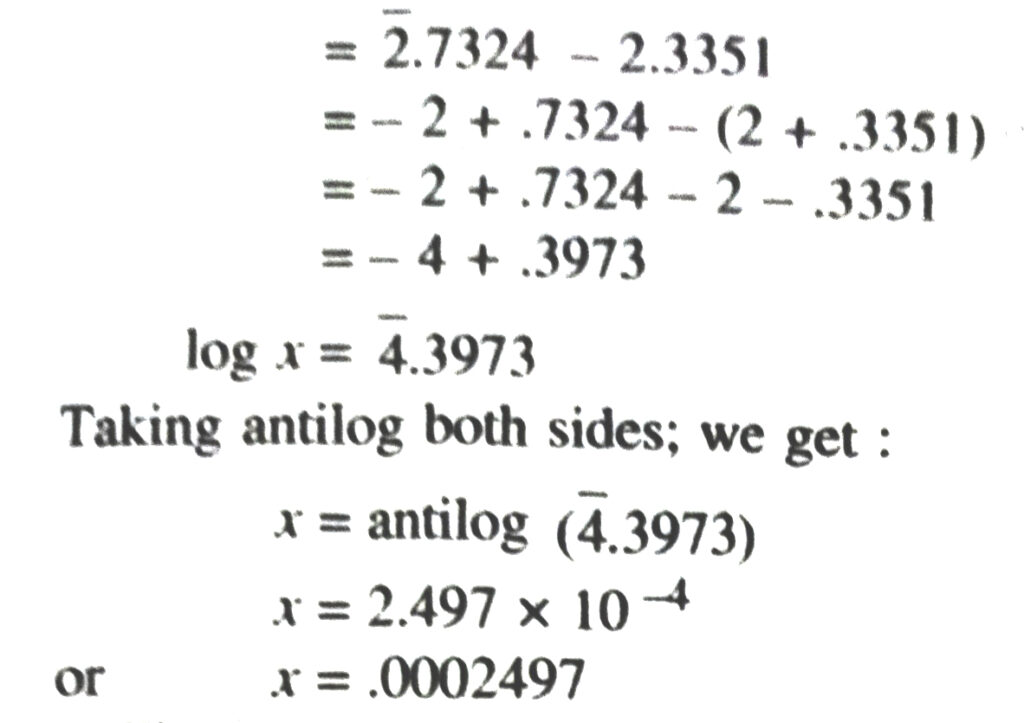
3. Find the value of :
(i) (.724)³
(ii)√42.36


4. Find the cube root of 48 correct to two decimal places.
Solution.— Let x be the cube root of 48.
∴ x = 3√48
or x = (48)1/3
Taking log both sides; we get” :
log x = log (48)1/3
= 1/3 log 48 [Using log mn = n log m]
= 1/3 × 1.6812
log x = 0.5604
Taking antilog both sides, we get :
x = antilog (0.5604)
x = 3.634
⇒ x = 3.63 correct up to two places of decimal.
5. Write down the logarithm of 64 and use it to state the number of digits in the numeral for 264.
Solution.— Let x = 264
Taking log both sides; we get :
log x = log 264
= 64 log 2 [Using log mn = n log m]
= 64 × .3010
log x= 19.264
To find the number of digits in numeral,
we take antilog both sides; we get :
x= antilog (19.264)
= 1.837 × 1019
or x = 1837 × 1016
Hence number of digits in 264 = 20
ALTER. To find the number of digits in numeral :
We have log x= 19.264
∴ Characteristic of log 264 = 19
∴ Number of digits in 264 = 19 + 1 = 20
6. Using logarithmic tables; evaluate :
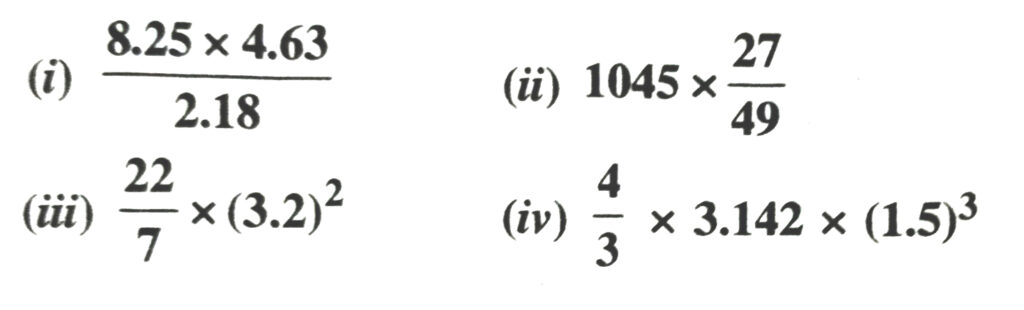



7. Find the values of the following :
(a) 3√0.0847
(b) (0.09634)3
(c) 4√.6789
(d) 5√42.7



Taking antilog both sides ; we get :
x = antilog × (0.3260)
= 2.118 × 100
x = 2.118
8. Using logarithms; simplify :
(a) 57.12 × 2.034
(b) 0.8623 × 0.000451
(c) 352.6 × 0.078 × 0.5943
(d) 2456 × 0.000071
(e) 328.4 × 12.65
(f) .3865 ÷ 0.000572
(g) 0.0953 + 3.794
(h) 25 ÷ 0.0683




9. Find the values of the following :
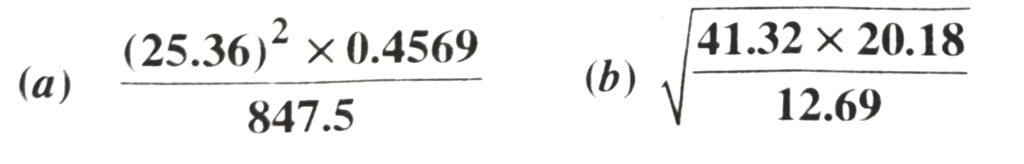
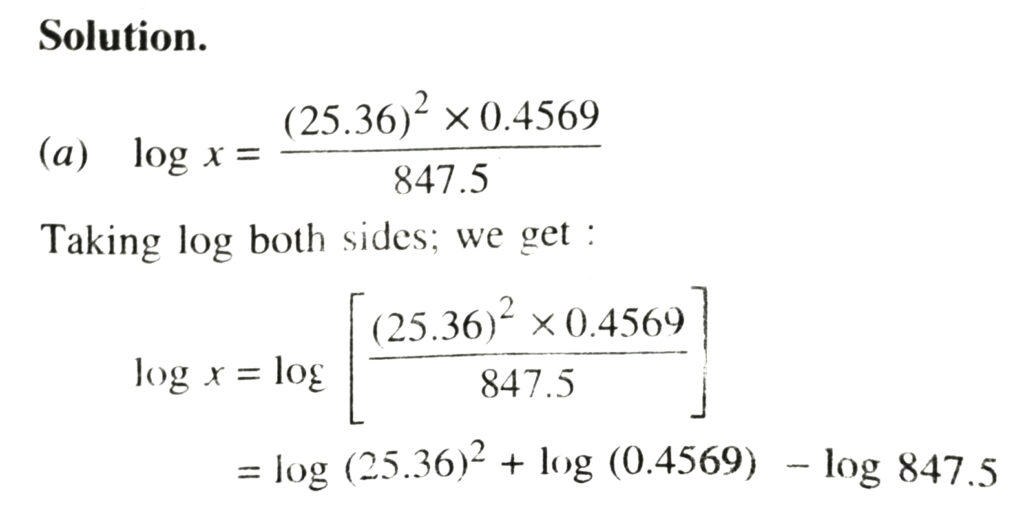


TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 4.8
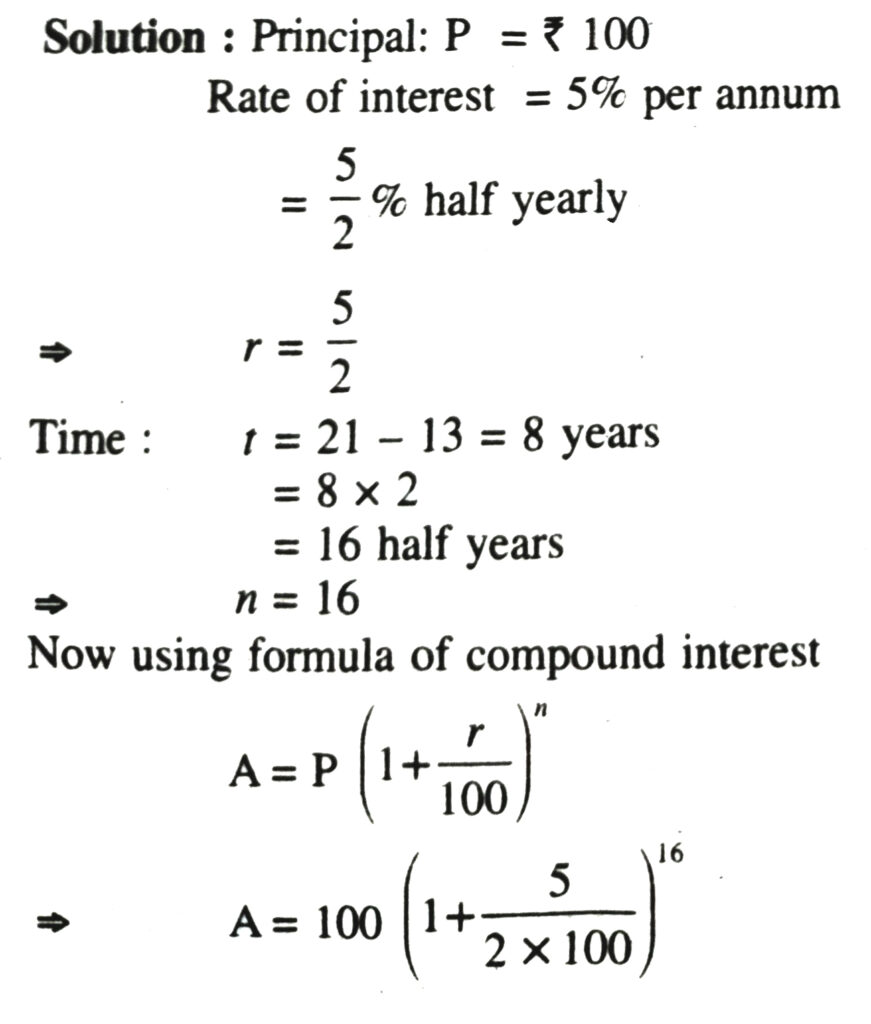
1. A savings bank account pays 5% interest (per year) and it compounded every six months. When a boy is 13 years old, ₹ 100 is deposited to his credit in a saving, bank account. How much is due to him when he is 21 years old ?

2. In how many years will an account double itself at 5% interest compounded annually ?

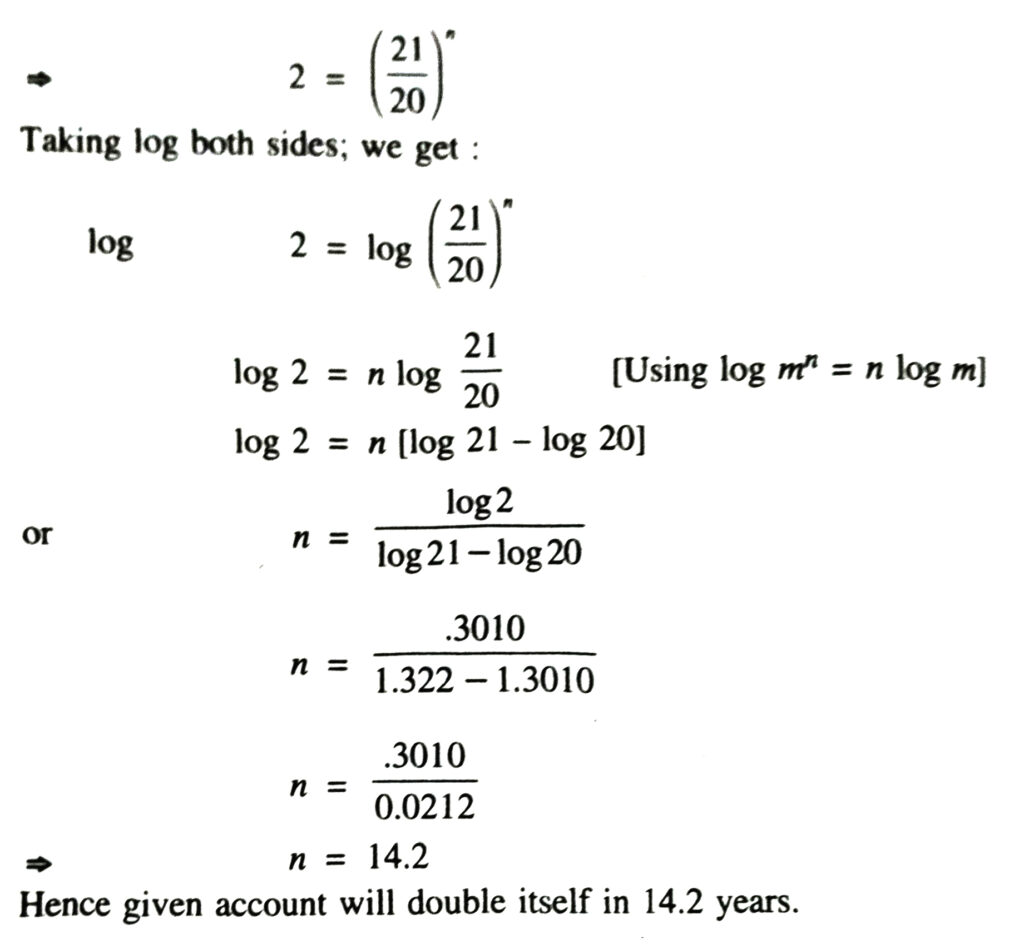
3. A nationalised bank issues “Re-investment Certificates” for a period of 3 years. If ₹ 5000 is invested in these certificates, their maturity value is ₹ 6725. Assuming that the interest is compounded every year, what is the rate of interest ?
Solution.— Let Principal sum; P = ₹ 5000
Amount; A = ₹ 6725 was
Time; n = 3 years
Let rate of interest be r% per annum
Now using the formula of compound interest;
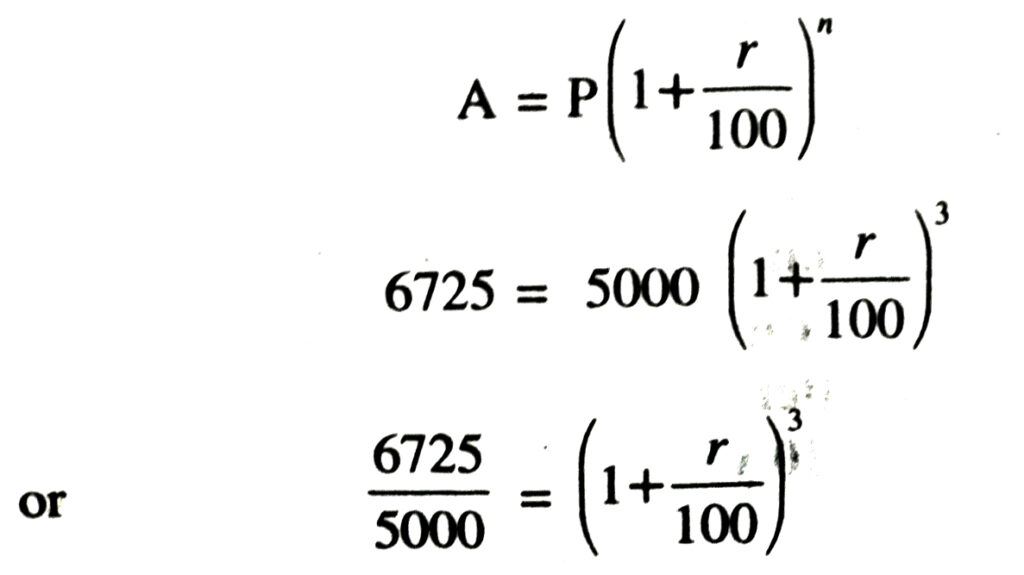

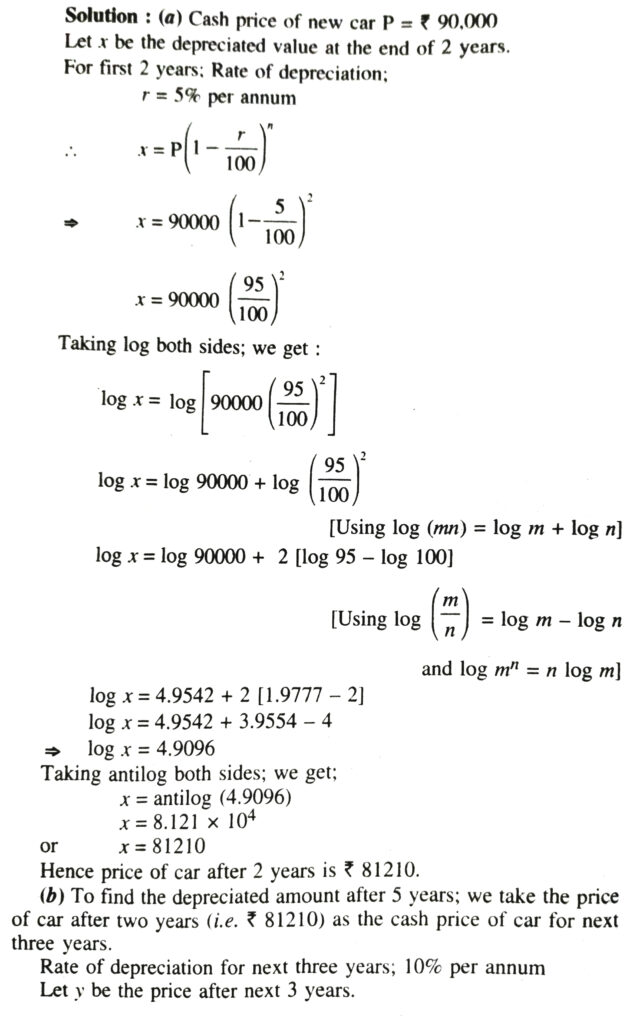
4. The cash price of a new car is ₹ 90,000. The insurance company calculates its price at any subsequent time according to the rule that the price depreciates at the rate of 5% a year during the first two years and at the rate of 10% a year thereafter. What will be the price of the car after
(a) 2 years (b) 5 years (c) 10 years.

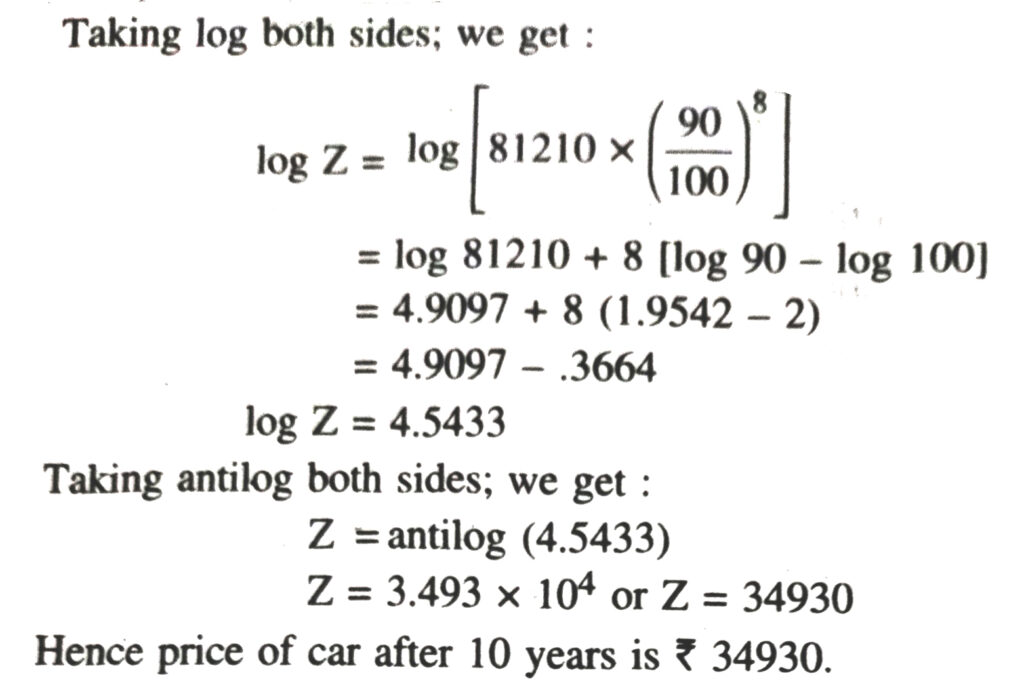
5. The cash price of a refrigerator is ₹ 5500. It can also be purchased for ₹ 2000 followed by 11 equal monthly instalments of ₹ 400 each. What is the rate of interest charged under instalment plan?


6. The lengths of adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 51 cm and 37 cm. The length of one of the diagonals is 20 cm. Find its smaller altitude.
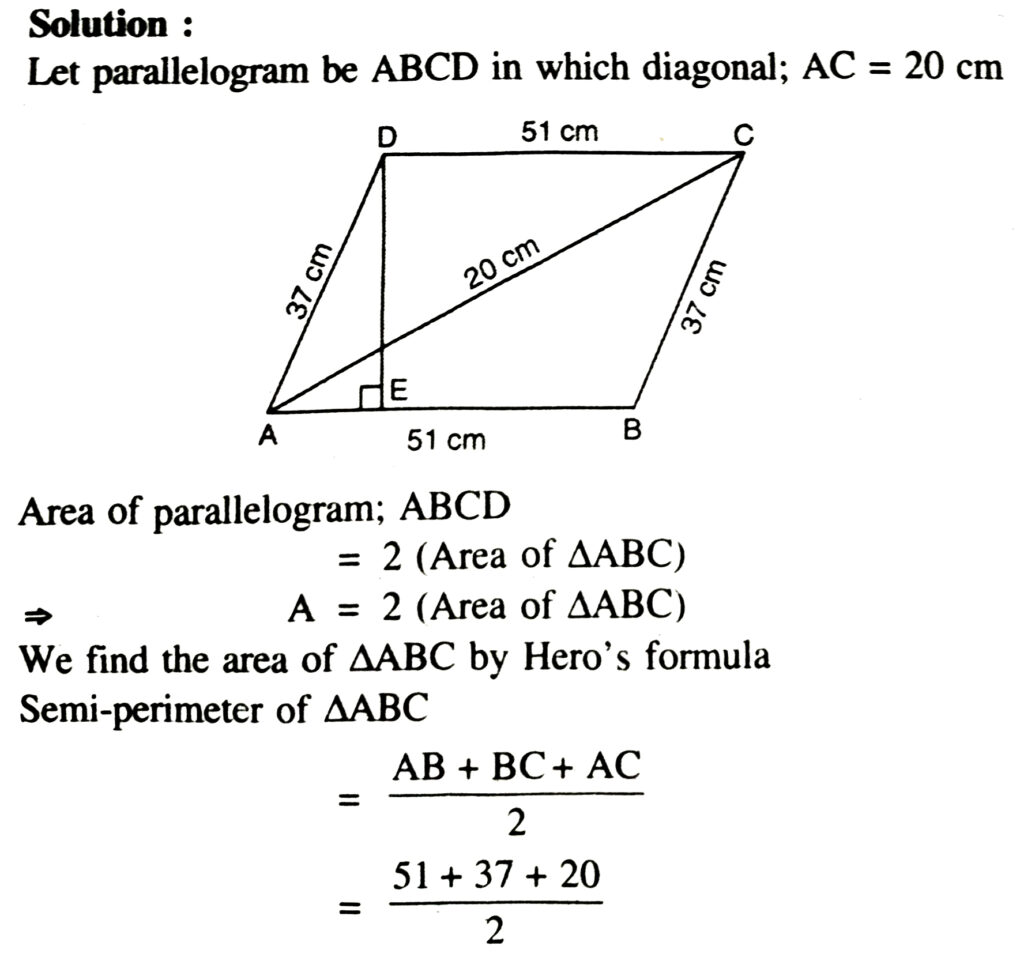
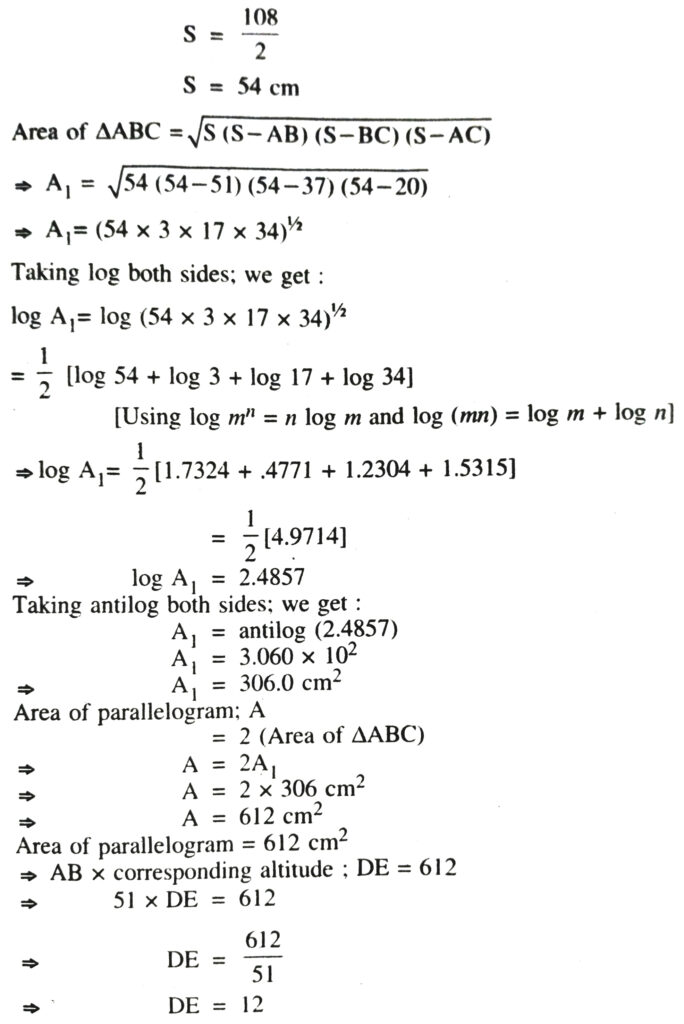
[Altitude corresponding to the larger side is always smaller. AB = 51 cm is the larger side. So corresponding smaller is DE.]
Hence length of required smaller altitude is 12 cm.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here