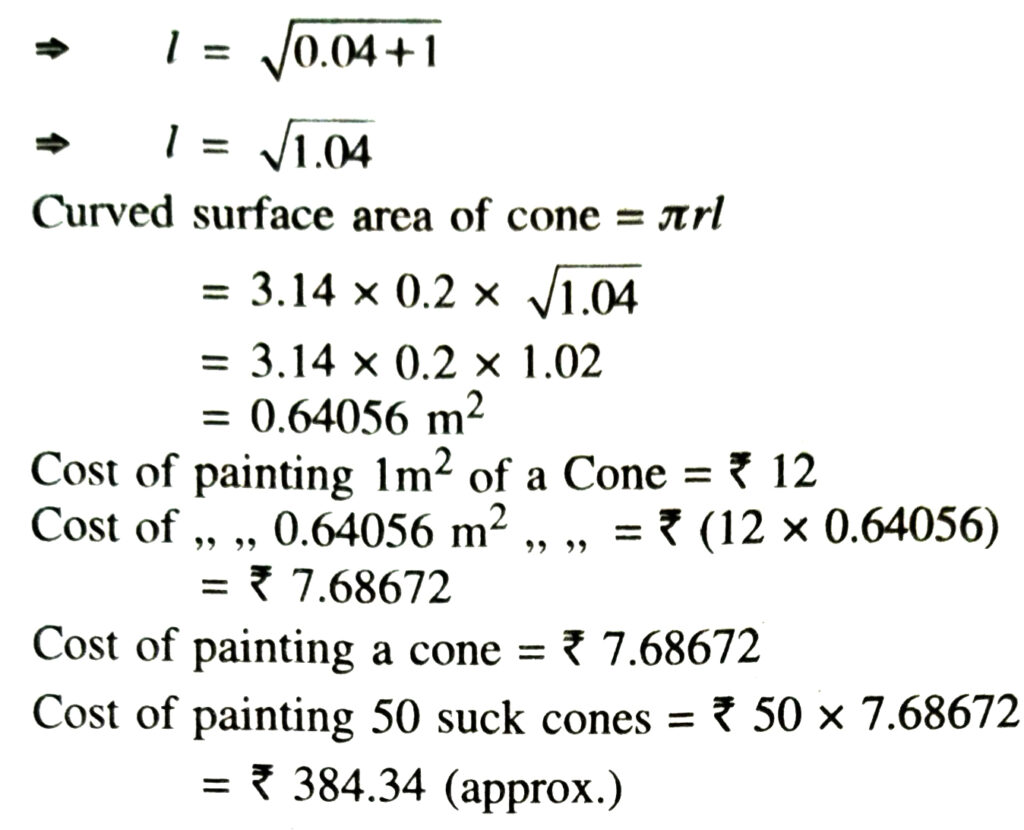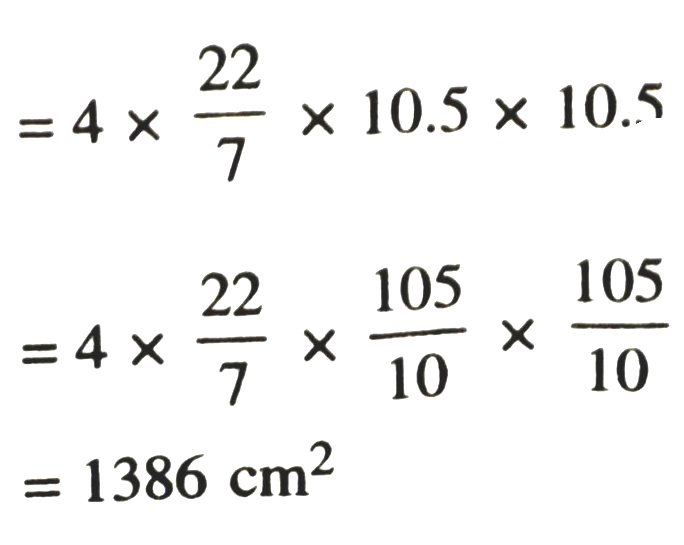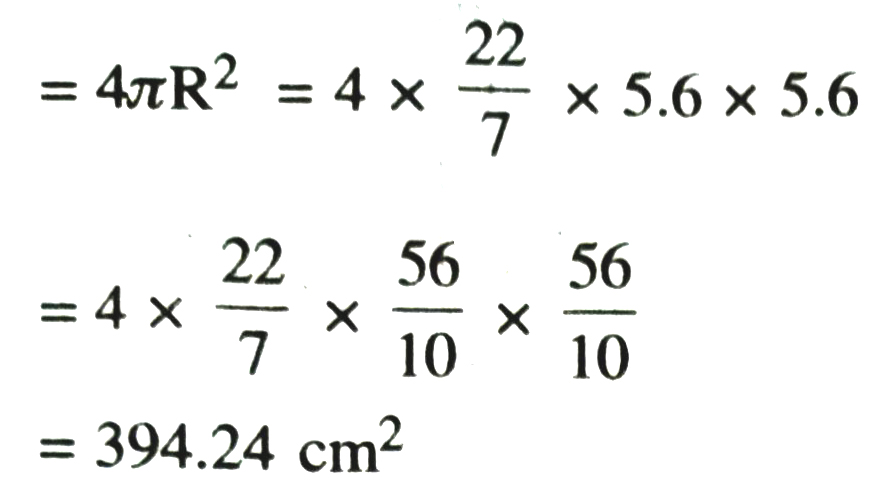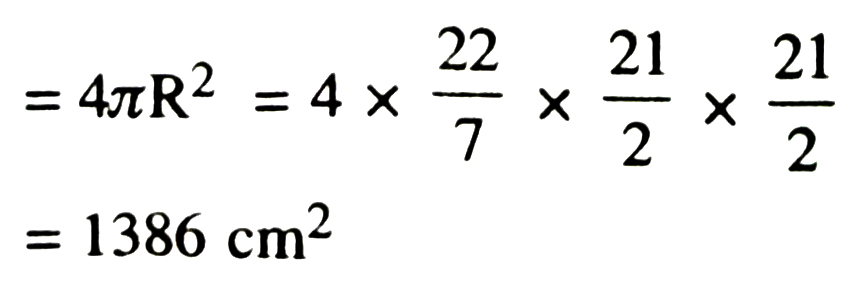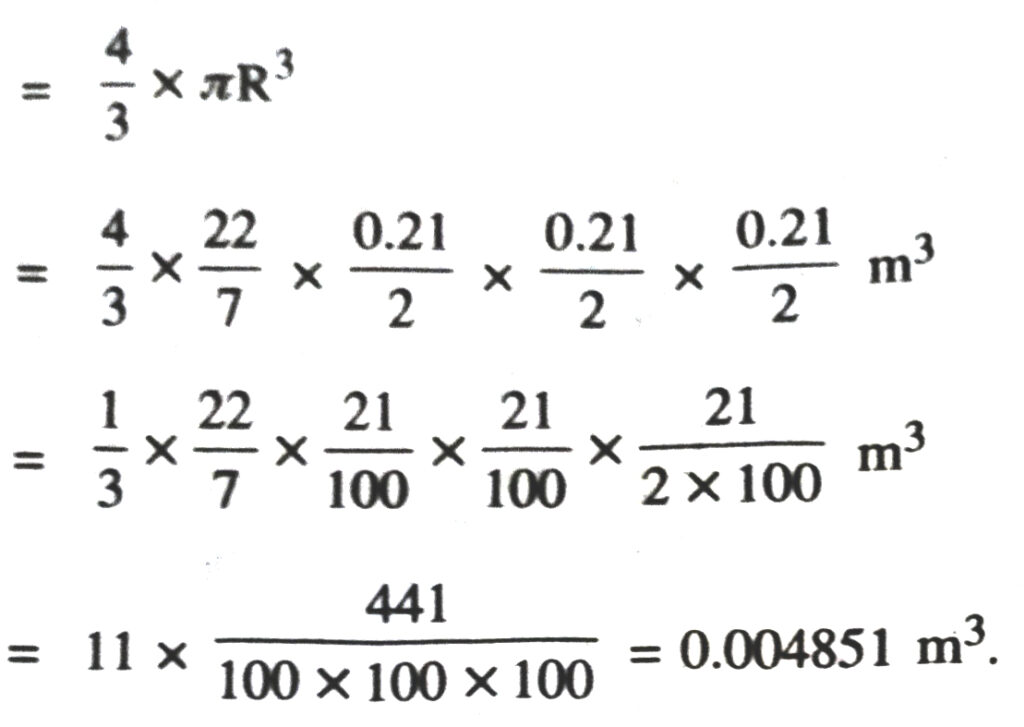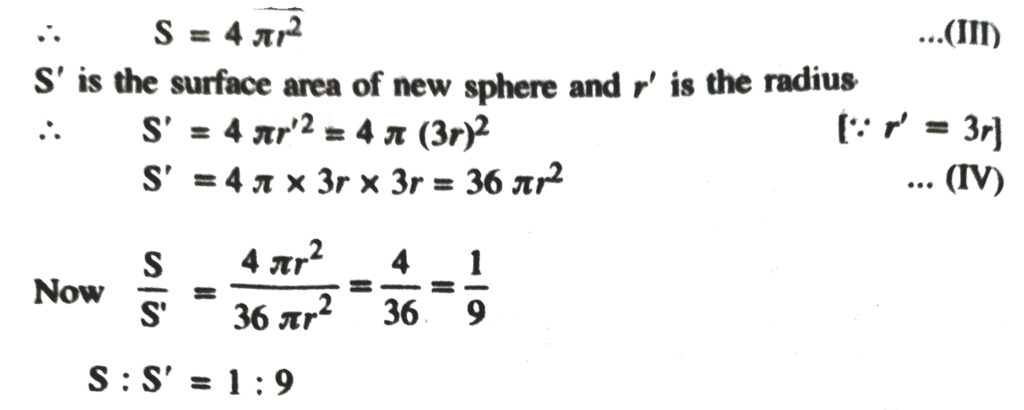INTRODUCTION
Wherever we look, we see solids. So far, in all our study, we have been dealing with figures that can be easily drawn on our note books or blackboards. These are called plane figures. We have understood what rectangles, squares and circles are, what we mean by their perimeters and areas, and how we can find them. We have learnt these in earlier classes. It would be interesting to see what happens if we cut out many these plane figures of the same shape and size from cardboard sheet and stack them up in vertical pile. By this process we shall obtain some solid figures (briefly called solids) such as a cuboid, a cylinder, etc. In the earlier classes, we have also learn to find the surface areas and volumes of cuboids, cubes and cylinders. We shall now learn to find the surface areas and volumes of cuboids and cylinders in detail and extend this study to some other solids such as cones and spheres.
Surface Area of a Cuboid and a Cube
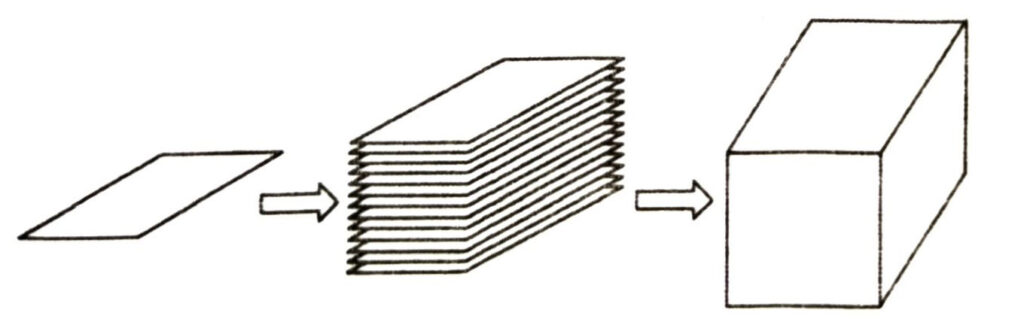
Look at a bundle of many sheets of paper.
It looks like what you see in Fig.
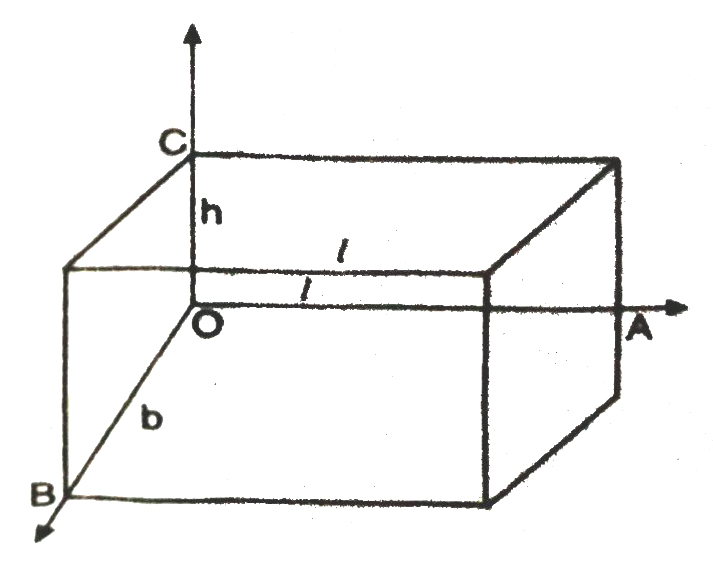
That makes up a cuboid. If you want to cover this cuboid with brown paper.
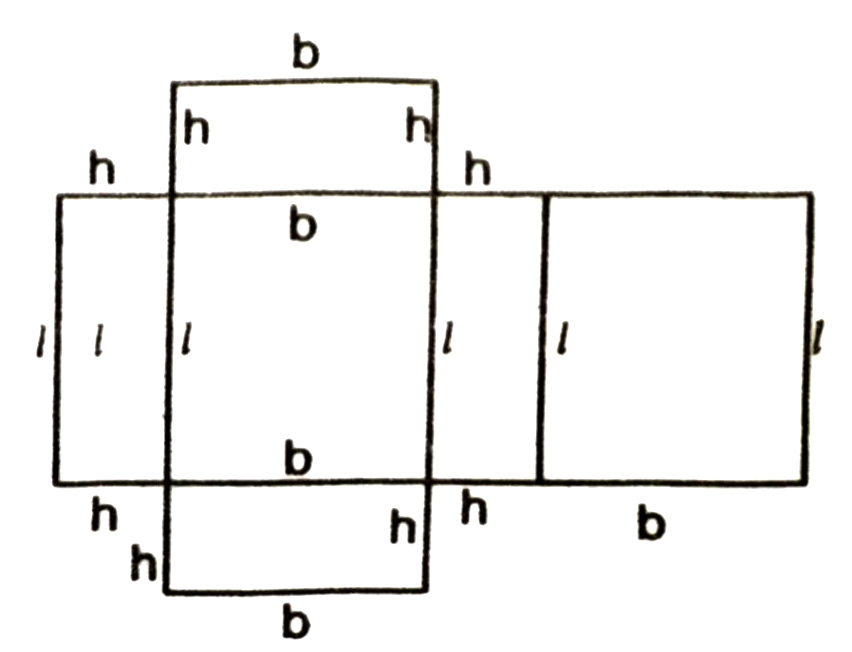
So we have to use six rectangular pieces to cover complete outer surface of the cuboid as shown in Fig.
Some of the areas of the six rectangles becomes ; 2 (lb + bh + hl)
Thus ;
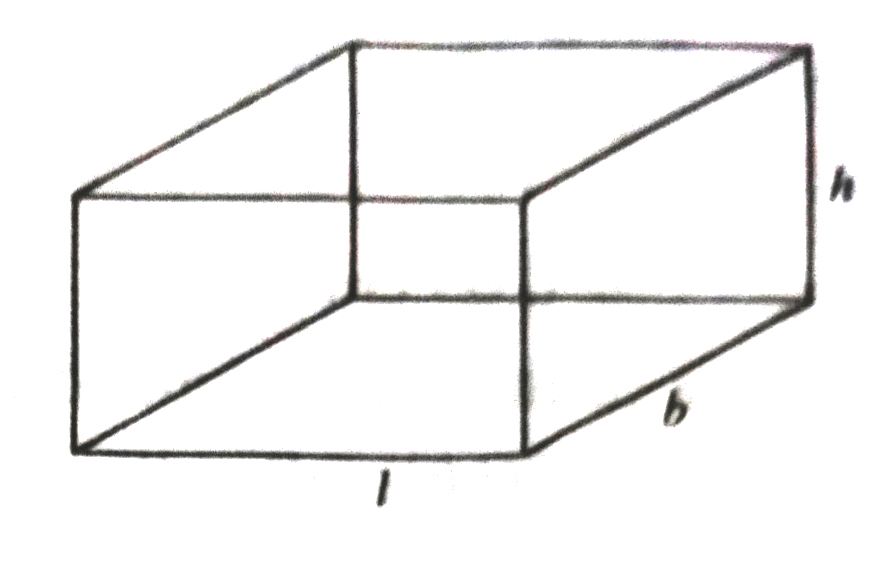
Surface Area of a Cuboid = 2 (lb + bh + hl)
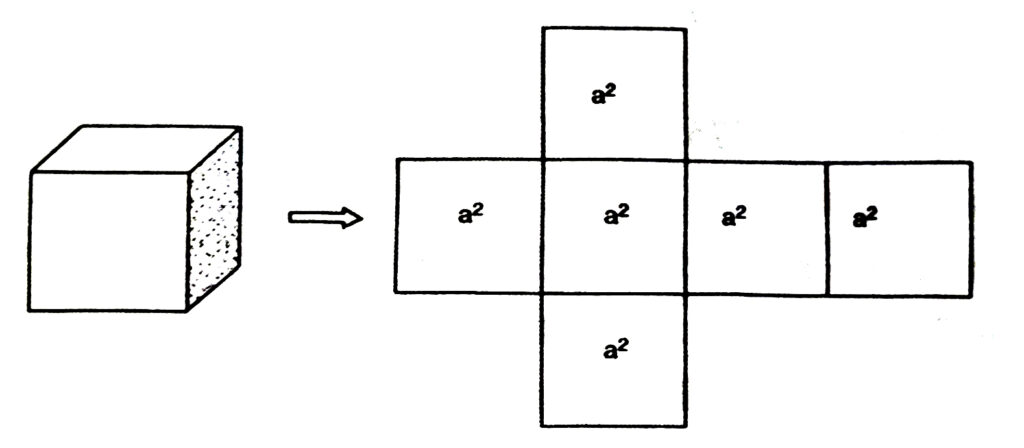
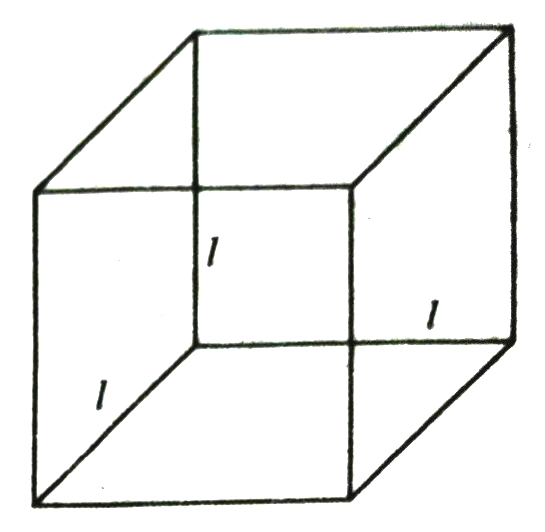
(where l, h and h are respectively the three edges of the cuboid) Recall that a cuboid whose length, breadth and height are all equal to each other is called a cube. If each edge of the cube is a, then the surface area of this cube would be
2(a × a + a × a + a × a)
= 2 (a² + a² + a²)
[See Fig.], giving us.
Surface Area of a Cube = ба²
(where a is the edge of the cube)
Suppose out of the six faces of a cuboid, we only find the area of the four faces, leaving the bottom and top faces. In such a case, the area of these four faces is called the lateral surface area of the cuboid. So, lateral surface area of a cuboid of length l, breadth b and height h is equal to 2lh + 2bh or 2(l + b)h. Similarly, lateral surface area of a cube of side a is equal to 4a².
Keeping in view the above, the surface area of a cuboid (or a cube) is sometimes also referred to as the total surface area.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 13.1
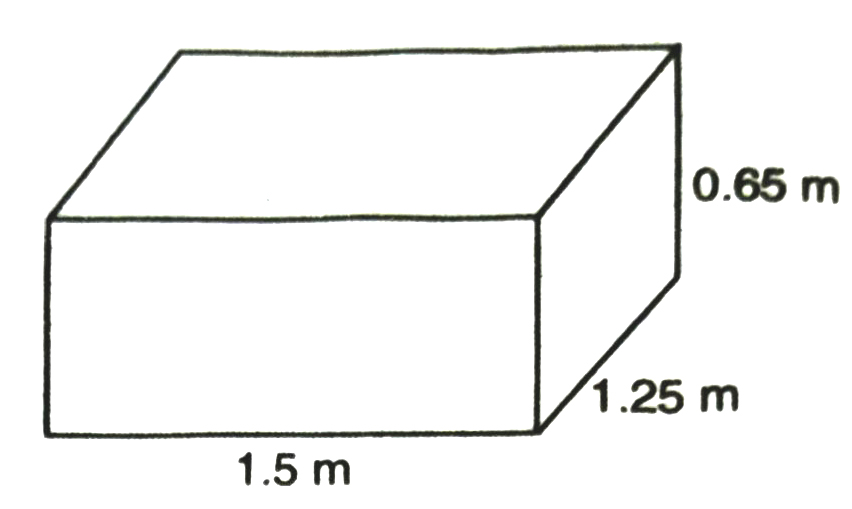
1. A plastic box 1.5 m long, 1.25 m wide and 65 cm deep is to be made. It is to be open at the top. Ignoring the thickness of the plastic sheet, determine :
(i) The area of the sheet required for making the box.
(ii) The cost of sheet for it, if a sheet measuring 1 m² cost 20.
Solution.— (i) Let length (l) of plastic box = 1.5 m
width (b) = 1.25 m
and depth (h) = 65 cm
Area of the sheet required for making the box open at the top
= 2(bh + hl) + lb
= 2{1.25 × 65/100 + 65/100 × 1.5} + 1.5 × 1.25
= 2 (0.8125 + 0.975) + 1.875
= 2 (1.7875) + 1.875
= 3.575 +1.875
= 5.45 m²
(ii) If cost of 1 m² sheet = ₹ 20
Cost of 5.45 m² sheet = ₹ (20 × 5.45) = ₹ 109
2. The length, breadth and height of a room are 5 m, 4 m and 3 m respectively. Find the cost of white washing the walls of the room and the ceiling at the rate of 7.50 per m².
Solution.— Let length of the room (l) = 5 m
Breadth (b) = 4 m
and Height (h) = 3 m
Area of the four walls of room = Lateral surface area
= 2 (bh + hl)
= 2(b + l) h
= 2 (4 + 5) 3
= 2 × 9 × 3
= 54 m²
Area of the ceiling = l × b
= (5 × 4) m²
= 20 m²
So, total area of walls and ceiling of the room
= 54 m² + 20 m²
= 74 m²
Cost of white washing 1 m² = ₹ 7.50
Cost of white washing 74 m²
= ₹ (7.50 × 74)
= ₹ 555
3. The floor of a rectangular hall has a perimeter 250 m. If the cost of painting the four walls at the rate of ₹ 10 per m² is ₹ 15000, find the height of the hall.
Solution.— Let length of the rectanglar wall = l m
breadth = b m
∴ Perimeter of rectanglar hall = 2 (l + b) = 250 m …(i)
Now area of the four walls of the room
Total cost to paint four walls of room / Cost to paint 1m² of the walls
= ₹ 1500/ ₹ 10
= 1500 m² …(ii)
Let height in meters of the rectangular hall = h
Area of four walls (lateral surface area)
= 2 (l + b) h = 1500 m² [Using (ii)]
⇒ 250 × h = 1500 [Using (ii)]
⇒ h = 1500/250
⇒ h = 6 m
Hence required height of the hall is 6 m.
4. The paint in a certain container is sufficient to paint an area equal to 9.375 m². How many bricks of dimensions 22.5 cm × 10 cm × 7.5 cm can be painted out of this container ?
Solution.— Let length of brick = l = 22.5 cm
breadth = b = 10 cm
and height = h = 7.5 cm
Area of brick = 2 (lb + bh + hl)
= 2 (22.5 × 10 + 10 × 7.5 + 7.5 × 22.5)
= 2 (225 +75 + 468.75)
= 2 × 468.75
= 937.5 m²
Hence 100 bricks can be painted out of the paint given in the container.
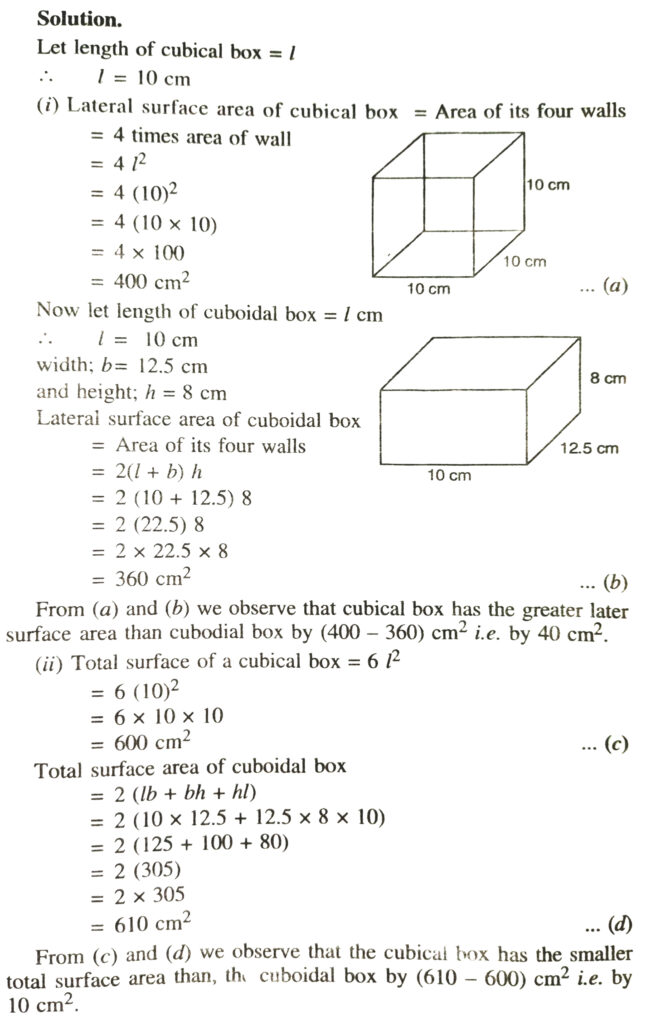
5. A cubical box has each edge 10 cm and a cuboidal box is 10 cm wide, 12. 5 cm long 8 cm high.
(i) Which box has the greater lateral surface area and by how much ?
(ii) Which box has the smaller total surface area and by how much ?
Solution.—
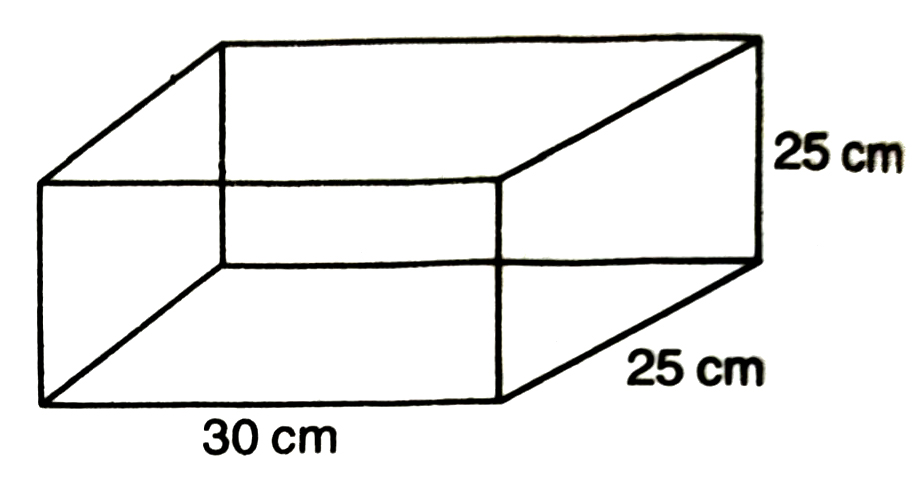
6. A small indoor greenhouse (herbarium (is made entirely of glass panes (including base) held together with tape. It is 30 cm long, 25 cm wide and 25 cm high.
(i) What is the surface area of the glass ?
(ii) How much of tape is needed for all the 12 edges ?
Solution.— (i) Let length of glass herbarium = l
∴ l = 30 cm
breadth (width); b = 25 cm
and height; h = 25 cm
Total surface area of the glass
= 2 (lb + bh + hl)
= 2 (30 × 25 + 25 × 25 + 25 × 30)
= 2 (750 + 625 + 750)
= 2 × 2125
= 4250 cm²
Hence 4250 cm² of the glass is required to make a herbarium.
(ii) Tape is used at 12 edges
i.e. at 4 lengths, 4 breadths and 4 heights.
Total length of tape = 4 (l + b + h)
= 4 (30 + 25 + 25)cm
= 4 (80) cm
= 320 cm
Hence 320 cm of the tape is needed to fix 12 edges of herbarium.
7. Shanti Sweets Stall was placing an order for making cardboard boxes for paking their sweets. Two sizes of boxes were required. The bigger of dimensions 25 cm by 20 cm by 5 cm and the smaller of dimensions 15 cm by 12 cm by 5 cm. 5% of the total surface area is required extra, for all the overlaps. If the cost of the cardboard is ₹ 4 for 1000 cm², find the cost of cardboard required for supplying 250 boxes of each kind.
Solution.— Let length of bigger cardboard box = L cm
∴ L = 25 cm
breadth; B = 20 cm
and height; H = 5 cm
Total surface area of bigger cardboard box
= 2 (15 × 12 + 12 × 5 + 5 × 15) cm²
= 2 (180 + 60 + 75) cm²
= 2 (315) cm²
= 630 cm²
5% of extra surface of total surface area is required for all the overlaps.
∴ 5% of 630 cm²
= 5/100 × 630
= 31.5 cm²
Now total surface area of smaller cardboard box with extra overlaps
= (630 + 31.5) cm²
= 661.5 cm²
Total surface area (with extra overlaps) of 250 such smaller boxes
= (661.5 × 250) cm²
= 165375 cm²
Cost of the cardboard for 1000 cm² = ₹ 4
Cost of the cardboard for 1 cm² = ₹ {4/100}
Cost of the cardboard for 165375 cm²
= ₹ {4 / 1000 × 165375
= 661.5
Total cost of the cardboard required for supplying 250 boxes of each kind
= cost of the bigger boxes + cost of the smaller boxes
= ₹ 1522.5 + ₹ 661.5
= ₹ 2184
8. Parveen wanted to make a temporary shelter for her car, by making a box-like structure with tarpaulin that covers all the four sides and the top of the car (with the front face as a flap which can be rolled up). Assuming that the stitching margins are very small, and therefore negligible, how much, tarpaulin would be required to make the shelter of height 2.5 m. with base dimensions 4 m × 3 m ?
Solution.— Let length of base = l
∴ l = 4 m
and breadth of base = b
∴ b = 3 m
and height of structure = h
∴ h = 2.5 m
Tarpaulin required to make the shelter = Surface are of four walls + Area of the roof
= 2 (l + b)h + lb
= 2 (4 + 3) 2.5 + 4 × 3
= 2 × 3 × 2.5 + 12
= 35 + 12
= 47 m²
Hence 47 m² of the tarpaulin is required to make the shelter for the car.
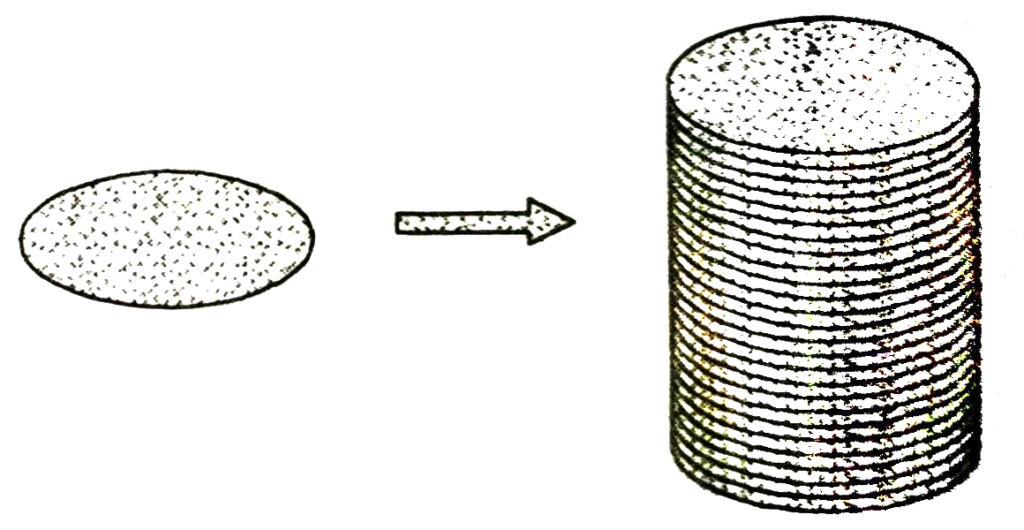
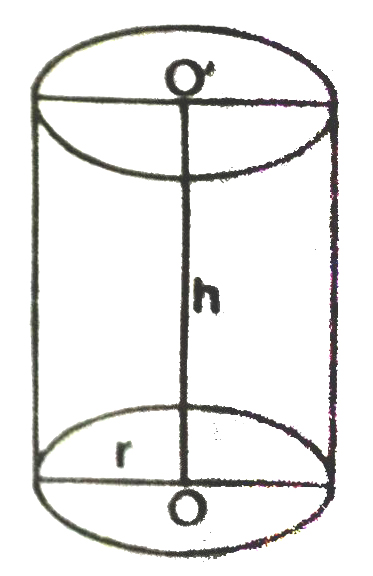
RIGHT CIRCULAR CYLINDER
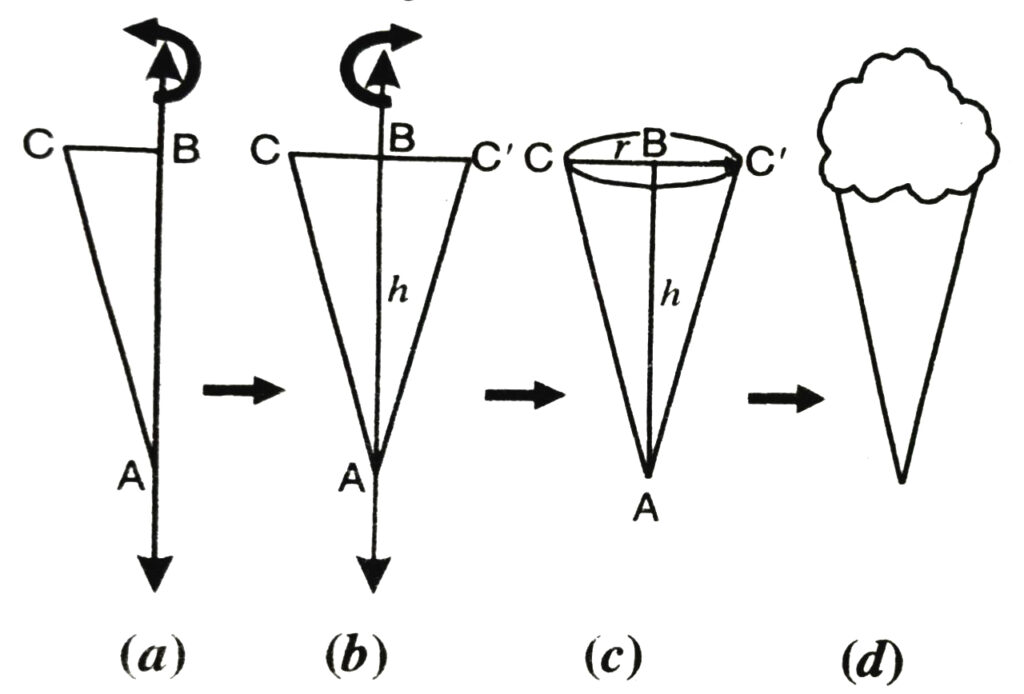
If we take a number of circular sheets of paper and stack them up what should we get ? [See Fig.]
Here, if the stack is kept vertically up, we get what is called a right circular cylinder, since it has been kept at right angles to the base, and the base is circular.
Let us define right circular cylinder and its parts as follows :
(a) The solid right circular cylinder is the region in space bounded by the two circular ends and the lateral surface of the cylinder.
(b) Each plane end of a right circular cylinder is called its base.
(c) The line segment joning the centres of the circular ends of a right circular cylinder is called is axis. The length of the axis is called the height of the cylinder.
(d) The curved surface which joins the two bases of a right circular cylinder is called its lateral surface.
Surface Area of Right Circular Cylinder
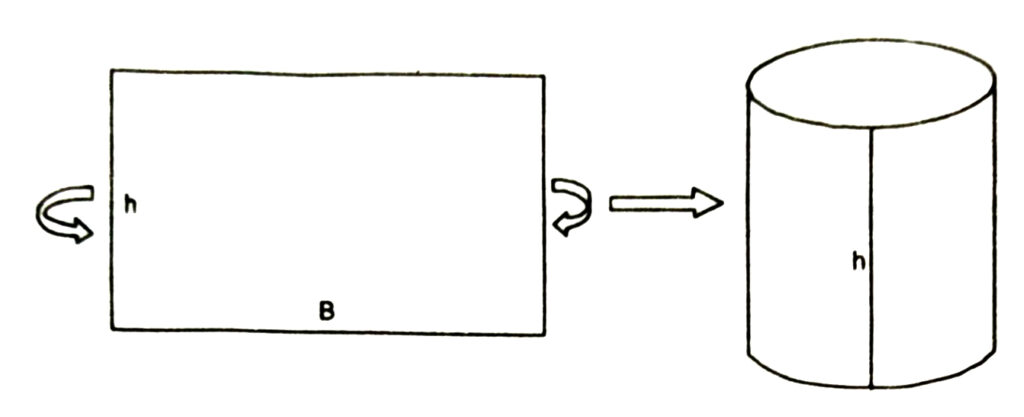
(i) Lateral (or Curved) surface area of Cylinder
= Length × breadth of rectangular sheet
= Perimeter of the base of the cylinder × h
= 2πr × h
Therefore,
Curved Surface Area of a Cylinder = 2πrh
(Where r is the radius)
(ii) Total Surface Area of a Cylinder
= 2 × (Area of Base) + (Area of Lateral Surface)
Total Surface Area = 2лr (h + r).
Remark :
(i) Right circular cylinder may be hollow or solid.
(ii) Hollow circular cylinder is just formed by the lateral surface of the cylinder.
(iii) The part of the space enclosed by a right called its interior.
(iv) A right circular cylinder along with its interior is called right circular region which is generally referred to as a solid right circular cylinder.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 13.2
Assume π = 22/7 unless stated otherwise.
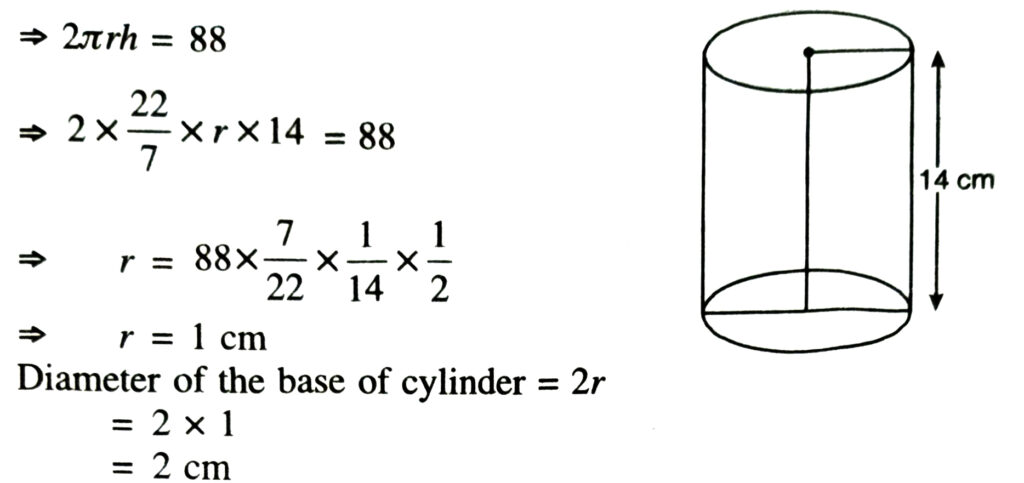
1. The curved surface area of a right circular cylinder of height 14 cm is 88 cm². Find the diamter of the base of the cylinder.
Solution.— Let radius of base of right circular cylinde = r cm
Height of cylinder = h = 14 cm
Curved surface area of cylinder = 88 cm²
2. It is required to make closed a cylindrical tank of height 1 m and base diameter 140 cm from a metal sheet. How many square metres of the sheet are required for the same ?
Solution.— Let radius of base of cylinder tank = r cm
∴ diameter; 2r = 140 cm
⇒ r = 140/2
⇒ r = 70 cm
⇒ r = 70/100 cm
⇒ r = 0.7 m
Height of cylinder = h = 1m
Total surface area of cylinder = 2лr (r + h)
= 2 × 22/7 × 0.7 (0.7 + 1)
= 2 × 22 × 0.1 × 1.7
= 7. 48 m
Hence 7.48 m² metal sheet is required to make the close cylindrical tank.
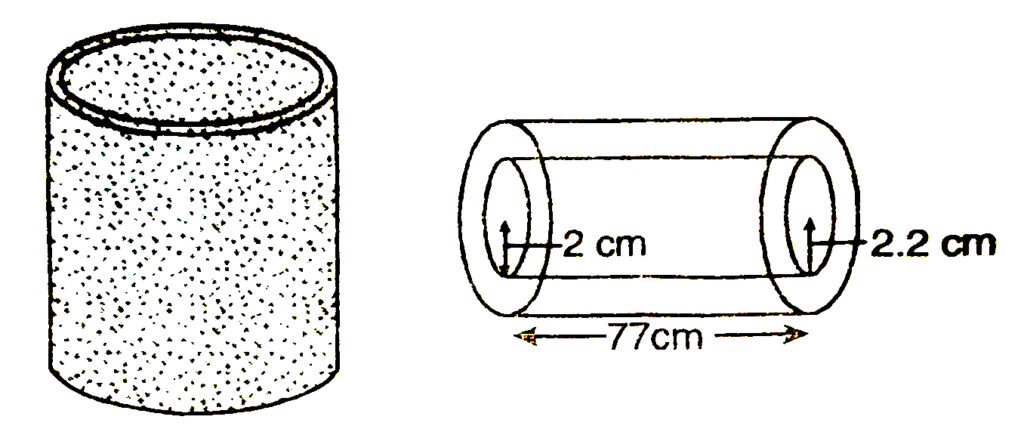
3. A metal pipe is 77 cm long. The inner diameter of a cross section is 4 cm, the outer diameter being 4.4 cm [See Fig.]. Find its
(i) inner curved surface area,
(ii) outer curved surface area,
(iii) total surface area.
Solution.— Length of pipe 77 cm
(i) Inner diameter of cross-section = 4 cm
∴ Inner radius of cross-section; r = 4/2 = 2 cm
As the pipe is the shape of cylinder
∴ Inner curved surface area = 2лrh [∴ Length of pipe = height].
= 2 × 22/7 × 2 × 77
= 2 × 22 × 2 × 11 = 968 cm²
(ii) Length of pipe = 77 cm
Outer diameter of pipe = 4.4 cm
Outer radius of pipe; R = 4.4/2 = 2.2 cm
∴ Outer curved surface area of cylinder
= 2лrh
= 2 × 22/7 × 2.2 × 77
= 44/7 × 22/10 × 77
= 44 × 22/10 × 11 cm²
= 1064.8 cm²
(iii) Now there are two circles of radii 2 cm and 2.2 cm at both the ends of the pipe
∴ Area of two edges of the pipe
= 2 (Area of outer circle – Area of inner circle)
= 2 (лR² – лr²)
= 2π (R² – r²)
= 2 × 22/7 [(2.2)² – (2)²] cm²
= 44/7 [4.84 – 4]cm²
= 44/7 × 0.84 = 5.28 cm²
∴ Total surface ara of pipe = Inner curved surface area + Outer curved surface area + Area of two edges
= 968 cm² + 1064.8 cm² + 5.28 cm²
= 2038.08 cm²
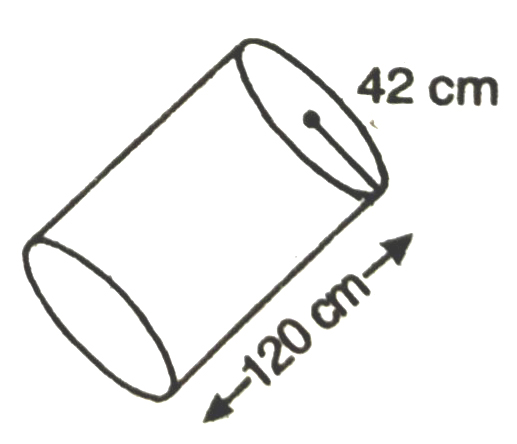
4. The diameter of a roller is 84 cm and its length is 120 cm. It takes 500 complete revolutions to move once over to level a playground. Find the area of the playground in m².
Solution.— Diameter of roller = 84 cm
Radius of roller; r = 84/2 = 42 cm
Length of roller; l = 120 cm
∴ Roller is in the shape of a cylinder
∴ Curved surface area of roller = Curved surface area of cylinder
= 2л rh (Here l = h)
= 2 × 22/7 × 42 × 120
= 31680 cm²
= 31680/100 × 100 m²
= 3.1680 m²
Now area levelled by roller in one revolution = 3.1680 m²
∴ Area levelled by roller in 500 revolutions = 500 × 3.1680
= 1584.0000
= 1584m²
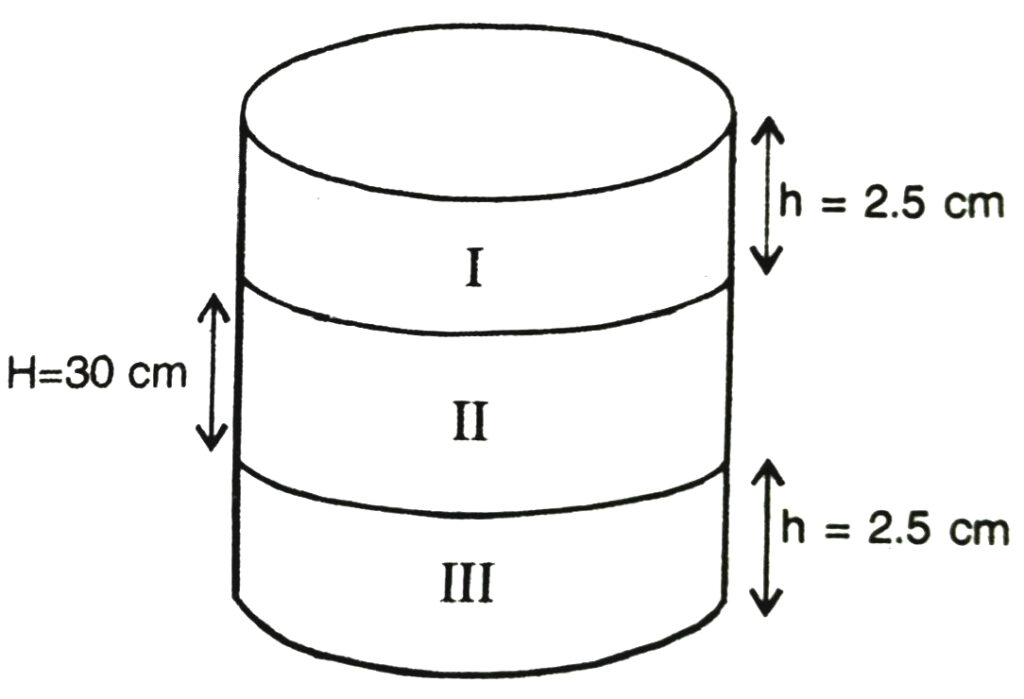
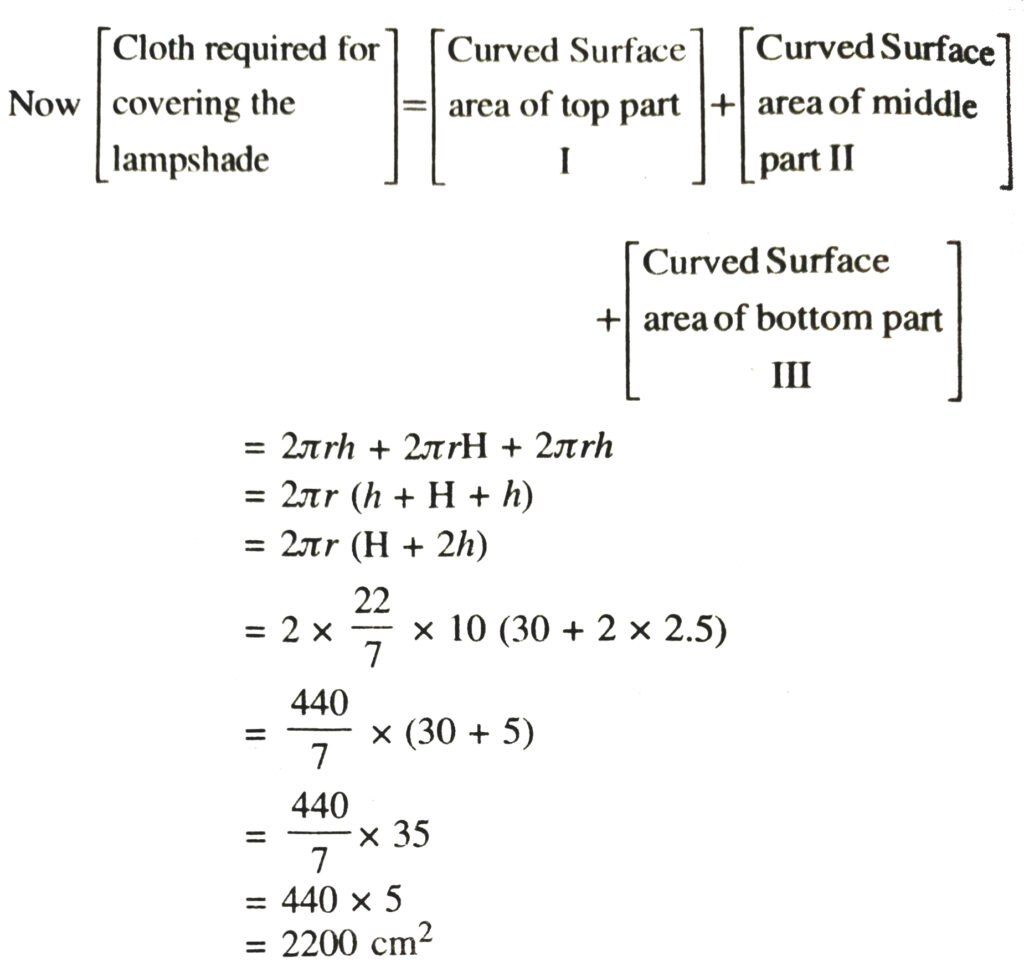
5. In the adjoining figure, you see the frame of a lampshade. It is to be covered with a decorative cloth. The frame has a base diameter of 20 cm and height of 30 cm. A margin of 2.5 cm is to be given for folding it over the top and bottom of the frame. Find how much cloth is required for covering the lampshade [See Fig.]
Solution.— Height of each of the foldings at the top and bottom = h = 2.5 cm
Height of frame = H = 30 cm
Let radius of each part = r
⇒ r = 20/2
⇒ r = 10 cm
6. The students of a Vidyalaya were asked to participate in a competition for making and decorating penholders in the shape of a cylinder with a base, using cardboard. Each penholder was to be of radius 3 cm and height 10.5 cm. The Vidyalaya was to supply the competitors with cardboard. If there were 35 competitors, how much cardboard was required to be bought for the competition ?
Solution.— Let radius of a cylindrical penholder = r
∴ r = 3 cm
and height of cylindrical pen holder = h
Cardboard required for a pen holder
∴ h = 10.5 cm
= Curved surface area of a pen holder + area of the circular base
= 2лrh + πr²
= лr (2h + r)
= 22/7 × 3 (2 × 10.5 + 3)
= 22/7 × 3 (21 + 3)
= 22/7 × 3 × 24
= 226.28 cm²
Now; cardboard required for making
one penholder = 226.28 cm²
∴ Cardboard „ „ „ 35 pen holders
= (226.28 × 35) cm²
= 7919.8 cm²
or = 7620 cm² (approx)
III. Right Circular Cone
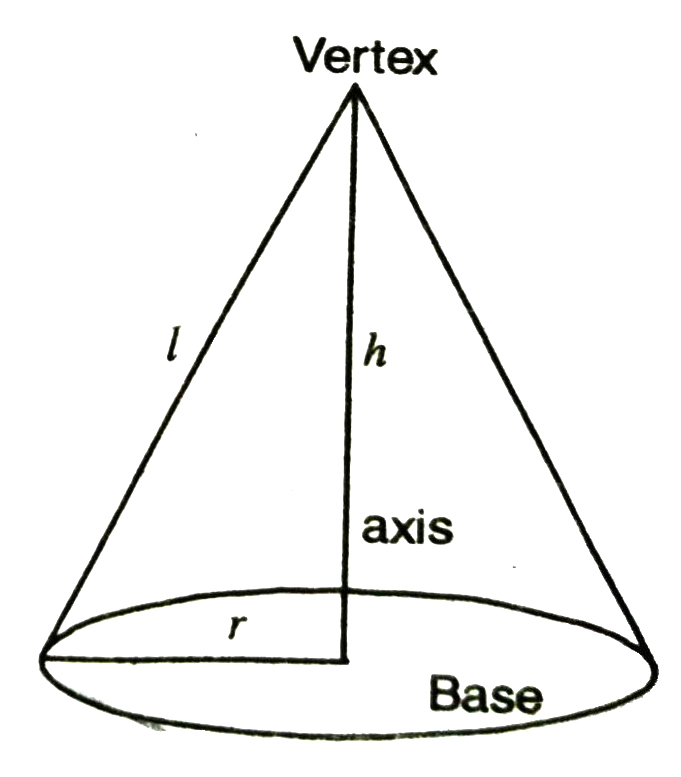
Let us define right circular cone as in follows :
(a) Cone: The solid cone is the figure in space, bounded by the curved surface of the cone and its plane end.
(b) The plane circular end of a right circular cone is called its base. The only corner of the cone, the point of the cone farthest from the base, is called its vertex.
(c) The line segment joining the vertex to the centre of the base of the cone is called its axis. The length of the axis is called the height of the cone.
(d) The curved surface connecting the vertex of the circular edge of called its lateral surface.
(e) The length of the line joining a point on the circular edge of the base to the vertex is called the slant height of the cone.
Surface Area of the Cone
(i) Area of lateral (curved) surface of a cone
= 1⁄2 × x (circumference of base) x (Slant height)
S = лrl.
(ii) Total surface area of cone
= Lateral surface area of cone + Area of circular base of cone
= πrl + πr²
= πr (l + r) where slane height; l = √r² + h²
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 13.3
Assume π = 22/7 unless stated otherwise.
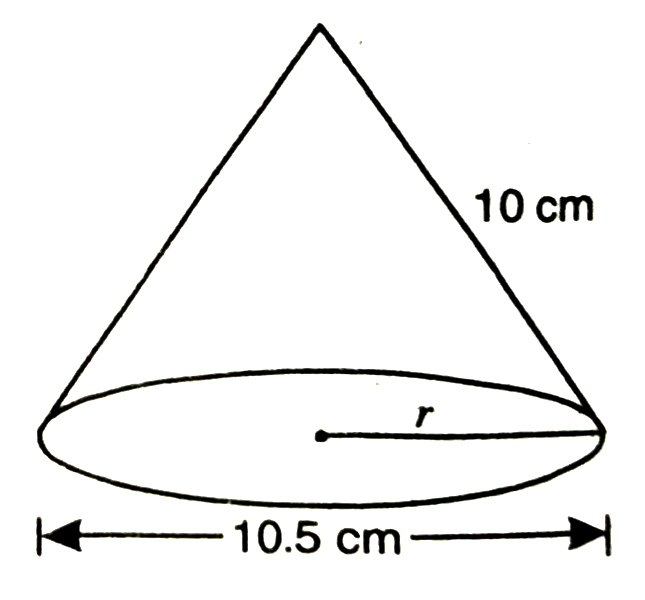
1. Diameter of the base of a cone is 10.5 cm and its slant height is 10 cm. Find its curved surface area and its total surface area.
Solution.— Let radius of the circular base of cone = r cm
∴ diameter; 2r = 10.5 cm
⇒ r = 10.5/2
⇒ r = 105/20
⇒ r = 21/4
Start height of cone = l = 10 cm
So, curved surface area of cone = лrl
= 22/7 × 21/4 × 10
= 165 cm²
Total surface area of cone
= curved surface area of cone + Area of circular base of cone
= лrl + лr²
= πr (l + r)
= 22/7 × 21/4 {10 + 21/4}
= 22/7 × 21/4 × 61/4
= 251.625 cm²
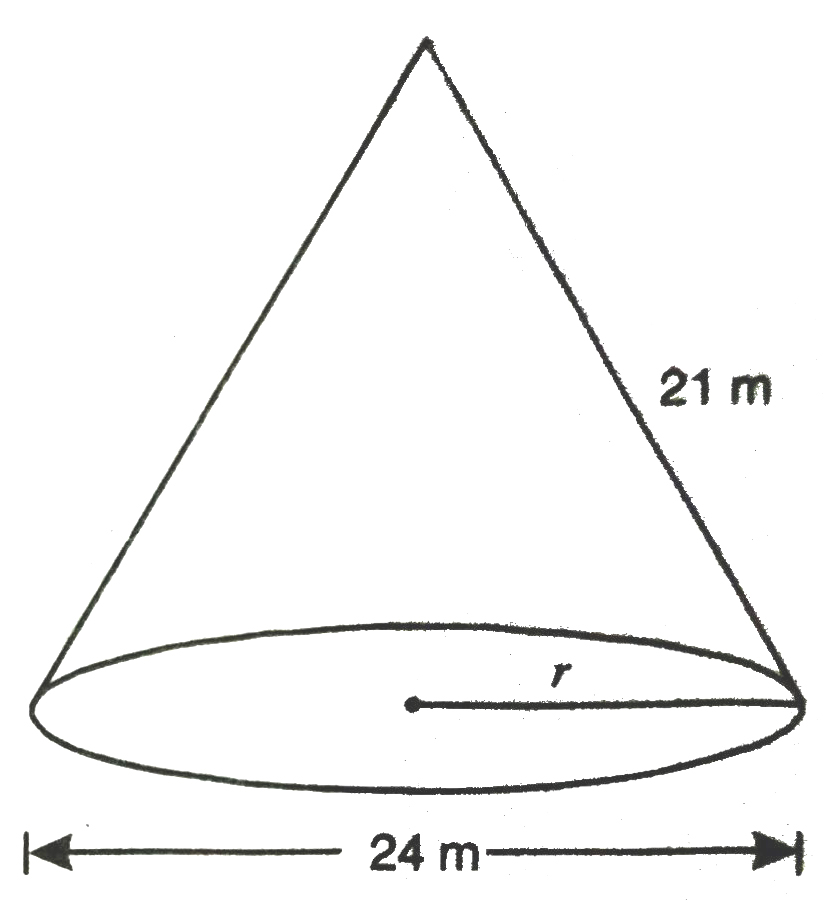
2. Find the total surface area of a cone, if its slant height is 21 m and diameter of its base is 24 m.
Solution.— Slant height of cone = 21 m
Diameter of cone = 24 m
Radius of cone = 24/2 = 12 m
Total surface area of cone = πrl + πr²
= πr (l + r)
= 22/7 × 12 (21 + 12) m²
= 264/7 × 33 = 1244.57 m²
3. Curved surface area of a cone is 308 cm², and its slant height is 14 cm. Find (i) radius of the base and (ii) total surface area of the cone.
Solution.— (i) Let radius of the circular base of cone = r
Slant height; l = 14 cm
Curved surface area of cone = 308 cm² (given)
⇒ лrl = 308
⇒ 22/7 × r × 14 = 308
⇒ r = 308 × 22/7 × 1/14
⇒ r = 7 cm
(ii) Total surface area of the cone
= curved surface area of the cone + Area of circular base of cone
= 308 + πr²
= 308 + 22/7 × 7²
= 308 + 22 × 7
= 308 + 154
= 462 cm²
4. A conical tent is 10 m high and the radius of its base is 24 m.
Find
(i) slant height of the tent.
(ii) cost of the canvas required to make the tent, if the cost of 1 m² canvas is ₹ 70.
Solution.— Height of conical tent; h = 10 m
Radius of conical tent; r = 24 m
(i) Slant height of tent ; l = √r² +h²
= √(24)² + (10)²
= √576 + 100
= √676
= 26 m
For (ii) Canvas required to make the tent = Curved surface area of tent
= πrl
= 22/7 × 24 × 26 = 13728/7 m²
Cost of 1 m² canvas = ₹ 70
Cost of 13728/7 m² canvas
= ₹ 70 × 13728/7
= ₹ 137280
5. What length of tarpaulin 3 m wide will be required to make conical tent of height 8 m and base radius 6 m ? Assume that the extra length of material that will be required for stitching margins and wastage in cutting is approximately 20 cm (use π = 3.14).
Solution.— Height of tent; h = 8 m
Radius of tent ; r = 6 m
Slant height of tent ; l = √r² + h²
= √(6)² + (8)²
= √36 + 64
= √100
= 10 m
Area of tarpaulin = curved surface area of tent = πrl
= 3.14 × 6 × 10 = 188.4 m²
Width of tarpaulin = 3 m
Let length of tarpaulin = L
∴ Area of tarpaulin = Length × Width = L × 3 = 3L
3L = 188.4 [∴ Area = 188.4 m²]
L = 188.4 = 62.8 m 3
The extra length of the material required for stitching margins and cutting is 20 cm i.e. 0.2 m
[∴ 1 cm = 1/100 m]
So, the total length of tarpaulin bought is (62.8+ 0.2) m = 63 m
6. The slant height and base diameter of a conical tomb are 25 m and 14 m, respectively. Find the cost of whitewashing its curved surface at the rate of ₹ 210 per 100 m².
Solution.— Slant height of conical tomb, l = 25 m
Diameter of conical tomb = 14 m
Radius of conical tomb, r = 14/2 = 7 m
Curved surface area of tomb = πrl
= 22/7 × 7 × 25 = 550 m²
Cost of white washing 100 m² = ₹ 210
Cost of white washing 1 m² = ₹ 210/100
Cost of white washing 550 m² = ₹ 210/100 × 550 = ₹ 1155
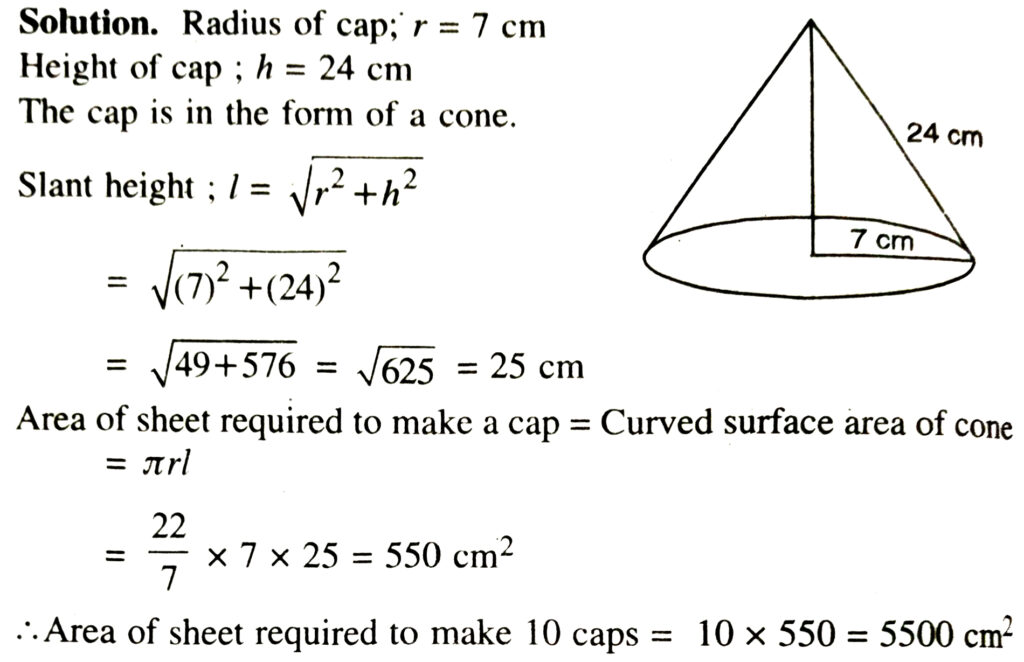
7. A Joker’s cap is in the form of a right ciruclar cone of base radius 7 cm and height 24 cm. Find the area of the sheet required to make 10 such caps.
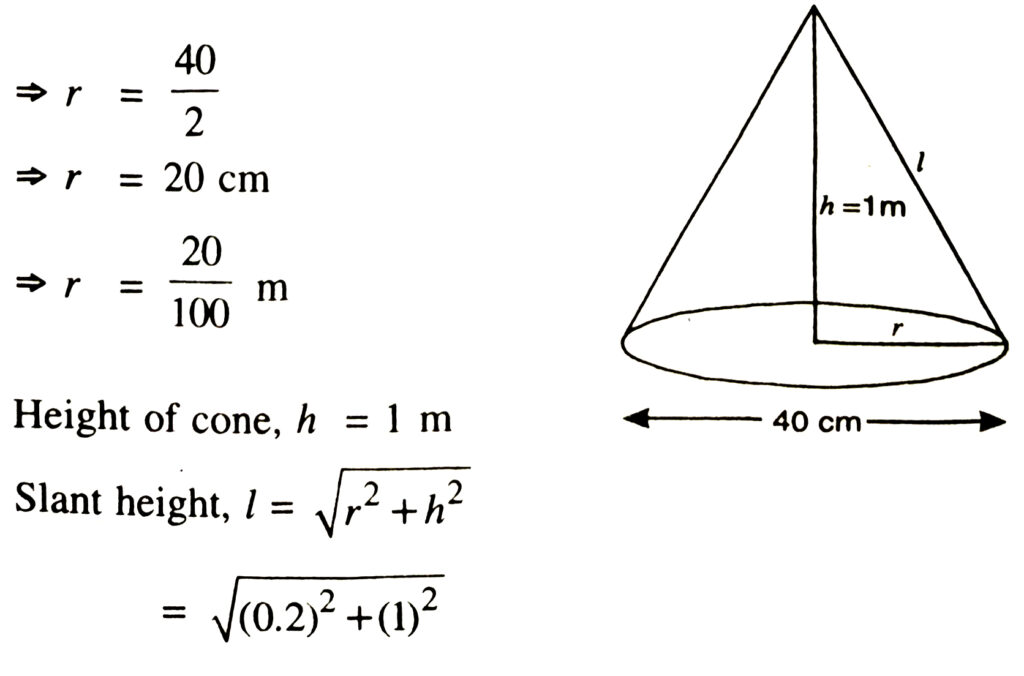
8. A bus stop is barricaded from the remaining part of the road, by using 50 hollow cones made of recycled cardboard. Each cone has a base diameter of 40 cm and height 1 m. If the outer side of each of the cones is to be painted and the cost of painting is ₹ 12 per m², what will be the cost of painting all these cones ?
[use π = 3.14, and take √1.04 = 1.02)
Solution.— Let radius of the circular base of cone = r
∴ diameter; 2r = 40
SPHERE
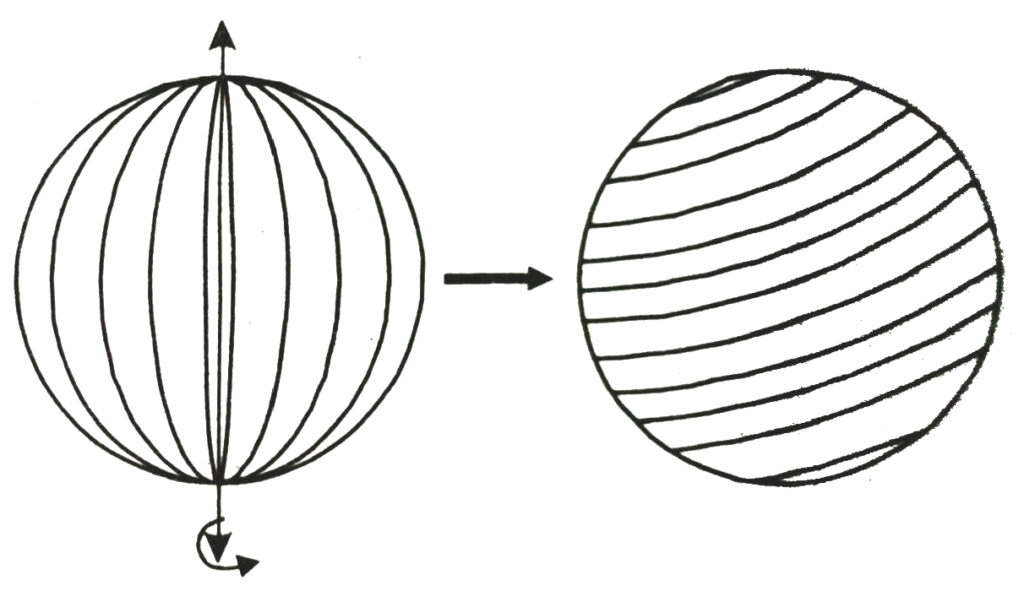
Paste a string along a diameter of the circular disc and rotate it as you had rotated the triangle in the previous section, you see a new solid [see Fig.]. What does it resemble ?
It resembles with a ball and it is called a sphere.
Let us define sphere and its parts as in follows :
(i) Sphere : A sphere is a solid which is made up of all points in the space, which lie at a constant distance (called the radius), from a fixed point called the centre of the sphere.
(ii) A sphere has a centre. The line segment joining a point on the sphere to the centre is called a radius of the sphere. A line segment through the centre of a sphere, and its end-points on the sphere is called a diameter of the sphere.
(iii) The length (r) of a radius is also called the radius of the sphere. The length (d) of a diameter is also called the diameter of the sphere. Also, d = 2r.
(iv) The sphere (hollow sphere) with centre O and radius r is the figure (in space) consisting of all the points (in space) which are at a distance r from O.
(v) The solid sphere with centre O and radius r is the region in space enclosed. by the sphere.
(vi) A plane through centre of a sphere divides it into two equal plarts, each of which is called a hemisphere.
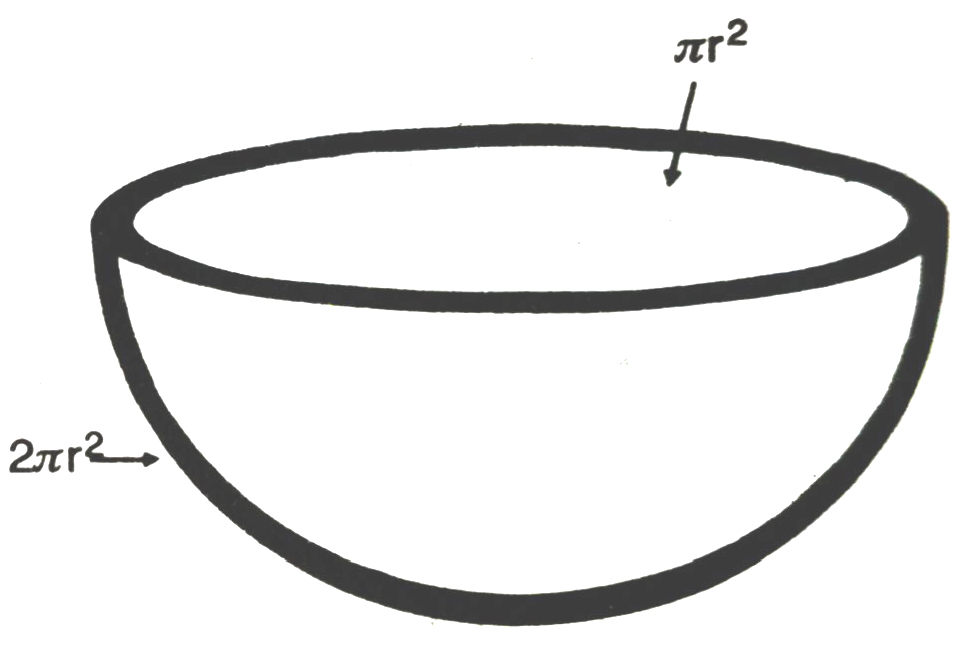
Surface Area of sphere and hemisphere
(i) Surface area of sphere = 4 × π × (radius)²
S = 4πr²
(ii) Curved surface area of Hemisphere = 2π × (radius)²
S = 2πr²
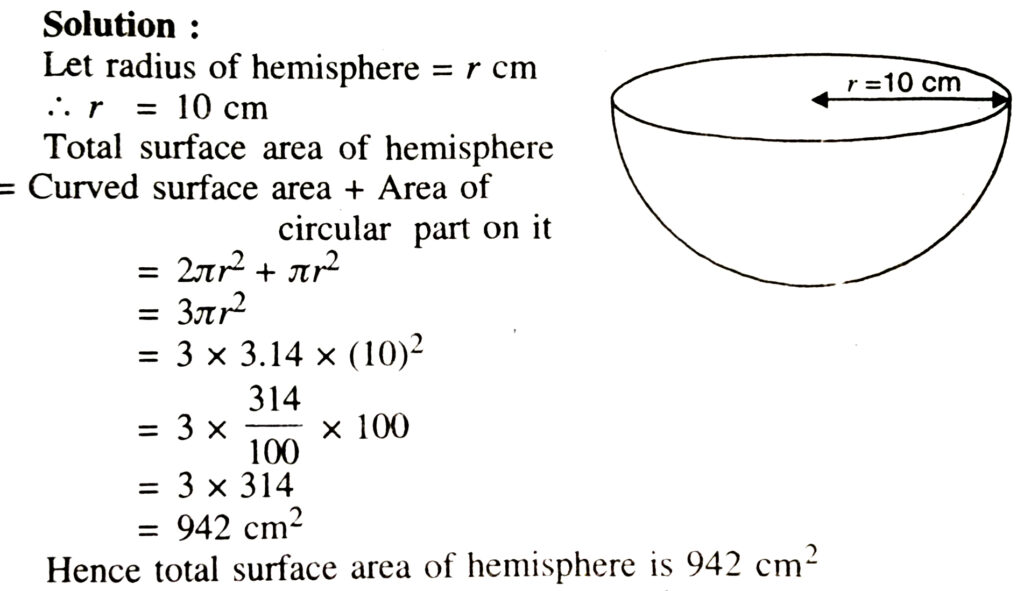
(iii) Total surface area of Hemisphere = curved surface area of hemisphere + area of circle = 2лr² + лr² = 3πr²
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE – 13.4
Assume π = 22/7 unless stated otherwise.
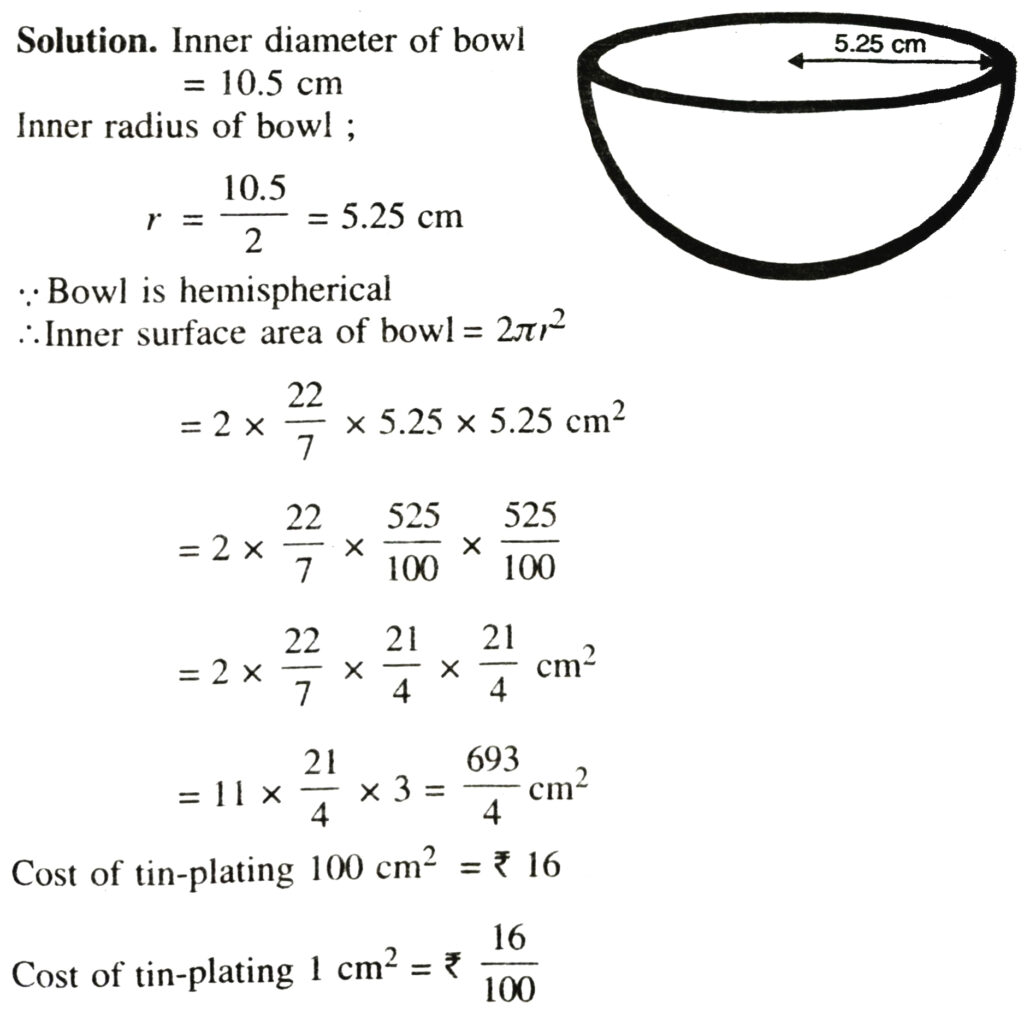
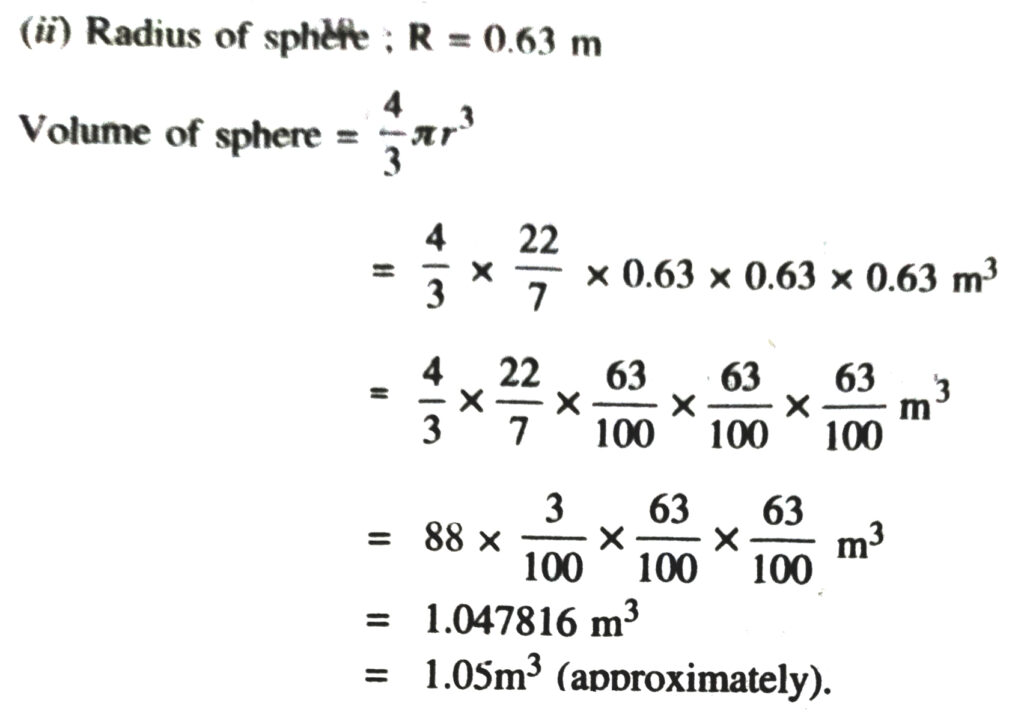
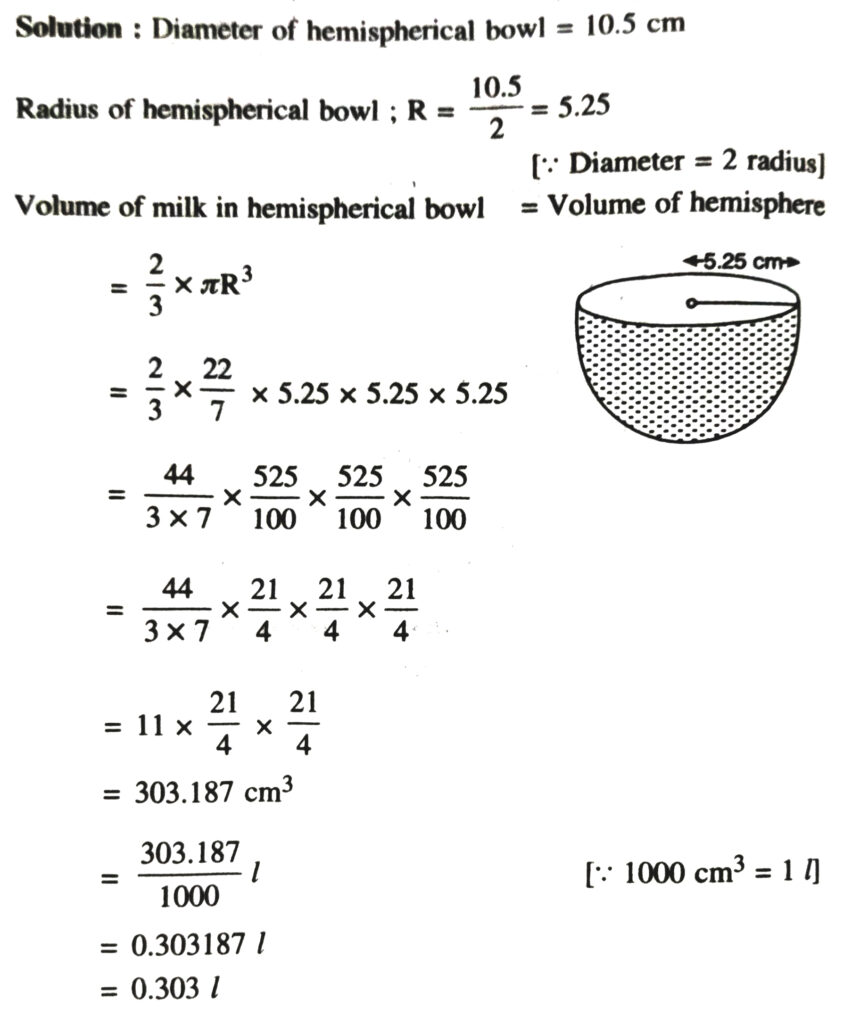
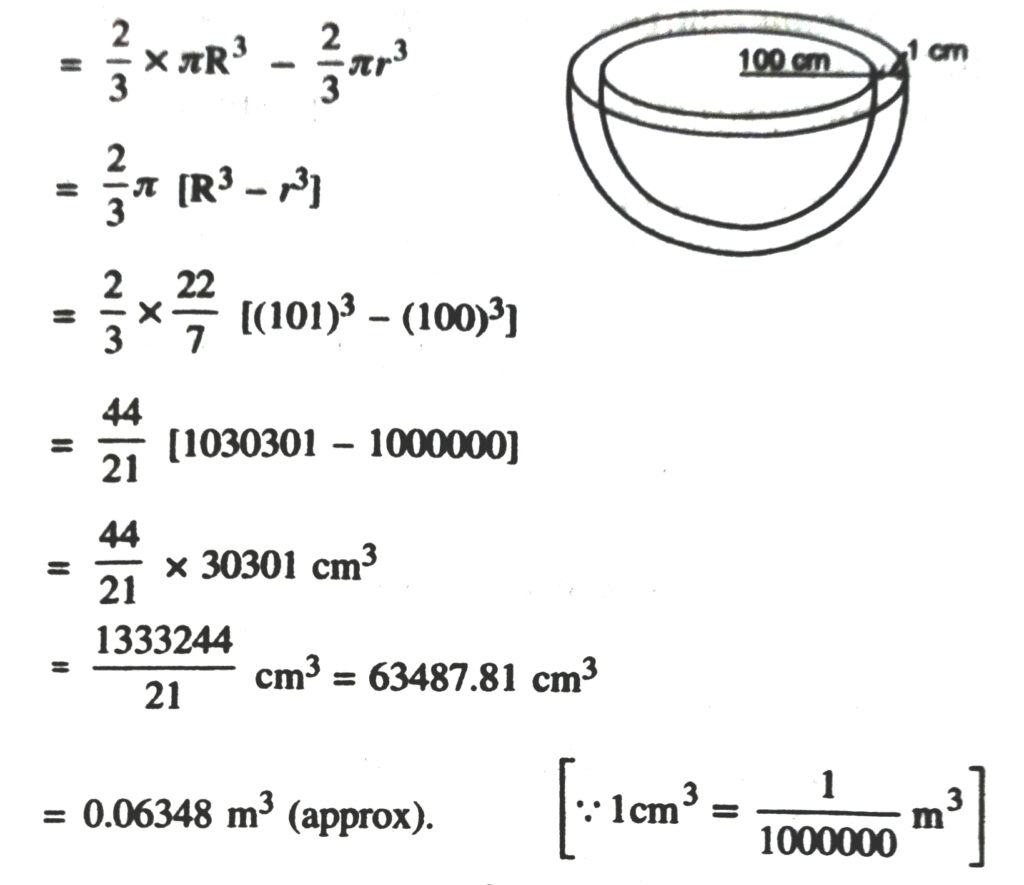
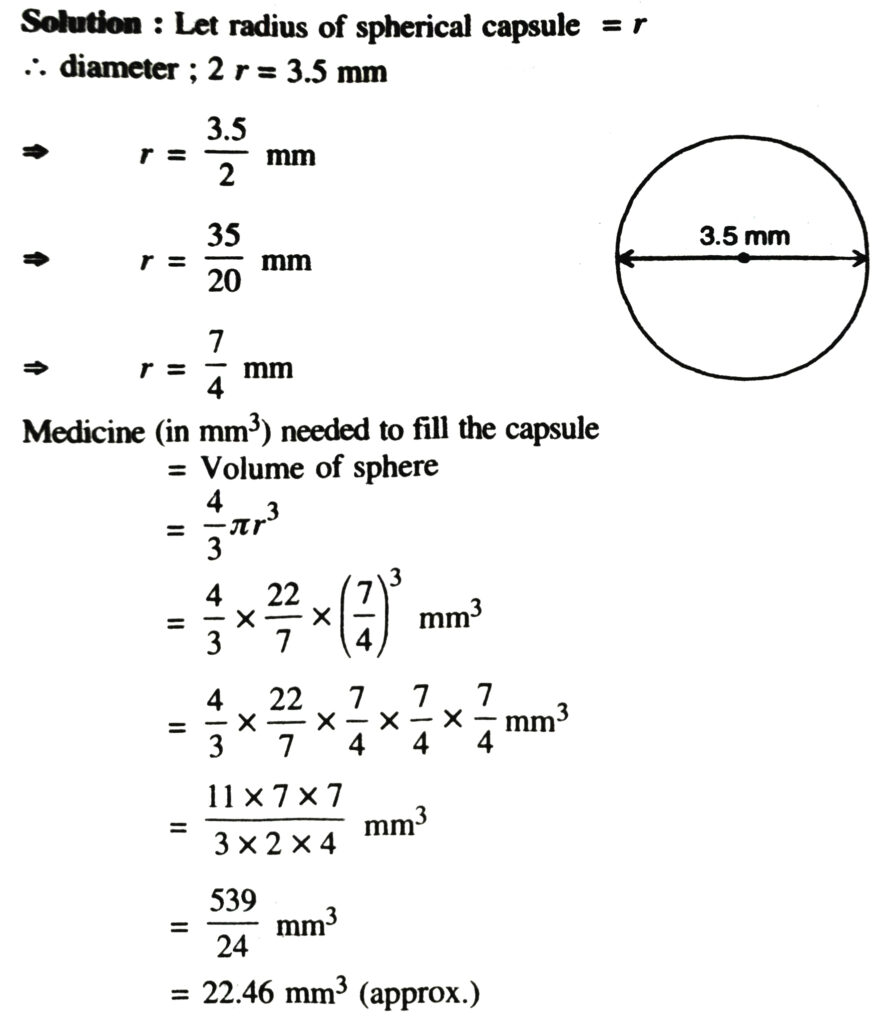
1. Find the surface area of a sphere of radius.
(i) 10.5 cm (ii) 5.6 cm (iii) 14 cm
Solution.— (i) Radius of sphere = 105 cm =
∴ surface area of sphere = 4πR²
(ii) Radius of sphere = 5.6 m
Surface area of sphere
(iii) Radius of sphere = 14 cm
Surface area of sphere
2. Find the surface area of sphere of diamter :
(i) 14 cm (ii) 21 cm (iii) 3.5 m