JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 1 India—Size and Location
JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 1 India—Size and Location
JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 1 India—Size and Location
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions
J&K class 9th Social Science India—Size and Location Textbook Questions and Answers
MAIN POINTS
● Location—A tropical country. (7th largest country in the world)
● Total Geographical Area Pentium—32,87,263 km². (2.42% of the world)
● Latitudinal extent—8°4′ North to 37°6′ North. (Northern Hemisphere)
● Longitudinal extent—68°7′ East to 97°25′ East.
● North-South extent—3214 km.
● East-West extent—2933 km.
● Southernmost tip of mainland—Kanyakumari.
● Number of States—28
● Number of Union Territories—9
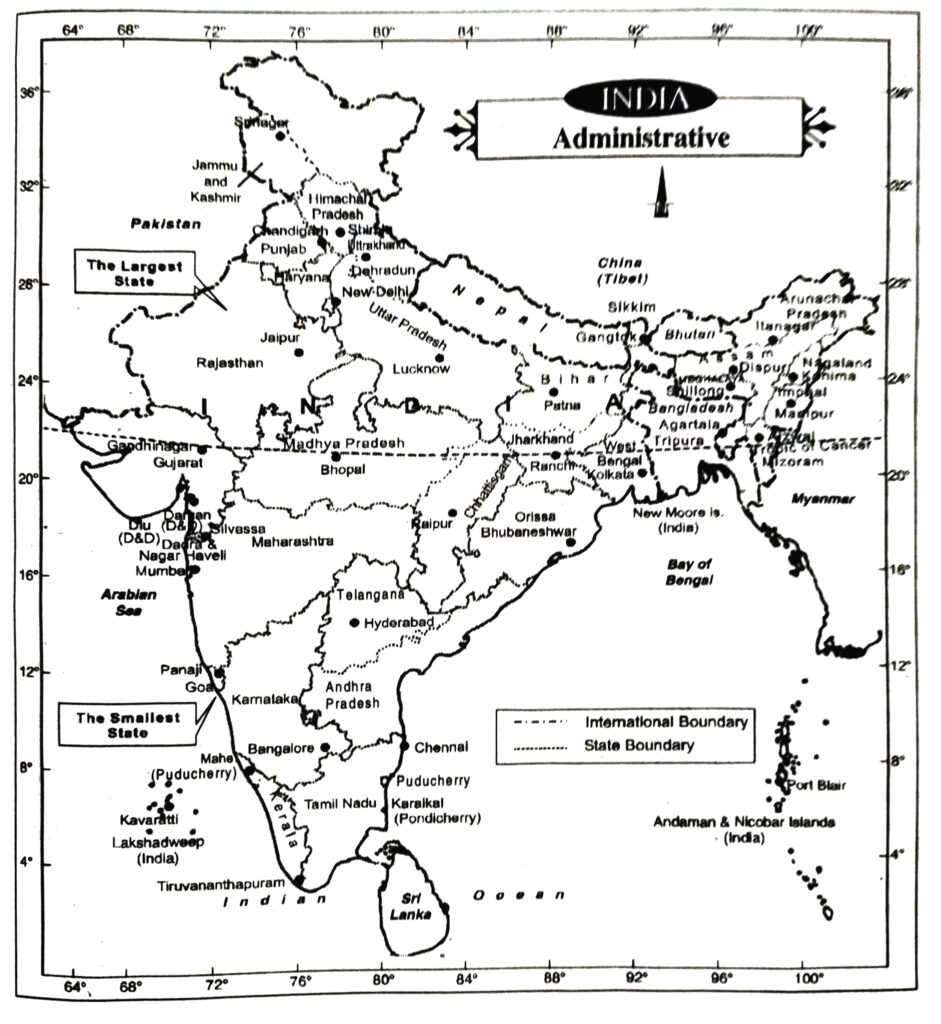
● The Largest State—Rajasthan.
● Coastline—7,516 km.
● Standard Meridian—82 1/2° East longitude.
● Southernmost point—Indira point.
● Land Frontiers—15,200 km.
● The Smallest State—Goa.
● Geographical Regions of J & K—Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh.
GEOGRAPHICAL TERMS
1. Northern Hemisphere : The area between Equator and North Pole.
2. Tsunami : Tidal waves caused due to submarine earthquake.
3. Latitude : It is the angular distance of a place from the plane of equator.
4. Longitude : It is angular distance of a place from the plane of Prime Meridian.
5. Young fold mountains : Fold mountains formed in tertiary period like Himalayas.
6. Standard Meridian : A line of longitude passing through middle of a country whose time is used for the whole country.
7. Trans-Indian Ocean Routes : Ocean routes which run through Indian Ocean from west to east.
8. Peninsula : A land mass surrounded by sea on three sides.
9. Strait : A narrow channel of sea.
10. Gulf : A shallow indented coast.
11. Tropic of Cancer : Line of latitude with a value of 23½° N.
12. Maritime : The zone connected with oceans.
13. Lakshadweep : A group of islands in Arabian Sea.
14. Indira Point. The southernmost point of Indian Union.
15. Merchandise : Goods exported to other countries.
16. Maldives : A group of islands forming southern neighbour of India.
17. Countries larger than India : Russia, Canada, U.S.A., China, Brazil and Australia.
18. Line dividing India into two equal halves : Tropic of Cancer.
19. Land locked countries. Surrounded by land on all sides.
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below :
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through :
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Odisha
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) Tripura.
Ans.— (b) Odisha.
(ii) The easternmost longitude of India is :
(a) 97°25′ E
(b) 68°7′ E
(c) 77°6′ E
(d) 82°32′ E.
Ans.— (a) 97°25′ E.
(iii) Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim have common frontiers with :
(a) China
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal
(d) Myanmar.
Ans.— (c) Nepal.
(iv) If you intend to visit Kavarati during your summer vacations, which one of the following union territories of India will you be going to :
(a) Puducherry
(b) Lakshadweep
(c) Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
(d) Delhi.
Ans.— (b) Lakshadweep.
(v) My friend hails from a country, which does not share land boundary with India. Identify the country.
(a) Bhutan
(b) Tajikistan
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Nepal.
Ans.— (b) Tajikistan.
Q. 2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea.
Ans.— Lakshadweep.
(ii) Name the countries which are larger than India.
Ans.— Russia, Canada, China, USA, Brazil and Australia.
(iii) Which island group of India lies to to its South-East ?
Ans.— Andaman and Nicobar.
(iv) Which island countries are our southern neighbours ?
Ans.— Maldives and Sri Lanka.
Q. 3. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does it happen ?
Or
State the reason for time lag between sunrise in the easternmost and westernmost horizons of India.
Ans.— India has a longitudinal extent of 30° from east to west. Due to this, there is a time lag of two hours between sunrise on the esternmost and the westernmost horizons of India. The earth takes 4 minutes to cover 1° of longitude. Therefore, in order to cover 30° of longitude, a time period of two hours is required. Hence, when it is 6 a.m. in Arunachal Pradesh, it is still 4 a.m. in Gujarat. But the clocks in all parts of India run according to the standard time measured from 82% E longitude. So, the clocks in Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat show the same time despite the difference in the time of sunrise.
Q. 4. The central location of India at the head of the India Ocean is considered of great significance’. Why ?
Ans.— India lies at the head of the Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean extends between 40° E to 120° E longitudes, with Kanniyakumari located along 80° E longitude. The Indian Ocean encloses India from three directions East, West and South. India occupies a centrally located strategic position in the Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean is the only ocean in the world named after a country. In the past, Indian culture spread towards East and South-East Asia through the Indian Ocean. Now, India is well connected to the European countries in the west and the countries of East Asia through the trans-Indian Ocean routes.
MAP SKILLS
Q.1. Show the following on the outline map of India.
(i) The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) The countries constituting Indian Subcontinent.
(iii) The states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
(iv) The northernmost latitude in degrees.
(v) The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees.
(vi) The eastern and the western most longitude in degrees.
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
(viii) The strait separating Sri Lanka from India. .
(ix) The Union Territories of India
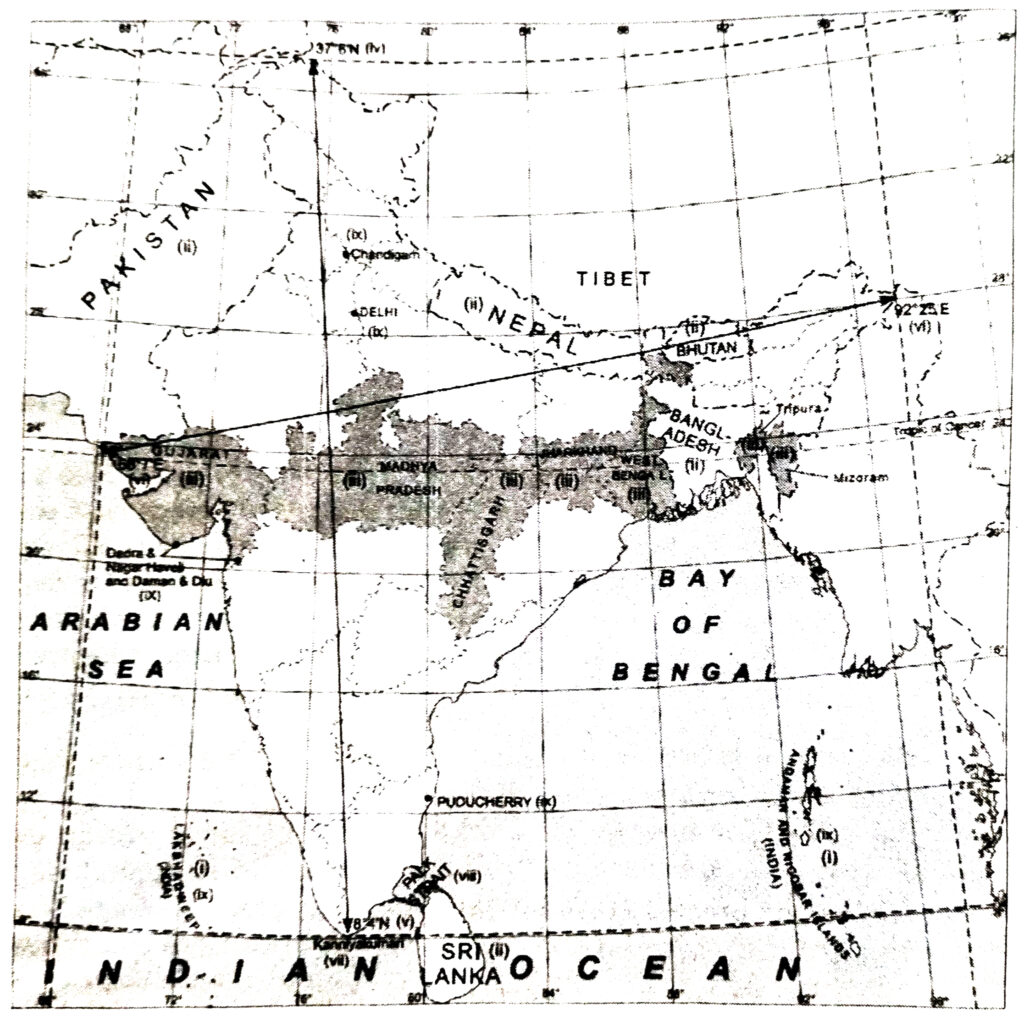
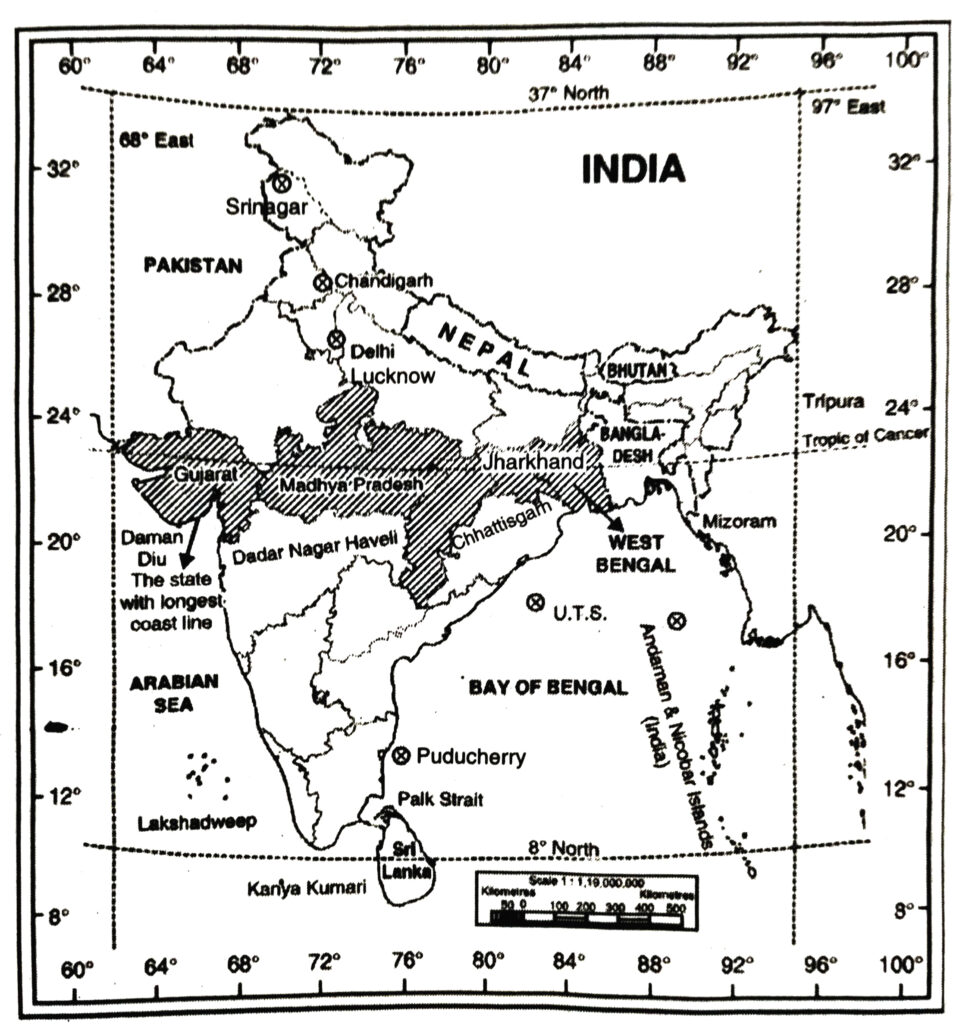
Ans.— (i) Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(ii) India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangaladesh, Sri Lanka.
(iii) Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, Mizoram.
(iv) 37°6′ N (iv)
(v) 8°4′ N
(vi) 97° 25′ E and 68° 7′ E
(vii) Kanniyakumari
(viii) Palk Strait
(ix) Chandigarh, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar.
PROJECT ACTIVITY
(i) Find out the longitudinal and latitudinal extent of your state.
Ans.— Do it yourself.
(ii) Collect information about the ‘Silk Route’. Also find out the new developments, which are improving communication routes in the regions of high altitude.
Ans.— Do it yourself.
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Objective Type Questions
I. Multiple Choice Questions
SET-I
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives :
Q. 1. India has a total geographical area of lakh km² :
(i) 32.80
(ii) 22.80
(iii) 42.08
(iv) 30.80.
Ans.— (i) 32.80.
Q. 2. Which line of latitude bisects India into two almost equal halves ?
(i) Equator
(ii) Tropic of Cancer
(iii) Tropic of Capricorn
(iv) Arctic Circle.
Ans.— (ii) Tropic of Cancer.
Q. 3. Which is the largest state of India? (as regards area)
Or
The biggest state of India in terms of area is …… .
(i) Maharashtra
(ii) Uttar Pradesh
(iii) Rajasthan
(iv) Madhya Pradesh.
Ans.— (iii) Rajasthan.
Q. 4. Suez canal was opened in the year :
(i) 1849
(ii) 1859
(iii) 1869
(iv) 1879.
Ans.— (iii) 1869.
Q. 5. The capital of Sikkim is :
(i) Dispur
(ii) Shillong
(iii) Gangtok.
(iv) Kohima.
Ans.— (iii) Gangtok.
Q. 6. India has total number of states :
(i) 18
(ii) 24
(iii) 28
(iv) 30.
Ans.— (iii) 28.
Q. 7. Where does India rank in the world ? (as regards area)
(i) Fifth
(ii) Sixth
(iii) Seventh
(iv) Eighth.
Ans.— (iii) Seventh.
Q. 8. Lakshadweep is situated in …….. .
(i) Bay of Bengal
(ii) Arabian Sea
(iii) Indian Ocean Ocean
(iv) Gulf of Cambay.
Ans.— (ii) Arabian Sea.
SET-II
Q. 1. India lies in the ………………… hemisphere. (As regards Latitudes)
(i) Northern
(ii) Southern
(iii) Eastern
(iv) Western
Ans.— (i) Northern.
Q. 2. India’s mainland extends between :
(i) 8°4′ N to 37°6’N
(ii) 9°4′ N to 38°6’N
(iii) 10°4′ N to 39°6’N
(iv) 11°4′ N to 40°6’N.
Ans.— (i) 8°4′ N to 37°6’N.
Q. 3. What is the latitude of tropic of cancer ?
(i) 21°30’N
(ii) 22°30’N
(iii) 23°30’N
(iv) 24°30’N.
Ans.— (iii) 23°30′N.
Q. 4. Andaman Nicobar islands lie in ……… .
(i) Arabian Sea
(ii) Bay of Bengal
(iii) Indian Ocean
(iv) None.
Ans.— (ii) Bay of Bengal.
Q. 5. Which is the Southernmost point of mainland of India ?
(i) Kanyakumari
(ii) Indira point
(iii) Rameshwarm
(iv) Barren Island.
Ans.— (i) Kanyakumari.
Q. 6. The mainland of India begins is to taper South of Latitude :
(i) 20°N
(ii) 21°N
(iii) 22°N
(iv) 23°N
Ans.— (iii) 22°N.
Q. 7. There is a time lag between Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh of ……….
(i) 1 hour
(ii) 2 hours
(iii) 3 hours
(iv) 4 hours.
Ans.— (ii) 2 hours
II. Fill in the Blanks
1. ………….. is a narrow channel of sea.
2. ………….. is a group of islands in the Arabian Sea.
3. ………….. is the largest Geographical region.
4. ………….. is the standard meridian of India.
5. ………….. is called the Land of Dawn.
6. …………… and ………………. states are two types of states before 1947.
7. …………… island is an active volcanic island in India.
8. ………….. is country lying in the west of J&K.
Ans.— 1. strait, 2. Lakshadweep, 3. Ladakh, 4. 82Y2°E, 5. Arunachal Pradesh, 6. Provinces, Princely 7. Barren, 8. Pakistan.
III. True/False
1. There are 22 districts in J&K.
2. There is a time lag of four hours between Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh.
3. Rajasthan is the largest state of India.
4. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands lying in the Indian Occean.
5. Gujarat state has the longest coastline.
Ans.— 1. x, 2. x, 3. √, 4. x, 5. √.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
LOCATION AND SIZE
Q. 1. What is the total Geographical area of India ?
Ans.— 3.28 million sq. km.
Q. 2. Where does India rank in the world as regards area ?
Ans.— Seventh.
Q. 3. What is the latitudinal extent of India ?
Ans.— 8°4′ North to 37°6′ North.
Q. 4. Which is the Southernmost tip of Indian mainland ?
Ans.— Kanyakumari.
Q. 5. Which place in India is situated on three Seas ?
Ans.— Kanyakumari.
Q. 6. Which is the Southernmost point of India ?
Ans.— Indira Point (Nicobar Islands). It got submerged under the sea water in 2004 during the Tsunami disaster.
Q. 7. What is the North-South extent of India ?
Ans.— 3214 km.
Q. 8. What is the East-West extent of India ?
Ans.— 2933 km.
Q. 9. Which meridian is the standard meridian of India ?
Ans.— 82°30′ East between Allahabad and Mirzapur.
Q. 10. Which line of latitude passes through the centre of India ?
Ans.— 23°30′ North (Tropic of Cancer).
Q. 11. Name the countries constituting the Indian Sub-Continent.
Ans.— India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanamar, Sri Lanka.
Q. 12. How many states are there in India ?
Ans.— 28.
Q. 13. How many union territories are there in India ?
Ans.— 8.
Q. 14. Which is the largest state of India ? (as regards area)
Ans.— Rajasthan.
Q. 15. Which is the smallest state of India ? (as regards area)
Ans.— Goa.
Q. 16. Name a state which has the longest coastline.
Ans.— Gujarat.
Q. 17. Name the Island group of India lying in the Bay of Bengal.
Ans.— The Andaman-Nicobar Islands.
Q. 18. Name the Island group of India lying in the Arabian Sea.
Ans.— The Laskshadweep Island.
Q. 19. What is the time difference between western-most and eastern most tips of India ?
Ans.— Two
INDIA AND THE WORLD
Q. 1. Which state is called “The Land of Dawn’ ?
Ans.— Arunachal Pradesh.
Q. 2. Which channel separates India from Sri Lanka ?
Ans.— Palk Strait and Gulf of Manar.
Q. 3. Name a U.T. whose area is found on both the Eastern Coast and Western Coast.
Ans.— Puducherry.
Q. 4. Name an active volcanic island in India.
Ans.— Barren island near Nicobar island.
Q. 5. Name the continents bordering Indian Ocean.
Ans.— Africa, Asia, Australia and Antarctica.
Q. 6. Name the states which do not have an international border or lie on the coast.
Ans.— Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Haryana.
Q. 7. What is the effect of tapering shape of Indian peninsula ?
Ans.— It divides the Indian Ocean into two seas-Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
Q. 8. With which countries India shares its land boundaries ?
Ans.— With Pakistan and Afghanistan (North-west), China (Tibet) Nepal, Bhutan (North), Myanmar and Bangladesh (East).
Q. 9. Which group of Islands was submerged under sea during Tsunami of 2004 ?
Ans.— Andaman-Nicobar Islands.
Q. 10. Name two types of states before 1947.
Ans.— (i) Provinces (ii) Princely states.
Q. 11. Name two routes by which India is connected with Europe and North America.
Ans.— Cafe of Good Hope and The Suez Canal.
J&K
Q. 1. Name two countries bordering J&K in the North.
Ans.— China and Afghanistan.
Q. 2. Name a country lying in West of J&K.
Ans.— Pakistan.
Q. 3. Name two states lying South of J&K.
Ans.— Punjab and Himachal.
Q. 4. Name two regions of J&K.
Ans.— Jammu, Kashmir.
Q. 5. What is longitudinal extent of J&K ?
Ans.— 32° 17’N to 37°6’N.
Q. 6. What is the latitudinal extent of J&K ?
Ans.—73° 26′ E 80°30′ E.
Q. 7. Name the Capital of J&K.
Ans.— (i) Summer-Srinagar (ii) Winter-Jammu.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What is a sub-continent ? Which countries make the Indian subcontinent ?
Ans.— A sub-continent is a vast independent geographical unit. This land mass is distinctly separated from the main continent. India is a vast country. It is often described as “Indian sub-continent”. The great mountain wall of Himalayas isolates these countries from the mainland of Asia. India forms the core of the sub-continent.
The following countries are included in the Indian sub-continent :
(i) Pakistan is in the North-West. (ii) Nepal is in the North. (iii) Bhutan is in the North-East. (iv) Bangladesh is in the East. (v) Sri Lanka is in the South.
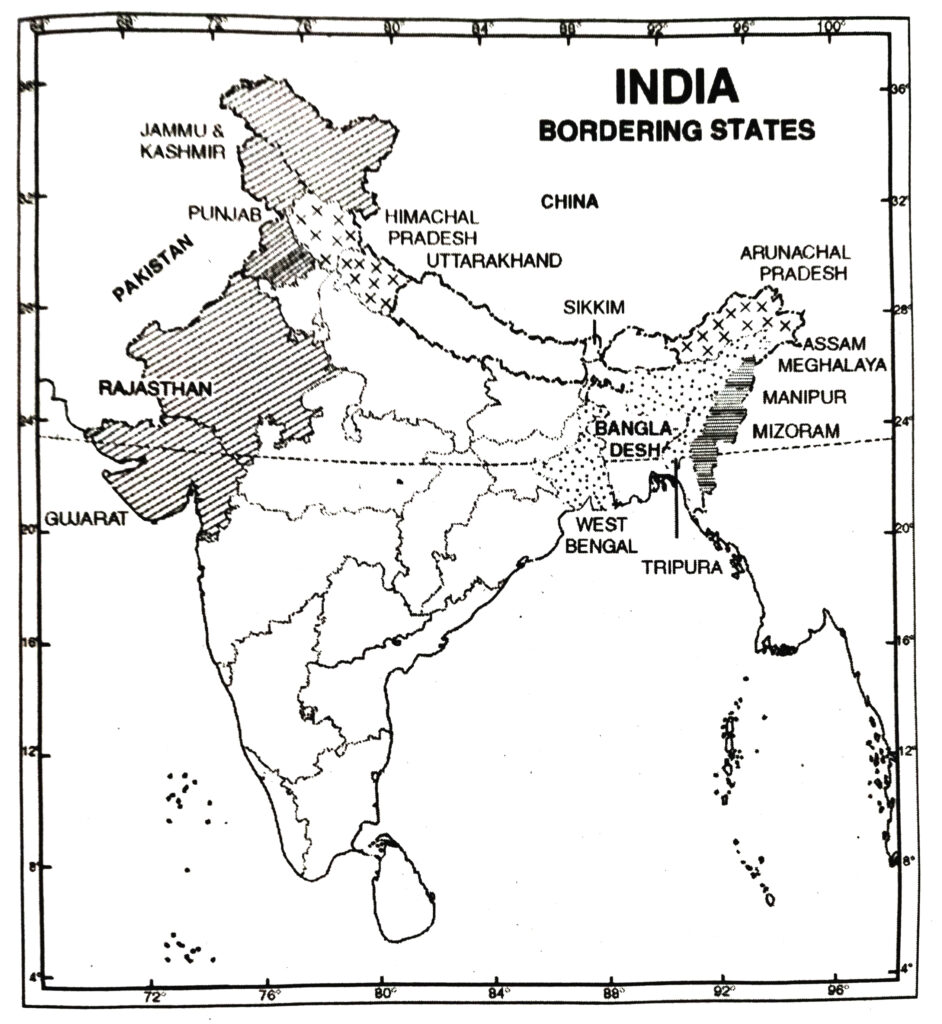
Q. 2. Classify the states of India in four groups each having common frontiers with (i) Pakistan (ii) China (iii) Myanmar (Burma) (iv) Bangladesh.
Ans.— States with common frontiers are :
(i) Pakistan : Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
(ii) China : Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
(iii) Myanmar : Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh.
(iv) Bangladesh : West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
Q. 3. Name the States and Union Territories from north to south situated on the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Ans.— There are six states on the Arabian Sea :
(i) Gujarat, (ii) Maharashtra (iii) Karnataka (iv) Kerala (v) Goa (vi) Tamil Nadu.
The Union Territories are : (i) Daman and Diu (ii) Dadra and Nagar Haveli (iii) Lakshadweep.
There are four states along the Bay of Bengal :
(i) Tamil Nadu (ii) Andhra Pradesh (iii) Orissa (iv) West Bengal.
The Union Territories are : (i) Puducherry (ii) Andaman & Nicobar islands.
Q. 4. Name the place situated on three seas. Name the island groups in the Arabian sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Ans.— The southernmost tip of mainland of India, Kanyakumari is situated on the following three seas : (i) The Arabian Sea (ii) The Indian Ocean and (iii) The Bay of Bengal.
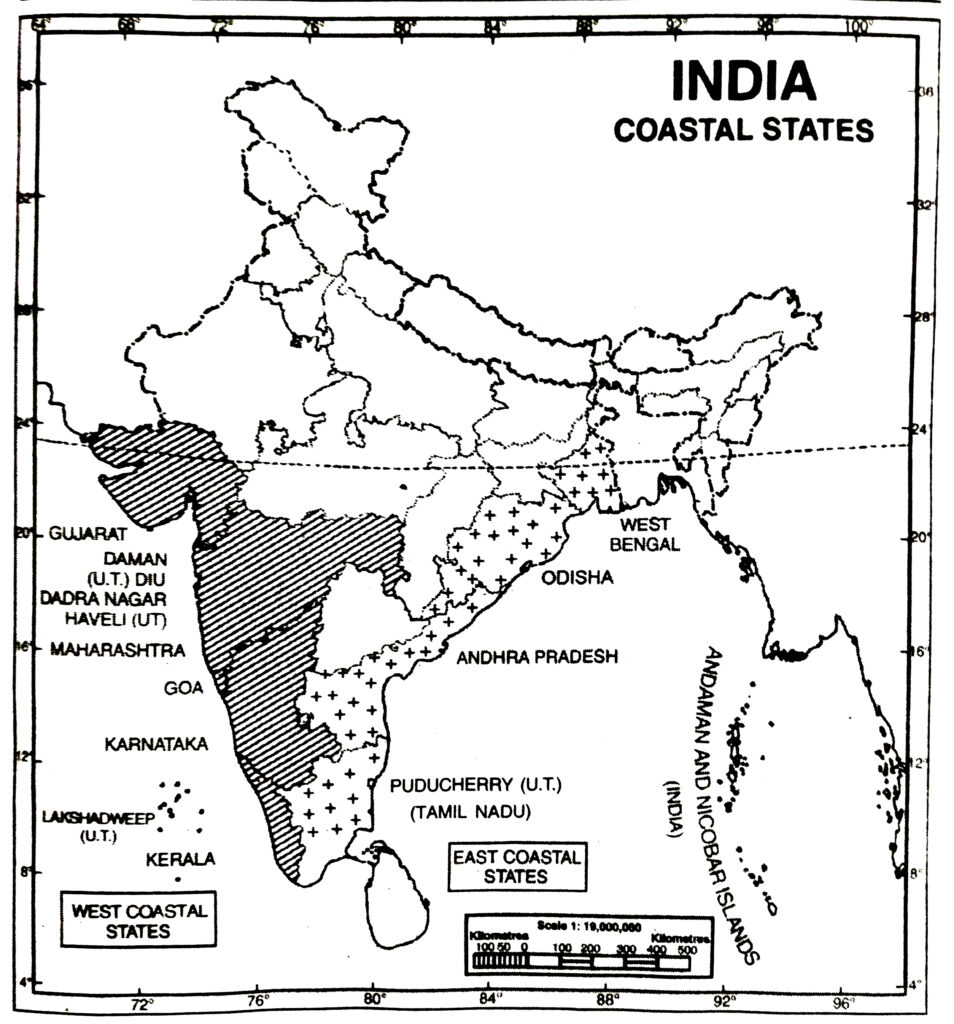
(i) The Bay of Bengal has Andaman group of islands and Nicobar group of islands.
(ii) The Arabian Sea has Lakshadweep group of islands (Coral islands). India has a total of 247 islands out of which 204 lie in the Bay of Bengal.
Q. 5. ‘India is a vast country.’ Support the fact with three facts.
Ans.— India is a vast country. It is the seventh largest country of the world. It has a latitudinal and longitudinal extent of about 30°. Its area accounts 2.4 per cent of the total geographical area of the world. India has central location in the Indian Ocean.
Q. 6. What are the implications of the great north-south extent of our country ?
Or
What is the latitudinal extent of India ? What are its implications ?
Ans.— Latitudinal extent of India. (8°4’N to 37°6’N). India’s main land extenda between 8°4′ North and 37°6 North latitudes. North-south extent is 3214 km. which is 1/12th of the total circumference of the earth. Implication. (1) Due to this, the southern parts of India have overhead sun for most of the year and get more insolation. (ii) The southern parts have almost equal days and nights. (iii) But in the northern parts, days are longer than nights in summer because of inclination of this part towards sun.
Q. 7. What is the longitudinal extent of India ? What are its implications ?
Ans.—Longitudinal extent of India. (68°7′ E to 97° 25′ E). India extends between 68°7’E to 97°25′ E longitudes. The East-West extent is 2933 kms. which is roughly 1/12th of the circumference of the earth. Thus India has a longitudinal extent of about 30° longitudes. Implications. (1) There is a time lag of 2 hours between the sunrise in the easternmost and the westernmost horizons of India. (ii) It means that the sun takes two hours to rise in Saurashtra after it has risen in Arunachal Pradesh.
Q. 8. Distinguish between the following :
Ans.— Continent and Sub-continent.
| Continent | Sub-Continent |
| 1. A continent is a vast land mass continent, that stands as a separate physical unit such. as Asia | 1. A sub-continent is a part of continent an independent geographical unit, distinctly separated from the main continent such as India |
| 2. Asia is a continent | 2. India is a sub-continent. |
Q. 9. Where does India rank in area among the countries of the world ?
Or
List six countries of the world bigger than India. Compare the area of India and China.
Ans.— India is the seventh largest country in the world occupying about 2.2% of total geographical area. Countries larger than India in size. (i) Russia (ii) Canada (iii) China (iv) U.S.A. (v) Brazil and (vi) Australia are the six countries which are larger in size than India.
Area and Population of Main Countries
| S.No. | Name of the country | Area (Million sq. kms.) | Population (millions) |
| 1. | Russia | 17.07 | 290 |
| 2. | Canada | 9.97 | 26 |
| 3. | China | 9.59 | 1277 |
| 4. | U.S.A. | 9.36 | 245 |
| 5. | Brazil | 8.51 | 150 |
| 6. | Australia | 7.68 | 20 |
| 7. | India | 3.28 | 1210 |
China, (the third largest country) is almost three times as large as India (the seventh largest country).
Q. 10. ‘India is neither a Pigmy nor a Giant.’ Discuss.
Or
‘India is a vast country.’ Discuss.
Ans.— India is not a giant country like Russia and U.S.A. Examples. (i) Russia is about six times as large as India. (ii) U.S.A. and China are thrice as big. But India is not a small country either. Examples. (i) It is as big as Europe. (ii) It is 13 times as large as Britain. (iii) It is 9 times as large as Japan. (iv) It is six times larger than France. (v) It is 23 times larger than Bangladesh. It has rightly been said, “India is neither a pigmy nor a giant.”
Q. 11. State briefly three facts about the favourable location of India.
Ans.— Location. (i) The Tropic of Cancer (23½° N) runs almost through the centre of the country. (ii) It is situated in the realm of South Asia. India’s geographical location is favourably important for international trade and commerce. (iii) Suez Canal and Cape of Good Hope routes connect India with Europe, North America and South America.
Q. 12. Why is India called a sub-continent ?
Ans.— India stands as a sub-continent in South-Asia. The natural frontiers of India provide an isolated character to the vast Indian landmass. The Himalayas in the North, the Indian Ocean in the South, thick and dense forests on the East, and Thar desert on the West separates it from the main continent. These enclose India and practically give it an independent character.
Q. 12. (A). Describe the land and water frontiers of India.
Ans.— India has a land border 15,200 km long and a long coastline forming water frontiers of 7,516 km.
(i) The great mountain wall in the North is a natural boundary between China and India.
(ii) Thar desert and Punjab plains form the western border with Pakistan.
(iii) A series of mountain ranges form the boundary with Myanmar; the Ganges delta forms the boundary with Bangladesh.
(iv) The Arabian Sea, Indian Ocean and Bay of Bengal form the water frontiers of India.
Q. 12. (B). “The opening up of Suez Canal in 1869 proved to be a great advantage for India.” Write in your own words.
Ans.— The opening up of Suez Canal in 1869 proved to be a great advantage to India as :
(i) It reduced the distance between India and Europe by 7000 km.
(ii) Most of the Indian foreign trade began to carry out through Suez Canal.
(iii) It helped in maintaining India’s trade relations with the European countries.
Q. 12. (C) (a) Name the Indian place situated on three seas.
(b) Justify the naming of Indian Ocean after India.
Ans.— (a) Kanyakumari
(b) India lies at the head of Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean extends between 40°E longitude to 120°E longitude, with Kanyakumari located along 80° longitude. It encloses India from three directions-West, South and East. South Indian culture has spread towards the East and South-East Asia due to the Indian Ocean.
Q. 13. What is the location of the Tropic of Cancer ? What are its implications ?
Or
Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts, Discuss.
Ans.— The Tropic of Cancer (23½° N) runs almost through the centre of the country being 15° away from either end. It divides the country into almost two equal halves :
(i) Sub-tropical zone-The Northern India.
(ii) Tropical zone-The Southern India.
Implications. (i) Thus India is considered a tropical country of the Northern Hemisphere.
(ii) The climate of India is dominated by tropical monsoons.
(iii) The sun’s rays never fall vertically in the areas north of tropic, but the southern areas experience overhead sun twice a year.
Q. 14. What is the effect of latitudinal extent on length of day in different parts of the country ?
Ans.— India has a latitudinal extent of 30° almost 1/12th of the circumference of the earth. It affects the Ealtitude of sun and inclination of sun’s rays. The difference between length of day and night is above 6 hours in Kashmir. But the days and nights are almost equal in Kerala.
Q. 15. Reason out why the difference between the duration of day and night is hardly felt at Kanyakumari, but it is not so in Kashmir.
Or
“The latitudinal extent influences the duration of day and night.” Explain.
Ans.— The North-South extent affects the length of day and night in different parts of India. Kanyakumari (8°N) is close to the equator. Here the sun is almost overhead all the year round. With the result, the days and nights are equal. The maximum difference between the length of day and night is hardly 45 minutes. But in Kashmir (37°N), the rays of the sun are always oblique. The difference between the length of day and night is as large as five hours. Days are longer than nights, due to the inclination of this part towards the sun.
Q. 16. What are the main features of Political division of India ?
Ans.— (i) The republic of India is a union of states.
(ii) India is the largest democracy in the world.
(iii) India comprises of 28 states and 9 union territories.
(iv) Rajasthan is the largest state of India.
(v) Goa is the smallest state of India.
(vi) There are nine coastal states and U.T.’s on the west coast, while east coast has 6 states and U.T.’s.
(vii) M.P. is located in the heart of the country and surrounded by land boundaries of five states. Assam, in the North East, is also surrounded by five states.
(viii) The state of Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh do not touch either any international boundary or the sea.
Q. 16. (A) “India has achieved multifluid socio-economic progress during the last five decades.” Write any three arguments in support of this statement.
Ans.— (i) India has moved forward displaying remarkable progress in almost all the fields.
(ii) It has developed agriculture with the help of Green Revolution.
(iii) It has set up new industrial complexes and progressed in Technology and I.T.
Q. 16. (B) ‘India has contributed significantly to the making of world history.’ Give two facts.
Ans.— (i) India is one of the ancient civilisations of the world. Indus valley civilisation is one of the ancient civilisations.
(ii) The Aryans settled in India. The traders, invaders, scholars entered India and returned after gaining a lot of knowledge.
Q. 16. (C) Why is I.S.T. 5 hours ahead of G.M.T. ?
Ans.— G.M.T. is measured from Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) while I.S.T. is measured from 82°30′ longitude. There is a difference of 82°30′ longitude between the two meridians.
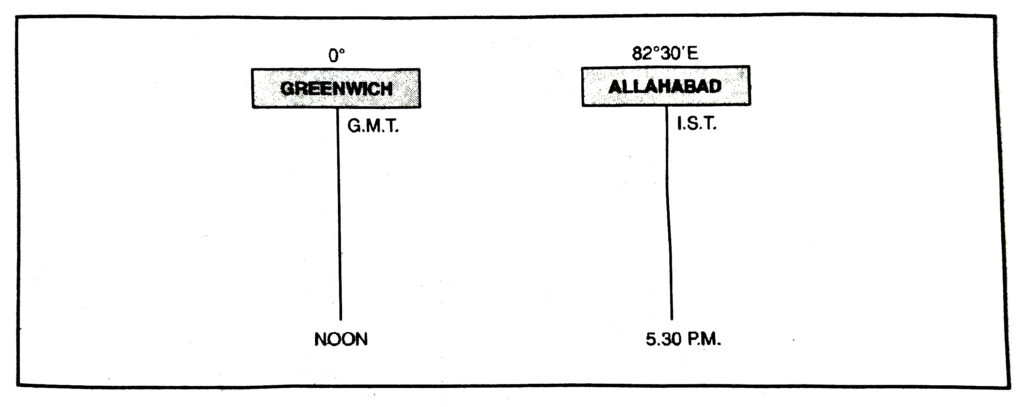
For a difference of 1° longitude, difference in time = 4 mts.
” ” ” 82º ” ” ” = 165/2 × 4 mts. = 330 mts. = 5 hrs. – 30 mts.
As India lies in the East, therefore, I.S.T. is 5%2 hours ahead of G.M.T.
Q. 17. Describe the political division of India.
Ans.— The Republic of India is called the Union of States. India is the largest democracy in the world. It comprises 29 States and 7 Union Territories. Some details about the States and Union Territories are given below :
AREA, POPULATION AND DENSITY OF STATES AND UNION TERRITORIES (2011)
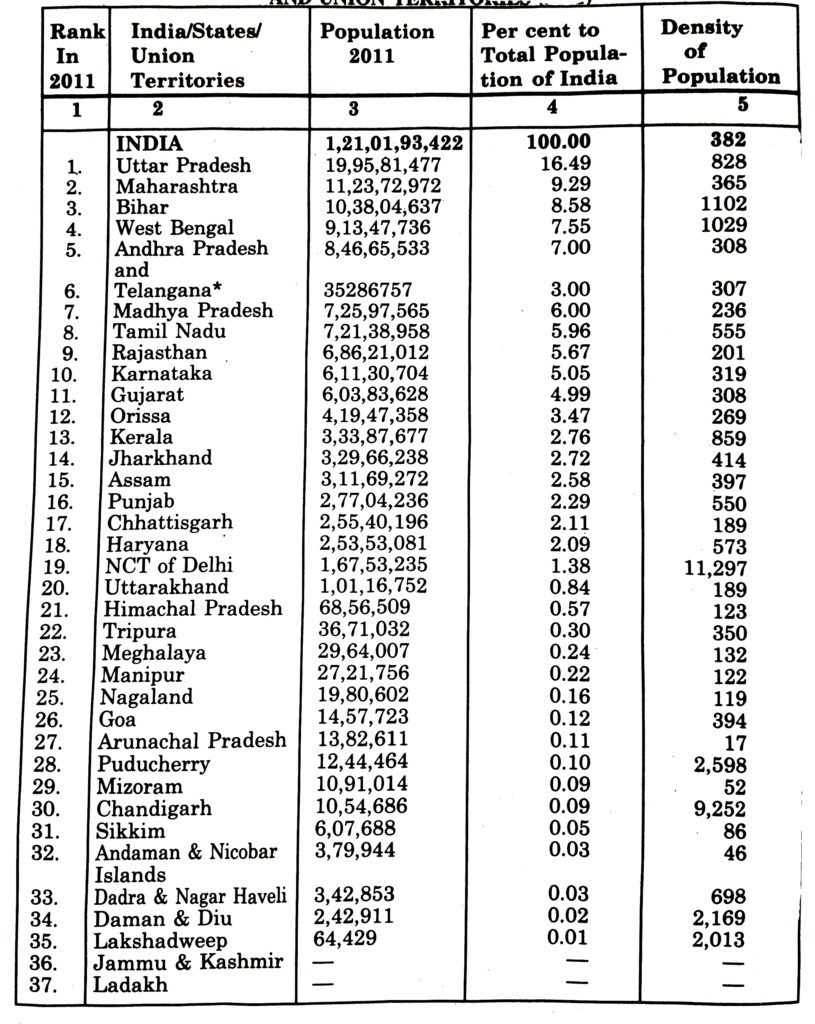
* Telengana is a new state and now India has 28 States and 9 Territories.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Describe how geographical features of the country have fostered unity and homogeneity in the Indian society.
Ans.— The vastness of India has produced a diversity in the physical conditions of the country. But there is a fundamental cultural unity behind all this diversity. Indian culture has developed independently. The land frontiers and the water frontiers have given a partially enclosed character to the Indian sub-continent.
The following two features have fostered a unique homogeneity in the Indian civilization :
(i) The unbroken chain of lofty mountains in the north has isolated India from the rest of Asia. It has played a great unifying role in strengthening our people.
(ii) The vast expanse of Indian Ocean has separated India as an independent unit. The Indian Ocean has provided our links with countries of West Asia and South East Asia.
Q. 2. Explain that the exchange of ideas and goods from India dates back to ancient times.
Or
‘India had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours.’ Explain giving examples.
Or
India’s strategic location on the head of the Indian Ocean had helped her in establishing land and maritime contacts with the outside world in the ancient and medieval times. Explain.
Ans.— India has been linked with S.E. Asia, West Asia, Africa, Central Asia. Indian culture spread to many distant countries such as Indonesia, Bali island, Cambodia and Egypt. These cultures also had an impact on the Indian culture.
(i) The Indian culture spread to distant lands through ocean routes of the Indian Ocean. The muslin, spices, were sent to other countries.
(ii) The mountain passes in the north provided many openings and transport facilities for the outsiders.
(a) The pastoral nomads entered India through the mountain passess of Khyber and Bolan. “
(b) The Buddhist Bhikshus crossed into Tibet, China and Japan to carry their message of peace.
(c) Alexander invaded India through these mountain passes and brought Greek sculptures, domes, and minarets to India.
(d) Indian merchants had trade links with Central Asia, Afghanistan and Iran through these routes.
(e) The Mongols, Turks, Arabs and Iranians came as conquerers and settled down in India. They took back the Indian numerals, the decimal system and the ideas of the Upanishads to their countries.
This give and take, this exchange of ideas, goods and art have enriched the Indian culture.
Q. 3. Describe the importance of Geographical location of India.
Ans.— 1. Central Location : India is centrally located in the Eastern Hemisphere.
2. Trade Routes : India is favourably located for international trade. Many trade routes pass through the Indian Ocean.
3. Nearness to Tropic of Cancer : The tropic of cancer passes through the centre of India. So India is a tropical country. The long growing season makes India an agricultural country.
4. Long Coastline : India has long coastline which provides many deep, protected and natural harbours.
5. Defence : The natural boundaries are favourably located from defence point of view.
6. Effect of Indian Ocean : The Indian Ocean leads to the origin of rain giving monsoons.
7. Effect of Himalayas : The unbroken chain of Himalayas acts as a climatic barrier. It forces monsoons to give rainfall and protects northern India from cold polar winds.
Q. 4. Describe the area, extent and neighbouring countries of J&K and Ladakh territories.
Ans.— Area. A part of the territory is held by China and a part by Pakistan. Presently geographical area of the territory with India is only 101387 sq. km.
Geographical Regions.
It is divided into three geographical regions. The Percentage area of each region is given below :
Jammu : 19%
Kashmir : 11%
Ladakh : 70%
Total : 100%
Extent :
It is about 425 kms from North to South and extends over 520 kms from East to West. The locational setting of the State is :
Latitudes : 32°17′ – 37º 6’N
Longitudes : 73°26′ – 80° 30’N.
Standard Time
20 The standard time of the part of the state with India is 5½ hours ahead of GMT whereas the Pak held part is only 5 hours ahead of GMT. This means that there is difference of 30 Minutes between the two parts of the state.
Neighbouring countries.
The countries bordering the state are: Pakistan, Afghanistan & China. The state of Punjab & Haryana are the neighbouring states.
Regions
It is divided into three distinguished physical regions of Jammu, Kashmir & Ladakh Ut’s with varied culture, language, climate, settlements, soils, flora and fauna and the way of life. People of different religions live amicably here.
Q. 5. Describe the districts of three main regions of J&K.
Ans.— The three main region of J&K are Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh Ut’s.
Ladakh is the largest
Jammu Region
1. Jammu
2. Kathua
3. Samba
4. Udhampur
5. Reasi
6. Rajouri
7. Poonch
8. Doda
9. Ramban
10. Kishtwar.
Kashmir Region
1. Anantnag
2. Kulgam
3. Pulwama
4. Shopian
5. Budgam
6. Srinagar
7. Ganderbal
8. Bandipora
9. Baramula
10. Kupwara.
Ladakh Territory
1. Leh
2. Kargil.
Q. 6. Explain the time lag between the sunrise in the easternmost and westernmost horizons of India.
Or
“When the sun has already risen in Arunachal Pradesh, it is still night in Gujarat.” Explain. (Important)
Or
The sun rises two hours earlier in Eastern parts of Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the West but the watches show the same time. How does it happen ?
Ans.— India has a longitudinal extent of 30°. Due to this there is a time lag of two hours between the sunrise on the easternmost and the westernmost horizons of India. Due to rotation, the earth takes 4 minutes to rotate through 1° of longitude. The difference in time is one hour for 15° of longitude. Therefore, for a longitudinal extent of 30° of India, there is a time lag of 2 hours. When it is 6 a.m. in Arunachal Pradesh, it is still 4. a.m. in Gujarat. But the watches in all parts of India are run according to standard time measured from 82°30′ longitude. So the watches in Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat show the same time despite the different sunrise.
MAP SKILLS
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Identity the following with the help of map reading.
(i) The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) Show neighbours of India.
(iii) The states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
(iv) Southern most tip of India.
(v) The capital of UP.
(vi) The capital of J&K.
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
(viii) The strait separating Sri Lanka from India.
(ix) The Union Territories of India.
Ans.— (i) Lakshadweep and Andaman Nicobar Islands.
(ii) Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka.
(iii) Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, Mizoram.
(iv) (Indira Point) 97° E and 68° E.
(v) Lucknow
(vi) Srinagar.
(vii) Kanya Kumari
(viii) Palk Strait
(ix) Chandigarh, Delhi, Daman Diu, Dadra Nagar Haveli, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Andaman Nicobar, J&K and Ladakh.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here