JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 3 Road Safety Education
JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 3 Road Safety Education
JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions Chapter 3 Road Safety Education
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 9th Class Social Science Solutions
J&K class 9th Social Science Solutions Road Safety Education Textbook Questions and Answers
INTRODUCTION
● Road Safety Education : It refers to the methods and measures for reducing the risk of a person using the road network for being killed or seriously injured.
● Road Safety Strategy : Best practice road safety strategies focus upon the prevention of serious injuries and death crashes inspite of human fallibility.
● Good and Safe Habits on the Road :
(i) When you walk : Walk only on the footpath if there is no footpath walk, only on the left side of the road.
(ii) When you cross the Road : Always cross on the Zebra Crossing. Cross when the road is clear. Look for the red signal before crossing because at red light the traffic comes to a halt.
(iii) When you cycle : Keep to left side of the road. Give a hand signal before taking a turn to the left or the right. Avoid cycling on the busy road.
(iv) Going to School : Never jump on or get down from the school bus before it stops completely. Never lean out of the bus. Never talk to aber in the driver when he is driving.
(v) When you Drive : Stop or slow down for the pedestrian to cross the road. Buckle up while driving. Obey traffic rules and signs. Obey speed limits. Never use mobile while driving wear helmet. Never drive dangerously. Be courteous. Never rage on the road. Never mix drinking and driving.
● Safe Driving Techniques : Care for your vehicle. Be safe. Better be late than never. Be on time you are human.
● Family First Aid Kit : It must contains:
(i) Adhesive bandages (ii) Sterile Gause Pads (iii) Antiseptic wipes (iv) Cold Pack (v) Aspirine or Non-Aspirine Pain reliever (vi) Torch (vii) Whistle.
● Significance of Road Safety Education :
Road Safety Education covers all measures that aim at positively influencing traffic behaviour pattern with an emphasis on promotion of knowledge and understanding of traffic rules and situation.
It emphasis on improvement of skills through training and experience.
● Traffic Lights : Traffic Lights alternate the right of way accorded to users by displaying lights of a standard colour (Red, Yellow, Green) following a universal colour code.
(i) The Red light indicates stop sign.
(ii) The Yellow Light warns that the signal is about to change.
(iii) The Green Light allows traffic to proceed in the direction denoted.
● Pedestrian Crossing : A pedestrian crossing is a place designated for pedestrian to cross a road.
● Types of Crossings : Crossings are of various types. (i) Unmarked du crossing may occur at an intersection. (ii) The simplest marked crossing may just consist of some marking on the road surface. (iii) Some crossings have special signals consisting of electric lamps or light emtting diode panels. (iv) Sites with extremely high traffic or roads where pedestrians are not allowed may instend be crossed via pedestrian bridges or tunnels.
● Road Signs : Road signs play an important role in the regulation of traffic and are e the building blocks for ensuring road safety. Road signs are devices placed along, beside or above highway, road ways, pathways or other routes to guide, warn and regulate the flow of traffic. These and signs can be seen as part of the road and are used for the purpose of on a number of issues.
● Classification of Road Signs : Road signs are classified under following three heads : (i) Mandatory (ii) Cautionary (iii) Informatory.
● Mandatory signs : These signs are used to inform road users of certain laws and regulations to provide safety and free flow of traffic.
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS
Suggested activities
Q. A week should be marked as a road safety week where different activities relating to road safety should be organised like.
1. Poster Making
2. Slogan Writing
3. Essay Writing
4. Role Play
5. Collage Making
Ans.— Road Safety week was celebrated in our state from 11th of January, 2017 to the 17th of January, 2017.
In this connection following activities were organised like :
1. Poster Making :

Note : Student can make more posters in their concerned classes.
2. Slogan Writing :
Slogans on Road Safety : Road safety methods and measures are very necessary to all of us to reduce the risk of accident of serious injury. It is very necessary for the safety of common people including cyclists, pedestrians, motorists and passengers. Everyone must follow traffic and road rules made by the government. Following slogans on road safety can help you to make people aware about the road safety as well as encourage them to follow the road safety measures. You can use road safety slogans to motivate people during any related event or campaign celebration.
ROAD SAFETY SLOGANS
Be alert to be safe and secure.
Be alert while driving on road.
Follow road safety rules !
Keep you informed with road safety norms.
Be alert to save your life.
Be alert as accidents hurts.
Normal speed meets the road safety needs.
Be alert to reduce road side accidents.
Alert today to live tomorrow.
Don’t be fool, respect road safety rules.
Be a driver not clever while driving.
Be a best driver to be a survivor.
Remember it just, road safety is must.
Wrong driving may stop your breathe and cause death !
Fast driving is prohibited, follow it !
Fast driving is not safe follow the limit to avoid chafe.
Be sure to tie seat belt before driving the car.
Be sure to wear helmet before driving bike.
Think about safety first then drive.
Always remember ; drive slower to live longer.
Drive slowly someone is waiting at home.
Stop driving fast before accident stop you.
Obey traffic police; follow traffic rules to avoid accidents.
Drive safety to make accidents rarely.
Follow road culture to save your future.
Fast speed driving becomes thriving but life taking.
Don’t use phone while driving. It will leave your family alone.
Adjust mirrors while driving can save you from dying.
Your destination is sure with safe driving.
Don’t drive in wrong lane it will leave you in pain.
Roads are made to drive but not to fly.
Accidents are held by mistake, if you take road rules as fake.
Drink and drive cannot go together.
Never drink while driving.
Drive slowly as fast drive can be last drive.
Always use seat belt to reduce accident rate.
Follow driving tips all through the day to keep accidents away.
Your little care while driving can make accidents rare.
Injury gives you tears whereas safety cheers.
Always wait for red don’t go for bleed.
Don’t be foot follow traffic rules.
It’s wise to be slow while driving.
Don’t be in hurry otherwise you will get worry.
Keep your eyes on the road even in the lack of crowd.
Follow traffic rules and save lives.
Don’t be blind keep in mind all the road safety measures.
Drug, drink and drive never go together.
Teach your neighbour to be a good driver.
3. Essay Writing:
ROAD SAFETY
Everyday many people are involved in road accidents. Some are killed. Many more are injured or maimed. So it is important for us to learn to use the roads properly and safely. No sane person would like to be involved in an accident.
As the roads are very busy nowadays, we should be very careful when crossing one. It is safer to use a pedestrian crossing or an overhead bridge whenever one is available. Never cross a road by dashing across it. That is inviting trouble. If there are no crossings, then we must look carefully right and left and cross only when it is safe to do so.
Some of us take the bus to school. It is important that we do not try to get on or off a bus while it is still moving. I tried to get on a moving bus once. It dragged me a short distance and nearly ran over me. I was lucky to escape with only some scratches on my legs. Also we must not fool around while in the bus. A suddenly lurch can send us knocking our heads against something hard.
Using a bicycle can be dangerous too. We must pay attention on the road and never cycle too far out to the middle of the road. We must obey all traffic rules. Also we must make sure our bicycles are in good condition with working brakes, lights etc.
These are some things we can do to avoid accidents. However there is no guarantee that we will never be involved in one. The important thing is to stay alert at all times while using the roads. We must know what is happening around us. In that way we can take necessary action to avoid danger whenever we see one. Road safety is very much up to how we use the roads. Use them carefully and we may be able to use them for a long time. Use them carelessly and we may never be able to use them again.
4. Role Play. Children love road safety role play. Here are a few new ideas, which the children can play the role in the following way :
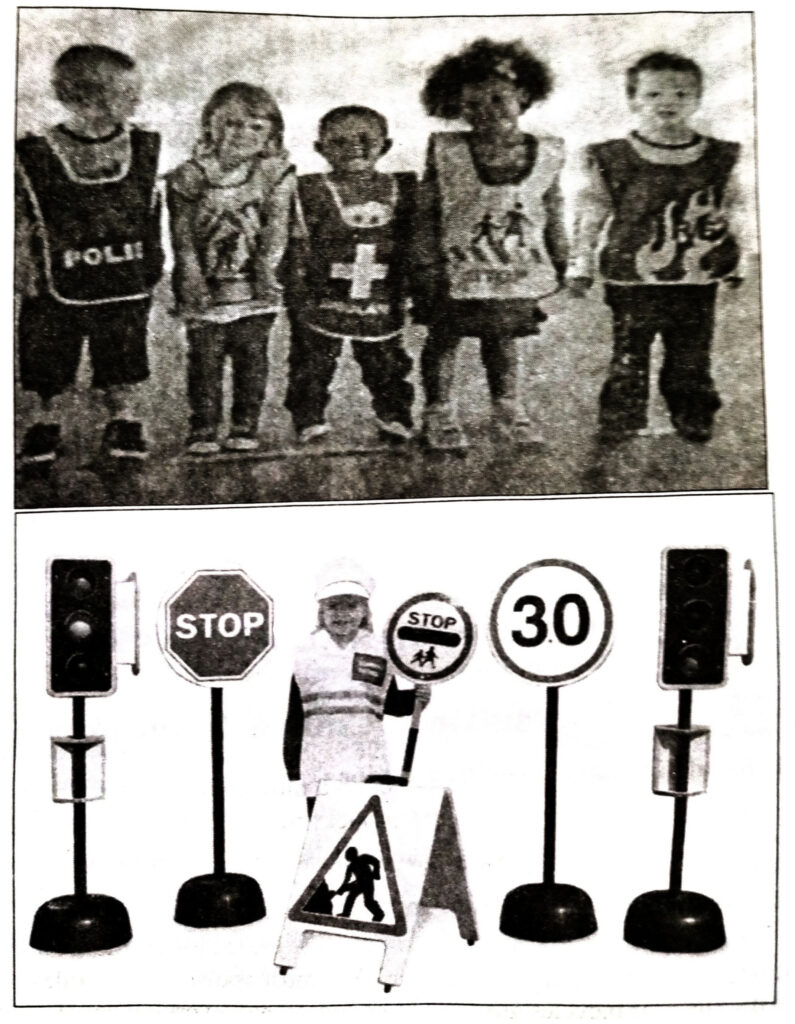

5. College Making :

Note : Students can make more collage at their own level.
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Multiple Choice Questions
Q. 1. Road signs are classified under :
(i) 2 Heads
(ii) 3 Heads
(iii) 4 Heads
(iv) 5 Heads.
Ans.— (ii) 3 Heads.
Q. 2. Crossings are classified into :
(i) 3 Types
(ii) 4 Types
(iii) 2 Types
(iv) 5 Types.
Ans.— (ii) 4 Types.
Q. 3. How many people are killed in road accidents each year ?
(i) 500,000
(ii) 700,000
(iii) 900,000
(iv) 300,000
Ans.— (i) 500,000.
Q. 4. How many people are killed in road accidents in developing countries each year ?
(i) 200,000
(ii) 350,000
(iii) 600,000
(iv) 400,000
Ans.— (ii) 350,000.
Q. 5. Seat belts reduce chances of death of car occupant in accident by over :
(i) 50%
(ii) 40%
(iii) 60%
(iv) 70%.
Ans.— (iii) 60%
Q. 6. Among the following which one is the Road sign :
(i) Mandatory
(ii) Cautionary
(iii) Informatory
(iv) All the above.
Ans.— (iv) All the above.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What do you mean by Road Safety Education ?
Ans.— It refers to methods and measures for reducing the risk of a person using the road network for being killed or seriously injured.
Q. 2. What is Road Safety Strategy ?
Ans.— It focuses upon the prevention of serious injuries and death crashes inspite of human fallibility.
Q. 3. What are safe Driving Techniques ?
Ans.— Care for your vehicle, be safe, better be late than never. Be on time, you are human.
Q. 4. What does Family First Aid kit contain ?
Ans.— It contains : (i) Adhesive bandage, (ii) Sterile Gause Pads, (iii) Antiseptic wipes, (iv) Cold Pack, (v) Aspirine or Non-Aspirine Pain reliever, (vi) Torch and (vii) Whistle.
Q. 5. What is the importance of Road Safety Education ?
Ans.— Road Safety Education covers all measures that aim at positively influencing traffic behaviour pattern with an emphasis on promotion of knowledge and understanding of traffic rules and situation.
Q. 6. What are Traffic lights ?
Ans.— Traffic lights alternate the right of way accorded to users by displaying lights of a standard colour (Red, Yellow, Green) following a universal colour code.
Q. 7. What is pedestrian crossing ?
Ans.— A pedestrian crossing is a place designated for pedestrian to cross a road.
Q. 8. What are road signs ?
Ans.— Road signs are devices placed along, beside or above highway, road ways, pathways or other routes to guide, warn and regulate the flow of traffic.
Q. 9. Give the classification of Road signs.
Ans.— Road signs are classified under following three heads :
(i) Mandatory, (ii) Cautionary, (iii) Informatory.
Q. 10. What are Mandatory Road signs ?
Ans.— These signs are used to inform road users of certain laws and regulations to provide safety and free flow of traffic.
Q. 11. What are Cautionary Road Signs ?
Ans.— These signs are used to warn the road users of the existence of hazardous conditions either on or adjacent to the roadway.
Q. 12. What are Informatory Signs ?
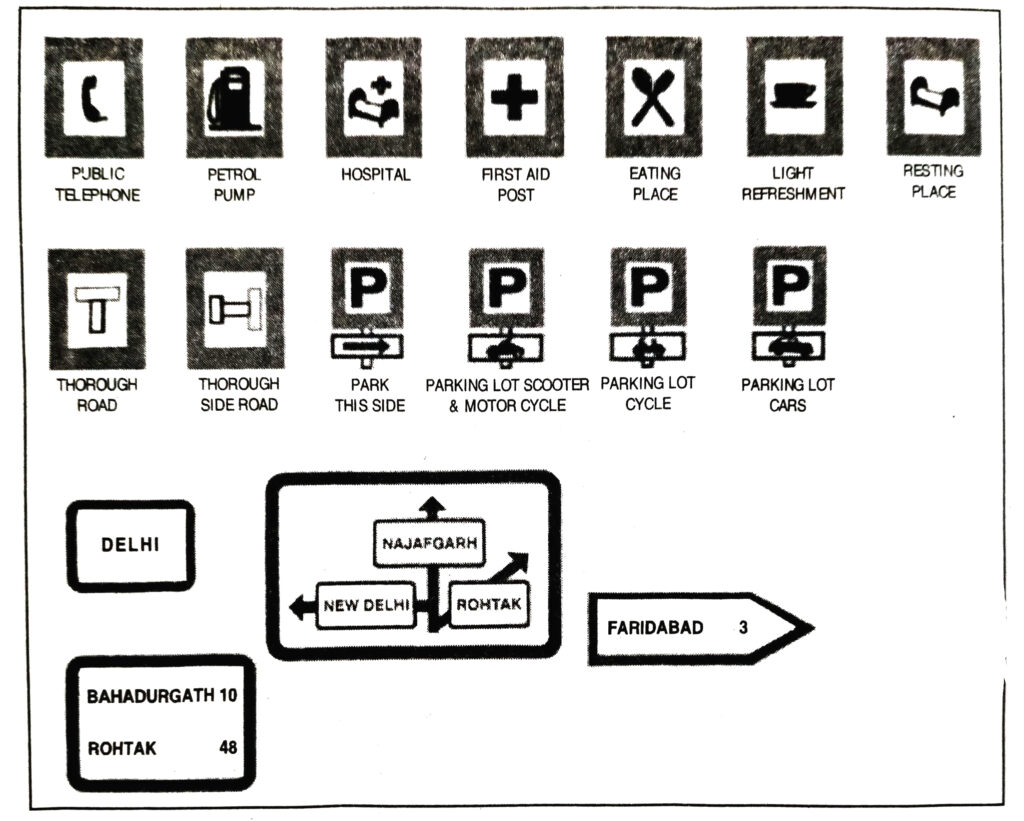
Ans.— These signs are used to guide road users about routes, destination, distance, identity points of geographical and historical interest.
Q. 13. Write two mitigation measures of transport accidents.
Ans.— (i) By strict enforcement of traffic rules.
(ii) By Encouragement and appreciation to good drivers.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What do you understand by Road Traffic Safety ?
Ans.— Road Traffic Safety refers to methods and measures for reducing the risk of a person using the road network being killed or seriously injured. The users of a road include pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, their passengers, and passengers of on-road public transport, mainly buses and trams. Best-practice road safety strategies focus upon the prevention of serious injury and death crashes in spite of human fallibility (which is contrasted with the old road safety paradigm of simply reducing crashes assuming road user compliance with traffic regulations). Safe road design is now about providing a road environment which ensures vehicle speeds will be within the human tolerances for serious injury and death wherever conflict points exist.
The basic strategy of a Safe System approach is to ensure that in the event of a crash, the impact energies remain below the threshold likely to produce either death or serious injury. This threshold will vary from crash scenario to crash scenario, depending upon the level of protection offered to the road users involved. For example, the chances of survival for an unprotected pedestrian hit by a vehicle diminish rapidly at speeds greater than 30 km/h, whereas for a properly restrained motor vehicle occupant the critical impact speed is 50 km/h (for side impact crashes) and 70 km/h (for head-on crashes).
Q. 2. Write significance of Road Safety education.
Ans.— Significance. The number of vehicles is increasing every year. In Delhi alone, over 2000 persons die in road accidents every year. The figure for India as a whole was over 1.42 lakh deaths in 2011. India accounts for 13 per cent of total road accidents in the world. The economic loss of accidents in India is around Rs. 55,000 crores every year. The problem for punjab is not less severe. The number of persons that died in road accidents increased from 3400 in 2010 to 3613 in 2011 in Punjab.
In this light, safety of persons using roads have become a vital issue. It has been experienced in the western countries that the following major factors lead to road casualties (i) failure to use crash helmets and seat belts (ii) overspeeding (iii) drunken driving (iv) unexperienced drivers (v) stress (vi) fatigue or driving continuously for long hours etc.
The imparting of road safety education to road users particularily the students at college level has become a high priority area. The paper on Road Safety Education have been introduced by the university keeping in view that young minds will learn better about these issues in their formative years. They will learn the basics of road safety and make it a habit for themselves and will teach others about it. Road safety has now become a global problem. The UN General Assembly, has passed a resolution and declared 2011-2020, a `Decade of Action for Road Safety’. It aims to save lives by reducing the number of deaths and casualties on roads worldwide.
Road Safety Education has become more significant as it will bring a behavioural change in young minds and would go a long way in reducing casualties and fatalities due to road accidents.
Q. 3. Discuss the principles of Road Safety.
Ans.— Road safety has become an urgent need because of increasing road accidents. It has some basic principles as :—
1. Respect for traffic rules/regulations and signs/symbols. A road user should have a will to be safe and let others travel safely on roads. It can be possible only if one is ready to respect traffic rules and regulations. The person should took at road signs and symbols and follow them religiously.
2. Sharing space with others. A road user should keep in mind that he is not alone on a road. It is a public space which is to be shared with other users. He should be ready to yield space to others on a road.
3. Care and Concern for others. As a driver or a sitting passenger you should keep in mind that road is not a place to show anger. A road user should care and feel concerned about other persons and vehicles travelling on the road. Prevention of injury and accident should be a major concern for a road user.
4. Maintaining cool in adverse situations. A driver is a social person, always burdened with problems at home or office. But while driving he should maintain his cool and keep these problems aside. Keeping yourself fresh and cool will help in road safety for you and others.
5. Be prepared for any kind of eventuality. While driving you should be ready to tackle any kind of eventuality. A stray dog or cow may come before your vehicle, a cyclist or scooterist may turn all of a sudden to your side, a bus driver may be overtaking at a wrong place and at a high speed, the vehicle behind you may be honking endlessly without reason, the vehicle ahead of you might make a sudden stop without any indication etc. As a good road user, you should judge the situation correctly and act accordingly in a swift and cool manner.
Q. 4. List some tips for driving which a person must follow for safe driving a vehicle.
Or
What are do’s and don’t while driving ?
Ans.— Maybe you just got your driver’s license, or maybe you have driving for years, but feel that it is time for a brush-up on good driving techniques. Here are some tips for behind the wheel behaviour that might save you from getting a ticket or getting in an accident.
1. DO always wear your seat belt.
2. DO keep children in tested and approved car seats, no matter how much they beg or plead to get out. If you need, take frequent breaks so that little ones stretch their legs.
3. DO review the official rules of the road for your jurisdiction periodically, and follow them always.
4. DO follow the speed limits.
5. DO pay attention when you are driving, even if you are familiar with the area. A surprising number of accidents happen only blocks from home !
6. DO be courteous towards other drivers.
7. DO give pedestrains the right-of-way in crosswalks.
8. DO make room for bicycles.
9. DO pay for your parking tickets or traffic tickets on time, unless you plan to contest them.
10. DO keep a winter survival kit in your car for bad weather conditions, A good survival kit should contain a cell phone, matches, flares, a working flashlight, food, water and blankets.
11. DO make sure that your spare tire is in your car and that you have a working jack.
12. DO make time for routine preventative maintenance on your car. Breakdowns can be dangerous and costly.
13. DO plan your route out in advance for long car trips and keep a map or atlas in the car in case you get lost.
Q. 5. Discuss various points which a driver must avoid while driving a vehicle.
Ans.— 1. DON’T drink and drive, and don’t get in a car with a driver who has been drinking or using drugs.
2. DON’T make assumptions about what other drivers are going to do. Just because someone has their turn signal on does not mean they are actually going to turn. They may be like the rest of us, and have forgotton that it is on !
3. DON’T assume that other cars know what you are doing, either. Make sure that you use your turn signals and give yourself, and the cars around you, plenty of room to maneuver.
4. DON’T tailgate other cars, pass on shoulders, fail to yield, run stoplights or stop signs (even if no one else seems to be around), or break any other rules of the road on purpose. If you act like you are above the law when you operate a car, you will sooner, rather than later, find out that you are not.
5. DON’T play your car stereo so loudly that you are disruptive to others, or so loudly that you are unable to hear train signals or emergency vehicle sirens.
6. DON’T talk on your cell phone and drive at the same time, If you need to make or answer a telephone call while you are driving, pull over at a safe place, use the phone, and then resume your journey.
7. DON’T engage in other activities, while driving, that distract your attention or reduce your reaction time. Eating, changing clothes, or putting on makeup while driving is dangerous. In some states, if you are caught doing these things while driving you can be cited for “driver inattention” and given a ticket.
8. DON’T treat a car like it is a toy. It is not. Don’t use your car to play chicken, race, or give another car a friendly “tap.”
9. DON’T let your emotions and frustrations get the best of you. Don’t engage in road rage, no matter how irritating another driver might be to you. 10. DON’T leave valuables in your car, especially in places where they can be seen, no matter where you are parked.
Q. 6. Give an account of National Road Safety policy.
Ans.— National Road Safety Policy. The ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Govt. of India, prepared a National Policy on Road Safety in 1992. It was adopted by the National Road Safety Council in 1994. It contained the following points :–
1. Classification of the causes of accidents and preventive action in terms of vehicle, driver and engineering factors.
2. List of safety features for vehicle design e.g. safety belt, air bags, collapsible steerings, braking performance etc.
3. Fitness certification and maintenance of vehicles.
4. Proper training and effective licensing for drivers.
5. Road design and geometric improvements to compensate for inadequacies of road users.
6. Warning signs for road users.
7. Accident black spot identification and rectification through road design.
8. Design of road junctions.
9. Design of roads in built up and residential areas etc.
10. Traffic guidance, road signs, speed limit posts, and other traffic control devices.
11. Road pavement markings, construction of foot paths/cycle tracks, bus bays, truck parking complexes and other wayside amenities etc.
12. Traffic education and campaign on traffic discipline, inclusion of traffic education in school curriculum, promotion of defensive driving etc.
13. Enforcement of maximum speed limits, and campaign on helmet use and seat belt use, curbing drunken driving etc.
14. Emergency medical service with emphasis on saving the lives of victims etc.
Q. 7. Write the various road rules for pedestrians and cyclists.
Ans.— Pedestrians. Over 50 per cent of those killed in road accidents in India are pedestrians. A person walking on a road should :
(i) Wear bright or fluroscent clothes during daytime and at dusk.
(ii) At night wear white colour dress or clothes with reflective stripes.
(iii) Walk on a footpath.
(iv) If there is no footpath, walk on right side of the road so that you are able to see traffic coming towards you.
(v) Use zebra crossing, foot overbridge or subway to cross road.
(vi) Always cross the road when vehicles are at a safe distance.
Cyclists :
About 10 per cent of persons killed in road accidents in India are cyclists. They should take safety tips as:
(i) Cycle should have proper brakes, bell, rear view mirror etc.
(ii) Both the front and back mudguards of cycle should be painted white, should have reflectors or tape.
(iii) If cycle track is available, never enter in the main road, Cycle on the entreme left side of the road if there is no separate track.
(iv) Cycle at a safe distance from fast and heavy loaded vehicles.
(v) Watch traffic from both sides and give proper indication before turning or crossing a road.
(vi) Do not hold on a fast moving vehicle.
(vii) Load on the cycle should not be too heavy.
(viii) Move in a queue. Do not keep your cycles parallel to each other.
Q. 8. Discuss the road rules and safety tips for driving two wheeller and while travelling in a bus.
Ans.— In recent years, the number of persons dying in accidents on two wheelers is fast increasing. Over 20 per cent of those killed on roads in India are on twowheelers. Safety tips for them are as :
(i) Always wear a good quality BIS approved helmet.
(ii) Helmet is also necessary for pillion rider.
(iii) If the rider is wearing a turban, it should be tied properly. In some cases it has been seen that a loose turban falls on road before the person himself and is no guarantee of safety.
(iv) Check air in both the tyres.
(v) During night check that both the front and back lights are functional.
(vi) Do not carry heavy load on a two-wheeler.
(vii) Do not enter the road from a blind corner.
(viii) Give proper hand indication or indicator before turning. After turning switch off the indicators.
(ix) Never allow a minor to ride.
(x) Do not do stunts on road.
(xi) Never enter in the right lane if the road has a divider and more than two lanes.
While Travelling in a Bus
A lot of people, especially students use buses as a medium of transport. Safety tips for bus travellers are as under :
(i) Never try to catch a running bus. Get up early and start from home well before time.
(ii) Never alight from a bus till it stops completely. Alight with your face towards front of the bus. Never jump from a halting bus with face towards back.
(iii) Never cross in front of the bus you have alighted.
(iv) Never put your head or arm outside a moving bus.
(v) Buses have to reach their destination at time. To save time leave your seat before your stop and reach near the door.
(vi) Never stand in the steps of the bus.
(vii) Never shout or make a noise in the bus, it can distract the driver. Donot use your mobile while driving.
Q. 9. What are traffic sign ? Show the various mandatory/regulatory.
Ans.— Traffic signs are divided into 3 main categories :
* Mandatory/Regulatory signs
* Cautionary signs
* Informatory signs.


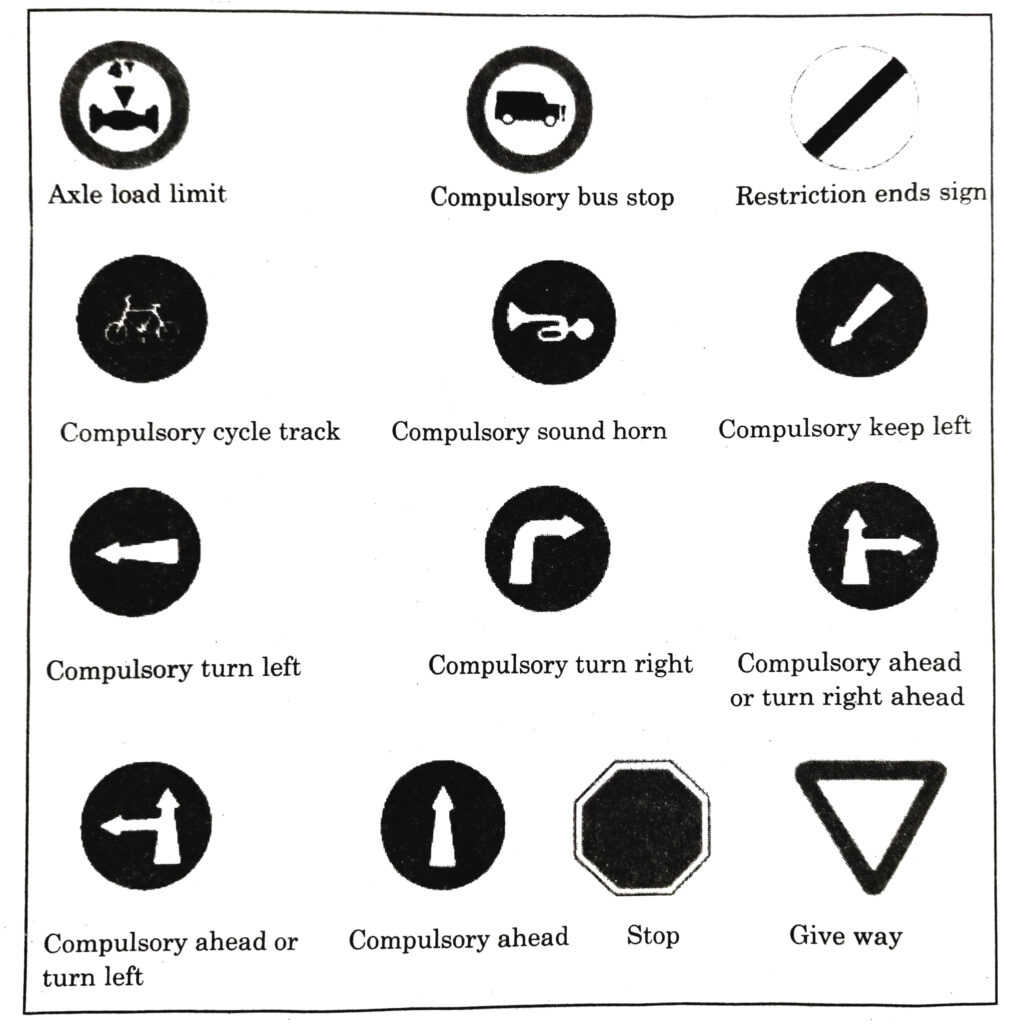
Q. 10. What documents required while driving motor vehicle ?
Ans.— The following documents are required to be kept with the driver when he is on a road.
1. Valid driving licence.
2. Registration Certificate of Vehicle. (RC)
3. Insurance certificate.
4. Pollution under control certificate.
For commercial vehicles fitness certificate and permit are also required.
Q. 11. Can a doctor/hospital refuse medical care to emergency cases ?
Ans.— “Every doctor whether at a Government hospital or otherwise has the professional obligation to extend his services with due expertise for protecting life. No law or State action can intervene to avoid/delay the discharge of the paramount obligation cast upon members of the medical profession. The obligation being total, absolute and paramount, laws of procedure whether in status or otherwise which would interfere with the discharge of this obligation cannot be sustained and must, therefore, give way.”
Q. 12. Should the doctors/hospitals wait for the police to arrive or any legal formalities before attending to a road accident victim ?
Ans.— No. “The treatment of the patient should not wait for the arrival of the police or completion of legal formalities. All hospitals and doctors are required to provide immediate medical aid to all the cases, whether medico-legal or not.”
Q. 13. Is the duty of the driver of the vehicle involved in an accident & the doctor attending the victim mandated by any law ?
Ans.— Yes. Following the Supreme Court order in 1989, the Motor Vehicles Act was amended in 1994, to make it mandatory on both the driver/ owner of the vehicle to take the accident victim to the nearest doctor, and the doctor to treat the victim without waiting for any formalities. The provisions of Section 134, Motor Vehicles Act 1988 read as follows—
Duty of driver in case of accident and injury to a person—When any person in injured or any property of third party is damaged, as a result of an accident in which a motor vehicle is involved the driver of the vehicle or other person in charge of the vehicles—
(i) Unless it is not practicable to do so on account of mob fury or any other reason beyond his control, take all reasonable steps to secure medical attention for the injured person (by conveying him to the nearest medical practitioner or hospital, and it shall be the duty of every registered medical practitioner or the doctor on the duty in the hospital immediately to attend the injured person and render medical aid or treatment without waiting for any procedural formalities), unless the injured person or his guardian, in case he is a minor, desires otherwise.
(ii) Give on demand by a police officer any information required by him, or, if no police officer is present, report the circumstance of the occurrence, including the circumstances, if any, for not taking reasonable steps to secure medical attention as required under clause (a) at the nearest police station as soon as possible, and in any case within twenty-four hours of the occurrence ;
(iii) Give the following information in writing to the insurer, who has issued the certificates of insurance, about the occurrence of the accident, namely :—
(i) Insurance policy number and period of its validity;
(ii) Date, time and place of accident;
(iii) Particulars of the persons injured or killed in the accident;
(iv) Name of the driver and the particulars of his driving licence.
Q. 14. Is failure to comply with this action punishable ?
Ans.— Yes under section 187 of MV Act, 1988 whoever fails to comply with the provisions of the clauses of Section 134, shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 3 months, or with fine which may extend to Rs. 500, or both. If it is the second time for the person concerned, then the penalty is harsher. The imprisonment may extend to 6 months, or with fine, which may extend to Rs. 1000 or both.
Q. 15. Write a short note on traffic police public relationship.
Ans.— Traffic police has now become an integral part of governance not only road traffic out also lives of persons associated with it. It must focus on development and maintenance of a good relationship with general public. It should work in such a way to inculcate a sense of security and responsibility in public. The proper enforcement and implementation of traffic and road safety laws is only possible with the support of public. The traffic police and public must understand and appreciate each other’s problems and view points.
The public must understand that traffic police is to help him and not to harass him by asking to belt up or stop on a red light. The traffic police has to remember that law enforcement is not an end in itself but a means to an end which is road safety. The efficiency and administration of traffic police is always judged by individual citizens from public. So good public-traffic police relations are a must. Traffic police should take care that public should not consider or see it as “Terrific Police.’
Q. 16. What is road safety education ?
Ans.— Road safety education is the program of educational activities around road safety that should be provided to children and young people in formal and community education settings – early childhood services, primary and secondary schools.
Road safety education also encourages and supports the role that parents and teachers need to play in helping their children/students to be safe in traffic and to learn about road safety.
Road safety education seeks to develop the behaviours and attitudes for safe road use relevant to the development of children and young people as passengers, pedestrians, cyclists and as novice drivers.
To be effective, road safety education must be evidence-based and match the child/young person’s stage of development and level of independence as a road user.
Q. 17. What are Cautionary signs ?
Ans.— Cautionary signs: These signs are used to warn the road users of the existence of hazardous conditions either on or adjacent to the roadway, so that the motorists are cautious and take the desired action.
Though violation of there road signs do not attract any legal action, they are very important for the fact avoiding them could result in major accidents. Some of the signs, which fall under this category are provided as follows :
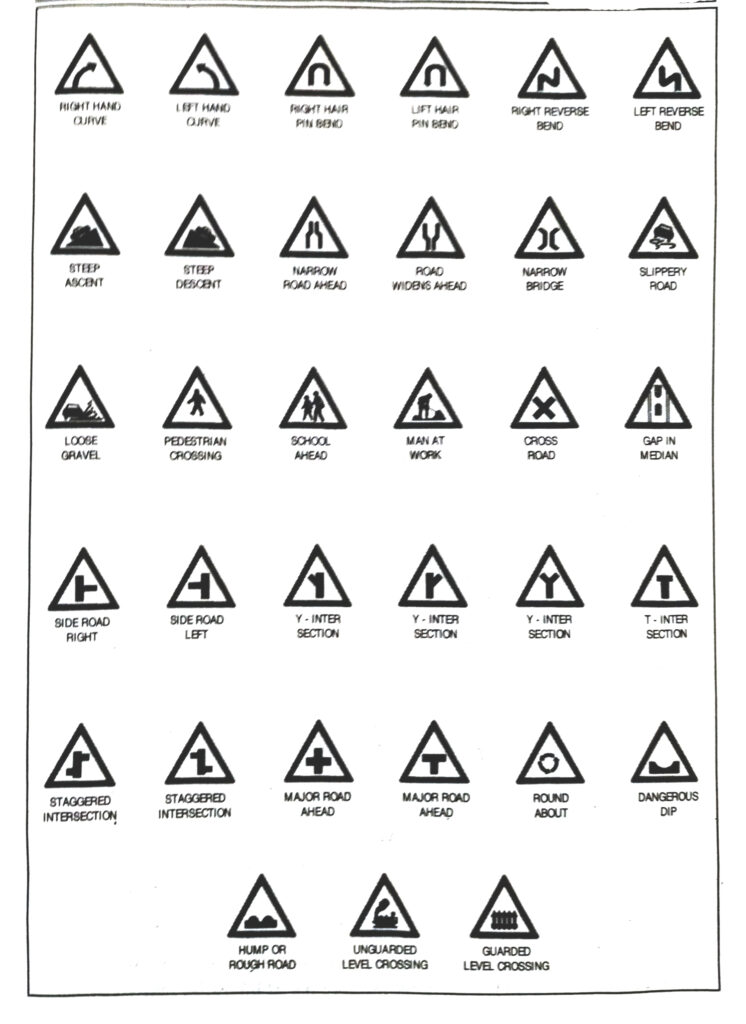

Q. 18. What are Informatory signs ?
Ans.— Informatory signs : These signs are used to guide road users along routes. Inform them about destination and distance, Identify points of geographical and historical interest and provide other information that will make travel easier, safe and pleasant. Some of the signs which fall under this category are as follows :
Long Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Give a detailed account of road safety concept.
Ans.— Road safety concept developed by Siddney Williams of the U.S. National Safety council focussed on 3E’s-Education, Engineering and Enforcement. This concept has been a corner stone of road safety improvement programmes throughout the West. These countries achieved a major breakthrough in decreasing road crashes and fatalities by implementing this concept.
1. Education : Education about road safety is considered as a method that will lead to a total accident prevention. Educating people about causes and dangers of road accidents is often done with other inputs such as improved road construction. formulation of traffic laws and their implementation. Road safety education can be carried out by schools, colleges, universities, parents, media, NGOs and other social organisations. It is a life long process. Though road safety education is most important, it has to compete with other subjects in school curriculum.
The first week of January every year is celebrated as road safety week during which a number of activities are under taken by States, NGOs, transport organisations, schools, colleges etc. to spread the message of road safety.
2. Engineering : The planning, design and maintenance of roads is another factor in road safety. Modern engineering techniques are important in reducing a significant number of road accidents such as :
(i) Construction of pedestrian bridges.
(ii) Provision and construction of bicycle lanes.
(iii) Side walks.
(iv) Improved lane width.
(v) Traffic signals at crossings.
(vi) Improvements in Vehicles such as sensors, radar systems, speed controllers, ABS brakes, air bags etc. are also important.
3. Enforcement : India and other countries have enacted enough laws for improvement of road conditions and safety. But proper implementation and enforcement is still lacking. The Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 and Motor Vehicle Rules, 1989 pertain to or have a bearing on road safety. The implementation and enforcement of these rules rests with the State Governments: The responsibility for measures like testing the drivers before issuing a driving licence, checking fitness of vehicles, use of helmets, seat belts, overloading of commercial vehicles, drunken driving etc. rest with transport department and traffic police but are seldom implemented. In Punjab it is a common belief that every driver entering Chandigarh becomes educated, civilized and fearful of traffic violations. All this is because of proper enforcement of traffic laws. People are seen removing seat belts and helmets entering from Chandigarh to Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh as police is considered generally lase in these states.
These basic concepts of road safety can be further beneficial if we add further E’s Emergency, Evaluation and Encouragement.
1. Emergency : Emergency service in case of road accident is very crucial in preventing deaths and injuries. The person who arrives at the scene of accident first, should call emergency service. The person should apply first aid till the ambulance reaches the site of accident. People should be made aware that emergency vehicles such as ambulance, fire engine, police car etc. should have the right of way.
2. Evaluation : Evaluation of various road safety schemes and programmes is a must for further improvements and policy making.
3. Encouragement : The government, traffic police and transport ministry should encourage people to help in implementing new road safety programmes and policies. The persons or organisations that help in awareness campaigns, accident victims or in controlling traffic in areas of congestion should be suitably rewarded. It will further provide motivation to general population.
Q. 2. List the role of different sectors of society to make driving a success.
Ans.— Different sectors of society should come forward and join hands in this direction to make Indian roads a safer journey. This page enlists what different sectors of society can do to make this drive a success.
1. Government and the public Sector can work on :
● Development and Implementation of effective road safety policies.
● Accountability in meeting road safety objectives and to ensure the effective use of resources.
● Funds for road safety programs.
2. Local and Regional Governments can :
● Take a leading role in coordinating the road safty effort of all relevant agencies and community groups within their particular administrative area. These activities should be consistent with the National Road Safety Plan, and coordinate activity across all relevant agencies in that gerographic area.
● Ensure that planning of local facilities and residential areas effectively takes account of the road safety needs of the community.
● Where possible, fund and implement road safety programs and initiatives.
● Ensure effective policies for the control and enforcement of liquor laws.
3. Communities and Cultural or Ethnic Organizations can :
● Provide support and leadership for road safety campaigns and initiatives.
● Demostrate a concern for the number of road deaths occurring and a commitment to foster improvements.
● Persuade various communities to accept a greater participatory role in road safety improvements.
● Work with other organisations in providing road safety education/ publicity and other road safety programmes.
4. Education Sector can :
● Make a formal commitment to promote effective road safety education in schools and pre-schools so that appropriate behaviour is fostered from early age.
● Develop links between schools and other agencies, such as the MOT, NRSC and police, in relation to road safety.
● Assist in the life-long education of road users.
5. Media can :
● Enhance community awareness and understanding of the causal factors and real costs of road crashes.
● Support road safety initiatives through responsible and objective reporting.
● Influence societal changes which lead to a reduction in unacceptable driver behaviour and poor attitudes.
6. Police and Enforcement Agencies can :
● Improve road user behaviour and vehicle standards through a balance of education, encouragement and effective enforcement strategies.
● Maximise enforcement effectiveness using proven enforcement systems and technology.
● Maintain a high level of expertise in crash/casualty reporting.
● Focus on high-risk behaviours and use casualty and crash data to identity locations and where police enforcement could minimise such unsafe behaviours.
7. Health Agencies and Professionals can :
● Ensure development of effective emergency medical/services.
● Advise patients on their fitness to use the road, including prescribed drugs and medication on road user performance.
● Provide feedback from injury assessment to improve vehicle occupant protection and road safety policy.
● Provide health promotion road safety programmes.
● Liaise with other practitioners in the road safety field to avoid duplication of effort.
Q. 3. Describe role of traffic police in road safety.
Ans.— Traffic police is a wing of Police Department that is responsible for enforcement and implementation of traffic laws. The main task of traffic police is traffic control and traffic direction. The traffic control includes the protection of all road users against each other and even an individual road user against himself. In year 2011, about 1,40,000 persons were killed in India in road accidents. Traffic police works to reduce the number of accidents and resulting fatalities by implementing various measures such as checking over speed overloading, drunk driving, etc. The duties of traffic police can be summed in following points :
1. Providing safe and smooth flow of traffic on roads. –
2. Preventing road accidents.
3. Effective enforcement of traffic rules and regulations.
4. Inculcating a sense of discipline amongst road users and educating the general public including school children, on road safety.
5. Ensure smooth and secure traffic movement for special occasions and VIP movements with minimal inconvenience to public.
Besides regulating traffic it is also responsible for :—
1. Rendering assistance to public in various stressful conditions such as prompt first aid to road accident victims.
2. Assisting and advising various agencies in coordinated development of infrastructure for safe and smooth flow of traffic.
3. Protection of environment by taking appropriate steps for prevention of noise and air pollution.
4. Encouraging participation and involvement of public in traffic management and regulation.
5. Imparting training in traffic parks to school children.
6. Promotion of road safety through mobile exhibition van, painting competitions, skit competitions, essay competitions, debates etc.
7. Granting of N.O.C. for speed breakers.
8. Installation of traffic signals/blinkers.
9. Issue of permissions to commercial vehicles to ply in “No Entry Zones”.
10. Issue of N.O.C. for “No Challan Due” etc.
11. Notification of Taxi Stands.
12. Smooth functioning of Pre-paid Taxi/TSR booths.
Q. 4. Show various road marking.
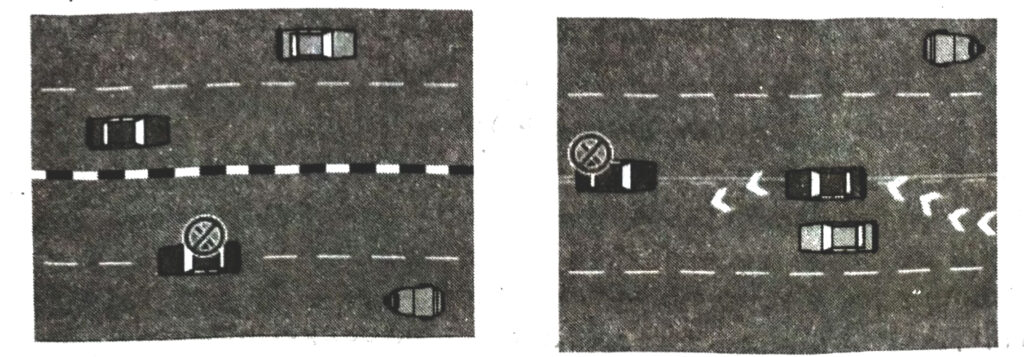
Ans.— Driving Lines. A dividing line is a road marking formed by a white/yellow line or two parallel white/yellow lines (broken or continuous) designed to seperate the parts of a road to be used by vehicles travelling in opposite directions.
Broken Line (or Broken Line to the left or a Continuous Line)
You must keep to the left of these lines. You may cross them to overtake or make a turn, but you must only do so if it is safe.
Single Continuous Line (or Single Continuous Line to the left of a Broken Line)
You must keep to the left of these lines. You must not cross these lines to overtake or make a U-Turn but may cross them to enter or leave the road or to go past an obstruction.
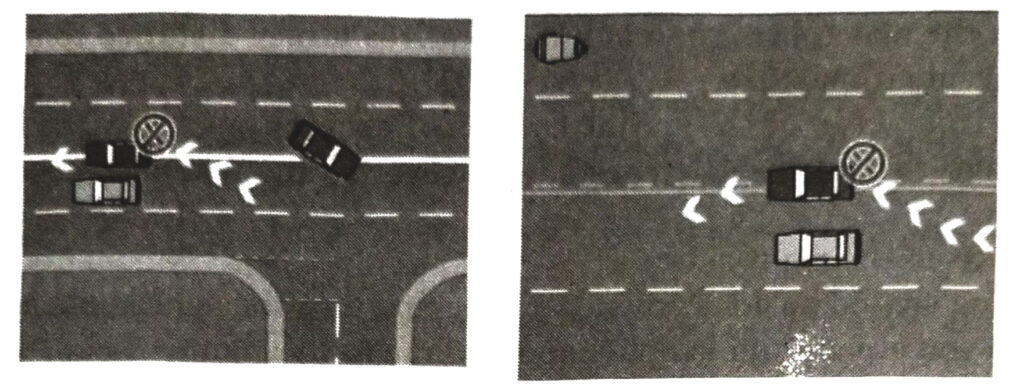
Parallel Lines
You must keep to the left and must not cross these lines, unless you have to avoid an obstruction.
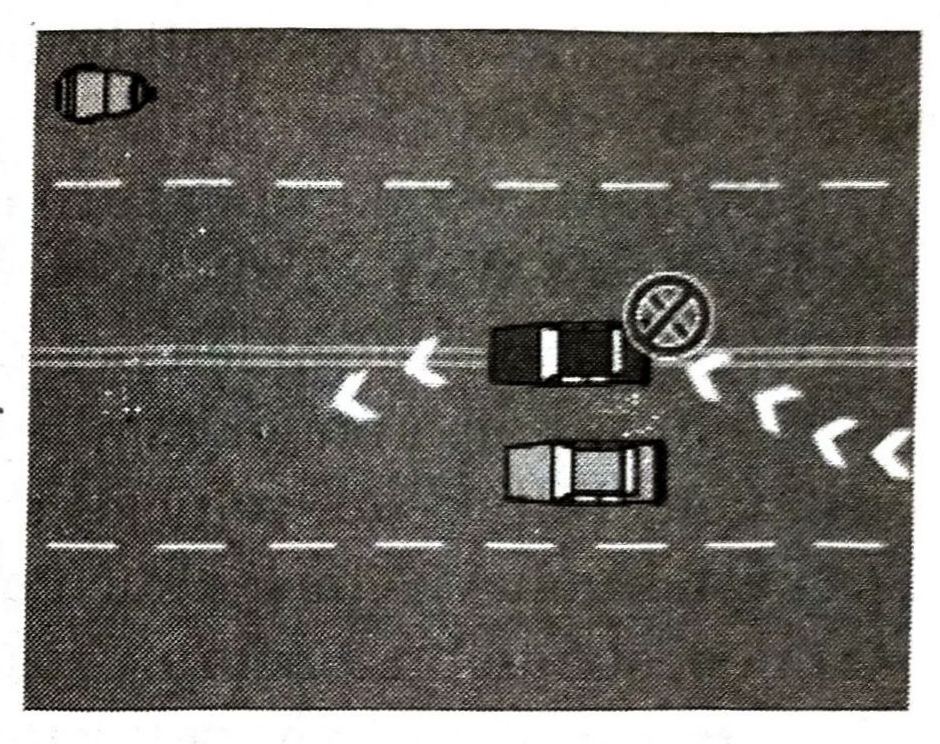
Avoiding an obstruction
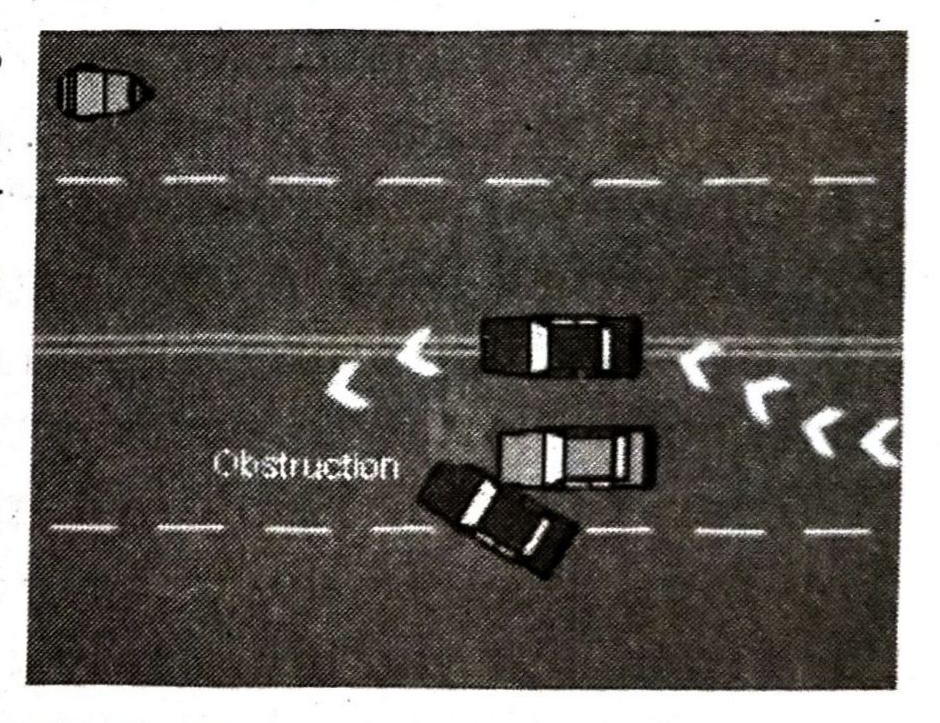
You are permitted to cross single or double continuous lines in order to avoid an obstruction – This does not include a slower moving vehicle or a vehicle stopped in a line of traffic, but may include a fallen tree, a crashed vehicle, or a car that has broken down or is illegally parked. Before crossing the line, you must have a clear view of the road ahead and it must be safe. You must also be very sure that you cross safely because the onus is on you to take the risk of danger into account.
DIVIDING LINE VS LANE LINE
A “Lane” is the space between two lines (or a line and the kerb) painted to divide the road into two or more lines of traffic travelling in the same direction. A “Laned” road therefore has at least 2 Lanes. A road without marked lanes is an “Unlaned” road regardless of its width. A “Multi-lane” Road is a one-way road or a two-way road with 2 or more marked lanes that are on the side of the dividing strip or median strip (road divider) where the driver is driving and for the use of vehicles travelling in the same direction.
Broken Lane Line
When lanes are marked by broken lines the driver may change lanes when it is safe to do so by indicating the intention through proper signal.
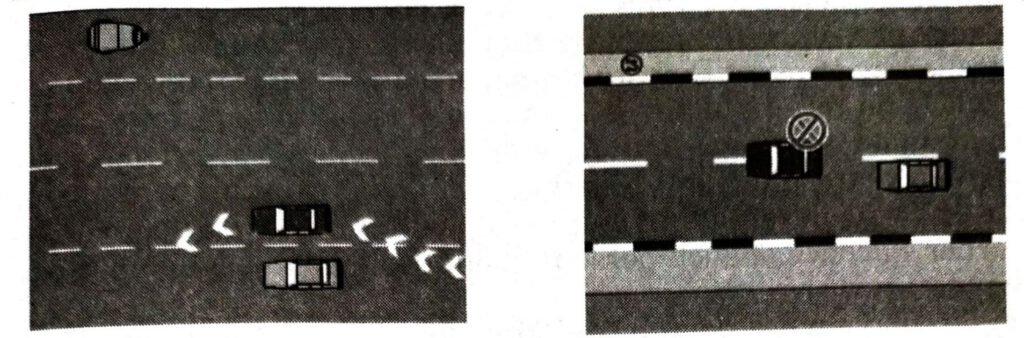
When driving on a road marked with Lane Lines, you must keep your vehicle entirely within a lane. It is an offence to straddle a line. The red car in the illustration is straddling the lane line.
Solid Lane Line.
The lanes near intersections are often marked by Solid Lane Lines where no lane changing is permissible. The traffic driving along such lanes bound by solid lines has to move along the same direction or the direction indicated by road marking arrows thus a No-Lane changing zone is created near intersection to prevent last minute change of direction by the traffic, that may obstruct the smooth flow of traffic and cause accidents. Motorists are expected to change lanes while driving in the Lane Change Zone (marked by lanes with broken lines) so that they are in the appropriate line when they enter the No Lane Changing Zone near the intersection (marked by Solid Lane Lines). The red car in the illustration is committing an offence.
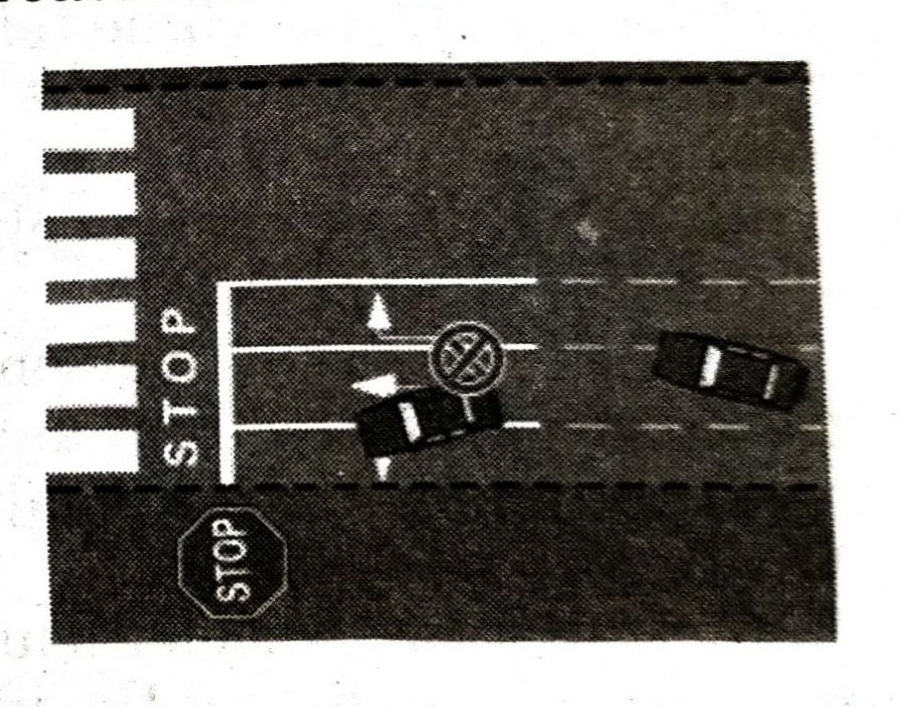
EDGE LINES
These are continuous lines at the edge of the carriageway and mark the limits of the main carriageway upto which a driver can safely venture.
Yellow Edge Lines
You must not stop or park your vehicle in any area where a continuous yellow edge line is applied even to pick up or set down passengers or goods.
Q. 5. Describe significance of first aid in road safety.
Ans.— Whenever a road accident happens, someone is injured or killed on the road. In case of an injury initial care or first aid is very significant. Over 5% per cent of deaths occur on roads itself. One of the most common causes of a road accident death is due to loss of oxygen supply. It is mainly caused by blocking of airway. So the first four minutes after accident are very critical as it takes less than four minutes for a blocked airway to cause death.
The first hour after accident is called the ‘golden hour’. If proper first aid is given, road accident victims have a greater chance of survival and reduction in severity of their injuries. Over 35 per cent of people die in first hour of accident due to significant blood loss, abdominal injury or major head crest. If a person is given first aid at the time of injury, the chances of survival will increase.
The Govt. of India and various international organizations have been working to create awareness and train people in first-aid. Several countries have made first aid training obligatory for getting a driving licence. Red Cross and Red Crescent societies train people in first-aid worldwide. First aid training is not long or complicated. Just 6 to 8 hours of dedicated training is sufficient to help victims in case of an emergency.
Every car now is equipped with a first aid box which normally contains bandages, dressing pads, scissors, plastic tweezers, note pad and pencil, torch, cold pack, safety pins, tape etc.
HELPING ROAD ACCIDENT VICTIMS—In the case of Pt. Parmanand Katara vs Union of India in Criminal Writ Petition No. 270 of 1988, D/-28.8.1989 (AIR 1989 Supreme Court 2039) the Hon’ble Supreme Court of India has observed :
“Every injured citizen brought for medical treatment should instantaneously be given medical aid to preserve life and thereafter the procedural criminal law should be allowed to operate in order to avoid negligent death. There is no legal impediment for a medical professional when he is called upon or requested to attend to an injured person needing his medical assistance immediately. The effort to save the person should be the top priority not only of the medical professional but even of the police or any other citizen who happens to be connected with that matter or who happens to notice such an incident or a situation.”
“There are no provisions in the Indian Penal Code, Criminal Procedure Code, Motor Vehicles Act, which prevents doctors from promptly attending to seriously injured persons and accident cases before arrival of the police and their taking into cognizance of such cases, preparation of FIR and other formalities by Police.”
“There can be no second opinion that preservation of human life is of paramount importance. This is so on account of the fact that once life is lost, the status quo ante cannot be restored, as resurrection is beyond the capacity of man.”
The other orders and observations given by Hon’ble Supreme Court of India related with helping road accident victims are given in Question/Answer form.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here