Genetics
Genetics
⇒ Transmission of character from one generation to next generation is called heredity.
⇒ The process of transfer of hereditary character from generation to generation is called genetics.
⇒ The name genetics was first coined by W. Wattson in 1905.
⇒ Johannes was first used the name gene in 1909.
⇒ Gregar Johan Mendal was the first who gave the idea of heredity based on his experiment in 1822-1884. He is also known as father of genetics.
⇒ Mendal chosen pea plant for his experiment.
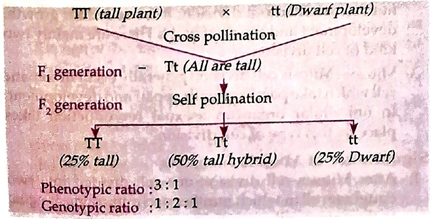
⇒ Mendal made a cross between two pure plant having contrasting character for single trait called monohybrid cross i.e. tall and dwarf plant for height.
Monohybrid Cross
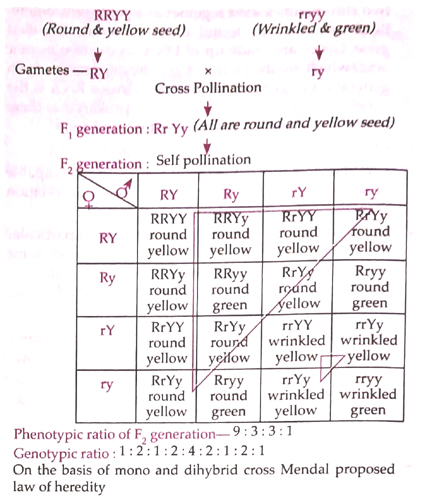
Dihybrid cross:Mendal made a cross between two pure plant having pair of contrasting character i.e. colour and shape of seed called dihybrid cross.
He made a cross between plant having round seed with yellow colour and wrinkled seed with green colour.
1. Law of paired unit: Mendal proposed that when two dissimilar unit factors are present in an individual only one is able to express. One that expresses itself is dominant unit factor while other which fail to express is recessive unit factor. For example tallness is dominant over dwarfness.
2. Law of dominance : Offspring of cross breed parent only show dominant characters in F1 generation.
3. Law of segregation: In F2 generation both the character which is governed by gene is separated.
4. Law of independent assortment : During dihybrid and tribhybrid cross two or three pair of characters are taken. These characters segregate separately without depending on other in F₂ generation.
Term related to genetics :
Linkage Linkage is an exception of Mendel law. When two different gene are present on the same chromosome they express themself together instead of independently. This phenomenon is known as Linkage. The word linkage first coined by Morgan (1910).
Mutation: A sudden change in the gene which is heritable from one generation to other. The term Mutation was first coined by Hugo De Vries.
Variation: When characters are transmitted from one generation to next generation there is some change. Change in characters by recombination of gene in offspring. So, they looks different from their parents. This phenomenon is known as Variation.
Chromosomal aberrations : Any change in chromosomal structure is known as Chromosomal aberrations.
Cloning: It is a process of producing identical organism from a single cell having same genetic character as his mother. Ex: Sheep Dolly was produced from single cell.
Dolly was assigned to the world’s first clone of an adult animal by the British Scientists.
Totipotency : It is the potential ability of a plant cell to grow in a complete plant.
Pluripotency : It is the potential ability of a cell to develop into any kinds of the cell of animal body.
Genetically modified organism (GMO): Manipulation of gene by cutting or joining the segment of DNA to get desired varieties of organism is called genetically modified organism. This is also known as genetic engineering.
Autosomes Chromosomes found in cell which are responsible for characters other than sex are called autosomes.
Sex chromosome: The pair of chromosome which determine the sex of organism is called sex chromosome. Human have 23 pair of chromosomes in which 22 pair are autosomes and one pair is sex chromosome.
Genome : All gene present in a haploid cell is called genome.
Plasmagen: Gene which are found in organelles of cytoplasm called plasmagen.
Cistron: Functional unit of gene is called citron.
Muton: Unit of gene responsible for mutation.
Recon: Unit of gene take part in recombination.
Note :
S.Benzer (1962) had given the modern definition of gene.
The gene which exhibits multiple effects is called pleiotropic.
When one gene pair hide the effect of other unit, it is called epistasis.
DNA fingerprinting is a technique used for the detection of disputed parentage.
Reverse transcription was discovered by Temin & Baltimore.
Targeted drug delivery and gene therapy are made possible by the use of nanotechnology in health sector.
Bt brinjal is a genetically engineered form of brinjal has been developed to make it pest resistant.
In the recent developments of science a functional chromosomes cannot be created by joining segment of DNA taken from the cells of different species.
Genetic predisposition of some people is the reason of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens.
Taking incorrect doses of antibiotic to cure disease is the reason of developing multi-drug resistance.
Cas I protein is a molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing which is often mentioned in news.
In normal cell, the process of the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA is called transcription.
In Eukaryotic cells genes present in the cytoplasm are found in the mitochondria and inherited via egg cytoplasm.
Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in-vitro fertilization of egg.
A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from mother and not from father.
Extranuclear genes occur in mitochondria inherited by female.
Chromosomal theory of inheritance was given by Slutton & Boveri.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here