JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 1 Power Sharing
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 1 Power Sharing
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 1 Power Sharing
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions
INTRODUCTION TO THE CHAPTER
- This chapter tells us that power sharing is very important for the smooth functioning of democracy. Power in democracy rests in the hands of people and by power sharing, we can ensure their participation in the running affairs of the country.
- Belgium is a very small country in Europe whose population is around half of the I population of Haryana and its area is also less than the area of Haryana. People residing in Belgium have to face an ethnic situation. Around 59% people speak Dutch language, 40% speak French language and 1% speak German language.
- This type of ethnic situation also exists in Sri Lanka where majority of people belong to Sinhala speakers (74%) and the Tamil speakers are in minority (18%). Tamils are divided in two groups. Original inhabitants of Sri Lanka are Sri Lankan Tamils (13%) and rest of the Tamils are those whose forefathers went over there during colonial period from India as plantation workers. Around 7% people are Christians.
- In Sri Lanka tendency of Majoritarianism exists among Sinhalas because they are in majority. That is why they took many constitutional measures to establish Sinhala supremacy. That is why a feeling of alienation came among Sri Lankan Tamils.
- In contrast to that, Belgium introduced many constitutional reforms to reduce ethnic conflict in the country and it made many arrangements that the people should live together in the country. They gave equal representation to all the groups and ensure their participation in the country’s political system.
- From these two examples it is clear that the concept of power sharing not only reduces the tension among different ethnic groups of the country but it increases peace and stability in the country. Dominance of one ethnic group can undermine the unity of the country.
- Power sharing is very much necessary because it suits to the spirit of democracy and it involves people’s participation in the government. A legitimate government is that which has enough scope of people’s participation in the power.
- Power sharing is of different types. Power can be shared among different organs of government. Power could be shared among government at different levels. Power can also be shared among different social groups and it can be shared by different political parties, pressure groups and movements.
- Power sharing is good for two reasons. First one is called Prudential because it reduces the possibility of conflict between different social groups. It is a short term arrangement and it undermines the unity of the nation. Second deeper reason is that power sharing is spirit of democracy and power should reside in the hands of the people. This reason is called as moral.
- A violent conflict between different ethnic groups of the country is known as civil war and it looks like a war due to its intensity.
IMPORTANT TERMS
- Ethnic. Any group of a nation, race or tribe that has a common cultural tradition. People of one ethnic group believes that all of them belong to a common descent because of their similar physical traits. It is not necessary that all of them belong to one religion or nation.
- Majoritarianism. A feeling in the majority community of the country that they can rule the country according to their own wishes and by neglecting the feelings and needs of minority groups of that country.
- Civil War. A violent conflict between different ethnic groups of the country which looks like a war due to its intensity.
- Regional Autonomy. Demanding independence of any particular area or demanding equal power with rest of the country.
- Community Government. The government which is elected by the people belonging to one language community and which has power related to educational, cultural and linguistic issues.
- Prudential. It is a careful calculation of all the gains and losses about any particular decision or issue. Prudential decisions are generally opposite to the decisions of moral values.
- Democracy. Democracy is the government of the people, for the people and by the people.
- Power Sharing. Sharing power by different groups or levels for the smooth | functioning of any system.
J&K class 10th Social Science Power Sharing Textbook Questions and Answers
Q. 1. What are the different forms of power sharing in modern democracies? Give an example of each of these.
Or
What are the different forms of power sharing in modern democracies ? Explain your answer with examples.
Ans. There are certain forms of power sharing in modern democracies. Actually there is no single form in all the democracies which can be given about power sharing. All the forms of power sharing are different from each other from the point of view of their structures, objectives, results, etc. Some of these forms are given below :
1. Power is shared among different organs of government, and these organs are Legislature, Executive and Judiciary. Legislature is an organ of the government which makes laws for the country. Executive is that organ which executes or implements the decisions of legislature and judiciary is that organ of the government which uses those laws. It means that judiciary uses those laws, to give punishment to law breakers, which are implemented by executive and which are made by legislature. It is so because power is shared among different organs of government so that no organ should be able to execute its power on others.
Example: Powers in our country are divided among government, bureaucracy and courts by our Constitution.
2. Power is shared among governments at different levels’. It means that in Federal system of government there is one central government which has the power to execute decisions on the whole country and there are many different provincial governments for different provinces of the country. This is known as Federal division of powers. In the same way this principle is also extended to lower levels of governments which are lower than the state governments. This is also known as vertical division of power.
Example: In India powers are divided among central government and state governments and these are divided by our Constitution.
3. Third form of power sharing is that power is shared among different social groups of the country like linguistic groups and religious groups. This method of power sharing is used in many countries to give proper share of power to minority communities. In Belgium, ‘community government’ is formed to give proper share of power to all the three major and minor linguistic groups. Some countries also have made constitutional arrangements to provide representation to socially weaker sections of the society.
Example : Community government of Belgium is an example of this type of power sharing.
4. Fourth and last form of power sharing is that the power is shared among different ENER political parties and pressure gr groups. In the multi-party system, every party contests the election to grab the power of the country and every party is free to get as many votes as it can. Any party can win majority in the election. There is a trend these days that every election brings new party to the power. Many parties also come forward to make a coalition government.
Example: In India there is a multi-party system like Congress, B.J.P., B.S.P. etc., and every party has a fair chance to contest election and win majority in the country.
Q. 2. State one prudential reason and one moral reason for power sharing with an example from the Indian context.
Or
State one prudential reason and one moral reason for power sharing with an example.
Ans. In any country, which has many ethnic, religious and linguistic groups, power sharing is very much necessary because it gives equal amount of power to every group. This is very much necessary that every group should get enough representation in running affairs of the country and it should not feel neglected. There are two sets of reasons which could be given in favour of power sharing and these are :
(i) Prudential Reason. Prudential reason of power sharing says that power sharing reduces the chances of conflict between social groups in the country where a number of different linguistic, ethnic and religious groups reside. Because the result of social conflict comes in the form of political instability and violence, this power sharing helps in a number of ways to increase the stability of political order. If any majority group of the country tries to impose its will on the minority group then it can increase the tension in the country and it increases tension in those groups. Power sharing means the joint exercise of power. If power is exercised jointly then it will become more constructive for the country in the long run. If the majority will become opressive against minority then it also brings ruin to majority as well.
(ii) Moral Reason. Second reason of power sharing is moral reason and this reason of power sharing is good for modern democracies. In democracy power is shared between them who (i) exercise the power which is vested in their hands and (ii) on whom this power is being exercised. In democracy people have the last say because they are responsible in giving and taking of power. Basic principle of moral reason says that all political parties get power in coalition government, decentralization of power, protection of rights of minority groups and everyone has the say in the decision making process.
These are the two main reasons of power sharing. Power sharing not only manages to reduce conflict between groups in a deeply divided society but it also ensures the equal representation of all the groups in the governance of the country. So prudential reason says that better results can be taken by power sharing and moral reason says that power sharing is valuable for the country.
Q. 3. After reading this chapter, three students drew different conclusions, which of these do you agree with and why ? Give your reasons in about 50 words.
Thomman-Power sharing is necessary only in societies which have religious, linguistic or ethnic divisions.
Mathayi-Power sharing is suitable only for big countries that have regional divisions.
Ouseph-Every society needs some form of power sharing even if it is small or does not have social divisions.
Ans. This process of power sharing has nothing to do with the size of the country. Any country where a number of groups based on religion, ethnicity, etc. lives, needs to have a process of power sharing. Power sharing is very much necessary in the deeply divided societies because it not only reduces the social unrest in the different groups but it increases political stability as well. Every social ethnic and religious group have its vested interests and the representation of every group is very much required to give share to their voice. Representation of every group is necessary in the working system to reduce tension and to increase belief in different groups. Political stability and maintenance of peace has nothing to do with the size of the country. They both are required in every country. So we agree with the ‘Ousept’s views that every society needs some form of power sharing even if they are small or do not have social division. Other factors which are involved in power sharing are cultural, social, regional, linguistic differences and multi-ethnicity in the country.
Q. 4. The Mayor of Merchtem, a town near Brussels in Belgium, has defended a ban on speaking French in the town’s schools. He said that the ban would help all non-Dutch speakers integrate in this Flemish town. Do you think that this measure is in keeping with the spirit of Belgium’s power sharing arrangements ? Give your reasons in about 50 words.
Ans. No, the step taken by Mayor of Merchtem is not according to the spirit of power sharing arrangement of Belgium. 59% people of Belgium speak Dutch and 40% people of Belgium speak French. His steps of banning French in town’s schools will lead to the minglement of both the groups and it will increase the sense of suspicion and distrust among the French speaking people. It is against the spirit of power sharing of Belgium because that spirit has tried to accommodate every linguistic group of Belgium in the process of power sharing so that every one could be able to live in peace with each other. This ban on French language can increase civic strife in different groups and it will lead to the division of Belgian society on linguistic basis.
Q. 5. Read the following passage and pick out any one of the prudential reasons for power sharing offered in this.
“We need to give more power to the panchayats to realise the dream of Mahatma Gandhi and the hopes of the makers of our Constitution. Panchayati Raj establishes true democracy. It restores power to the only place where power belongs in a democracy-in the hands of the people. Giving power to Panchayats is also a way to reduce corruption and increase administrative efficiency. When people participate in the planning and implementation of developmental schemes, they would naturally exercise greater control over these schemes. This would eliminate the corrupt middlemen. Thus, Panchayati Raj will strengthen the foundations of our democracy.”
Ans. Many prudential reasons are given in this passage about power sharing and these reasons are given below :
- Reducing corruption. This passage says that if the power will be given in the hands of the people then they will become responsible in taking their decisions and it will lead to reduce corruption in the country.
- Increasing Administrative efficiency. This passage says that if people will be involved in power sharing process then it will lead to increased administrative efficiency because people themselves will take their own decisions.
- Reducing middlemen. This passage says that this system will reduce the middlemen to a great extent between the people and executives and between the planning and implementation of the schemes.
Q. 6. Different arguments are usually put forth in favour of and against power sharing. Identify those which are in favour of power sharing and select the answer using the codes given below.
Power sharing:
(A) reduces conflict among different communities
(B) decreases the possibility of arbitrariness
(C) delays decision making process
(D) accommodates diversities
(E) increases instability and divisiveness
(F) promotes people’s participation in government
(G) undermines the unity of a country
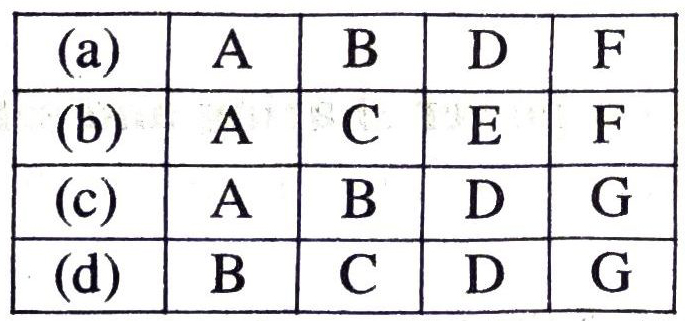
Ans. Power sharing :
(i) Reduces conflict among different communities
(ii) decreases the possibility of arbitrariness
(iii) accommodates diversities
(iv) promotes people’s participation in government.
Ans. option (a)-ABDF.
Q. 7. Consider the following statements about power sharing arrangements in Belgium and Sri Lanka.
(A) In Belgium, the Dutch-speaking majority people tried to impose their domination on the minority French-speaking community.
(B) In Sri Lanka, the policies of the government sought to ensure the dominance of the Sinhala-speaking majority.
(C) The Tamils in Sri Lanka demanded a federal arrangement of power sharing to protect their culture, language and equality of opportunity in education and jobs.
(D) The transformation of Belgium from unitary government to a federal one prevented a possible division of the country on linguistic lines.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B, C and D (b) A, B and D (c) C and D (d) B, C and D.
Ans. Option (a) is correct.
Q. 8. Match List I (forms of power sharing) with List II (forms of government) and select the correct answer using the codes given below in the lists:
| S.L. | List – I | List – II |
| 1. | Power shared among different organs of government | A. Community government |
| 2. | Power shared among governments at different levels | B. Separation of powers |
| 3. | Power shared by different social groups. | C. Coalition government |
| 4. | Power shared by two or more political parties | D. Federal government |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| (a) | D | A | B | C |
| (b) | B | C | D | A |
| (c) | B | D | A | C |
| (d) | C | D | A | B |
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Q. 9. Consider the following two statements on power sharing and select the answer using the codes given below :
(A) Power sharing is good for democracy.
(B) It helps to reduce the possibility of conflict between social groups.
Which of these statements are true and false ?
| (a) A is true but B is false |
| (b) Both A and B are true |
| (c) Both A and B are false |
| (d) A is false but B is true |
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
J&K class 10th Social Science Power Sharing Important Questions and Answers
Objective Type Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Sri Lanka emerged as an independent country in :
(A) 1946
(B) 1947
(C) 1948
(D) 1949
Ans. (C) 1948
2. Belgium was declared independent in :
(A) 1830
(B) 1842
(C) 1836
(D) 1838.
Ans. (A) 1830.
3. Beirut is the Capital of:
(A) Belgium
(B) Spain
(C) Germany
(D) Lebanon.
Ans. (D) Lebanon.
4. Which of these languages is spoken in Belgium ?
(A) French
(B) Dutch
(C) German
(D) All of these.
Ans. (D) All of these.
5. Which of these languages is spoken in Sri Lanka ?
(A) Sinhala
(B) Tamil
(C) English
(D) All of these.
Ans. (D) All of these.
6. When Sinhala language was made official language of Sri Lanka ?
(A) 1955
(B) 1948
(C) 1956
(D) 1958.
Ans. (C) 1956.
7. What percentage of Belgium population lives in the flemish region ?
(A) 40%
(B) 59%
(C) 20%
(D) 46%
Ans. (B) 59%.
8. Which of these is the part of government ?
(A) Legislature
(B) Executive
(C) Judiciary
(D) All of these.
Ans. (D) All of these.
9. Idea of community government came forward in :
(A) France
(B) Germany
(C) Belgium
(D) India.
Ans. (C) Belgium.
10. How many sets of reasons of power sharing are given ?
(A) Two
(B) Four
(C) Three
(D) Five.
Ans. (A) Two.
11. Which of these is the reason of power sharing ?
(A) Prudential
(B) Moral
(C) Both (A)&(B)
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Both (A)&(B).
12. What Percentage of Christians is in Sri Lanka ?
(A) 10%
(B) 7%
(C) 12%
(D) 15%.
Ans. (B) 7%.
13. Brussels is the capital of :
(A) Sri Lanka
(B) Nepal
(C) Belgium
(D) Vietnam.
Ans. (C) Belgium.
14. Sri Lanka emerged as an independent country in :
(A) 1946
(B) 1947
(C) 1948
(D) 1949.
Ans. (C) 1948.
15. Power sharing is good as it involves :
(A) Prudential reasons
(B) Moral reasons
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Both (A) and (B)
16. The Tamil speakers in Sri Lanka population is:
(A) 74%
(B) 18%
(C) 13%
(D) 5%.
Ans. (A) 74%.
Fill in the blanks
1. Around …………… people speak Dutch language in Belgium.
Ans. 59%
2. Around …………… people speak French language in Belgium.
Ans.40%
3. In Sri Lanka …………… are in majoritarian.
Ans. Sinhalas
4. J&K legislative Assembly consist of ………….. members.
Ans. 107
5. The major religion of Sri Lanka is ………………. .
Ans. Buddhism
True or False
1. Power sharing is a Democratic Process.
Ans. True
2. Around 95% people speak Dutch language in Belgium.
Ans. False
3. In Sri Lanka Tamil speakers are in minority.
Ans. True
4. In Sri Lanka tendency of Majoritarianism exists in Tamil because they are in majority.
Ans. False
5. Power may also be shared among different social groups.
Ans. True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Who are Sri Lankan Tamils and Indian Tamils ?
Ans. Original Tamil natives who were born in Sri Lanka are known as Sri Lankan Tamils. Indian Tamils of Sri Lanka are those Tamils whose forefathers went over to Sri Lanka as plantation workers during colonial rule. They both form around 18% population of the Sri Lanka.
Q. 2. What is Majoritarianism ?
Ans. Majoritarianism is the feeling in the majority community of the country that they can rule the country according to their own wish and they can neglect the feelings, needs and wishes of the minority group of that country.
Q. 3. What do you mean by Civil War ?
Ans. Civil War is a violent conflict between different ethnic groups of the country which looks like a war due to its intensity. It means that different groups of a country collide with each other in violent conflict due to neglectedness of interests of one group.
Q. 4. What is Power Sharing ?
Ans. Power sharing is a scheme of sharing power by different groups or levels for the smooth functioning of any system. It rests on the basic principle of giving permanent share in government to all the ethnic groups of the country.
Q. 5. What do you mean by ‘Community Government’ ?
Or
Write down the main elements of the Belgium Model.
Ans. The idea of community government came forward in Belgium where many linguistic groups are living. Community Government is the government elected by the people of one linguistic community and it has many powers related to many issues like cultural, linguistic, educational, etc. This government works jointly for the culture of common people without giving much emphasis to any group or without undermining any group.
Q. 6. What do you mean by Democracy?
Ans. In simple language democracy is the government of the people, for the people and by the people. In this system of government, people are free to elect their leaders and these leaders take decision as their representatives. People in democracy are free to elect their representatives by giving them votes and are free to express their views.
Q. 7. What are Prudential reasons ?
Ans. Prudential reasons are those reasons which are given careful thought about the gains and losses of anything. In this due care is given to calculate the gains and losses.
Q. 8. What are Moral reasons ?
Ans. If sense of right or wrong comes in any event then these are known as moral reasons. These reasons are based on the notion of right or wrong and are concerned with principles of behaviour. These decisions are practical, not psychological.
Q. 9. What are different organs of Government ?
Ans. There are three different organs of government-Legislature, Executive and Judiciary. Legislature means Parliament which makes the laws, Executive means bureaucracy which implements these laws and Judiciary means courts which uses those laws for giving punishment to law breakers.
Q. 10. What is Regional Autonomy?
Ans. Regional Autonomy is the demand of freedom by any particular regional group for their area and demand of more power in the governance of the country.
Q. 11. What is meant by Power ?
Ans. Power denotes the ability of persons or groups to fulfill their desires, or to achieve their objectives. In politics, power is usually thought of as a relationship : that is, as the ability to influence the behaviour of others in a manner not of their choice.
Q. 12. What do you mean by ethnic nationalism ?
Ans. Ethnic nationalism is a form of nationalism that is fueled primarily by a keen sense of ethnic distinctiveness and the desire to preserve it.
Q. 13. What do you mean by checks and balances system?
Ans. It is a system of power sharing arrangement in which every organ of government checks the functioning of the other and it results in balance of power among various institutions. This system ensures that no organ of the government should have excess power or unlimited power.
Q. 14. What is the Ethnic Composition of Belgium ?
Ans. Flemish speaking people (57%), French speaking people (32%), German speaking people (0.7%) live over here. 10% people in Brussels are bilingual.
Q. 15. In which year Sri Lanka emerged as an independent nation ?
Ans. Sri Lanka emerged as an independent nation in 1948.
Q. 16. How many amendments were done in Belgium constitution between 1970 & 1993 ?
Ans. Four amendments were done in Belgium constitution between 1970 & 1993.
Q. 17. Who holds an important place in power sharing ?
Ans. Political parties, pressure groups and Social Movements holds an important place in power sharing.
Q. 18. What do you mean by Ethnic ?
Ans. Any group of a nation, race, etc which has a common cultural tradition. People of one ethnic group believe that all of them belong to a common descent and have similar physical traits. People of this group identify with each other on many traits like linguistic cultural, religious, etc.
Q. 19. Write down the elements of the Belgium model.
Ans.
- Number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central govt.
- Many powers of the central government have been given to state government of the two regions of the country.
Q. 20. Write down the power sharing arrangements in modern democracies.
Ans.
- Power is divided in Legislature, Executive and Judiciary in India.
- Power is divided in centre, states and local bodies.
- In Belgium community govt. is also an example of power sharing.
Q. 21. Where is the capital of Belgium ?
Ans. Brussels the capital of Belgium is in the Flemish region.
Q. 22. What is the percentage of Christians in Sri Lanka ?
Ans. Christians are 7% in Sri Lanka.
Q. 23. What percentage of Belgium population lives in Flemish region?
Ans. 59% of the Belgium population lives in Flemish region.
Q. 24. What is Coalition Government ?
Ans. When any party is unable to get clear cut majority in Lok Sabha or State Legislative Assembly, then many parties come together to form the government which is known as the Coalition Government.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Describe the Ethnic composition of Belgium.
Ans. Belgium is a very small country of Europe whose area is smaller than the area of Indian state Haryana. Its population is around one crore which is also less than the population of Haryana. Ethnic composition of Belgium is very complex as three linguistic groups are living in it. 59% population of Belgium belongs to the speakers of Dutch language and lives around Flemish region. 40% of the total population of Belgium speaks French language and resides around the Wallonia region. Rest 1% people speaks German language. Ethnic composition of the capital city of Belgium, Brussels, is also on the same line that is 80% people speak French language and 20% people speak Dutch language. Due to this linguistic diversity there was a tension between Dutch and French speaking communities and later on government came out with new arrangements to maintain peace in the country.
Q. 2. What do you know about the Ethnic composition of Sri Lanka ?
Ans. Sri Lanka is a neighbouring country of India. It is an island nation in South Asia and is very few kilometres away from the Southern Coast of Tamil Nadu. Around 20 million people are living in it which is almost equal to the population of Haryana. Sri Lanka’s population is also full of diversity where mainly three linguistic groups are living. Around 74% population of Sri Lanka speaks Sinhala language and forms a major group of the country. 18% people speak Tamil language and these Tamil people are further divided in two groups. First one is Tamil natives means original born of Sri Lanka who are known as Sri Lankan Tamils (13%). Rest of the Tamils are those whose forefathers came from India as plantation workers during colonial rule. Around 7% people are Christians who speak both Sinhala and Tamil language. Most of the Tamils are Hindus or Muslims and most of Sinhala speakers are Buddhists. Around 8% people speak English and English language is used for many purposes.
Q. 3. What do you know about Majoritarianism in Sri Lanka of one particular group ?
Ans. Sri Lankan became independent in 1948. Sinhala community was in majority over there and that is why they tried to dominate the government. In 1956, an Act was passed to make Sinhala language as official language. Government gave a number of incentives to Sinhala people by giving them favour in government jobs and many positions. State also had tried to protect Buddhism religion. A new constitution was also adopted to promote Sinhala language and culture as Sinhala leaders were very sensitive to their culture. Due to these governmental measures, other groups started to feel alienated and due to this, struggle started between Tamil communities and Sinhala communities.
Q. 4. What was the reaction of Tamil people towards majoritarianism policies of government ?
Ans. Sri Lankan government took a number of steps to promote Sinhala people and culture. Due to these steps Tamil people felt alienated. They felt that constitution and government denied them governmental jobs, equal opportunities and equal political rights. That is why Tamils launched parties and struggle by demanding regional automony and equal opportunities in every sphere. But their demands were denied. By 1980’s many Tamil political parties were formed and they started to demand an autonomous Tamil Eelam State. Due to this a civil war was started in Sri Lanka and this struggle is going on even till today.
Q. 5. What is Power Sharing ?
Ans. Power sharing is a scheme of sharing power by different groups or levels for the smooth functioning of any system. It rests on the basic principle of giving permanent share in government to all the ethnic groups of the country. In the deeply divided societies, like India, where a number of ethnic, religious and linguistic groups are living, power sharing is very much necessary because none of the groups should feel alienated and should not stand up with arms against the state. It includes many political arrangements like equal opportunities, equal say in political affairs, etc.
Q. 6. What do you mean by Majoritarianism ?
Ans. Majoritarianism is the feeling or philosophy in the majority community of the country that they can rule the country according to their own wish and they can neglect the feelings, needs and wishes of the minority groups. The result of majoritarianism often comes in the preferential policies followed by government that it gives preference to the majority groups in governmental jobs, positions, etc.
Q. 7. Why Sri Lankan Tamils felt alienated ?
Ans. In 1956 Sri Lankan government, which was basically a Sinhalese government, introduced a number of amendments in the constitution because of which Sri Lankan Tamils felt alienated. They felt that no political party is sensitive and serious about their culture and language. Moreover through constitutional amendments and government policies they were denied equal political rights, their share in government jobs and ignoring their interests. That’s why they felt alienated.
Q. 8. Why power sharing is necessary for culturally diverse country like India ?
Or
Why Power sharing is good for democracies ? Explain.
Or
How can be power sharing is good for democratic system?
Ans. Generally large countries are bound to be culturally diverse and have strong regional traditions. This thing creates great pressure for division of power which can usually be accommodated within a unitary system. Another factor which encourage the adoption of power sharing is cultural and ethnic heterogeneity. Division of power is often an institutional response of social diversity. It also helps to reduce possibility of conflict between social groups and ensures stability of a political system.
Q. 9. What is the role of different groups in power sharing ?
Ans. Different groups play a very important role in power sharing. Different political parties, pressure groups and parliamentary institutions are very much essential for achieving the ends or objectives of power sharing. Actually all the groups should be accommodated in 0 power sharing. If it could not happen then it will be against spirit of power sharing and democracy. In this way all the groups of society get proper share in shaping government policies and thus have an important role to play in power sharing.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What is the need of Power Sharing in the country?
Or
Is it possible for a country to become powerful by dividing powers at different levels ?
Or
Why Power Sharing is desirable ?
Ans. Power sharing is very much a necessity in any country where a number of ethnic, linguistic and religious groups exist. It not only gives representation to all the ethnic, religious and linguistic groups of the country but it maintains political stability in the country as well. In the deeply divided societies like, India, power sharing is very much necessary. Every group in these types of societies has its own ambitions, wishes and they want that these wishes should be fulfilled. Resentment comes in them in the absence of fulfilment of these wishes. Examples of resentment can be seen in the form of Naxalities, terrorism of Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir, etc. So if all the groups one given fair share of power then there would be no resentment in them and they can give their full support to the progress of the country. Power sharing brings the sense of trust and belongingness among the people and it reduces the tensions in the different groups. It also brings smooth functioning to the political system of the country.
Q. 2. What was the system of accommodation started in Belgium to accommodate all the groups in the country?
Ans. Belgium is a country where three linguistic groups are living i.e. Dutch, French and German speakers. Dutch speakers are in majority (59%) and that is why tension occurred between Dutch speakers and French speakers (40%) during 1950’s and 1960’s. So Belgian leaders amended their constitution in 1970 and 1993 to bring out an arrangement of power sharing so that every one would live in harmony with each other. Some of the elements of those changes are given below :
- Provision in constitution was kept for equal number of ministers of both the groups in central government. Some laws need support of majority of members of every group that’s why no community was free to take decisions on its own.
- State governments of the two regions were given many powers of central government. State governments are not subordinate to central government and have equal powers like central government.
- Capital city of Belgium, Brussels was given a separate government and equal power was distributed in both the communities.
- One community government was also formed which is to be elected by people belonging to one language community. This government was given powers on many issues like linguistic, educational, cultural, etc.
Q. 3. Here are some examples of power sharing. Which of the four types of power sharing do these represent? Who is sharing power with whom?
Ans.
- The Bombay High Court ordered the Maharashtra state government ……… at seven children’s homes in Mumbai-In this type of power sharing Bombay High Court shares power with Maharashtra state government and in this arrangement of power sharing, it is shared by different organs of the government.
- The government of Ontario has agreed to a land claim settlement with the Aboriginal community …………and cooperation. Under this type power is shared by government of Ontario state and Aboriginal community means power sharing arrangement is between state government and community government.
- Russia’s two influential political parties………….in the next parliamentary elections. In this type two parties agreed to unite with each other to contest election to grab power. This is a coalition type of government where many parties join hands with each other.
- The Finance Ministers of various states………….distributed to various state governments. This type of power sharing can be seen in Federal type of government where power is shared by central government and different provincials or state governments.
Q. 4. What are different organs of Government ?
Ans. The most fundamental aspect of power sharing within a political system is the division of powers among different organs of the government. That’s why government’s powers are divided in three parts and these are (i) Legislature (ii) Executive and (iii) Judiciary. Their description is given below :
- Legislature. It is the first organ of the government which makes the laws for the country. Parliament and state legislative assemblies come in it. They debate on certain issues, makes laws and runs the government. M.P.’s and MLA’s are their members.
- Executive. It is the second organ of the goverment which implements or executes the laws made by legislature. Bureaucracy, different officials come under this category. They implements laws in the country.
- Judiciary. It is the third and last organ of the government. Judiciary means courts or judges. They use those laws made by legislature and orders the executive to implement those laws. Judiciary is also guardian of constitution of the country.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here