JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 9 Metals and Non-Metals
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 9 Metals and Non-Metals
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 9 Metals and Non-Metals
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Metals and Non-Metals Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ Elements can be classified into metals, non-metals, metalloids and noble gases.
◆ Nearly 80% of the known elements are metals.
◆ Metals. The element which show bright lustre, melleability and ductility, high thermal and electrical conductivities are called metals. The metals have good tendency to lose electrons and are therefore, electropositive in nature.
◆ Non-metals. Non-metals donot have the above properties. They have the tendency to accept electrons and form anions. Thus, non-metals are electronegative in nature.
◆ Metalloids. The elements which show the properties of metals as well as non-metals.
◆ Metals are placed on the left hand side and in the centre of the periodic table. Non-metals are placed on the right hand side of the periodic table.
◆ Malleability. It is the property due to which metals can be hammered into very thin sheets.
◆ Ductility. It is the property by which metals can be drawn into thin wires.
◆ Electrical conductivity. Metals are generally good conductors of electricity.
◆ Reactivity series of metals. It is the arrangement of metals in the decreasing order of their reactivities. For example, reactivity of common metals decreases as :
K> Na > Mg > Al > Fe > Cu > Ag > Au (A part of reactivity series of metals)
◆ Sodium and potassium metals are very soft and they can easily be cut with a knife.
◆ Occurrence of metals.
The earth’s crust is the major source of metals. Sea water also contains soluble salts of metals like sodium chloride, magnesium chloride etc.
◆ Minerals. The naturally occurring compounds of metals associated with earth impurities are called minerals.
◆ Ores. The minerals from which the metals can be conveniently and profitably extracted. e.g., The chief ore of iron is haematite (Fe2O3) and the chief ore of aluminium is bauxite (Al2O3. 2H2O).
◆ Gangue or matrix. The earthly impurities such as sand, stone, earthly particles, lime stone, mica, etc. present in the ore.
◆ Metallurgy. The process of extracting pure metals from their ores is called metallurgy, Concentration or enrichment of ore or ore dressing. The process of removal of unwanted impurities (gangue) from the ore is called concentration of the ore.
◆ Calcination. It is the process of heating the concentrated ore in the absence of air below its melting point.
◆ Roasting. It is the process of heating the concentrated ore strongly in the presence of excess air, below its melting point.
◆ Electrometallurgy. It is the process of extraction of metals by electrolysis process.
◆ Electrorefining. It is the process of refining of the metal through the use of electrolysis.
◆ Refining. The process of purifying the crude metal.
◆ Strategic metals. Metals such as titanium, chromium, manganese, zirconium etc. are called strategic metals because they are essential for the country’s economy and defence.
◆ Alloy. A homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or metals and non-metals. e.g. Brass, Bronze, Steel etc.
◆ Pure gold is known as 24 carat gold and is very soft.
◆ Amalgam. Special class of alloys in which there is mixture of metal and mercury.
◆ Corrosion of metals. The process of deterioration of a metal as a result of its reaction with air (or oxygen) and moisture (present in environment) surrounding it is called corrosion.
◆ Rust. It is a special case of corrosion of iron. Chemically rust is hydrated ferric oxide, Fe2O3.2H2O.
◆ Chemical bond. It is the attractive force which holds the constituent particles together in a chemical species (molecule or ion).
◆ Cause of chemical combination. It is the atoms of various elements, combine with each other in order to :
(i) Complete their octet i.e. to acquire the stable nearest noble gas configuration.
(ii) Acquire a state of minimum energy.
◆ Electrovalent or ionic bond. It is the strong electrostatic forces of attraction which bind the oppositely charged ions together produced by the transfer of electrons from the valence shell of one atom to another.
◆ Electrovalency. It is the number of electrons lost or gained by an an atom of e of element to complete its octet during the formation of electrovalent bond.
◆ Galvanisation. It is the process of covering iron surface with zinc to prevent rusting.
TBQ TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Give an example of a metal which :
(a) is a liquid at room temperature.
(b) can be easily cut with a knife.
(c) it is the best conductor of heat.
(d) is a poor conductor of heat.
Ans. (a) Mercury
(c) Silver
(b) Sodium
(d) Lead.
Q. 2. Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Ans. Malleable. A substance is said to be malleable if it can be beaten into sheets. e.g. metals are malleable.
Ductile. A substance is said to be ductile if it can be drawn into wires e.g. the metals are ductile.
Q. 3. Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil ?
Ans. This is because in contact with moist air containing carbon dioxide, it is covered with a carbonate layer.
4Na + O₂ → 2Na₂O
Na₂O + H₂O → 2NaOH
2NaOH + CO₂ → Na₂CO3 + H₂O
Also sodium reacts with water.
2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
Hence, sodium is kept immersed in kerosene oil.
Q. 4. Write equation for the reactions of
(a) iron with steam;
(b) calcium and potassium with water.
Ans.
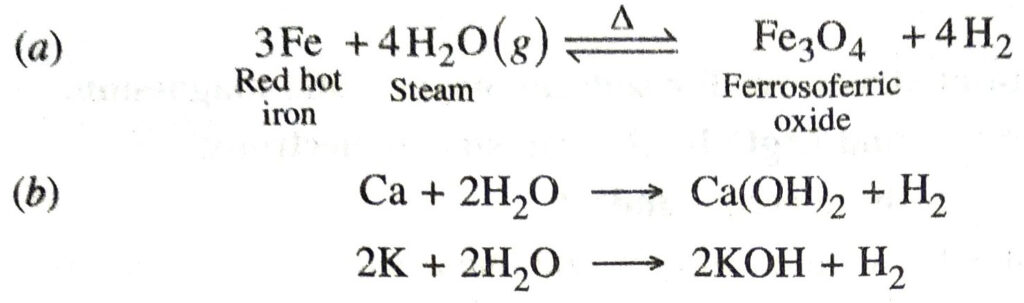
Q. 5. Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows:
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the table above to answer the following questions about metals, A, B, C and D.
1. Which is the most reactive metal ?
2. What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate ?
3. Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Ans. 1. B is the most reactive metal.
2. B will displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
3. The decreasing order of reactivity is
B > A > C > D.
Q. 6. Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Ans. Hydrogen gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal.

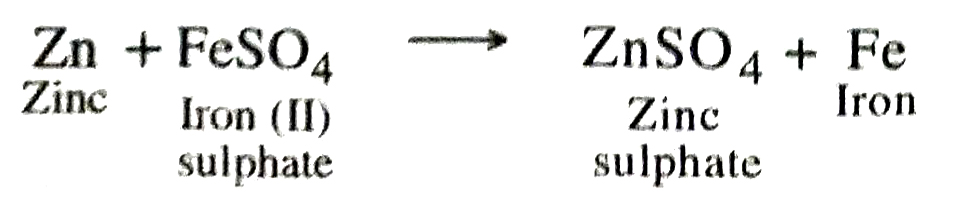
Q. 7. What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate ? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Ans. When zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate it will displace iron from it and light green colour of solution gradually fades away.
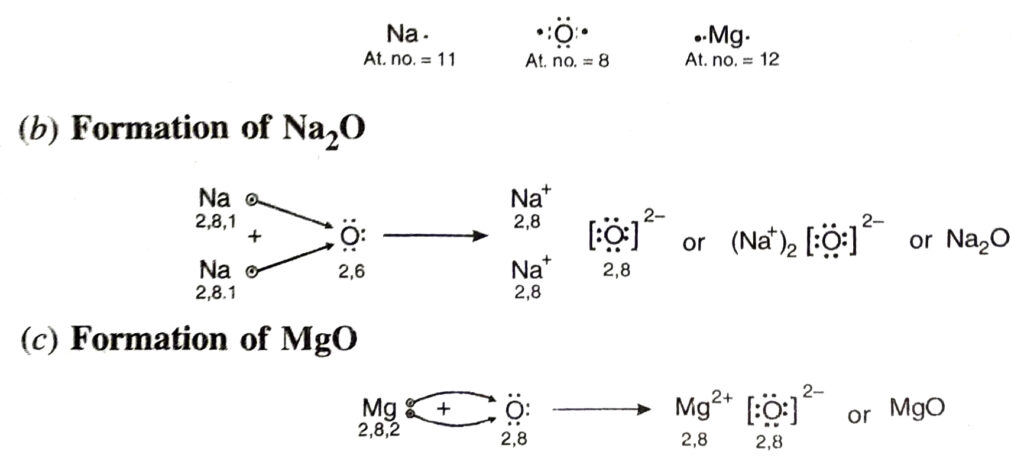
Q. 8. (a) Write the electron-dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(b) Show the formation of Na₂O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(c) What are the ions present in these compounds ?
Ans. (a) Electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium are
Q. 9. Why do ionic compounds have high melting points ?
Ans. In ionic compounds there are strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions and a considerable amount of energy is required to break the strong interionic attraction.
Q. 10. Define the terms:
(a) Mineral (b) ore and (c) gangue.
Ans. (a) Mineral. The compounds of elements occurring in earth’s crust which are associated with earthly impurities are called minerals.
(b) Ore. An ore is a mineral from which metal can be extracted conveniently and
(c) Gangue. The earthly impurities such as sand, lime stone, rocks etc. associated with minerals and ores are collectively known as gangue or matrix.
Q. 11. Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Ans. Gold and Platinum.
Q. 12. What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide ?
Ans. Reduction process.
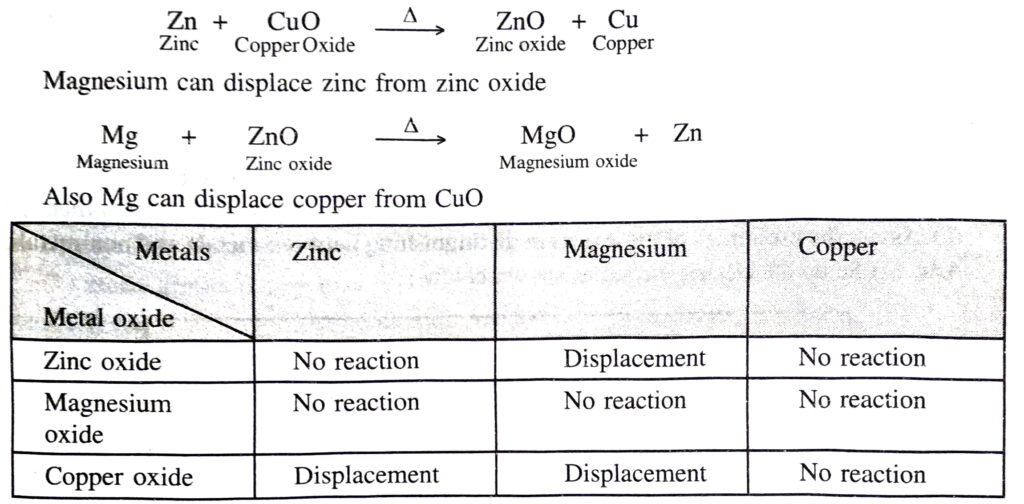
Q. 13. Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals:
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper |
| Zinc oxide | |||
| Magnesium oxide | |||
| Copper oxide |
In which cases will you find displacement reactions taking place ?
Ans. Zinc can displace copper from copper oxide
Q. 14. Which metals do not corrode easily?
Ans. The metals which are not attacked by air and moisture don’t corrode easily.
Q. 15. What are alloys ?
Ans. Alloys. These are the homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals or metals and non-metals. e.g. Brass is an alloy of Copper and Zinc.
TBE TEXT BOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions :
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal ?
Ans. (d)
Q. 2. Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting :
(a) applying grease
(b) applying paint
(c) applying a coating of zinc
(d) all of the above.
Ans. (c)
Q. 3. An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be :
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron.
Ans. (a)
Q. 4. Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because :
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
(c) zinc is more reactive than tin
(d) zinc is less reactive than tin.
Ans. (c)
Q. 5. You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Ans. (a) Setup the electric circuit as shown below :
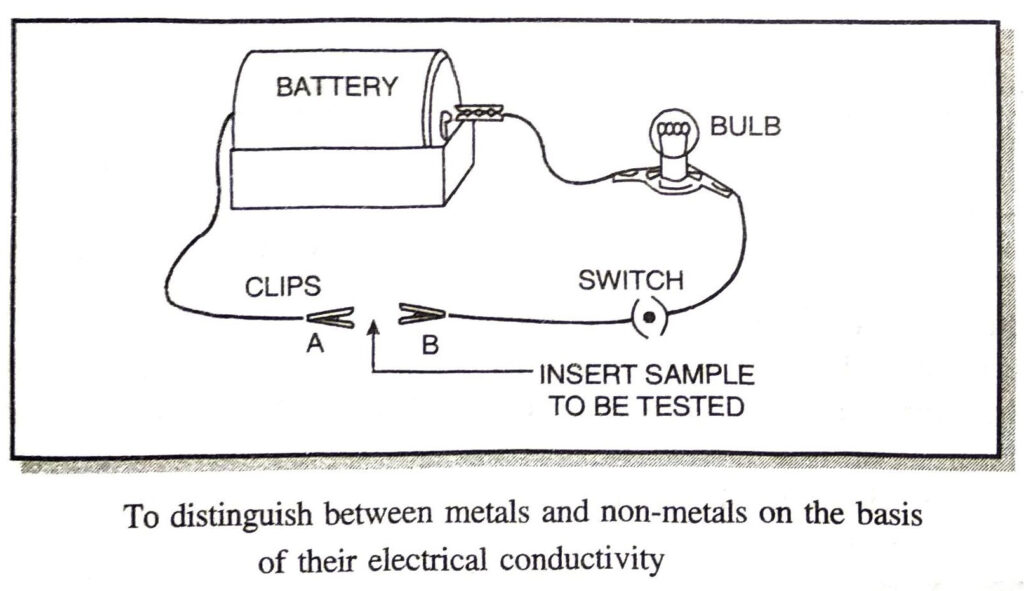
Insert the sample to be tested between clips A and B.
If the bulb glows, the sample is metal.
If the bulb does not glow, the sample is non-metal.
As metals are good conductors of electricity whereas non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
(b) If a substance produces a sound when struck beating with a hammer, it is a metal and if no sound is produced, it is a non-metal.
Metals are sonorous whereas non-metal are non-sonorous.
Q. 6. What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Ans. Amphoteric oxides. The metal oxides which react both with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are known as amphoteric oxides.
Examples. Zinc oxide, ZnO ; Aluminium oxide, Al2O3
Q. 7. Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Ans. Zinc and magnesium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids. Copper and silver cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Q. 8. In the electrolytic refining a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Ans. During the electrorefining of metal, the impure metal is made as anode, a thin strip of pure metal M is made as cathode. The electrolyte used a soluble salt of metal M, to be refined.
Q. 9. Aamir took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it as shown in figure.
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper ?
(ii) moist litmus paper ?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Ans. (a) (i) No action.
(ii) It turns moist litmus paper red and then bleaches it.
(b) S + O₂ → SO₂
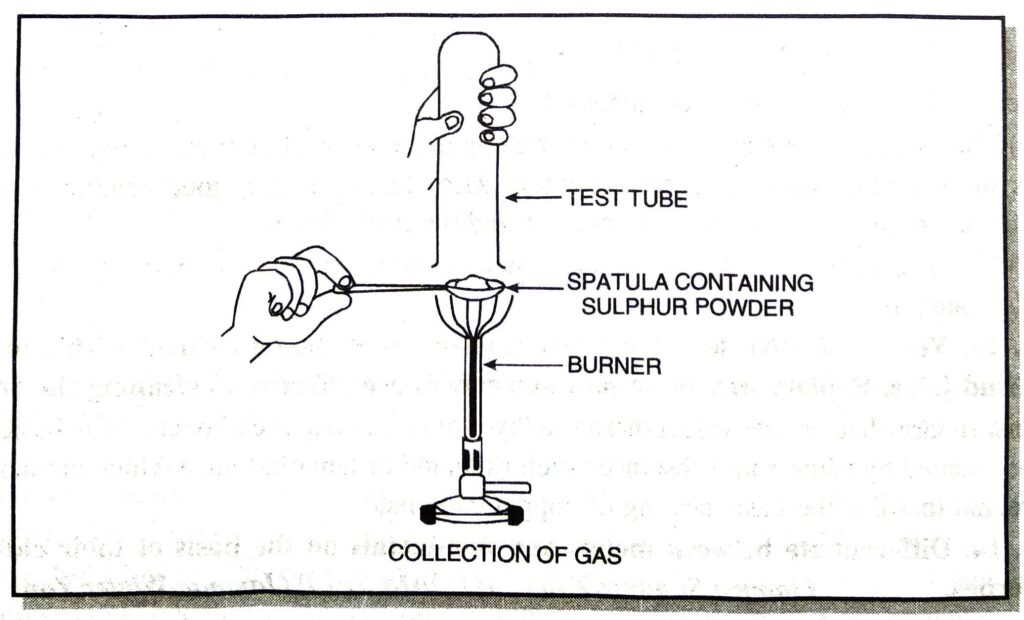
Q. 10. State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Or
How corrosion can be prevented ?
Ans. The rusting can be prevented by :
1. painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, chrome plate or anodising.
2. forming alloys.
Q. 11. What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen ?
Ans. As they form two types of oxides :
(a) Neutral oxides such as CO, NO etc.
(b) Acidic oxides such as SO2, CO2 etc.
Q. 12. Give reasons :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Ans. (a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery because these are not attacked by air and moisture. They don’t undergo corrosion and retain their lustre for a long time. Also these metals are malleable and ductile.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil because in contact with moist air containing carbon dioxide, these are covered with a carbonate layer.
e.g. 4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
2NaOH + CO2 → Na2CO3 + H2O
Also they react with water.
e.g. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2.
Hence, these metals are stored under oil.
(c) This is due to the reason that a thin sticking oxide layer of aluminium oxide is formed on its surface which prevents further reaction. Also aluminium is a good conductor of heat and the oxide layer (Al2O3) is stable even at high temperatures.
(d) This is because it is easier to obtain a metal from its oxide as compared to its sulphide and carbonate ore.
Q. 13. You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Ans. In tarnished copper vessel there is a layer of basic copper carbonate. This basic layer can be cleaned by using sour substances such as lemon or tamarind juice which are acidic in nature and dissolve the basic coating of copper carbonate.
Q. 14. Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Ans. Differences between metals and a non-metals on the basis of chemical properties.
| Metals | Non-Metals |
|
|
Q. 15. A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Ans. The solution used by goldsmith to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments was aqua regia. It is a freshly prepared mixture of conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in the ratio 3:1 by volume. It can dissolve gold.
Q. 16. Give the reason why copper is used to make hot water tanks but steel (an alloy of iron) is not.
Ans. This is because iron present in steel reacts with steam to form ferrosoferric oxide whereas copper has no action with water. As a result of it, the body of the steel tank becomes weaker and weaker in case of iron and not in case of copper.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Define metallurgy. Name the steps involved in metallurgy. What are the various methods used for crushing and grinding and concentration of ore ?
Or
What is meant by the concentration of the ores ? Describe the methods for the concentration of ores.
Ans. Metallurgy. The process of extracting metals from their ores is called metallurgy. The process of metallurgy depends upon the nature of the ore, nature of the metal and the types of impurities present in the ore.
Various steps involved in the extraction of metal from an ore are :
- Crushing and grinding of the ore.
- Concentration or enrichment of the ore.
- Extraction of metal from the concentrated ore.
- Purification or refining of the impure metal.
These steps are briefly discussed below :
1. Crushing and grinding.
Most of the ores occur in nature as big rocks. They are broken to small pieces with the help of crushers. These pieces are then broken to fine powder with the help of a ball mill or stamp mill.
2. Concentration or Enrichment of ore or Ore dressing.
The process of removal of unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earthy particles etc. from the ore is called ore concentration or ore dressing. The finely ground ore is concentrated by any of the following processes :
(a) Hydraulic washing. This method depends upon the difference in the densities of the ore particles and the impurities (gangue). The crushed and powdered ore is taken in large wooden tables with small obstacles. A stream of water is passed over the shaking table. The lighter impurities are washed away with the running stream of water while the heavier ore particles are left behind. This method of concentration is usually applicable to oxide ores.
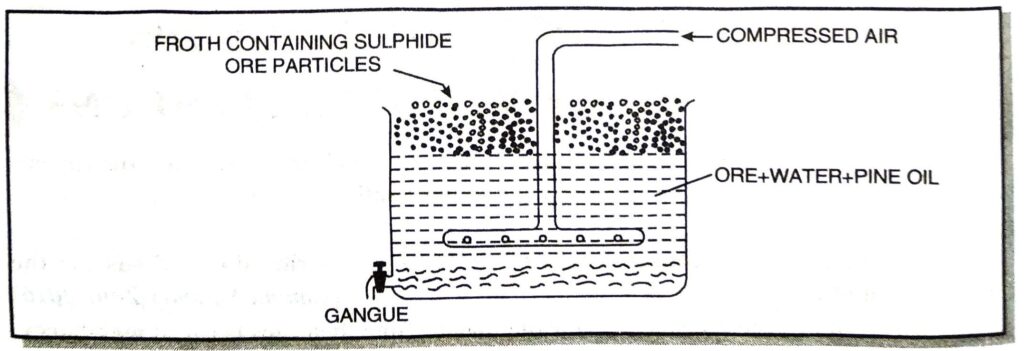
(b) Froth floatation process. This method is used for the concentration of sulphide ore particles which are preferentially wetted by oil and gangue by water. The powdered ore is mixed with water containing small quantities of oil (pine oil or eucalyptus oil) in a large tank (Fig. 9.3). The mixture is agitated by blowing air violently, when a froth (or foam) is formed. The froth carries the lighter ore particles along with it to the surface. The heavier impurities are left behind in water and these settle to the bottom. Since the ore particles float with the froth at the surface, this process is called froth floatation process. The froth at the surface is transferred into another tank. The froth is broken by adding some acid and ore particles are separated by filtration and dried.
For example, the froth floatation process is commonly used for the sulphide ores of copper, zinc, lead, etc.
(c) Magnetic separation. The ores which are attracted by a magnet can be separated from the non-magnetic impurities with the help of magnetic separation method. For example, this method is used for the concentration of haematite, an ore of iron. It consists of a leather belt moving over two rollers, one of which is magnetic in nature. This is shown in Fig. The powdered ore is dropped over the moving belt at one end. At the other end, the magnetic
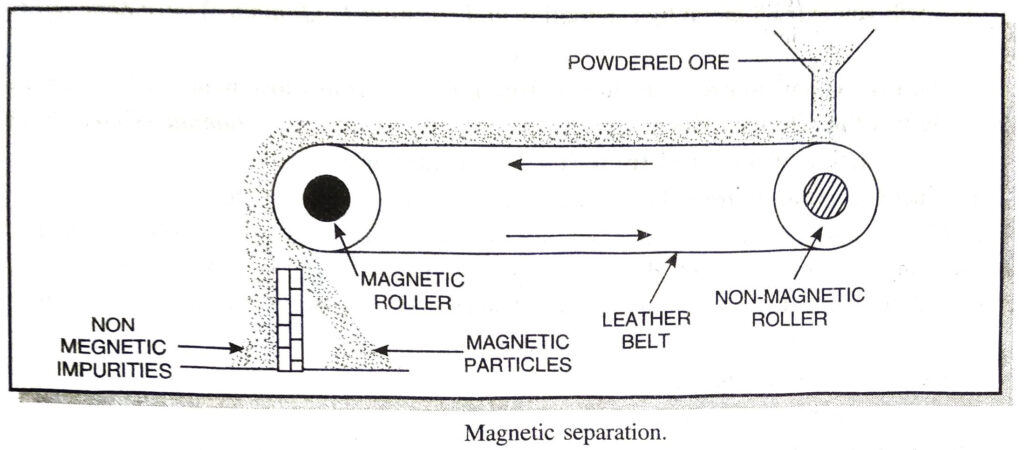
portion of the ore is attracted by the magnetic roller and falls nearer to the roller while the non-magnetic impurities fall farther off.
(d) Chemical method or Leaching. The chemical method used for concentration of the ore is based on the difference in some chemical property of the metal and the impurities. In this method, the powdered ore is treated with certain chemical reagents in which the ore is soluble but the impurities are not soluble. The impurities left undissolved are removed by filtration.
For example, bauxite ore of aluminium is concentrated by this method. This method is known as Baeyer’s process. In this method, the ore is treated with hot sodium hydroxide solution. Sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium oxide present in bauxite ore to form sodium meta-aluminate which is soluble in water. The solution is filtered to remove the gangue present in the ore because it does not dissolve in sodium hydroxide.

The filtered solution (containing NaAlO₂) is acidified with hydrochloric acid. On acidification, sodium meta aluminate gets converted into a precipitate of aluminium hydroxide.

The precipitate is separated by filtration. It is dried and heated to get pure aluminium oxide.
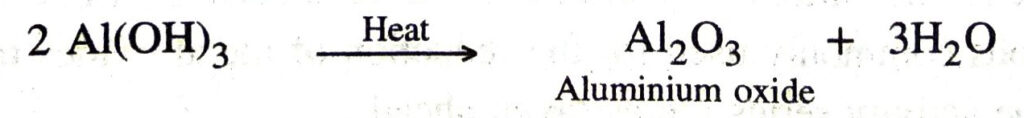
Q. 2. How will you get metal from concentrated ore ?
Or
Differentiate between roasting and calcination.
Or
How will you extract metal by calcination and roasting?
Or
Explain the chemical processes for obtaining metals from those oxides which are in the middle of the activity series.
Ans. Extraction of the metal from the concentrated ore.
The metal extracted from the concentrated ore by the following steps:
(i) Conversion of the concentrated ore into its oxide. This is usually done by calcination and roasting process. The method depends upon the nature of the ore. A carbonate ore is converted into oxide by calcination while a sulphide ore is converted into oxide by roasting.
(ii) Conversion of oxide to metal by reduction process.
(i) Conversion of ore into metal oxide
It can be done by two methods :
(a) Calcination. It is the process of heating the concentrated ore in the absence of air. The calcination process is used to remove volatile impurities, water from the hydrated ores and to convert carbonate ores into metal oxide.
For example:
(i) Zinc occurs as zinc carbonate in calamine (ZnCO3). The ore is calcinated (heated strongly) in the absence of air to convert it to zinc oxide. During calcination, carbon dioxide is expelled.

(ii) Aluminium occurs as Al2O3. 2H2O in its bauxite ore. When the bauxite ore is calcined, water vapours are expelled and anhydrous aluminium oxide is obtained.

(b) Roasting. It is the process of heating the concentrated ore strongly in the presence of excess air. This process is used for converting sulphide ores to metal oxide. For example, zinc occurs as sulphide in zinc blende (ZnS). It is strongly heated in excess of air when it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide gas is expelled.

(ii) Conversion of metal oxide to metal.
The metal oxide formed after calcination or roasting is converted into metal by reduction. Some of the methods commonly used for the reduction of metal oxides to metals which are in the middle of the activity series are as given ahead :
I. Reduction by heating in air.
Metals low in the reactivity series can be obtained from their oxides by heating in air. For example, mercury is obtained from cinnabar (HgS) ore by this me 13d. The method involves the following steps:
(i) The concentrated mercuric sulphide (cinnabar ore) is roasted in air when mercuric oxide is formed.
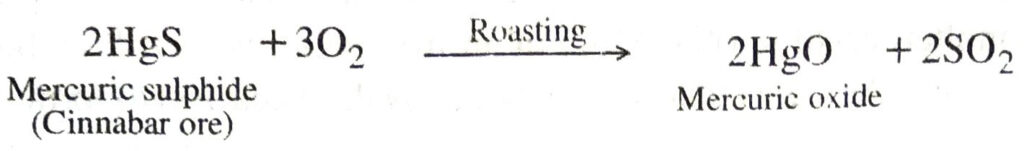
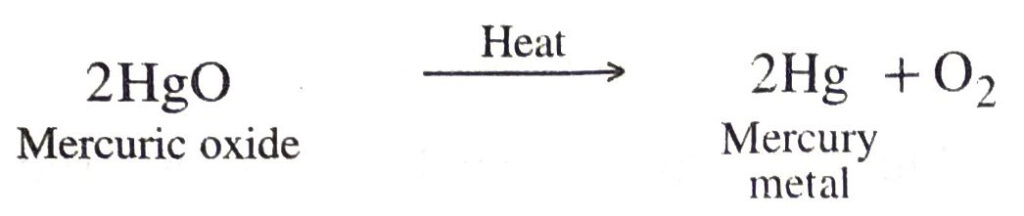
(ii) Mercuric oxide is heated to about 300° C and it decomposes to give mercury metal.
II. Chemical Reduction.
The metal oxides from calcination or roasting processes are reduced to free metal by using chemical agents like carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
(a) Reduction with carbon. The oxides of moderately reactive metals like zinc, copper, nickel, tin, lead, etc. can be reduced by using carbon as reducing agent. In this process, the metal oxide is mixed with coke and heated in a furnace. Carbon reduces the metal oxide to free metal. For example, when zinc oxide is heated with carbon, zinc metal is produced.
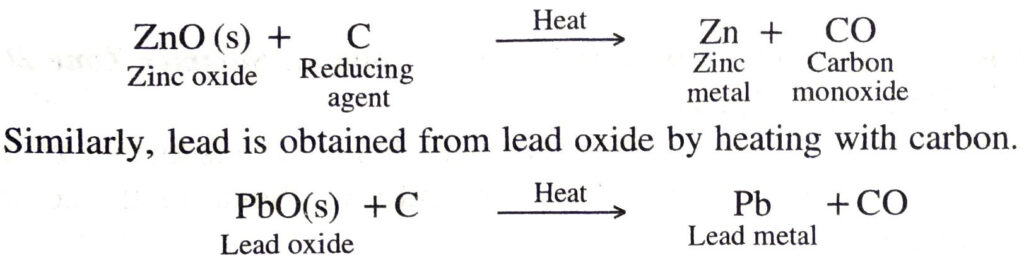
Coke is very commonly used as a reducing agent because it is cheap.
(b) Reduction with carbon monoxide. Metals can be obtained from oxides by reduction with carbon monoxide in the furnace. For example, iron is obtained from ferric oxide by heating with carbon monoxide.
(c) Reduction with aluminium. Certain metal oxides are reduced by aluminium to metals. The method is known as aluminothermy or thermite process. For example, chromium, manganese, titanium, vanadium metals are obtained by the reduction of their oxides with aluminium powder.
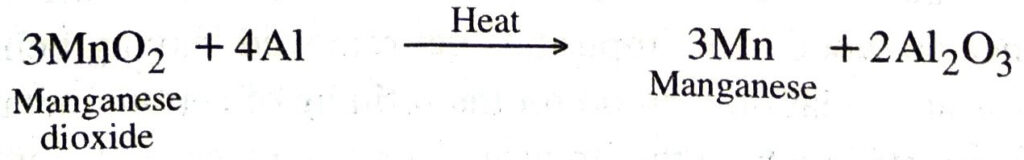
Similarly, chromium is obtained by heating chromium oxide with aluminium powder.
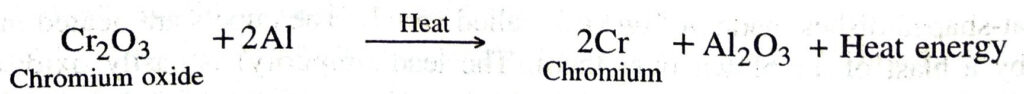
(d) Reduction by electrolysis or electrolytic reduction. The oxides of active metals are commonly extracted by the electrolysis of their fused salts using suitable electrodes. This is also called electrolytic reduction. The process of extraction of metals by electrolysis process is called electrometallurgy.
For example, aluminium oxide is very stable and aluminium cannot be prepared by reduction with carbon. It is prepared by the electrolysis of molten alumina (Al2O3). In this process pure alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite (Na3AlF6) in an iron tank lined with carbon. During electrolysis, the aluminium ions, Al3+ are reduced at cathode (by the electrons) to form aluminium.
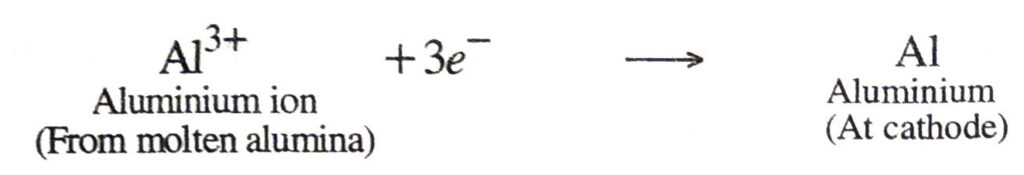
During electrolytic reduction of molten salts, the metals are always produced at the cathode (negative electrode).
Q. 3. What are the various methods used for the refining of metals ?
Or
Explain electrolytic refining of copper.
Or
Explain electrolytic refining of metals.
Or
How is copper refined by electrolytic process ?
Ans. Purification or Refining of Metals.
The metal obtained by any of the above methods is usually impure and is known as crude metal. The process of purifying the crude metal is called refining. Some of the common methods of refining are discussed below :
(a) Liquation. This method is used for refining the metals having low melting points, such as tin, lead, etc. This is based on the principle that the metal to be refined is easily fusible but the impurities do not fuse easily. In this method, the impure metal is placed on the sloping hearth of the furnace and is gently heated in an inert atmosphere of carbon monoxide. The hearth is maintained at a temperature slightly above the melting point of the metal. The metal melts and flows down leaving the non-fusible impurities on the hearth. The pure metal is collected at the bottom of the sloping hearth in a receiver.
(b) Poling. This process is used to remove reducible oxides from the metal. For example, copper containing cuprous oxide as impurity is refined by this method. In this method, the impure metal is melted on a shallow hearth of a furnace. The molten metal is stirred with the logs of green wood. Any metal oxide present is reduced to metallic state by the reducing gases coming from the heated wood. The impurities get removed leaving behind pure metal.
(c) Cupellation. This is an oxidation method for the refining of certain metals. This method is used for refining those metals in which the impurities have greater tendency to get oxidised than the metal itself. Silver is refined by this method. The impure silver metal is fused in small boat-shaped dishes made of bone ash called cupels. The cupels are heated in a suitable furnace by a blast of air blown over them. The lead (impurity) is easily oxidised to lead monoxide (PbO) and is carried away by the blast, while pure silver is left behind.
(d) Electrorefining. This is most general method for the refining of metals. In this method, the crude metal is cast into thick rods and are made as anodes, while the thin sheets of pure metal are made as cathodes. An aqueous solution of some salt of the metal is used as an electrolyte. For example, in the electrolytic refining of copper. (Fig.), crude copper is made anode, a thin sheet of pure copper is made cathode and copper sulphate solution is used as an electrolyte. On passing the electric current, metal ions from the electrolyte are deposited at the cathode in the form of pure metal. On the other hand, an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the electrolyte in the form of metal ions.
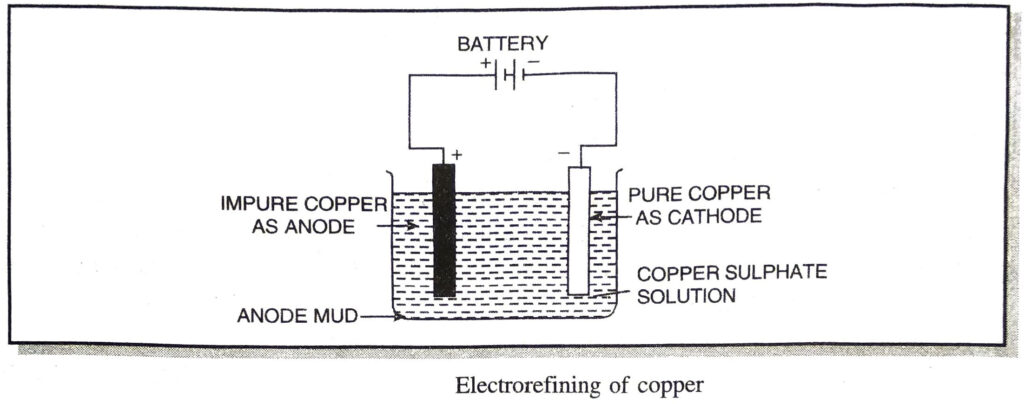
The following reactions occur at the electrodes :

The copper atoms get deposited on cathode giving pure copper.
Copper atoms of impure anode lose two electrons each to anode and form copper ions, Cu2+, which go into the solution.
At anode :

As the process continues, impure anode, goes on dissolving the solution and becomes thinner and thinner. At the same time, pure copper gets deposited on the cathode. The impurities present in the crude copper either go into the solution or get collected at the bottom of the cell below the anode. This is called mud.
Q. 4. Why are noble gases chemically inert ?
Ans. The inertness or reluctance of the members of the noble gas family is linked with their structure. The first member helium (He) has two electrons in the only shell which is the K-shell. The atoms of all other members have eight electrons in their outermost shell, also called valence shell. The electronic configuration of the members of the family are as follows:
| Noble gas element | Symbol | Atomic No. (Z) | Electronic Configuration | No. of electrons in outermost shell |
| Helium | He | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 2, 8 | 8 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 2, 8, 8 | 8 |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 2, 8, 18, 8 | 8 |
| Xenon | Xe | 54 | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 | 8 |
| Radon | Rn | 86 | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 | 8 |
This is the maximum number of electrons which the atoms of these elements can have in their outermost shell. They have, therefore, no tendency to either lose or gain one or more electrons. In other words, these atoms are fully satisfied. The members of the family are called inert gases or noble gases.
The formation of ionic bond can also be shown as follows:
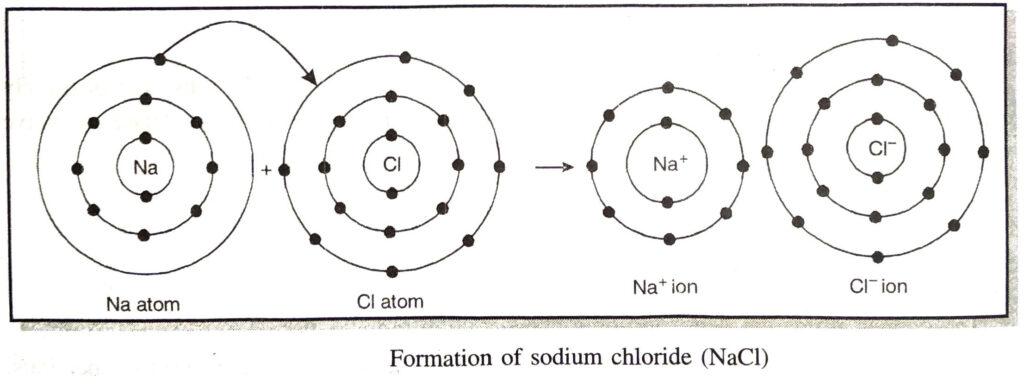
Q. 5. (a) Which types of atoms take part in the formation of ionic bond ?
(b) Explain the formation of magnesium chloride.
Ans. (a) The ionic bond is formed as a result of transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to the other. The atom which loses electrons is generally a metal atom. It belongs to group 1 or 2 of the periodic table. The metal which gains electrons is a non-metal atom. It normally belongs to group 16 or 17 of the periodic table. For example, in the formation of sodium chloride.
(i) Sodium is a metal and is present in group 1.
(ii) Chlorine is a non-metal and is present in group 17.
Thus, an ionic or electrovalent bond is formed by the transfer of one or more electrons from the atom of a metal to the atom of non-metal.
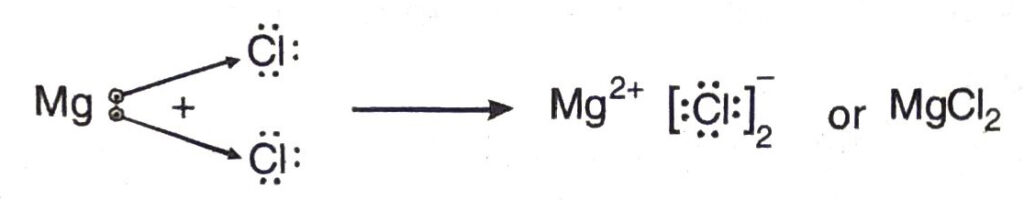
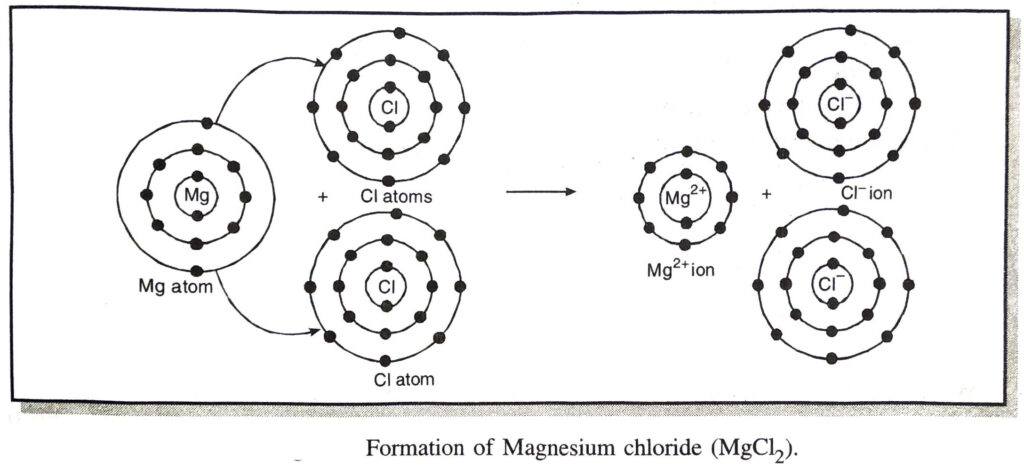
(b) Formation of magnesium chloride
Atomic number of magnesium = 12
The electronic configuration of magnesium = 2, 8, 2
Atomic number of chlorine = 17
The electronic configuration of chlorine = 2, 8, 7
During the formation of magnesium chloride, magnesium atom transfer one electron to each of the two chlorine atoms from its valence shell.
The electron transfer may also be shown as follows:
Q. 6. Discuss the important properties of ionic compounds.
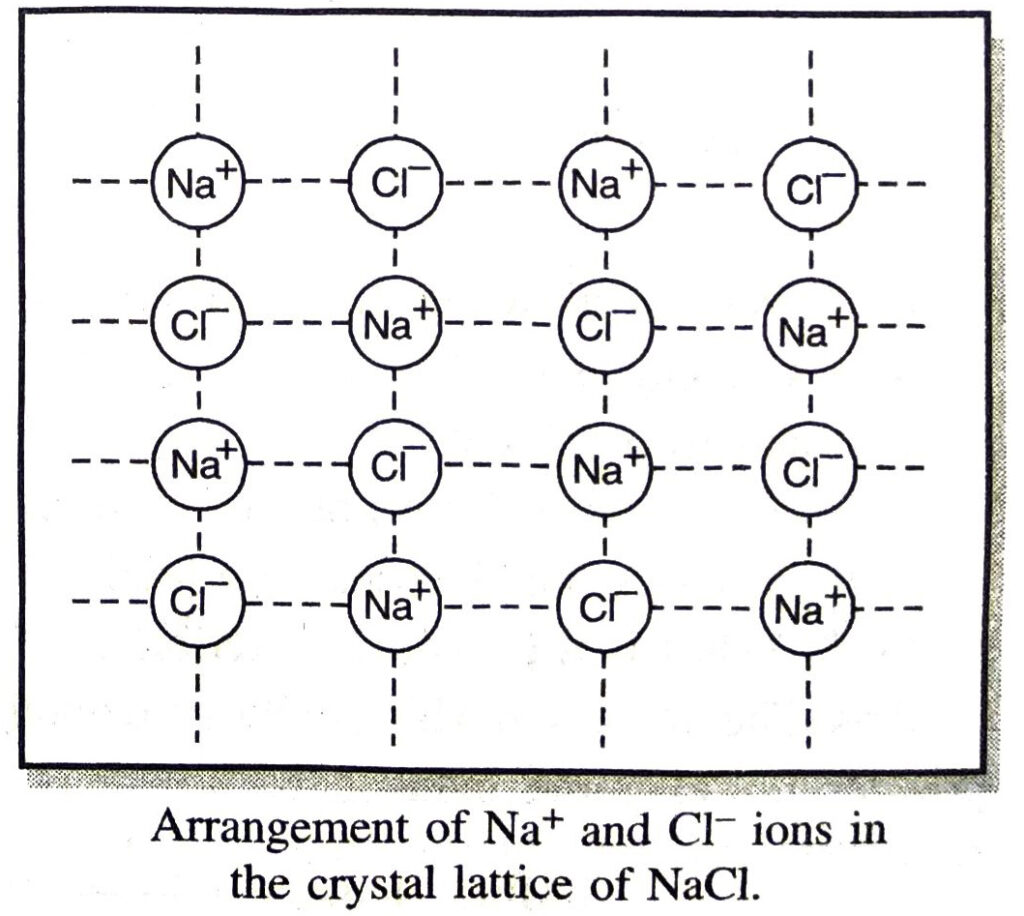
Ans. Important properties of ionic compounds
The important properties of the ionic or electrovalent compounds are given below :
1. Ionic compounds consist of ions.
2. Ionic compounds are crystalline solids.
3. Ionic compound have high melting and boiling points.
4. Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
5. Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state or in solution.
6. Ionic compounds have high densities.
7. Ionic compounds are hard and brittle.
8. Ionic compounds undergo ionic reactions which are quick and proceed to completion.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What is an alloy ? In what ways alloys are better than constituting metals ?
Ans. (a) Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal.
(b) Alloys are prepared to include certain properties which are not possessed by constituent metals like:
(i) to increase resistance to corrosion. e.g stainless steel.
(ii) to increase hardness. e.g. steel.
(iii) to increase tensile strength. e.g. magnalium.
Q. 2. Explain why red phosphorous is kept under water.
Ans. This is because red phosphorous reacts with air or oxygen.
Q. 3. Write an equation for the reaction of:
(a) iron with steam,
(b) calcium with water, and
(c) potassium with water.
Ans. (a) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 H2
Steam
(b) Ca + H2O → CaO + H2
(c) 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2.
Or
Write the Electronic dot structure of Sodium, Oxygen and Magnesium.
Ans. Electronic dot structure of

Q. 4. Why is alumina dissolved in cryolite?
Ans. Cryolite is used because of the following reasons :
1. It acts as a solvent.
2. It lowers the melting point of alumina.
3. It increases the electrical conductivity of alumina.
Q. 5. What is a thermite reaction ?
Ans. The process in which metals are obtained by the reduction of their oxides by aluminium powder. For example, manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder to get manganese.
Q. 6. Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not displace.
Ans. Metals which can displace H₂ : Zinc, magnesium.
Metals which cannot displace H₂ : Copper, silver.
Q. 7. What important properties of aluminium are responsible for its great demand in industry?
Ans. The important properties of aluminium responsible for its great demand in industry are :
1. It is very good conductor of heat and electricity.
2. It is very ductile and malleable and has high tensile strength.
3. It is a light metal having low density. It is very useful in construction industry.
4. It forms highly useful alloys. For example, alloys such as duralium, magnalium, etc. are used for making bodies and other parts of aeroplanes, cars, buses, etc.
Q. 8. What is the effect of temperature on the electrical conductivity of metals ?
Ans. With the increase in temperature, the electrical conductivity of metals decreases.
Q. 9. In electrorefining of a metal M, name the anode, the cathode and electrolyte.
Ans. Anode: Crude metal, M
Cathode: Pure metal sheet
Electrolyte Aqueous solution of soluble salt of the metal.
Q. 10. Why is iron more useful when it is mixed with a little carbon ?
Ans. Iron in the pure form is soft and stretches easily when hot. But if it is mixed with a small amount of carbon (about 0.50%), it becomes very hard and strong.
Q. 11. What is the difference between pig iron and steel?
Ans. Pig iron contains 2 to 4.5% of carbon alongwith traces of impurities such as sulphur, phosphorus, manganese, etc.
Steel contains 0.5 to 1.5% of carbon alongwith varying amounts of other elements.
Q. 12. What is 24 carat gold? How will you convert it into 18 carat gold ?
Ans. 24 carat gold is pure gold (100%). It is very soft and, therefore, it is not suitable for making jewellery. It can be converted to 18 carat gold by alloying with 6 parts of either silver or copper. 18 carat gold corresponds to 75% gold and 25% silver or copper.
Q. 13. Give one example of a metal in each of the following cases :
(a) liquid at room temperature.
(b) used as a reducing agent to obtain other metals.
(c) shows variable valency.
(d) combines with oxygen at room temperature.
(e) used in electrical appliances.
Ans. (a) Mercury (b) aluminium (c) iron (d) sodium (e) copper.
Q. 14. Why are sodium and aluminium extracted electrolytically ?
Ans. Sodium and aluminium are quite reactive metals. Their positions in the activity series are quite above hydrogen and carbon. Therefore, their ores cannot be reduced by either carbon or hydrogen. Thus, they are extracted electrolytically by supplying electrical energy for the reduction of their ores to metals.
Q. 15. Differentiate between metals and non-metals (Based on Physical Properties).
Or
Mention some physical properties of metals and non-metals.
Or
Give important characteristics of metals and non-metals.
Ans.
| Metals | Non-metals |
|
|
Q. 16. A student has been collecting silver coins and copper coins. One day she observed a black coating on silver coins and a green coating on copper coins. Which chemical phenomenon is responsible for these coatings ? Write the chemical name of black and green coatings.
Ans. Corrosion is responsible for coatings on metals. Black coating on silver coin is due to silver sulphide (Ag2S). Green coating on copper is due to the formulation of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3. Cu(OH)2.
Q. 17. With the help of an example explain the formation of an ionic compounds.
Ans.

During the formation of Na+CI–, one electron is transferred from Na to Cl atom. The bond so formed is ionic or electrovalent bond.
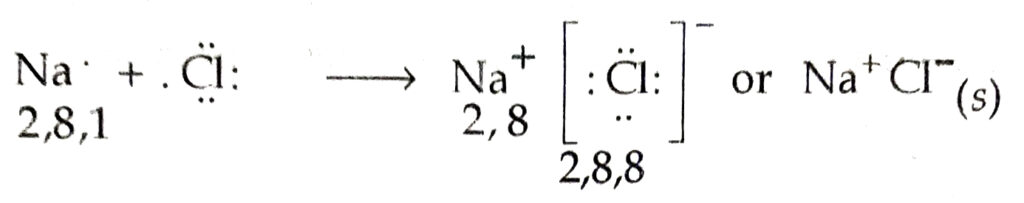
Q. 18. Helium has only 2 electrons but still it is called inert gas element. Why?
Ans. The two electrons in the helium atom are present in the K-shell which is the first shell. As the K-shell cannot have more than 2 electrons in it, therefore, helium atom has a stable electronic configuration. It is, therefore, an inert gas.
Q. 19. Write two examples of each of the following types of ores :
1. Oxide ores
2. Halide ores
3. Sulphide ores
4. Carbonate ores.
Ans.

Q. 20. Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when :
1. Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
2. Steam is passed over hot iron.
Ans.

Q. 21. Give reasons for the following:
1. Na, K and Ca metals form hydrides by combination with hydrogen gas, but most other metals do not.
2. Aluminium easily combines with oxygen but still it can be used for making kitchen utensils.
Ans. 1. Active metals like Na, K and Ca have greater tendency to lose electrons and therefore, these force the hydrogen atom to accept electrons to form salts called hydrides. For example, NaH, KH, CaH2, etc.
2. Aluminium readily combines with oxygen to form oxides. The layer of oxide formed remains sticking prevents the metal from further oxidation. Also this oxide layer is stable even at high temperature. Therefore, it can be used for making kitchen utensils.
Q. 22. Give reasons for the following:
1. Metals conduct electricity.
2. Reaction of nitric acid with metals generally does not evolve hydrogen gas.
3. For making gold ornaments, 22-carat gold is preferred to 24-carat gold.
Ans. 1. Metals conduct electricity because they have electrons which are free to move. They offer little resistance to the flow of current. Silver and copper are the best conductors of electricity.
2. Reaction of metals with nitric acid does not evolve hydrogen gas. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises H2 produced to water and is itself reduced to any of its oxides such as N2O, NO or NO2.
3. Pure gold is 24 carat and is very soft. Therefore, it is not suitable for making jewellery. It is alloyed with Cu or Ag to make it hard. Generally, 22 carat gold is used for making ornaments, which contains 22 parts pure gold and 2 parts of either Cu or Ag.
Q. 23. Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity whereas molten sodium chloride conducts electricity. Explain.
Ans. The electrical conductivity of sodium chloride is due to the movement of Na+ and Cl– ions. In the solid state, the ions cannot move. Therefore, sodium chloride does not conduct electricity in the solid state. In the molten state, the ions are free to move. Therefore, sodium chloride conducts electricity in the molten state.
Q. 24. The atomic number of an element X is 17.
(a) What must an atom of X do to achieve the nearest inert gas configuration ?
(b) Which inert gas is nearest to X ?
Ans. (a) The electronic configuration of X is 2, 8, 7. It has seven electrons in the valence shell of its atom. Therefore, an atom of X must take up one electron to complete its octet or to have eight electrons in its outermost shell. It will form anion X¯ .
(b) The element X with atomic number 17 is nearest to the inert gas argon (Ar) having atomic number 18.
Q. 25. Give experiment to prove that iron can displace copper from copper (II) sulphate solution but copper can’t displace iron from iron (II) sulphate solution.
Ans. Method. Take a clean wire of copper and an iron nail. Put the copper wire in a solution of iron sulphate and the iron nail in a solution of copper sulphate taken in test tubes (Fig.). Record your observations after 20 minutes.
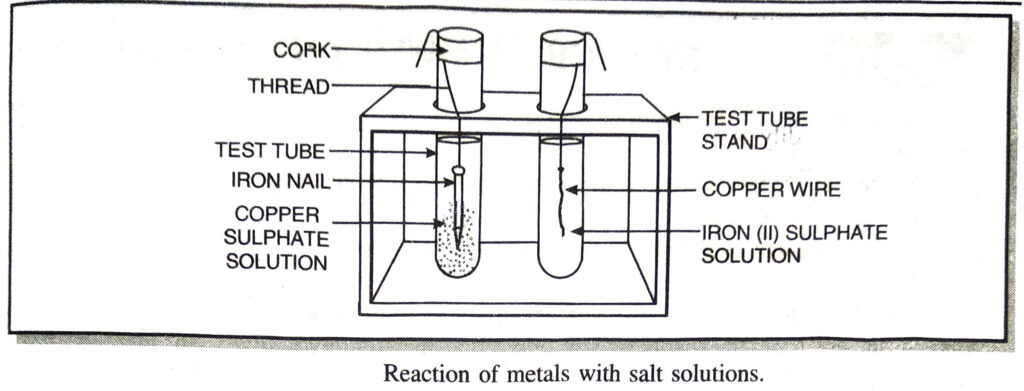
From above experiment it is clear that iron can displace copper from copper (II) sulphate solution but copper can’t displace iron from iron (II) sulphate
Fe (s) + CuSO4 → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu ↓
Cu (s) + FeSO4 (aq) → No reaction.
Therefore iron is more reactive than copper.
Q. 26. (a) Indicate the gas produced from reaction occurring in following diagram.
(b) Also write down the balanced equation for the reaction taking place.
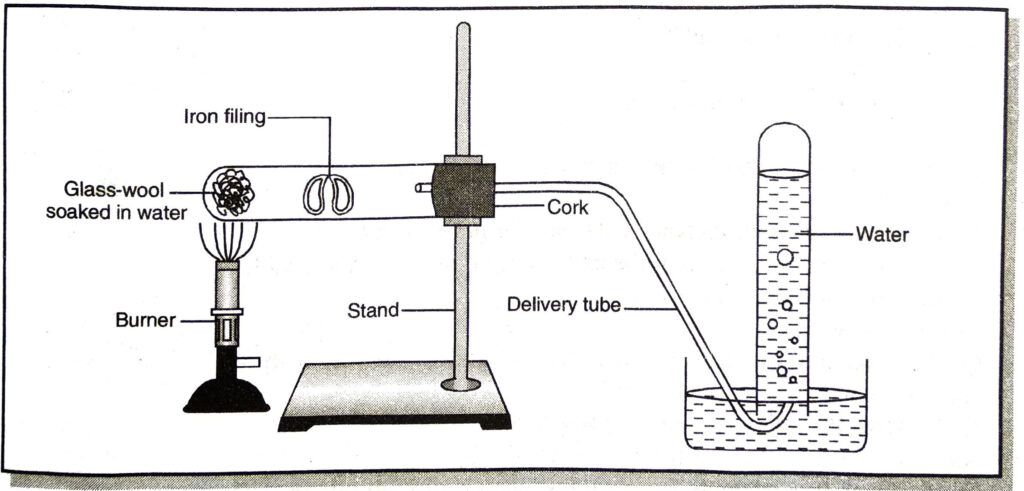
Ans.
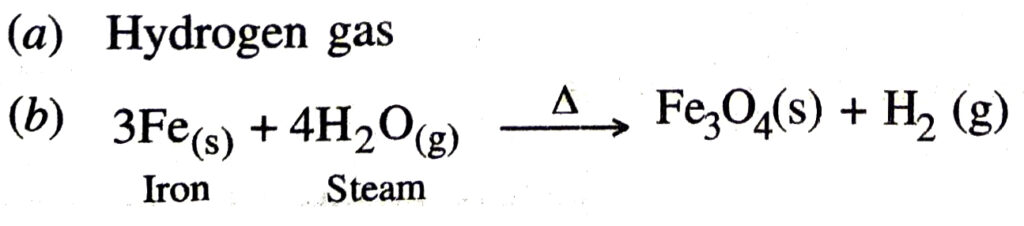
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Name the ore of the metal (sodium).
Ans. Rock salt, NaCl.
Q. 2. Name two metals which occur in free state in nature.
Ans. (i) Gold (ii) Platinum.
Q. 3. Name the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust.
Ans. Aluminium.
Q. 4. Which metals were known to the people in ancient times?
Ans. In ancient times the people knew only eight metals-gold, silver, tin, mercury, lead, copper, iron and antimony.
Q. 5. Which is the lightest metal known to us?
Ans. Lithium.
Q. 6. Name the metal that gives a green coating when exposed to moisture.
Ans. Copper.
Q. 7. Which non-metal is a good conductor of electricity ?
Ans. Graphite.
Q. 8. What do you mean by lustre.
Ans. It is the property due to which metal surface has shine appearance in light.
Q. 9. Name two metals which :
(a) readily burn in air and
(b) do not burn.
Ans. (a) (i) sodium (ii) magnesium.
(b) (i) copper (ii) iron.
Q. 10. Name one metal which reacts with cold water.
Ans. Sodium.
Q. 11. Where are non-metals located in the periodic table ?
Ans. Non-metals are located at the extreme right of the periodic table.
Q. 12. Give one ore of mercury.
Ans. Cinnabar (HgS).
Q. 13. Name any two metals which are soft and can be cut with an ordinary knife.
Ans. (i) Sodium (ii) Potassium.
Q. 14. Give the names of two important ores of iron.
Ans. (i) Haematite (Fe2O3) (ii) Magnetite (Fe3O4).
Q. 15. Name two methods for obtaining metals of high purity.
Ans. (i) Zone refining (ii) Van Arkel method.
Q. 16. For the reduction of a metallic oxide, suggest a reducing agent cheaper than aluminium.
Ans. Carbon.
Q. 17. Name the metal which is best conductor of electricity.
Ans. Silver.
Q. 18. Alloys are used in electrical heating devices rather than pure metals. Give one reason.
Ans. This is because alloys have lesser conductivity or more resistance than metals.
Q. 19. Name one metal (i) more reactive than hydrogen and (ii) less reactive than hydrogen.
Ans. (i) Sodium (ii) Silver.
Q. 20. Why is copper used in calorimeters ?
Ans. Copper is used in calorimeters because it is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Q. 21. Why does aluminium not occur in free state in nature ?
Ans. Aluminium does not occur in the free state in nature because it is very reactive.
Q. 22. Give electron dot structure of sodium chloride.
Ans. 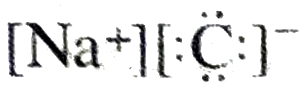
Q. 23. What are ionic compounds ?
Ans. The compounds which contain ionic bonds are called ionic compounds e.g. Na+Cl–, K+Br– etc.
Q. 24. Name two elements which show both metallic and non-metallic characters. What are such elements called ?
Ans. (i) Arsenic (ii) Antimony.
These elements are called metalloids.
Q. 25. Give reason – An iron grill is painted frequently.
Ans. An iron grill is painted to prevent it from rusting.
Q. 26. Name the property for which aluminium is used for overhead electric transmission.
Ans. Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity.
Q. 27. Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Ans. (i) Copper (ii) Aluminium.
Q. 28. Name the constituent of an alloy called German silver.
Ans. Copper, zinc and nickel.
Q. 29. Which is more metallic : sodium or aluminium ?
Ans. Sodium is more metallic than aluminium.
Q. 30. Define the term galvanisation.
Ans. The process of coating a thin layer of zinc on the surface of an iron object is called galvanisation.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Metalloid is :
(A) Hydrogen
(B) Helium
(C) Boron
(D) Argon.
Ans. (C) Boron
2. The metal which is liquid at room temperature :
(A) Mercury
(B) Silver
(C) Copper
(D) Aluminium.
Ans. (A) Mercury
3. Aqua-regia is a mixture of :
(A) Conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 (3 : 1)
(B) Conc. H2SO4 and conc. HNO3 (3:1)
(C) Conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl (3 : 1)
(D) Conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 (1 : 1)
Ans. (A) Conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 (3 : 1)
4. Silicon is. :
(A) Non-metal
(B) Metal
(C) Metalloid
(D) Halogen.
Ans. (B) Metal
5. The flux used in blast furnace to remove the unwanted impurities is :
(A) Basic
(B) Acidic
(C) Neutral
(D) Amphoteric.
Ans. (A) Basic
6. The non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity :
(A) Sulphur
(B) Phosphorus
(C) Graphite
(D) Iodine.
Ans. (C) Graphite
7. Which non-metal is liquid at room temperature ?
(A) Carbon
(B) Sulphur
(C) Bromine
(D) Oxygen.
Ans. (C) Bromine
8. Which is the most malleable metal?
(A) Gold
(B) Lead
(C) Iron
(D) Copper.
Ans. (A) Gold
9. The metal which will displace zinc from ZnSO4 solution is :
(A) Copper
(B) Silver
(C) Magnesium
(D) Iron.
Ans. (C) Magnesium
10. Metals of low reactivity are extracted by :
(A) heating alone
(B) electrolysis
(C) reduction
(D) None
Ans. (A) heating alone
11. An alloy is :
(A) an element
(B) a compound
(C) a homogeneous mixture
(D) a heterogeneous mixture.
Ans. (B) a compound
12. Most of the highly reactive metals are extracted by :
(A) heating alone
(B) reduction
(C) electrolysis
(D) none of these.
Ans. (C) electrolysis
13. Which of the following is an iron ore ?
(A) Cinnabar
(B) Calamine
(C) Haematite
(D) Rock salt.
Ans. (C) Haematite
14. The process of extraction of metal from its ore is called :
(A) Smelting
(B) Refining
(C) Metallurgy
(D) Calcination.
Ans. (C) Metallurgy
15. Zn metal does not react with :
(A) HCI
(B) NaOH
(C) NaHCO3
(D) CH3COOH.
Ans. (C) NaHCO3
16. Which metal is most reactive ?
(A) Sodium
(B) Calcium
(C) Magnesium
(D) Aluminium.
Ans. (A) Sodium
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here