WBBSE 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 4.6 Water
West Bengal Board 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 4.6 Water
WBBSE 9th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
Synopsis
- Water possesses high specific heat, high boiling point, capillary action and an ability to dissolve almost all substances. Due to these unique properties of water, it helps living organisms to survive and flourish.
- Both ionic and covalent compounds existing in solid, liquid or gaseous state can dissolve in water. Thus, water is known as the universal solvent.
- Only 1% of the total water content of the earth constitutes of fresh water which can be used for different purposes. Rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, swamps, glaciers and groundwater are the different sources of fresh water on the earth.
- The pH range of drinking water should be between 6.5 to 8.5 and the amount of dissolved oxygen must be 4-6 mg.L-¹ as recommended by WHO.
- Excessive presence of chlorides, fluorides and arsenic compounds in drinking water makes it unsafe for consumption.
- The number of colonies of coliform bacteria such as E. coli present in 100 mL of a water sample is known as the coliform count of that water sample. The coliform count of drinking water must be zero.
- Some common methods of purification of water are boiling, chlorination and use of ultraviolet rays.
- Proportionate amount of bleaching powder is added to water in a closed vessel to make it germ-free. Then this water is left open for some time when excess chlorine evaporates from the water. The water thus obtained is safe for drinking. Sometimes, chlorine tablets are also used for the purification of water.
- Organic substances present in water react with chlorine to form trihalomethanes (THMs) and trihaloacetic acids. (TAAs). These compounds are highly carcinogenic in nature (i.e., these cause cancer).
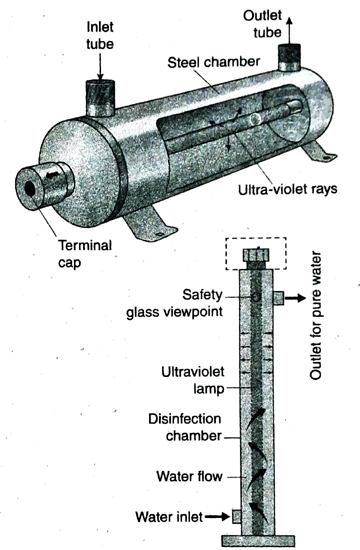
- Ultraviolet rays are passed through water in aqua filters to make it germ-free. This method is better than any other water purification methods as it does not require any chemicals. Also, this method is more effective than chlorination in killing viruses present in water.
TOPIC – A
Role of Water in Development of Life and Drinking Water
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What property of water makes it excellent for fomentation?
Ans. Water has the highest value of specific heat (1 cal g-1. °C-1). Hence, it can absorb large amount of heat with small increase in temperature and can similarly release large amount of heat with small decrease in temperature. So, water cools down less readily than other liquids. This is the reason for which water can be used for fomentation (i.e., to provide warmth). .
2. Mention one practical application of high specific heat of water.
Ans. Water has a very high specific heat 4200 J · kg-¹. K-1 as compared to other substances (solids or liquids). Hence, the amount of heat required by a fixed quantity of water to raise its temperature by 1°C or 1K is relatively higher than that required by the same quantity of some other solids or liquids. Thus, water is used as a coolant in different industries (it helps to cool the machinery) and in radiators of automobiles.
3. Land breeze e and sea breeze ar sea breeze are formed due to high specific heat of water-explain.
Ans. Due to high specific heat of water, during daytime the landmass heats up more as compared to sea water. Consequently, air adjacent to the landmass gets heated up, becomes lighter and finally rises up to create a void space. Cold air adjacent to the sea water rushes towards the landmass to fill up the void. This is how sea breeze is resulted.
After sunset, the landmass cools down more rapidly than sea water. Air adjacent to the warm sea water heats up, becomes lighter and then rises up. Cold air adjacent to the landmass rushes towards the sea to fill up the formed void. This is how land breeze is resulted.
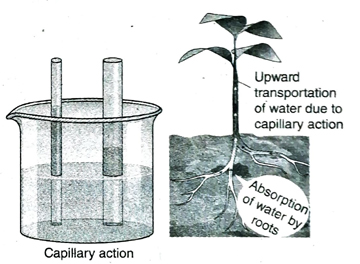
4. What is capillary action?
Ans. Due to cohesive force acting between the molecules of a liquid and adhesive force operating between the liquid molecules and the surface of the vessel, a liquid elevates along a very narrow tube against the force of gravity. This phenomenon is known as capillary action.
5. Discuss the significance of capillary action.
Ans. (1) Water and minerals absorbed by roots of plant reach the leaves by capillary action.
(2) When sufficient water is not present in the upper layers of the earth’s crust, water from the lower layers come up to the upper layers by capillary action and supply water to the plants.
(3) Water comes out through numerous pores on earthen pots due to capillary action. This water evaporates and consequently, cools the water within the pot.
6. How do aquatic plants and animals survive in cold countries?
Ans. The latent heat of freezing of water is very high. In cold countries, when water at the upper layers of ponds and lakes freezes, large amount of heat is released. The lower layers of water absorb this heat and consequently the temperature of this part of the water body increases. Thus, water at the lower levels of the water body remain at higher temperature even though the surface of the water freezes. This helps the aquatic plants and animals to survive throughout the winter season in cold countries.
7. Discuss the significance of dissolved oxygen for aquatic plants and animals.
Ans. Aquatic plants and animals are dependent on dissolved oxygen for carrying out their respiratory activities. A certain amount of dissolved oxygen is necessary for the aquatic organisms to survive. Dissolved oxygen is very important for fish. If dissolved oxygen in a water body decreases, then the aquatic plants and animals will die due to lack of oxygen.
8. Mention two physical properties of water which are important for evolution of life.
Ans. Two physical properties that are very important for evolution of life are:
(1) higher specific heat of water (4200 J. Kg-¹. K-1)
(2) polar nature of water molecule.
9. Why is water called a universal solvent?
Ans. (1) Water can dissolve most of the solids, liquids and gases.
(2) It has very high value of dielectric constant (80.4) and so, almost all ionic compounds are soluble in water.
(3) Water is a polar compound. Hence, polar covalent compounds are highly soluble in it.
(4) Water exists in the liquid state over a wide range of temperature from 0°C to 100°C.
10. Why is water called a polar solvent?
Ans. Though water molecule is formed by covalent bonds, the oxygen atom being more electronegative than. hydrogen atom, becomes partially negatively charged while the hydrogen atoms become partially positively charged. As a result, the oxygen atom of water molecule can attract the positive part of a solute molecule while hydrogen atoms of water can attract its negative part by electrostatic force of attraction. So water is called a polar solvent.
11. How do electrovalent or ionic compounds easily dissolve in water?
Ans. Water has a very high value of dielectric constant (80.4). Due to this, water as a solvent can separate the positively charged and negatively charged ions in an ionic compound by opposing the electrostatic force of attraction between them. Thus, molecules of these compounds easily dissociate in water yielding the constituent ions. Hence, electrovalent or ionic compounds easily dissolve in water.
12. What are the essential criteria of drinking water?
Ans. (1) It must be colourless, odourless, tasteless and clear.
(2) It must be free from floating impurities.
(3) It must be free from germs and suspended particulate matter.
(4) It should not contain excess minerals than permissible limit.
(5) It must be free from harmful compounds such as urea, cyanide salts, nitrate salts etc.
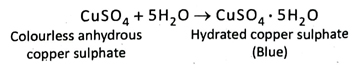
13. How do you identify a colourless liquid do you identify a colourless as water.
Ans. If colourless, anhydrous copper sulphate turns blue by coming in contact of a colourless liquid, then it can be told that the colourless liquid must be water.
14. What will be the harmful effects if excess chloride salts are present in drinking water?
Ans. The nature and extent of pollution caused by excess chloride salts in water largely depends on the cations of the salts. Prolonged intake of water containing excess sodium chloride may cause high blood pressure. It must be noted that, this adverse effect is related to the presence of sodium ion in water and has no relation with the chloride ion concentration of water.
15. How does the pH value of water affect our health?
Ans. The pH of drinking water should be ranging from 6.5 to 9.2 as recommended by WHO. If the pH of water exceeds the upper limit, then it may cause burning sensation in eyes, skin and mucous membrane. Water having a pH value more than 11 is very harmful to eyes and skin. If pH of water is in the range of 10-12.5, then it may cause inflation of hair fibres and reduce our digestive capacity. When pH of water is less than 4, it causes redness and burning sensation in eyes. If pH of water is less than 2.5, it causes extensive and irreparable damage to our skin. The immunity of animals is also largely dependent on the pH level of water.
16. What is meant by coliform count of water?
Ans. The number of colonies of coliform bacteria such as E. coli present in 100 mL of a sample of water is known as coliform count of that sample of water.
17. How water is purified or disinfected before distribution in township?
Ans. Before distribution in towns, water is disinfected. This disinfection or purification is done by adding chlorine tablets or bleaching powder. This process is called chlorination. Chlorine, by oxidation, destroys the harmful microbes present in water and thus disinfected drinking water.
18. Mention the limitations of purification of water by boiling.
Ans. The limitations of purification of water by boiling are as follows-
- Though most of the germs are killed at a temperature near the boiling point of water, some germs still remain active at that temperature.
- Harmful metals and some toxic chemical compounds cannot be removed from water by boiling.
- Most of the essential minerals present in water are removed by boiling.
19. Write down two advantages of chlorination process.
Ans. Two advantages of chlorination process are:
- Application of this process is easier and advantageous.
- Since chlorine remains in water even after a long time from the time of application, the disinfection property also remains active:
20. Mention two limitations of purification of water by chlorination.
Ans. Two limitations of purification of water by chlorination are as follows-
- Chlorine reacts with organic substances dissolved in water to form trihalomethanes (THMS) and trihaloacetic acids (TAAS). Among the trihalomethanes, bromoform adversely affects the brain and decreases its efficiency thereby causing drowsiness. Prolonged exposure to bromoform & dibromochloromethane may cause cancer in liver & kidneys.
- Chlorine being volatile in nature quickly evaporates from water and mixes with the surrounding air thereby causing air pollution.
21. Mention the advantages of purification antages of purificat of water by UV-rays.
Ans.
- The purification of water by UV-rays is fast and effective. It does not affect the taste or smell of water. So, it is very effective in purification of drinking water and water used in food processing industries.
- Purification of water by this method is safe. As no harmful chemicals are used in this method, there is no chance of pollution.
- UV-rays are more effective than chlorine in removing viruses from water.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. In SI unit, the specific heat of water is
A. 4200 J · kg-1 · K-1
B. 2100 J · kg-1 · K-1
C. 6300 J · kg-1 · K-1
D. 4500 J · kg-1 · K-1
Ans. A
2. Water is a
A. non-polar solvent
B. polar solvent
C. organic solvent
D. none of these
Ans. B
3. An organic compound that dissolves in water is
A. benzene
B. alcohol
C. wax
D. carbon tetrachloride
Ans. B
4. An inorganic compound that does not dissolve in water is
A. sodium chloride
B. potassium nitrate
C. calcium carbonate
D. zinc sulphate
Ans. C
5. The tendency of a liquid to flow against gravity in a narrow tube is called
A. surface tension
B. viscosity
C. capillary action
D. none of these
Ans. C
6. The water content in a fully grown human being with respect to his total body weight is almost
A. 65%
B. 30%
C. 40%
D. 10%
Ans. A
7. The word ‘coliform’ is related to
A. bacteria
B. virus
C. algae
D. fungus
Ans. A
8. pH of a solution indicates the concentration of
A. OH– ions
B. Cl– ions
C. H+ ions
D. Na+ ions
Ans. C
9. pH of an acidic solution is
A. less than 7
B. more than 7
C. equal to 7
D. none of these
Ans. A
10. pH of an alkaline solution is
A. less than 7
B. more than 7
C. equal to 7
D. none of these
Ans. B
11. The maximum permissible limit of dissolved oxygen in drinking water (in mg · L-¹) as recommended by WHO is
A. 1-2
B. 4-6
C. 8-10
D. 12-15
Ans. B
12. The maximum permissible limit of dissolved chlorides in drinking water (in mg · L-¹) as recommended by WHO is
A. 100
B. 200
C. 300
D. 250
Ans. D
13. The maximum permissible limit of dissolved fluorides in drinking water (in mg · L-¹) as recommended by WHO is
A. 1-1.5
B. 11-20
C. 21-30
D. 31-40
Ans. A
14. The maximum permissible limit of dissolved arsenic in drinking water (in mg · L-¹) as recommended by WHO is
A. 0.05
B. 0.25
C. 0.5
D. 1
Ans. A
15. Which of the following is used for the purification of water?
A. infrared rays
B. X-rays
C. ultraviolet rays
D. gamma rays
Ans. C
16. Chlorination of water is done to
A. destroy the microbes
B. precipitate the suspended impurities
C. improve the taste of water
D. increase the clarity of water
Ans. A
17. Which property of water helps to control the temperature of atmosphere?
A. specific heat
B. dielectric constant
C. bad conductivity of heat
D. polar nature
Ans. A
18. Specific heat of which of the following liquids is the highest?
A. water
B. kerosene
C. petrol
D. mercury
Ans. A
19. Example of a water soluble organic compound is
A. toluene
B. acetic acid
C. xylene
D. chloroform
Ans. B
20. Example of universal solvent is
A. water
B. kerosene
C. benzene
D. alcohol
Ans. A
Answer in brief
1. What is meant by the statement-‘Specific heat of water is 1 cal · g-1 · °C-1?
Ans. The above statement means that 1 cal of heat is required to raise the temperature of 1 g of pure water by 1°C.
2. At what temperature, the density of water is maximum?
Ans. The density of water is maximum at 4°C (1g · cm-3).
3. What is a capillary tube?,
Ans. A capillary tube is a long and thin tube made of rigid materials like glass or plastic. The diameter of a capillary tube generally ranges from 0.5 mm to 3 mm.
4. Which property of water makes it a coolant for different machinery used in the industries?
Ans. High specific heat of water makes it an excellent coolant for different machinery used in the industries.
5. Give an example of a covalent compound which is soluble in water.
Ans. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is a covalent compound which is soluble in water.
6. Give an example of a covalent compound which is insoluble in water.
Ans. Benzene (C6H6) is a covalent compound which is insoluble in water.
7. What must be the coliform count of drinking water?
Ans. The coliform count of drinking water must be zero (0).
8. What is meant by the statement-‘Coliform count of a sample of water is zero’?
Ans. The above statement means that the sample of water does not contain any colony of coliform bacteria (Escherichia coli).
9. What is the value of dielectric constant of water?
Ans. The value of dielectric constant of water is 80.4.
10. How can water be purified without using any chemicals?
Ans. Water can be purified by using ultraviolet rays (UV-rays) as no chemicals are required in this method.
11. Which halogen used for the purification of water?
Ans. The halogen used for the purification of water is chlorine.
12. Name two absorbents of water.
Ans. Concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) are two absorbents of water.
13. How does chlorine destroy the microbes present in water?
Ans. Chlorine destroys the microbes present in water by the process of oxidation.
14. How pH of water changes with increase in temperature?
Ans. pH of water generally decreases with increase in temperature.
15. Give an example of coliform bacteria?
Ans. E.coli.
16. Why chlorination of water is done?
Ans. To destroy the microbes present in water.
17. What should be the permissible limit of oxygen in drinking water as per order of WHO?
Ans. 4-6 mg · L-1
18. Give the formula of heavy water?
Ans. The formula of heavy water is D2O.
19. For which property, water can be used for cooking purposes?
Ans. Boiling point of water is comparatively higher, that is why it is used for cooking.
20. What type of harm occur if pH of drinking water becomes more than 10.5?
Ans. It causes disturbances in digestion.
21. What type of harm occur if the pH of drinking water becomes less than 4?
Ans. It causes damages of nervous system, lungs, and respiratory tracks and also disturbs the digestion system.
22. How the surgical apparatus and instruments are disinfected?
Ans. The surgical instruments are boiled at a higher temperature more than 100°C, at a higher pressure in autoclave and thus disinfected.
23. For which property of water, different types of salt dissolve in it?
Ans. For polar nature of water molecule.
24. Due to which physical property of water, the water bodies like ponds and lakes do not freeze immediately on a cold day in wintercountries?
Ans. Latent heat of solidification of water has a higher value (336 J/g). This property of water helps in the mentioned process.
Fill in the blanks
1. Specific heat of water is ………….. than ice.
Ans. greater
2. Water is a …………. solvent.
Ans. polar
3. Water absorbed by the roots of plants reach the leaves through stem due to ………….
Ans. capillary action
4. …………. is generally used to precipitate the impurities suspended in water.
Ans. Alum
5. Only ………….. % of total water content found on the earth’s surface is usable.
Ans. 1
6. pH is the negative logarithm of …………. ion concentration of a solution.
Ans. hydrogen
7. pH of pure water is …………..
Ans. 7
8. UV-rays destroy the ……….. present in water.
Ans. microbes
9. Taste of water depends on the amount of ………… dissolved in it.
Ans. salts
10. Purification of water by boiling also leads to the removal of essential …………. dissolved in water.
Ans. minerals
11. ………….. % of total water content on the earth’s surface constitutes of sea water.
Ans. 97
State whether true or false
1. The pH of drinking water should range between 4.5 to 6.5.
Ans. False
2. The coliform count of drinking water must be zero.
Ans. True
3. Chlorination is an effective method for removing permanent hardness of water.
Ans. False
4. The density of water is minimum at 0°C.
Ans. False
5. Consumption of deionised water is good for the human body.
Ans. False
6. Fluoride salts can be eliminated from water by passing through activated alumina.
Ans. True
7. Distilled water is less pure than deionised water.
Ans. False
8. Water is used as a coolant because of its low value of specific heat.
Ans. False
9. Magnesium reacts with water at ordinary temperature.
Ans. False
10. Capillary action of water is responsible for the absorption of water by roots and its subsequent transportation to the leaves.
Ans. True
11. Specific heat of water is the highest among known liquids.
Ans. True
TOPIC – B
Soft Water and Hard Water
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
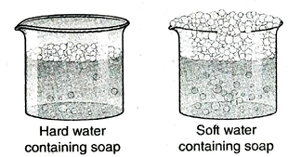
1. What is meant by hard water and soft water? Give examples.
Ans. Hard water: The type of water that barely produces lather with soap or does so after consuming a large amount of soap is called hard water. For example, river water, sea water, waterfalls etc., are natural sources of hard water. Soft water: The type of water that easily forms lather with soap is called soft water. For example, distilled water, deionised water etc.
2. What is the cause of hardness of water? What are the different types of hardness of water?
Ans. Hardness of water is resulted due to the presence of bicarbonate, sulphate and chloride salts of calcium, magnesium and iron which remain dissolved in water.
On the basis of the nature of dissolved salts, hardness of water is of two types- (1) temporary hardness and (2) permanent hardness.
3. What do you mean by temporary hardness of water?
Ans. Hardness produced due to the presence of dissolved bicarbonate salts of calcium and magnesium [Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2] and to some extent iron which can be removed by simply boiling the water is known as temporary hardness.
4. What do you mean by permanent hardness of water?
Ans. Hardness produced due to the presence of dissolved sulphate and chloride salts of calcium, magnesium and iron [CaCl2, CaSO4, MgCl2, MgSO4, FeSO4] which cannot be removed by simply boiling the water is called permanent hardness or non-carbonate hardness.
5. Name two processes for the removal of hardness of water.
Ans. Two processes for the removal of hardness of water are: boiling (Process for removal of temporary hardness) and ion-exchange process (Process for removal of both temporary and permanent hardness of water).
6. Which one of these has the higher probability of being hard: spring water or rain water.
Ans. Probability of being hard water is more in case of spring water. Water from different water bodies get evaporated and forms cloud in the higher part of sky which when condense, form rain where the minerals remain absent as those were not evaporated at all. That is why rain water remains soft in nature. On the other hand, spring water flows above rocks and minerals. During this flow the metallic salts, responsible for hardness dissolve in it and make the spring water hard.
7. Temporary hardness of water caused by magnesium bicarbonate cannot be removed completely by boiling. Explain with reason.
Ans. On boiling hard water (containing magnesium bicarbonate), the soluble bicarbonate decomposes to form water insoluble carbonate salt.
Mg(HCO3)2 → MgCO3 ↓ + H2O + CO2 ↑
As MgCO3 is sparingly soluble in water, temporary hardness of water caused by magnesium bicarbonate cannot be removed completely by boiling.
8. How is the degree of hardness of water the degree of hardness of water expressed?
Ans. Degree of hardness of water is defined as the number of parts by mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) equivalent to various calcium and magnesium salts present in one million (106) parts by mass of water. Degree of hardness of water is expressed in terms of ppm (parts per million).
9. What do you mean by the statement- ‘Hardness of a sample of water is 300 ppm’?
Ans. The above statement means that 300 parts by mass of calcium carbonate equivalent to various salts causing hardness of water is present in one million parts by mass of that water sample.
10. Mention two disadvantages of using hard water.
Ans. (1) Hard water can not be used in cooking as the food particles are not boiled properly in hard water.
(2) Hard water is not suitable for drinking as it affects the digestive system.
11. What are cation exchange resins?
Ans. A cation exchange resin is an artificially synthesised organic polymer having a complex network structure in which an acidic group, -SO3H (sulphonic acid) is attached to a large hydrocarbon chain. The general formula of a cation exchange resin is R-SO3H.
12. What are anion exchange resins?
Ans. An anion exchange resin is an artificially synthesised organic polymer having a complex network structure in which an alkaline OH- group is present as substituted ammonium hydroxide attached to a large hydrocarbon chain. The general formula of a anion exchange resin is R-NH3+OH– .
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. If hardness of water increases, then it
A. can easily produce lather
B. cannot produce lather
C. can produce lather only by consuming large amount of soap
D. none of these
Ans. C
2. The hardness of water can be of
A. 4 types
B. 3 types
C. 2 types
D. 5 types
Ans. C
3. A salt responsible for permanent hardness of water is
A. CaCl2
B. Ca(HCO3)2
C. NaCl
D. Na2CO3
Ans. A
4. A salt responsible for temporary hardness of water is
A. CaCl2
B. Ca(HCO3)2
C. NaCl
D. Na2CO3
Ans. B
5. If acid (H+) is added to water, then water will behave as
A. soft water
B. hard water
C. pure water
D. deionised water
Ans. B
6. Boiling can be used to
A. remove permanent hardness of water
B. deionise water
C. remove temporary hardness of water.
D. decolourise water
Ans. C
7. Cation exchange resins are regenerated by using a dilute solution of
A. NaOH
B. HCl
C. NaCl
D. Na2SO4
Ans. B
8. Anion exchange resins are regenerated by using a dilute solution of
A. NaOH
B. HCl
C. NaCl
D. Na2SO4
Ans. A
9. The type of water used in boilers of factories is
A. soft water
B. hard water
C. deionised water
D. germ-free water
Ans. A
10. Which of the following happens when hardness of water increases?
A. lather forms easily
B. lather does not form at all
C. lather forms after rubbing the soap for a long time
D. none of the above
Ans. C
11. Hardness of deionised water is
A. 0
B.1
C. 3
D. 7
Ans. A
12. pH of deionised water is
A. 0
B. 2
C. 4
D. 7
Ans. D
13. Which of the following processes can remove temporary and permanent hardness of water simultaneously?
A. boiling
B. chlorination
C. U.V. ray
D. ion-exchange process
Ans. D
14. Which of the following ions is absent in hard water?
A. carbonate
B. bicarbonate
C. chloride
D. sulphate
Ans. A
15. Which of the following is used for injection?
A. soft water
B. hard water
C. deionised water
D. distilled water
Ans. D
Answer in brief
1. What is the working principle of pressure cooker?
Ans. In a pressure cooker, the steam, so produced increases the pressure above the surface of water. As a result, water boils at higher temperature than its normal boiling point due to elevation of boiling point. As a result, food gets boiled properly and rapidly.
2. ‘Hard water is suitable for washing clothes’- Is the statement right or wrong?
Ans. When hard water is used, large amount of soap is required to produce lather which results in wastage of soap. Hence, hard water is not suitable for washing clothes.
3. Name two metals that react with water at room temperature.
Ans. Sodium (Na) and calcium (Ca) react with water at room temperature.
4. Name a salt which causes temporary hardness in water.
Ans. Calcium bicarbonate [Ca(HCO3)2] causes temporary hardness in water.
5. Name a sulphate salt responsible for permanent hardness in water.
Ans. Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4) causes permanent hardness in water.
6. What is meant by reversibility of resins?
Ans. Salts are formed due to exchange of H+ and OH– ions of the resins with the cations and anions present in hard water. The activity of resins can be regenerated by treating these salts with dilute acid or alkali solutions. This is known as reversibility of resins.
7. Name a fatty acid from which soap is prepared.
Ans. A fatty acid from which soap is prepared is stearic acid.
8. Which type of hardness can be removed by boiling?
Ans. Temporary hardness of water caused by bicarbonate salts of calcium and magnesium can be removed by boiling the water.
9. State if aquatic organisms can survive in distilled water or not.
Ans. No, aquatic organisms cannot survive in distilled water due to lack of dissolved oxygen in it.
10. Which part of a salt is responsible for causing hardness of water?
Ans. The cation of a salt is responsible for causing hardness of water.
11. Two samples of water contain dissolved Zn-salts and Na-salts respectively. Which one is hard water?
Ans. Zn-salts cause hardness of water. Hence, the sample having dissolved Zn-salt in it will be hard water.
12. Which method is effective in removing all types of hardness of water?
Ans. Ion-exchange method is effective in removing all types of hardness of water.
13. By which process permanent hardness of water can be removed?
Ans. Ion exchange process.
14. Which ions are present in deionised water?
Ans. H+ and OH– ions are present in deionised water.
15. If or whenever the efficiency of the cation exchange resin reduces, what should be passed through them to regain the efficiency?
Ans. Dilute H2SO4 or dilute HCl is passed though the resin layer.
16. Which type of hardness is removed by ion exchange process?
Ans. Both temporary and permanent hardness are removed.
17. Name a calcium salt, responsible for hardness of water.
Ans. Calcium sulphate (CaSO4).
18. Name a magnesium salt, responsible for temporary hardness.
Ans. Magnesium bicarbonate [Mg(HCO3)2].
19. NaCl and K2SO4 are dissolved is a sample of water. Mention whether it is soft or hard water.
Ans. Soft water.
20. Name a halogen whose water soluble salts cause water pollution.
Ans. Fluorine causes water pollution as it remains in water as soluble fluoride salts.
Fill in the blanks
1. Cation exchange resins are organic …………. acids having high molecular mass.
Ans. sulphonic
2. …………. is a useful method for the removal of permanent hardness of water.
Ans. Ion-exchange
3. If the hardness of water increases, then the amount of soap required to form lather in that water also ………….
Ans. increases
4. It is preferable to use ………… over soap in hard water.
Ans. detergents
5. Detergents can produce lather even in ……….. water.
Ans. hard
6. Water after treating with cation exchange resin is ……….. in nature.
Ans. acidic
7. Permanent hardness is also known as ………….. hardness.
Ans. non-carbonate
8. Temporary hardness is also known as ………….. hardness.
Ans. carbonate
9. Efficiency of anion exchange resin is regained by passing …………. solution.
Ans. NaOH
10. ………… hardness cannot be removed by boiling.
Ans. Permanent
11. …………. water should be used for cooking.
Ans. Soft
State whether true or false
1. The hardness which can be removed by simply boiling the water is known as permanent hardness.
Ans. False
2. Both temporary and permanent hardness of water can be removed by using ionexchange resin.
Ans. True
3. The cationic part of a salt is responsible for imparting hardness to water.
Ans. True
4. Spring water is the example of soft water.
Ans. False
5. Water will be hard if Na or K-salt are present in it.
Ans. False
6. Hardness of distilled water is zero.
Ans. True
7. Deionised water is completely pollution free.
Ans. False
8. Deionised water is used for injections.
Ans. False
TOPIC – C
Water Pollution
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is meant by water pollution?
Ans. Undesired changes in the physical, chemical or biological parameters of water that results in contamination of water bodies thus, making it unsafe for living organisms (both terrestrial and marine) is called water pollution.
2. Mention three major causes of water pollution.
Ans. Three major causes of water pollution are as follows-
(1) Disposal of domestic wastes like detergents, plastics etc., in water bodies.
(2) Industrial wastes like oil, grease, acid etc., released in water bodies.
(3) Mixing of fertilisers, pesticides and insecticides used in agricultural lands with nearby water bodies.
3. Name two pesticides which cause water pollution. Mention their harmful effects.
Ans. Two commonly used pesticides which cause water pollution are-DDT (p, p’-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) and gammaxene.
These pesticides affect the function of brain and may cause cancer (carcinogenic in nature).
4. Discuss how pesticides cause water pollution.
Ans. Pesticides are chemical compounds used to preserve crops from the attacks of insects, fungi etc. (collectively called pests). These pesticides are washed off by water into nearby rivers, ponds, lakes etc. causing water pollution. Pesticides are mostly non-biodegradable compounds and do not decompose biochemically. These substances enter into the human bodies and other animals through food chain and cause biomagnification. This leads to headache, nervous breakdown, slackening of muscles, convulsions etc. Prolonged exposure to these substances may even cause tumour or cancer.
5. Discuss how fertilisers cause water pollution.
Ans. Fertilisers are chemical compounds used to increase the fertility of soil thereby increasing the yield of crops such as, urea, ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitrate etc. When fertilisers are applied to agricultural fields, these are washed away by water into nearby rivers, ponds, lakes etc. causing water pollution. Excessive nitrate salts in drinking water may cause methaemoglobinaemia in infants. Presence of excessive phosphate salts results in eutrophication in water bodies.
6. How do nitrate fertilisers cause water ter pollution?
Ans. Nitrate fertilisers are widely used in agricultural lands. These salts being soluble in water dissolve in it and are washed away to nearby water bodies. Excess quantity of these salts act as pollutants rather than nutrients. If excess quantity of nitrate salts enter the body through consumption of drinking water, it may cause methaemoglobinaemia in infants. It can also interfere with the ability of red blood corpuscles to transport oxygen to different parts of the body thereby disrupting physiological processes like circulation and respiration.
7. What are detergents? What is the advantage of using detergents in hard water?
Ans. Detergents are artificially synthesised mixtures of two or more substances which have cleansing property. A detergent contains two major components- (1) a surface active substance (like, alkyl benzene sulphonate) and (2) a builder or filler (like sodium tripolyphosphate).
Detergents can produce lather or foam even in hard water causing less wastage.
8. Discuss how detergents cause water pollution.
Ans. Detergents are the major water pollutants. They cause water pollution in the following ways- (1) Lather produced by detergents accumulate on the surface of water thereby preventing air and sunlight from entering into the depths of water. Consequently, dissolved oxygen of water decreases. (2) Detergents contain surface-active compounds which form layers on the organic pollutants present in water and prevent their biochemical decomposition. This increases the pollution level of water. (3) Phosphate compounds are used as fillers in detergents. These phosphate compounds cause eutrophication.
9. What is eutrophication?
Ans. The phenomenon of rapid growth in the population of aquatic plants (mainly algae) in water bodies due to enrichment of water with excess phosphate fertilisers, phosphate compounds of detergents etc. (which act as nutrients) is known as eutrophication.
10. Discuss the harmful effects of eutrophication.
Ans. (1) Due to rapid population growth of aquatic plants, demand of oxygen for their respiration also increases. Thus, amount of dissolved oxygen in water decreases rapidly thereby threatening the survival of aquatic life.
(2) Rapid decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water leads to an abnormal increase in population of anaerobic bacteria. These bacteria acts on the different organic and inorganic waste materials present in water to produce gases such as, methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide etc. which leads to emission of foul smell in water.
11. What is algal bloom? Mention its effects.
Ans. The rapid increase in the population of algae in stagnant due to presence of excess nutrients water bodies is known as algal bloom.
Due to this increased population growth of algae, the surface of water gets entirely covered with algae. This prevents sunlight from reaching the depths of the water body. The level of dissolved oxygen also decreases rapidly due to algal bloom. Due to insufficient oxygen, aquatic plants and animals die which disrupts the overall functioning of aquatic ecosystem. Apart from this, bacterial decom-position of dead plants and animals in the water body makes it more polluted. O
12. What is arsenic pollution? Is the element arsenic directly responsible for arsenic pollution?
Ans. The undesired effects on living beings (mainly human beings) caused due to the presence of arsenic compounds in water, in an amount greater than the permissible limit, is known as arsenic pollution.
No, the element arsenic is not directly responsible for arsenic pollution. Presence of certain arsenic salts like arsenate and arsenite in water causes arsenic pollution in water.
13. Mention one natural and one artificial reason for arsenic pollution.
Ans. Natural reason: Insoluble layer of arsenic compounds are present in contact with the ground water layer. Excessive use of this ground water helps air to come in contact with this insoluble salts. As a result soluble arsenite and arsenate salts are produced which is the main cause of arsenic pollution in water.
Artificial reason: Different arsenic containing compounds e.g., sodium arsenite, lead arsenate, calcium arsenate etc. are used as antifungal and pesticidal substance. They are when dissolved in water make the water polluted.
14. Discuss the harmful effects of arsenic pollution on human beings.
Ans. (1) Consumption of water containing arsenic disturbs the blood circulation in our body.
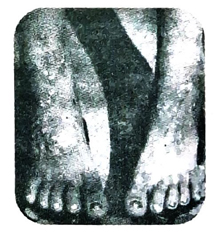
(2) It makes the skin rough and black patches appear on the skin in the neck, shoulder and back region of the body. Long term exposure to arsenic salts may cause blackfoot disease which causes appearance of black spots on palms and feet.
(3) Consumption of water containing arsenic for a long time may lead to cirrhosis of liver and even cancer in lungs and intestine.
15. How can water be made arsenic-free? Mention any two processes.
Ans. (1) Adsorption method: Both the salts of arsenic that cause pollution i.e., arsenate and arsenite, are adsorbed by activated alumina (Al2O3). So tube wells are fitted with columns of alumina to remove arsenic from water.
(2) Co-precipitation method: If alum and hydrated ferric oxide are added to water and left undisturbed for a long period of time, then the arsenic-containing compounds gradually settle down at the bottom and are separated from water by filtration.
16. What is the is the maximum permissible limit of fluorides in drinking water? Discuss the harmful effects of excess fluorides in drinking water.
Ans. As recommended by WHO, the maximum permissible limit of fluoride salts in drinking water is 1.5 mg. · L-1.
The presence of 1.0 mg · L-1 of fluoride salts in drinking water is essential as it prevents the decay of tooth enamel. However, if the amount of fluoride salts slightly exceeds this permissible limit, then it may cause dental fluorosis and if the amount largely exceeds the permissible limit, then it may lead to osteofluorosis.
17. How is dissolved fluoride salts removed from water?
Ans. Methods of removal of fluorides from water are-
- If water contains large quantities of fluoride salts, then it is passed over activated alumina to eliminate fluoride salts.
- Water containing fluoride salts is treated with potash alum and lime and is kept undisturbed for some hours. The fluoride salts settle down and is then removed by filtration.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. The type of salt responsible for algal bloom in water is
A. chloride
B. phosphate
C. arsenic
D. fluoride
Ans. B
2. DDT is used as a
A. fertiliser
B. detergent
C. pesticide
D. soap
Ans. C
3. Which of the following is not a water-borne disease?
A. typhoid
B. cholera
C. malaria
D. jaundice
Ans. C
4. The quantity of oxygen (in mg) required for complete oxidation of the dissolved organic substances in 1 litre of water is known as
A. AOD
B. BOD
C. COD
D. DOD
Ans. B
5. The value of COD is generally
A. equal to BOD
B. less than BOD
C. greater than BOD
D. none of these
Ans. C
6. Degree of hardness of deionised water is
A. 0
B. 2
C. 4
D. 7
Ans. A
7. Which of the following is caused in human body due to arsenic pollution in water?
A. decay of tooth enamel
B. black patches on the skin of mainly feet and palms
C. methaemoglobinaemia
D. typhoid
Ans. B
8. What type of salt present in water causes dental erosion?
A. chloride
B. bromide
C. iodide
D. fluoride
Ans. D
9. Which class of compounds present in detergents is responsible for causing water pollution?
A. sulphates
B. chlorides
C. phosphates
D. carbonates
Ans. C
10. Soap is a
A. calcium salt of fatty acids having high molecular mass
B. sodium salt of fatty acids (organic acid) having high molecular mass
C. aluminium salt of fatty acids having low molecular mass
D. magnesium salt of fatty acids having high molecular mass
Ans. B
11. In which of the following districts of West Bengal, arsenic contamination of groundwater is maximum?
A. Purulia
B. Darjeeling
C. West Midnapore
D. Murshidabad
Ans. D
12. Which of the following is not responsible for fluoride pollution of groundwater?
A. cryolite
B. fluorapatite
C. fluorspar
D. sodium fluoride
Ans. D
13. Which of the following methods is used to control arsenic pollution?
A. adsorption method
B. co-precipitation method
C. ion-exchange method
D. all of these
Ans. D
14. Cause of minamata disease is
A. arsenic pollution
B. fluoride pollution
C. mercury pollution
D. phosphate pollution
Ans. C
15. Which one is the purest form?
A. de-ionised water
B. distilled water
C. rain water
D. tubewell water
Ans. B
16. Which of the following is formed when chlorine reacts with water?
A. HOCl
B. HCl
C. nascent oxygen
D. all of the above
Ans. D
17. Which one of the following is the process for removal of fluoride pollution?
A. passing through Al2O3 column
B. addition of lime and alum
C. co-precipitation process
D. all of the above
Ans. D
18. The disease caused due to drinking of water containing nitrate ions is
A. black-foot disease
B. itai-itai
C. methamoglobinemia
D. fluorosis
Ans. C
19. Which of the following reduces in water as a result of eutrophication?
A. dissolved hydrogen
B. dissolved oxygen
C. dissolved nitrate
D. dissolved minerals
Ans. B
20. Which of the following is present in the toxic chemicals excreted from paper industry?
A. Cd
B. Hg
C. Pb
D. Ni
Ans. B
21. Itai-itai disease is caused by
A. mercury pollution
B. phosphate pollution
C. cadmium pollution
D. sulphate pollution
Ans. C
22. Which of the following medium is polluted mostly by arsenic?
A. air
B. water
C. soil
D. all of the above
Ans. B
Answer in brief
1. Name three metals pollutants present in industrial wastes.
Ans. Cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) and lead (Pb).
2. Name a pesticide that causes water pollution.
Ans. DDT (p, p’-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) is a pesticide that causes water pollution.
3. Which type of fertiliser present in water may cause methaemoglobinaemia in children?
Ans. Presence of nitrate fertilisers in water may cause methaemoglobinaemia in children.
4. Which type of fertiliser is responsible for causing algal bloom in water bodies?
Ans. Mainly phosphate fertilisers are responsible for causing algal bloom in water bodies.
5. State whether eutrophication increases or decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
Ans. Eutrophication decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
6. What is the full form of BOD?
Ans. BOD stands for Biochemical Oxygen Demand (or Biological Oxygen Demand).
7. What is the permissible value of BOD for pure water?
Ans. The permissible value of BOD for pure water is 5 ppm.
8. What does a high value of BOD of water indicate?
Ans. A high value of BOD of water indicates the presence of large amount of organic pollutants in water.
9. Waste water released from a factory has a pH value less than 3.7 – From this given statement, what can you conclude about the quality of the waste water?
Ans. The waste water released from the factory is highly acidic in nature and thus, will cause water pollution.
10. What are the major causes of thermal pollution of water?
Ans. Hot water released from the thermal power plants, oil refineries and other industries mixes with the nearby water bodies to cause thermal pollution.
11. Presence of which metal in drinking water causes Minamata disease?
Ans. The presence of mercury or mercury containing compounds in drinking water causes Minamata disease.
12. Name a disease caused due to fluoride pollution of water.
Ans. Dental fluorosis is a disease caused due to fluoride pollution of water.
13. Name a disease caused due to arsenic pollution of water.
Ans. Black, foot disease is caused due to arsenic pollution of water.
14. Name a pesticide that contains arsenic.
Ans. Lead hydrogen arsenate (PbHAsO4) is an inorganic pesticide that contains arsenic.
15. Name a metal ore found in the earth’s crust that contains arsenic.
Ans. Arsenopyrites (FeAsS) is an ore of iron that contains arsenic and is found in the earth’s crust.
16. Which soluble salts are produced when water insoluble arsenic compounds present in the earth’s crust react with air?
Ans. When water insoluble arsenic compounds present in the earth’s crust react with air, soluble arsenate and arsenate salts are produced.
17. Which substance is used as the semipermeable membrane during removal of arsenic from water by reverse osmosis?
Ans. During removal of arsenic from water by reverse osmosis method, cellulose triacetate is used as the semipermeable membrane.
18. What amount of arsenic in blood may cause arsenicosis?
Ans. If blood contains more than 60μg · L-1 of arsenic, then it may cause arsenicosis.
19. What is biological magnification?
Ans. Biological magnification or biomagnification is a phenomenon by which the toxic chemical substances (such as DDT, aldrin which are generally not decomposed by biochemical reactions) are continuously deposited in the fat-tissues of living organisms through intake of food (food chain).
20. Which disease is caused by Arsenic Pollution?
Ans. Arsenicosis.
21. What is the pollution of water caused due to the algal decomposition called?
Ans. Algal bloom.
22. Name two permanent organic pollutant?
Ans. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and methyl murcury.
23. Which metalloid-compound in responsible for water pollution?
Ans. Arsenic.
24. What is fluorosis disease?
Ans. Fluorosis is a crippling disease resulted from deposition of fluorides in the hard and soft tissues of body caused by excess intake of fluoride through drinking water and affects teeth and bones.
25. Due to the presence of which element itaiitai occurs?
Ans. Due to the presence of cadmium in drinking water itai-itai disease occurs.
Fill in the blanks
1. The metalloid whose compounds are responsible for water pollution is ……….
Ans. arsenic
2. High ………… power of water makes it more vulnerable towards pollution.
Ans. solvation
3. Water soluble arsenic compounds like arsenite and arsenate salts are adsorbed by active ……….
Ans. alumina (Al2O3)
4. The full form of COD is …………..
Ans. Chemical Oxygen Demand
5. An example of a water-borne disease is ………..
Ans. typhoid
6. Malathion and parathion are ………..
Ans. insecticides
7. ……….. is an example of organoarsenic compound.
Ans. Cacodylic acid
8. Continuous lifting of groundwater increases the amount of ……….. in water.
Ans. arsenic
9. …………. are used as fillers in detergents.
Ans. Phosphates
10. There are ………….. layers of filters in a filtration tank.
Ans. three
11. The extent of water pollution …………. as the BOD value of water increases.
Ans. increases
12. The phenomenon of continuous accumulation of toxic chemicals in the fat tissues of living beings is known as ………..
Ans. biomagnification
13. ……….. which is a fluoride-containing mineral causes fluoride pollution in water.
Ans. Cryolite
14. DDT, a widely used pesticide is not ……….. in nature.
Ans. biodegradable
15. The amount of dissolved oxygen in water ………….. due to eutrophication.
Ans. decreases
16. Presence of ………….. of fluorides in drinking water is favourable for teeth.
Ans. 1 mg · L-1
17. As a result of eutrophication, the extent of dissolved oxygen in water rapidly ………….
Ans. decreases
18. ………… is used for the removal of arsenic by adsorption method.
Ans. Activated alumina
State whether true or false
1. Sulphate salts are responsible for algal bloom in water bodies.
Ans. False
2. Blackfoot disease is caused due to arsenic pollution of water.
Ans. True
3. High value of BOD of a water sample indicates decreased level of water pollution.
Ans. False
4. The two major components of detergent are a surface-active agent and a builder or filler.
Ans. True
5. The element arsenic is directly responsible for arsenic pollution of water.
Ans. False
6. The toxic effects of DDT disrupts the food chain and ultimately causes an imbalance in the ecosystem.
Ans. True
7. Eutrophication can lead to a decrease in the depth of a water body.
Ans. True
8. As COD increases, extent of pollution also increases.
Ans. True
9. Value of COD is generally lower than that of BOD for a sample of water.
Ans. False
10. Malaria is a water-born disease.
Ans. False
11. For prolonged intake of arsenic contaminated water arsenicosis occurs.
Ans. True