WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 6 The Second World War and its Aftermath
WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 6 The Second World War and its Aftermath
WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 6 The Second World War and its Aftermath
West Bengal Board 9th History Solutions
WBBSE 9th Class History Solutions
Salient points – At a glance
1. The germs of the Second World war lay in the Treaty of Versailles (1919) which was imposed on defeated Germany after the First World War. It was a humiliating and shameful treaty for Germany which imposed drastic losses and unbearable burdens on her. The treaty made the Germans feel a desire to have the treaty nullified as soon as possible.
2. The problems and needs of the victorious powers in the First World War were also not settled by the Treaty of Versailles. The new states which had arisen in central Europe felt insecure about their fate. There were also rivalries over political ideologies of democracy and dictatorship. There was also the challenge of communism.
3. The western democratic countries were not happy with the growing power of the USSR and the spread of communism in Eastern Europe. So the western democratic countries preferred to appease Germany and Italy.
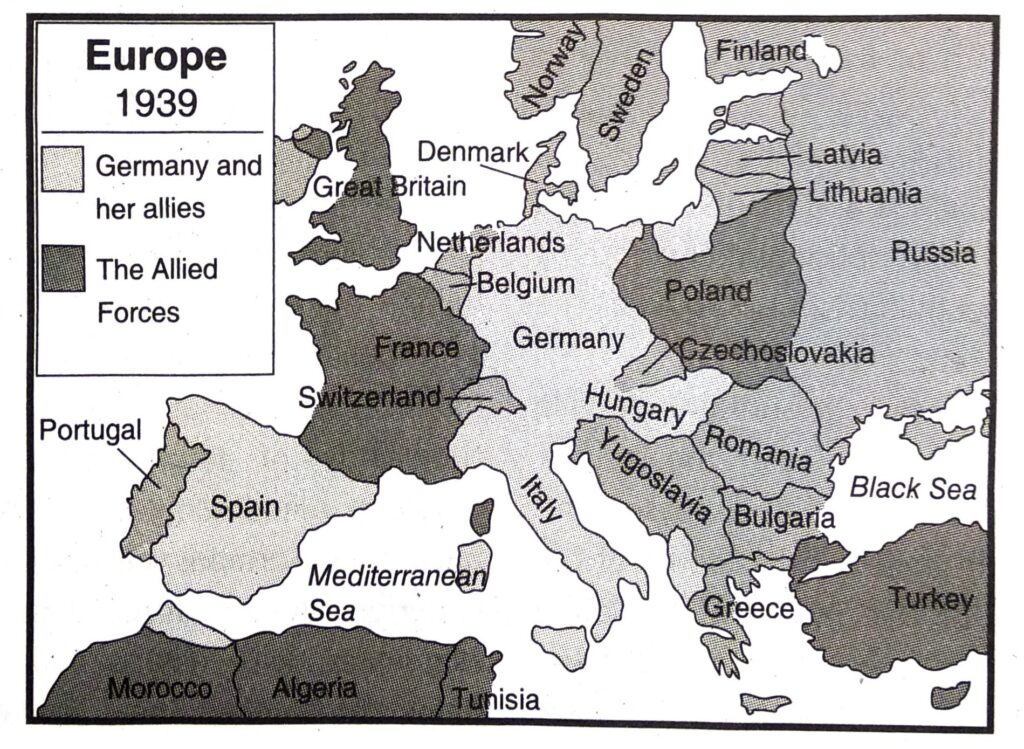
4. This emboldened Hitler. In 1938 he first occupied Austria and then Czechoslovakia, then Danzig on the Baltic Sea. On 1 September, 1939 the German army marched into Poland. So Britain and France declared war on Germany on September 3 and the Second World War started.
5. The war in the beginning proved to be highly favourable to Germany. From the end of 1944 the war situation began to change in favour of the Allies.
6. In early 1945 the Allies launched massive attacks on Germany and the German armies surrendered. Japan’s surrender came a few months later when the USA dropped two atom bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August, 1945.
7. The Second World War destroyed far more lives and properties than the First World War. In Germany, Russia and Japan several millions of people lost their lives.
8. The signing of treaties after the Second World War did not mean the coming of peace. Armed conflict ended but a cold war between two superpowers-the USA and USSR started.
9. International agencies like the UNO were set up to settle international issues and for the establishment of peace, but these have not been able so far to prevent the race for armament, in particular, nuclear armament which is a great menace to world peace even today.
10. One positive result of the war was that the war weakened the old colonial empires and forced them to grant independence to their colonies which they had held for generations
TOPIC – A
The Causes and Course of the Second World War
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. What were the causes of the Second World War ?
Ans. The causes of the Second World War which broke out on 13 September 1939 may be discussed as follows:
[1] Unjust terms of the Treaty of Versailles: The Treaty of Versailles (1919) imposed unjust and humiliating terms on defeated Germany and therefore the Germans continued to nourish their grievances against the Treaty of Versailles.
[2] Hitler’s ambition to become master of Europe: Hitler became the dictator of Germany in 1934 and began to violate the humiliating terms of the Treaty of Versailles.
[3] Weakness of the League of Nations: The League of Nations which had been formed to prevent future war became weak and aggressive nations like Germany, Italy and Japan defied the League openly.
[4] Lack of cooperation between England and France: There was very little cooperation between England and France, the two important powerful member countries of the League of Nations. France wanted to take action against Germany for denying the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, but England did not give full support to this and Hitler took full advantage of this.
[5] Italy’s ambition to become a world power: Italy, which became one of the most powerful nations of Europe, captured Abyssinia in 1936. Italy’s ambition to become a world power with the help of the Nazi leader of Germany was also a cause of anxiety for England, France and Russia and they apprehended danger from Italy.
[6] Japanese Imperialism: After the First World War Japan became a warlike nation and conquered Manchuria and half of China in 1939. The war between China and Japan later merged into the Second World War.
[7] Immediate cause: The immediate cause of the Second World War is to be found in a series of acts of aggression by Hitler. Germany annexed Austria and then demanded Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia. Soon after Germany swallowed up the remaining portion of Czechoslovakia and demanded Danzig from Poland. Britain, France and Poland formed an alliance to resist German aggression upon Poland. Meanwhile, Great Britain and France were engaged in negotiations with Russia. But the world was surprised by the news that Germany and Russia had concluded Non-Aggression Pact for 10 years (1939) and this emboldened Hitler to invade Poland without any formal declaration of war. So Great Britain and France declared war against Germany in September 1939 and the World War II began.
2 . The fundamental cause of World War II must be sought in the Treaty of Versailles-Discuss.
Ans. [1] The Treaty of Versailles has been called ‘a dictated treaty’ which was imposed upon vanquished Germany by the victorious Allied Powers. The delegates of Germany were not invited to the Paris Peace Conference (1919) and the treaty was a revengeful treaty. [2] The treaty did not adhere to the principle of self-determination. The right of selfdetermination was not applied for Sudetenland which was transferred to Czechoslovakia. It led to a loss of balance of power in Europe. [3] While England and France increased their colonies, German colonies were confiscated in the name of good government. [4] The provinces of Alsace and Lorraine were taken away from Germany and were given back to France. The Saar Valley on the western frontier of Germany was handed over to France for fifteen years after which fate of the region was to be settled by a plebiscite. The port of Danzig was also snatched away from the possession of Germany. [5] Germany was saddled with a huge reparation amount by the Treaty which was impossible for her to pay. [6] The German bared of staff or general of the army was dissolved. Germany had to surrender her fleet to the Allies. According to Wilson’s Fourteen Points, it was decided that all the states would reduce their war armaments. But this clause was only applied to Germany.
Humiliated Germany was looking forward to another war as an opportunity to avenge her defeat. So it is said that the fundamental cause of World War II must be sought in the Treaty of Versailles.
3. How did the failure of the League of Nations constitute a cause of the Second World War ?
Ans. The terrible effects of the First World War (1914-18) had stunning effects on the minds of the people and made them cry for peace. President Wilson of America took the initiative and made a plan for the League of Nations which was established in 1920, the primary object of which was to prevent armed conflict.
Many international problems arose after the First World War. At first the problems were comparatively easy and the League of Nations was able to solve some of them by peaceful methods. But the League’s inability to control the Great Powers become quite evident in the thirties which constituted a cause of the Second World War. In 1931 when Japan swallowed Manchuria the League did not adopt any penal measure against Japan, the grievances of China remained unredressed. Encouraged by the failure of the League the autocrats of different countries also started aggression totally ignoring the League of Nations.
In 1935 Italy under the dictatorship of Mussolini invaded and occupied Ethiopia (Abyssinia) in Africa. Ethiopia complained to the League and a decision was made by the League Council for enforcement of economic sanctions against Italy. But Italy did not obey League’s order and resigned from the League of Nations. During Spanish Civil War the League was unable to adopt effective measures to restore peace in Spain and to prevent external intervention. Franco became victorious and this added to German confidence. For this reason the Spanish Civil War is regarded as the stage rehearsal for the Second World War. The failure of the League made Hitler and Mussolini bolder.
Immediately after assumption of dictatorial power Hitler withdrew Germany from the Disarmament Conference in 1933 and from the League of Nations. Within a few years Hitler swallowed Austria and Czechoslovakia (1938-39) and invaded Poland in 1939. The invasion of Poland by Germany was the signal for the outbreak of the Second World War. In no case could the League of Nations prevent or restrict Hitler’s aggressions. Thus the failure of the League of Nations in different international disputes constitute a cause of the Second World War.
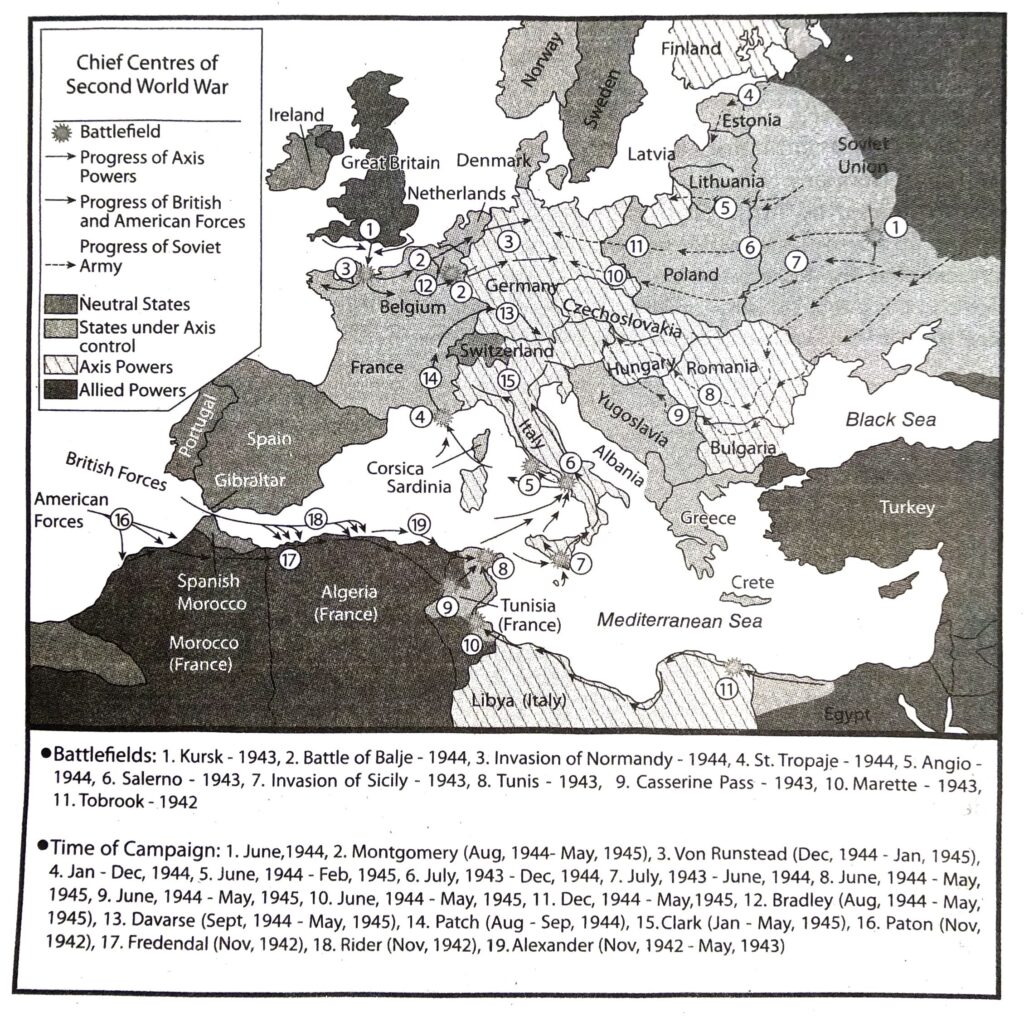
4. Describe the course of the Second World War.
Ans. The shameful Treaty of Versailles (1919) was imposed (1914-18) by the Allied powers. Hitler rejected the Treaty of Versailles and invaded Poland in 1939 which led to the outbreak of the Second World War. Germany occupied half of Poland. After conquering Denmark and Norway, Germany turned westward and attacked Holland, and Belgium. Germany occupied France in 1940. Then Germany invaded Russia and at the Battle of Stalingrad Germany was defeated.

Fascist Italy invaded North Africa after joining World War Il as an ally of Germany.
Italy was defeated by Anglo-American forces. Anglo-American forces landed at Normandy in France and attacked Germany. At last Germany was defeated after a strong resistance. Germany was attacked by the Russians in the East Frontier and Anglo-French-American army in the west frontier and Germany surrendered. The eastern bank of river Elb was occupied by Russia and the western bank of Elb was occupied by Anglo-American forces.
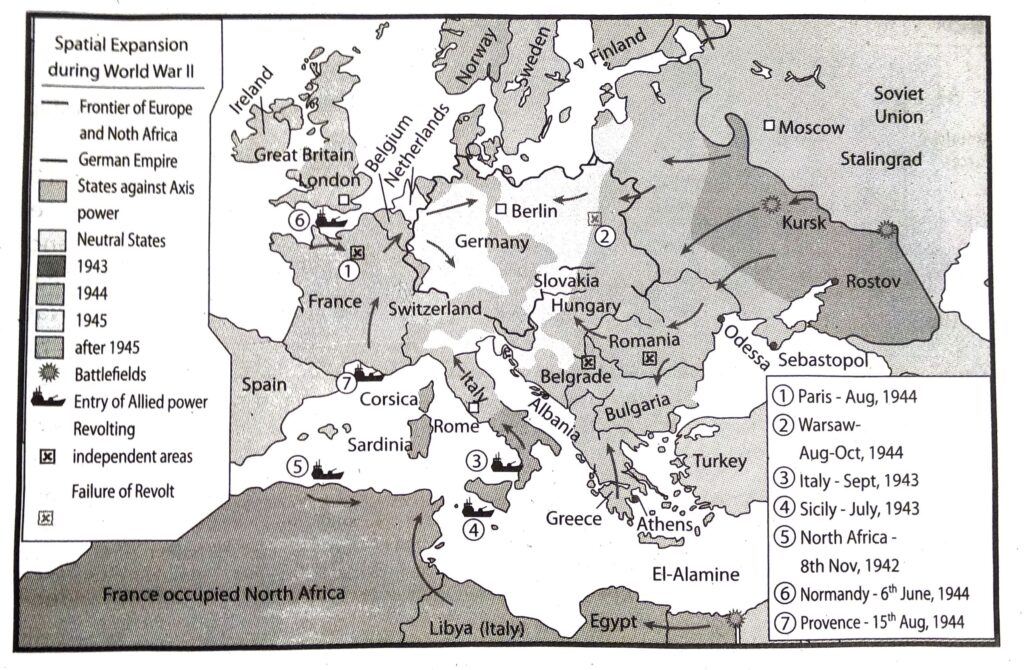
In the far east Japan invaded Manchuria in 1931 and China in 1936. She attacked and destroyed American naval base at Pearl Harbour in 1941 and joined the Second World War. After the defeat of Germany and Italy the Allies attacked Japan in full force. After atom bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan surrendered to the Allies. With the fall of Japan the Second World War came to an end.
5. Give an account of the struggle between Soviet Russia and Germany.
Ans. The Russo-German Non-Aggression Pact was signed in 1939 for 10 years between Russia and Germany. Hitler violated this pact and attacked Russia in 1941. He did this because he feared that Russia was fast building her defence and increasing her armaments. He suspected that Russia might attack Germany. Without warning, Hitler sent three large armies across Russia’s western frontier. Vast areas of Russia were under Nazi control. But the Germans were still not complete victors. The Russians adopted guerilla tactics and ‘scorched earth’ policy to harass the Germans. The Germans could not capture key cities of Leningrad, Moscow, Stalingrad and Sebastopol. The German soldiers were halted due to severe winter. Hitler ordered a limited withdrawal in 1942.
Hitler in the meantime was planning a new offensive which was to concentrate on Caucasus oil field. Despite the resistance of the Russians, the German army occupied the Don. His objective was to capture Caucasus and Stalingrad. Exhausted by immense distance and extreme winter Germany failed to capture Stalingrad. In 1942 Hitler decided to break of the offensive.
6. Write a note on Japanese attack on Pearl tack on Pearl Harbour.
Ans. On December 7, 1941 the Japanese launched a surprise attack on the US Naval Base at Pearl Harbour. The Japanese destroyed many US ships and killed many soldiers. It was this attack that forced US to enter World War II.
Pearl Harbour is located in Hawaii on the island of O’ahu. Hawaii is located in the Pacific Ocean between California and Japan. During the time of World War II, Hawaii was not a state, but a US territory.

World war II had been raging in Europe and Asia for 2 years but the US had not entered the war. Japan was trying to take over much of Asia and was worried about the US Navy in Hawaii. Japan decided to strike the Pearl Harbour to cripple the US navy and to prevent the US from attacking them.
The attack on Pearl Harbour came as a complete surprise. Hundreds of Japanese fighter planes and bombers flew to Pearl Harbour and attacked the US warships. The bombers dropped bombs and torpedoes on the US warships while the fighter planes attacked the US fighter planes on the ground. A number of US ships were destroyed. The next day, December 8, 1941, the US declared war on Japan. Three days later Japanese allies, Germany and Italy, declared war on the US. The US was now a major part of World War II.
7. Discuss the role of USA in the Second World War.
Ans. USA followed a policy of neutrality towards international politics after the First World War. She did not join the Second World War and kept herself aloof from the war. But when Japan attacked the US naval base at Pearl Harbour on 7 December, 1941, USA joined the war.
[1] Deviation from the path of neutrality: During World War II, the USA was sympathetic towards the Allied powers. In 1939 the American legislature allowed USA to help the western democratic states and sell arms and ammunitions to them. This policy was known as ‘Cash and Carry Policy’. It was a policy to preserve neutrality while aiding the Allies. It allowed sale of arms, ammunitions and war materials to belligerents (countries engaged in war) as long as the recipients arranged for transportation using their own ships and paid immediately in cash, assuming all risk in transportation.
[2] System of conscription: In the USA a system of conscription was introduced. According to this, all youths in the age group between 21 and 31 were obliged to join the army.
[3] Lend-lease Act: The American Senate enacted the Lend-Lease Act in March 1941 and allowed the US government to offer warships, war planes and other weapons to the Allied Powers to fight against fascism. USA become the arsenal of democracy.
[4] Incident of Pearl Harbour: Japan attacked the American fleet at Pearl Harbour in the Hawaiian islands on 7 December, 1941 with 360 aircraft and wiped out all the American planes on the ground there. This incident forced USA to join the Second World War.
8. What were the causes of defeat of Axis Powers in the Second World War?
Ans. In the Second World War (1939-45) the Axis powers (Germany, Italy and Japan) were defeated by the Allied powers (England, France, Russia, USA and China). The causes of the defeat of Axis Powers are as follows: [1] The Axis Powers were not equipped for a major world war and could not withstand the combined attack of three advanced nations like

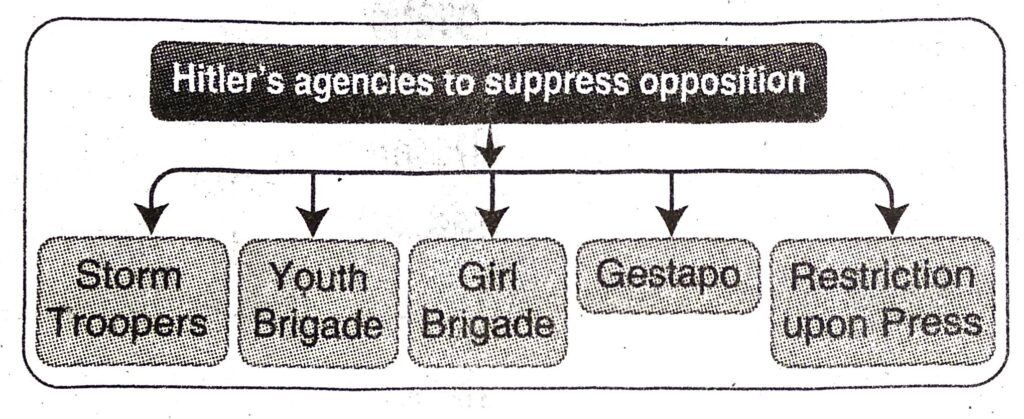
Britain, USA and Soviet Union. [2] Germany produced all sorts of wonderful gadgets during World War II-except the one that mattered: the atomic bomb. Germany’s nuclear project was disjointed and poorly supported. [3] Hitler relied on the strength of the German airforce which was outnumbered due to the entry of USA and Soviet Union. [4] The German attackers believed that Soviet Communism was a corrupt and primitive system that would collapse. But the air and tank armies were reorganised and technology available was hastily modernised to match the Germans. [5] Spain was a member of the Axis Power during the war, but it never committed troops to the effort. Led by Fascist dictator Francisco Franco, the country steadfastly refused to enter into the thrall. [6] The Allied Powers who wanted to establish democracy had world sympathy behind them which the Axis Powers failed to get. [7] The people of the territories conquered by the German armies were harshly treated and the Nazis faced opposition from the conquered territories. [8] Intrigue among the German Generals also contributed to the defeat of Germany. [9] When USA joined the war, the power of the Allies exceeded all that Germany, Japan and her allies could summon together and led to the defeat of Germany. [10] Hitler’s high ambition and dominating nature was also responsible for his failure. He was suspicious and even distrusted his lieutenants like Goering and Himmler which brought about his downfall.
Know More
Last Days of Hitler: When the Allied army recovered France, Hitler realised that his defeat and fall was not very far off. The Germans also started revolting against him. Even bombs were hurled to kill him (20 July 1944). His trusted friends also deserted him. He had with him his lover Eva Braun, propaganda minister Dr. Goebbels, personal physician and the driver of his car. He took shelter in a 50 feet deep bunker in Berlin (January 1945). Hitler called a priest and married his mistress Eva (29 April 1945). Next day both of them committed suicide in the underground bunker. The driver of his car burnt their dead bodies with petrol.
Analytical Answer (AA) Type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1. What was the immediate cause of the Second World War ?
Ans. In the Second World War (1939-1945) Germany, Italy and Japan were on one side and Britain, France, USSR, USA and China were on the other.
The immediate cause of the Second World War is to be found in a series of acts of aggression by the German leader Hitler. Germany annexed Austria and then demanded Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia. By the Munich Pact of 1939 the Allies admitted the German claim. Soon after, Germany swallowed up the remaining portion of Czechoslovakia and demanded Danzig from Poland. Britain, France and Poland formed an alliance against German aggression. Great Britain and France were engaged in negotiations with Russia. In the meantime Germany and Russia concluded a Non-Aggression Pact for 10 years (1939). Hitler thus emboldened invaded Poland without any formal declaration of war. Great Britain and France declared war against Germany in September 1939 and the Second World War started.
2. How far was Hitler responsible for the outbreak of the Second World War ?
Ans. The main causes of the Second World War according to many historians was the aggressive policy of the German dictator Adolf Hitler. He treated the Treaty of Versailles (1919) as a scrap of paper. After making Germany economically and politically strong he began to disobey the conditions of the Versailles Treaty. He began to reorganise the

German army with a motive of aggressively violating the Versailles Treaty. He followed an aggressive policy towards the neighbouring countries, violating treaties and promises. He annexed Austria violating the Treaty of Versailles. He violated the Munich Pact and annexed Czechoslovakia. In order to wreck the Balance of Power, he concluded the Rome-Berlin Axis. Finally in 1939 he invaded Poland disregarding the warning given by England and France. Thus the aggressive policy of Hitler made the Second World War inevitable.
3. How was the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis formed ?
Ans. Adolf Hitler, the Nazi dictator of Germany, repudiated the Locarno Pact in 1936. He militarized the left bank of the river Rhine. In the same year Germany and Japan concluded the Anti-Commintern Pact which was aimed against Russia. Hitler also established friendly contact with Mussolini, the Fascist dictator of Italy and formed the Rome-Berlin Axis. Italy occupied Abyssinia in 1936 in defiance of the League of Nations and found it necessary to secure friends in Europe. In 1937 Italy left the League of Nations and joined the AntiCommintern Pact. Thus the Rome-Berlin Axis was converted into Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis.

4. When and between whom was the Munich pact signed? What is the importance of the Munich Pact (1938)?
Ans. The Munich Pact was signed in 1938 between Chamberlain (The British Prime Minister), Daladier (Prime Minister of France), Hitler (the Nazi dictator of Germany) and Mussolini (the Fascist dictator of Italy).
England and France followed a policy of appeasement towards Hitler and signed the Munich Pact in 1938 in which the unjust demands of Hitler were accepted. [1] Germany was authorised to occupy four border provinces of Czechoslovakia within ten days. [2] The government of Czechoslovakia was forced to release all the political prisoners of Sudetenland. Sudetenland was also given to Germany. This emboldened Hitler and encouraged him to make more and more territorial demands. At last when Hitler invaded Poland, Britain and France could not tolerate it and declared war against Germany. Thus the Second World War started.

5. What is meant by the policy of appeasement?Who followed the policy of appeasement and why?
Ans. The policy of appeasement means giving a person or party whatever they want. By 1939 aggressive militarism of Italy and Germany in Europe and Japan in East Asia created alarm. But throughout the spell of aggression the great powers like England and France remained inactive and timid. Their policy of doing nothing or little when facing militarism is known as the policy of appeasement.
The Prime Minister of Britain, Neville Chamberlain and Edward Daladier, the Premier of France, followed the policy of appeasement. Neville Chamberlain believed that some of the territorial clauses of the Treaty of Versailles (1919) were unnecessarily harsh to Germany and an appeasement policy towards Hitler would prevent another war. He believed that if Germany became strong and if she was satisfied by the amendment of the Treaty of Versailles, she would stand as a bulwark against communist influence of Russia.
6. What is ‘Cash and Carry’ policy ?
Ans. USA followed a policy of neutrality towards the international politics after the First World War. She did not join the Second World War and kept herself aloof from the war but was sympathetic towards the Allied powers. In 1939 the American legislature allowed USA to help the western democratic states and sell arms and ammunitions to them. This policy was known as ‘Cash and Carry’ policy. It was a policy to preserve neutrality while aiding the Allies. It allowed sale of arms, ammunition and war materials to belligerents (countries engaged in war) as long as the recipients arranged for transportation using their own ships and paid immediately in cash, assuming all risk in transportation.
7. What was the ‘D-Day’?
Ans. ‘D-Day’ was the Deliverance Day, (June 6, 1944). On that day vast Anglo-American force landed at the Normandy coast of northern France by crossing the English Channel. The operation was gigantic. The Military General of USA Eishenhower took the leadership. One thousand Anglo-American air crafts conducted a massive dropping of Allied air-troopers behind the German lines by parachute. Nearly 11 thousand war planes were ready for their defence. Four thousand Allied naval ships and thousands of land forces joined. Caught between Allied army in the front and at the back, the Germans became bewildered. The superior Âllied forces captured Toulon, Marseilles, Nice, Lyons and the German air fields in France. They liberated Paris from foreign occupation on April 25, 1944. The Allied army then proceeded towards Germany.

8. When was the Potsdam Conference held? Name the countries which took part in the Potsdam Conference. What was decided in the Potsdam Conference?
Ans. The Potsdam Conference was held in 1945.
The countries which took part in the Potsdam Conference were Russia, America and Britain.
At the Potsdam Conference it was decided: [1] Germany was to be divided into four zones namely American, Soviet, French and British. [2] Like Germany its capital Berlin was also to be divided into four zones. [3] Berlin would be placed under a council named ‘Allied Kommandatura’. [4] Though Germany was divided into four zones she was to be treated as a single economic unit. [5] Allied Control Council would be formed to supervise the working of Germany as a single economic unit. [6] Germany would undergo ‘Five Ds’ (demilitarization, deindustrialisation, decentralisation, democra – tization and denazification).
9. What were the main theatres of the Second World War?
Ans. The Second World War began in 1939 and ended in 1945 after lasting for six years. Around 60 countries were involved in this violent war. The war was fought on the Mediterranean, the Atlantic and the Pacific, and in four major land campaigns-in the Soviet Union, North Africa and the Mediterranean, western Europe, and the Far East. The main theatres of the war were: [1] The Russian Theatre or Eastern Theatre [2] The Mediterranean Theatre [3] The African Theatre [4] The Pacific Theatre [5] The Asian Theatre [6] Arctic and Atlantic Theatre.
Short Answer (SA) Type Questions
Answer in 2 to 3 sentences
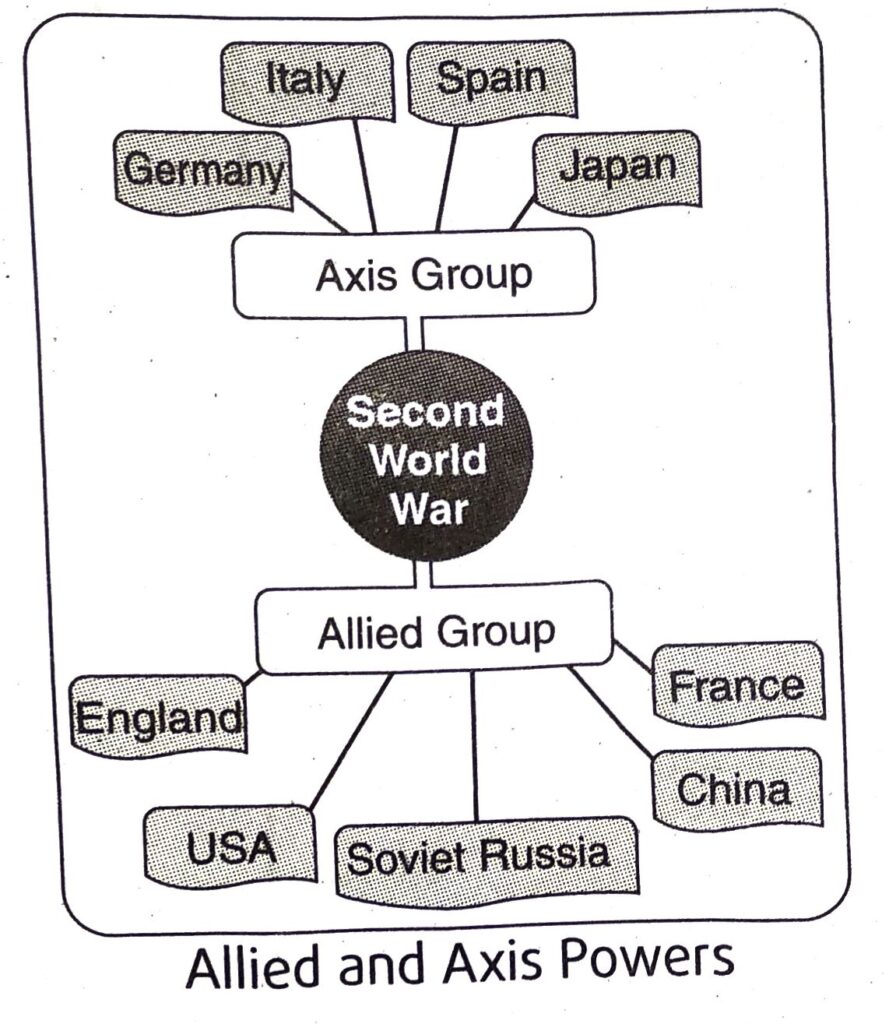
1. Name the Allied and Axis powers in the Second World War.
Ans. In the Second World War, the Allied powers were England, France, USSR, USA and China. The Axis powers were Italy, Germany and Japan.
2. Through which military campaign did Mussolini try to fulfil his imperial ambition ?
Ans. The fascist government under Mussolini became hungry for colonies and Mussolini tried to fulfil his imperial ambitions through his military campaign in the East African country of Ethiopia (Abyssinia). In 1935 he attacked Ethiopia to exploit its minerals and raw materials for industrial development and Ethiopia was formally annexed in 1936.
Know More
Mussolini with his mistress Clara Pretarchy was shot to death by a patriotic group of Italy.
3. Write a note on bombing by USA at Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Ans. USA prepared a plan to drop newly discovered atomic bomb on Japan on August 6, 1945. The atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, the industrial town in Japan, which destroyed half the city and caused 80,000 deaths. This was the first use of atom bomb during the World War II. On August 9, a second atomic bomb was dropped in Nagasaki in Kyum, destroying the whole municipal area and killing 40,000 people. The whole world was alarmed at the extensive destructive capacity of these new weapons.

4. Why did Hitler sign the Munich Pact ?
Ans. England and France followed the policy of appeasement towards Hitler and signed the Munich Pact in 1938. Hitler agreed to sign the Munich Pact because-[1] Germany was authorised to occupy four border provinces of Czechoslovakia within ten days. [2] The Czechoslovakian government was forced to release all the political prisoners of Sudetenland. This territory was also given to Germany.
5. Which incident forced the USA to join the Second World War ?
Ans. The sudden Japanese air attack with 360 aircraft struck at the American fleet at Pearl Harbour in the Hawaiin Islands on 7 December, 1941 and wiped out all the American planes on the ground there. This incident at Pearl Harbour forced USA to join the Second World War.
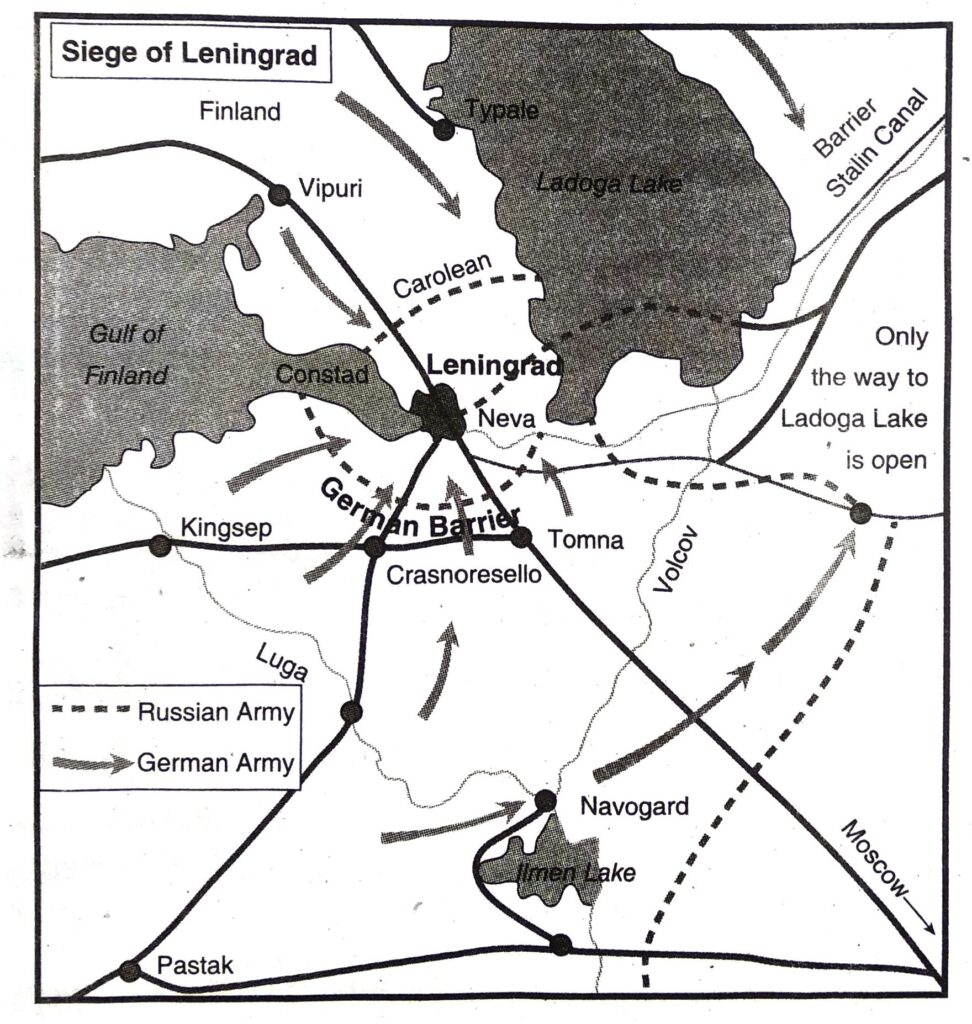
6. Write a note on the Battle of Leningrad.
Ans. At the initial stage of the Second World War, the German army achieved great success. They besieged Leningrad. The Soviet army followed the ‘Scorched-Earth’ policy and guerilla model of warfare. As a result the Nazi forces began to retreat. In the beginning of 1942 Leningrad was vacated by the Russian Red Army.
7. Which book is known as the ‘Bible of the Nazi Party’? Who was its author?
Ans. ‘Mein Kampf’ is known as the Bible of the Nazi Party.
Its author was Hitler.
8. Why did Germany withdraw from the League of Nations ?
Ans. In 1933 Germany withdrew from the League of Nations. According to the terms of the Treaty of Versailles Germany was disarmed. Germany’s demands for military parity with other European powers was refused by the western powers, so Germany withdrew herself from the League of Nations.
9. What was Vichy government?
Ans. A puppet French government led by Petain was established under the control of Germany in France. As Vichy was the capital of this new French government it was also called the Vichy Government.
10. When was the Yalta Conference held? Name the countries which took part in the Yalta Conference.
Ans. The Yalta Conference was held in 1945.
The countries which took part in the Yalta Conference were USA, Britain and Russia.
11. Name three prominent leaders who attended the Yalta Conference. Name any two military alliances which came into being as a consequence of Cold War.
Ans. Three prominent leaders who attended the Yalta Conference were- -[1] Roosevelt, the President of America [2] Churchill, the British Prime Minister and [3] Stalin, the President of USSR.
Two military alliances which came into being as a consequence of Cold War were-[1] NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) and [2] Warsaw Pact.

12. What is Operation Barbarossa ?
Ans. On June 22, 1941 Nazi Germany and her allies began a massive invasion of the Soviet Union under Operation Barbarossa. Hitler changed the original name Operation Fritz to Operation Barbarossa to refer to Frederick Barbarossa, the Holy Roman Emperor, who had set out to conquer the Holy land in 1190.
13. What is Seigfreid Line ?
Ans. Seigfreid Line was a line of defensive forts and tank defences built along the German western frontier opposite the French Maginot Line in the 1930s and greatly expanded in 1941.
14. Name the principal dictators of Europe who rose to power after the first World War.
Ans. The principal dictators of Europe who rose to power after the First World War were Mussolini of Italy, Hitler of Germany and general Franco of Spain.
15. What were the main aims of Hitler’s foreign policy ?
Ans. The main aims of Hitler’s foreign policy were: [1] To revise the humiliating treaty of Versailles. [2] To unify Germany and to unite all German speaking people into one Reich. [3] Eastward expansion of Germany to achieve ‘Lebensraum’ (Living space). [4] To make Germany a strong and powerful nation and to destroy communism.
16. What is the significance of Italy’s attack on Abyssinia ?
Ans. The significance of Italy’s attack on Abyssinia was: [1] It exposed the weakness of the League of Nations. [2] The prestige of the League of Nations was damaged. [3] Italy’s attack on Abyssinia encouraged Hitler in his aggressive policy. [4] Italy and Germany came closer together.
17. What steps were taken by the League of Nations when Italy attacked Abyssinia?
Ans. When Italy attacked Abyssinia, the League of Nations declared Italy as an aggressor country. Moreover, the League of Nations directed the member countries of the League to stop all sorts of commercial relationship with Italy.
18. Why did Hitler and Mussolini come closer to each other and become allies?
Ans. The reasons why Hitler and Mussolini came closer to each other and became allies were: [1] Both were against the Treaty of Versailles signed in 1919. [2] France was the enemy of both Italy and Germany. [3] Both the countries were supporters of aggressive nationalism.
19. Give some examples of Anglo-French policy of appeasement.
Ans. Some examples of Anglo-French policy of appeasement were: [1] Italy’s attack on Abyssinia. [2] Franco’s military regime was supported by Hitler and Mussolini during the Spanish Civil War. [3] Occupation of Austria by Germany, England and France remained inactive during the aggressive policy of Italy and Germany.
Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
1. Which treaty is known as a ‘dictated peace’?
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles is known as a ‘dictated peace’.
2. What is the name of the republic that was established after 1918 in Germany?
Ans. The name of the Republic that was established after 1918 in Germany was known as the Weimer Republic.
3. On which date did the Second World War begin?
Ans. The Second World War began on 1st September, 1939.
4. Who was the Prime Minister of England when the Second World War started?
Ans. Nevielle Chamberlain was the Prime Minister of England when the Second World War started.
5 . Who was the Prime Minister of France when the Second World War broke out?
Ans. Daladier was the Prime Minister of France when the Second World War broke out.
6. Who was the founder of the Nazi Party?
Ans. The founder of the Nazi Party was Hitler.
7. When did Germany withdraw from the League of Nations?
Ans. Germany withdrew from the League of Nations in 1933.
8. Which country was first attacked by Hitler during the Second World War?
Ans. Poland was first attacked by Hitler during the Second World War.
9. Which port of Poland was demanded by Hitler?
Ans. Danzig, a port of Poland was demanded by Hitler.
10. Who was Hindenburg?
Ans. Hindenburg was the President of German Republic.
11. Which country other than Germany and Italy was part of the Axis group of nations?
Ans. Japan was part of the Axis group of nations other than Germany and Italy.
12. Which British Prime Minister appeased Germany?
Ans. The British Prime Minister who appeased Germany was Neville Chamberlain.
13 .When did Japan attack Manchuria?
Ans. Japan attacked Manchuria in 1931.
14. Which British warships were drowned by German U-boats?
Ans. The British warships HMS Courageous and the HMS Royal Oak were drowned by German U-boats.
15. Who was Mac Arthur ?
Ans. Mac Arthur was the American military General.
16. Which American naval base in the Pacific Ocean was attacked by Japan?
Ans. The American naval base at Pearl Harbour was attacked by Japan.
17. In which year was Pearl Harbour attacked by Japan?
Ans. Pearl Harbour was attacked by Japan in 1941.
18. In which year did Hitler attack Russia?
Ans. Hitler attacked Russia in 1941.
19. In which year did Japan surrender to the Allies during the Second World War?
Ans. Japan surrendered to the Allies during the Second World War in 1945.
20. When did the Second World War come to an end ?
Ans. The Second World War came to an end in 1945.
21. Where is Pearl Harbour located?
Ans. Pearl Harbour is located on the island of O’ahu in Hawaii.
22. Who were the US Presidents during World War II?
Ans. Franklin Delano Roosevelt and Harry S Truman-both served as United States Presidents during World War II.
23. Name the World War II General who went on to become President of the United States of America.
Ans. The World War II General Eishenhower went on to become the President of United, S AN States of America.
24. In which year was the Tehran Conference held?
Ans. The Tehran Conference was held in 1944.
25. In which year was the San Francisco Conference held?
Ans. The San Francisco Conference was held in 1945.
26. Who is the author of the poem ‘The White Man’s Burden’?
Ans. The author of the poem ‘The White Man’s Burden’ is Rudyard Kipling.
27. What is the concept of ‘The White Man’s Burden’?
Ans. ‘The White Man’s Burden’ is the idea that white people are superior to the non-white races and so, colonial rulers have a duty to take care of and ‘civilise’ the native inhabitants of their colonies.
28. When and between whom was the RussoGerman Non-Aggression Pact signed ?
Ans. The Russo-German Non-Aggression Pact was signed on 23 August, 1939 between Russian foreign minister Molotov and German foreign minister Ribbentrop.
29. After which incident did USA join the Second World War ?
Ans. When Japan attacked the US naval base at Pearl Harbour, USA joined the World War II.
30. What was the direct cause of Second World War? onsign
Ans. The direct cause of Second World War was Hitler’s attack on Poland.
31.Which day is known as the ‘D-Day’ (Deliverance Day)?
Ans. 6th June, 1944 is known as the ‘D-Day’.
32. Who followed the policy of appeasement ?
Ans. The Prime Minister of Britain, Neville Chamberlain and Edouard Daladier, the Premier of France followed this policy.
33. Name the countries which took part in the Second World War.
Ans. The countries which took part in the Second World War were Germany, Italy, Japan, Britain, France, Soviet Union, USA, Poland, Yugoslavia, Romania, Greece, Austria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Holland, Belgium, Finland, Bulgaria, Albania, Norway, Denmark etc.
34. When did the Second World War come to an end ?
Ans. The Second World War came to an end on 2 September, 1945.
35. For how many years did the Second World War continue?
Ans. The Second World War started on 1 September, 1939 and ended on 2 September, 1945-so the war continued for 6 years.
36. What was the aim of the Versailles Treaty ?
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles aimed to weaken Germany both economically and militarily.
37. In which year was the Battle of Britain fought?
Ans. The Battle of Britain was fought in 1940.
38. What was the main reason of the defeat of Germany in the Second World War ?
Ans. The main reason of the defeat of Germany in the Second World War was the conspiracy of the German generals and the discontent of the soldiers.
39. Name the Czar of Russia who established his capital at Leningrad.
Ans. The Czar of Russia who established his capital at Leningrad was Peter the Great.
40. Who followed ‘One by one policy’?
Ans. Hitler, the German dictator, followed ‘One by one’ policy.
41. Why was Hitler in favour of union between Germany and Austria?
Ans. Hitler was in favour of union between Germany and Austria as a sizeable number of Germans lived in Austria.
42. Under whose leadership did the Russian army defeat the Germans?
Ans. Under the leadership of Marshall Zhukov the Russian army defeated the Germans.
43. How did the USA become the arsenal of democracy ?
Ans. USA became the arsenal of democracy when the American Senate enacted the Lend-Lease Act in March 1941 and allowed the US government to offer warships, war planes and other weapons to the Allied powers to fight against Fascism.
44. Which Act made USA the ‘Arsenal of Democracy’?
Ans. The Lend-Lease Act enacted by the American Senate in 1941 made USA the ‘Arsenal of Democracy’.
45. Which day is regarded as ‘a date which will live in infamy’ in the USA?
Ans. The day which is regarded as ‘a date which will live in infamy’ in the history of USA is 7 December, 1941 as Japan bombed the US naval base at Pearl Harbour on this day.
46. When was ‘Victory-in-Europe Day’ observed ?
Ans. Germany surrendered to the Allied Powers formally on May 7, 1945 and the whole of Europe observed May 8, 1945 as ‘the Victory-in-Europe Day’.
47. What was the Grand Alliance?
Ans. USA, Great Britain and Soviet Russia formed an alliance against the Axis powers which is known as the Grand Alliance.
48. What was the ‘Lend-Lease Act’ ?
Ans. The American Senate enacted the LendLease Act in March 1941 and allowed the US government to offer warships, war-planes and other weapons to the Allied powers to fight against fascism.
49. Under whose leadership did the German soldiers start ‘Operation Barbarossa’?
Ans. The German soldiers started ‘Operation Barbarossa’ under the leadership of Hitler.
50. When and by whom was the Anglo-Russian Alliance signed ?
Ans. Churchill, the British Prime Minister, concluded the Anglo-Russian Alliance of 1941.
51. Which incident made Far East the centre of war during World War II?
Ans. The Japanese attack on the US naval base at Pearl Harbour made the Far East the centre of war during the World War II.
52. After which invasion did the ‘Beginning of the end’ of Germany start under the leadership of Hitler?
Ans. After the invasion of Russia, the ‘Beginning of the end’ of Germany started under the leadership of Hitler.
53. Name the two atom bombs dropped by USA on Japan.
Ans. USA dropped the atom bombs named ‘Little boy’ on Hiroshima and ‘Fat man’ on Nagasaki in Japan.
54. Why did Hitler attack Poland?
Ans. After the Munich Pact, Hitler demanded the use of the port of Danzig and also the Polish corridor to reach the port. When Poland refused this demand, Hitler attacked Poland.
55. What was the aim of Hitler’s foreign policy ?
Ans. Hitler’s foreign policy aimed at German expansion in East Europe in order to carve out some ‘Living Space’ (Lebensraum) for surplus German population.
Mark True or False
1. The Treaty of Versailles (1919) was humiliating for France.
2. One of the main points in Hitler’s foreign policy was Pan Germanism.
3. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939.
4. Germany attacked France in 1939.
5. The Red Army of the Soviet Union followed the ‘Scorched Earth Policy’.
6. With the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbour, there was the extension of the Second World War in Asia.
7. Russia was attacked by the German Nazis in 1942.
8. Leningrad was besieged by the German army.
9. Hitler committed suicide in 1945.
10. Germany abandoned her membership of the League of Nations in 1944.
Answers :
1. False, 2. True, 3. True , 4. False , 5. True , 6. True , 7. False , 8. True , 9. True , 10. False.
Fill in the blanks
1. The Treaty of Versailles was imposed on _________(Italy/France/
2. Japan attacked Manchuria in ________(1930/ 1931/1932).
3. In 1935 Mussolini attacked __________(Abyssinia/Danzig/Rhineland).
4. Haile Selassie was the emperor of ___________ (Ethiopia/Poland/Syria).
5. After the Second World War __________(England/France/
6. General Eisenhower was appointed the Supreme Commander of the Allied invasion in _______(Asia/Europe/Africa).
7. The Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression pact was signed in _____(1938/1939/1990).
8. The dictator of Italy who installed a fascist regime was (Adolf Hitler/Benito Mussolini/Joseph Stalin).
9. The title Adolf Hitler took in 1934 that meant leader was _____ (Fuhrer/Dictator/ Minister).
10. Hitler invaded Poland on ___________ 1939. (1 September/4 September/15 October)
11. Pearl Harbour was attacked by Japan in _________ (1941/1942/1943).
12. In 1941 Pearl Harbour was attacked by ________ (Belgium/USA/Japan).
13. ________ (Belgium/Austria/Germany) suffered setback at Stalingrad.
14. Atomic bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in ____________ (1939/1941/1945).
15. _______(USA/Britain/Austria) dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
16. USA entered into Second World War in ________ (1939/1941/1943).
17. Admiral Hideki Tojo was the Prime Minister of ________(Britain/USA/Japan).
18. The Japanese launched a surprise attack on the ______ (British/German/US) naval base at the Pearl Harbour.
19. Perhaps the largest leap in technology during World War II was the ________ (bouncing/atom/cluster) bomb.
20. Japan was worried about _________(US/French/British) navy in Hawaii.
21. On the ‘D-Day’ Anglo-American force landed at _________(Lyons/Normandy/Marseilles) coast.
22. Francisco Franco was the Fascist dictator of _______(Italy/Germany/Spain).
23. The provinces of Alsace and Lorraine were taken away from _________(France/England/ Germany).
24. _______(Britain/Japan/France) had built a strong underground line of fortresses and gave it the name Maginot Line.
Answers :
1. Germany
2. 1931
3. Abyssinia
4. Ethiopia
5. Czechoslovakia
6. Europe
7. 1939
8. Benito Mussolini
9. Fuhrer
10. 1 September
11. 1941
12. Japan
13. Germany
14. 1945
15: U.S.A
16. 1941
17. Japan
18. US
19. atom
20. US
21. Normandy
22. Spain
23. Germany
24. France
Choose the best explanation
1. Statement: Mussolini occupied the Greek island Corfu in 1923.
Explanation (A) : Italy deserved Corfu island.
Explanation (B) : Italy accused Greece of killing several Italians.
Explanation (C) : Italy was deprived of getting Corfu island at Paris Peace Conference (1919).
2. Statement: Japan and Germany signed Anti-Comintern Pact in 1936.
Explanation (A) : Japan and Germany planned to occupy Manchuria of China.
Explanation (B) : Japan and Germany wanted to stop England’s effort.
Explanation (C) : Japan and Germany wanted to stop progress of Communism.
3. Statement:Munich Agreement (1939) was failed.
Explanation (A) : France was not interested in signing the Munich Agreement.
Explanation (B) : England was not interested in signing the the Munich Agreement.
Explanation (C) : Hitler seized the whole Czechoslovakia.
4. Statement: Mussolini invaded and occupied Abyssinia in Africa.
Explanation (A) : Abyssinia was located between Somaliland and Eritrea which were under Italian rule.
Explanation (B) : Abyssinia attacked the Italian border.
Explanation (C) : Abyssinia was previously under Italian rule.
Answers :
1. Explanation (B)
2. Explanation (C)
3. Explanation (C)
4. Explanation (A)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. The main cause of World War II was the –
A. Balkan War
B. Russo-German War
C. World War I
D. Anglo-French War
Ans. C
2. Chamberlain took an assurance from Hitler that Germany would be satisfied by –
A. Occupation of Rhineland
B. Occupation of Poland
C. Cession to her of Sudetenland
D. Cession to her of Baltic states
Ans. B
3. A secret additional pact to divide Poland was made between –
A. Russia and Germany
B. Germany and Italy
C. Italy and France
D. England and France
Ans. A
4. To plan global military strategy, top Allied leaders held a series of conferences such as the ones at –
A. Versailles
B. Paris
C. Tehran
D. Berlin
Ans. C
5 At the Munich Conference in 1938, a region of this nation was given to Adolf Hitler by the British and the French –
A. Czechoslovakia
B. Poland
C. Holland
D. Austria
Ans. A
6. Which Allied army fought its way to Berlin and reached the city first ?
A. England
B. France
C. Soviet Russia
D. USA
Ans. C
7. When did Hitler become Chancellor of Germany ?
A. 1793
B. 1795
C. 1796
D. 1801
Ans. B
8. What was the last major attempt at a peaceful resolution with Germany prior to the outbreak of World War II?
A. Potsdam Conference
B. The Washington Conference
C. The Munich Conference
D. Yalta Conference
Ans. C
9. The main Axis Powers of World War II consisted of –
A. Germany, Finland, Japan
B. Germany, Italy, Japan
C. Germany, Russia, Italy
D. Germany, Italy, Belgium
Ans. B
10. The term ‘D-Day’ refers to –
A. Allied invasion of the coast of Normandy
B. Allied invasion of Italy
C. Allied invasion of Germany
D. Allied invasion of Poland
Ans. A
11. World War II broke out on –
A. 1 September, 1938
B. 3 September, 1939
C. 9 August, 1937
D. 5 December, 1933
Ans. B
12. What agreement did Hitler defy when the invasion of the USSR began ?
A. Hitler-Stalin agreement
B. Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
C. Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
D. Treaty of Versailles me
Ans. B
13. What day was the invasion of Normandy or D-Day ?
A. 6 June, 1943
B. 6 June, 1944
C. 12 May, 1940
D. 3 September, 1946
Ans. B
14. What caused the United States to enter the war on the side of the Allies?
A. Germany’s invasion of France
B. Germany’s invasion of Poland
C. Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbour
D. Russia’s entry into the war
Ans. C
TOPIC – B
Impact of the Second World War and Ultranationalism vs. Internationalism
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. What was the impact of the Second World War on contemporary history ?
Ans. The Second World War (1939-45) was a momentous event which changed the whole world. The impact of the war on contemporary history were as follow: [1] After the Second World War two great powers called ‘Superpowers’ emerged- the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republic. [2] The powers like Britain and France which were important before the war were pushed to the background. [3] In the struggle between the two ideologies-democracy and communism, the latter emerged with more strength. [4] During 1946-47 the government of Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Rumania were converted into communist dictatorships. [5] Democracy remained in western Europe. [6] The post-war world saw a growing tension among the Alliesbetween East and West, and more specifically between Russia and the United States. The result was the Cold War. [7] To counteract communism the western responses were the Truman Doctrine, Marshall plan and the North Atlantic Treaty Organisations. The Warsaw Pact was the Soviet response. [8] After the Second World War, a third force i.e., the Non-aligned nations emerged which refused to join either of the two power blocks. [9] The Second World War quickened the national feeling among the people of the colonies all over the world. Many of the colonised countries of which India was one, won their independence through antiimperialist movement. Between 1945 and 1960 no less than 40 countries revolted against colonialism and won their independence. [10] International organisations like the U.N.O was established in 1945 for the maintenance of peace and security throughout the world.
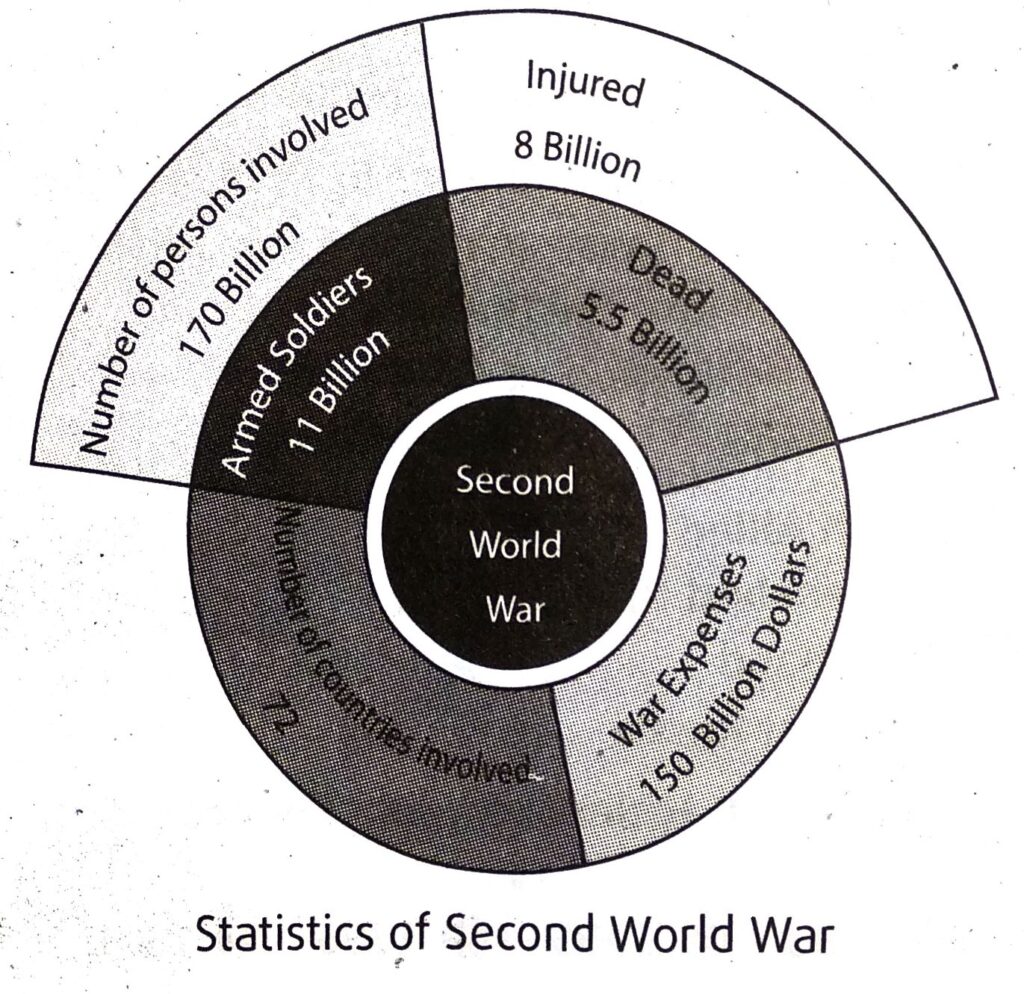
2. Write a note on the qualitative and quantitative changes brought about by the destructiveness of the Second World War.
Ans. The Second World War which broke out in 1939 continued for a long period of six years and came to an end in 1945. The war is known as the most destructive of all wars fought ever before. There was world wide destruction of life and wealth. The vast destruction of material wealth and loss of human life during the course of war could not be exactly estimated.
[1] In the war at least 57 million people lost their lives. About 7.5 million Russians, 3.5 million Germans, 2.2 million Chinese, 1.2 million Japanese lost their lives. Many people died in Korea, Italy, Canada, Greece, Belgium, Rumania, Bulgaria, Hungary. USA dropped atom bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. About 70 thousand people in Hiroshima and 40 thousand people in Nagasaki died. At least 6 million Jews were killed by the Nazi government. [2] It is estimated that near about one lac crore rupees must have been spent over the war by the nations which participated in it. Great Britain alone had to suffer the economic loss of about 2000 crore rupees. The national property of various countries of the world was destroyed in the war. The European economy collapsed with 70% of the industrial infrastructure destroyed. [3] Destruction of property was the highest in Russia. Due to German attack vast areas of Russia including Leningrad and Stalingrad were completely destroyed. Not only was there loss of lives, many cities and industrial areas of Russia were totally destroyed. But Japan suffered most. In Hiroshima and Nagasaki houses and roads were completely destroyed. At least 30% people of 60 big cities became homeless in Japan. In Britain and France thousands of houses and roads were completely destroyed.

Analytical Answer (AA) Type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1. What is Truman Doctrine ?
Ans. On March 11, 1947 President Truman of USA, in a lecture in the American Congress, gave a call to frustrate the onslaught of communism on the free world. He declared:
[1] USA seeks to protect the independence and territorial integrity of free democratic nations from communist aggression. [2] Whenever free lawful government was threatened by an armed minority and the lawful government tried to resist the aggression, USA would render help to the lawful government. [3] USA would help Greece and Turkey with 400 million dollars with the aim of freeing these countries from Soviet influence.
This declaration of Truman is known as Truman Doctrine.
2. What was Cold War ?
Ans. Tension of war without an actual shooting of war has been termed as the Cold War. Cold War is a state of tension between countries in which each side adopts policies designed to strengthen itself and weaken the other by falling short of actual war. It is a kind of verbal war and even more terrible than the ‘Warm War’. It is an atmosphere of artificial tension and distrust either due to virtual utterances or war like preparation which may at any moment degenerate into a ‘Warm War’ or a shooting war.
3. What was ‘NATO’ and ‘Warsaw Pact’?
Ans. After the Second World War USA and Soviet Russia who had helped each other in the Second World War became rivals and a competition arose between them to assume leadership of the world.
In 1949 USA formed a military alliance called NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) with 16 nations as its members. It was strong enough to repulse any invasion of West Europe by the Red Army.
The Soviet Union, on the other hand, apprehended an invasion of East Europe and Russia by NATO army. She entered into the Warsaw, Pact with East European countries in 1955.
4. Write a note on the evolution of internationalism after the Second World War.
Ans. The destructive effect of the Second World War (1939-45) opened the eyes of different countries of the world. They realised that peace and cooperation could not be established without mutual cooperation and trust. They also realised that war was not the ultimate means to solve problems. The international peace organisation-The League of Nations which was established after the First World War collapsed before selfish motives of different nations. International cooperation failed in the field of politics and the Second World War broke out in 1939. After the Second World war, different nations again realised the importance and necessity of mutual cooperation. They decided to solve their problems through peaceful meetings, so that the damage of war might be removed for ever and peace might be established among different nations of the world. The United Nations Organisation (UNO) was established in 1945 the sole aim of which was to maintain international peace and security, to develop friendly relations and international cooperation.
5. State the differences between ultranationalism and internationalism.
Ans. Differences between ultranationalism and internationalism
| Ultranationalism | Internationalism |
| 1. Ultranationalism leads to war among different nations. | 1. Internationalism advocates world peace and is against wars among different nations. |
| 2. Ultranationalism involves contempt for other nations. | 2. Internationalism advocates cooperation among different nations for the benefit of all. |
| 3. Ultranationalism is the most destructive force in the world which might create international anarchy. | 3. Internationalism replaces international anarchy by international order. |
Short Answer (SA) Type Questions
Answer in 2 to 3 sentences
1. How can you explain the Second World War as a struggle between Fascism and Nazism versus Democratic ideals ?
Ans. The Second World War was in fact, the struggle of two contradictory principles, i.e, Fascism and Nazism versus democratic principles. England, France and America were the supporters of the principles of democracy, while the principles of autocracy were fully supported by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. Thus war was inevitable between the supporters of these two contradictory principles.
2. What is UNRRA?
Ans. As a result of the Second World War there was total destruction, devastation and despair in the whole of Europe. In order to regenerate the economy of the devastated countries United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA) was set up in 1943 in Washington, USA. It was an international body to provide relief to countries liberated from the German occupation. This economic recovery programme provided substantial economic help to the war ravaged countries like Poland, Yugoslavia, Czechoslovakia, Greece, Italy, Austria etc.
3. What was ‘Fulton Speech’?
Ans. On 5 March, 1946 the former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill delivered a’ speech at Westminster College, Fulton in the state of Missouri, USA. He warned that a large part of Europe from Stettin to Triest had passed under the ‘iron curtain’ of the Soviet Union. He warned that America should become alert otherwise the Soviet Union would one day conquer the entire continent of Europe.

4. What is Marshall Plan?
Ans. The American Foreign Secretary, George Marshall, in a lecture at Harvard University spoke of a plan of economic resurgence of the war ravaged countries like France, Britain, Belgium, Italy, West Germany etc. Marshall observed, “It is logical that the United States should do whatever it is able to do to assist in the return of normal economic health in the world, without which there can be no political stability and no assured peace.” This plan of Marshall which wanted to save Europe from poverty, hunger and lawlessness is known as Marshall plan, a programme to finance recovery of European economy.
5. What is internationalism ?
Ans. Internationalism is a movement which advocates economic and political cooperation among nations for the benefit of all. It is the belief that countries can achieve more advantages by working together and trying to understand each other than by arguing and fighting wars with each other.
6. What is nationalism?
Ans. Nationalism is basically a collective state of mind or consciousness in which people believe their primary duty is loyalty to the nation state. It implies national superiority and glorifies various national virtues. It is a political or social philosophy in which the welfare of the nation state as an entity is considered paramount.
7. What do you mean by ultranationalism?
Ans. Nationalism is an ideology that emphasises devotion and loyalty to a nation or nation state. Ultranationalism is an extreme form of nationalism. It is simply extreme devotion to one’s own nation and of the paramount importance of advancing it regardless of the effect on any other nation.
8. What was decided in the Potsdam Conference?
Ans. The decisions arrived at the Potsdam Conference were [1] Germany will be de-Nazified. The Nazi Party would be banned and its leaders would be tried as war criminals. [2] Germany will be demilitarized [3] Germany’s large industrial factories would be dissolved.
9. What are the features of ultranationalism?
Ans. The features of ultranationalism are as follows:
[1] It is an extreme form of nationalism.
[2] It believes in the superiority of one’s own nation.
[3] It glorifies national identity.
[4] It includes elements of racism and fanaticism which can lead to conflict.
[5] It may involve contempt for other nations.
[6] It supports authoritarian political arrangements.
10. Name the leaders who joined the Potsdam Conference.
Ans. The leaders who joined the Potsdam Conference were Joseph Stalin of Russia, Harry S Truman of USA and Clement Attlee of Britain.
11. How was Germany divided after the Second World War ?
Ans. After the Potsdam Conference, Germany was divided into four occupied zone: France in the south-west, the United States is the south, Great Britain in the north-west and Soviet Union in the east. Berlin, the capital of Germany was also divided into four occupied zones.
12. Mention some military equipments used during the Second World War.
Ans. Some military equipments used during the Second World War were machine gun, long range rocket, handgun, marine, mortar, grenade launcher, submarine, modern tank, mine etc.
13. What do you understand by the term ‘Third World’ ?
Ans. While the post 1945 world saw a ‘bi-polar’ world (divides into USA and Soviet spheres of influence), it also witnessed the emergence of the Third World’. A group of countries in Asia, Africa and Latin (South) America which achieved independence after the Second World War and did not formally belong to either of the two rival blocs and later launched the Non-Alignment Movement in international relations is known as the Third World.
Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
1. Who first popularised the term ‘Cold War’?
Ans. The term ‘Cold War’ was first popularised by Walter Lipmann.
2. Name the two parties in the Cold War.
Ans. The two parties in the Cold War were[1] United States of America and [2] Soviet Russia.
3. Which two superpowers were the main rivals in the Cold War?
Ans. The two superpowers who were the main rivals in the Cold War were-[1] United States of America and [2] Soviet Russia.
4. What does NATO stand for ?
Ans. NATO stands for North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
5. What does SEATO stand for ?
Ans. SEATO stands for South East Asia Treaty Organisation.
6. In which year was Truman Doctrine proclaimed ?
Ans. Truman Doctrine was proclaimed in 1947.
7. In which year was Marshall Plan proclaimed ?
Ans. Marshall Plan was proclaimed in 1947.
8. What is meant by Third World countries ?
Ans. A group of developing countries in Asia, Africa and South America which achieved independence after the Second World War were known as the Third World countries.
9. When was the UNO established?
Ans. UNO was established on 24 October 1945.
10. What is Non-Alignment policy ?
Ans. Non-Alignment policy which aims ensuring international peace, means keeping away from the two military blocks led by USA and USSR and solving all international conflicts and disputes peacefully through cooperation.
11. To which country did admiral Karl Donitz belong during the Second World War ?
Ans. Karl Donitz was the admiral of Germany during the Second World War.
12. Who wrote the poem ‘The White Man’s Burden’?
Ans. Rudyard Kipling wrote the poem ‘The White Man’s Burden’.
13. In which essay did Rabindranath criticise radical nationalism?
Ans. Rabindranath in his essay ‘The Crisis in Civilisation’ criticised radical nationalism.
14. What is V-2? Which country used the V-2 during the second World War?
Ans. V-2 was the rocket used during the Second World War.
V-2, the long range rocket was used by Germany during the Second World War.
15. Which country used V-2 rocket and against whom?
Ans. During the Second World War Germany used V-2 rocket against England.
16. Who coined the term ‘Third World’?
Ans. Alfred Sauvy coined the term ‘Third World’.
17. What was the name of the atomic bomb dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima?
Ans. The name of the atomic bomb dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima is ‘Little Boy’.
18. Which day is celebrated as the Hiroshima and Nagasaki Day ?
Ans. August 9 is celebrated as the Hiroshima and Nagasaki Day.
19. Name the international organisation established after the Second World War.
Ans. The international organisation established after the Second World War was the United Nations Organisation (UNO).
Mark True or False
1. After the Second World War two great powers United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republic emerged.
2. Two ‘superpowers’ which emerged after the Second World War were Great Britain and United States of America.
3. During 1946-47 the government of Poland, Romania, Albania were converted into communist dictatorships.
4. To counteract communism, the western responses were Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan.
5. The Non-aligned nations emerged after the First World War.
6. The United Nations Organisation was established in 1940.
7. Due to German attack during the Second World War, vast areas of Russia including Leningrad and Stalingrad were completely destroyed.
8. USA entered into Warsaw Pact with East European countries in 1955.
9. President Truman of America declared that USA would help Greece and Turkey with the aim of freeing these countries from Soviet influence.
10. After the Potsdam Conference France was divided into four occupied zones.
11. The ‘Third World’ countries launched the Non-Alignment Movement.
12. Harry Truman of Britain and Clement Attlee of USA joined the Potsdam Conference.
13. The decision that Germany will be de-Nazified was taken at the Potsdam conference.
14. Scorched earth policy means the policy of destroying everything that might be of use to an invading enemy.
Answers :
1. True, 2. False, 3. True, 4. True, 5. False, 6. False, 7. True, 8. False, 9. True, 10. False, 11. True, 12. False, 13. True , 14. True.
Fill in the blanks
1. Daladier was the Prime Minister of ________ (Britain/USA/France).
2. Hideki Tojo was the Prime Minister of __________ (USA/Ethiopia/Japan).
3. ‘The Crisis in Civilisation’ was written by ________(Rabindranath/Marx/
4. The term ‘Cold War’ was popularised by _________(George Kennan/Walter Lippmann/ Bernard Baruch).
5. USA joined the Second World War in _________ (1930/1940/1950).
6. Germany surrendered unconditionally in ________ (1940/1942/1945).
7. Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan was declared by __________ (USA/Britain/Italy).
8. The _________(SEATO/CENTO/Warsaw Pact) was a military alliance formed by Soviet Union as a counter balance to the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Answers :
1. France
2. Japan
3. Rabindranath
4. Watter Lippmann
5. 1940
6. 1945
7. USA
8. Warsaw Pact
Choose the best explanation
1. Statement: America formed NATO after World War II.
Explanation (A) : To be saved from war in future.
Explanation (B) : To counter the aggression of communist Russia.
Explanation (C) : To plan the Third World War.
2. Statement: After World War II, Cold War started between USA and USSR.
Explanation (A) : Mutual suspicion grew between the two powers after the war.
Explanation (B) : Cold War was the inevitable consequence of World War.
Explanation (C) : USA and USSR no longer agreed to participate in a direct conflict.
Answers :
1. Explanation (B)
2. Explanation (A)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. A great supporter of aggressive nationalism –
A. Churchill
B. Hitler
C. Stalin
D. Roosevelt
Ans. B
2 The top allied leaders held a conference in –
A. Tehran
B. Normandy
C. Moscow
D. Venice
Ans. A
3. European Recovery Programme was announced by –
A. Hitler
B. Goering
C. Mussolini
D. George Marshall
Ans. D
4. The United Nations Organisation was established –
A. to divide Germany into four zones
B. to establish international peace
C. to supervise the working of Germany
D. to preserve neutrality among the allies
Ans. B
TOPIC – C
Miscellaneous
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. What role did technology play in the Second World War ?
Ans. Technology played an important role in World War II. Major advances in weaponry by both the Allied and the Axis powers impacted the way the war was fought and eventually the outcome in the war.
[1] Tanks: It was during World War II that tanks become a major military force. Some of the most famous tanks from World War Il include Germany’s Tiger Tank, the Soviet Union’s T-34 tank, and the United States’ Sherman Tank.
[2] Aircraft: The airforce became one of the most important part of the military during World War II. There were small, fast fighter planes designed for air-to-air combat, large bombers that could drop huge bombs on enemy targets, military helicopter and jetpowered fighter planes.
[3] Radar: Radar, new technology, developed right before the war. It used radio waves to detect enemy aircraft which helped the British to fight off the Germans in the Battle of Britain.
[4] Aircraft Carrier: One of the biggest changes in naval technology in World War Il was the use of the aircraft carriers which were able to launch air attacks from anywhere in the ocean.
[5] Bombs: World War II saw the invention of many new types of bombs. The Germans invented the long range flying bomb called the V-I as well as a rocket bomb called the V-2. Others specialized bombs included bouncing bomb, bunker busters and cluster bombs.
[6] The Atom bomb: Perhaps the largest leap in technology during World War II was the atom bomb which caused a massive explosion by using nuclear reaction. It was used by the United States to bomb the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
[7] Secret Codes: In order to keep communications secret, both sides developed their own secret codes. The Germans used a machine called the Enigma Machine to code and decode their messages.
[8] Propaganda: New technology like motion pictures, the radio and the microphone. were all used by governments to broadcast their message to the people.

2. Make a comparative study related to the expansion and impact of the two World Wars.
Ans. Comparative study related to the expansion and impact of the two World Wars.
| Subject of comparison | First World War 1914-1918 | Second World War 1932-1945 |
| Expansion | The war touched all the parts of Europe. Fighting initially developed on three major European fronts: Eastern, Western and Serbian. As the war progressed, two new fronts emerged: Turkish and Italian. It also touched the Far-Eastern and Central Asian countries. | Around 60 countries were involved in war which extended in three fronts-land, air and water. The war was fought on the Mediterranean, the Atlantic and the Pacific and in four major land campaigns in the Soviet Union, North Africa and the Mediterranean, Western Europe and the Far East. |
| Methods of warfare | Fought from lines of trenches and supported by machine guns, artillery and rifles, use of tanks, airplanes and poisonous gas. | In the war tanks, fast fighter planes, large bombers, military helicopters, jetpowered fighter planes, bouncing bombs, bunker blaster, cluster bombs, submarines and nuclear bombs were used. |
| Casualties | Death of about 10 million military and seven million civilians, 22 millions wounded and about 8 millions imprisoned or missing. Many people took shelter in refugee camps. | About 60 million people died and millions of people in different countries became homeless. As a result of the war 13-20 million people died due to famine and different kinds of diseases. |
3. Prepare a comparison chart of the First and Second World Wars.
Ans. Comparison Chart of the First and Second World Wars
| Subject of comparison | First World War | Second World War |
| Period | First World War 1914 to 1918 Duration 4 years 3 months 14 days | Second World War 1939-1945 Duration 6 years 1 day |
| Nature of war | War between countries for acquiring colonies or territories | War of ideologies |
| Causes | Murder of Archduke Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the Austrian throne, in June, 1914 |
The humiliating and shameful conditions of the Treaty of Versailles
Hitler’s ambition to become master of Europe. Hitler’s invasion of Poland in 1939
|
| Contending parties |
Central Powers: Germany, Austria- Hungary, Turkey.
Allied Powers: France, Britain, Russia, Italy, Japan and USA.
|
Allied Powers: France, Britain, Soviet Union, US, China
Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, Japan
|
| Casualties | Estimated to be: Death of 10 million military; death of 7 million civilians, 22 millions wounded and about 8 millions imprisoned or missing | Estimated to be: Death of 60 million people. Death of 40-55 civilians. |
| Genocide | The Ottoman Empire committed genocide against the Armenians | Nazi Germany carried out genocide of Jews |
| Methods of warfare |
Fought from lines of trenches and supported by machine guns and artillery, use of tanks, airplanes and poisonous gas.
|
Use of nuclear power and missiles, submarines and tanks; encryption codes for secret communication; Blitzkrieg fighting method used by Germany. |
| Results | The Central Powers were defeated. A world peace organisation, the League of Nations was established. | The Axis Powers were totally defeated. A world peace organisation, the United Nations Organisation was established. The Soviet Union and USA emerged as rival superpowers. |
| Post world war Politics | Germany could not accept the humiliating Treaty of Versailles. The seeds of the Second World War lay in the Treaty of Versailles. | Cold war broke out between USA and Union. |
Analytical Answer (AA) Type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1. Was the Second World War truly a global war?
Ans. In the Second World War (1939-1945) the Allied powers were England, France, USSR, USA and China. Three Axis powers were Italy, Germany and Japan. World War II was truly a global war. This extensive war was fought on all major seas and in Africa, Asia and Europe. It involved almost 60 nations, seven of them on the side of the Axis. The war in the Mediterranean took military conflict beyond these seas in Europe. The war against Japan was fought over two-thirds of the world’s surface with USA and her allies taking part in air, land and sea battles. It turned World War Il into a global conflict. To plan global strategy, top Allied leaders held a series of conferences such as the ones in Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam.
2. What are the major differences between democracy and Fascism?
Ans. The major differences between democracy and Fascism are: [1] Democracy allows and encourages different political parties and political views to function in the political system to turn the wheels of the political machinery. On the other hand, Fascism does not tolerate any political party or political views other than the view sponsored by the Fascist dictator. [2] Democracy develops balanced, healthy and creative nationalism. This appears to be a source of strength and progress in the life of a nation. But Fascism generates hatred and preaches aggressive nationalism. Such perverted nationalism is the cause of conflict among different nations.
3. Discuss the nature of the Second World War.
Ans. Within twenty years of the First World War (1914-18) the Second World War broke out on 13 September, 1939. The nature of the Second World War is discussed below.
[1] The Second World War was more destructive and extensive than the First World War. [2] This was for the first time that the war was extended in three fronts-land, air and water. It was fought on all major seas in Asia, Africa and Europe. Sixty nations were involved in the war, seven of them on the side of the Axis. [3] Deadly weapons and the dreadful atom bombs were used in the war. Airplanes played a major role. Fleets of aeroplanes attacked troops and naval units, destroyed rail roads and prepared the way for invasion. [4] The war was fought not only by armed forces at the battle field but also by civilians in the factories and at home. School children also took part in the war, collecting rubber, newspapers and scrap metal, assisting in War Bond drives and helping air raid wardens.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here