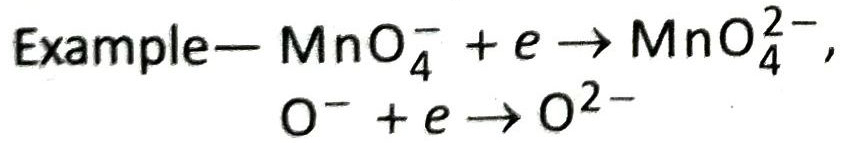WBBSE 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.5 Metallurgy
West Bengal Board 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.5 Metallurgy
WBBSE 10th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
8.5 Metallurgy
Synopsis
Ores, Minerals and Alloys
- Metals such as, iron, copper, zinc, aluminium. etc., have immense practical applications in our daily life.
- Naturally occurring inorganic substances derived from the earth’s crust which contain metals in their free state or in the form of compounds with earthy and rocky impurities are called minerals.
- Minerals from which high grade metals can be conveniently and economically extracted on a large scale are called ores.
- All ores are minerals, but all minerals are not ores.
-
A homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a nonmetal having different characteristic properties than the constituent elements is called an alloy.
Alloys are stronger, have greater tensile strength and are less reactive than the individual constituent metals or non-metals. These properties make them less susceptible towards corrosion and weathering.
Principles of Metal Extraction and Oxidation-Reduction
- A chemical reaction in which an atom, an ion or a molecule loses one or more electrons is called an oxidation reaction.
- A chemical reaction in which an atom, an ion or a molecule gains one or more electrons is called a reduction reaction.
- Extraction of a metal from its corresponding oxide by elimination of oxygen is known as reduction.
- Extraction of metals such as iron, chromium, manganese etc., from their oxides by heating the oxides wi aluminium powder at a high temperature is known as Goldschmidt’s thermite process. mixture of 3 parts of Fe2O3 and 1 part of aluminium powder is known as thermite mixture.
- The vertical arrangement of metals in decreasing order of their relative reactivity is known as metal activity series.
- A metal occupying a higher position (more reactive) in the metal activity series can displace another metal occupying a relatively lower position(less reactive) from the aqueous solution of its salt.
- Metals present in the middle of the activity series such as Zn, Fe etc., can be extracted from their ores by carbon reduction process.
- Metals present at the top of the metal activity series are extracted by electrolysis of their fused salts.
TOPIC – A
Ores, Minerals and Alloys
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Classify iron on the basis of carbon content. Which among these is the purest?
Ans. On the basis a carbon content, iron is divided into three categories-cast iron (C 2-4.5%), wrought iron (C: 0.1-0.15%) and steel (C: 0.151.5%).
Wrought iron is the purest form of iron.
Q.2 Write some uses of cast iron.
Ans. Cast iron is used in the making of (1) wrought iron and steel, (2) tubes, iron, railing, cauldron, lamp post etc.
Q.3 Write some uses of wrought iron.
Ans. Wrought iron is used in the making of (1) core of electromagnet, (2) wires, nails, rods, chains etc.
Q.4 Write some uses of steel.
Ans. Steel finds extensive use in modern civilization. It is used in the making of (1) automobiles, rails, knives, scissors, surgical instruments, ships, blades tankers etc. (2) cooking utensils, (3) alloy steel is made by adding other metals with steel.
Q.5 Why is copper used in the making of electrical wires and instruments?
Ans. Copper is a metal of low resistance and high malleability. Thus, it has a high value of electrical conductance and also it can be easily shaped into wires. Hence, it is used in the making of electrical wires and instruments.
Q.6 Copper is a good conductor of heat-state one application of this property.
Ans. (1) Copper is used in making cooking utensils because it is a good conductor of heat. (2) Copper is used in the construction of calorimeter which is quite helpful in measuring the amount of absorbed or released heat. (3) Copper is used in making of boilers in factory. Being a good conductor it helps in boiling of water quickly.
Q.7 Write some important uses of zinc.
Ans. (1) Zinc is used as a reagent in the laboratory for the preparation of hydrogen. (2) It is used in electrochemical cells and batteries. (3) It is also used in making of zinc white. (4) Zinc is coated over iron to protect it from rusting.
Q. 8 Aluminium is a light non-corrosive metal -state applications of this property.
Ans. (1) Being a light metal aluminium is used in the manufacture of body parts of machines. (2) As it is non-corrosive and light, it is used in making the body of automobiles, aeroplanes, window frames, buckets, tanks, boxes etc.
Q.9 Some properties of aluminium are mentioned below. State the applications of these properties- (1) Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity. (2) Aluminium can be easily beaten into thin sheets.
Ans. (1) Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, it is used for making electrical wires and electrical instruments. (2) Aluminium can be easily beaten into thin sheets. Due to this property, aluminium is used in making packing foils.
Q.10 What is an alloy? Name a common alloy and state its composition.
Ans. An alloy is a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture of two or more metals or sometimes of metals and non-metals having characteristic properties different from their constituent elements.
A common and widely used alloy is brass. It is made of copper (60-80%) and zinc (20-40%).
Q.11 State two important characteristics of alloys.
Ans. Some important characteristics of alloys are discussed below-
(1) An alloy may be homogeneous or heterogeneous in nature.
(2) An alloy has different characteristic properties than its constituent metals.
Q.12 Write down the advantages of using alloys.
Ans. The advantages of using alloys are-
- Alloys have more tensile strength than their constituent elements. E.g., brass or bell metal is more tensile than copper.
- Metals melt at very high temperatures. When a pure metal is alloyed with another metal or non-metal, its melting point generally reduces.
- Metals are extremely susceptible to chemical and weather attacks. Alloys are more resistant to corrosion. When a metal is alloyed, it becomes less reactive, thereby enhancing its corrosion resistance.
- To increase or decrease the conductivity of metals, alloying can be done. E.g., specific resistance of nichrome is greater than its component metals, i.e., conductivity of nichrome is less than that of its component metals and thus it is used in electric heater.
Q.13 Write down the name of the main component of brass. Why is the use of brass more advantageous than that of its main component ?
Ans. The main component of brass is copper (Cu : 60-80%, Zn : 20-40%).
Advantages of using brass compared to copper are as follows-
- Brass has more tensile strength than the soft metal copper.
- Reactivity of brass is less than that of copper and hence brass is less corrosive in nature.
Q.14 What do you mean by amalgam and give example. Mention some uses of mercury alloys.
Ans. The alloys which contain mercury (Hg) as one of their constituents are commonly known as amalgams. E.g., sodium-amalgam (Na-Hg), magnesium-amalgam (Mg-Hg) etc.
The uses of mercury alloys, i.e., amalgams are as follows-
- Tin-amalgam (Sn-Hg) is used in preparation of mirror.
- Sodium-amalgam (Na-Hg) and zinc-amalgam (Zn-Hg) are used as reagents (reductant) in organic reactions.
- 3 Silver-amalgam (Ag-Hg) is used in dental treatment.
Q.15 Define minerals and give examples.
Ans. Minerals may be defined as the naturally occuring inorganic substances found in earth’s crust or on earth surface which contains metals in their native state or in the form of compounds mixed with other impurities. Example-red haematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), iron pyrites (FeS₂) are minerals containing iron.
Q.16 Define ores and give examples.
Ans. The minerals from which a metal can be conveniently and economically extracted are known as ores of the metal. For example-High quality iron can be conveniently and economically extracted from red haematite (Fe2O3). Hence, red haematite is an ore of iron.
Similarly, malachite [CuCO3 Cu(OH)2] is an ore of copper.
Q.17 All ores are minerals, but all minerals are not ores – justify the statement.
Ans. Minerals are the naturally occuring inorganic substances which contain one or more metals, in their native state or as their compounds, along with impurities. On the other hand, the minerals from which a metal can be conveniently and economically extracted are called ores of that metal. Obviously, all ores are minerals. But, we cannot extract metals from any mineral by convenient and cheap methods. Hence, all minerals cannot be called ores.
For example, both bauxite and china-clay are the minerals of aluminium. But, only bauxite is considered as the ore of aluminium, not china-clay.
Q. 18 Why zinc blend can be termed as both and can be termed as both mineral and ore?
Ans. Zinc blend (ZnS) is a solid metal compound which can be found in earth crust or in mines. Hence it can be termed as mineral of zinc. Moreover, high quality metallic zinc can be extracted from zinc blend using easier metallurgical technique. Hence zinc blend can be termed as ore of zinc metal, too.
Q.19 Write down the name and formula of important ores of copper.
Ans. Oxide ore – cuprite (Cu2O)
Sulphide ore – copper pyrites (Cu2S · Fе2S3 or CuFeS2), copper glance (Cu2S)
Carbonate ore – malachite [CuCO3 · Cu (OH)2]
Q.20 Write down the names of important wines ores of iron.
Ans. Oxide ore – red haematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4)
Carbonate ore – spathic iron or sedarite (FeCO3)
Q.21 Write down the names of important ores of zinc.
Ans. Oxide ore – zincite (ZnO)
Sulphide ore – zinc blend (ZnS)
Carbonate ore – calamine (ZnCO3)
Q.22 Write down the names of important ores of aluminium.
Ans. Oxide ore – bauxite (Al2O3 · 2H2O), gibbsite (Al2O3 · 3H2O)
Fluoride ore – cryolyte (AlF3 · 2NaF)
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. The core of an electromagnet is made of
A. cast iron
B. steel
C. wrought iron
D. magnetite
Ans. C
2. The metal used in making of electrolytic cells and dry cells is
A. Al
B. Sn
C. Zn
D. Cu
Ans. C
3. Which of the following is the purest form of iron?
A. cast iron
B. wrought iron
C. steel
D. invar
Ans. B
4. The amount of carbon present in steel is
A. 0.01-0.2%
B. 0.15-1.5%
C. 2-4.5%
D. 5-5.6%
Ans. B
5. Which of the following is not a constituent of the alloy, duralumin?
A. copper
B. magnesium
C. manganese
D. nickel
Ans. D
6. The percentage of silver in German silver is
A. 2-5%
B. 5-10%
C. 10-15%
D. 0%
Ans. D
7. Which of the following alloys does not contain zinc as a constituent metal?
A. brass
B. german silver
C. bell metal
D. gem metal
Ans. C
8. Which of the following alloys does not contain nickel as a constituent metal?
A. stainless steel
B. manganese steel
C. german silver
9. Which of the following minerals is not an ore?
A. red haematite
B. zinc blende
C. bauxite
D. iron pyrites
Ans. D
10. The oxide ore of zinc is
A. calamine
B. zinc blende
C. zincite
D. willemite
Ans. C
11. Tin-amalgam is used
A. to make spectacles
B. as a reducing agent
C. to make mirrors
D. to make thermometers
Ans. C
12. Which of the following is a mineral of iron but not its ore?
A. red haematite
B. magnetite
C. iron pyrites
D. siderite
Ans. C
13. Gibbsite is the ore of
A. Al
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. Fe
Ans. A
14. Calamine is the ore of
A. iron
B. copper
C. zinc
D. aluminium
Ans. C
15. Components of German silver are
A. Cu, Zn, Sn
B. Al, Cu, Mg, Mn
C. Fe, Cr, Ni, C
D. Cu, Zn, Ni
Ans. D
16. Which one of the following is the ore of aluminium?
A. red haematite
B. malachite
C. chalcopyrites
D. bauxite
Ans. D
17. Main component of duralumin is
A. Al
B. Mg
C. Cu
D. Sn
Ans. A
18. Chalcopyrites is the ore of
A. Zn
B. Fe
C. Mg
D. Cu
Ans. D
19. Which of the following is a sulphide ore?
A. bauxite
B. zincite
C. haematite
D. zinc blende
Ans. D
20. Composition of brass is
A. Cu and Sn
B. Zn and Cu
C. Cu and Pb
D. Cu and Al
Ans. B
21. Which of the following is not an ore of Cu?
A. haematite
B. chalcosite
C. azurite
D. malachite
Ans. A
22. Which of the following metal pair is present in both bronze and bell metal?
A. iron, nickel
B. copper, tin
C. zinc, copper
D. iron, tin
Ans. B
23. Among the components of amalgam, one must be
A. Fe
B. Ag
C. Au
D. Hg
Ans. D
24. The amount of carbon is highest in
A. steel
B. wrought iron
C. cast iron
D. chrome steel
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. Arrange wrought iron, steel and cast iron in the order of increasing carbon content present in them.
Ans. Wrought iron < steel < cast iron.
2. Which metal is present in each of bronze, brass and bell metal?
Ans. In each of bronze, brass and bell metal, copper is present.
3. What are the major constituents of stainless steel?
Ans. The major constituents of stainless steel are iron (73%), chromium (18%) and nickel (8%).
4. Name any two alloys of aluminium.
Ans. Two alloys of aluminium are- (1) magnelium (Mg, Al) and (2) alnico (Al, Ni, Co, Fe).
5. Name any two alloys of iron.
Ans. Two alloys of iron are- (1) stainless steel (Fe, Cr, Ni and traces of carbon) and (2) invar (Fe, Ni).
6. Name any two alloys of zinc.
Ans. Two alloys of zinc are (1) brass (Cu, Zn) and (2) german silver (Cu, Zn, Ni).
7. Name some important ores of iron.
Ans. Some important ores of iron are red haematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), siderite (FeCO3) etc.
8. Name some important ores of copper with their formulas.
Ans. Some important ores of copper copper pyrites [(Cu2S · Fe2S3) are or CuFeS2], copper glance (Cu2S), malachite [CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2], cuprite (Cu2O) etc.
9. Name the major ores of zinc with their respective formulas.
Ans. The major ores of zinc are zinc blende (ZnS), calamine (ZnCO3), zincite (ZnO) etc.
10. Name the major ores of aluminium with their respective formulas.
Ans. The major ores of aluminium are bauxite (Al2O3 · 2H2O), gibbsite (Al2O3 · 3H2O), cryolite (AlF3 · 3NaF) etc.
11. Name a mineral of aluminium which is not considered as its ore.
Ans. China-clay (Al2O3 · 2SiO2 · 2H2O) is a mineral of aluminium but is not considered as its ore.
12. Name a metal which is found in nature in its free state.
Ans. Gold (Au) is found in nature in its free state.
13. Why is invar used in making metre scale?
Ans. Invar is used in making metre scale because its coefficient of linear expansion is very small.
14. What are noble metals? Give examples.
Ans. The metals which are chemically not so reactive are known as noble metals. Example: Gold, platinum.
15. Write down the percentage of carbon in wrought iron.
Ans. The percentage of carbon in wrought iron is 0.1-0.15%.
16. Which type of iron is used to prepare electric iron?
Ans. Cast iron is used to prepare electric iron.
17. Which metallic powder is mixed with ammonium nitrate to prepare the explosive called ‘ammonal’?
Ans. Aluminium powder.
18. Why is copper used as electrode in electrical cells?
Ans. Due to its high electrical conductivity.
19. Which metal is used to prepare calorimeter and why?
Ans. Copper, due to its high conductivity of heat, is used to prepare calorimeter.
20. Which metal is used in print-block?
Ans. Zinc is used to prepare print-blocks.
21. Mention the metallic components of bronze?
Ans. Copper (80%), tin (18%) and zinc (2%).
22. Name the metal pair which is present in both of bronze and bell metal.
Ans. Copper and tin.
23. Which metal is common in brass and bronze?
Ans. Copper.
24. Name the non-transition metal present in bell-metal.
Ans. Tin (Sn).
25. Percentage of which metal is higher in brass?
Ans. Copper (60-80%).
26. Write down the composition of German silver.
Ans. Cu : 50%, Zn : 20%, Ni : 30%
27. Write down the name of the main component of duralumin.
Ans. Aluminium (95%).
28. Which alloy is used to prepare the structure of aeroplane?
Ans. Duralumin is used to prepare the structure of aeroplane.
29. Give examples of two alloys made up of four metals.
Ans. Duralumín (Al + Cu + Mn + Mg) and alnico (Fe +Ni+ Al + Co).
30. Which alloy is used to prepare permanent magnet?
Ans. Alnico (Fe + Ni + Al + Co).
31. Which alloy is used to prepare pressure cooker?
Ans. Duralumin.
32. Which one of iron pyrites and red haematite, is the ore of iron?
Ans. Red haematite is the ore of iron.
33. Write down the name and formula of a substance which is a mineral of iron but not its ore.
Ans. Iron pyrites (FeS2).
34. Calamine is the ore of which metal?
Ans. Calamine (ZnCO3) is the ore of zinc.
35. Write down the formula of zinc white?
Ans. Chemical formula of zinc white is ZnO.
36. Write down the formula of the ore- Gibbsite.
Ans. The formula of Gibbsite is Al2O3 · 3H2O.
Fill in the blanks
1. An explosive is prepared by mixing ………….. powder with ammonium nitrate.
Ans. aluminium
2. The percentage of carbon in wrought iron is …………. %.
Ans. 0.1-0.15
3. The non-metal present in stainless steel is ………….
Ans. carbon
4. The carbonate ore of iron is ………….
Ans. siderite
5. The amalgam of …………. metal is used as a reducing agent in organic reactions.
Ans. sodium
6. The alloy of aluminium used in making electromagnets is ………….
Ans. alnico
7. Metals can be extracted conveniently and economically from their ………….
Ans. ores
8. Cryolite is an ore of ……….
Ans. aluminium
9. The oxide ore of copper is ………….
Ans. cuprite (Cu2O)
10. …………. foil is used for packaging of food.
Ans. Aluminium
11. German silver is the alloy of …………. , zinc and nickel.
Ans. copper
12. Percentage of silver in German silver is ………..
Ans. zero
13. The main component of duralumin is …………
Ans. aluminium
14. If one of the components of an alloy be mercury, then the alloy is termed as an ………..
Ans. amalgam
15. …………. is the ore of aluminium.
Ans. Gibbsite/Bauxite
16. All the ores are minerals, but all of the minerals are not ………….
Ans. ores
17. Name of the sulphide ore of copper is ………….
Ans. copper glance (Cu2S)
18. Formula of bauxite is …………
Ans. Al2O3 · 2H2O
State whether true or false
1. All minerals are ores, but all ores are not minerals.
Ans. False
2. Calamine is the chief ore of zinc.
Ans. True
3. Cast iron is the purest form of iron.
Ans. False
4. Zincite is the oxide ore of zinc.
Ans. True
5. The percentage of silver present in the alloy German silver is 2-5%.
Ans. False
6. Tin-amalgam is used to make spectacles.
Ans. False
7. The alloy named invar is used to prepare metre-scale.
Ans. True
8. A component of bell-metal is zinc.
Ans. False
9. Components of brass are Cu and Sn.
Ans. False
10. Chalcosite is the ore of copper.
Ans. True
TOPIC – B
Principles of Metal Extraction and Oxidation-Reduction
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 How does oxidation occur?
Ans. Oxidation takes place in three different ways-
- Oxidation takes place when an atom loses electron(s).
Example – Na + → Na+ + e ; Al → Al3+ + 3e
- Oxidation takes place when a cation loses electron(s).
Example – Cu+ → Cu2+ + e ;
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e
- Oxidation takes place when an anion loses electron(s).
Example – S2– → S + 2e ; 2Cl¯ → Cl2 + 2e.
Q.2 How does reduction occur?
Ans. Reduction takes place in four different ways-
- Reduction takes place when an atom accepts electron(s).
Example – Cl + e → Cl¯ ; O + 2e → O2–
- Reduction takes place when a cation accepts electron(s).
Example – Na+ + e → Na ; Mg2+ + 2e → Mg.
- Reduction takes place when an anion of lower charge accepts electron(s) and is converted into an anion of higher charge.
- Reduction takes place when a cation of higher charge accepts electron and is converted into another cation of lower charge.
Q.3 Discuss the electronic theory of oxidation and reduction.
Ans. Oxidation: The process of removal of one or more electrons from an atom or ion is known as oxidation.
Example: Na → Na+ + e, Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e
Reduction: The process of acceptance of one or more electrons by an atom or ion is known as reduction.
Example: Cl + e → Cl¯, Na+ + e → Na
Q.4 Identify which one is oxidation and which one is reduction—
Ca → Ca2+ + 2e ; O + 2e → O2–
Ans. Ca → Ca2+ + 2e –In this reaction a Ca-atom loses two electrons to form Ca2+ ion. Hence it is an oxidation reaction as losing of electrons means oxidation.
O + 2e → O2– –In this reaction an O-atom gains two electrons to form O2– ion. Since gaining of electrons is termed as reduction, so this reaction is a reduction process.
Q.5 with the help of electronic theory, show that oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously in the following reaction:
2Fe3+ + Sn2+ → 2Fe2+ + Sn4+
Ans. 2Fe3+ + Sn2+ → 2Fe2+ + Sn4+
Here each Fe3+ ion accepts an electron to form Fe2+ ion. Hence it is a reduction process as gaining of electron is termed as reduction.
Fe3+ + e → Fe2+
Again each Sn2+ ion loses 2 electrons from its valence shell. Hence the process is oxidation as losing of electron in termed as oxidation.
Sn2+ → Sn4+ + 2e
Hence, it can be said that oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
Q.6 Extraction of metals from their ores is basically a reduction process-explain with example.
Ans. In the ore, metal remains in a positive oxidation state but, after extraction of the metal, the oxidation number becomes zero. Thus, during extraction of the metal, the metal ion accepts electron to become a free atom. Hence, we can say that extraction of metals from its ores is a reduction process.
Mn+ (metal ion) + ne → M( free metal)
Example: Zinc oxide (ZnO) is mixed with excess coke and heated at a temperature of about 1300-1400°C in a retort when zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO↑
Q.7 What do you mean by metal activity series? Name the metals at the top and bottom of the series.
Ans. The series obtained by vertically arranging the metals from top to bottom in decreasing order of their electropositivity or decreasing order of chemical reactivity is called metal activity series.
The metal placed at the top of the series is potassium (K) while gold (Au) is placed at the bottom.
Q.8 Arrange Cu, Fe, Ag and Zn in increasing order of their reactivity on the basis of the following reactions.
(1) CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
(2) 2AgNO3 + Cu → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(3) FesO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Fe
Ans. A more reactive metal replaces a less reactive metal from its salt. So, according to reaction, (1) Fe is more reactive than Cu. According to reaction, (2) Cu is more reactive than Ag. According to reaction, (3) Zn is more reactive than Fe. Hence, the order of increasing reactivity:
Ag < Cu < Fe < Zn.
Q.9 How are the metals placed at the top of the metal activity series extracted?
Ans. These metals are usually extracted by electrolytic method. The molten hydroxide or chloride salts of the metal is electrolysed using suitable electrodes, and the metal deposits on the cathode.
For example, sodium is extracted by electrolysing a molten solution of sodium chloride using iron cathode and graphite anode. Sodium is deposited at the cathode.
Dissociation of NaCl: NaCl (molten) → Na+ + Cl–
Reaction at cathode: Na+ + e → Na
Reaction at anode: Cl– → Cl + e (oxidation);
Cl + Cl → Cl2 (reduction)
Q.10 Describe the extraction of aluminium from pure alumina by electrolytic method.
Ans. Aluminium is generally extracted from bauxite ore Al2O3 · 2H2O. At first, bauxite is converted into pure alumina. Pure alumina is then mixed with proportionate amount of cryolite (CaF2) and fluorspar (AlF3 · 3NaF) and the mixture is heated at around 900°C. When electricity is passed through the fused mixture, aluminium is deposited at the cathode.
Electrolytic dissociation: Al2O3 (molten) → 2Al3++ 3O2–
Cathode reaction: 2Al3+ + 6e → 2Al
Anode reaction: 3O2– → 3O + 6e ;
3O + 3O → 3O2
Q.11 Why are the strong electropositive metals like Na, K etc., not extracted from the aqueous solution of their salts?
Ans. An aqueous solution of a salt of a strong electropositive metal contains H+ ions formed due to dissociation of water, along with the metal cations. Now, the tendency of H+ ions to be discharged at cathode is stronger than that of metals like Na, K etc. Hence, on electrolysis of the aqueous solution, H+ ions will be reduced at cathode instead of metal ions. Hence, hydrogen gas will be produced at cathode instead of desired metal. This is why a strong electropositive metal is extracted from its salt by electrolysis of the fused salt but not the aqueous solution of the salt.
Q.12 Which method is suitably used for the extraction of metals (such as Fe, Zn etc.) occupying the middle part of the metal activity series? Explain with reasons.
Ans. The metals occupying the middle part of the metal activity series are moderately reactive and hence have relatively less tendency than carbon to combine with oxygen. Therefore, these metals can be extracted from their oxides by carbon reduction process at high temperature.
Example: ZnO + C(coke) → Zn + CO
Q.13 When an iron nail is dipped into an aqueous solution of copper sulphate, a reddish brown layer is developed over the nail. Explain why.
Ans. A metal occupying a higher position relative to another metal in the metal activity series can replace the latter from the solution of it’s salt. In metal activity series, iron is placed above copper. Hence iron can replace copper from copper sulphate solution. So, when an iron nail is dipped into an aqueous copper sulphate solution, reaction takes place between them at the surface of iron nail and hence a reddish brown layer of metallic copper is formed over the iron nail.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu↓ (red)
Q.14 What happens when a piece of zinc is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate?
Ans. In the metal activity series, zinc is placed above copper. Hence zinc can replace copper from copper sulphate solution. So, when a small piece of zinc is dipped in copper sulphate solution, reaction takes place between zinc and copper sulphate and copper is precipitated. The precipitated copper deposits on the surface of zinc and hence a reddish brown layer is formed over zinc.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu↓ (red)
Q.15 What is carbon reduction process of metal extraction?
Ans. Reduction of a metal oxide by heating the mixture of metal oxide with carbon at a very high temperature in a blast furnace is called carbon reduction process. ‘Coke powder’ is used as a reducing agent for this process. Besides, CO produced due to incomplete oxidation of carbon also acts as reducing agent.
Q.16 Aluminium cannot be extracted by carbon reduction process. Explain with reasons.
Ans. Aluminium occupies the top portion of the metal activity series. Hence, it is a highly reactive metal and possesses strong reducing property. Carbon reduction process is applicable for the extraction of those metals which have relatively greater tendency to combine with carbon than oxygen. However, aluminium has a greater tendency to combine with oxygen than carbon and also the oxide of aluminium (Al2O3) is more stable as compared to the oxides of carbon. Thus aluminium cannot be extracted by carbon reduction process. Al is generally extracted by electrolysis of molten alumina (Al2O3).
Q.17 How is zinc extracted. by carbon reduction process?
Ans. During zinc extraction by carbon reduction process, the zinc ore, i.e., zinc blende (ZnS) or calamine (ZnCO3) is converted into zinc oxide. Zinc oxide is then mixed well with excess coke powder. The mixture is then taken in a retort made of fireclay and heated at a temperature of about 1300-1400°C. At this temperature zinc oxide is reduced metallic zinc and carbon monoxide (CO) is evolved.
ZnO + C → Zn + Co↑
Coke acts as a reducing agent in this reaction.
Q.18 Write down advantages and disadvantages of carbon reduction process.
Ans. Advantages of carbon reduction process:
- The reductant used in this process, i.e., coke, is easily available and cheap.
- Large amount of metal oxide can be reduced using a comparatively smaller amount of coke.
- CO gas, formed in the reaction acts as reducing agent in addition to coke, in this process.
Disadvantages of carbon reduction process:
- Highly electropositive metals like Na, K, Al, Mg etc., cannot be extracted by this process.
- A few metals like Ca, Al etc., react with coke at higher temperature to form carbide compounds.
Q.19 Describe the principle of thermite process with example.
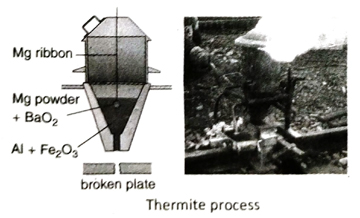
Ans. Al has strong affinity for oxygen at high temperature. When oxides of relatively less reactive metals such as Fe, Mn, Cr etc., are heated with Al powder at a very high temperature, the oxides are reduced by Al to the corresponding metal. This is the basic principle of Goldsmith’s thermite process. The process produces large amount of heat and the reaction temperature reaches as high as 2000°C. At this temperature, the extracted metal is obtained in molten state.
Q.20 What is thermite mixture? Write two practical applications of thermite process.
Ans. A mixture of 3 parts of ferric oxide (Fe2O3) by mass with 1 part of powdered aluminium is known as thermite mixture.
Some important applications of thermite process are discussed below-
- Thermite process is applied in repairing broken parts of rails, tram lines, ship, machines made of iron etc.
- Metals like chromium, manganese etc., are extracted by thermite process.
Q.21 What is used as reducing agent in thermite process? What is ignition mixture?
Ans. Aluminium powder is used as reducing agent is thermite process.
In thermite process, thermite mixture is taken in a crucible made of fire clay (high temperature resistant). A mixture of magnesium powder and barium peroxide or potassium chlorate is taken over the thermite mixture which is then ignited with a burning magnesium ribbon. The mixture of magnesium powder and potassium chlorate or barium peroxide is called ignition mixture.
Q. 22 State three advantages of thermite process.
Ans.
- Metal extraction by thermite process doesn’t require large machineries. Metals can be extracted in small scale by this method for different purposes.
- Broken parts of large machineries, rail lines, tram lines, ships can be repaired by thermite process. But, it is not required to transport the damaged parts to the factories.
- A huge quantity of Al2O3 is produced as a by- product. This can be used for the preparation of emery powder used in metal polishing and manufacture of bricks used in the inner layer of furnace.
Q.23 Why are the metals occupying lower positions in the metal activity series often found in nature in their native state?
Ans. The metals occupying lower position in the metal activity series (Hg, Ag, Au) have very little chemical reactivity. Hence, they are not easily affected by atmospheric oxygen, water vapour, CO2 etc., and thus exist in nature in their native state.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. During extraction of aluminium, alumina is reduced by
A. H2
B. carbon
C. H2S
D. electrolysis
Ans. D
2. During extraction of zinc, ZnO is reduced by
A. H2
B. carbon powder
C. H2S
D. electrolysis
Ans. B
3. In thermite mixture, the ratio of Fe2O3 and Al powder is
A. 1:2
B. 2:1
C. 1:3
D. 3:1
Ans. D
4. In thermite process, the substances present apart from the thermite mixture are
A. Fe, Cr
B. ZnO, Mg
C. BaO2 , Mn
D. BaO2 , Mg
Ans. D
5. Which of the following metals react with boiling water to evolve H2 but does not do so with cold water?
A. Ca
B. K
C. AL
D. Na
Ans. C
6. Which of the following metals is placed below Pb and above Hg in the metal activity series?
A. Sn
B. Ag
C. Cu
D. Au
Ans. C
7. Which of the following reactions is feasible?
A. Zn + FeSO4 →
B. MgSO4 + Fe →
C. CuSO4 + Ag →
D. ZnSO4 + Pb →
Ans. A
8. Which of the following metals can be extracted by thermite process?
A. Fe
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. Al
Ans. A
9. In thermite process, the metal used as the reducing agent is
A. Al
B. Ni
C. Zn
D. Fe
Ans. A
10. Metals placed at the top of the metal activity series are usually extracted by
A. carbon reduction method
B. reduction by H2
C. self-reduction
D. electrolytic reduction
Ans. D
11. Metals placed at the middle region of the metal activity series are usually extracted by
A. carbon reduction method
B. reduction by H2
C. self-reduction
D. electrolytic reduction
Ans. A
12. Metals which can exist in free state in nature are
A. placed at the top of the metal activity series
B. placed at the middle of the metal activity series
C. placed at the bottom of the metal activity series
D. not included in the metal activity series
Ans. C
13. Which of the following orders correctly represents the reactivity of metals?
A. Pb < Fe < Mg
B. Mg > Ca > Zn
C. Ag < Zn< Pb
D. Al > Cu > Fe
Ans. A
14. Which of the following metal pairs reacts with both acids and alkalies to produce hydrogen gas?
A. Cu, Zn
B. Na, Cu
C. Pb, Zn
D. Al, Zn
Ans. D
15. Na cannot be extracted from its oxide by carbon reduction process because
A. oxide of Na is unstable
B. Na does not exist in its oxide form
C. oxide of Na is more stable
D. oxide of Na is volatile
Ans. C
16. Metals placed at the top of the metal activity series are
A. strong reducing agents
B. weak reducing agents
C. strong oxidising agents
D.weak oxidising agents
Ans. A
17. In the metal activity series, the only nonmetal present along with the metals is
A. carbon
B. hydrogen
C. chlorine
D. iodine
Ans. B
18. Thermite mixture is
A. Fe2O3 + Al
B. Fe2O3 + Cu
C. FeO + Al
D. FeO + Cu
Ans. A
19. In which of the following change in colouration can be observed when an iron nail is immersed in it?
A. ZnSO4
B. Al2(SO4)3
C. FeSO4
D. CuSO4
Ans. D
Answer in brief
1. Give an example of a reduction process where an anion accepts an electron.
Ans. MnO4– + e → MnO42– ; In this reaction an anion accepts an electron and gets reduced.
2. Cu2+ + Zn → Cu + Zn2+ −Identify the oxidant and reductant in the given reaction.
Ans. In the given reaction, Zn acts as the reductant while Cu2+ acts as the oxidant.
3. Name some metals other than iron that can be extracted by thermite process.
Ans. Some metals other than iron that can be extracted from their oxides by thermite process are chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), titanium (Ti), manganese (Mn) etc.
4. Why is aluminium used in thermite process?
Ans. At high temperatures, aluminium exhibits strong reducing power, i.e., it has a strong affinity towards oxygen. For this reason, aluminium is used in thermite process.
5. Name the element below which copper is placed in the metal activity series.
Ans. The element below which copper is placed in the metal activity series is hydrogen.
6. Arrange Pb, Ca, Cu, Zn, Mg in increasing order of their reactivity.
Ans. Cu < Pb < Zn < Mg < Ca.
7. Which metals are extracted by carbon reduction method?
Ans. Metals which are placed in the middle region of the metal activity series are extracted by carbon reduction method.
8. Arrange Na, Al, Fe, Pb in increasing order of their reducing power.
Ans. The increasing order of reducing power of the given elements is – Pb < Fe < Al < Na.
9. Between aluminium and tin, which one occupies a higher position in the metal activity series?
Ans. Aluminium occupies a higher position than tin in the metal activity series.
10. Name a metal which reacts only with acids to produce hydrogen (H2).
Ans. Tin (Sn) reacts only with acids to produce hydrogen (H2).
11. Give the equation of the reaction in which Mn+ ion is converted into metal M at the cathode during electrolysis of a fused salt containing Mn+ ion.
Ans. The equation is: Mn+ + ne → M.
12. What happens during the electrolytic reduction of fused NaCl?
Ans. During the electrolytic reduction of fused NaCl, Na is deposited at the cathode and Cl2 gas is liberated at the anode.
13. Give example of a metal which can form H2 in reaction with steam.
Ans. Iron (Fe) forms H2 in reaction with steam.
14. Which one among Fe, Cu, Zn and Al does not form H2 in reaction with dil H2SO4?
Ans. Cu is present in a lower position than H in metal activity series and thus does not form H2 in reaction with dil. H2SO4.
15. Write down the principle of Goldschmidt’s thermite process.
Ans. The fundamental principle of Goldschmidt’s thermite process is the reduction of the oxide of a less electropositive metal by another metal with higher electropositivity.
16. Which substance is used as oxidant in thermite process?
Ans. Oxides of Fe, Cr, Mň etc., are used as oxidant in thermite process.
17. Write down the reaction temperature of thermite process.
Ans. 2000°C.
18. Write down an use of thermite process.
Ans. Thermite process is used welding broken parts of heavy machineries, rail lines, tram lines, ships etc.
19. Give example of two metals which cannot be extracted by carbon reduction process.
Ans. Sodium (Na) and aluminium (Al).
20. What is the name of the gas formed along with metals in carbon reduction process?
Ans. Carbon monoxide (CO).
21. Which process of metal extraction is applied for the extraction of K, Ca, Na etc.?
Ans. Electrolytic process.
22. In which electrode metal atoms are deposited in the electrolytic reduction method of metal extraction?
Ans. Cathode.
23. Write down the name of two metals that can be extracted by electrolytic reduction method.
Ans. Aluminium (Al) and calcium (Ca).
Fill in the blanks
1. During electrolysis, metal cations move towards the cathode and get …………. by accepting ……….
Ans. reduced, electron(s)
2. A metal oxide gets ………….. when oxygen is removed from it.
Ans. reduced
3. On moving down the metal activity series, reducing power of the metals gradually …………..
Ans. decreases
4. The extraction of a metal from the corresponding metal compound is always a ……….. process.
Ans. reduction
5. The metal occupying the topmost position in the metal activity series is …………
Ans. potassium
6. …………. is also known as zinc white.
Ans. ZnO
7. The constituents of thermite mixture are ………….. and ………….
Ans. Fe2O3, Al-powder
8. Less reactive metals are found in nature in their …………. state.
Ans. free
9. In aqueous solution, a more reactive metal can ………….. or ………… a less reactive metal from its salt.
Ans. precipitate, reduce
10. Metals placed at the top of the metal activity series have …………. affinity towards oxygen.
Ans. high
11. In the metal activity series, Zn is placed …………. Cu.
Ans. above
12. Among Fe, Cu, Zn and Al, ………… occupies the highest position in the metal activity series.
Ans. Al
13. ………….. dust is used as reductant in thermite process.
Ans. Aluminium
14. Generally …………… is used as reductant in carbon reduction process.
coke
15. Example of a metal that can be extracted by carbon reduction process is …………
Ans. zinc
16. The metal occupying the last position in the metal activity series is ………..
Ans. gold
State whether true or false
1. Fe can be extracted by thermite process.
Ans. True
2. Metals placed at the top of the metal activity series are extracted by carbon reduction procedure.
Ans. False
3. Metals placed at the top of the metal activity series are strong oxidising agent.
Ans. False
4. Extraction of metal from ore is mainly oxidation.
Ans. False
5. Thermite reaction is endothermic.
Ans. False
6. Carbon is used as reductant in thermite process.
Ans. False
7. Zinc cannot be extracted by carbon reduction process.
Ans. False
8. Metals are obtained at cathode in electrolytic reduction process.
Ans. True
TOPIC – C
Corrosion of Metals
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What is corrosion of metal?
Ans. When a piece of metal is kept in open air for a long time, the metal chemically reacts with atmospheric oxygen, CO2, water vapour etc., and is converted into other substances.
As a result the metal piece erodes. This natural phenomenon is known as corrosion of metal.
Q.2 Why impure metals undergo quicker weathering as compared to the pure metals?
Ans. When a piece of impure metal is kept in open air, the impurities present in the metal acts as tiny electrochemical cells on the surface of the metal. Hence, it can be affected readily by atmospheric oxygen, water vapour etc. Pure metal generally does not form such cells and thus they are not weathered easily.
Q. 3 What do you mean by rusting of iron? Why are metal articles corroded due to rusting?
Ans. When iron or iron objects are kept in moist air for a few days, a reddish brown layer of hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3 · xH2O) is formed over the objects. This reddish brown layer is called rust and the process is called rusting.
The volume of rust is generally greater than the volume of pure iron. Hence, after the formation of rust, the surface becomes flaky and comes out of the metal easily. Therefore, the objects undergo corrosion.
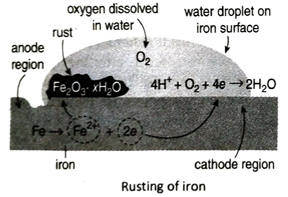
Q. 4 Explain the mechanism of rusting.
Ans. Rusting of iron is basically an electrochemical reaction. Due to the presence of impurities and rough surface, the oxidation of iron atoms do not take place uniformly. Some parts of iron gets readily oxidised than some other parts. The part where oxidation takes place easily is called the anode region while the part where oxidation does not take place easily is called the cathode region. At anode region, Fe-atoms give up electrons and gets oxidised to Fe2+ ions which dissolve in water. The released electrons move to the cathode region. At cathode region, O2 dissolved in water accept these electrons and is reduced to water. The reduction takes place in presence of H+ ions that are obtained from the dissociation of carbonic acid (H2CO3). Anode reaction: 2Fe →2Fe2+ + 4e
Cathode reaction: 4H+ + 4e →4H;
4H + O2 → 2H2O
Net reaction: 2Fe + O2 + 4H+ → 2Fe2+ + 2H2O
Fe2+ ions produced at anode are further oxidised by aerial oxygen to form hydrated ferric oxide or rust (Fe2O3 · xH2O).
4Fe2+ + O2 + 4H2O → 2Fe2O3 + 8H+
Fe2O3 + xH2O → Fe2O3 · xH2O (rust)
Q.5 What are the factors which accelerates the process of rusting?
Ans. The process of rusting is accelerated by the following factors-
- Presence of less electropositive metals in iron as impurity.
- The presence of gases like CO2, SO2, SO3, NO, NO2 etc.
- Presence of chloride (Cl–) or sulphate (SO42–) ions in water.
Q.6 Discuss the harmful effects of rusting.
Ans.
- Rusting affects the metallic lustre of iron.
- Iron is used to prepare substances for household works, transportation, agricultural and defence instruments. These substances corrode due to rusting causing huge economic losses.
- Houses, bridges etc. contain iron pillars. Similarly bodies of ships are made of iron. Rusting, makes them weak and brittle, which may lead to accidents.
Q.7 Why is rusting called ‘slow combustion’?
Ans. In the presence of aerial oxygen and water vapour, iron is oxidised to hydrated ferric oxide (Fе2O3 · xH2O) or rust. During this process, small amount of heat is also produced. Hence, it is sometimes called a ‘slow combustion’.
Q.8 Give some methods to prevent rusting of iron.
Ans.
- The iron articles can be protected from rusting by coating their surfaces with varnishes, paints or coal tar.
- Rusting can be prevented by electroplating iron with zinc, tin or chromium.
- When steam is passed over red hot iron, a thin layer of ferrosoferric oxide (Fe3O4) is formed on the surface of iron which protects it from rusting.
- The underground oil pipelines through water, made of iron are protected by using Mgblocks.
Q.9 Why do the oil or water pipelines through oceans and seas tend to form rust readily? How are they protected from rusting?
Ans. Ocean and sea water contains dissolved chloride (Cl–) and sulphate (SO42–) ions. These ions facilitate the process of rusting. Hence, oil or water pipelines through oceans and seas tend to form rust readily.
To protect the underground or underwater pipelines from rusting, a block of more electropositive metal (like Mg) is connected to the pipe through an insultated wire. In this case, the iron pipes act as cathode, the magnesium block as anode and water as electrolyte. Magnesium being more reactive than iron is readily oxidised and hence prevents iron from rusting. The Mg block needs to be replaced after sometime as it corrodes gradually.
Q.10 Several magnesium blocks are attached s are attached the bottom of ships. Why?
Ans. The salty water of seas and oceans accelerates the process of rusting. The magnesium blocks attached to the bottom of the ships protect the iron parts of ships from rusting. Here, the ship acts as an electrochemical cell. Mg is placed above iron in the metal activity series and hence, Mg acts as anode while iron acts as cathode. The salty water of ocean acts as an electrolytic solution. As oxidation takes place at anode, Mg is preferably oxidised to Mg2+ ions. Thus iron remains unaffected as long as Mg blocks are present. New blocks replaces the already attached blocks that gets corroded.
Q. 11 What do you mean by galvanisation?
Ans. To protect iron from rusting and corrosion, sometimes a zinc coating is applied over iron objects mainly by electrolytic method. This is known as galvanisation. Iron coated with zinc is called galvanised iron.
Q.12 Why is zinc used in galvanisation to prevent rusting?
Ans. In the metal activity series zinc is placed above iron. Hence, zinc is more electropositive than iron and it is more easily oxidised than iron. So, when iron is coated with zinc, zinc is more readily affected by oxygen and water vapour. This protects iron from being oxidised. Thus, rusting is prevented.
Q.13 Zinc is more electropositive than iron, so it should be corroded more readily than iron. But, this doesn’t happen. Instead, zinc is coated over iron to prevent rusting. How will you explain this?
Ans. When zinc is exposed to air it is affected by oxygen, CO2 and water vapour present in the air to form a layer of basic zinc carbonate [Zn(OH)2 · ZnCO3].
This layer shields zinc from atmospheric air and hence further corrosion is prevented. This is why zinc is used to protect iron from rusting.
Q.14 Will it be justified to coat an iron cauldron, used for cooking, with zinc to protect the cauldron from rusting?
Ans. The melting point of zinc is 420°C while that of iron is 1525°C, i.e., zinc has a much lower melting point than iron. At about 250°C, zinc becomes brittle and the layer may break on application of higher temperature. Hence, it is not suitable to coat an iron cauldron, used for cooking, with zinc to protect the cauldron from rusting.
Q.15 To protect iron from rusting which one between zinc-plating and tin-plating is more effective and why?
Ans. When a crack on the surface of zinc-plated iron exposes the metallic iron, the metallic iron remains unaffected by the action of moist air and does not corrode. This is because, zinc is more reactive than iron(zinc is at higher position than iron in metal activity series) and hence zinc is affected by moist air more readily than iron.
On the other hand, any crack on the surface of tinplated iron which exposes iron makes the iron part vulnerable to rusting. This is because iron is more reactive than tin and hence iron is affected by moist air more readily than tin.
This is why zinc-plating is more effective in preventing rust than tin-plating.
Q.16 Explain why tin-plated utensils are used instead of zinc plated utensils to store food.
Ans. Zinc is more effective in preventing rusting and corrosion. Yet, tin-plated containers are widely used to store food than zinc-plated containers because zinc may react with some acids present in food to produce toxic substances which may cause food poisoning. Tin does not produce such toxic substances. Hence, it is safer to use tinplated containers to store food.
Q.17 Why is aluminium called ‘selfprotecting metal?
Ans. When metallic aluminium is kept in moist air, it reacts oxygen and water vapour to form a nonconducting thin layer of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) over it’s surface. As a result, the metallic lustre is lost. But, the layer formed is in-soluble in water and protects the metal from further oxidation. Hence, corrosion of the metal is prevented. This is why aluminium is called a ‘selfprotecting’ metal.
Q.18 Copper objects turn green when kept in air for a long time. Explain.
When exposed to moist air for a long period of time, copper is oxidised by aerial oxygen to copper oxide (CuO) which deposits on the surface of the object. Due to presence of H2S in the air of industrial area, black layer of copper sulphide (CuS) is formed on the surface of the article. This layer is further oxidised to form green coloured basic copper sulphate [CuSO4 · 3Cu(OH)2] . Sometimes, copper is also oxidised by O2, CO2 and water vapour to green coloured carbonate basic copper [CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2]. Due to the formation of these compounds, the object turns green.
Q.19 Copper vessels are sometimes cleaned with lemon or tamarind. What is the possible reason for this?
Ans. Copper vessels are oxidised by O2, CO2 and water vapour to form a thin layer of green coloured basic copper carbonate [CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2]. Lemon or tamarind contains organic acids. These organic acids reacts with basic copper carbonate and remove the green patches. Hence, the green patch or stain gets removed from the vessels.
Q.20 Copper utensils which are not used for a long time should be used only after thorough cleaning-explain.
Ans. Green coating of basic copper carbonate is formed on copper utensils which are not used for a long time as a result of reaction of copper with atmospheric oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour,. Basic copper carbonate is toxic in nature. It causes toxicity if it is consumed along with food. Moreover several micro-organisms which can cause diseases may be present on those utensils. That is why these copper utensils should be used only after thorough cleaning.
Q.21 Gold ornaments are often covered with green patches on their surfaces. Why?
Ans. To increase the strength of gold for making ornaments, copper is added as an impurity. In moist air, this copper is slowly oxidised over a long period of time to form green coloured basic copper sulphate [CuSO4 · Cu(OH)2] or basic copper carbonate [CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2]. The green patches on the gold ornaments appears due to the formation of these compounds.
Q.22 Explain why it is harmful to eat pickles or chutneys kept in an aluminium foil.
Ans. Vinegar is generally used as an ingredient for making pickles or chutneys. Vinegar is nothing but an aqueous solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH). Thus, it reacts with aluminium to form poisonous aluminium salt. Hence, it is harmful to eat pickles or chutneys kept in aluminium foil as it may cause food poisoning.
Q.23 Food or fruits having sour taste should not be stored in containers made of aluminium, zinc or copper. Why?
Ans. Food or fruits having sour taste contains organic acids. These organic acids reacts with aluminium or zinc to form water soluble salts. Similarly, copper may also form water soluble salts with organic acids in the presence of oxygen. Some of the produced salts are toxic and may cause food poisoning. Hence, it is advisable not to store food or fruits having sour taste in containers made of aluminium, zinc or copper.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. The chemical formula of rust is
A. FeO · xH2O
B. Fe3O4
C. Fe2O3
D. Fе2O3 · xH2O
Ans. D
2. Presence of which of the following ions accelerates the process of rusting? .
A. Na+
B. Ca2+
C. Cl–
D. O2–
Ans. C
3. Which of the following is used to protect the iron parts of ships from rusting?
A. copper blocks
B. aluminium blocks
C. zinc blocks
D. magnesium blocks
Ans. D
4. Which of the following methods does not prevent rusting?
A. painting the surface
B. galvanisation
C. using a Mg-block
D. immersing in MgCl2 solution
Ans. D
5. During rusting, presence of which of the following ions in water causes the reduction of dissolved O2?
A. Fe2+
B. Fe3+
C. H+
D. self-reduction occurs in this case
Ans. C
6. To prevent rusting, Mg-block is attached to iron pipes because
A. Mg more electropositive than Fe
B. Mg has a greater tendency to get oxidised than Fe
C. both A and Ⓡ
D. none of these
Ans. C
7. Galvanised iron is actually
A. Zn-coated iron
B. Sn-coated iron
C. Ni-coated iron
D. Cr-coated iron
Ans. A
8. Green layer formed over copper and most of its alloys when exposed to moist air, is of
A. basic copper nitrate
B. acidic copper hydroxide
C. basic copper carbonate
D. acidic copper sulphate
Ans. C
9. Which of the following metals can protect itself from corrosion?
A. Al
B. Fe
C. Na
D. Cu
Ans. A
10. The white layer formed over metallic aluminium in presence of moist air is of
A. AlCl3
B. Al(OH)3
C. Al2O3
D. AlN
Ans. C
11. Which metal protects itself by forming a coat of oxide?
A. Cu
B. Al
C. Fe
D. Zn
Ans. B
12. Necessary component required for rust formation is
A. N2 ,O2
B. N2 , H2
C. O2 , H2O
D. CO2 , H2O
Ans. C
13. Which of the following is formed by the reaction of Al or Zn with organic acidic substances?
A. soluble metallic salts
B. insoluble metallic salts
C. addition compound
D. metallic hydroxides
Ans. A
14. Which of the following metals is used for galvanisation?
A. Fe
B. Ca
C. Zn
D. Mg
Ans. C
15. Rusting is a
A. oxidation process
B. reduction process
C. redox process
D. neutralisation reaction
Ans. C
16. Rapid rusting of iron occurs in presence of Cl– because
A. dissociation increases of water molecule
B. dissociation of water molecule decreases
C. chlorine gas reacts with iron
D. none of the above
Ans. A
Answer in brief
1. Apart from aerial oxygen, which other component of the atmosphere is responsible for rusting of iron?
Ans. Apart from aerial oxygen, water vapour is responsible for rusting of iron.
2. Which type of impurity facilitates the rusting of iron?
Ans. Presence of less electropositive metals in iron as impurities facilitates rusting.
3. Name an electrochemical process.
Ans. Rusting of iron is an electrochemical process.
4. Write the reactions that occur at the anode and cathode during rusting of iron.
Ans. Anode reaction: 2Fe → 2Fe2+ + 4e
Cathode reaction: O2 + 4H+ + 4e → 2H2O
5. Name a metal apart from zinc that can be used as a coating over iron to protect it from rusting?
Ans. Apart from zinc, tin can be used as a coating over iron to protect it from rusting.
6. The presence of chloride ions facilitate rusting of iron. Mention one practical disadvantage of it.
Ans. Underwater pipelines made of iron are easily corroded by rusting due to the presence of Cl– ions in sea water.
7. How can you protect iron from rusting?
Ans. If steam is passed over red hot iron, a thin layer of ferrosoferric oxide (Fe3O4) is formed over iron, which protects it from rusting.
8. Write the composition of the green coloured layer formed on copper and most copper alloys when exposed to moist air for a long time.
Ans. Basic copper carbonate
[CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2].
9. What are the necessary conditions required for rusting?
Ans. The process of rusting requires (1) presence of atmospheric oxygen, (2) presence of water vapour.
10. Why does rusting not occur in pure iron?
Ans. Many electrochemical cells are formed on iron during rusting. In absence of impurities these cells cannot be formed and hence rust is not formed on pure iron.
11. Presence of which ion accelerates rusting?
Ans. Presence of Cl– ion accelerates rusting.
12. Why does rusting accelerate in presence of CO2?
Ans. CO2 forms carbonic acid by dissolving in the rate of water which increases dissociation of water. Hence rusting is accelerated.
13. Name a process which protects iron from rusting.
Ans. Galvanisation.
14. Which metal is used in galvanisation?
Ans. Zinc (Zn).
15. What is ‘galvanised iron’?
Ans. Iron coated with metallic zinc is termed as ‘galvanised iron’ or G.I.
16. Write down the advantage of galvanisation.
Ans. Galvanisation protects iron from rusting and corrosion.
17. Which metal is used in cathodic protection of iron?
Ans. Magnesium is used in cathodic protection of iron.
18. What is used as a suicidal electrode to prevent rust on a ship?
Ans. Magnesium block.
19. What is passive iron?
Ans. A coating of iron oxide is formed over iron when it comes in contact with conc. nitric acid. This makes iron chemically inert and this type of iron is called passive iron.
20. Which metal is called ‘self protecting metal’?
Ans. Aluminium is called ‘self protecting metal’.
Fill in the blanks
1. During rusting, oxygen dissolved in water gets reduced to form ………….
Ans. H2O
2. Presence of ………… substances prevents rusting of iron.
Ans. alkaline
3. Rusting can be prevented if iron is kept in contact with ……….. electropositive metals than iron.
Ans. more
4. A thin non-conducting layer of …………. over Al prevents the metal from getting attacked by atmospheric O2 and moisture.
Ans. Al2O3
5. Acidic food or fruits should not be kept in containers made of ………….. or …………..
Ans. Al, Zn
6. Different weather conditions causes metallic objects to lose their …………
Ans. lustre
7. Rust do not occur in ………….. iron.
Ans. pure
8. Rate of rusting ………….. with increase in temperature.
Ans. increases
9. Process of coating ………….. on iron substances is called galvanisation.
Ans. zinc
10. Mg-block attached with iron pipes for oil transportation, acts as ………….
Ans. anode
11. The fine coating formed on Al metal in presence of moist air is of …………
Ans. Al2O3
12. ………… coloured patches occur on copper containers if they are kept in open air.
Ans. Green
13. Due to formation of basic ………… in presence of moist air, zinc becomes faded.
Ans. zinc carbonate
14. Mg-blocks attached to underground pipes carrying oil act as the …………….
Ans. anode
State whether true or false
1. Cl– ion accelerates the process of rusting.
Ans. True
2. Objects made of copper turn green on prolonged exposure to air due to the formation of basic copper carbonate.
Ans. True
3. It is justified to coat an iron cauldron used for cooking, with zinc to protect the cauldron from rusting.
Ans. False
4. Ni-coated iron is known as galvanised iron.
Ans. False
5. Chemical formula of rust formed on iron is FeO · xH2O.
Ans. False
6. Rusting occurs in the presence of water only.
Ans. False
7. Pure metals are weathered more readily compared to impure metals.
Ans. False
8. Rusting is a mild combustion.
Ans. True
9. No atmospheric corrosion occurs on aluminium if it is kept in open air.
Ans. True
10. Aluminium pot is very useful for storing pickles and sauces.
Ans. False
11. Sour fruits should not be kept cut in zinc coated containers.
Ans. True