WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 5 Europe in the Twentieth Century
WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 5 Europe in the Twentieth Century
WBBSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions History Chapter 5 Europe in the Twentieth Century
West Bengal Board 9th History Solutions
WBBSE 9th Class History Solutions
Salient points – At a glance
1. In the early years of the 20th century, the political atmosphere of the European continent was quite tense. Europe was in the throes of a devastating war-The First World War (1914-18). Another epochmaking event of the 20th century was the outbreak of the Russian Revolution (1917).
2. The Russian Revolution brought an end to Czarist autocracy and established socialist Russia. The Czars of Russia were corrupt. Nicholas II had to abdicate the throne and Russia became a republic. The Republican Government was deposed by the Bolsheviks and they seized power. This Great Revolution is known as the Russian Revolution.
3. The First World war broke out in 1914 and ended in 1918. The war was waged between the allied powers (comprising Britain, France, Russia and Serbia) and the central powers (comprising Germany, Austria, Hungary and Turkey).
4. The Treaty of Versailles was concluded in 1919 between the victorious allies (comprising Britain, France, Russia, Serbia, etc.) and the defeated Germany after World War I.
5. After the First World War (1914-18) an international organisation known as the League of Nations was established in 1920 to prevent armed conflict.
6. The Treaty of Versailles was a very harsh and humiliating treaty for Germany. Hitler bitterly opposed those conditions of the treaty by which Germany had been responsible for the war.
7. The Great Economic Depression of 1929 had a profound effect on every part of the globe. Faced with economic crisis the Germans lost their faith in the Republican Government. The Nazis promised to nationalise the big business, provide employment for all workers and implement land reforms. It is not surprising that the people turned to Nazism for remedy.
8. After the First World War, the political, social and economic condition of Spain was not stable. In 1931, General Election was held in Spain in which the monarchists were defeated. Democratic Republican government was established in Spain. But the newly established Republican Government could not work successfully. The banner of revolt was raised in 1936 under the leadership of General Francisco Franco. The Republicans were defeated and Franco established dictatorship in Spain.
TOPIC – A
The Russian Revolution
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. What was the Narodnik Movement? What was the aim of the movement? Was the movement a failure ?
Ans. The most important movement in Russia in the 60s of the 19th century was the Narodnik movement. The Russian word ‘Narod’ means the people’. One who sought to help the people (peasants i.e. narod) take the path of revolutionary struggle for a just life was known as Narodnik.
The aim of the Narodnik movement was [1] overthrow the rule of the autocratic Czars in Russia, [2] destruction of the prevalent social structure, [3] agrarian socialist society to be established.
The Narodniks failed to motivate the peasants with their ideology. Their movement, though a failure, made the doctrine of socialism known to the people. People were trained for future revolution.
2. What were the causes of Russian Revolution ?
Ans. The Russian Revolution of 1917 is a very important event in world history. It brought an end to Czarist autocracy and established socialist Russia. The causes of the Russian Revolution are as follows:
[1] The Czars were corrupt. There was absolutely no progress in any aspect of life of the common Russians. Though the life of the people was miserable, no effort was made to remove their grievances. Naturally the Russians desired the fall of Czarist rule.

[2] The intellectual ground for the outbreak of the revolution was prepared by writers like Gorky, Turgenev, Dostoevsky, Leo Tolstoy and others.

[3] The Russian army was inefficient. Russia was defeated in the Crimean War (185466) and the Russo-Japanese War (1905). This exposed the weakness of the Czarist rule.
[4] Russian society was divided into the ‘Haves’ and the ‘Have-nots’. The ‘Haves’ were those who were very rich. The ‘Have nots’ were poor farmers and labourers. This created a feeling of class struggle among the people.

[5] The Industrial Revolution was another factor contributing to the outbreak of the Russian Revolution. Owing to the use of machines the labourers were thrown out of employment and were forced to live in miserable conditions.
[6] The bureaucracy of Russia was also responsible for the outbreak of the Russian revolution. Most of the high officers belonged to rich families. They had no sympathy for the common people and always exploited them. The people of Russia were thus firmly determined to bring about a thorough change in the system of administration. Thus the Russian Revolution broke out.
3. What was Lenin’s ‘April Thesis’ ?
Ans. Lenin, the leader of the Bolshevik party in Russia, was the pioneer of the October Revolution. The Menshevik thesis was rejected by Lenin. The people were attracted the Bolshevik when they promised bread to the workers, peace to the army and land to the peasants. Yet the people could not decide their future plan . In early April 1917 Lenin returned from his exile in Switzerland and announced his

famous ‘April thesis’ titled “What is to be done”. In his thesis he said: [1] History has given a very opportune time to the Bolsheviks. [2] The provisional republic is yet out of roots. Once it wins a general election it will be impossible for the Bolsheviks to overthrow it. So Lenin put forward his idea of ‘Now or Never’.

[3] Since the Bolsheviks were the architects of the 1917 revolution they have every right to hold a government lawfully. [4] The bourgeoise and the proletarian revolution-both will happen simultaneously and the proletarian will overthrow the bourgeoise system. [5] The Russian workers, peasants and soldiers will offer their allegiance to the Soviet only and those who will not do so will be punished. [6] In the villages and towns workers’ Soviets will capture power and they will defy the provisional republican government. [7] The war with Germany launched by the Provisional Government was an imperialist war-the Russian people had no sympathy for it.
4. Discuss Lenin’s New Economic Policy.
Ans. The Civil War in Russia that had begun in 1918 and continued till 1921 was a crucial time of the newly founded Bolshevik government. During this time, the Bolshevik government faced financial crisis. The situation in Russia was saved by Lenin, the Bolshevik leader who introduced ‘New Economic Policy’ (NEP). The chief features of the NEP were: [1] The farmers were allowed to sell their produce in the open market; [2] Private enterprise was allowed on a small scale; [3] Nationalisation was applied only to big industries; [4] The workers were allowed to enjoy suitable wages; [5] Heavy industries like iron, coal, railways were kept under state control; [6] There was acute scarcity of capital in Russia. So, profit sharing concessions were allowed to foreign capitalists for large scale agricultural and engineering projects; [7] Power was allocated between the central and constituent republics.

The New Economic Policy of Lenin stimulated production and thus the condition of agriculture and industries was immensely improved. Though the introduction of NEP led to the reestablishment of capitalism to a great the Russian government still extent, maintained its control over important aspects of economic life of the country such as foreign trade, railways and big industries.
Analytical Answer (AA) Type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1. When did the Nihilist movement break out in Russia? What did the Nihilists believe in ?
Ans. The Nihilist movement broke out in Russia during the reign of Czar Alexander II (1855-81).
They believed in: [1] Total destruction of the Old Order and to create a vacuum so that only then, a new civilisation could grow. [2] Freedom of thought and action is the starting point of liberty. [3] War against the Czardom, the orthodox church, the feudalism, the aristocracy, the existing values of society. [4] New ethics, a new social code and a morality of revolution to break the Old Order and creating a happier and better world.
2. Name some repressive measures introduced by Czar Alexander II.
Ans. Czar Alexander III of Russia introduced the following repressive measures: [1] Russification of minorities. [2] The administration of the Mirs or village communities were put under the control of the landed proprietors who were appointed by the Central Government.

[3] Censorship was imposed upon all kinds of publication. Even private correspondence could be interfered with. [4] Restrictions were imposed on associations and meetings. [5] The state tried to control the curriculum and teaching staff of the universities. [6] Political offenders were liable to be exiled to Siberia or imprisoned in Russia.
3. Describe the social condition of Russia on the eve of the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Ans. The social condition of Russia in 1917, on the eve of the Russian Revolution was the same as it was before the outbreak of the French Revolution. The society of Russia was divided into two divisions.
The Haves: The ‘Haves’ were those people who were very rich. They fully supported the autocratic Czar. All the administrative posts were occupied by them. They possessed whole land of the country.
The Have-nots: The ‘Have-nots’ were the farmers and labourers. Their economic condition was deplorable. They were badly treated by the rich. Though the slave system was abolished in Russia, it did not bring any basic change in the condition of the poor. The poor decided to make a thorough change in the social condition of the country.
4. What do you know about Bloody Sunday? Or, Who was Father Gapon?
Ans. In 1905, on 9 January Sunday about 6000 industrial workers under the leadership of Gapon assembled in front of the Winter Palace at St. Petersburg to present a petition to Czar Nicholas II. The demands of the workers were:

[1] Release of the political prisoners; [2] summoning of a representative assembly; [3] eight hours of work a day for the workers. The peaceful assembly was headed by Father Gapon, a priest who was in reality a secret police agent. Nicholas II ordered his troops to open fire on the workers. The firing caused the death of about one thousand workers and more than 2000 were injured. This incident is known in history as the ‘Bloody Sunday’ as January 9 (1905) was a Sunday.
5. What was the impact of Bolshevik Revolution on Europe and the world?
Ans. The Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 was primarily aimed at the reconstruction of the Russian government and society according to the ideals of socialism. It was both a political and an economic revolution. In fact the motive behind the revolution was the establishment of proletarian rule all over the world. The Bolshevik attempts to bring about a global socialist revolution through the Third International formed in 1919 ended in failure. But as years went by the ideal of socialist government became popular. As a result, several states in North, Central and Eastern Europe like Poland, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria, Albania and East Germany set up communist governments. Outside Europe the most successful country with a communist regime is provided by the People’s Republic of China. Cuba in South America is another country that is a communist state.
Know More
The Bolshevik Revolution of 7 November (common calendar) took place on 25 October according to the old Russian calendar. That is why the Bolshevik Revolution of Russia is known as both November and October Revolution.
Short Answer (SA) Type Questions
Answer in 2 to 3 sentences
1 Mention two instruments through which Czar Nicholas I followed a policy of repression.
Ans. Two instruments through which Czar Nicholas I followed a policy of repression were: [1] The Board of Censorship kept a close watch on the people. The universities, the schools and the press were particularly controlled by it. [2] The Third Section or the secret police was a body vested with unlimited powers to arrest, imprison, exile and even execute people.
2 . Mention two important contributions of Czar Nicholas I.
Ans. Two contributions of Czar Nicholas I were: [1] His reign was marked by the emergence of industrial revolution in Russia. There was tremendous growth of light industry and particular progress in cotton textile and beet sugar industries. [2] Study of literature was encouraged by him so that people might forget politics.
3. Give some examples of the withdrawal of repressive policy by Czar Alexander II.
Ans. Czar Alexander II withdrew the repressive policies existing in Russia. [1] He showed his liberalism by releasing the Dekabrists from the prison and calling back the others from exile, who had been punished by his father 30 years ago for revolting against him. [2] He relaxed the censorship. [3] The universities were free to follow their own philosophy of teaching. [4] Restrictions on foreign travel were removed.
4. What was the condition of the serfs during the rule of the Czars?
Ans. During the rule of the Czars the condition of the serfs was miserable. They were like the personal possessions of the lords and had no freedom. They lived on small portions of land assigned to them and had to work four to five days per week in the lord’s manor without any wage. The law did not acknowledge or protect their rights. Their masters treated them as animals. They could be auctioned and they were subjected to physical punishment.
5. What was the total number of serfs in Russia at the time of emancipation?
Ans. At the time of emancipation there were about 45 million serfs in Russia comprising about 50% of the total population. Of the total number of serfs, 23 million belonged to the crown and the rest to the private lords.
6. What do you mean by ‘Policy of Russification’?
Ans. ‘Policy of Russification’ was implemented by the Russian government. It means the imposition of Russian culture on those who were of non-Russian nationality but lived within the Russian empire. It greatly affected the Ukranians, Poles and the Lithuanians. The aim of the policy was to bring non-Russians under more direct political control of the Russian government.
7. Name some important movements which broke out during the rule of the a Russian Czars.
Ans. The important movements which broke out during the rule of the Russian Czars were: [1] Russian literary. movement (1840’s); [2] Nihilist movement (1860’s); [3] Populist or Narodnik movement (1870’s); [4] The Revolution of 1905; [5] The Bolshevik Revolution of 1917.
8. Who is known as the ‘Father of modern Russia’ and why ?
Ans. Peter the Great is known as the ‘Father of modern Russia’. He introduced administrative reforms, established peace in the country, improved the economic of condition the country, introduced religious reforms. He reorganised and strengthened the Russian army. He designed the city of St. Petersburg after several modern European cities. He followed a successful foreign policy and Russia became a major European power during this time.
9. What a ‘Duma’ and ‘Zemstvo’? ‘
Ans. The Parliamant of Russia is known as Duma. In 1905 Czar Nicholas II established the Duma and its first assembly was held in 1906.
Zemstvo was an organ of rural self government in Russia. It was an elected local assembly established in 1864 by Czar Alexander II.
10. What in the meaning of ‘Menshevik’ and ‘Bolshevik’ in Russian?
Ans. In Russian ‘Menshevik’ means ‘minority’ and Bolshevik means ‘majority’.
11. Why is the Russian Revolution of 1905 called a ‘dress rehearsal’ of the Revolution of 1917 ?
Ans. The Russian Revolution of 1905 is called the ‘dress rehearsal’ of the Revolution of 1917. Czar Nicholas II ruthlessly and mercilessly suppressed the revolutionaries of 1905. Though the revolutionaries were defeated, the Revolution of 1905 inspired the people to launch a protest against the Czar and his policy. Thus they prepared the path for the Revolution of 1917.
12. What were Kerensky’s sky’s go causes of the failure of government?
Ans. The provisional government under Kerensky set up in February 1917 to govern Russia collapsed in October due to the following reasons: [1] Price rise and the economic distress of the people of Russia due to participation of Russia in the First World rar caused discontent among the people. [2] Kerensky’s government failed to check the advancement of the Germans into Russia. [3] The soldiers, influenced by Bloshevism, refused to take part in the First World War.
13. Mention two consequences of the Russian Revolution.
Ans. Two consequences of the Russian Revolution were: [1] Russia became a socialist country ending Czarist autocracy and aristocratic privileges. [2] In 1922 the formation of Union of Soviet Socialist Republic (USSR) was formally declared. USSR became a federation of 15 Soviet Socialist Republics with its object of socialism which ran as: “from each according to his capacity to each according to his work.”
14. What is ‘October Manifesto’ ?
Ans. After the violent incident on 9 January 1905 (Bloody Sunday) Czar Nicholas II of Russia bowed down to the storm and purchased peace by introducing certain liberal reforms published in a document known as October Manifesto. Through this Manifesto he granted: [1] Freedom of speech; [2] Freedom of press; [3] Freedom of public meetings; [4] legislative powers to the Duma; [5] that a new legislative assembly would be elected on the basis of universal suffrage.
15. What do you understand by the term derstand b ‘War Communism’ ?
Ans. During the civil war in Russia the Bolshevik government faced a major problem of production and supply of necessary articles due 14 to the occupation of food-producing and » industrial areas by the opponents or the ‘whites’. To tide over the situation, Lenin introduced ‘War Communism’ which meant total control of state over every aspect of economic activity.
Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
1. What was the Russian Parliament called ?
Ans. The Russian Parliament was called Duma.
2. What is ‘Narodniya Volya’?
Ans. ‘Narodniya Volya’ was a secret society of Russia.
3. Why did the Narodnik movement fail?
Ans. The Narodnik movement failed due to repressive measures of Czar Alexander III.
4. What were the revolutions which broke out during the reign of Czar Alexander II?
Ans. The Revolution of 1905 and the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 broke out during the reign of Czar Alexander II.
5. Between whom was the Treaty of Portsmouth signed?
Ans. The Treaty of Portsmouth was signed between Japan and Russia.
6. What were the two groups into which Russia’s ‘Social Democratic Party’ came to be divided ?
Ans. Russia’s ‘Social Democratic Party’ came to be divided into two groups-[1] the Bolsheviks and [2] the Mensheviks.
7. Which incident marked the end of the Romanov dynasty of Russia?
Ans. The Romanov dynasty of Russia ended after the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917.
8. Who was Queen Alexandra?
Ans. Alexandra was the queen of Czar Nicholas II.
9. Which incident led to the Russo-Japanese War (1904-05)?
Ans. The conquest of Manchuria and Korea by Russia led to the outbreak of RussoJapanese War.
10. Which revoluktion is known as the ‘Socialist Revolution’?
Ans. The November Revolution of 1917, in Russia is known as the Socialist Revolution.
11. What is ‘Pravda’ ?
Ans. Pravda’ was the mouthpiece of the Bolshevik Party.
12. When did Czardom come to an end in Russia?
Ans. Czardom came to an end in Russia on 13 March 1917.
13. Who was the Czar of Russia when the Bolshevik Revolution broke out?
Ans. Nicholas II was the Czar of Russia when the Bolshevik Revolution broke out.
14. Who was Lenin ?
Ans. Lenin was the leader of Bolshevik Revolution and the first president of Soviet Union.
15. Who was Trotsky ?
Ans. Trotsky was a leader of the Bolshevik Revolution and the first foreign minister of Soviet Union.
16. What was the new name of Russia after the Bolshevik Revolution?
Ans. The new name of Russia after the Bolshevik Revolution was Union of Soviet Socialist Republic.
17. What is the full name of Lenin ?
Ans. Lenin’s full name is Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov.
Know More
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin was the noisiest and the most mischievous of all his brothers and sisters. His parents called him Kubyshkin, i.e. the pot with a fat belly.
18. In which year did the Bolshevik Revolution break out?
Ans. The Bolshevik Revolution broke out in 1917.
19. Name the leader who led the procession of workers to the Winter Palace.
Ans. The leader who led the procession of workers to the Winter Palace was Father Gapon.
20. Into how many classes the Russian society was divided in the 19th century and what are these ?
Ans. The Russian society was divided into two classes in the 19th century and these were [1] the aristocrats and [2] the peasants.
21. Who established the Bible Society and when ?
Ans. The Bible Society was established by the Russian Czar Alexander I in 1812.
22. Name two intellectuals of Russia who demanded abolition of serfdom.
Ans. Two intellectuals of Russia who demanded abolition of serfdom were Tolstoy and Turgenev.
23. What is the most remarkable contribution of Czar Alexander II ?
Ans. The most remarkable contribution of Czar Alexander II was the abolition of serfdom.
24. Who announced ‘New Economic Policy’ (NEP) in Russia ?
Ans. Lenin announced ‘New Economic Policy’ in Russia.
25. What does the Russian word ‘Narod’ mean ?
Ans. The Russian word ‘Narod’ means ‘the people’.
26. What does ‘NEP’ stand for?
Ans. ‘NEP’ stands for New Economic Policy.
27. What were the two factions of the Social Democrats of Russia ?
Ans. The two factions of the Social Democrats of Russia were [1] the Bolsheviks and [2] the Mensheviks.
28. Name the reigning Czar of Russia when the Revolution of 1917 broke out.
Ans. The reigning Czar of Russia during the outbreak of the Revolution of 1917 was Nicholas II.
29. Who was Rasputin ?
Ans. Alexandra, the queen of Czar Nicholas II, was enamoured by a fake priest named Rasputin who charmed the Queen to such a degree that his voice became the ultimate commanding force in the government.
30. What is the importance of 1917 in the history of Europe ?
Ans. The importance of 1917 in the history of Europe are: [1] Fall of Czardom in Russia [2] Under the leadership of Lenin Bolshevik Revolution broke out in Russia. [3] Russia emerged as the first socialist state in the world.
31. Name one Russian philosopher who helped to create the climate for the outbreak of the Russian Revolution.
Ans. The Russian philosopher Gorky contributed to prepare the climate for the outbreak of the Russian Revolution.
32. When and where was the ‘Social Democratic Party’ established? What were its two factions ?
Ans. The ‘Social Democratic Party’ was established in Russia in 1898.
Its two factions were [1] the Bolsheviks and [2] the Mensheviks.
33. Who announced the ‘April Thesis’?
Ans. Lenin announced the ‘April Thesis’.
34. Mention any one of the principles of NEP (New Economic Policy).
Ans. One principle of NEP introduced by Lenin was that henceforth peasants could sell their surplus produce freely in the open market according to market prices.
35. Who was ‘the Father of the Russian Revolution’ ?
Ans. Lenin was the ‘Father of the Russian Revolution’.
36. When did the Bolsheviks capture the Winter Palace ?
Ans. The Bolsheviks captured the Winter Palace on 7 November 1917.
37. What do you mean by October Revolution in Russia?
Or, What do you mean by November Revolution in Russia ?
Ans. The Bolshevik Revolution of 7th November (common calender) took place on 25th October according to the old Russian calendar. That is why the Bolshevik Revolution of Russia is known as both ‘November’ and ‘October’ Revolution.
38 What was the name of the Bolshevik Party’s newspaper ?
Ans. The Bolshevik Party’s newspaper was Pravda.
39. Name the leader who led the procession of workers to the Winter Palace.
Ans. The leader who led the procession of workers to Winter Palace was Father Gapon.
40. What is Third Section’ ?
Ans. The ‘Third Section’ or the secret police was a body created by Nicholas I, vested with unlimited power to arrest, imprison, exile and even execute people.
41. Name some thinkers of Russia who influenced the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Ans. Some thinkers who influenced the Russian Revolution were Gorky, Turgenev, Dostoevsky, etc.
Mark True or False
1. By the October Revolution under Lenin, the Bolsheviks seized the government in the capital St. Petersburg.
2. In 1878, the Narodniks started a violent movement in Russia.
3. The New Economic Policy was declared by Lenin in 1921.
4. The Russian philosopher who prepared Russia mentally for the Russian revolution was Rousseau.
5. The ‘April Thesis’ was announced by Stalin.
6. The Union of Soviet Socialist Republic was a federation of 15 Soviet Socialist Republics.
7. On 7 November 1918, the Bolsheviks captured the Winter Palace.
8. A special secret police called Duma was formed by Bolsheviks.
9. The mental climate for the outbreak of the Russian Revolution was prepared by philosophers like Montesquieu and Rousseau.
10. The Bolshevik Revolution broke out under the leadership of Stalin.
11. Alexandra, the queen of Czar Nicholas II was enamoured by a fake priest named Rasputin.
12. The Third Section was the secret police introduced by Czar Nicholas I.
13. One important movement which broke out in Russia in 1870’s was the Narodnik movement.
14. In 1905, on a January Sunday about 6000 industrial workers under the leadership of Thiers assembled in front of the Winter Palace.
15. The Nihilist movement broke out during the reign of Czar Alexander I.
16. Father Gapon led the procession of workers to the Winter Palace.
17. Before the outbreak of Russian Revolution the Russian Society was divided into two classes.
18. The Bible Society was established by Alexander II in 1812.
19. Narodnik Volya was a secret society of Russia.
Answers :
1. True, 2. True , 3. True , 4. False, 5. False, 6. True , 7. False , 8. False, 9. False , 10. False , 11. True, 12. True , 13. True , 14. False , 15. False , 16. True, 17. True , 18. False , 19. True.
Fill in the blanks
1. By the October Revolution of 1917 the ______(Mensheviks/Bolsheviks/
2. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed between Germany and ____(Britain/Italy/ Russia).
3. The Red Army was organised by______ (Stalin/Trotsky/Lenin).
4. The New Economic Policy of Lenin was a compromise between socialism and __________(capitalism/communism/Nazism).
5. The Revolution of 1905 in Russia broke out during the reign of _________(Czar Alexander II/Nicholas I/Peter the Great).
6. ‘Pravda’ was the mouthpiece of the_______(Menshevik/
7. The two factions of Social Democratic Party are Bolsheviks and __________(Communists/ Mensheviks/Socialists).
8. Czar ________ (Alexander 1/Alexander II/ Nicholas ) showed his liberalism by releasing the Dekabrists.
9. Kaiser William II abdicated the throne in _________ (1916/1917/1918).
10. ‘War Communism’ was introduced by __________ (Trotsky/Lenin/Franco).
11. The ruler of Russia was called _____(Strorm Trooper/Czar/Duma).
12. The legislature of Russia is known as ________ (Mir/Pravda/Duma).
13. The word ‘Communism’ was first used by ________(Nicholas I/Lenin/Karl Marx).
14. The author of the novel ‘Mother’ is ________ (Lenin/Engles/Maxim Gorky).
15. The writer of the novel ‘Father and Sons’ was ________ (Maxim Gorky/Lenin/Ivan Turgenev).
16. The meaning of the word ‘Narod’ is ________ (Czar/people/monarch).
17. The newspaper ‘Pravda’ was published in the year ___________(1911/1910/1912).
18. The leader of the Russian Revolution of 1917 was ________ (Vladimir Lenin/Kerensky/ Karl Marx).
19. The leader of the Mensheviks was _________ (Vladimir Lenin/Trotsky/Julius Martov).
20. The New Economic Policy was introduced by _________(Karl Marx/Vladimir Lenin/ by Kerensky).
Answers :
1. Bolsheviks
2. Russia
3. Trotsky
4. Capitalism
5. Czar Alexander II
6. Bolshevik
7. Mensheviks
8. Alexander II
9. 1918
10. Lenin
11. Czar
12. Duma
13. Karl Marx
14. Maxim Gorky
15. Ivan Turgenev
16. people
17. 1912
18. Vladimir Lenin
19. Julius Martov
20. Vladimir Lenin
Choose the best explanation
1. Statement: In 1921, Lenin announced a New Economic Policy.
Explanation (A) : Lenin wanted to establish his dominance in the country’s economy.
Explanation (B) : Lenin wanted to give more benefits to the workers than to any other class.
Explanation (C) : Lenin Wanted to save the country from economic crisis.
2. Statement: Czar Nicholas 11 issued ‘October Manifesto’.
Explanation (A) : He wanted to reform Russia.
Explanation (B) : He wanted to resist the revolution through compromise.
Explanation (C) : He wanted to create revolution in industrial sector.
3. Statement: The Russian peasants supported the Bolsheviks in the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Explanation (A) : Bolsheviks promised to redistribute the land owned by the nobility.
Explanation (B) : Bolsheviks promised to introduce modern technology to Russian farms.
Explanation (C) : Bolsheviks promised to redistribute the land owned by the government.
Answers :
1. Explanation (C)
2. Explanation (B)
3. Explanation (C)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. The Bolshevik Revolution broke out in Russia in –
A. 1915
B. 1916
C. 1917
D. 1918
Ans. C
2 The formation of Union of Soviet Socialist Republic was formally declared in –
A. 1920
B. 1921
C. 1922
D. 1923
Ans. C
3 The Bolsheviks captured power in Russia by the –
A. November Revolution
B. July Revolution
C. February Revolution
D. October Revolution
Ans. D
4. A special secret police was formed by the Bolsheviks called –
A. Duma
B. Cheka
C. Soviets
D. Aurora
Ans. B
5. What was the date and year of Bloody Sunday ?
A. 9 January 1905
B. 12 January 1905
C. 4 April 1906
D. 9 August 1906
Ans. A
6. Rasputin was –
A. Minister
B. Czar of Russia
C. Mystic Saint
D. Close relative of Czar
Ans. C
7. Bolshevik Revolution was led by –
A. Stalin
B. Lenin
C. Trotsky
D. None of them
Ans. B
8. Who was known as ‘Czar The Liberator’?
A. Czar Alexander II
B. Czar Nicholas II
C. Czar Alexander III
D. Czar Nicholas III
Ans. A
9. The leadership in the march to St. Petersburg by the workers was given by –
A. Stalin
B. Father Gapon
C. Trotsky
D. Lenin
Ans. B
10 . The emperor of Russia is called –
A. Sultan
B. Czar
C. Kaiser
D. Chancellor
Ans. B
11 Who was the first to be proclaimed Czar of Russia ?
A. Czar Alexander I
B. Alexander II B
C. Nicholas II
D. Ivan IV
Ans. D
12. Who first introduced Czarism ?
A. Mikhial Romanov
B. Czar Peter the Great
C. Alexander II
D Ivan IV
Ans. D
13. Czarism ended in the year –
A. 1905
B. 1900
C. 1917
D. 1927
Ans. C
14. The father of modern Russia –
A. Ivan IV
B. Nicholas II
C. Czar Peter the Great
D. Alexander I
Ans. C
15. The Romanov dynasty came to an end during the reign of –
A. Nicholas I
B. Alexander I
C. Alexander II
D. Nicholas II
Ans. D
16. The Russian Revolution broke out during the reign of –
A. Nicholas I
B. William II
C. Nicholas II
D. Ivan IV
Ans. C
17. The party which gave leadership in the Russian Revolution of 1917 was –
A. Bolshevik Party
B. Young Italy
C. Menshevik Party
D. Nazi Party
Ans. A
18. The leader of November Revolution was –
A. Luvov
B. Kerensky
C. Trotsky
D. Lenin
Ans. D
19. Who put forward ‘April Thesis’?
A. Trotsky
B. Karl Marx
C. Stalin
D. Lenin
Ans. D
20. The meaning of ‘Pravda’ is –
A. Truth
B. Iron
C. People
D. Communism
Ans. A
21. Leningrad was seized during the reign of –
A. Nicholas
B. Alexander II
C. Peter the Great
D. Catherine
Ans. C
22. The meaning of Iskra, the newspaper published by Lenin –
A. New life
B. Truth
C. Spark
D. Iron
Ans. C
23. Nihilist movement broke out during the reign of –
A. Peter the Great
B. Nicholas I
C. Alexander II
D. Nicholas II
Ans. C
24. Father of socialism in Russia –
A. Karl Marx
B. Engels
C. Lenin
D. Stalin
Ans. C
25. The Third Commintern was established in –
A. Moscow
B. Taskhent
C. Bombay
D. Geneva
Ans. A
26. The leadership of the Red Army to Petrograd on 7 November 1917 was given by –
A. Lvov
B. Kerensky
C. Trotsky
D. Lenin
Ans. C
27. The first socialist country in the world is –
A. United Kingdom
B. Poland
C. America
D. Soviet Russia
Ans. D
28. ‘New Economic Policy’ was introduced by—
A. Stalin
B. Gapon
C. Lenin
D. Turgenev
Ans. C
TOPIC – B
The First World War and Aftermath
Explanatory Answer (EA) type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. Describe the major events of the First World War.
Ans. The First World War broke out in 1914 and ended in 1918. The war was waged between the Allied powers (comprising Britain, France, Russia and Serbia) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria, Hungary and Turkey).

[1] On 28 June 1914 Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the Austrian throne, was assassinated at Sarajevo. Austria held Serbia responsible for the murder. England declared war on Serbia. Russia joined hands with Serbia. It declared war on France and Russia invaded Belgium to reach France. France was helped by Britain. [2] Japan attacked Germany in order to get control of her colonies in the Far East. Turkey and Bulgaria sided with Germany. [3] Italy joined France and England. The German army marched towards Paris but were stopped near the river Marne. The German army was defeated in the Battles of Marne and Somme. [4] The United States of America joined the war in 1917 when the British ship Lusitania carrying American passengers was sunk by a German U-Boat. At first the Germans were winning. They used U-boats to sink enemy ships as well as ships of neutral countries going to Britain. [5] In 1917 the new communist government under the leadership of Lenin was established. In 1918 Russia signed the treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Germany and withdrew from the war. [6] Germany mounted violent attacks on France and Belgium. [7] America entered the war and the Germans started losing. The allies started counter attacks forcing the Germans back. Germany was devastated and emperor William Il fled. [8] The Central Powers surrendered and accepted an armistice in 1918. Shortly thereafter, the 1919 Treaty of Versailles ended World War I.
2. What were the effects of the First World War ?
Ans. The outbreak of the First World War on July 28, 1914 is the most outstanding event of the early 19th century. The effects of the First World War are as follows: [1] About one crore thirty lakh soldiers died during the First World War. The death rate of the civilians was much more. About 28 thousand crore dollars were spent during the war. After the war there was acute financial crisis. [2] Severe economic difficulties created by the war and the demand for reparation caused despair and hardship which ensured an uncertain future for Germany. [3] The Great War sounded the death knell for monarchies in Germany and Russia which became republics. [4] The Ottoman empire and Austria-Hungary completely collapsed. [5] The USA emerged from the war clearly as the greatest power as well as the creditor nation of the world. [6] In Russia the war led to the Russian Revolution and a civil war broke out in Russia which continued for three years beyond World War I. [7] World War I was also the cause for a rise in nationalistic tendencies leading to the demand for independence in many British colonies outside Europe. [8] On most countries after the Great War, monarchy came to an end and democratic governments were established. [9] After the Great War the prices of articles went up. [10] Almost all the countries were so heavily burdened that for years together their path of progress remained impeded. [11] With men having joined the war, the women of most countries took over business and establishment. [12] One distinct positive outcome of the World War I was the boost received by research and technology. Rail and automobile transport, radio and wireless communications, research and development of weapons and arms including nuclear research ‘boomed. [13] To curb the wars and maintain global peace the League of Nations was established in 1919 due to the persistent efforts of Woodrow Wilson.
3. What were Wilson’s ‘Fourteen Points’?
Ans. With the surrender of Germany in 1918, the First World War came to an end. As an answer to all European problems the President of America Woodrow Wilson came up with peace proposals known as the ‘Fourteen Points’. It said that: [1] There would be no secret treaties among different countries. All terms will be openly discussed and agreed upon. [2] The seas should be free in peace and in war to ships of all nations. [3] The American Doctrine of ‘Open Door’ in China i.e. right of all nations to enjoy equal rights of trade in China will be implemented. [4] Colonial questions to be settled peacefully. [5] Russia should be allowed to choose whatever form of government it wanted. [6] Germany shall restore genuine French territories to France. [7] The barriers to trade between countries such as customs duties should be removed (free trade). [8] The Habsburg and the Turkish Empires would be reorganised and reconstructed according to the doctrine of ‘one nation one state’. [9] All countries should reduce their armed forces to the lowest possible levels. [10] Poland should be constituted as an independent sovereign and united country. [11] The national groups in Europe should, wherever possible, be given their independence. [12] Russian territories may be restored to Russia. [13] Readjustments of the frontiers of Italy to be made. [14] The League of Nation would be formed for prevention of war and for peaceful settlement of international dispute.
4. What were the treaties signed in the Paris Peace Conference (1919) ?
Ans. The First World War came to an end in 1918 with the surrender of Germany. In the Paris Peace Conference (1919) the following peace treaties were concluded:
[1] The Treaty of Versailles: The Treaty of Versailles was concluded in 1919 between the victorious allies (comprising Britain, France, Russia, Serbia) and the defeated Germany after World War 1. [i] Germany lost Alsace-Lorraine to France, Upen, Malmedy, Moresnet to Belgium, Memel to the Allies, west Prussia and most of Posen to Poland. She handed over the province of Schleswig to Denmark. [ii] Danzig was made a free port. [iii] The Saar Valley was put under an international commission for 15 years. [iv] Germany was required to surrender her colonies, navy and coal mines. [v] Germany had to pay heavy war reparations.
[2] The Treaty of Saint Germain: This treaty was signed between victorious Allies and defeated Austria in 1919. By this treaty [i] The old House of Hapsburg was abolished. [ii] Austria had to accept the true existence of Hungary, Poland and Czechoslovakia.
[3] The Treaty of Neuilly: This treaty was signed between the victorious allies and Bulgaria in 1919. According to this treaty [i] Four provinces of Western Bulgaria were given to Yugoslavia; [ii] The strength of Bulgarian army was reduced to ten thousand.
[4] The Treaty of Trianon: The Allied powers concluded this treaty with Hungary in 1920. By this treaty [i] large portion of territory was taken away from Hungary; [ii] The strength of the Hungarian army was reduced.
[5] The Treaty of Sevres: The victorious Allies concluded this treaty with Turkey in 1920. By this treaty [i] The Turkish empire was abolished [ii] Turkey had to give up her rights over Egypt, Cyprus, Morocco, Palestine, Arabia and Mesopotamia. Turkey’s army was also reduced.
5. Criticise the treaty of Versailles.
Or, The Treaty of Versailles contained the seeds of the Second World War-Discuss.
Ans. [1] The Treaty of Versailles has been called ‘a dictated treaty’ which was imposed upon by the defeated Germany by the Allied powers. The delegates of Germany were not invited to the Paris Peace Conference (1919) and the treaty was a vengeful treaty. [2] The Treaty did not adhere to the principle of selfdetermination. The right of self determination was not applied for Sudetenland which was transferred to Czechoslovakia. It led to a loss of balance of power in Europe. [3] While England and France increased their colonies, German colonies were confiscated in the name of good government. [4] Germany was saddled with a huge reparation amount by the Treaty which was impossible for her to pay. [5] According to Wilson’s Fourteen Points, it was decided that all the states would reduce their war armaments. But this clause was only applied to Germany. Humiliated Germany was looking forward to another war as an opportunity to avenge his defeat. It is thus said that the Treaty of Versailles contained the seeds of the Second World War.
Know More
The Treaty of Versailles Timeline
◆ 18 January 1919: The Paris Peace Conference opened in Versailles, France.
◆ 19 June 1919: The victorious powers gave an ultimatum to Germany to agree to the Treaty of Versailles by 24 June 1919.
◆ 24 June 1919: The German Reichstag agreed to the Treaty of Versailles.
◆ 28 June 1919: The Treaty of Versailles and the Covenant of the League of Nations were signed in Paris, France.
6. How was the League of Nations founded?
Or, What was the role of Woodrow Wilson in the foundation of the League of Nations ?
Ans. The terrible effects of the First World War (1914-18) had stunning effects on the minds of the people. It made the people cry for peace. At Paris in 1919 a peace conference was convened in order to solve the problems of the countries to conclude a treaty with the vanquished. The meeting was called to find out a way to maintain peace and order in the world in future on a permanent basis. Wilson had also come to attend the conference. He put before the Allies his ‘Fourteen Points’ for consideration. The Allies agreed to work according to these points. The last point of Wilson was directly related to the formation of the League of Nations. The Allies agreed that this organisation should be formed and its constitution should be prepared Wilson separately. suggested that the constitution of the League of Nations should be included in the Treaty of Paris. Ultimately the Allies accepted the demand of Wilson. A document called Covenant was drafted at the Paris Peace Conference which led to the foundation of the League of Nations.
7. What do you mean by Great Economic Depression? What were the causes of economic depression of 1929 ?
Ans. The Great Economic Depression was a severe worldwide economic crisis in the decade preceding World War II that affected most of the developed world except Soviet Union throughout 1930.
The causes of the Great Depression in America or world economic crisis were as follows: [1] After the First World War there was overproduction of industrial goods in America. The surplus goods could not be sold in the domestic market or across the Atlantic. [2] After the First World War different European countries increased their industrial production. As a result demand for American goods dropped leading to economic crisis. [3] During the First World War farmers produced far more food than the population consumed. Farmers expanded their production to aid the war effort. After the war as demand dropped with increasing supply the prices of products fell and farmers suffered. They fall into debt. [4] On 24 October 1929 the American share market crashed. As the shareholders were panicked millions of shares had been sold on this fateful day. [5] America imposed high rate of tariff on goods imported from different European countries. The European countries also adopted the same policy. As surplus goods could not be sold in the market America’s foreign trade suffered. Many industries were closed and the people became jobless.
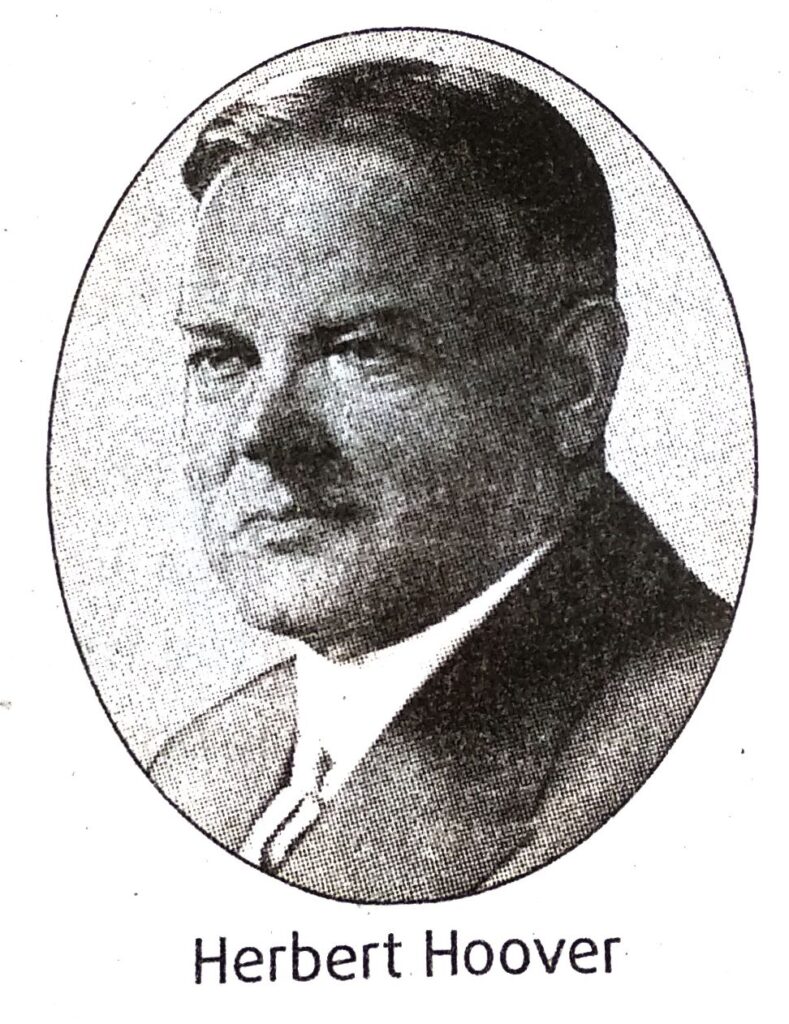
8. Write a note on Hoover’s Moratorium.
Ans. Herbert Hoover became the President of the USA in 1929. He said, “We in America are nearer to the final triumph over poverty than ever before in the history of any land”. But very soon came the economic crash of 1929. Total industrial production fell by 48 percent, the result being a rapid growth of unemployment. The business houses faced a great deal of losses. In order to speed up economic revival, Hoover proposed an international moratorium from mid 1931 to mid 1932. To meet rising unemployment, the government allotted large sums for the construction of public buildings and highways. The threatened insolvency of many banks and many railways forced the government to underwrite the credit structure. A Reconstruction Finance Corporation was created which was authorised to lend money for three years for financing commerce, industry and agriculture and for exportation of agricultural and other products. All these measures to solve the economic depression of the country failed. By 1932 over five thousand banks collapsed and the number of unemployed people rose to over 12 million. The Americans turned with hope to the new leadership of Franklin Roosevelt.
9. What is ‘New Deal’ of Roosevelt?
Ans. When Franklin Delano Roosevelt became the President of USA in 1933 the country was on the verge of complete collapse. He prophesied that USA would ‘revive and prosper’ and he promised a New Deal for the American people.
The New Deal was a series of domestic programme enacted in the United States between 1933 and 1938 and a few that came later. They included both laws passed by Congress as well as presidential executive orders during the first term (1933-37) of President Roosevelt. The programme were in response to the Great Depression and focussed on what historians call the 3R’s-‘Relief, Recovery, Reform’, that is Relief for the unemployed and poor, Recovery of the economy to normal level and Reform of the finances.
In the realm of ‘Relief’ the government gave federal loans to rich business. It inaugurated a programme of public works in order to stimulate business and provide employment. It set up elaborate system of conservation of nature resource. The New Deal reopened banks under strict supervision of the government. It controlled the selling of stocks and bonds and other securities. The New Deal paid particular attention to agriculture, labour and social security.
10. What were the reasons that led to the substitution of Europe by the USA as the he USA as t power centre of the world ?
Ans. In the beginning of the 20th century the centre of power of the world was shifted from Europe to USA due to the following reasons: [1] With the entry of USA into the First World War in 1917 a new chapter opened in world history. Her participation changed the course of the war and enabled Britain and France to win the war. [2] At the Paris Peace Conference (1919) President Wilson was one of the Big Four who laid the foundation of the world peace organisation, the League of Nations USA’s prestige was raised and she became a prominent power in the world. [3] USA’s emergence as a world power was also caused by her economic prosperity. The economic depression of 1929-33 affected not only USA but also other countries of the world. President Roosevelt of USA helped other countries to tide over this economic crises and USA’s prestige was raised as a first class world power. [4] USA rendered military and material help to the allies and totally changed the course of the war. USA forced Japan to surrender in 1945 and played a leading role in the Second World War. She made her the arbiter of international politics. [5] USA’s advancement in science and technology especially in weapons of mass destruction raised her status. She was the first to invent atom bomb and the successful dropping of it in Japan made her the most prominent power in the world. [6] USA took the lead to counteract Russia’s influence. She took the initiative of extending economic assistance to Europe especially through the Marshall Plan. USA helped to restore all economies and modernise the armed forces of western Europe and became the centre of world politics. [7] The Second World War (1939-45) weakened Britain and France. Britain’s economic crisis after the war was relieved to some extent by loan from the USA which heightened the prestige of USA.
Analytical Answer (AA) type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1.What were the causes of victory of the Allied Powers in the First World War ?
Ans. The First World War ended in 1918 with the victory of the Allied Powers and defeat of the Central Powers. The causes of victory of the Allied Powers are discussed below:

[1] The Allied Powers had greater manpower and resources than Germany. [2] The entry of USA in the war turned the tide in favour of the Allied Powers. [3] The Alied Powers had greater manpower than Germany. [4] The democratic countries like England, France got the support of the people than an autocratic country like Germany. [5] The Allies by opening two fronts the war forced Germany to meet the challenge from two sides. Germany could not continue the war because Germany had neither the war equipment nor financial resource to continue the war for long on two frontiers. [6] One important reason for the victory of the Allied Powers was their superiority in naval strength compared to Germany and her associates.
2. Was the Treaty of Versailles (1919) based on Wilson’s ‘Fourteen Points’?
Ans. With the surrender of Germany in 1918, the First World War came to an end. As an answer to all European problems, the President of the United States of America, Woodrow Wilson came up with a peace proposal known as the Fourteen Points. The Fourteen Points of Wilson did not receive much importance at the Paris Peace Conference. The Treaty of Versailles made between the victorious powers and Germany was not purely based on Fourteen Points. Throughout the Paris Peace Conference there was a conflict between Wilson’s idealism and nationalist realism. In fact, the Fourteen Points of Wilson was given only lip service. Wilson had to make a compromise between Clemenceau’s practicalism and Lloyd George’s opportunism. The Fourteen Points did not provide for any partition of German territory. But the Versailles Treaty partitioned Germany.
3. What were the economic clauses of the Treaty of Versailles ?
Ans. In the First World War (1914-1918) Germany was defeated and the Treaty of Versailles was imposed upon Germany in 1919. The economic clauses of the Treaty were: [1] Germany was guilty of war and had to pay $ 6600 million in reparations partly in cash, partly in kind and in services. [2] Germany had to surrender Alsace and Lorraine to France for fifteen years after which the fate of the region was to be settled by a plebisite. [3] Germany lost all her colonies in Africa and Pacific. [4] Rivers of Germany-Elba, Rhine, Danube, etc. will remain under international control. [5] It became obligatory for Germany to supply a special quality of coal, timber, rubber, iron ore and other minerals to Italy, France, Belgium and Luxemburg.
4. Justify the Treaty of Versailles (1919). aines pas
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles (1919) imposed on Germany by the victorious Allied Powers has been justified on the following grounds: [1] According to the principles laid down by President Wilson the League of Nations was established with the avowed aim to establish permanent peace and order in the world. [2] When the frontier areas of Germany were partitioned the principal and integral part of Germany was kept united under a sovereign government. [3] The colonies of Germany were divided among the Allies on the basis of the Mandate system. [4] Germany was not asked to pay the whole expenses of war. She was asked to pay only the damages suffered by the civilian population of the Allied countries due to the German aggression. [5] According to the principle of nationalism and self-determination, many new states were created, viz., Poland, Finland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Lithuania etc. It was for the first time, when the principle of nationalism was enforced on a large scale. As a result of this, only three percent people of the total population of Europe remained under the yoke of the foreigners.
5. With what aims was the League of Nations founded ?
Ans. After the First World War (1914-18), an international organisation known as the League of Nations was established in 1920 with the following aims in view : [1] To prevent armed conflict and to promote international peace and cooperation; [2] To establish honourable and just relation among different nations, [3] To implement the provisions of the treaties registered at the Paris Peace Conference; [4] To promote international disarmament in order to reduce tension and to find out ways and means for peaceful settlement of international disputes; [5] To protect the weaker section of humanity specially women and children; [6] To promote just treatment to working class and [7] To promote the health of mankind.
6. Briefly describe the causes of the failure of the League of Nations.
Ans. After the First World War (1914-18) an international organisation, known as the League of Nations, which was formed to promote international cooperation and peace failed due to various reasons: [1] The League was never able to make itself truly ‘representative of the entire world’. Countries like USA, Russia, Germany, Japan and Italy were not members of the League at different stages and no international organisation can be really successful if some of the Great Powers remain outside its orbit. [2] Mere protests could not check the aggressive policy of the members of the League. Effective economic and military sanctions were necessary but military sanctions were left to the discretion of the members. Without military punishment the aggressor could not be checked. [3] The League had no army, navy or airforce of its own nor was it in a position to apply economic sanctions without the cooperation of the great powers. But the great powers looked after their own interests instead of fulfilling their obligations to the League. [4] The rise of dictatorship in different countries in the third decade of the 20th century frustrated the peace-making efforts of the League.
Short Answer (SA) Type Questions
Answer in 2 to 3 sentences
1. Give two examples of insatiated nationalism before the outbreak of the First World War.
Ans. Two examples of insatiated nationalism before the outbreak of the First World War were: [1] Italians of Trieste, Trentino and Tyrol who were under the rule of the Dual Monarchy of Austria. Hungary wanted to join Italy. [2] Ambition of Alsace and Lorraine which was under German occupation to join France.
2. What were the two rival contending parties in the First World War ?
Ans. In the First World War the two rival contending parties were: [1] On one side was the Triple Entente of twenty-three countries including France, England and Russia. Later on Italy (which was a member of Triple Alliance), Romania, Japan, China, Portugal joined the Triple Entente. They were known as Allied Powers. [2] On the other side were the members of Triple Alliance-Germany, Austria, Turkey, Bulgaria etc. They were called ‘Axis Powers’ or ‘Central Powers’.
3. What was the Bosnia-Herzegovina problem before the outbreak of the First World War ?
Ans. Before the First World War Bosnia and Herzegovina were annexed by Austria. This injured the nationalistic feelings of the people of these two places as they desired to unite with Serbia. The people supported by Serbia Government rose in revolt against Austria.
4. What is Moroccan Crisis ?
Ans. France had vital colonial interests in Morocco in north Africa-a region rich in mineral resources and dominated by the Muslims. Kaiser William of Germany protested against the supremacy of France in Morocco and appeared in the port of Tangier in 1905. He provoked the Sultan of Morocco against the French and declared that he would support Moroccon independence against France. This led to a war situation between France and Germany. This is known as Moroccan Crisis (1905).
5. What is Agadir Crisis? s Agadir Crisis ?
Ans. In 1911 in Morocco in North Africa some Europeans lost their lives during a tribal movement. Under this circumstance France occupied a part of Morocco. Germany protested against this and the German gunboat ‘Panther’ was sent to the port of Agadir in Morocco with the ulterior motive of establishing German claim in Morocco. England in support of France sent warships to Agadir. This led to a war situation which is known in history as the Agadir crisis.
6. Why did the United States of America join the First World War ?
Ans. The United States of America joined the First World War due to the aggressive policy of Germany. The USA suffered great losses when American ships were destroyed by Germany. America asked Germany not to attack vessels of neutral countries and the American ships in the open seas but Germany paid no heed to this. So the USA joined the First World War.
7. When did Russia withdraw herself from the First World War ?
Ans. Russia signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Germany in 1918. After signing the Treaty Russia withdrew herself from the First World War.
8. Who were the Big Four at the Paris Peace Conference (1919) ?
Ans. The ‘Big Four’ at the Paris Peace Conference were: [1] Woodrow Wilson of America [2] Lloyd George of England [3] Clemenceau of France and [4] Orlando of Italy.
9. What were the five treaties concluded at the Paris Peace Conference ?
Ans. The five treaties concluded at the Paris Peace conference were: [1] Treaty of Versailles [2] Treaty of St. Germain [3] Treaty of Neuilly [4] Treaty of Trianon [5] Treaty of Sevres.
10. Mention three territorial clauses of the Treaty of Versailles. ritorial clauses of the
Ans. Three territorial clauses of the Treaty of Versailles (1919) were: [1] The provinces of Alsace and Lorraine were taken away from Germany and were given back to France. [2] The Saar Valley on the western frontier of Germany was handed over to France for fifteen years after which the fate of the region was to be settled by a plebiscite. [3] The port of Danzig was also snatched away from the possession of Germany and was declared a free port under the League of Nations.
11. Mention three military clauses of the Treaty of Versailles.
Ans. Three military clauses of the Treaty of Versailles were: [1] The German board of staff or generals of the army was dissolved. [2] The universal compulsory military service was dissolved. [3] Germany had to surrender her fleet to the Allies.
12. What were the economic implications of the Treaty of Versailles (1919) ?
Ans. In the First World War Germany was defeated and the Treaty of Versailles (1919) was imposed upon Germany. The heavy burden of compensation imposed upon Germany brought in a host of evils like unemployment, taxation and hyperinflation. The hyperinflation combined with the effects of the Great Depression undermined the stability of German economy and destabilized the Weimer Republic and paved the path for Hitler’s rise to power.
13. Why is the Treaty of Versailles known as ‘dictated peace’?
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles (1919) has been called a ‘dictated peace’ because the treaty was imposed upon defeated Germany by the victorious powers of World War 1. The delegates of Germany were not invited to the conference of Paris and the treaty was not based on mutual negotiation. The German representative was forced to sign the treaty on threat of aerial bombardment of Germany.
14. How did economic crisis begin in USA?
Ans. In USA economic crisis began with the crash of the Wall Street Exchange in 1929, when USA could not recover back loans. Fearing a fall in price, people made frantic efforts to sell their shares. On a single day, 13 million shares were sold. Factories were shut down, banks became bankrupt, exports fell, farmers were badly hit leading to unemployment.
15. Why 24 October 1929 known as the ‘Black Thursday’?
Ans. 24 October 1929 is known as the ‘Black Thursday’ because on this day the American share market crashed. As the share holders were traumatised millions of shares had been sold on this fateful day.
16. Why is the share market crash of 24 October 1929 known as the ‘Wall Street Crash’?
Ans. On 24 October 1929 the American share market crashed because on this day the panicked shareholders sold millions of shares. The crash is known as Wall Street Crash because Wall Street in New York, USA was the location of the principal share market.
17. What was the effect of the Great Depression of 1929 on USA ?
Ans. The Great Great Depression of 1929 had profound effect on USA. Over the next three years, between 1929 and 1932, the national income of the USA fell by half. The speculators withdrew their money from the market. Factories shut down, exports fell, farmers were badly hit and millions of workers lost their jobs.
Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
1. Which period is known as the period of armed peace?
Ans. 1871-1913 is the period of armed peace.
2. Who was murdered in Sarajevo and when?
Ans. Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the Austrian throne and his wife Sophia were murdered in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914.
3. Who was responsible for the murder at Sarajevo?
Ans. Gavrilo Princip, a member of the terrorist organisation ‘Black Hand’ was responsible for the murder at Sarajevo.
4. What new weapons were manufactured during the First World War ?
Ans. During the First World War many new weapons were manufactured, such machine guns and tanks, German-made submarines called U-boats, ‘poison gas’ was used for the first time as were chlorarsines, mustard gas and phosgene.
5. What was the period of the First World War ?
Ans. The period of the First World War was 19141918.
6. Which country declared war on Serbia in 1914 ?
Ans. Austria declared war on Serbia in 1914.
7. What is ‘Polish Corridor’?
Ans. According to the Treaty of Versailles (1919) a 27-mile-wide corridor through Germany was given to Poland for reaching the Baltic Sea which is known as ‘Polish Corridor.
8. When did the Paris Peace Conference meet ?
Ans. The Paris Peace Conference met in 1919.
9. Name the treaty that was concluded after the end of the First World War.
Ans. The treaty that was concluded after the First World War was the Treaty of Versailles.
10. Which treaty contained the seeds of the Second World War ?
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles contained the seeds of the Second World War.
11. Between whom was the Battle of Jutland fought?
Ans. The Battle of Jutland was fought between England and Germany.
12. In which year was the Treaty of St. Germain signed?
Ans. The Treaty of St. Germain was signed in 1919.
13. Who received the ‘Polish Corridor according to the Treaty of Versailles?
Ans. Poland received the ‘Polish Corridor’ according to the Treaty of Versailles.
14. What was the amount of reparation imposed on Germany ?
Ans. The amount of reparation imposed on Germany was 660 crore pound.
15. Who were the members of the Triple Alliance?
Ans. Germany, Austria and Italy were the members of the Triple Alliance (1882).
16. Who were the members of Triple Entente?
Ans. England, France and Russia were the members of the Triple Entente.
17. Who were the Axis powers in the First World War ?
Ans. The Axis powers in the First World War were Germany, Austria, Turkey, Bulgaria, etc.
18. Name the allied powers of the First World War.
Ans. The allied powers of the First World War were England, France, Russia, China, Japan, etc.
19. Who was the emperor of Germany when the First World War broke out ?
Ans. Kaiser William II was the emperor of Germany when First World War broke out.
20. When and between whom was the treaty of Brest Litovsk signed ?
Ans. The Treaty of Brest Litovsk was signed in 1918 between Germany and Russia.
21. In which year did Italy resign from the Triple Alliance?
Ans. In 1915 Italy resigned from the Triple Alliance.
22. What was the year of the World Wide Economic Depression ?
Ans. The year of the World Wide Economic Depression was 1929.
23. Who was the President of Paris Peace Conference ?
Ans. Woodrow Wilson, the President of America, was the President of Paris Peace Conference.
24. Where and between whom was the Treaty of Versailles signed ?
Ans. The Treaty of Versailles was signed in the city of Versailles in France between the Allied powers and Germany.
25. Which conference was called to fight the Great Economic Depression ?
Ans. The London Economic Conference was called in London to fight the Great Economic Depression.
26. Which country was held solely responsible for First World War?
Ans. Germany was held solely responsible for First World War.
27. Which day is known as ‘Black Thursday’?
Ans. 24 October 1929 is known as Black Thursday.
28. Where is the US Stock Market located ?
Ans. US Stock Market is located in New York.
29. Which day in American history is remembered as Black Tuesday ?
Ans. 29 October, 1929 is known as Black Tuesday in the history of America.
Mark True or False
1. According to the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles Germany lost Alsace-Lorraine to France.
2. The Treaty of Sevres was concluded in 1919.
3. The Polish corridor was given to Austria for reaching the Baltic Sea.
4. The port of Danzig was snatched away from the possession of Germany.
5. The Treaty of Versailles adhered to the principle of self determination.
6. The League of Nations was established with the aim to establish permanent peace.
Answers :
1. True, 2. False, 3. False, 4. True, 5. False, 6. True.
Fill in the blanks
1. Triple Alliance was formed in the year _______ (1880/1884/1882).
2. The Treaty of Versailles was opposed by _________ (Italy/Spain/Germany).
3. The Great Economic Depression of 1929 first started in __________ (Great Britain/America/ Germany).
4. _________ (Hoover/Woodrow Wilson/Clemenceau) is known as the ‘Father of the League of Nations’.
5. During the First World War the Emperor of Germany was ___________(Charles X/Kaiser William II/Kaiser William III/Frederick William III).
6. After the First World War, the humiliating treaty which was imposed on Germany was the Treaty of ________ (Brest-Litovsk/ Versailles/ Lussane/Sevres).
7. People of the Weimer Republic lost confidence in the democratic _________ (alliance/parliamentary system/values/ attitude).
8. After the First World War, the new Republican government of Germany was established in _________ (Berlin/Weimer/ Brussels).
9. The Great Depression was a period of ________(political crisis). crisis/economic crisis/religious
10. The Saar Valley was put under an international commission for ________ (13/14/ 15) years.
11. The Treaty of St. Germain was signed between the victorious allies and defeated Austria in ____________(1916/1918/1919)
12. The Treaty of ______ (Trianon/Neuilly/ Versailles) contained the seeds of the Second World War.
13. Morocco is in _______(Africa/Netherlands/China).
14. The Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis was signed in ________ (1932/1933/1934).
15. USA entered the First world war in __________ (1917/1918/1919).
16. Herbert Hoover was the President of_________ (Britain/America/France).
17. Archduke Francis Ferdinand was the heir to the throne of _____(Spain/Austria/ Herzegovina).
18. ________ (Llyod George/Woodrow Wilson/ Gorky) was called the ‘Father of the League of Nations’.
19. In _________(1928/1929/1930) the American share market crashed.
20. _________ (24 October 1929/26 October 1929/ 22 October 1939) is known as the Black Day in the history of USA.
Answers :
1. 1882
2. Germany
3. America
4. Woodrow Wilson
5. Kaiser William II
6. Versailles
7. Parliamentary system
8. Weimer
9. Economic crisis
10. 15
11. 1919
12. Versailles
13. Africa
14. 1932
15. 1917
16. America
17. Austria
18. Woodrow Wilson
19. 1929
20. 24 October 1929
Choose the best explanation
1. Statement: America joined the First World War.
Explanation (A) : American ships were destroyed by Germany.
Explanation (B) : Germany conquered America.
Explanation (C) : Germany joined France against America.
2. Statement: By the Treaty of Versailles Germany was demilitarised.
Explanation (A) : To establish balance of power.
Explanation (B) : To take control of German arms.
Explanation (C) : So that Germany could not disturb peace in future.
3. Statement: The Great Depression of 1929 was period of severe economic crisis.
Explanation (A) : Some banking policies were unsound and had led to the over expansion of credit.
Explanation (B) : Consumer goods relatively inexpensive. were
Explanation (C) : wave of strikes had paralysed the industries.
4. Statement: In 1931, Hoover Moratoriam was announced.
Explanation (A) : To save the world from economic crisis.
Explanation (B) : To provide financial assistance different European countires.
Explanation (C) : To save America’s economy.
Answers :
1. Explanation (A)
2. Explanation (C)
3. Explanation (A)
4. Explanation (A)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. The Paris Peace Conference took place in –
A. 1919
B. 1920
C. 1921
D. 1922
Ans. A
2. ‘Fourteen Points’ were put before Germany by –
A. Lloyd George
B. Orlando
C. Woodrow Wilso
D. Clemenceau
Ans. C
3. The country which did not join the League of Nations –
A. America
B. Germany
C. Spain
D. England
Ans. A
4. Lusitania was –
A. A country in Europe
B. The name of a ship
C. The name of a captain
D. The name of an island
Ans. B
5. The American President during World War I was –
A. Woodrow Wilson
B. Abraham Lincoln
C. George Washington
D. George Barlow
Ans. A
6. President Wilson belonged to –
A. Britain
B. China
C. America
D. Japan
Ans. C
7. The First World War broke out in –
A. 1912
B. 1915
C. 1913
D. 1914
Ans. D
8. The First World War came to an end in –
A. 1919
B. 1918
C. 1916
D. 1920
Ans. B
9. The Paris Peace Conference took place in –
A. 1918
B. 1919
C. 1920
D. 1921
Ans. B
10. Who of the following was most active in the establishment of League of Nations ?
A. Lloyd George
B. Orlando
C. Clemenceau
D. Woodrow Wilson
Ans. D
11. The League of Nations was formed after –
A. First Balkan War
B. World War I
C. 2nd Balkan War
D. World War II
Ans. B
12. Archduke Francis Ferdinand was assassinated in –
A. Bosnia
B. Sarajevo
C. Herzegovina
D. Poland
Ans. B
13. The Great Depression of 1929 first started in –
A. Germany
B. America
C. France
D. Spain
Ans. B
14. Which period is known as the ‘Era of Armed Peace’ ?
A. 1920-1939
B. 1871-1913
C. 1939-1945
D. 1914-1918
Ans. B
15. Sarajevo was the capital of –
A. Serbia
B. Hungary
C. Bosnia
D. Austria
Ans. C
16. In 1920 the Treaty of Sevres was signed with –
A. Russia
B. Austria
C. Hungary
D. Turkey
Ans. D
17. Where was the World Economic Conference held ?
A. Ukraine
B. London
C. Holland
D. Cuba
Ans. B
TOPIC – C
Aggressive Nationalism: Rise of Nazism and Fascism
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. What was the programme of Hitler and the Nazi Party ?
Ans. At the end of the First World War (191418) Germany was left in a state of confusion and anarchy. People were not satisfied with the republican government in Germany. There were some political groups in Germany who were opposed to the policy of the government. Among those parties was the Nazi Party led by Adolf Hitler.
The Programme of Hitler and his Nazi Party were as follows:
[1] To support one man’s rule: Hitler was a bitter opponent of the Weimer Republic and was a strong supporter of one man’s rule.
Formation of Greater Germany: Hitler’s aim was to form the Greater Germany which meant that the provinces of other European countries in which the German language was spoken should be merged in Germany.
[2] To oppose the Jews: Hitler’s aim was to organise the Greater Germany on the basis of pure blood and expel the Jews whom he considered as the enemies of Aryan race.
[3] Responsibility of the First World War: Hitler was never ready to accept that Germany was responsible for the beginning of the First World War and wanted that the blame should be removed at any cost.
[4] To oppose the Treaty of Versailles: Hitler never accepted the harsh conditions of the Treaty of Versailles and included the opposition of the Treaty as an important element in his programme.
[5] To oppose the payment of warindemnity: According to Hitler it was an act of great humiliation to Germany to pay the war indemnity and therefore Germany should not pay the reparation.
[6] To oppose the policy of disarmament: The allies compelled Germany to disarm herself. Hitler opposed this decision and wanted to increase the military power of his nation.
[7] Acquisition of old German colonies: Hitler’s programme also included the acquisition of old German colonies which had been snatched away by the allies according to the Treaty of Versailles.
[8] To take revenge in France: Hitler considered France as the greatest enemy of Germany and planned to avenge the defeat of Germany in the First World War.
2. What were the fundamental principles of Fascism?
Ans. Fascism had been established in Italy after the First World War. The founder of Fascism was Benito Mussolini. The basic and fundamental principles of Fascism were as follows:
[1] Opposition to individualism: The concept of Fascism was against individualism. Mussolini believed in the supremacy of the state and gave no importance to the interests of the people.
[2] Establishment of totalitarian state: Mussolini believed in one party and one leader for the welfare of the nation. He believed that the state was supreme to all and opposition has no importance.
[3] Opposition to democracy: Fascism is opposed to democracy. Mussolini had no faith in the majority and the public opinion. The order of the leader was the supreme law of Fascism.
[4] Opposition to communism: Communism believed that economic factor moulds the history of human development. On the contrary Fascism believed that political history moulds the history of mankind. So Fascism had no similarity with the principles of communism.
[5] Opposition to peace: Fascism was opposed to the policy of peace and supported war. Mussolini criticised the League of Nations and told that war was the only means to bring human power to success.
It is clear from the above that Fascism had some original principles which did good to the nation to a considerable extent.
3. Write a note on Spanish Civil War.
Ans. After the First World War the political, social and economic condition of Spain was not stable. In 1931 general elections were held in Spain in which the monarchists were defeated. Democratic Republican government was established in Spain. But the newly established republican government could not work successfully. General Franco attacked the republican government and overthrew it. Thus a civil war broke out in Spain.
In this civil war Italy and Germany helped General Franco. The attitude of India was different. In the Faizpur session of the Indian National Congress (1936) Jawaharlal Nehru, a leader of the Indian freedom movement, in his presidential address said that the civil war in Spain was not simply a war between Franco and the republican government or a war between Fascism and democracy. He called it a war between reactionary and progressive forces. He remarked, “The struggle today is fiercest and clearest in Spain and on the outcome of that depends war or peace in the world in the near future.”
An association was established in London by the Indians in support of the republican government in Spain. This association also raised a fund to support the republican government in Spain in 1937.
During the Spanish civil war Jawaharlal Nehru visited Spain in June 1938. In this year on 13 October Mahatma Gandhi sent a message to the Prime Minister of Spain telling him that his full sympathy was with them.
4. How was dictatorship established in Spain by General Franco ?
Ans. Dictatorship was established in Spain through different stages by General Franco.
[1] After the First World War the political, social and economic condition of Spain was not stable. In 1931 General Elections were held in Spain in which the monarchists were defeated. Democratic Republican government established in Spain. [2] But the newly established republican government could not work successfully. Political disturbances in many provinces, attempts by the monarchists to capture power, poor economic condition of the country, rise of socialism and the deficit budget were some of the problems which threatened the republican government. [3] The opponents of the republican government took full advantage of the discontent in Spain. The banner of revolt was raised by the army of Spain in Morocco in 1936 under the leadership of General Francisco Franco. He attacked the Republican Government with his army and overthrew it. Thus a civil war broke out in Spain. [4] In this civil war Italy and Germany helped General Franco, while Russia helped the Republicans. The Republicans were defeated in the civil war. In 1939 Barcelona fell into the hands of General Franco. Franco established his dictatorship in Spain.
Analytical Answer (AA) Type Questions
Answer in 7 to 8 sentences
1. Describe the problems faced by the Weimer Republic .
Ans. The problems faced by Weimer Republic were the following: [1] The infant Weimer Republic was forced to pay for the sins of the old empire. The republic carried the burden of war guilt and was financially crippled by being forced to pay compensation. [2] There was economic crisis of 1923. Prices of goods soared high. [3] There was revolutionary uprising of the Spartacist League on the pattern of Bolshevik Revolution in Russia. [4] The infant Weimer Republic was. fragile. System of proportionate representation and Article 48 gave President the powers to impose emergency, suspend civil rights and rule by decree. The Weimer Republic saw twenty different cabinets lasting on an average of 239 days and a liberal use of Article 48.
2. What was the effect of the Great Depression of 1929 on Germany ?
Ans. The Great Depression of 1929 had profound effect on Germany. The German economy was the worst hit by the Great Depression. By 1932, industrial production was reduced to 40% of the 1929 level. Workers lost their jobs or were paid reduced wages. The number of unemployed people touched an unprecedented 6 million. On the roads of Germany men could be seen with placards around their necks saying, Willing to do any work’. Unemployed young man played cards or simply sat at street corners or desperately queued up at the local employment exchange. As the young men had no jobs, they took to criminal activities.
3. How was the responsible for the rise of Nazism ?
Ans. The Great Depression of 1929 was to a large extent responsible for the rise of Nazism. The German government faced economic problems like mass unemployment and inflation. The American investors recalled their short term loans from Germany. One of Germany’s joint stocks bank collapsed in 1931. When America withdrew her loans from Germany her export trade and production declined considerably. The number of unemployed people rose. In Germany the jobless numbered 6 million.
Faced with economic crises the Germans lost their faith in the Republican Government. Within six years the working class and the middle class were ruined due to economic crash. The Nazis promised to nationalize the big businesses, provide employment for all workers and implement land reform for peasants. It is not surprising that the people turned to Nazism for remedy.
4. Briefly describe the reasons for the rise of the Nazis to power.
Ans. The reasons for the rise of the Nazis were as follows: [1] In the First World War (1914-18) Germany was defeated and the humiliating Treaty of Versailles was imposed upon Germany in 1919 and the rise of Nazis is traced to the severity of the terms imposed upon Germany by this shameful Treaty of Versailles. [2] The heavy burden of compensation imposed upon Germany brought in a host of evils like unemployment, price rise and taxation. [3] Democracy in Germany remained as weak as it could be and the suffering of the people knew no bounds. Hitler cleverly exploited the discontent of his countrymen and his theory of the superiority of the German race restored confidence in the people. [4] His oratory, uniform (Brown Shirt of the Nazi members), the swastika flag, use of violenceall together appealed to many classes of the German people. [5] The Nazis provided an outlet for the military leanings of the German youths. The German minds reacted favourably to dictatorial movements. Throughout their history the Germans have been wont to submit to the authority of one individual.’ [6] Moreover, due to the fear of a communist revolution, the opponents of communism supported the Nazis and it was under these circumstances that Nazism gained ground in German soil.
5. What were the main features of Nazi thinking ?
Ans. The main features of Nazi thinking were as follows: [1] It wanted to restore the dignity of Germany. [2] It was opposed to both democracy and communism. [3] It aimed at expansion of the German empire under the slogan, one person, one empire and one leader. [4] It was in favour of superiority of Aryan race. [5] The state is above all. [6] Depriving nonAryans from rights of citizenship and professions were important features of Nazi thinking.
6. What agencies did Hitler use to suppress all opponents and create total Nazi domination ?
Ans. Hitler used different agencies to suppress all opponents and create total Nazi domination. [1] Hitler formed a para-military force with unemployed youths known as ‘Storm Troopers’ who manhandled opposition leaders and disturbed the meetings convened by the opposition parties. [2] He also organised ‘Youth Brigade’ and ‘Girl Brigade’ who constantly shouted ‘Heil Hitler’ and silenced all criticism against him. [3] A secret police force named ‘Gestapo’ was organised the main function of which was to arrest those persons whose activities were found doubtful and against the principles of Nazism. [4] He imposed several restrictions upon the press, speech and parliamentary discussions.

Know More
The Nazis injected their hatred against Jews right from school.
◆ German children were not allowed to sit with Jewish children.
◆ German children were not allowed to play with Jewish children.
◆ Jewish teachers were dismissed from the schools.
◆ Text books of schools were rewritten with an introduction of Racial Science to justify Nazi ideas of racial purity.
◆ Hatred for the Jewish people was even popularised through maths class.
◆ Propaganda films were made to create hatred towards the Jewish people.
◆ In Nazi Germany, women who bore racially undesirable children were punished and those who produced racially desirable children were rewarded. They were given favoured treatment in hospitals. They were also entitled to concession in shops and railway fares.
◆ Aryan women who maintained contact with Jews, Poles and Russians were paraded through towns with shaved heads and blackened faces.
7. Why did Fascism rise in Italy ?
Ans. From the First World War (1914-18) Italy emerged with very little gains and there was a general feeling among the Italians that they had not been fairly treated in the Paris Peace Conference (1919). The situation in Italy became very serious when, after the war, price rose high and poverty and insufficiency stalked the land. Socialist propaganda naturally found eager ears in the Italians. Peasant revolts, strikes and labour unrest threatened the government of the day. The parliamentary system in Italy was weak and the ministers found themselves unable to control the situation. In this situation a section of the Italian middle class formed into a party called the Fascist party under the leadership of Mussolini. They organised themselves in the fashion of an army and adopted a black uniform. In 1922 Mussolini with his followers the ‘Blackshirts’ marched upon Rome, seized the government and established a Fascist government under his personal control.
8. The democratic system of administration was rooted out by Mussolini-Explain.
Ans. Mussolini had no faith in democracy. He hated democracy and according to him, the democratic government was always formed by the fools. Under Fascism, the people were expected to obey the orders of their leader. The local self-government bodies were abolished by Mussolini. Severe restrictions were imposed upon press. The democratic electoral system was overhauled. Spies were appointed all over the country to supply information. Thus dictatorship of Mussolini was established in Italy and the democratic system of administration was rooted out.
9. What were the measures adopted by Mussolini to crush his opponents?
Ans. Mussolini adopted some measures to crush his opponents. He took the following steps: [1] All political parties were banned. The cabinet system was also put to an end. [2] The local administrative bodies were suspended. [3] The police department was given unlimited powers to arrest the opponents. Members of the opposition parties were arrested and put to jail. [4] Education was imparted to the students on Fascism principles. [5] The army was reorganised on new principles. [6] Severe restrictions were imposed on press. The publication of many magazines and newspapers was prohibited.
Short Answer (SA) Type Questions
Answer in 2 to 3 sentences
1. Why was the new republican government set up in Germany after the First World War known as the Weimer Republic ?
Ans. After the defeat of Germany in the First World War there were protests from the industrialists, intellectuals and the common people. As Berlin, the capital of Germany, was a hotbed of discontent the new republican government began to function from nearby Weimer. This is why the Republic was called Weimer Republic.
Know More
As the Weimer Republic had to face too many complicated problems the situation in Germany has been called ‘The Dance on the Volcano’.
2. What was the main cause of the failure of the Weimer Republic ?
Ans. After the First World War there was an acute economic crisis in Germany. The main cause of the failure of the Weimer Republic was its inability to solve the economic crisis of the post-war period.
3. Before the Second World War what were the two anti-democratic ideals?
Ans. Before the Second World War two antidemocratic ideals were: [1] Fascism preached by Mussolini, the ruler of Italy. [2] Nazism preached by Hitler, the ruler of Germany.
4. What is Fascism?
Ans. Fascism means autocracy or dictatorship where all the powers of the state are vested in one person only and nobody can question, criticise and oppose that authority. It denies individualism, democracy and socialism.
5. What is the difference between Democracy and Fascism?
Ans. The difference between Democracy and Fascism are as follows: [1] Democracy means rule by the people. It is a form of government in which political control is exercised by the people through their elected representative. Fascism is a form of government where there is one party dictatorship ruled by an authoritarian leader. [2] In a democracy opposition plays a very important role but in Fascist government there is no opposition party.
6. Why did the people of Germany support the Nazis ?
Ans. The Great Economic Depression of 1929 had a profound effect on the Germans. Faced with economic crisis, the Germans lost their faith in the Republican government. Within six years the working class and the middle class were ruined due to economic crash. The Nazis promised to nationalise the big business, provide employment for all workers and implement land reforms for peasants. Naturally, the people turned to Nazism for remedy.
7. What kind of racial segregation was practised by the Nazis?
Ans. Once in power, the Nazis in Germany quickly began to implement their dream of creating an exclusive racial community of pure Germans by physically eliminating all those who were seen as ‘undesirable’ in the extended empire. The Nazis wanted a society of only ‘pure healthy Nordic Aryans’ who were considered ‘desirable’. This meant that even those Germans who were seen as impure or abnormal had no right to exist.
Know More
Concentration Camps: The Nazi maintained concentration camps throughout the territories they controlled. The first concentration camps were erected in Germany in 1933 immediately after Hitler became Chancellor. These camps were used to jail those who opposed Hitler’s government or were suspected to threaten it. These included trade union leaders, socialists, communists, Roman Catholics and Protestants. All Jewish people were brought to the concentration camps. People were forced to do hard labour. The weak were quickly killed or died of starvation. Some camps even had gas chambers. People would be led into the chambers in large groups only to be killed with poisonous gas. The concentration camps were places where inhuman torture was carried out every day.
8. What kind of political system did Mussolini set up in Italy ?
Ans. Mussolini established a totalitarian state with himself as ‘The leader’ or ‘Il Duce’. He controlled everything in the state, including the Fascist Party. Political liberty was abolished, censorship and espionage were introduced and all association were placed under the Fascist Party. Fascism was directed against individualism, democracy, socialism and international peace. As for the political system, majority rule was rejected in favour of dictatorial rule.
9. Who were the British and French Prime Ministers during the Spanish Civil War ?
Ans. During the Spanish Civil War the British Prime Ministers were Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain and the French Prime Minister was Leo Blum.
10. What were the four main organs of the League of Nations?
Ans. The four main organs of the League of Nations were-[1] The Assembly, [2] The Council, [3] The Secretariat, [4] Permanent Court of International Justice.
Very Short Answer (VSA) Type Questions
Answer in one sentence
1. In which year did Hitler occupy Austria?
Ans. Hitler occupied Austria in 1938.
2. Who set up a republican government after the fall of monarchy in Germany?
Ans. Fredrick Ebert set up a republic government after the fall of monarchy in Germany.
3. In which year and by whom was the ‘Rome Berlin Tokyo Axis’ signed?
Or, Mention the names of the Axis powers.
Ans. The Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis was signed in 1932 between Italy, Germany and Japan.
4. In which year was the Weimer Republic established?
Ans. The Weimer Republic was established in 1919.
5. Who was Mussolini ?
Ans. Mussolini was the leader of the Fascist Party and the dictator of Italy.
6 Who established the Fascist Party and when?
Ans. Mussolini established the Fascist Party in 1919.
7. What was the symbol of Fascist Party?
Ans. ‘Fasces’ were the symbol of Fascist Party which means a bundle of wooden stick, tied with a piece of rope.
8. Who established the Weimer Republic and when ?
Ans. The Weimer Republic was established by Friedrich Ebert in 1919.
9. Who was Friedrich Ebert ?
Ans. Friedrich Ebert was a socialist leader who established the Weimer Republic in Germany.
10. Who was Hitler?
Ans. Hitler was the leader of the Nazi Party and the dictator of Germany.
11. When did Hitler capture power?
Ans. Hitler captured power in 1933.
12. What is the full name of Nazi Party?
Ans. The full name of Nazi Party was National Socialist German Workers’ Party.
13. When and between whom was the AntiCommintern Pact signed?
Ans. The Anti-Commintern Pact was signed in 1936 between Germany and Japan.
14. What was German Parliament known as?
Ans. German Parliament was known as Reichstag.
15. Who was known as II Duce in Italy ?
Ans. Benito Mussolini was known as II Duce in Italy.
16. Which part of Poland was demanded by Hitler?
Ans. Danzig was demanded by Hitler.
17. Who was General Franco?
Ans. General Franco was the leader of the Spanish Civil War.
18. Which war is known as the ‘Little World War’?
Ans. The Spanish Civil War is known as the ‘Little World War.
19. Who formed the Popular Front in Spain?
Ans. In 1936 the Republicans, Socialists and Communists formed the Popular Front in Spain.
20. What is the Lower House of German Parliament known as ?
Ans. The Lower House of German Parliament is known as Reichstag.
21. What was the daily newspaper published by the Nazi Party?
Ans. The daily newspaper published by the Nazi Party was ‘People’s Observer.
22. What is Maginot Line?
Ans. Maginot Line, named after the French Minister of War, Andre Maginot, is a line of defence built by France in 1930s along France’s border to deter invasion by Germany.
23. What was the para-military group organised by Mussolini known as?
Ans. The para-military group organised by Mussolini is known as ‘Black Shirts’.
Mark True or False
1. The republican government in Germany after the fall of monarchy was set up by Himmler.
2. The three mottos of Fascism were Stateworship, leader worship and war-worship.
3. When Hilter invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, the Second World War started.
4. Hilter formed a para-military force with unemployed youths known as Gestapo.
5. A secret police force named Gestapo was organised by Hitler.
6. Both Nazism and Fascism were in favour of democracy.
7. The Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis was formed in 1932.
Answers :
1. False, 2. True, 3. True, 4. False , 5. True, 6. False, 7. True.
Fill in the blanks
1. ____(General France/ Mussolini/Hitler) formed the para-military force known as ‘Storm Trooper’.
2. Hitler occupied Rhineland in _________(1930/ 1936/1939).
3. The Russo-German Non-Aggression Pact was signed in _________ (1929/1939/1949).
4. Hitler considered the Germans to be the master race or _____________(Herrenvolk/ Lebensraum/Gestapo).
5. In 1922 _____(Franco/Mussolini/Hitler) captured power in Italy.
6. Mussolini occupied Ethiopia in _______(1930/1934/1936).
7. The programme of March to Rome was chalked out by _________(Nazis/Fascists/ Communists).
8. General Franco was the dictator of_______(Netherlands/Sardinia/
9. Spanish Civil War took place in _______ (1938/1937/1939).
10. _____ (Hitler/Mussolini/General Franco) came out victorious in the Spanish Civil War.
Answers :
1. Hitler
2. 1936
3. 1939
4. Herrenvolk
5. Mussolini
6. 1936
7. Fascists
8. Spain
9. 1939
10. General Franco
Choose the best explanation
1. Statement: The Spanish Civil War is known as ‘Little World War’.
Explanation (A) : World War II began in Spain.
Explanation (B) : The powerful countries of Europe were directly and indirectly involved in this war.
Explanation (C) : Spain was inhabitated by of different people ethnicities.
2. Statement: Hitler and Mussolini supported the Spanish leader Franco.
Explanation (A) : Hitler and Mussolini realized that Franco’s rebellion is beneficial for Spain.
Explanation (B) : By supporting Franco, Hitler and Mussolini sought to their strengthen dictatorial regime.
Explanation (C) : Hitler and Mussolini thought that, if they did not support Franco, he would attack them in future.
Answers :
1. Explanation (B)
2. Explanation (B)
Multiple Choice Questions ( MCQ)
1. Nazism cropped up after First World War in –
A. Italy
B. Spain
C. Russia
D. Germany
Ans. D
2. Hitler became the Prime Minister of Germany in –
A. 1931
B. 1932
C. 1933
D. 1934
Ans. C
3. Swastika was the symbol of the –
A. Nazi Party
B. Fascist Party
C. Communist Party
D. Socialist Party
Ans. A
4. Mussolini’s party came to be known as –
A. Fascist Party
B. Socialist Party
C. Nazi Party
D. Communist Party
Ans. A
5. The members of the Fascist party were known as –
A. Red Shirts
B. Brown Shirts
C. Black Shirts
D. Blue Shirts
Ans. C
6. The leader of the Spanish Civil War was –
A. Goebels
B. Hitler
C. General Franco
D. Himmler
Ans. C
7. Mussolini assumed the title –
A. Czar
B. Kaiser
C. Fuhrer
D. II Duce
Ans. D
8. Fascism rose in –
A. Italy
B. Spain
C. Germany
D. Russia
Ans. A
9. In Germany Nazi dictatorship was established by –
A. Bismarck
B. Hitler
C. Franco
D. None of the above
Ans. B
10. General Franco was the dictator of –
A. Germany
B. Italy
C. Spain
D. France
Ans. C
11. Japan withdrew from the League of Nations in –
A. 1930
B. 1931
C. 1932
D. 1933
Ans. D
12. Weimer Republic was established in –
A. Spain
B. Germany
C. France
D. Italy
Ans. B
13. The first President of Weimer Republic was –
A. Hitler
B. August Bebel
C. Friedrich Ebert
D. General Franco
Ans. C
14. The last President of Weimer Republic was –
A. Friedrich Ebert
B. Hitler
C. Drexler
D. Hindenburg
Ans. D
15. The word ‘Fuhrer’ means –
A. Prime Minister
B. Leader
C. Dictator
D. Administrator
Ans. B
16. Victor Emmanuel was the king of –
A. Italy
B. Germany
C. Spain
D. Bulgaria
Ans. A
17. The first President of the Spanish Republic was –
A. Franco
B. Chamberlain
C. Niceto Zamora
D. Victor Emmanuel
Ans. C
18 ‘Lebensraum’ means –
A. Living space
B. Leader
C. Party
D. German Parliaments
Ans. A
19. Goebbels was the Minister of Propaganda of –
A. Germany
B. Italy
C. Spain
D. Cuba
Ans. A
20. The worst sufferers in Nazi Germany were the –
A. Jews
B. Christians
C. Muslims
D. Russians
Ans. A
21. Hitler chose the war as the way out of the approaching –
A. Political crisis
B. Border crisis
C. Economic crisis
D. Religious crisis
Ans. C
TOPIC – D
Miscellaneous
Explanatory Answer (EA) Type Questions
Answer in 12 to 15 sentences
1. Give an outline of the historical events in twentieth century Europe.
Ans. In the early years of the 20th century, the political atmosphere of the European continent was quite tense. Europe was in the throes of a devastating war-the First World War (1914-18). Never before had a war been fought over an area which was nearly as wide as the world. It is one of the deadliest conflicts in history.
[1] Outbreak of First World War (1914): The First World War was fought between the Allied Powers comprising Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia and the Central Powers comprising Germany, Austria, Hungary, and Turkey. With the surrender of Germany in 1918, the First World War came to an end.
[2] Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points: As an answer to all European problems the President of America, Woodrow Wilson, came up with peace proposals known as the Fourteen Points. The defeated Germans expected a peace settlement to be based upon the Fourteen Points.
[3] Treaty of Versailles: The most important of the peace settlements that terminated the First World War was the Treaty of Versailles. This treaty imposed unjust and humiliating terms on defeated Germany. Naturally, Germany continued to nourish grievances about the treaty.
[4] Establishment of League of Nations: The next major event of 20th century Europe was the establishment of an international peace organization. That organisation was known as the League of Nations. It was established after the First World War. Its aim was to prevent armed conflict and to establish honourable and just relationship among different nations.
[5] Establishment of Fascist Party: The next historical event was the establishment of dictatorial governments in different parts of Europe. After the First World War, the situation in Italy was very serious. Prices soared high and poverty and insufficiency stalked the land. Mussolini established the Fascist party and became the dictator of Italy.
[6] Establishment of Nazi Party: The First World War and the Treaty of Versailles brought in a host of evils like unemployment, price rise and taxation. The Weimar Republic in Germany failed to solve the economic problems. Hitler fully exploited the discontent of his countrymen. He established the Nazi Party and became a dictator.
[7] Outbreak of Russian Revolution: Another epoch-making event of the 20th century was the outbreak of the Russian Revolution (1917). Various socio-political, economic and intellectual causes were responsible for the Russian Revolution. The Russian Revolution had a tremendous impact on the Russian and non-Russian nationalities. It ushered in a great socialist movement and created panic in the capitalist world. The revolution started an era of nationalist struggle against colonial rule.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here