Classification of Plantae
Classification of Plantae
In the year 1883, Eichler has classified the Botanical world as under :
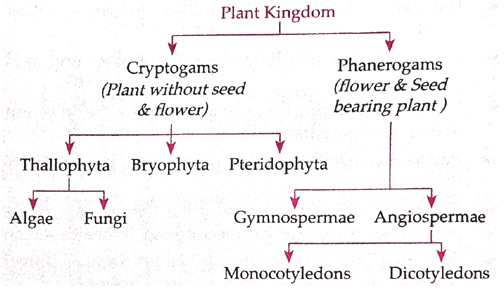
I. Cryptogamous Plants (Non-flowering Plant)
There are no flower and seed in these types of plants.
These are classified into the following groups:
(A) Thallophyta:
1. This is the largest group of the plant kingdom.
2. The body of plants of this group is thallus like i.e., plant are not differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
3. It is the lower most group of plant kingdom.
4. There is no conducting tissue. It is divided into two groups. (a) Algae and (b) Fungi
(a) Algae
1. The study of algae is called Phycology.
2. The algae normally have chlorophyll and autotrophic mode of nutrition.
3. Its body is thallus like. It may be unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
4. Classification of the group algae is based on nature of pigment.
Useful Algae:
1. As a food: Porphyra, Ulva, Sargassum, Laminaria, Nostoc etc.
2. In making Iodine: Laminaria, Fucus, Echlonia etc.
3. As a manure : Nostoc, Anabana, kelp etc.
4. In making medicines: Antibiotic Chlorelline from Chlorella and Tincher iodine is made from Laminaria.
5. In research works: Chlorella, Acetabularia, Belonia etc.
⇒ Spirogyra is commonly known as ‘Pond Silk’.
Note: An astronaut can get protein food, water and oxygen by sowing the chlorella algae in the tank of the aircraft so chlorella is known as space algae.
Agar is prepared from algae like Gelidium and Gracilaria. It is used to grow microbes and in preparation of icecreams and jelly.
(b) Fungi
1. Study of fungi is called Mycology. Organism of this group may be unicellular or multicellular.
2. Fungi is without chlorophyll, central carrier tissue less, Thallophyta.
3. Accumulated food in fungi remains as Glycogen.
4. Its cell wall is made up of chitin. Ex. Albugo, Phytophthora, Mucor, Yeast etc.
Fungi may creates serious diseases in plants. Most of the damage is caused by rust and smut. Main Fungal diseases in plants are as –
White rust of crucifer, Loose smut of wheat, Rust of wheat, early Blight of potato, Red rot of sugarcane, Tikka diseases of groundnut, Wart disease of potato, Brown leaf spot of rice, Late blight of potato, Damping off of seedlings etc.
⇒ Rhizopus is a fungi commonly known as ‘bread mould’.
⇒ Heterothallism in fungi was discovered by AF Blakelee
⇒ Alfa-toxins are produced by fungi.
⇒ Lichens are the association of algae and fungi.
⇒ Lichens developing on rocky substrates are called saxicolous.
⇒ Lichens are the first organism which colonise on bare rock.
⇒ Yeast is unicellular fungi reproduce through budding.
⇒ The sexual reproductive organ of aspergillus are antheridium and ascogonium.
(B) Bryophyta
This is the first group of land plants. In this division approximately 25,000 species are included.
1. In bryophyta there is lack of xylem and phloem tissue.
2. Plant body may be of thallus like and leafy erect structure as in moss.
3. They lack true roots, stem and leaves.
4. This community is also called Amphibian category of the plant kingdom.
⇒ Water conduction takes place in mosses through parenchyma.
The moss namely Sphagnum is capable of soaking water 18 times of its own weight. Therefore, gardeners use it to protect from drying while taking the plants from one place to another.
⇒ The Sphagnum moss is used as fuel.
⇒ The Sphagnum moss is also used as antiseptic.
(C) Pteridophyta
The plants of this group is mostly found in wet shady places, forests and mountains.
1. The body of plants is differentiated into root, stem and leaves. Stem remains as normal rhizome.
2. Reproduction occur by spores produced inside the sporangia.
⇒ Sporangia bearing leaf of a fern is called ‘Sorus’.
3. Gametophytic phase is short lived. The diploid zygote develop into an embryo.
⇒ Gametophyte is called prothallus in pteridophytes.
4. Plants of this community have conducting tissues. But xylem does not contain vessels and phloem does not contain companion cells.
Examples: Ferns, Azolla, Pteridium, Lycopodium etc.
⇒ In the neck cell of archegonium of fern one binucleated cell is present.
⇒ Mosses (Bryophytes) and ferns (Pteridophytes) are called amphibian of plant kingdom.
⇒ Marsileo, Fern and Horse tail are example of pteridophyta.
⇒ Fernand Fernallies belong to the kingdom pteridophyta.
II. Phanerogamous (Flowering Plant)
Plants of this group is well developed. All the plant in this group bear flower, fruit and seed. Plants of this group can be classified into two sub-groups – Gymnosperm and Angiosperm.
(A) Gymnosperm (Naked Seed)
1. These plants are in the forms of trees and bushes. Plant body are differentiated into root, stem & leaves.
2. Plants are woody, perennial and tall. Plant bear naked seed.
3. Its tap roots are well developed.
4. Pollination takes place through air.
The longest plant of the Plant kingdom, Sequoia gigentia comes under it. Its height is 120 meters. This is also called Red Wood of California.
⇒ The smallest plant is Zaimia Pygmia.
⇒ Living fossils of plant are Cycas, Ginkgo biloba and Metasequoia.
⇒ Ginkgo biloba is also called Maiden hair tree.
⇒ Ovule and Antherozoids of Cycas is largest in Plant kingdom.
⇒ Corolloid root of cycas help in absorption of water and fixation of nitrogen.
⇒ The pollen grains of Pinus are so much in number that later it turns into Sulphur showers.
Importance of Gymnosperm
1. As a food-Sago is made by extracting the juice from the stems of Cycas. Therefore, Cycas is called Sago-palm.
2. Wood-The wood of Pine, Sequoia, Deodar, Spruce etc is used for making furniture.
3. Vapour oil – We get Tarpin oil from the trees of Pine, Cedrus oil from Deodar tree and Cedcast oil from Juniperous wood.
4. Tannin – It is useful in tanning and making ink.
5. Resin Resin is extracted from some conical plants which are used in making varnish, polish, paint etc.
⇒ Resin is the product of coniferous tree.
⇒ Best example of polyembryony is citrus fruit.
(B) Angiosperm (Covered Seed)
1. In the plants of this sub-group seeds are found inside the fruits. (Concealed Seeds)
2. In these plants root leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds are fully developed.
Plants of this sub-group have seed-coat in seeds. On the basis of number of cotyledons plants are divided into two categories 1. Monocotyledon and 2. Dicotyledon
⇒ Leaves are the lung of plant.
⇒ Plant from which coca and chocolate are obtained is a shurb.
⇒ Banana is a shurb.
⇒ Trochodendron is a vesselless angiosperm.
⇒ Pulses are obtained from the family Leguminacae.
⇒ From the bark of cinchona a drug quinine is obtained used in malaria fever.
⇒ Chloroplast found in sugarcane plant shows dimorphism.
⇒ The maximum fixation of solar energy is done by green plant.
⇒ Golden rice contain ß-carotene gene which comes from carrote. It is a variety of rice produced by genetic engineering to biosynthesis of ß-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A.
⇒ Potato, Tomato and Brinjal are three different species but all belong to genus Solonum.
⇒ Alphanso is a mango variety which is mostly exported from India.
⇒ The botanical name of macroni wheat is Triticum durum.
⇒ Chopping of an onion makes one cry because of the chemical containing sulphur.
⇒ Maize-Potato-Sugarcane-Moong is the example of crop rotation for two years.
⇒ First herbicide produced in the world is 2, 4-D.
⇒ World most problematic aquatic weed is Eichhornia crassipes which is also known as “Terror of Bengal”.
⇒ An artificial method of asexual reproduction, used to produce plant, combining desired stem with favourable root characteristics is Graffting.
⇒ Water passes from soil into the root by a physical process called osmosis.
⇒ Insectivorous plants grow in soil deficient in nitrogen.
⇒ Pneumatophores are specialised root in hydrophytes.
⇒ Drosera is a carnivorous plant.
⇒ Lemon grass is used in preparing a natural mosquito repellent.
Virus
⇒ Study of virus is called virology.
⇒ Virus was discovered by Russian scientist Ivanovsky in the year 1892. (During the tests of Mosaic disease in tobacco).
⇒ In nature, there are ultra microscopic particle known as viruses.
⇒ It has both the characters of living and non living, so it is a connecting link between living & non living.
⇒ Dr. Stanley first isolated the virus causing mosaic disease in tobacco in the form of crystals.
Characters of virus
⇒ Virus is made up of nucleic acid and protein.
1. They became active inside a living cells or host cell.
2. Nucleic acids replicate themselves and they reproduce rapidly.
3. They cause disease like bacteria & fungi.
According to parasitic nature, virus is of three types
1. Plant virus – RNA is present as nucleic acid in 75% plant virus. Some have DNA as nucleic material.
2. Animal virus-DNA or sometimes RNA is found in it.
3. Bacteriophage – A virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. They kill the bacteria. Example-T-2 phage. Bacteriophages are composed of nucleic acid molecule surrounded by a protein sheath.
⇒ In man virus cause disease like mumps, chicken pox, hepatitis, polio, AIDS, Herpes etc.
⇒ HIV often change its structure due to the presence of an enzyme reverse transcriptase.
⇒ The enzyme integrase produced by virus allow the integration of HIV-DNA into the host cell DNA.
⇒ EBOLA is a virus, causes ebola fever. Fruit Bats are the natural host of this virus, first outbreak in West Africa.
Note: Those viruses in which RNA is found as genetic material are called Retrovirus.
⇒ Viruses are parasite which need living cell to reproduce. Outside host it is smilar to chemical substance.
⇒ Virus have no enzyme of their own.
⇒ Many plant and vertebrate animals produce an antiviral substance which inhibits the multiplication of virus called interferon.
⇒ Water of holy Ganga river is pure due to presence of bacteriophages.
⇒ The term ACE-2 is talked about in context of spread of viral disease.
⇒ Virus can not be cultured in artificial synthetic medium.
Bacteria
It was discovered by Antony Von Leeuwenhook of Holland in the year 1683.
⇒ Leeuwenhook is called the father of Bacteriology. In the year 1829 Ehrenberg called it bacteria.
⇒ The year 1843-1892 – Robert Koch discovered the bacteria of Tuberculosis diseases.
⇒ The year 1812-1892 – Louis Pasteur discovered the vaccine of Rabies and pasteurization of milk.
On the basis of shape, bacteria are of different types :
1. Bacillus :This is rod-like or cylindrical.
2. Round or Cocus: These are round and the smallest bacteria.
3. Comma shaped or Vibrio: Like the English sign (,) example – Vibrio cholerae etc.
4. Spirillum :Spring or screw shaped.
⇒ Some species of Azotobacter, Azospirillum and Clostridium bacteria live freely in the soil and fix atmospheric nitrogen into the nitrogenous compound.
⇒ The Bacteria capable of converting nitrite to nitrate is nitrosomonas.
Anabaena and Nostoc cynobacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into soil.
⇒ The species of Rhizobium like Bradyrhizobium bacteria live in the roots of the Leguminous plants capable of converting atmospheric nitrogen into its compound. Example-Peas, Pegion Peas, Gram etc.
⇒ Rhizobium are called symbiotic bacteria.
⇒ The harmful substances produced by the microbes are known as Toxins.
Note: To preserve the milk for many days pasteurization is done. There are two methods of pasteurization –
(a) Low temperature holding method (LTH) :Milk is boiled at 62.8 degree celsius for 30 minutes.
(b) High temperature short time method (HTSt): Milk is for 15 seconds.
boiled at 71.7 degree celsius
⇒ In leather industry separation of hair and fat from leather is done by bacteria. This is called tanning of leather.
⇒ Pickles, syrup is kept in salt or in dense liquid of sugar so that in case of bacterial attack bacteria are plasmolysed and destroyed. Therefore, pickles do not get spoiled soon and can be preserved for long time.
⇒ The citrus fruit and pickels are not stored in iron container because it contain organic acid.
⇒ In the cold storage objects are kept at low temperature (-10 degree celsius to -18 degree celsius).
⇒ Mycoplasma :Smallest known prokaryotic cell causing pleuropneumonia. It is also known as PPLO.
⇒ Waksman got the nobal prize for the discovery of antibiotic streptomycin.
⇒ Alexender Fleming discovered first antibiotic – Penicillin
⇒ Xenobiotics are inherently resistant to microbial attack mare called recalcitrant.
⇒ Microbial type culture collection centre is situated at Chandigarh.
⇒ Honey has high concentration of sugar does not decay because bacteria can not survive in a solution of high osmotic strength as water is drawn out.
⇒ Bacteria are useful for commercial as well as industrial application like fermentation, production of vaccine, cleaning of oil spills and producing other bioactive molecules.
⇒ Bacterial decomposition of biological material under anaerobic condition is called composting.
⇒ The most extensive use of molasses after fermentation is for producing ethanol.
⇒ Among fungi, virus, bacteria and protozoa the phototrophic nutrition is only found in Bacteria.
⇒ Bacteria having flagella all over the body is known as keperitrichous.
⇒ Legumes fix nitrogen only through the specialized bacteria that live in their roots nodules.
⇒ Nitrifying bacteria like Nitrosomonas and Nitrobactar convert ammonia or ammonium compounds into nitrates.
⇒ Bacterial genome contains DNA without histone.
⇒ Escherichia coli commonly lives in animal and human In intestine.
⇒ In bacteria plasmid is extra-chromosomal DNA.
⇒ The most important bacteria which produce maximum number of antibiotics is streptomyces.
⇒ Antibiotics are the chemical substance produced by living microorganism capable of inhibiting or destroying other microbes.
⇒ Cyanobacteria helps farmers by reducing the acidity of 6/ 2015 Hist soil.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here