PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
PSEB 10th Class Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
→ The sour taste of foods is due to acids and the bitter taste is due to bases present in them. Acids turn blue litmus into red and bases turn the red litmus into the blue.
→ Acids and bases neutralize each other’s effects.
→ Acids and bases can be tested using litmus, turmeric, methyl orange, and phenolphthalein indicators.
→ On passing carbon dioxide gas through lime water, lime water turns milky.
→ On passing, excess carbon dioxide gas through lime water, its milky colour disappears due to the formation of soluble calcium bicarbonate.
→ Bases turn phenolphthalein pink in colour.
→ Acids and bases react to produce salt and water.
→ The flow of current in the solution is due to ions present in the solution.
→ In acids H+ ions are present. Acids produce hydrogen ion H+(aq) in a solution due to which solutions become acidic.
→ Bases produce hydroxide (OH–) ions in water.
→ Alkali is a base that dissolves in water.
→ Bases are soapy to touch, bitter, and corrosive.
→ All acids produce H+(aq) and bases produce OH–(aq) in an aqueous solution.
→ The process of the dissolving of acids or bases in water is highly exothermic, therefore to dilute them these should be added and mixed slowly in water. Never add water to concentrated acid.
→ A universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators.
→ Universal indicators show different colors for different concentrations of hydrogen ions in the solution.
→ A scale known as the pH scale has been developed for measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions present in the solution.
→ The ‘p’ in pH stands for ‘potenz’ this is a German word which means power.
→ On the pH scale, we can measure pH generally from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic).
→ Higher is the concentration of hydronium ion, less is the value of pH. A neutral solution has a pH value of 7.
→ If the value of pH is less than 7 then the solution is acidic and if pH lies between 7 to 14 then the solution is basic.
→ Those acids which produce a large number of H+ ions are called strong acids and those acids which produce less H+ ions are weak acids.
→ Our body works in the range of 7.0 to 7.8.
→ When the pH value of rainwater is less than 5.6 it is called acid rain.
→ To get rid of acidity in the body, and antiacid like magnesium hydroxide which is a weak base is used.
→ If the pH value is less than 5.5 in the mouth, decay of teeth starts.
→ Nettle is a herbaceous plant that causes painful stings due to methanoic acid present in stinging hair. A traditional remedy is rubbing the area with the leaf of the dock plant.
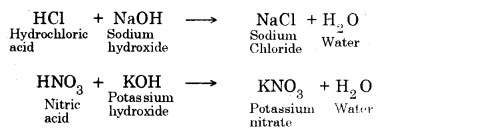
→ Common salt (NaCl) is produced by the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
→ Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime.
→ Bleaching powder is used in the paper and textile industry for bleaching. It acts as an oxidant and as a disinfectant.
→ Baking soda (NaHCO3) is produced from sodium chloride.
→ Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a mild non-corrosive base. It is used in the production of Baking powder and used in the preparation of cakes. It is also used in fire extinguishers.
→ Washing soda (NagCO3.10H2O) is prepared from sodium chloride. It is used in the glass, soap, paper industries. It is used to remove the permanent hardness of the water.
→ The chemical formula for hydrated copper sulfate is CuSO4.5H2O and of gypsum is CaSO4.2H2O.
→ Plaster of Paris is obtained from calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4. 1/2 H2O) by heating it at 373K.
→ Plaster of Paris is used for making toys and material for decoration.
→ Indicators: These are the substances that give different colors in acidic and basic solutions e.g. litmus, turmeric, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, etc.
→ Olfactory Indicators: There are some substances whose odour changes in acidic or basic media, which are known as olfactory indicators.
→ Acid: Those compounds which have one or more hydrogen atoms and which give hydrogen (H+) or hydronium (H3O+) ions (H3O+) ion in an aqueous solution are called acids. These are sour in taste.
→ Ionization: It is a process in which a substance produces ions in water, ionization.
→ Basicity of an acid: Basicity of an acid is the number of hydronium ions [H+] produced when one molecule of acid gets completely ionized in an aqueous solution.
→ Base: Bases are those compounds which are metal oxides or metal hydroxide or aqueous ammonia and these react with hydronium ion (H3O+) of acids to produce salt and water.
→ Neutralization: Due to the reaction between acids and bases, salt and water are produced. This is called a neutralization reaction.
→ Alkali: Those basic hydroxides which on dissolving in water form hydroxyl (OH–) ions, are called alkali.
→ Universal indicator: It is a mixture of various organic substances which show different colours with solutions having different pH values.
→ Dissociation: When a molecule or ionic compound dissociates into two or more atoms or ions, this is called dissociation.
→ Chemical dissociation: A reaction in which a molecule of a compound breaks into atoms or ions is called chemical dissociation.
→ The water of Crystallisation: Water, which is present in crystals of a substance is called water of crystallization. e.g., FeSO4.7H2O, Al2O3.2H2O, CuSO4.5H2O, Na2CO3.10H2O.
→ Efflorescence: The process of release of crystalline water from hydrated salts into the air is called efflorescence.
→ Deliquescence: This is a process in which a substance absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and dissolves in the absorbed water to form a solution.
→ Dilution: On mixing acid or base in water, the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH–) per unit volume becomes less. This is called dilution.
→ Chlor-alkali process: The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution is called chlor-alkali process.
Science Guide for Class 10 PSEB Acids, Bases and Salts InText Questions and Answers
Question 1. You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer:
Dip red litmus paper in solution repeatedly in each tube.
(a) The tube in which the red litmus paper turns purple contains distilled water.
(b) The tube in which red litmus paper turns blue contains basic solution.
(c) The tube in which red litmus paper remains red contains acidic solution.
Question 2. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer:
Curd and other sour substances contain acids which react with the metal surface of brass and copper vessels to produce toxic compounds which are unfit for consumption.
Question 3. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer:
When an acid reacts with metal, generally hydrogen is produced.
e.g. Mg + 2 HCl(Dil) → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
Pass this gas (H2) through soap solution. The soap bubbles filled with the gas will rise up. If a burning splinter is brought near the gas, the bubble will burn with a ‘pop’ sound.
Question 4. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer:
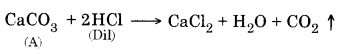
CO2 extinguishes a burning candle.
Question 5. Why do HCl, HNO3 etc. show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer:
HCl, HNO3 etc undergo dissociation in water to give Hydrogen ions, H+(aq) ions and show acidic characteristics. There are compounds like alcohol and glucose don’t dissociate in water to give hydrogen ions, H+(aq) ions. Hence, they don’t show acidic properties.
Question 6. Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
Answer:
The aqueous solution of an acid contains ions such as hydrogen ions, H+(aq) and other anions. Hence it conducts electricity.
Question 7. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour on the dry litmus paper?
Answer:
This is because dry HCl gas is a covalent compound and it does not undergo dissociation to give hydrogen ions, H+(aq) and hence no change in colour of dry litmus paper.
Question 8. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer:
The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is an exothermic process. This is because if water is added to concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating.
Question 9. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Answer:
The concentration of hydronium ions decreases when a solution of an acid is diluted.
Question 10. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH–] affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Answer:
When excess of base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide, the concentration of OH ions increases.
Question 11. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer:
In solution A, [H+(aq)] = 10-6 M, pH < 7
In solution B, [H+(aq)] = 10-8 M. pH > 7
∴ Then the solution A has more hydrogen ion concentration.
Solution A is acidic.
Solution B is basic.
Question 12. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer:
- If [H+] < 10-7 M, it is basic solution.
- If [H+] >10-7 M, it is an acidic solution.
- If [H+] = 10-7 M, it is a neutral aqueous solution.
Question 13. Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Answer:
Basic solutions also contain H+(aq) ions. But in basic solutions :
[H+(aq)] < 10-7 M
and [OH–] > 10-7 M
Since [OH–(aq)] is more than [H+(aq)], hence these are basic solutions.
Question 14. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his Helds with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer:
If the pH of the soil is less than 7, i.e. it is acidic, the farmer will treat the soil with quick lime, slaked lime, chalk.
Question 15. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Answer:
Bleaching powder.
Question 16. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer:
Dry slaked lime.
Question 17. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer:
Washing soda.
Question 18. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer:
It decomposes to give sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas (which is colourless, odourless and turns lime water milky).
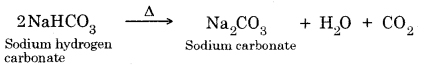
Question 19. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer:
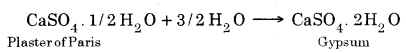
PSEB 10th Class Science Guide Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be :
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10.
Answer:
(d) 10.
Question 2. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime- water milky. The solution contains:
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KC1.
Answer:
(b) HCl
Question 3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be :
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL.
Answer:
(d) 16 mL.
Question 4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic.
Answer:
(c) Antacid
Question 5. Write word equations and then balance equations for the reaction taking place when :
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
Answer:
Zinc granules + Dilute sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
![]()
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
![]()
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
Answer:
Aluminium powder + Dilute sulphuric acid → Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen
![]()
(d) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with iron filings.
Answer:
Iron filings + Dilute sulphuric acid → Iron (II) sulphate + Hydrogen.

Question 6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Answer:
Fix two nails on a cork and place it in a 100 ml beaker. Connect these nails to a 6 volt battery through a bulb and switch as shown in the figure.
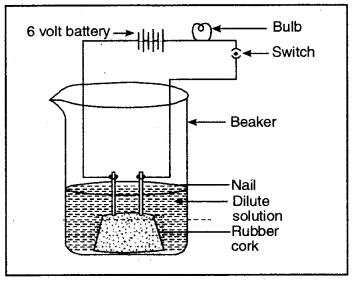
Aqueous solution of alcohol or glucose does not conduct electricity
Pour some aqueous solution of alcohol or aqueous solution of glucose in the beaker so that nails dip in it. Switch on the current. The bulb does not glow indicating that alcohol and glucose don’t dissociate in aqueous solution and hence
do not produce H+ ions although they (aq)
contain hydrogen.
Question 7. Why does not distilled water conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Answer:
- Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it contains no ions.
- Rainwater contains ions due to dissolved salts, hence it conducts electric current.
Question 8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer:
This is because in the absence of water, acids do not dissociate to give hydrogen ions > H+(aq)
Question 9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is :
(a) neutral?
(b) strongly alkaline?
(c) strongly acidic?
(d) weakly acidic?
(e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
| Solution | pH | Nature of Solution |
| A | 4 | Weakly acidic |
| B | 1 | Strongly acidic |
| C | 11 | Strongly alkaline |
| D | 7 | Neutral |
| E | 9 | Weakly alkaline |
The increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration is :
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1 (pH values).
Question 10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer:
Fizzing occurs more vigorous in test tube A as compared to in test tube B. This is because concentration of hydrogen ion, It is more in test tube A than in test tube B, as hydrochloric acid a strong acid and acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid.
Question 11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Its pH will decrease due to the production of lactic acid which is acidic in nature.
Question 12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
Answer:
So that the milk is not spoiled readily and medium remains basic.
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer:
Because the lactic acid produced during curding reacts with baking soda.
Question 13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer:
This is because in presence of moisture, plaster of Paris sets to give a hard mass.
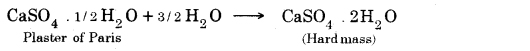
Question 14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer:
The interaction of an acid with a base to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction.
Examples :
Question 15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer:
(a) Uses of washing soda :
- It is used in the manufacture of glass and soap.
- It is used in the manufacture of borax.
(b) Uses of baking soda :
- It is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher.
- It is used for making baking powder.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1. pH of an acidic solution is:
(A) >7
(B) <7
(C) 7
(D) 14.
Answer:
(B) <7
Question 2. Neutral solution has pH:
(A) 7
(B) >7
(C) < 7
(D) 14.
Answer:
(A) 7
Question 3. Common name of NaCO3. 10H2O is :
(A) Bleaching powder
(B) Baking powder
(C) Plaster of Paris
(D) Washing soda.
Answer:
(D) Washing soda.
Question 4. Acid and base react to form salt and water. This reaction is called:
(A) Washing soda.
(B) Chioro-alkali
(C) Reduction
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(D) None of these.
Question 5. What is used for plastering fractured bones?
(A) Cement
(B) Gypsum
(C) Plaster of Paris
(D) Soda.
Answer:
(C) Plaster of Paris
Question 6. Toothpaste used for cleaning teeth is :
(A) Acidic
(B) Neutral
(C) Basic
(D) None.
Answer:
(A) Acidic
Question 7. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is :
(A) 1
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 10
Answer:
(D) 10.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What makes food sour?
Answer:
Presence of acids.
Question 2. What is the reason of bitterness?
Answer:
Presence of bases.
Question 3. What is the reason of acidity in stomach?
Answer:
excess of HCl acid.
Question 4. What is the effect of acid on litmus?
Answer:
Blue litmus changes to red.
Question 5. What are olfactory indicators?
Answer:
Some substances which change their smell in acidic or basic medium are called . olfactory indicators.
Question 6. Give three examples of olfactory indicators.
Answer:
Chopped onions, clove coil, vanilla essence.
Question 7. Which gas is produced when Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas.
Question 8. Which gas is produced when metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acid?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 9. What happens when CO2 is passed through lime water?
Answer:
Lime water turns milky.
Question 10. Why milkiness of lime water disappear when excess of CO2 is passed through it?
Answer:
Due to formation of Ca(HCO3)2 which is soluble in water.
Question 11. Write the name and colour of the compound formed when copper oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Blue-green copper chloride.
Question 12. Which name is used for metal oxide?
Answer:
Alkaline oxide.
Question 13. What is the nature of non-metal oxide?
Answer:
Acidic nature.
Question 14. Why does current flow in acids?
Answer:
Due to ions.
Question 15. Which ion is produced in acidic solution?
Answer:
Hydrogen ion (H+).
Question 16. What is used to dry, moist gas?
Answer:
Calcium chloride.
Question 17. How do we represent hydrogen ion?
Answer:
H+(aq) or hydronium ion (HgO+).
Question 18. Which ions is produced by bases in water?
Answer:
Hydroxide (OH–) ion.
Question 19. What is base?
Answer:
Alkalies which are soluble in base.
Question 20. What should we do to dilute an acid?
Answer:
We should add acid to water slowly and not vice versa.
Question 21. What is dilution?
Answer:
When we add acid or base in water, concentration of ions (HgO+/OH–) per unit volume decreases, this is known as dilution.
Question 22. What is name of mixture of various indicators?
Answer:
Universal indicator.
Question 23. What is that which show different colour at different concen-tration of hydrogen ion in a solution?
Answer:
Universal indicator.
Question 24. What is pH scale?
Answer:
To know the strength of H+ ion in a solution a scale is used known as pH scale.
Question 25. What is p in pH?
Answer:
‘p’ means ‘potenz’.
Question 26. What is the range of pH scale?
Answer:
0 to 14.
Question 27. What is pH value of neutral solution?
Answer:
pH value is 7.
Question 28. If pH value of solution is less than 7, then what does it indicate?
Answer:
Acidic solution.
Question 29. If pH value of a solution is more than 7, then what does it indicate?
Answer:
Solution is basic.
Question 30. What is the value on pH scale for lemon juice?
Answer:
Nearly 2.2.
Question 31. What is the value on pH scale for pure water?
Answer:
7
Question 32. What is the value on pH scale for milk of magnesia?
Answer:
10.
Question 33. What is the value on pH scale for sodium hydroxide?
Answer:
Nearly 14.
Question 34. What is pH range in which our body works?
Answer:
Our body works in the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8.
Question 35. What is pH value of acid rain?
Answer:
It is less than 5.6.
Question 36. In which type of river survival of aquatic animals is difficult?
Answer:
When acid rain water flows to the river.
Question 37. What surrounds the venus planet?
Answer:
Thick white and yellow clouds of sulphuric acid.
Question 38. Which acid is produced in our stomach?
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid.
Question 39. What is produced in the stomach when there is indigestion.
Answer:
Excess of HCl.
Question 40. What is used for treating excess of acid in the stomach?
Answer:
Antacids (mild bases).
Question 41. When does tooth decay begin?
Answer:
When pH value in less than 5.5.
Question 42. Teeth are made up of which substance?
Answer:
Calcium phosphate.
Question 43. Why do we feel pain due to bee sting?
Answer:
Due to acid.
Question 44. Which substance is applied on the stinging area which gives relief from pain?
Answer:
Weak base like baking soda.
Question 45. What do the stinging hair of nettle plant secret?
Answer:
Methanoic acid.
Question 46. What is the remedy for sting of herbaceous plant Nettle?
Answer:
Rub leaves of dock plant.
Question 47. Which acid is there in vinegar?
Answer:
Acetic acid.
Question 48. Which acid is there in lemon, orange?
Answer:
Citric acid.
Question 49. Which acid is in curd and milk?
Answer:
Lactic acid.
Question 50. What is main source of salt?
Answer:
Sea water.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are indicators? How do indicators are categorized? Explain.
Answer:
Those substances which change their colour in acidic and basic solutions, are called indicators.
Indicators are categorized into two types on the basis of their special properties and characteristics.
- Indicators which give colour to acids and basic medium.
- Indicators which give smell to acids and basic medium.
1. Colour giving indicators :
(A) Litmus solution: Litmus solution is purple dye which is obtained from Lichen plant. This is available as red or blue solution and also in the form of litmus paper. Blue litmus turn to red in the presence of acids and Red litmus turns to blue in the presence of basic media. Litmus is neither acidic nor basic by itself.

(B) Turmeric: Turmeric change to red-brown colour in the presence of bases. That is why vegetable stain on the clothes becomes red brown when washed by applying soap which is alkaline.
(C) Phenolphthalein: This is synthetic indicator. It gives pink colour in the presence of bases.
(D) Methyl orange: This is also synthetic indicator. It gives pink colour in the presence of acidic medium and yellow in the presence of bases.
2. Olfactory indicators: Chopped onion, vanilla essence and clove oil change smell in the presence of acids and bases act as olfactory indicators.
Question 2. What is dilution?
Answer:
When we mix an acid or base with water, the number of H+/OH~ ions per unit volume decreases, it is called dilution. By dilution, acids and bases are ionized.
Question 3. Give characteristics of acids.
Answer:
- They are sour to taste.
- They turn blue litmus to red.
- Their solution is not like soap solution.
- They produce hydrogen gas when reacts with metals.
- They react with carbonates to produce carbon dioxide.
- Acid react with bases to produce salts and water.
Question 4. Give four uses of acids in our everyday life.
Answer:
- Vinegar is used in cooking food and acts as preservative and used in pickles.
- HCl in our stomach destroys the harmful bacteria, which reach there with our food.
- Tartaric acid is used to prepare baking soda.
- Carbonic acid is used in soft drinks.
Question 5. What are the harmful effects of acids in everyday life?
Answer:
- They can destroy living cells.
- Concentrated acids can badly damage the skin and soft organs.
- These can damage eatables.
Question 6. Differentiate between strong acids and weak acids.
Answer:
| Strong acids | Weak acids |
| 1. These get completely dissolved in water and produce H+ ions and negative ions. | 1. These do not completely dissociate into H+ ions and negative ions. |
| 2. Equilibrium is not established. | 2. Equilibrium is established between ions and undissociated ions. |
| 3. Example: H2SO4, HNO3. | 3. Example: H2CO3, CH3COOH. |
Question 7. Differentiate between strong base and weak base.
Answer:
| Strong base | Weak base |
| 1. These get completely dissolved in water to produce OH– ions. | 1. These are partially soluble in water. |
| 2. Example: NaOH, KOH | 2. Example: Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2. |
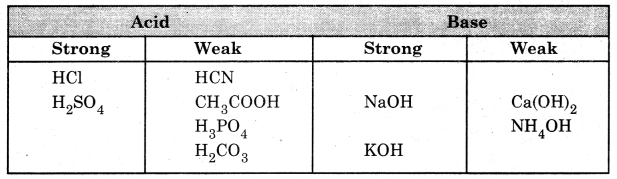
Question 8. Categorize the following compounds as strong and weak acids and bases,
(i) HCl
(ii) H2SO4
(iii) CH3CHOOH
(iv) HCN
(v) NH4OH
(vi) H3PO4
(vii) NaOH
(viii) Ca(OH)2
(ix) KOH
(x) H2CO3
Answer:
Question 9. What is the reason for electric conduction in acids? Explain.
Answer:
Acids produce H+ ions. Due to ions acids can conduct electricity. This conduction takes place in water solution.
HCl + H2O → H3O + +Cl–
HNO3 +H2O → H3O+ +NO3–
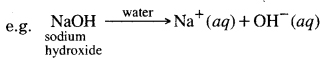
Question 10. What happens when a base is dissolved in water? Explain it.
Answer:
Bases when dissolved in water give hydroxide OH– ion. The water-soluble bases are called alkalis.
Question 11. Why are bases not touched or tasted?
Answer:
Bases have a bitter taste like soaps and are harmful to skin. They are harmful when touched or tasted.
Question 12. Write uses of alkalies/bases.
Answer:
- These are used to make soap.
- These are used in basic batteries.
- These are used in making antacids.
- Used in Petrol refining and paper industry.
- To remove stains of grease from cloths.
- To make hard water, soft.
Question 13. Give normal characteristics of bases.
Answer:
- They are bitter to taste.
- They are soapy to touch and are harmful for skin.
- These turn litmus to blue.
- These turn turmeric to red brown colour.
- These react with acids to produce salts and water.
- They turn phenolphthalein solution to pink.
Question 14. What is difference between alkali and base?
Answer:
Those alkalies which are soluble in water are called bases. This means all bases are alkalies but all alkalies are not bases, e.g. Ferric hydroxide [Fe(OH)3] and cupric hydroxide [Cu(OH)2] are alkalies but are not bases since these are not soluble in water.
Question 15. What are the sources to get common salt (NaCl)? Explain.
Answer:
We can get common salt from following sources :
- Sea water: A huge amount of salt is dissolved in sea water. Salt in obtained from sea water through salt shallows. Solar heat and air help in the evaporation of sea water. We get salt.
- Mineral salt: Deposits of solid salt are found in many parts of the world. These beds of rock salts were formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. This salt is mined similar to the mining of coal. These rocks are found in Mandi (Himachal Pradesh), Khewra (Pakistan). Due to impurities this salt is brown in colour.
- From Lakes: Salt is obtained from Sambher lake in Rajasthan, great salt lake in America, Lake Elton in Roose etc. This salt in obtained by evaporation.
Question 16. Write characteristics of common salt.
Answer:
- Colour and state: It is colourless crystalline substance which melts at 820°C.
- Solubility: Salt is soluble in water.
- Effect of heat: On heating salt a cracking sound is produced due to breaking of ‘ salt crystals.
- Hygroscopic: Salt absorb moisture from the air, This is due to presence of magnesium and calcium chloride.
Reaction with sulphuric acid. Salt reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid to produce HCl gas.
![]()
Reaction with silver nitrate. Salt reacts with silver nitrate to form white precipitates of silver chloride.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Question 17. Give uses of common salt.
Answer:
- Salt is important constituent of our food.
- This is used as preservative in many eatables.
- It is used in soap, pottery industry.
- It is used in making freezing mixture.
- It is used in the preparation of bleaching powder, caustic soda, hydrochloric acid, washing soda, Baking powder etc.
Question 18. What is chlor-alkali process? Give pictorial representation of the products of this reaction. Give their uses.
Answer:
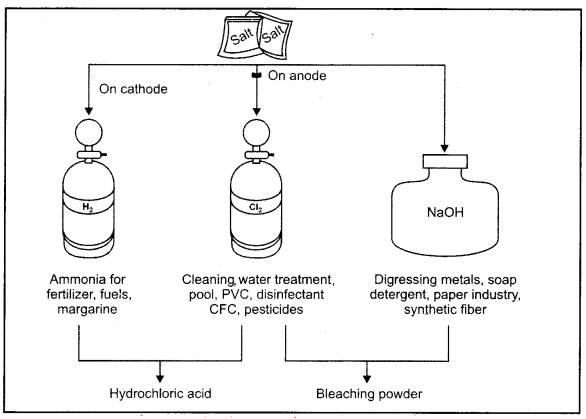
Important products of chior-alkali process.
When current is passed through aqueous solution of salt gets dissociated and sodium hydroxide is produced. This is known as chlor-alkali process because the products in this reaction are chlorine (chlore) and sodium hydroxide (base)
2NaCl(aq)+ 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
All these products are very important and useful in industry medicine, home and cosmetics etc. Chlorine and hydrogen are the by products of this process.
Question 19. How is bleaching powder prepared? Give its common characteristics and uses.
Answer:
Bleaching powder is obtained by the reaction of chlorine with slaked lime.
![]()
To manufacture bleaching powder at large scale, we have a special tower there is a hopper at the top of tower, slaked lime is added through this hopper. At the bottom hot air and chlorine gas are blown. Chlorine moves upwards and is absorbed completely by slaked lime and bleaching powder is produced.
Characteristics :
- Bleaching powder is light yellow coloured powder, It has a sharp smell of chlorine.
- It is soluble in water, but not completely.
- It reacts with CO2 of air and loose its chlorine.
CaOCl2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + Cl2 - It reacts with acids
CaOCl2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
CaOCl2 +H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O + Cl2
Uses
- It is used in paper and textile industry.
- Used to disinfect drinking water to make it free from germs.
- It is used to make unshrinkable work.
- It is used for preparing chloroform.
- It acts as oxidising agent.
Question 20. Write chemical formula for washing soda. When its crystals are open in air, then what happens?
Answer:
Chemical formula for washing soda is Na2CO3. 10H2O. When its crystals are left open in air then due to efforescence nine molecules of water are lost in the air.
Na2CO3.10H2O → Na2CO3 .H2O + 9H2O
Question 21. What happens when solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated? Give chemical reaction for the equation.
Answer:
When sodium hydrogen carbonate solution is heated then carbon dioxide gas is produced and sodium carbonate is produced.
![]()
Question 22. What is common name of the compound CaOCl2? Name the substance which reacts with chlorine to produce bleaching powder?
Answer:
Common name of compounds CaOCl2 is bleaching powder. The substance which reacts with chlorine to produce bleaching powder is slaked lime [Ca(OH)2],
Question 23. If during the preparation of plaster of Paris the process of heating is not controlled then which substance is formed?
Answer:
Temperature should be maintained at 373 K during the preparation of plaster of Paris. If temperature is not controlled then unhydrated calcium sulphate (CaSO4) is produced which do not have the properties of plaster of Paris. This is known as dead burnt Plaster.
Question 24. Explain preparation, properties and uses of baking soda (NaHCO3).
Answer:
Chemical formula for baking soda is NaHCO3 and its chemical name is sodium bicarbonate. It is formed when CO2 is passed through aqueous solution of Na2CO3.
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O → 2NaHCO3
It can also be prepared from sodium chloride.

Properties: When it is heated it swells and becomes light. On heating it produces CO2. It is soluble in water.
Uses :
- It is used in the preparation of baking powder.
- It acts as antacid in case of acidity in the stomach.
- It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Question 25. Explain the following processes.
(i) Deliquescence
Answer:
Deliquescence: When some compounds absorb moisture from air and change to solution then this process is called deliquescence.
e.g. common salt is deliquescence.
(ii) Bleach.
Answer:
Bleach: When some gas or compound decolourises something, this is known as bleach, e.g. bleaching powder or chlorine is used for this purpose.
Question 26. What happens when carbon dioxide is passed through fresh lime water?
Answer:
When carbon dioxide is passsed through fresh lime water in small quantity then insoluble calcium carbonate is formed and colour of lime water turns to milky.

If excess of CO2 is passed through this solution, calcium carbonate change to soluble bicarbonate and milkiness disappears.
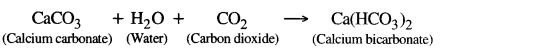
If this solution is heated again, milky colour again appears because calcium bicarbonate again change to calcium carbonate.
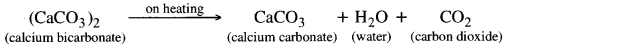
Question 27. What is pH scale? How does it respresent acidic and basic nature of a solution? Represent whole range of pH and [H3O]+.
Answer:
A scale which is used to know the concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution is called pH scale. Here ‘p’ stands for ‘potenz’ a German word which means power. We can measure from zero to 14 on this scale. Zero represents strongest acid, and 14 represents strongest base. pH is such a number which represents acidic or basic nature of a solution. More is the concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution less is its pH value. If a solution is neutral its pH value is 7. If pH is lower than 7 then solution is acidic and if pH is more than 7 then solution is basic. Normally pH can be found by using universal pH indicator paper.

Question 28. Are salt crystals really dry? Explain.
Answer:
Copper sulphate crystals which seems to be dry contains water of crystallization. These seem to be dry hut are not. When we heat the crystals then this water is removed and colour of salt become white. When salt is made wet its colour again change to blue.
Fixed number of molecules of water present in unit formula of salt is called water of crystallization. In unit formula of copper sulphate, there are five molecules of water. Formula for hydrated copper sulphate is CuSO4. 5H2O. In Na2CO3.10H2O there are 10 molecules of water.
Gypsum is another salt which contains water of crystalization. There are two molecules of water in it.
Its formula is CaSO4.2H2O.
Question 29. How is washing soda prepared? Give its uses.
Answer:
Washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) is obtained from sodium chloride. By heating soda, we get sodium carbonate. By recrystallization of sodium carbonate, washing soda is obtained. This is a basic salt.
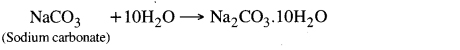
Sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate are useful in several industrial processes.
Uses of washing soda :
- Sodium carbonate is used in glass, soap and paper industry.
- It is used in the manufacturing of sodium compound such as Borax.
- It is used in cleaning agent for domestic purpose.
- It is used to remove permanent hardness of water.
Question 30. What is efflorescence? Name one compound which shows efflorescence? Explain your answer with an equation.
Answer:
The phenomenon of losing some part of water of cyrstallization into air from a crystal is called efflorescence. This phenomenon takes place on heating or some times spontaneously. Washing soda contain water of crystallization hence its formula is Na2CO3. 10H2O. When it is placed in open then it loose its 9 molecules of water and single hydrate is left.
Na2CO3.10H2O → Na2CO3.H2O + 9H2O
on heating it looses all of its water.
Na2CO3.10H2O → Na2CO3 + 10H2O
Question 31. A baker found that a cake prepared by him is small in size and hard. Which constituent, he forgot to add, due to which cake can become soft and big. Give reason.
Answer:
Baker forgot to add baking powder. When baking powder (a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and Tartaric acid) is added to cake and on heating tartaric acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide makes the cake to swell and cake becomes light. Baker, definitely forgot to add baking powder that is why cake is small and hard.
Question 32. When bleaching powder is left open in air, then what happens?
Answer:
When bleaching powder is left open in air, then its properties change. C02 present in air reacts with it due to which calcium carbonate and chlorine gas are produced. Properties of bleaching are lost.
CaOCl2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + Cl2
Question 33. What are the important uses of bleaching powder?
Answer:
- It is used to bleach cotton cloths, linen and wood pulp.
- It is used to disinfect drinking water and to make it free of germs.
- It is used to make chloroform.
- Unshrinkable wool is prepared using bleaching powder.
- It acts as oxidizing agent in Laboratories and in industry.
Question 34. Name the compounds used in hospitals for supporting fractured bones in the right position. How is it prepared?
Answer:
The compound used in hospitals for supporting fractured bones in the right position is plaster of paris. It is calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4. 1/2 H2O). It is prepared at a temperature of 373 K by heating gypsum.
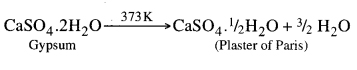
Question 35. Write important uses of Plaster of Paris.
Answer:
- It is used in making toys, moulds, ceramic, containers etc.
- It is used for making material for decoration and statues.
- In hospitals it is used by doctors to set fractured bones and by dental doctors for creating mould to make dentures.
- Used in buildings, to give plane look to walls and ceiling.
- Material used by fire fighters.
- It is used to stop leakage of gases in Laboratories.
Question 36. Many people complaint about gas problem in stomach. What is main reason for this? Why do they use ‘milk of magnesia’ to get relief from this?
Or
What are antacids?
Answer:
A juice is secreted in the stomach which contains enzyme pepsine and hydrochloric acid. Enzyme pepsine is active in acidic medium. When hdyrochloric acid is produced in excess quantity, then we get burning and pain in the stomach, which is known as acidity.
Those substances which are used to neutralize this acid are called antacids. Usually people take a mild base like milk of magnesia for this purpose. It neutralizes the excess acid and provide relief.
Question 37. Idols and utensils made up of copper and brass become shiny when rubbed with lemon? Why?
Answer:
Idols and utensils made up of copper and brass become dull due to coating of copper oxide. Citric acid present in lemon react with it to form salt, which can be easily washed with water. Brass and copper surface becomes shiny.
Question 38. For the safety of teeth what type of toothpaste should be used. Why?
Or
How does change in pH-value helps in tooth decay?
Answer:
Bacteria present in mouth produce acid by degradation of sugar and food particles. This reduces the pH value of mouth which causes tooth decay. After foods we should used basic tooth pastes to prevent tooth decay. Mild bases present in it neutralizes the excess acid. This reducing the chances of tooth decay.
Question 39. What is the remedy for sting of Nettle plant? Write.
Answer:
Nettle is a herbaceous plant found in jungles. Its leaves have stinging hair. These hair cause painful sting if touched accidentally. This pain is due to the secretion of methanoic acid by stinging hair in the body. To get rid of this pain leaves of dock plant are rubbed on the area of sting. Leaves of dock plant have base in them. This plant often grows beside the nettle plant. It neutralizes the acidic effect and gives relief from pain.
Question 40. What is acidic rain? How is the pH of soil can be measured?
Answer:
Some of the gases like SO2, SO3, NO2 etc. present in the atmosphere gets dissolved in rain water and fall on earth in the from of acid is called acid rain. This corrodes some of the metals and marble.
pH value of soil can be measured by using paper soaked in universal indicator. This way we can know the nature of soil as acidic or basic. When pH value of rain water is less < than 5-6 then it is called acid rain. To know the pH value of soil, it is dissolved in water in a test tube and its filter is tested with universal indicator pH paper.
Question 41. Is human life possible on venus planet?
Answer:
No, human life is not possible on venus plant the atmosphere of venus is covered with thick white and yellow clouds of sulphuric acid. If there is a rain is presence of water, it will be acidic and the existence of human life will be impossible.
Question 42. Magnesium is treated with dil. H2SO4. The gas evolved is collected as shown below. Name the method used for collection of gas and the gas produced.
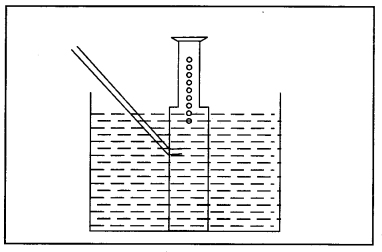
Answer:
Downward displacement of water. The gas produced is hydrogen.
Question 43. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
![]()
Answer:
Fix two nails on a cork and place it in a 100 ml beaker. Connect thses nails to a 6 volt battery through a bulb and switch as shown in the figure.
Pour some aqueous solution of alcohol or aqueous solution of glucose in the beaker so that nails dip in it. Switch on the current. The bulb does not glow indicating that alcohol and glucose don’t dissociate in aqueous solution and hence do not produce H+(aq) ions although they contain hydrogen.
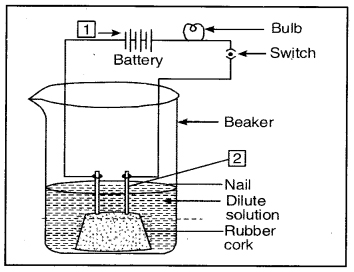
Aqueous solution of alcohol or glucose does not conduct electricity
1 — Cathode
2 — Anode
Question 44. Observe the figure and answer the following:
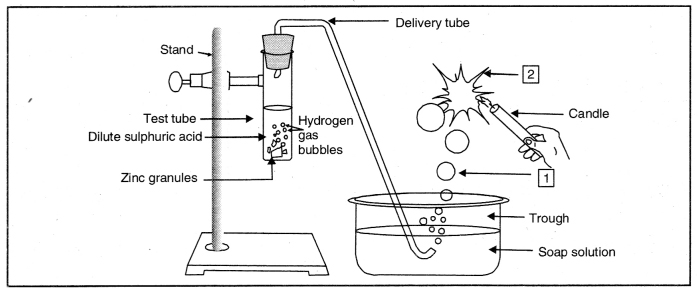
(i) What are 1 and 2?
Answer:
1-Soap bubble filled with hydrogen 2-Burning of hydrogen gas with a pop sound
(ii) Write down the reactions taking place in test tube.
Answer:
![]()
Question 45. In the pH paper shown in figure given below, pH of lemon juice is 2.2 and that milk of magnesia is 10. What is its significance?

Answer:
- Lemon justice is acidic because pH is less than 7.
- Milk of magnesia is basic because pH is more than 7.
Question 46. Which gas is being produced during reaction in the test tube? How does this gas react with Calcium Hydroxide/Lime water?
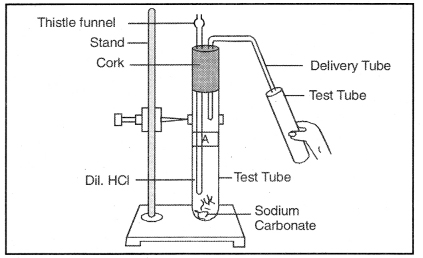
Answer:
Carbon dioxide (CO2).
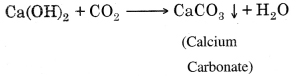
Long Answer Type Questions
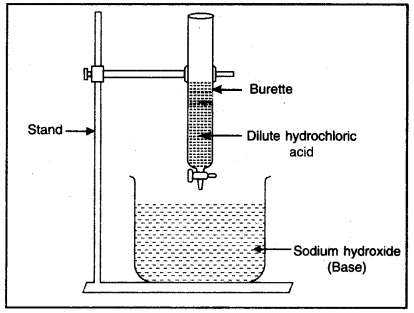
Question 1. What do you mean by neutralization reaction? Explain with an experiment.
Answer:
It is a chemical reaction in which acids reacts with base to form salt and water. It is known as neutralization reaction.
Process of neutralization
Experiment: Take a solution of dilute sodium hydroxide in a beaker. Add few drops of phenolphthalein in this solution. Its colour changes to pink. Take a burette filled with dilute hydrochloric acid. Fix it vertically on a stand as shown in Fig. Place a beaker under it. Add the hydrochloric acid slowly to the beaker with the help of burette and go on swirling the beaker slowly. When the colour of solution disappears then stop adding acid to beaker. Now there is no effect of Red to Blue litmus to the solution. Now there is only salt and water in the beaker which is neutral to litmus. This is known as neutralization reaction.
Example:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
HCl + KOH → KCl + H2O
Question 2. Write briefly chemical properties of acids.
Answer:
Acids have several chemical properties :
1. Reaction with metals. Acids reacts with active metals. Zinc, Magnesium, Iron, Mangenese etc. reacts with them to produce hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + dil. H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Mg(s) +dil.2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Fe(s) + dil. H2SO4 (aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Mn(s) + dil. HNO3 (aq) → Mn(NO3)(aq) + H2 (g)
2. Reaction with metals carbonate and metal bicarbonate. Acids reacts with metal carbonate and metal bicarbonate to produce C02.
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
K2CO3 + 2HCl → 2KCl + H2O + CO2
3. Reaction with bases. Acids reacts with base to show neutralization. They produce salt.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
HCl + KOH → KCl + H2O
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
4. Reaction with sulphites and bisulphites. Acids react with metal sulphite and bisulphite to produce SO2 gas.
CaSO3 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O +SO2 (g)
NaHSO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + SO2(g)
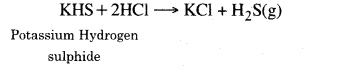
5. Reaction with metal sulphides and hydrogen sulphides. Acids react with metal various metal sulphide and hydrogen sulphides to produce H2S gas.
FeS + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2 S(g)
6. Reaction with metal Chlorides. When metal chloride heated with acids the reaction takes place.
NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl (g)
NaCl + NaHSO4 → Na2SO4 + HCl (g)
7. Reaction with metal nitrates. Concentration acid reacts with metal nitrate.
NaNO3 +H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3
NaNO3 + NaHSO4 → Na2SO4 + HNO3
8. Reaction with metal oxides. Metal oxides reacts with dilute acids to form salts of
Na2O + 2HNO3 → 2NaHO3 + H2O
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
Question 3. Write in brief chemical properties of bases/alkalis.
Answer:
Important chemical properties of bases/alkalis are given below :
1. Reaction with metals, Bases react with some metals to produce hydrogen gas.
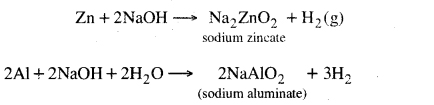
2. Reaction with air. Some bases react with CO2 present in air.
2NaOH + CO2 → Na2CO3
2KOH + CO2 → K2CO3
3. Reaction with acids. Bases react with acids to produce salts.
NaOH+ HCl → NaCl + H2O
Fe(OH)2 + 2HCl → FeCl2 + 2H2O
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
4. Reaction with salts. Salts of copper, iron, Zinc etc. react with bases and produce insoluble metal hydroxides.
ZnSO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + Zn(OH)2 ↓
CuSO4 + 2NH4OH → (NH4)2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 ↓
FeCl3 + 3NaOH → 3NaCl + Fe(OH)3 ↓
Question 4. What is the importance of pH in everyday life?
Answer:
pH has very important role in our life :
1. In animal world. Many of the processes in our body occur within the pH range of 7-0 to 7-8. We can survive only in this narrow range. pH value of our blood, tears, saliva is nearly 7-4. Survival will become impossible if this value becomes less than 7-0 or more than 7-8. When pH of rain water decreases from 7-0 to 5-6 or less then it is called acid rain. WThen acid rain flows to the rivers then pH value of river water lowers. Survival of aquatic life in such rivers become difficult.
2. For plants. For healthy growth of plants a specific pH range of soil is required. If soil becomes more basic or acidic, produce badly affected.
3. Digestive system. Our stomach produces HCl, which without harming us help in the digestion of food. Duiing indigestion the stomach produces too much of acid. This causes pain and irritation in the stomach. To get rid of this pain, bases are used which are called antacids. For this weak base like milk of magnesia is used.
4. Tooth decay. If pH value of the mouth is lower than 5-5, then tooth decay begins. Our teeth are made up of calcium phosphate which is hardest substance in our body. It is not soluble in water but starts decaying when pH of the mouth is lower than 5-5. Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids by .degradation of sugar and food particles. To get rid of this we should use basic tooth paste. This will neutralize the acid and tooth decay can be prevented.
5. Relief from insect stings. When some insects sting us, they leave a special type of acid in our body. Bees, ants etc. leave methanoic acid in our body by their sting. To get relief from pain, mild base like baking soda is rubbed on the stung area.
6. Safety from special plants. Plants like nettle have stingging hair. By touching them we feel pain similar to insect sting. This pain is due to methanoic acid. Conventionally, one can get relief by rubbing leaves of dock plant on the stung area.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here