JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 2 Federalism
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 2 Federalism
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 2 Federalism
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions
INTRODUCTION TO THE CHAPTER
- Federalism is a system in which two types of governments are there. First one is a central government which has more powers and second one is of provincial governments which has less powers as compared to central government.
- Federalism has many features like-it has two levels of government, every government has its own jurisdiction, jurisdiction of every level is specified in constitution, constitution can be changed with the consent of both the levels, courts can interpret the power and can resolve the disputes between centre and states.
- Two types of Federalism are there. First one is ‘coming together federation’ where centre and states both have equal powers. Second one is holding together federations in which centre is more powerful than states.
- India is a Federal country because all the powers are divided among centre and states but centre has more powers than that of states.
- There are three types of lists given in constitution in which different subjects are given. From Union list only centre can make law, from State list, state govt. can make law and from Concurrent list both centre and state can make laws. But in case of clash of laws, central law will prevail over state’s law.
- Constitution cannot be changed very easily. It needs consent of both centre and states and it requires atleast two third majority of parliament to change.
- After 1947 many states in India were formed on linguistic bases like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana, etc. But culture, ethnicity and geography has also played a vital role in the formation of the states.
- Centre-State relations are very important in Federalism. If the governments in centre and state are of same party then there would be no strain in these relations. But if the government in centre and state is of different party then it becomes very difficult to keep cordial relations in them.
- After 1990, a big change came in Indian politics and that was the uprising of regional parties. That’s why no national party has been able to win majority in Lok Sabha of its own. That is why coalition governments came into being and this process is going on even today.
- Powers in India are decentralized. Three-tier structure of local government is there in India. The lower level is of local self government which includes panchayats, panchayat samiti and zila parishad for villages and municipal councils, municipal committee and corporations for cities. Every level has been given certain powers to carry out developmental works in its particular area.
IMPORTANT TERMS
- Jurisdiction. The official power to make legal decisions and judgements about something or the limit within which legal authority can be exercised.
- Coalition Government. When atleast two political parties come together to form an alliance to win over majority in election then coalition government comes into being.
- Federalism. System of government in which power is divided among central authority and constituent units.
- Concurrent List. A list of subjects in which both central and state governments have common interests.
- Residuary Subjects. Those subjects which are not in Union, State and Concurrent lists and union government has the power to make laws on these subjects.
- Decentralisation. To transfer power, authority, etc. from central government to local government or division of powers from higher level to lower level.
- Panchayati Raj. Rural local government is popularly known as Panchayati Raj.
- Gram Sabha. A constitutional body constituted by all the adults of the village which elects the gram panchayat.
J&K class 10th Social Science Federalism Textbook Questions and Answers
Q. 1. Locate the following states on a blank outline political map of India : Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.

Ans.
- Manipur. Manipur is the north-eastern border state and it has boundries with Myanmar.
- Sikkim. Sikkim is the state of monestries and is between the countries of Nepal and Bhutan.
- Chhattisgarh. Chhattisgarh is in central India and has been formed by dividing Madhya Pradesh.
- Goa. Goa is situated on west coast of India and is surrounded by Karnataka and Maharashtra.
Q. 2. Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline political map of the world.
Ans. 25 countries of the world are federal countries out of 192. Main Federal states of the world are U.S.A., Canada, Australia, Russia, Brazil, Argentina etc.
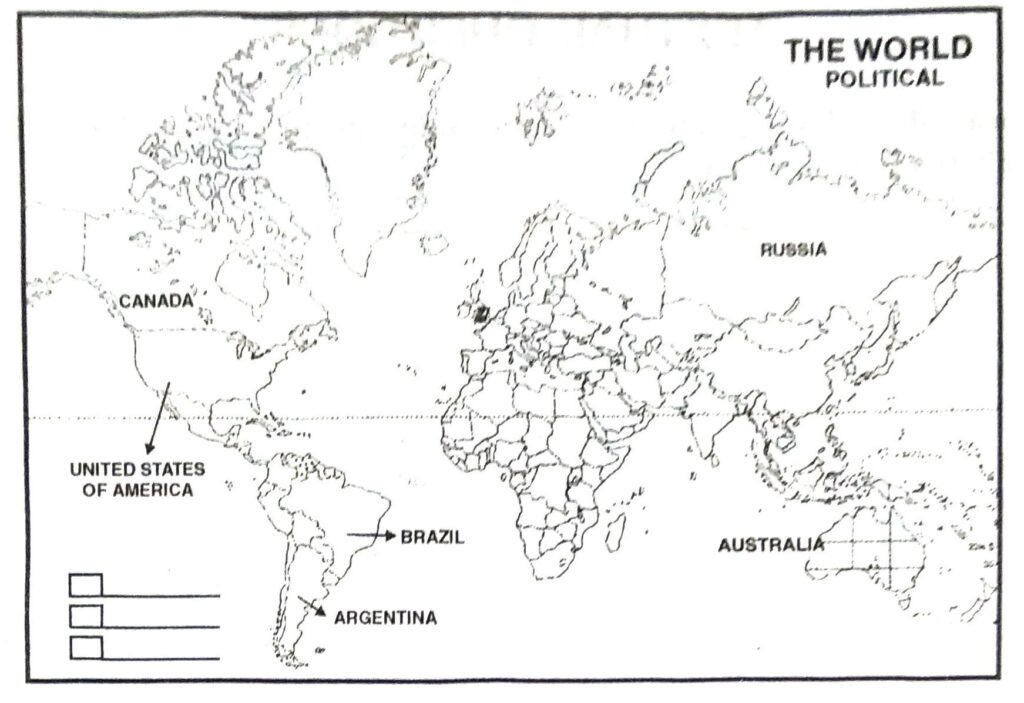
Q. 3. Point out one feature in practice of Federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Ans. Similar Feature. One similar feature in the Federalism of India and Belgium is that both the countries have federations in which two types of governments are there and out of these two governments, central government is more powerful as compared to state government.
Different Feature. Three types of linguistic groups are living in Belgium and three types of governments are there in the Belgium. First one is central government, second type is state government and third type of government is community government which is elected by people belonging to one language community and which has powers related to issues like educational, cultural, linguistic, etc.
But in India only two types of governments are there-central and state governments. There is no such community government like Belgium.
Q. 4. What is the main difference between a Federal form of government and a Unitary one ? Explain with an example.
Or
Identify the main difference between a Federal form of government and a Unitary one.
Ans. On the basis of relationship of the units with the Central governments, the government is of two types-unitary and federal government. In a unitary type of government the supreme authority is vested in the Central government but in a Federal government the authority is divided between the Centre and States. Following are the main points of differences between the two types of government.
- Firstly, in a unitary government there is a concentration of powers in the central government, whereas in a federal government powers are divided between the Centre and the Units.
- Secondly, in a unitary government the units are created for administrative convenience and they are mere parts or agents of the central government, whereas in a federation the units possess their own entities, In a federation the units derive their powers from the constitution and not from the central government and for their existence the units do not depend upon the central government.
- Thirdly, a unitary government there is single government in the country, while in a federation there is double set of government–one at the centre and the others in the units. Federation makes provsion for separate legislatures and executives for the centre as well as the units. But in a unitary government there is one legislature and one executive for the whole country.
- Fourthly, a unitary state is unity while a Federal state is only a union, not a unity.
- Fifthly, a federal constitution generally is the outcome of an government by which the constituent units create a new state for common purposes while retaining autonomous powers for themselves. Hence, such a constitution can be altered through a special method of amendment. But the constitution of a unitary government is not the outcome of a treaty. Hence the procedure of amendment is simple.
Q. 5. State any two differences between Local self government before and after the constitutional amendment in 1992.
Ans. 73rd constitutional amendment was passed in 1992. Some changes were made in constitution because Local Self governments were not working properly. Two differences between before and after constitutional amendment in 1992 are given below :
| Before 1992 | After 1992 |
|
1. Local self governments had no powers to collect taxes to meet their regular needs.
2. There were no regular elections held in local self governments.
3. There were no reserved seats for women in local self governments.
|
1. Local self governments were given some powers to collect some taxes to meet their needs.
2. It became mandatory to hold regular elections in local self governments after every 5 years.
3. 33% of total seats were kept reserved in local self governments for women.
|
Q. 6. Fill in the blanks :
Since the United States is a …………. type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are …………. vis-a-vis the federal government. But India is a ………….. type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the …………… government has more powers.
Ans. Since the United States is a Coming together type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are stronger vis-a-vis the federal government. But India is a Holding together type of federation and some States have more powers than others. In India, the Central government has more powers.
Q. 7. Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India.
Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta : The policy of accommodation have strengthened national unity.
Arman : Language based States has divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish : This policy has only helped to consolidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Ans. If we look at the given three arguments then we think the argument given by Sangeeta is the best because in Indian context the policy of accommodation have strengthened national unity.
Actually India is a multi-linguistic society in which alone 22 languages are given in Constitution. After 1947 a need was felt to reconstitute the states and after looking at all aspects, Central government has deliberately reorganized the states of India on the basis of language like Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana, etc. were formed. If these could not have been formed then the local linguistic groups could have stood up against the Central government and this could have been a danger to national unity. So the language policy followed by India has strengthened National Unity.
Q. 8. The distinguishing features of a federal government is :
(a) National government gives some powers to the provincial government.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Ans. Answer to this question is option (d) that governmental power is divided between different levels of government. We can take example of India where powers are divided in Central government, State governments and Local self governments.
Q. 9. A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below :
A. Defence; B. Police; C. Agriculture; D. Education. E. Banking; F. Forests; G. Communications; H. Trade; I. Marriages
| Union List | |
| State List | |
| Concurrent List |
Ans. Union List. Defence (A), Banking (E), Communication (G) State List. Police (B), Agriculture (C), Forests (F) Concurrent List. Education (D), Trade (H), Marriages (I).
Q. 10. Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched ?
| (a) State government | State List |
| (b) Central government | Union List |
| (c) Central and State governments | Concurrent List |
| (d) Local governments | Residuary powers |
Ans. Answer to this question is (d) that this pair is not correctly matched. It is so because state government makes laws from State List, Central government makes laws from Union List and Central and State governments both make laws from Concurrent List. But Local governments are not authorised to make any law. Power of making laws from Residuary powers rests in the hands of Central government.
Q. 11. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

Ans. Answer to this question is option (c) that is A-C-D-B.
Q. 12. Consider the following statements :
- In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial government are clearly demarcated.
- India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
- Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
- India is no longer a federation because some powers of the states have been devolved to the local government bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B and C (b) A, C and D (c) A and B only (d) B and C only.
Ans. Answer to this option is (c) that is A and B only are correct.
J&K class 10th Social Science The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Important Questions and Answers
Objective Type Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which type of government is there in Belgium ?
(A) Federal
(B) Unitary
(C) Dictator
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Federal.
2. Sri Lanka has …………. type of government.
(A) Federal
(B) Unitary
(C) Dictator
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Unitary.
3. A system of government in which powers are divided in central authority and its different constituents is known as …………
(A) Dictatorship
(B) Unitary
(C) Federalism
(D) Democratic.
Ans. (C) Federalism.
4. In Federal system of government who is more powerful ?
(A) Centre
(B) State
(C) Don’t know
(D) Can’t say.
Ans. (A) Centre.
5. The number of countries having federalism in the world is :
(A) about 25
(B) about 35
(C) about 45
(D) about 65.
Ans. (A) about 25.
6. In which year the State Reorganization Commission report was implemented ?
(A) Ist Nov, 1956
(B) Ist Nov, 1976
(C) Ist Nov, 1966
(D) Ist Nov, 1960.
Ans. (A) Ist Nov, 1956.
7. How many lists of subjects are given in Indian Constitution ?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four.
Ans. (C) Three.
8. Who makes laws from the subjects of Concurrent list ?
(A) Centre
(B) State
(C) A + B both
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) A + B both.
9. Who can make law from ‘residuary subjects’ ?
(A) State
(B) Centre
(C) A+B both
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Centre.
10. Which one of the given state has been given the ‘Special Status’ ?
(A) Punjab
(B) Uttar Pradesh
(C) Maharashtra
(D) Jammu and Kashmir.
Ans. (D) Jammu and Kashmir.
11. Which one of the given state was given the ‘Special Status’?
(A) Punjab
(B) Uttar Pradesh
(C) Maharashtra
(D) Jammu and Kashmir.
Ans. (D) Jammu and Kashmir.
12. Who is known as the Guardian of Constitution ?
(A) Supreme Court
(B) President
(C) High Court of a State
(D) Prime Minister.
Ans. (A) Supreme Court.
13. The number of languages included in eighth schedule of Indian Constitution is:
(A) 20
(B) 21
(C) 22
(D) 23.
Ans. (C) 22.
Fill in the blanks
1. Rural local govt. is popularly known as ……………
Ans.Panchayati Raj
2. Political head of ……….. Corporation is known as Mayor.
Ans.Municipal
3. …………… government is there in Belgium.
Ans.Federal
4. Sri Lanka has …………… type of government.
Ans.Unitary
True or False
1. Hindi is mother tongue of 90% people of the country.
Ans. False
2. In 1992, 73rd Constitutional Amendment was passed.
Ans.True
3. 75% seats are reserved in local government for women in India.
Ans. False
4. Centre govt. makes law from residuary subjects.
Ans.True
5. Hindi is the official language of India.
Ans.True
6. Considering languages, the most diverse country is India.
Ans.True
7. In federal system of government, state is more powerful.
Ans.False
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What is Federalism ?
Ans. Federalism is a type of government in which one central government is there for the country and different provincial governments are there. In this system central government is either more powerful than states or states have equal powers vis-a-vis central government.
Q. 2. What do you mean by Jurisdiction ?
Ans. Jurisdiction is the official power to make legal decisions and judgements about something or the limit within which legal authority can be exercised. It means that it is the particular area over which any one has legal authority or power.
Q. 3. How many and which lists are there regarding making laws in our country?
Ans. There are three types of lists regarding making laws in our country. First one is Union list on which union government is authorised to make laws. Second one is State list on which state governments are authorised to make laws. Third one is Concurrent list on which both centre and state can make laws. But in case of clash of laws, central law prevails.
Q. 4. What do you mean by Unitary form of government ?
Ans. In the unitary form of government, all powers are vested with a single central government which is supreme and powerful. The state governments act as the agents of the central government and central government can give order to state governments.
Q. 5. How are powers divided in a federal government ?
Ans. All subjects of national importance like defence, foreign affairs, post and telegraph, finance, etc. are entrusted to the centre. Similarly, subjects of local importance are delegated to the state governments. The residuary powers are entrusted to either of the two.
Q. 6. Give the names of some countries which have federal form of government and unitary form of government.
Ans. Countries with Federal government. Countries like India, U.S.A., Canada, Australia, Brazil, Argentina, Russia, etc. have federal type of government.
Countries with Unitary form of government. Countries like England, Italy, Japan, China, France, etc. have unitary form of government.
Q. 7. How many and which routes are there to form a federation ?
Ans. There are two types of routes through which federation can be formed and these two types are :
- Coming together federation. Countries like U.S.A., Australia, Switzerland, etc are included in this type of federation.
- Holding together federation. Countries like India, Russia, etc are included in this type of federation.
Q. 8. What do you mean by Union List ?
Or
Define Union List.
Ans. Union list is a list of certain subjects on which central government can make laws. Union list includes the subjects of national importance like Defence, Finance, Foreign affairs, Post and Telegrams, Banking, etc. Only central government can take decisions regarding these matters.
Q. 9. What is State List ?
Or
Define State List.
Ans. State list is a list of certain subjects on which central governments can make laws. Central government has nothing to do with it. Matters of local importance like police, agriculture, irrigation, commerce, trade, etc. are included in it. State government alone can make laws on the subjects given in this list.
Q. 10. What do you mean by Concurrent List ?
Or
Define Concurrent List.
Ans. Concurrent list is a list of subjects which are of common interest for both central and state governments. Issues like forests, education, trade unions etc. are included in it. Both central and state government can make laws on these issues. But if there is any clash of laws then the law made by central government will prevail.
Q. 11. What are residuary subjects?
Ans. There are three lists of subjects on which central and state governments can make laws. But if any other subjects do not fall in any of these three lists then what would happen? Who will make laws on those issues ? These issues are called as residuary subjects. According to our Constitution Central government can make laws on these subjects.
Q. 12. How many tier system of government are there in Federal of India ?
Ans. Originally two tier system of government was given to our country by our Constitution and these two are central government or union government and state governments which represents different states of the country. Later on a third tier of system was included in it in the form of Municipalities and Panchayats.
Q. 13. What do you mean by Union Territories ?
Ans. There are certain units in Indian Union System which have a very little power. These units or area are very small and cannot be changed into states and they also cannot be merged with other states. These are known as union territories and these are goverened, administered and cared by central governments. Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands, Dadar and Nagar and Haveli Daman and Diu, Chandigarh, Pondicherry, Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh are eight union territories in Indian Union.
Q. 14. How different governments carry out their responsibilities?
Ans. Every one carries out its responsibility with the help of its resources, funds, etc. In the same way different governments carry out their responsibilities by raising resources by levying taxes on the masses.
Q. 15. Why central government resisted to form states on linguistic lines ?
Ans. Central government later on resisted to form states on linguistic basis because some leaders felt that it would lead to the disintegration of the country and can harm the national unity.
Q. 16. What do you mean by the Decentralization of Power ?
Ans. When power is taken away from central and state governments and is distributed among local governments then it is called decentralization. In other words, decentralisation is the division or distribution of powers from higher level to local levels.
Q. 17. What is the need of Decentralization of powers in India ?
Ans. India is a vast country with a population of around 121 crores. It is not possible for central and state governments to look after every village and city due to vastness of the country. That’s why powers of administration are divided from higher level to lower for the welfare of the people.
Q. 18. What was the major step taken towards the decentralization of powers in India ?
Ans. The major step taken towards the decentralization of powers in India was the 73rd constitutional amendment. Constitution was amended 73rd time in 1992 to give more powers to local self governments so that they could be able to uplift their particular area.
Q. 19. Which are the three levels of Panchayati Raj System ?
Ans. Panchayati Raj System has three tier system. At village level there is panchayat to look after the people of the village. At block level there is Panchayat Samiti and at district level Zila Parishad is there to look after the welfare of the people of the district.
Q. 20. Who is Mayor ?
Ans. There is always a political head of Municipal Corporation in bigger cities who known as Mayor. He is generally directly elected by the people and the rank of Mayor is equivalent to the rank of Cabinet Minister in the state government.
Q. 21. Describe Gram Panchayat in brief.
Ans. Panchayats have been established in the villages. A village with a population of 200 or more than this can have a panchayat of its own. If the population of a village is less than 200 it can have a common Panchayat with some other village. All the adults of a village are the members of Gram Sabha. Gram Sabha elects members of the Panchayat.
Q. 22. In how many parts the legislative power between the union government and the state government was distributed ?
Ans. The legislative power between the union government and the state government was distributed into 3 parts.
Q. 23. What types of government are there in Federal System ?
Ans. There are two types of government in Federal System :
(i) union government, (ii) state government.
Q. 24. What is Quasi-Federal system ?
Ans. Quasi-Federal system is a political system which is not based typically on a federal distribution of power. Thus, the constitution of union is rightly regarded as Quasi-federal.
Q. 25. Languages are now included in which schedule of the Indian Constitution ?
Ans. In 8th schedue, 22 languages are given in the Indian Constitution.
Q. 26. How many countries of the world have federal ruling system?
Ans. 25 countries out of 192 countries have federal ruling system.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. How is Federalism Practiced ?
Ans.
- Every level of government has its own different powers.
- Powers of every level are clearly written in constitution.
- Harmoneous relation between centre and states.
- Decentralization should be adopted. lo poilungs
Q. 2. How Belgium was shifted from unitary to federal form of government ?
Ans. Actually in earlier times regional governments were there in Belgium. These regional governments had their own powers and roles. But central government was authorised to take back these powers. But in 1993 a drastic change was made in constitution and constitutional powers were given to regional governments. Now they were not dependent upon central government. In this way Belgium was shifted to federal form of government from unitary form of government.
Q. 3. Explain different routes to form federation.
Ans. Two types of routes are there through which federation can be formed. These two routes are given below :
- Coming Together Federation. The first route is coming together federation in which independent states come closer to each other, with their own wish, and form a bigger union. It not only pools the sovereignty but retains their identity as well. It also helps in increasing their security. In this type of federations, different units of union are also stronger vis-a-vis the union government. Australia U.S.A., etc. have this type of federation.
- Holding Together Federation. In this type of federation, powers are generally divided in union and in its constituent units. But central government is more powerful as compared to state governments. Some units have been given special powers. India, Belgium, Spain, etc. are some of its examples.
Q. 4. Why Jammu & Kashmir was given special status and which provisions were kept for it?
Ans. In the deeply divided country like India, where diverse population resides, it becomes necessary for central government to give special status some states. That is why special status is given to Jammu & Kashmir. Actually at the time of independence Maharaja Hari Singh of J&K has given sanction to merge J&K in Union of India on condition that it will be specially cared by government. And most important conflict between India and Pakistan is due to J&K. That is why according to article 370 special status is given to J&K.
Many special provisions are kept for J&K. Any person except resident of J&K, cannot buy property in J&K. Many provisions of Indian Constitution are not applicable in J&K and these provisions should be approved by state assembly.
Now article 370 has been removed and there is no special status and provisions for J&K.
Q. 5. What is the basic idea behind decentralization of powers ?
Or
What do you mean by decentralization ?
Ans. Actually India is a very large country and it is not possible for central government to look after all the problems of all the villages and towns. So the basic idea behind decentralization of powers is that many problems of local areas are there which could be best settled at local levels. People know very well about local problems. They also know that how the money could be better utilized in welfare works of local area. With this people also directly participate in decision making process. It is also on the lines of democracy. Local government can realise the problems of area and principle of democracy. So this was the basic idea behind the decentralization of powers.
Q. 6. Give some features of 73rd amendment of Constitution.
Ans. In 1992, 73rd amendment of Constitution was passed and some provisions were kept in it for local governments. Some features or provisions of this amendment are given ahead :
- Now there will be a three tier sytem in Panchayati Raj and these are Panchayat for village level, Block Samiti at block level and Zila Parishad at district level.
- Now it became mandatory to hold regular elections in all the local governments after five years.
- One third of the total seats in local governments will be kept reserved for women.
- Seats for scheduled castes, scheduled tribes and other backward classes will be kept reserved in local governments according to the ratio of their population in that area.
- Independent constitutional body state election commission will conduct fair election in all the local bodies.
Q. 7. Explain the three-tier system of Panchayati Raj.
Or
How Local Self Government works at village level ?
Ans. 73rd amendment of Constitution has provided the three tier system for Panchayati Raj. At village level the basic unit of democracy is Gram Sabha which is the sabha of all the adults of the village and this Gram Sabha elects the Panchayat and Sarpanch of a village. Panchayat looks after the needs of the village. Second level is of Block Samiti at block level and all the panchayats of the block are its members. It looks after the works done by panchayats in the block. It has one chairman, many elected and ex-officio members. Third level of Panchayati Raj is Zila Parishad at district level. All the Block Samiti’s of one district are its members. M.P., M.L.A.’s, D.C., Commissioner, etc. are its ex-officio members. It also has some elected members. Zila Parishad looks after the works done by panchayats and Block Samiti in the district.
Q. 8. What is Gram Sabha ? What are its functions ?
Ans. Gram Sabha is a Sabha of the adults of the village and it elects the Sarpanch and gram panchayat by exercising its right of universal adult franchise. Gram Sabha does a number of functions like :
- Gram Sabha elects Sarpanch, Panchayat and its members.
- Sarpanch produces budget of panchayat in Gram Sabha. It discusses about that budget.
- It decides on the developmental works being done in village.
- It can ask questions to members of panchayat about any issue of village importance.
Q. 9. What is the importance of Local Self government ?
Ans. In the democratic country like India, where a number of linguistic, ethnic and religious groups are living, local self government is very important due to following reasons :
- The matters of local interest like water supply, the cleaning and lighting of streets, maintenance of drainage system, etc. are better understood by the local residents. Hence, there is a need for local self government.
- The knowledge gained in running the administration of local affairs, proves to be a training ground for self government.
- Local functions are performed better by the local bodies at low cost.
Q. 10. Judiciary has played an important role in success of Indian federalism.’ Explain the comment.
Ans. It is right that judiciary has played an important role in success of Indian federalism. Actually powers between centre and states are divided by constitution and judiciary ensures that there should not be any crossing of limits by centre and states. It takes care that constitutional provisions and procedures should be implemented in a proper way. If any problem occurs between centre and state or between different states then judiciary acts as an arbitrator to solve that problem. All the concerned parties are bound to accept the decision of judiciary. We can say that judiciary is the guardian of Indian federalism.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Describe the key features of Federalism.
Or
Mention the major characteristics of Indian Federal system.
Or
What are the main features of Federalism ?
Ans. In the federal system, there are two types of governments central government and state governments. The central government solves the national problems and state governments solve local problems. Actually in this type of system powers are divided among central authority and the different units of that union. There is one government for the entire country and different provinces have different governments. Both levels have their own powers. Some of the main features of federalism are given below :
- Written Constitution. A written constitution is essential in a federation in the sense that both the centre and the states should be definite and about their sphere of action.
- Division of Powers. The powers of the government in a federation are distributed between the centre and the states.
- Independent Judiciary. The presence of an independent and powerful judiciary is most essential in a federation.
- Bi-cameralism. Some people are of the opinion that the legislature in a federation should be bi-cameral.
- Rigid Constitution. The constitution should be rigid so that it is not easily changed by impatient hands. The amending procedure is invariably more difficult than the enactment of ordinary laws. In almost all federal states amendments require favourable action by the parliament and a large majority of states.
- Supremacy of the Constitution. In a federation constitution is supreme both the centre and the states should run the administration in accordance with the provisions of the constitution. The supremacy of the constitution is maintained by the Supreme Court.
- Double Citizenship. In some federal states citizens enjoy double citizens. An individual is citizen of the state as well as he is citizen of the whole country.
Federation exists in U.S.A., Switzerland, India etc. India has a federal system of government having all features of a federation.
Q. 2. On what basis division of powers is made between the Union and the state governments in a federal system ?
Or
Describe the distribution of Legislative Powers between Union Government and State Government.
Or
What makes India a Federal Country? Discuss.
Ans. In our country India, Constitution has clearly demarcated the powers between different levels. Every level is given certain subjects to make laws related to its jurisdiction and they are not allowed to interfere in other’s matters. Actually this distribution is a three folded. Three types of lists are given in Constitution in which subjects are divided. These three lists and their jurisdiction is given below :
- Union List. Union list is a list of certain subjects on which Central government can make laws. Union list includes the subjects of national importance like defence, finance, foreign affairs, post and telegraph, banking, etc. Only Central government can take decisions regarding these matters.
- State List. State list is a list of certain subjects on which state government can make laws. Central government has nothing to do with it. Matters of local importance like police. agriculture, irrigation, commerce, trade, etc are included in it. State governments alone can make laws on the subjects given in this list.
- Concurrent list. Concurrent list is a list of subjects which are of common interest for both central and state government. Issues like forests, education, trade unions, etc are included in it. Both Central and state governments can make laws on these issues. But if there will be any clash of laws then the laws made by Central government will prevail. In this way powers are divided in Central and state governments in Indian federal system.
Q. 3. How is Federalism practised ?
Or
How federalism became a success in India ?
Ans. For the success of federalism, consitutional provisions are necessary but are not enough for its success. Federalism can get success only with the help of democratic policies made by government. Indian government has tried to practise federalism in India with the help of many policies which are given below :
- Formation of Linguistic States. After independence, a voice was raised to reorganize the state and govt. accepted the recommendation of commission that some states should be reorganized on linguistic basis. That is why many states were formed on linguistic basis like Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Tamil Nadu. This has increased the unity among Indian states and decreased the chances of tension among different states. With this the federalism has been practised in India.
- Language Policy. India is a multi-lingual country where people speak a number of languages. Yet Hindi is an official language but 22 languages are given in Indian Constitution. Every state is free to promote its language and culture. Any candidate giving exam of central government can give exam in any one of the prescribed language. States also have their own language. Yet in 1965, use of English language was stopped but states demanded the use of English language to continue. Central Government responded in the same way. In this way the language policy followed by federal government has united India and reduced the chances of conflict like in Sri Lanka.
- Centre-State Relations. Centre-state relations also play an important role in strengthening the practice of federalism. It is very important in a federal to keep cordial relations between centre and states. Till 1990’s Central government has always tried to dismiss the state governments if it is not of the same party. But, now this policy is not used very frequently. Now even if the parties ruling centre and state are different, they always try to keep cordial relations with each other because they both depend upon each others in one way or the other.
In this way after looking at this we can say that federalism is practised and India is a federal country which has always tried to practise federalism in a better way.
Q. 4. What are the major causes for slow progress of Panchayati Raj institutions in India ?
Ans.
- Lack of conceptual clarity. Some people treat it just as an administrative agency, some as an intention of democracy at grass root level and some treat it as a charter of rural, local government. So lack of conceptual clarity is one of the reason of slow success of panchayati raj institutions.
- Problem in functioning. There are certain problems in the functioning of these institutions. These institutions lack enough financial support, administrative support and help from bureaucracy. That’s why its success is very slow.
- Irregular Elections. It is right that 73rd amendment clearly says that elections in these institutions should be held exactly after 5 years but still irregularity is there in holding the elections.
- Relation of bureaucracy and elected representatives. Generally whole of the work of these institutions is being done by government officials and they play an important role in formulation any policy. Contradiction always comes in elected representatives and government officials because of which it progresses very slowly.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here