PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Land Utilization and Agriculture
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Land Utilization and Agriculture
PSEB 10th Class SST Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Land Utilization and Agriculture
PSEB 10th Class Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Land Utilization and Agriculture
→ Land under Agriculture – 46.6% of geographical area or 1530 lakh hectares.
→ Per capita cultivated land – 0.16 hectares.
→ Fallow land – 7.1% or 230 lakh hectares.
→ Distribution – Net sown area to geographical area varies from 3.4% in Arunachal Pradesh to 84.2% in Punjab.
→ Landholdings – One-third is small, less than one hectare in size.
→ Types of farming – Subsistence, shifting, plantation, intensive, sedentary, and commercial farming.
→ Contribution of Agriculture – 26% Gross Domestic Product (Down from 52% in the 1950s).
→ Major Crops – Cereals (rice, wheat, millets, maize), pulses (arhar, urad, moong, masur, peas, and gram), oilseeds (groundnut, sesamum, rapeseed, linseed, castor, fibre crops (cotton and jute), Beverage crops (coffee and tea) and cash crops (sugarcane, rubber, tobacco, spices and fruits, animal husbandry and fisheries.
→ Technology – Use of wooden plough, bullock cart, Persian wheel, and now water pump and tractors.
→ Irrigation Revolution – From flooding of the field to the canal, sprinkler, and drip irrigation.
→ Green Revolution – Increase in crop yield with the help of fertilizers, high yield varieties of seeds.
→ White Revolution – Increase in milk yield especially buffalo milk in India.
→ Institutional Reforms – Abolition of zamindari and jagirdari, ceilings on land holdings, consolidation of land holdings, credit reforms.
PSEB 10th Class Social Science Guide Land Utilization and Agriculture Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions in one word or one line:
Question 1.
How much percentage of population of India depends upon agriculture?
Answer:
70 percent,
Question 2.
Name an activity which besides cultivation is included in agriculture.
Answer:
Animal husbandry.
Question 3.
How much area is net sown area in India?
Answer:
143 million Hectare.
Question 4.
What is the percentage of fallow land?
Answer:
5%.
Question 5.
In which state is Jhumming practised?
Answer:
Meghalaya.
Question 6.
Name an important Rabi crop.
Answer:
Wheat.
Question 7.
Name an important Kharif crop.
Answer:
Paddy.
Question 8.
Name a plantation crop of India.
Answer:
Tea.
Question 9.
Where does India rank in world production of tea?
Answer:
First.
Question 10.
Name a fibre crop.
Answer:
Cotton.
Question 11.
From which liquid is rubber produced?
Answer:
Latex.
Question 12.
How much per cent area of India is under cultivation? Where does India rank in the world?
Answer:
About 51 per pent land of India is under cultivation. From this point of view, India ranks first in the world.
Question 13.
What do you mean by fallow land?
Answer:
Fallow land is that land which is used for one crop after 2 or 3 years. It is again left vacant so that its fertility can be restored.
Question 14.
The percentage of fallow land is decreasing in India. What does it suggest? Explain two points.
Answer:
- More manures and fertilizers are being used in fallow land.
- Scientific methods are being used to retain moisture in land.
Question 15.
Despite less area under pastures in India, India has the largest number of cattle in the world. How is it?
Answer:
Livestock are reared on fodder crops and grass.
Question 16.
How do forests check floods?
Answer:
Forests allow the seepage of rain water into land. So these help to retain water and control the destructive floods of rivers.
Question 17.
How can afforestation control droughts?
Answer:
Forests help in rainfall. Therefore droughts do not occur frequently.
Question 18.
What do you mean by wasteland?
Answer:
Wasteland is that land which is not used at present. It includes arid, rocky areas and sandy deserts. High rugged mountains and bad lands are included in it.
Question 19.
In which two ways wastelands are increased by man?
Answer:
- By overgrazing
- By deforestation.
Question 20.
Explain three methods of forests conservation.
Answer:
- Deforestation should be stopped.
- Forests should be declared reserved areas.
- More trees should be planted than cut during a year.
Question 21.
Why is the demand for land increasing in India? Give two examples.
Answer:
- More land is required for human settlements due to growing population.
- People want to live in open, spacious houses due to high standard of living.
Question 22.
Why is it necessary to plan the proper use of the land available?
Answer:
Land is a limited resource. It can neither be increased nor decreased. But pressure on land is increasing constantly. So it is necessary to plan the proper use of land.
Question 23.
State three steps which should be taken for the proper land-use.
Answer:
- Soil erosion should be checked.
- To check the advance of deserts.
- Steps be taken to use the wasteland.
Question 24.
The natural fertility of soils in India is decreasing. State two reasons for it.
Answer:
The following are the two main reasons for decreasing soil fertility in India:
- The absence of forests and pastures is affecting the natural fertility of soils.
- The poverty of farmers and their ignorance of scientific techniques are also responsible for the decrease in natural fertility of soils.
Question 25.
Explain the importance of bunding and contour ploughing in dry farming.
Answer:
Bunding and contour ploughing are useful in dry farming. It retains the moisture in soil. It also checks soil erosion.
Question 26.
What steps should be taken to maintain soil fertility in India?
Answer:
Green manures and Gobar manures should be used to maintain soil fertility. But a suitable amount of fertilizers should also be used at the same unit.
Question 27.
What is the function and importance of National Price Commission?
Answer:
National Price Commission fixes the standard rate of crops, useful for farmers.
Question 28.
Name the two agricultural seasons oflndia.
Answer:
In India, there are two main agricultural seasons, Kharif and Rabi. Rice is the main crop of Kharif season while wheat is the main foodgrain of Rabi season.
Question 29.
Where is most of wheat produced in India? Why?
Answer:
Wheat is mostly produced in northern plains. Punjab, Haryana and U.P. are the leading producers of wheat.
Question 30.
Explain the importance of cultivation of pulses in India.
Answer:
(i) Pulses are the major sources of protein for poor people in India.
(ii) Pulses fix nitrogen in the soil to restore its fertility.
Question 31.
What are oilseeds? Name some important oilseeds.
Answer:
Groundnut, Sesaum, Linseed, Sunflower, Castor seed, Rape seed, Mustard, etc. are important oilseeds.
Question 32.
Name four main fibres of India. How are these obtained?
Answer:
The four main fibres in India are:
- Cotton
- Jute
- Wool
- Silk.
Question 33.
What is the importance of forestry?
Answer:
- Forests maintain ecological balance and ecosystem.
- Forests provide timber, lac, gum, cane, fuel, medicines, etc.
Question 34.
Why is India considered a fortunate country as regards land available for cultivation?
Answer:
More than one half of total land is available for agriculture in India. No other country is so fortunate in this regard.
Question 35.
Why is it necessary to increase the area under forests for economic development?
Answer:
Many industries are based on forests. These increase the employment sources. Moreover, these check soil erosion and control floods. So the area under forests is to be increased.
Question 36.
State a problem related to Ecosystem of Punjab.
Answer:
Forests cover an area of 5.7 per cent in Punjab. This area is very low as regards scientific norm. The low forested area has an adverse effect on Ecosystem of Punjab.
Question 37.
How can you say that Punjab is an agricultural state?
Answer:
Most of the land of Punjab is being used for agricultural purpose. Waste land covers very small area as compared to the whole country. So we can say that Punjab is an agricultural state.
Question 38.
What do you know about social forestry? State its main aim.
Answer:
Social forestry includes a programme under which common wasteland in rural area is used for planting trees. Its aims is to make wasteland a green belt, provide employment in rural areas, and to solve fuel problem in villages.
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Net sown area in India is___________%.
Answer:
47
Question 2.
India has ____________ % area under forests.
Answer:
22.6
Question 3.
In Punjab _________% area is under forests.
Answer:
5.7
Question 4.
India is the largest exporter of ___________
Answer:
Tea
Question 5.
India is second largest producer of _________
Answer:
Rice.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
India is the largest producer of
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Rice
(d) Cotton.
Answer:
(a) Tea
Question 2.
Which state is the largest producer of wheat?
(a) Punjab
(b) U.P.
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Madhya Pradesh.
Answer:
(b) U.P.
Question 3.
Which is known as golden fibre?
(a) Cotton
(b) Silk
(c) Jute
(d) Wool.
Answer:
(c) Jute
Question 4.
Crops grown in _______season are called Kharif crops.
(a) Spring
(b) Summer
(c) Winter
(d) Rainy.
Answer:
(d) Rainy.
Question 5.
Black soils are ideal for cultivation of:
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Cotton
(d) Maize.
Answer:
(c) Cotton
True / False:
Question 1.
Rice is a product of moist tropical region.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Less fertile soil is needed for rice cultivation.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Jharkhand produces largest quantity of rice.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Wheat can be grown in areas of moderate rainfall.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Cotton is an important fibre crop.
Answer:
True.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which is the most satisfying feature of land use pattern in India? What are its main features?
Answer:
The most satisfying feature of land use in India is that net sown area is increasing. During last 3 decades 2.2 crore hectares has been added to it. Today net sown area is 16.2 crore hectares and it is about 47.7% of total area.
Main Features:
- The area under forests is low. It is only 22.7% of total area. But for a self-reliant economy and proper ecological balance, one third of the land should be under forests.
- The area under pastures is low.
Question 2.
Distinguish between fallow land and wasteland. What are two advantages of fallow land to farmers?
Answer:
Fallow lands are lands which are not cultivated annually for crops. Only one crop is grown on these-lands during two or three years. After getting one crop, it is left vacant to maintain its fertility. Its use depends on timely monsoonal rain. Wasteland is a land which is not used for cultivation. It includes arid, rocky and sandy land.
Advantages of Fallow Land:
- Fallow lands regain their lost fertility.
- Agricultural production is increased due to increase in productivity of land.
Question 3.
Distinguish between subsistence farming and commercial farming giving one example from each.
Answer:
Subsistence farming is the type of agriculture in which crops are grown for local consumption to meet the needs of the family. On the opposite, commercial farming meets the demand of market. In commercial farming, one crop is grown and cultivation is done on large farms using scientific techniques. Subsistence farming includes wheat farming while tea plantations are a type of commercial farming.
Question 4.
Name two agricultural seasons. Why is wheat mostly grown in Punjab? Give two reasons.
Answer:
The two agricultural seasons are:
- Kharif
- Rabi.
Wheat is mostly grown in Punjab due to these reasons:
- Punjab has fertile land deposited by alluvial soils. These loamy soils are best suited for wheat.
- Cyclonic rainfall, which occurs over a long period, is well suited for wheat.
Question 5.
Why is the rice cultivation increasing in Punjab? Give four reasons.
Answer:
Increase in rice cultivation is due to these reasons:
- Intensive farming is practised in Punjab with the use of better seeds and fertilizers.
- Irrigation methods are highly developed. In some districts, water logging has increased rice production.
- Land is fertile and farmers are hard working.
- Punjab Agriculture University has introduced new varieties of rice.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the major characteristics of land use pattern in India?
Answer:
Land use pattern. Land is a limited resource. Attempts are made to make the maximum use of land. India has total geographical area of 32.8 crore hectares. Out of it 92.2% area is used.
Main characteristics of land use are as under:
(а) Net sown area. About 51% of total land (16.3 crore hectares) is net sown area. This vast area shows the importance of agriculture in India. It includes 1.3% land under fruits and 5% under fallow land.
(b) Fallow land. About 5% land (2.2 crore hectares) is left as fallow land and is cultivated after two or three years. Fallow land has decreased due to use of fertilizers and manures.
(c) Forests. About 22.7% of land (6.7 crore hectares) is under forests. The actual area under forests is 4.6 crore hectares. According to scientific norms, l/3rd of area should be under forests.
(d) Pastures. About 4% land is under pastures. Still India has the largest number of cattle in the world. Cattle are reared on fodder crops.
(e) Other uses. Land under permanent grassland, cultivable waste, and not available for cultivation amounts to about 22% of total land. It includes wasteland also.
Moreover the demand for human settlements is increasing due to growing population.
Question 2.
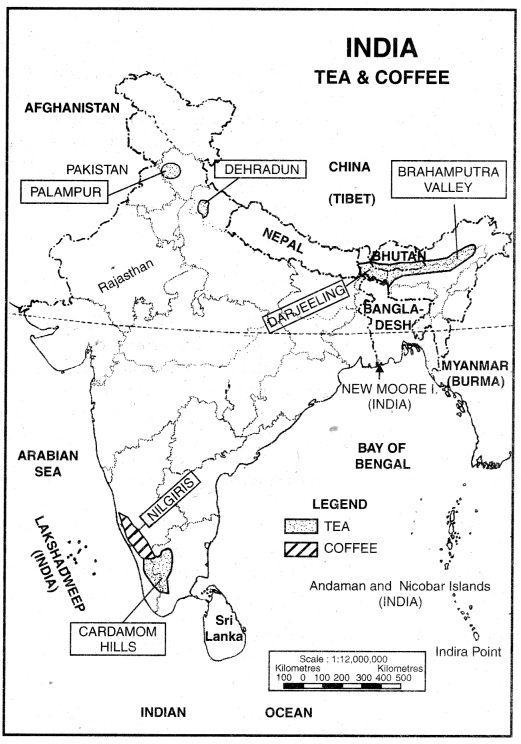
Describe the geographical conditions of growth, areas and production of tea in India. Also, discuss its International Trade.
Answer:
India is the leading producer of tea in the world. Tea plantations were started by the British for their own benefit. Now Indians are the owners of these plantations. About 10 lakh persons are engaged in Tea farming directly and same number of persons get employment indirectly. It is labour-intensive industry.
(а) Geographical conditions. The following geographical, conditions are suitable for cultivation of tea:
- Abundant rainfall (150 cms) is necessary for the growth of tea plants.
- Tea requires high temperature. An average temperature of 20°C to 30°C is suitable for its proper growth.
- The relative humidity should be high.
- The water should not stagnate in the roots of the plant.-Therefore tea is mostly grown on the hilly slopes.
- Tea requires fertile soil.
- Cheap labour is very essential for tea plantation as the picking of leaves requires human labour.
(b) Tea producing states. Assam is the biggest producer of tea in India. West Bengal is the second largest producer of tea in India. Tea is grown in Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri, Nilgiri hills. Tea is also grown in Bihar, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, U.P., Himachal Pradesh, Kerala and Karnataka.
(c) Production. In 1950-51, tea estates covered an area of 3,14,000 hectares. In 2000-01 the area under tea estates raised to 4,00,000 hectares. In 1950-51 total production of tea was .2,75,000 tonnes. In 2011-12, it rose to 8,00,000 tonnes. It amounts to one half of the world production.
(d) Trade. In 2010-11, India exported 2.03 lakh tonnes of tea valued at Rs. 1976 crores. Sri Lanka is a competitor of India as regards exports of tea. Kenya is a new tea-exporter. Tea consumption is increasing in India. So tea export is decreasing.
Question 3.
What are the main causes of backwardness of the Indian agriculture? Suggest remedies for its improvement.
Answer:
Causes of backwardness. The causes of backwardness of the Indian agriculture are as under:
- Dependence on rain. The Indian farmer depends on rain for irrigation. Only 23% of the cultivated land has irrigation facilities.
- Dearth of Nitrogen in the soil. Indian soil is poor in nitrogen. The land has been cultivated for thousands of years continuously and has, thus, affected the fertility of the soil.
- Poor labour. The Indian farmers are weak in health and they cannot provide the required amount of labor for agriculture.
- Subdivision of holdings. In India the land is equally distributed amongst all the sons after the death of the father. As a result the size of fields goes on decreasing and this affects the production.
- Primitive methods of agriculture. The Indian farmer is still following the
primitive methods of agriculture. Hence agriculture in India has suffered a setback. - Non-utilization of good seeds. Indian farmers are poor and do not use seeds of good quality. This lowers production.
- Poverty. Money is needed for agriculture but the farmers are poor.
- Weak cattle. Indian farmer cultivates his land with the help of bullocks but most of the bullocks in India are not of good breed. They are very weak and are thus unable to undertake agricultural activities properly.
- Illiteracy. The Indian farmer is illiterate. He finds it difficult to adopt new methods of agriculture.
SST Guide for Class 10 PSEB Land Utilization and Agriculture Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions objectively:
Question 1.
Name the crops which are sown in the Kharif season.
Answer:
The crops sown in the Kharif season are-Rice, Jowar, Bajra, Maize, Groundnut, Jute and Cotton.
Question 2.
which are the crops sown in Rabi season?
Answer:
Wheat, barley, grams, mustard and rapeseed etc, are grown in Rabi season.
Question 3.
What is difference between Green Manure and Fertilizer?
Answer:
Fertilizers and Manures. Fertilizers are chemically prepared but manures include gobar and green plants.
Question 4.
What are Milch Cattle?
Answer:
The cattle which provide milk are called Milch cattle. Cows and buffaloes are milch cattle.
Question 5.
What is Fallow Land?
Answer:
Fallow Land is a piece of land in which only one crop is grown during a period of two or three years.
Question 6.
What is the percentage area of our country under forests?
Answer:
23.3% area of country is under the forests.
Question 7.
How much area should be under the forests from the scientific point of view?
Answer:
According to scientific point of view, 33% of land of a country should be under forests.
Question 8.
How much percentage area in Punjab is under forest?
Answer:
5.7% area is under forest in Punjab.
Question 9.
How much percentage of land is under agriculture in India?
Answer:
50% of land of India is arable.
Question 10.
Whch is the largest wheat producing state of our country?
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh is the largest wheat producing state of India.
Question 11.
Which state of our country contributes largest amount of wheat to the central pool?
Answer:
Punjab has the largest contribution of wheat to the public distribution system in India.
Question 12.
What are the causes of decreasing pasture lands?
Answer:
The area under pastures is brought under cultivation to meet the needs of growing population of the country.
Question 13.
In the year 2001 how much food was available per person per year in India?
Answer:
458 grams was available per person per year in India in 2001.
Question 14.
Name the state that produces largest amount of Rice.
Answer:
West Bengal is the largest rice producing state in India.
Question 15.
What is the rank of Punjab in terms of per hectare production of wheat?
Answer:
Punjab ranks first in India as regards yield per hectare of wheat.
Question 16.
What is the rank of India in terms of producing pulses in world?
Answer:
India gets first position in the world in the production of pulses.
Question 17.
After the green revolution, what type of change occurred in production?
Answer:
Pulses were sown in 9.3 lakh hectare land in Punjab before green revolution. After green revolution this area has reduced and left 95 thousand hectares.
Question 18.
At the end of 21st century how much foodgrains would be required for the Indian population?
Answer:
40 crore tonnes of foodgrains would be required for the population of India at the end of 21st century (Almost 160 to 170 crores of population).
Question 19.
Write down any three problems of the present Indian agriculture.
Answer:
- Huge pressure of population on land.
- Unequal distribution of cultivated land.
- Uneducated farmers.
Question 20.
What is the rank of India in the world in the production of sugarcane?
Answer:
India has the fifth position in the world in the production of sugarcane.
Question 21.
Name the crops of oil seeds.
Answer:
Oil seeds are – Groundnut, Mustard and Rape Seed,-Sunflower, Cotton seeds, Coconut etc. We get oil from these.
Question 22.
Name any two states which produce maximum amount of groundnuts.
Answer:
Gujarat and Maharashtra are two largest groundnut producing states.
Question 23.
In which decade the area under oil seeds production had increased the most?
Answer:
In the decade of 1980 to 1990, India obtained the maximum increase in the production of oil seeds.
Question 24.
Which are the main cotton producing states of our country?
Answer:
The main cotton producing states of India are:
Maharashtra, Gujarat, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan. Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Question 25.
What is the per hectare production of cotton in our country?
Answer:
249 kilograms per hectare is the average yield of cotton.
Question 26.
Which are the main potato producing states of India?
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Bihar and Punjab are the main potato producing states.
Question 27.
Name the main potato producing districts of Punjab.
Answer:
Jalandhar, Hoshiarpur, Patiala and Ludhiana are the main potato producing districts of Punjab.
Question 28.
What is the rank of Punjab in our country in respect of cattle wealth?
Answer:
Punjab gets 13th position in India as regards to cattle wealth.
Question 29.
Which part of the country amounts the highest cattle wealth?
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh has the largest cattle resources in India.
Question 30.
What is the rank of India in the world in respect of fruit and vegetables?
Answer:
India gets second position in world in the production of fruit and vegetables.
Question 31.
Where does India rank in the world in production of cashewnuts?
Answer:
India gets first position in the world in the production of cashewnuts.
Question 32.
Name the apple producing states.
Answer:
Jammu-Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh are the main apple producing states.
II. Answer the following Questions in short:
Question 1.
Why is the agriculture called the basic mainstay of Economic system?
Answer:
Agriculture is the basis of Indian Economy. Agriculture contributes only 33.7% of National Production, still it is important.
- Two-thirds of our population gets livelihood from agriculture.
- Agriculture sector provides employment to two-third labourers of the country.
- Most of the industries get raw material from agriculture.
- The fact is that the industrial structure has been built on the foundations of Agriculture.
Question 2.
What are the main features of Green Revolution?
Answer:
Green revolution encourages mechanised agriculture and it increases the total production. Ploughing, planting the seeds and harvesting is done by machines. Fertilizers and better seeds are used.
Question 3.
Which items are included in agriculture side?
Answer:
Agriculture includes livestock farming, fisheries, forestry, sericulture, bee hiving, poultry farming etc.
Question 4.
What is the difference between milch cattle and working load animals?
Answer:
Dairy cattle and draught cattle Cows and buffaloes are dairy cattle. These provide milk to us. Bullocks and oxen are draught cattle. These help in ploughing, sowing, harvesting and transportation of agricultural products.
Question 5.
What is the difference between current fallow land and old fallow land?
Answer:
Current Fallow Land and Old Fallow Land
Fallow lands are marginal lands which are left free for only one year. Crops are not grown. After one year, these lands are again cultivated. It is called current fallow land. The remaining fallow land is called old fallow land which is never cultivated.
Question 6.
What climatic conditions are required for the wheat cultivation?
Answer:
Wheat is an important foodgrain.
Geographical conditions. The following geographical conditions are suitable for wheat cultivation:
- Wheat requires lower temperature during the growing period and high temperature at the harvesting period. At the sowing time temperature should be about 15°C to 20°C and at the time of ripening the temperature should be between 20°C and 25°C.
- Wheat can be grown in areas of moderate rainfall. 50 to 75 centimeters rainfall is quite suitable for its cultivation. The rain should be well distributed
- The soil should be fertile. Loamy soil is very suitable for wheat cultivation.
- The land should be even for the convenience of irrigation.
Production. India occupies fourth position as a producer of wheat in the world.
Green revolution has brought many changes. In 1960-61 wheat production was 1.6 crore tonnes. In 2011-12 it increased to 8.5 crore tonnes.
Wheat Producing States. Although wheat is cultivated in almost every part of the country except the southern part of the Indian peninsula, it is essentially a crop of North India. Uttar Pradesh produces highest quantity of wheat in India. Punjab occupies the second position as a producer of wheat in India. Haryana is also an important producer of wheat.

The states of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Maharashtra also grow some wheat.
Question 7.
Name the main paddy growing areas of our country.
Answer:
The following are the main rice producing areas of India:
Areas of Heavy Rainfall: Delta regions of East and West coastal plain. The plains and lower hills of N.E. India, lower slopes of the Himalayas; West Bengal, Bihar, Eastern U.P., Chhattisgarh; Northern Andhra Pradesh. Areas of Low Rainfall: Western U.P., Haryana, Punjab, and adjoining districts of Rajasthan.
Question 8.
Discuss the required condition for the production of Sugar Cane.
Answer:
Required condition for the production of Sugar Cane:
(а) Sugarcane requires well-drained fertile soil.
(b) It also needs large amount of chemical fertilizers and organic manure.
(c) Hot and humid climate is favourable for its higher yields.
(d) It grows well in areas with about 100 cm of rainfall.
Question 9.
What are the main uses of forests?
Answer:
Forests are a valuable resource. Following are the advantages of forests:
(a) Forests are helpful in maintaining ecological balance and natural Eco-system.
(b) Forests supply timber and fuel. It is used for making furniture, packing boxes, boats etc. and is used for buildings.
(c) Soft wood is used for preparing wood-pulp which has a large demand for paper
industry.
(d) We obtain lac, cane, gum, medicinal herbs from forests.
(e) We get fodder for cattle from forests.
Question 10.
Why is Indian agriculture known as ‘Subsistence Agriculture’?
Answer:
Most of land holdings in India are of small size. Large amount of capital and labour is applied on small farms, but economic benefit is small. Small farmers have to hire agricultural implements and tubewell water for irrigation. They have to purchase costly fertilizers from the market. It results in a small net savings. Therefore Indian agriculture is called Subsistence Agriculture.
Question 11.
Why some people call green revolution as ‘wheat revolution’?
Or
May green revolution be termed as wheat revolution only. How?
Answer:
Total production of wheat in 1960-61 was 1 crore 10 lakh tonnes. But due to green revolution it increased five times in 1993-94. Due to the enormous increase in wheat production, sometimes it is called wheat revolution,
Question 12.
Explain the efforts made for the development of animal wealth.
Answer:
Many attempts have been made by Central govt, and state govts, for the development of livestock farming in India.
Special attempts have been made to improve their breed, to protect them from different diseases, to control their diseases; and provide market facilities. At least one veterinary hospital has been started in each block. At village level, the health centres for livestock have been opened. In 1992-93, such health centres were more than 22,000. Besides this, 26 cattle injection centres in public and private sectors had been opened.
Question 13.
What are the reasons that are responsible for the increase in land use under non-agricultural purposes?
Answer:
There are two reasons for the increasing use of land for non-agricultural purposes growing population and economic development. The urban and rural areas are increasing in size due to growing population. Due to increase in economic development large area is being used for canals, roads, industries and irrigation projects.
Question 14.
Write in brief about the importance of forests.
Answer:
Forests are important in our daily life in the following ways:
- These maintain ecological balance.
- Trees absorb carbon dioxide and control the increase in temperature.
- Forests are the home of wild animals. These protect them.
- Forests increase the rainfall and droughts do not occur,
- Forests preserve water resources and control floods in rivers.
Question 15.
What effect incurred after independence on the requirement of foodgrains per head?
Answer:
After independence, many steps have been taken to develop agriculture. As a result, the production of foodgrains has increased. From 1950-51 to 1994-95, production of rice has increased four times and production of wheat has increased ten times. It has affected food for persons. In 1950 the availability of foodgrains was 395 grams per person per day. In 2000 it had increased to 458 grams per person per day.
Question 18.
What are the reasons of small land holdings in India? How these effect Indian agriculture?
Answer:
50% land holdings are less than one hectare in size. The main reason for it is law of inheritance. After the death of the father, the land is equally divided among the sons. Therefore size of the land holding is small due to increasing pressure of population on land. Due to small holdings the farmer cannot use machinery and the advanced methods of irrigation. As a result, he has to hire water and machinery. Therefore, net saving is less and the farmer is becoming poorer day by day.
Question 17.
Name the main paddy producing states.
Answer:
West Bengal was the largest rice producing state of India with a production of 1.39 crore tonnes in 2000-01. Other main producers are U.P., Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, Bihar. Punjab and Orissa. Each state produces more than 60 lakhs tonnes of rice. Besides this, M.P., Assam, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Haryana are other large producers of rice.
Question 18.
What are the causes for high per hectare yield of wheat in Punjab?
Answer:
Punjab is the second largest producer of wheat in India. Punjab ranks first in yield per hectare and its contribution towards national store of wheat is due to
- Wheat is cultivated on a large scale in Punjab because it is a commercial crop in Punjab.
- Better irrigation facilities are available.
- The yield per hectare is high.
- The yield per hectare has increased due to mechanised agriculture.
Question 19.
What are the causes of decrease in area under pulses cultivation?
Answer:
The production of pulses and oil seeds are still low due to the following reasons:
- The areas under cultivation of pulses and oil seeds is small. Pulses are grown on an area of 2.3 crore hectares.
- There is absence of irrigation.
- The yield per hectare is low. The green revolution has not affected it,
- The rate of growth of population is more than the rate of production of these crops.
Question 20.
Write down the benefits of Dairy Industry.
Answer:
Dairy farming includes rearing of cattle to get milk and milk products. It is a part of agriculture. It has the following advantages:
- It provides employment in drought areas.
- It provides additional income to farmer.
- It provides nutrients in diet by increasing the production of milk.
Question 21.
Why production of pulses and oil-seeds is still low?
Answer:
The production of pulses and oil seeds is lower and does not meet our needs. This is due to:
- Low production of Pulses. The production of pulses was 1.3 crore tonnes in 1960-61. It was 1.4 crore tonnes in 1993-94. Unfortunately, the yield of pulses per person has reduced to one half. This is due to the decrease in area under pulses. Much area has been brought under cultivation of rice and wheat. There has been decreasing of 34 lakh hectares under pulses during the last thirty years.
- Low production of Oil-seeds. The position of oil-seeds is opposite to-that of pulses. There has been increase in area under oilseeds as well as production of oilseeds. In 1960-61 area under oilseeds was 1.4 crore hectares. It increased to 2.23 crore hectares in 2000-01. The production increased two fold but still there is shortage of oilseeds. The demand is increasing by 5% annually and 2% growth of population is making the problem more severe.
Question 22.
What are the main problems of Indian agriculture?
Answer:
The following are the agricultural problems of India:
- There is a great soil erosion because the area under forests and pastures is small.
- Most of the soils are saline. More than one lakh hectares is affected by this in Ferozepur district.
- Most of the farmers are illiterate and are unable to practise crop rotation.
- Cultivated land is decreasing due to the increasing use of land for non-agriculturai purposes.
- The size of the land holding is small, uneconomic and there is small net saving. Because the farmers have to hire the costly machinery and costly fertilizer
- Fall in ground water and loss of fertility are other problems.
Question 23.
Explain the changes that have occurred rapidly in the diversification of crop rotation after Green Revolution.
Answer:
Rapid changes have taken in crop-rotation after Green Revolution. This is due to the increase in productivity in areas affected by Green Revolution (Punjab, Haryana and H.P.). Agricultural productivity has decreased in the traditional rice producing areas of the East. Besides this, the agricultural development, in Green revolution affected areas, has become stagnant. To meet these problems, the farmers have adopted new systems of crop rotation in different areas. For example, Punjab has adopted a Wheat-Rice rotation system, and U.P. has taken to Wheat-Sugarcane crop-rotation system.
Question 24.
What are the indications that depict that Indian agriculture is advancing towards commercial agriculture leaving behind the subsistence type of agriculture?
Answer:
Subsistence farming means the raising of crops for the local consumption according to needs of the farmer and his family. In commercial farming the surplus is sold in the market. The following factors have been responsible for transforming Indian agriculture from subsistence to commercial farming:
- The Govt, has passed legislative measures to abolish the Zamindari system.
- Chakbandi has consolidated scattered land holdings of the farmers to make it of economic size.
- Cooperative movement has helped the farmers to collectively tackle their problems of credit and marketing.
- National banks provide loans to farmers on relatively easy terms.
- The Agricultural Price Commission fixes the minimum support prices for various crops. The farmers are not compelled to sell their products at low prices,
Question 25.
What efforts have been made by Government of India for the development of Agriculture?
Answer:
The Central and State governments have taken the following five important steps for the progress of agriculture in India:
- Consolidation. The government under the five year plans have consolidated the small holdings into big blocks in order to mechanize the agriculture.
- Supply of quality seeds. The government has undertaken to supply seeds of good quality to the farmer so that agricultural output is increased.
- Supply of fertilizers. The government, therefore, has started supplying chemical fertilizers to the farmers. Many factories have been set up to meet the demand of chemical fertilizers.
- Modern means of agriculture. In order to increase the agricultural output new machines are being used for agriculture.
- Means of irrigation. Many multipurpose projects have been completed. Dams have been built across the rivers and the water thus stored is used for irrigation. Bhakra-Nangal project and Damodar Valley Corporation are examples of this type of projects.
III. Answer the following questions subjectively:
Question 1.
Explain, in detail, the problems being faced by the Indian Agriculture.
Answer:
The main problems of Indian Agriculture are as under:
- The most important problem of Indian Agriculture is the pressure of population on land. About 65% workers depend upon agriculture for their livelihood; but earn only 29% of the National income.
- Most of the land holdings are small and unequally distributed. These are uneconomic.
- The area under forests and pastures is low. Therefore soil erosion has an adverse effect on soil fertility.
- Most of the farmers are illiterate. They cannot practise crop-rotation. So the natural fertility of the soil decreases. So intensive agriculture affects the fertility of the soil.
- Irrigation has become a problem in India. There is necessity of extending irrigation facilities in Rajasthan, Maharashtra, M.P., Karnataka, etc.; but due to over-irrigation in Punjab the problems of water logging and saline soils have been created.
- The capital investment in Agriculture is decreasing. In 1980-81, the capital investment was Rs. 1769 crores, but in 1990-91 it decreased to Rs. 100 crores. After that this capital investment is on increase.
- Marginal development has taken place in development of better seeds.
- Diversification of crops and slow growth is also a problem.
- The fact is that Govt, has a strict control on agriculture and prices. Farmers cannot be provided adequate facilities like industries.
Question 2.
Write an explanatory essay on the Green Revolution of India.
Answer:
Green Revolution is a new strategy used to increase the production of foodgrains in the country. A revolution has taken place in the agricultural methods and technology. This revolution is known as Green Revolution. It includes the use of better quality seeds, high yielding varieties, chemical fertilizers, agricultural machinery and to provide irrigation facilities. It has led to a complete modernisation of Indian Agriculture.
This strategy was introduced to do away with food shortage and import of foodgrains. In 1961 seven districts were selected for this programme. In Punjab, Ludhiana was one of these districts. Green Revolution affected the whole of Punjab. Punjab became the bread basket of India. Yield per hectare of wheat rose to 3531 kg. in 1985-86. But in India it was 2132 kg. In fact, Green Revolution helped to increase production on less land.
Question 3.
Explain in detail about the cultivation of Paddy in India.
Answer:
Rice. Rice is the leading agricultural crop of India. It is the staple food of 2/3rd of her population. Suitable geographical environment for its cultivation, its production and trade are described ahead:

Geographical conditions. The geographical conditions suitable for rice cultivation are the following:
- Rice is the product of moist tropical region. It requires high temperature. The temperature should not be more than 25°C. At the harvest times especially, the temperature should be high.
- Rice requires great amount of water. A rainfall between 130 and 200 cms is suitable for it. A good crop of rice mainly depends on the Monsoon. Deficiency in rainfall can be made up by irrigation.
- Very fertile soil is needed for rice cultivation. Clay and delta soils are most suitable for it.
Rice requires a lot of manual labour. Therefore, cheap labour should be available for its cultivation. Therefore rice is grown in densely populated areas.
Rice Producing Areas. India stands next only to China in the production of rice. In India, West Bengal produces largest quantity of rice. Tamil Nadu and Jharkhand are second and third producers of rice respectively. Rice is also grown in Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, Assam, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Haryana. In 2011-12 rice was grown in 4.3 crore hectares of land in India and the total output of rice was 9.5 crore tonnes.
Question 4.
Explain in detail about the cultivation of wheat in India.
Answer:
Wheat is an important foodgrain.
Geographical conditions. The following geographical conditions are suitable for wheat cultivation:
- Wheat requires lowr temperature during the growing period and high temperature at the harvesting period. At the sowing time temperature should be about 15°C to 20°C and at the time of ripening the temperature should be between 20°C and 25°C.
- Wheat can be grown in areas of moderate rainfall. 50 to 75 centimetres rainfall is quite suitable for its cultivation. The rain should be well distributed
- The soil should be fertile. Loamy soil is very suitable for wheat cultivation.
- The land should be even for the convenience of irrigation.
Production. India occupies fourth position as a producer of wheat in the world.
Green revolution has brought many changes. In 1960-61 wheat production was 1.6 crore tonnes. In 2011-12 it increased to 8.5 crore tonnes.
Wheat Producing States. Although wheat is cultivated in almost every part of the country except the southern part of the Indian peninsula, it is essentially a crop of North India. Uttar Pradesh produces highest quantity of wheat in India. Punjab occupies second position as a producer of wheat in India. Haryana is also an important producer of wheat.

The states of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Maharashtra also grow some wheat.
Question 5.
Write about the cultivation of pulses in India.
Answer:
The production of pulses has not shown any marked increase in India. India is still the largest producer of the pulses. Main pulses include Grams, Arhar, Masur, Mung and Peas. It is grown in dry areas all over the country in both the Kharif and Rabi season.
The area under pulses has not increased because a large area was cultivated for wheat and rice after green revolution. In 1960-61 pulses were cultivated in an area of 2.6 crore hectares. But in 2000-01 it reduced to 2.23 crore hectares showing a decrease of 30 lakh hectares during the last 34 years.
The production of pulses was 1.3 crore tonnes in 1960-61 and increased to 2.5 crore tonnes in 2010-11. With better seeds, the production of pulses can be increased.
Question 6.
Highlight the causes that led to decrease in area under oilseeds after Green Revolution. What steps have been taken by the government to increase the cultivation of oilseeds?
Answer:
Oilseeds are grown in combination with other crops to increase the soil fertility. It acts as pivot in crop rotation. After green revolution the area under oilseeds had decreased. In 1975-76 the area under oilseeds was 3.2 lakh hectares. In 1991 it decreased to 1.0 lakh hectares.
Steps taken. The Government is providing better seeds to increase oilseeds production. Good prices have been offered for oilseeds so that farmers should take interest in its cultivation.
Question 7.
Write a comprehensive essay on the cotton production in our country.
Answer:
Cotton is an important fibre crop. The cotton yarn is used for manufacturing cloth. Cotton plantation in India has been done since ancient times (during Indus civilisation). The Babylonians called it ‘Sandhu’ and Greeks called it ‘Sindo’.
Geographical conditions. Given below are the physical requirements of cotton cultivation:
- High temperature is needed for cultivation of cotton crop. Average temperature should be between 30°C and 35°C.
- A moderate amount of rainfall is required for cultivation of cotton. Cotton can be easily grown in area with 50 to 100 cms of rainfall. Irrigation is used in dry areas.
- During the growing period of the cotton plants the relative humidity should be high. At the time of picking the weather should be dry.
- Cotton can be grown in many types of soils but loamy soil is ideal for its growth. In India it is mostly grown in the black cotton soil region of Gujarat and Maharashtra. A special feature of black soil is that it can retain moisture for a long period and the need for irrigation is minimised. In Punjab and Haryana cotton is grown in alluvial soil.
- Most of the activities connected with cotton cultivation require manual labour. Therefore large amount of cheap labour is essential.
Sowing and harvesting periods. In most parts of India cotton is a summer crop. It is sown from April to June and harvested in the months of September and October. In Gujarat it is sown in the month of June and harvested in October. In Tamil Nadu cotton is sown in September and harvested in the month of March.
Production. India is the fourth biggest producer of cotton in the world. India produces about 700 lakh bales of cotton, each bale weighing 170 kilograms. In 2011-12 the area under cotton cultivation was 86 lakh hectares.
State-wise distribution. Maharashtra state is the biggest producer of cotton in India and produces about 26.3 lakh bales of cotton. The other important cotton producing states of India are Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka. Punjab, Gujarat (second largest producer), Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh. Most of the cotton grown in India is of short staple type but the cultivation of long staple American and Egyptian cotton is on the increase.
Question 8.
Explain the main features of Horticulture in India.
Answer:
Horticulture means cultivation of vegetables, flowers and fruit. Its main characteristics are:
- India ranks second in the world in the production of fruit and vegetables. The production of fruit was 3.9 crore tonnes and the production of vegetables was 6.5 crore tonnes.
- Different types of fruit, vegetables and flowers are grown due to diverse climatic conditions. Tea and coffee on hill slopes and coconut in coastal areas are grown.
- India ranks first in the world in the production of bananas, mangoes, coconuts and cashewnuts. India is a large producer of oranges, apples, potatoes, tomatoes, onions and peanuts.
- The exports of these products is 25% of the total exports of India.
- Floriculture has increased due to demand in foreign countries. 200 units have been selected to export flowers.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh states lead in the production of apples, Maharashtra in the production of oranges and bananas, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in the production of mangoes and Kerala in the production of cashewnuts.
The production of fruits and vegetables has rapidly increased in Punjab. In 2000-01, the production was 8 lakh tonnes. Hoshiarpur, Ferozpur, Amritsar and Faridkot are the leading districts. 26.6 thousand hectares of land is under kinoo gardens and orange plantation.
IV. Show the following on the map of India:
Question 1.
(i) Main Wheat producing areas
(ii) Main Jowar-Bajra producing areas
(iii) Main Cotton producing areas
(iv) Main Rice (paddy) producing areas
(v) Main Oilseeds producing areas
(vi) Sugarcane producing areas
(vii) Main Pulses producing areas
(viii) Maize producing areas
Answer:

Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here