Gujarat Board Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles Ex 6.6
Gujarat Board Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles Ex 6.6
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles Ex 6.6
Question 1.
In the figure, PS is the bisector of ∠QPR of
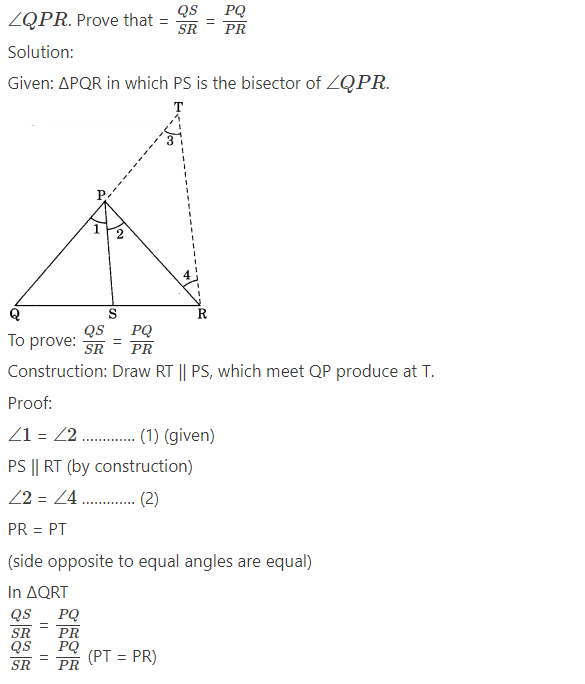
Question 2.
In the given figure, D is a point on hypotenuse AC of ∆ABC, such that BD ⊥ AC, DM ⊥BC and DN ⊥ AB. Prove that:
(i) DM2 = DN.
(ii) DM2 = DM . AN

Solution:
In the given figure ∆ABC in which
AB ⊥ BC and DM ⊥ BC,
AB || DM
Similarly CB ⊥ AB and DN ⊥ AB
CB || DN
Hence quadrilateral BMDN is a rectangle
BM = ND
(i) In ∆BMD
∠1 + ∠BMD + ∠2 = 180°
(by Angle sum property)
∠1 + 90° +∠2 = 180°
∠1 + ∠2 = 90° ……………(1)
Similarly, in ∆DMC we have
∠3 + ∠4 = 90° ……………. (2)
Since BD ⊥ AC
Therefore ∠2 + ∠3 = 90° ………….(3)
From eqn (1) and (3)
∠1 + ∠2 = ∠2 + ∠3
∠1 = ∠3
Also from eqn (2) and (3)
∠3 + ∠4 = ∠2 + ∠3
∠2 = ∠4
Thus is ∆DMB and ∆DMC
We have
∠1 + ∠3 and ∠2 + ∠4
∆B/ND ~ ∆D/NA
BN/DN = NDDA
DM/DN = DN/MC
DN2 = DM . MC
Question 3.
In figure ABC is a triangle in which 90° and AD ⊥ CB produced prove that
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC . BD

Solution:
Given : ∆ABC in which < ABC > 90° and AD ⊥ CB produced.
To prove: In right triangle ADC
∠D = 90°
AC2 = AD2 + DC2
(by Pythagoras theorem)
AC2 = AD2 + (BD + BC)2
(DC = BD + BC)
AC2 = AD2 + BD2 + BC2 + 2BC . BD ………….(1)
Now in right ∆ADB
AC2 = AD2 + BD2 ………………….(2)
(by Pythagoras theorem)
From eqn (1) and (2)
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC . BD
Question 4.
In figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠ABC ∠90° and AD ⊥ BC.
To Prove: AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC . BD
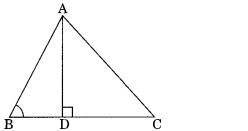
Proof: In right ∆ADC
∠D = 90°
AC2 = AD2 + (BC – BD)2
(DC = BC – BD)
AC2 = AD2 + BC2 + BD2 – 2BC . BD
AC2 = AD2 + BD2 + BC2 – 2BC . BD ……………(1)
Now in right ∆ADB
AB2 = AD2 + BD2 …………(2)
(by Pythagoras theorem)
From eqn (1) and (2) we have
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 – 2BC2 . BD
Question 5.
In figure AD is a median of a triangle ABC and AM ⊥BC prove that


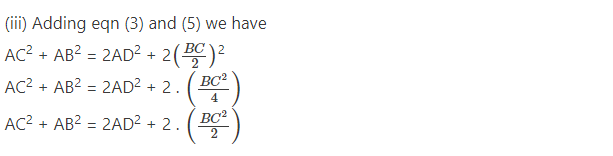
Question 6.
Prove that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of its sides.
Solution:
Given:
ABCD is a ||gm whose diagonals are AC and BD.

To prove:
AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + CA2 = AC2 + BD2
Construction:
Draw AM ⊥ DC and BN ⊥ DC (produced)
Proof: In right ∆AMD and ∆BNC
AD = BC (opposite sides of ||gm)
AM = BN (altitudes of same ||gm on the same base)
∆AMD ≅ ∆BNC (by RHS congruence Rule)
MD = CN …………..(1) (by CPCT)
Now in right triangle BND
∠N = 90°
BD2 = BN2 + DN2
(by Pythagoras theorem)
BD2 = BN2 + (DC + CN)2(DN = DC + CN)
BD2 = BN2 + DC2 CN2 + 2DC . CN
BD2 = BN2 + CN2 + DC2 + 2DC . CN ………….(2)
Now in right ∆BNC
BD2 = BN2 + CN2 ……..(3)
From eqn (2) and (3)
BD2 = BC2 + DC2 + 2DC . CN ………………(4)
Now in right ∆ADM
∠M = 90°
AC2 = AM2 + MC2 ………….
(by Pythagoras theorem)
AC2 = AM2 + (DC – DM)2
(MC = DC – DM)
AC2 = AM2 + DC2 + DM2 – 2DC . DM
AC2 = AM2 + DM2 + DC2 – 2DC . DM …………..(5)
Now in right ∆ADM
AD2 = AM2 + DM2 ……………(6)
(by Pythagors theorem)
From eqn (5) and (6) and we have
AC2 = AD2 + DC2 – 2DC . DM
AC2 = AD2 + AB2 – 2DC . CN …………..(7)
(DC = AB opposite sides of ||gm and DM = CN from eqn (1))
Adding eqn (4) and (7)
AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + AB2 + BC2 + DC2
AC2 + BD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2
Question 7.
In figure, two chords AB and CD intersect each other at the point P prove that
(i) ∆APC ~ ∆DPB
(ii) AP . PB = CP . DP
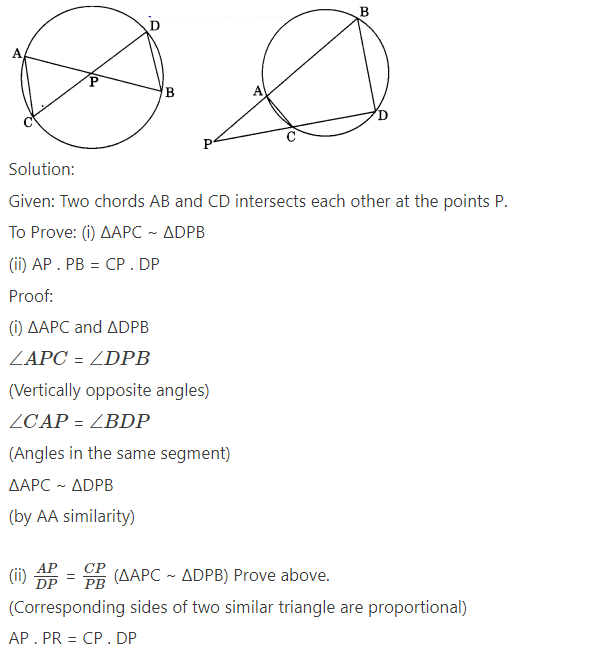
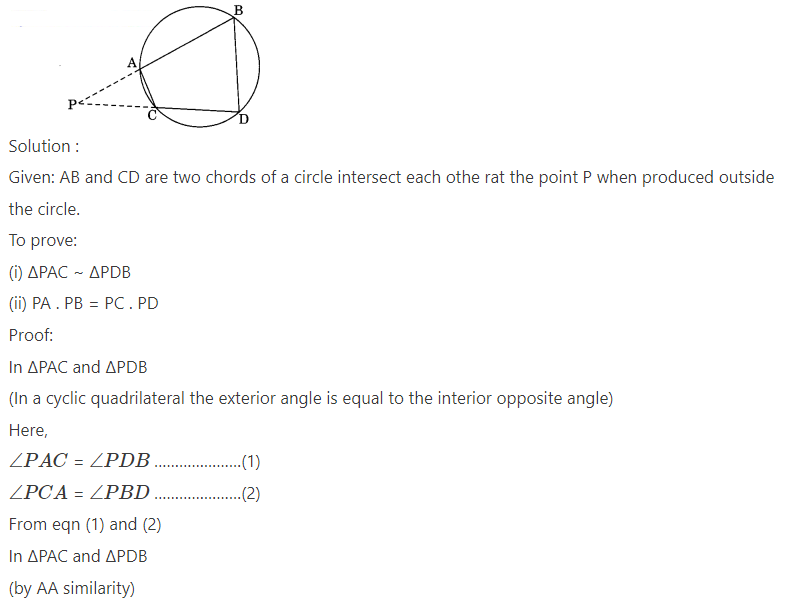
Question 8.
In figure, two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect each other at the point P (When produce) outside the circle. Prove that
(i) ∆PAC ~ ∆PDB
(ii) PA . PB = PC . PD

Question 9.
In figure, D is a point on side BC of ∆ABC such that BD/CD = AB/AC.
Prove that AD is the bisector of ∠BAC.

Question 10.
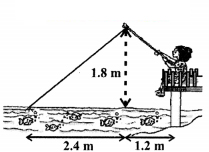
Nazima is fly fishing in a stream. The tip of her fishing rod is 1.8 m above the surface of the water and the fly at the end of the string rests on the water 3.6 m away and 2.4 m from a point directly under the tip of the rod. Assuming that her string (from the tip of her rod to the fly) is taut, how much string does she have out (see figure)? If she pulls in the string at the rate of 5 cm per second, what will be the horizontal distance of the fly from her after 12 seconds?
Solution:
Let us find the length of the string that the has out
In right ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
(by Pythagoras theorem)
AC2 = (2.4)2 + (1.8)2
AC2 = 5.76 + 3.24 = 9
AC = 3m
i.e length of string she has out = 3m since the string is pulled out at the rate of 5 cm/sec.
Length of the string pulled out in
12 seconds = 5 cm x 12 cm = 60 cm
= 60/100 m = 0.60 metre
Remaining string left out = (3 – 0.60) m
= 2.4m
To find horizontal distance
Inright ∆PBC, let PB the required horizontal distance of fly.
Since PC2 = PB2 + BC2
PB2 = PC2 + BC2
PB2 = (2.4)2 – (1.8)2
PB2 = 5.76 – 3.24
PB2 = 2.52
PB = 1.59 (approx)

Thus, the horizontal distance of the fly from nazima after 12 seconds
= 1.59 + 1.2 = 2.79 m (approx)
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here