PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Population
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Population
PSEB 10th Class SST Solutions Geography Chapter 7 Population
PSEB 10th Class Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Population
→ Manpower – A human resource.
→ Total Population of India:
- 126 crores
- The second-largest populated country in the world.
→ The average density of population (2011) – 382 persons per sq. km.
→ The State with the highest density of population – Bihar (1102 persons per km2)
→ The State with the lowest density of the population – Arunachal Pradesh (17 persons per km2)
→ The union territory with the highest density of population. – Delhi. (11297 persons per sq. km.)
→ The state has the largest population – U.P. (199581477 persons).
→ Rate of growth of population during 2001-2010 – 17.7%.
→ The State with the highest rate of growth of population – Meghalaya (27.8%).
→ The State with the lowest rate of growth of population – Kerala (4.9%).
→ Percentage of the urban population in India – 31.2%.
→ Total urban population – 37.7 crores.
→ The state with the highest % of urban population – Goa (49.77%)
→ Number of million towns (2011) – 53
→ The total population in million towns – 1500 lakh persons.
→ Average sex ratio in India (2011) – 940 females per 1000 males.
→ Highest sex ratio in India – Kerala (1084 females per 1000 males)
PSEB 10th Class Social Science Guide Population Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions in one word or one line:
Question 1.
What was the total population of India in 2011?
Answer:
121 crores.
Question 2.
Where does India rank in world population?
Answer:
2nd.
Question 3.
When was last census held in India?
Answer:
2011.
Question 4.
What is birth rate in India?
Answer:
26 per thousand.
Question 5.
What is sex ratio in India?
Answer:
940.
Question 6.
Which state ha’s highest sex ratio?
Answer:
Kerala
Question 7.
Which state has lowest sex ratio?
Answer:
Haryana.
Question 8.
What is literacy rate in India?
Answer:
65%.
Question 9.
Which state has the highest density of population?
Answer:
Bihar.
Question 10.
Which state has the largest poulation?
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh.
Question 11.
What is average density of population in India?
Answer:
382 persons per sq. km.
Question 12.
Which state has lowest density of population?
Answer:
Arunachal Pradesh.
Question 13.
Write down any four characteristics of population census.
Answer:
The four characteristics of population census are distribution of population, density of population, literacy, the age-sex ratio.
Question 14.
What do you mean by distribution of population?
Answer:
Distribution of population means the nature of population and its concentration at one place.
Question 15.
What do you mean by density of population?
Answer:
Density of population means the average number of persons living in a unit square area. It is shown per sq. km.
Question 16.
What is the main factor affecting the distribution of population and why?
Answer:
Agricultural production is the main factor affecting the distribution of population because India is an agricultural country.
Question 17.
Name any four factors affecting the structure of distribution of population.
Answer:
- Agricultural production
- Diversity in natural factors
- Industrialisation
- Cultural reasons.
Question 18.
Name the three states having low density of population.
Answer:
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Nagaland
- Manipur.
Question 19.
Which communities have .the highest and lowest sex ratio in India?
Answer:
Christians have the highest sex ratio (994 women per thousand men) and Sikhs have the lowest sex ratio (886 per thousand men) in India.
Question 20.
What are the bad results of increasing population in urban areas?
Answer:
There is heavy rush on available sources and public services due to increase in population in urban areas. It becomes very difficult for people to meet fMeir basic needs.
Question 21.
What is meant by sex ratio? :
Answer:
The numerical ratio between females and males is called sex ratio.
Question 22.
Distinguish between productive and dependent population.
Answer:
By productive population we mean those persons who follow different professions and earn money. Children and old persons are included in the dependent persons.
Question 23.
Name four racial groups living in India.
Answer:
The racial grqups living in India are:
- Dravid, Mangol,
- Arya, Caucasiun
Question 24.
Which languages of India are of Dravidian origin?
Answer:
- Tamil in Tamil Nadu State
- Telugu in Andhra Pradesh
- Kannada in Karnataka
- Malayalam in Kerala.
Question 25.
What are the two reasons of decrease in death rate?
Answer:
- The main reason is increase in health services.
- Due to spread in education, death rate has fallen down.
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1 .
_______ is a human resource.
Answer:
Population
Question 2.
India ranis _______ in world population.
Answer:
second
Question 3.
India has a total population of ______ crores.
Answer:
131
Question 4.
Punjab has a population of ________crores.
Answer:
77
Question 5.
Most of population lives in _________ areas.
Answer:
rural.
Mulitiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
What is the total population of India (2011)?
(a) 102 crore
(b) 112 crore
(c) 118 crore
(d) 131 crore.
Answer:
(d) 131 crore.
Question 2.
When was first census held in India?
(a) 1971
(b) 1881
(c) 1891
(d) 1861.
Answer:
(b) 1881
Question 3.
Which state has the lowest population?
(a) Punjab
(b) Sikkim
(c) Assam
(d) Rajasthan.
Answer:
(b) Sikkim
Question 4.
What is the average sex ratio in India ?
(a) 910
(b) 930
(c) 933
(d) 940.
Answer:
(d) 940.
Question 5.
The literacy rate in India is :
(a) 55%
(b) 60%
(c) 65%
(d) 67%.
Answer:
(c) 65%
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State three reasons for the uneven distribution of population in India.
Answer:
The distribution of population in India is unequal. According to 2011 census, the total population of India is 121 crore and the density of population is 382 persons per sq. kilometre. The density of population varies according to relief, climate and the agricultural productivity of the land. The density of population depends on the amount of rainfall.
The areas of sufficient rainfall can support a large number of people.
1. Densely populated areas. These areas have a density’of more than 400 persons per sq. kilometre. The high density areas make a girdle round the Deccan plateau. Right from Sutlej-Beas plain to Brahmputra valley, the density of population is very high.
(a) West Coastal Plain: Kerala has 859 persons per sq. kilometre density of population.
(b) East Coastal Plain: Tamil Nadu has a density of 555 persons per sq, kilometre.
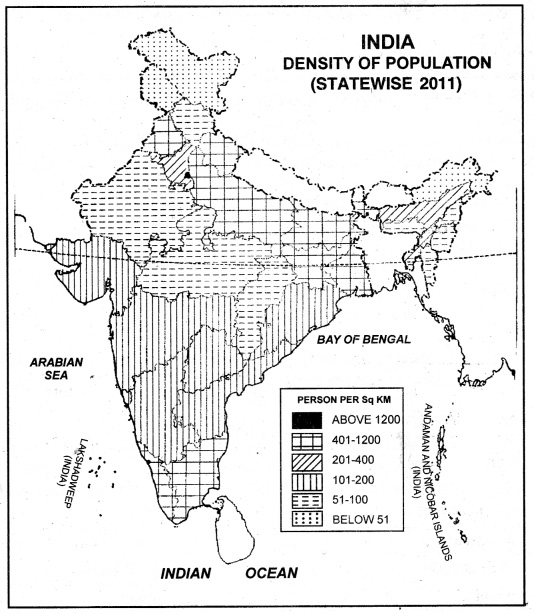
(c) The Northern Plain: It includes West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab.
Factors favouring high density:
(0 Sufficient rainfall
(ii) Fertile river valleys and deltas.
(iii) 2 to 3 crops of rice in a year.
(iv) Irrigation facilities.
(iv) Healthy climate.
(vi) Rich in mineral and power resources.
2. Moderately populated areas. These include the areas with a density between 200 to 400 persons per sq. kilometre. These areas are surrounded by Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats. Haryana, Maharashtra, Andhra Pardesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Orissa, Goa, Assam have a moderate density.
Factors for moderate density:
- Agriculture is not developed due to thin and rocky soils.
- Rainfall is uncertain.
- Means of transportation are not developed.
- Some areas have high density of population due to irrigation, lava, soils and mineral resources.
3. Sparsely populated areas.
These areas have a density less than 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(a) North Eastern India. This region includes Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(b) Rajasthan Desert. Rajasthan has a density of 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(c) Western Himalayas. It includes Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. Factors for low density :
- The hilly nature of the land.
- Dense forests.
- Low rainfall
- Poor econoufic development.
- Absence of minerals.
- Lack of irrigation and agriculture.
- Cold climate.
Question 2.
Throw light on some important aspects of population of India.
Answer:
- India is one of the selected countries where population concentration is found.
- After independence, population of India has increased 4 times.
- India has an average population of 3 crores for each state.
- U.P. has the highest population in India.
- Average density of population is 382 persons per sq. km.
- West Bengal has the highest density of population.
Question 3.
How is the growth of population a problem for India ?
Answer:
After independence, the land-area has been fixed in India but the population has increased manifold. The growth of population is 1.7 per-cent. It is a great problem to provide basic amenities to such a huge population. It is not easy to provide the facilities of education, hospitals and other facilities to all. We shall have to increase the transport and communication facilities also. We shall have to cultivate quality in our population.
Question 4.
State the adverse effects of rapid growth of population in India.
Answer:
The rapid growth of population has posed many socio-economic problems in different countries. The main problems are:
- Food problem. Growth of the population has led to shortage of foodgrains in many areas.
Agricultural production has increased due to new technology, yet many countries have to import agricultural products. - Housing problem. Housing conditions are poor in over-populated countries. People live in slum areas. Skyscrapers are being built in many Metropolitan towns.
- Unemployment. Rapid increase in population leads to unemployment. Migration of people from over-populated rural areas has added to Unemployment.
- Low standard of living. Per capita income is low in overcrowded areas so living conditions are poor. People do not afford to have basic necessities of life. Population explosion leads to poverty and a poor standard of living.
- Dependent population. A large percentage of young people become dependent on a small working population.
- Social problems. Many social problems arise due to overcrowding. Poor health and bad sanitary conditions lead to epidemics.
Question 5.
Why is the occupational structure of India lop sided?
Answer:
Two thirds of our population still lives on agriculture. Only 10% of the working population is engaged in industry. The rest one fourth of population is in the tertiary or service sector. This makes clear that a small proportion of our population is engaged in secondary sector of economy. The secondary sector includes manufacturing by which we can increase our national income by producing useful products. So there are not more people employed in manufacturing. So our occupational structure is lop sided.
Question 6.
Why are the Northern plains densely populated?
Answer:
The distribution of population in India is unequal. According to 2011 census, the total population of India is 121 crore and the density of population is 382 persons per sq. kilometre. The density of population varies according to relief, climate and the agricultural productivity of the land. The density of population depends on the amount of rainfall.
The areas of sufficient rainfall can support a large number of people.
1. Densely populated areas. These areas have a density’of more than 400 persons per sq. kilometre. The high density areas make a girdle round the Deccan plateau. Right from Sutlej-Beas plain to Brahmputra valley, the density of population is very high.
(a) West Coastal Plain: Kerala has 859 persons per sq. kilometre density of population.
(b) East Coastal Plain: Tamil Nadu has a density of 555 persons per sq, kilometre.
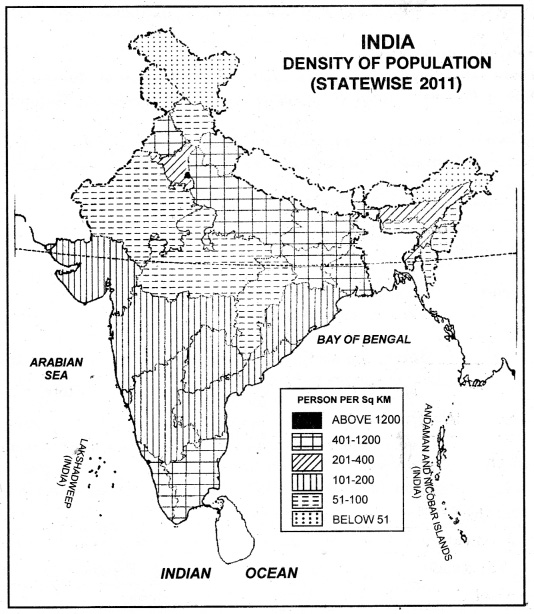
(c) The Northern Plain: It includes West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab.
Factors favouring high density:
- Sufficient rainfall
- Fertile river valleys and deltas.
- 2 to 3 crops of rice in a year.
- Irrigation facilities.
- Healthy climate.
- Rich in mineral and power resources.
2. Moderately populated areas. These include the areas with a density between 200 to 400 persons per sq. kilometre. These areas are surrounded by Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats. Haryana, Maharashtra, Andhra Pardesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Orissa, Goa, Assam have a moderate density.
Factors for moderate density:
- Agriculture is not developed due to thin and rocky soils.
- Rainfall is uncertain.
- Means of transportation are not developed.
- Some areas have high density of population due to irrigation, lava, soils and mineral resources.
3. Sparsely populated areas.
These areas have a density less than 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(a) North Eastern India. This region includes Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(b) Rajasthan Desert. Rajasthan has a density of 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(c) Western Himalayas. It includes Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. Factors for low density :
- The hilly nature of the land.
- Dense forests.
- Low rainfall
- Poor econoufic development.
- Absence of minerals.
- Lack of irrigation and agriculture.
- Cold climate.
Question 7.
Name three sparsely populated areas of India. Give reasons.
Answer:
The rapid growth of population has posed many socio-economic problems in different countries. The main problems are:
- Food problem. Growth of population has led to shortage of foodgrains in many areas.
Agricultural production has increased due to new technology, yet many countries have to import agricultural products. - Housing problem. Housing conditions are poor in over-populated countries. People live in slum areas. Skyscrapers are being built in many Metropolitan towns.
- Unemployment. Rapid increase in population leads to unemployment. Migration of people from over-populated rural areas has added to Unemployment.
- Low standard of living. Per capita income is low in overcrowded areas so living conditions are poor. People do not afford to have basic necessities of life. Population explosion leads to poverty and a poor standard of living.
- Dependent population. A large percentage of young people become dependent on a small working population.
- Social problems. Many social problems arise due to overcrowding. Poor health and bad sanitary conditions lead to epidemics.
Question 8.
Explain the following with reference to population of India.
(a) census
(b) density of population
(c) growth of population
(d) death rate.
Answer:
(a) Census. After every ten years, the Government arranges the counting of all persons of the country. It is called census. Some social and economic data is also collected. The last census in India was held in 2011. According to this census, the total population of India was 121 crores.
(b) Density of Population. Density of population means the average number of persons living in a unit sq. area. It is shown per sq. km. According to 2011 census, density of population in India was 382 persons per km2.
(c) Growth of Population. People, sometimes, migrate from one area to another due to epidemics or droughts or in search of employment. It increases or decreases the population of an area. In the area to which people migrate population increases. It is known as growth of population or decrease in population.
(d) Death Rate. Death rate means the number of deaths per 1000 persons.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Dependency Ratio? Why is it high in India? Give two reasons.
Answer:
The proportion between productive and dependent population is dependency ratio. Children and old people are dependent population. India has a joint family system. Therefore children and old people get livelihood automatically. Illiteracy has also increased it. Orthodox views increase this ratio.
Question 10.
What is major mistake done by Indian planning? What are its effects?
Answer:
The most important and pathetic mistake of the Indian Planning according to Dr. Sen is the development of institution, on the basis of caste etc. In Delhi, he said, “several buildings do not have public toilets, which is important for every building. As compare to other such as China, Pakistan, Bangladesh have expanded education system and health care facilities. But this is a pathetic condition in India.
Question 11.
Distinguish between distribution of population and density of population.
Answer:
Population in India is not evenly distributed. Many factors are responsible for this:
- Fertility of the soil. The states in which there is a large fertile area the density of population is high. U.P. and Bihar are such states.
- Amount of rainfall. The density of population is higher in regions of abundant rain. In northern India the amount of rainfall goes on decreasing from east to west. The density of population also goes on decreasing in the same direction.
- Climate. Wherever the climate is congenial the density of population will be high. In Assam even though there is abundant rainfall but the density of population is low because the climate is unhealthy. The malaria is always there is an epidemic form.
- Developed means of transportation. With development of means of transportation the business makes rapid progress and the density of population increases. The reason for high density of population in U.P., Bihar and West Bengal is the development of means of transportation.
- Industrial development. At places where the factories are located the density of population also increases. The reason is that people like to live in those areas where industrial development takes place. They can carry on their business more easily in such areas and they have better chances of earning more money. That is why the density of population is high in Delhi, Mumbai and Kolkata.
Question 12.
Why is the conservation of resources necessary?
Answer:
Man depends upon the environment to meet his needs. He uses water, land, soil, vegetation, etc. to satisfy his needs. Man is using these resources at such an alarming rate that there will be serious shortage of these resources in the near future. Natural resources are of limited supply. So, conservation of resources is essential for the survival of man.
To some people conservation means that the available resources should not be used. These should be held back. But conservation of resources means a careful and rational utilization of resources. These resources should be used intelligently for the welfare of mankind. It means a careful control and management of resources so that these may be usd for the benefit of future generations also. These should be preserved from reckless exploitation and wanton destruction. These resources should not be wasted in a short time. The resources should be maintained in a healthy condition for their use as to achieve a high standard of living for mankind.
Question 13.
Why is low density of population found in Rajasthan and Arunachal Pradesh?
Answer:
In some areas, it is difficult to get means of livelihood. These have a harsh climate. The soils are sandy or hilly. Agriculture is not possible. There is absence of irrigation and the production is low. Industries can not be developed in such areas. Therefore low density of population is found in Rajasthan and Arunachal Pradesh.
Question 14.
The people are important to develop the economy and society. Give three facts.
Answer:
- People use available resources.
- They create a social and cultural environment..
- Intelligent and hard working people make the real man power.
Question 15.
Define birth rate. What is its function with reference to population?
Answer:
Birth rate is the number of live births per 1000 persons in a year. It is a component of growth of population; because birth rate is always higher than death rate. The population increases when birth rate is higher tMn death rate.
Question 16.
Define death rate. What is its function with reference to population?
Answer:
Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year. It is a component of growth of population. Due to declining death rate, there is a rapid growth of population in India. When death rate is more than birth rate, the population growth is negative.
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
List factors influencing the distribution of population.
Answer:
The following factors influence the distribution of population:
1. Fertility of the soil. The states in which there is a large fertile area, the density of population is high. U.P. and Bihar are such states.
2. Amount of rainfall. The density of population is higher in regions of abundant rain. In. northern India, the amount of rainfall goes on decreasing from east to west. The density of population also goes on decreasing in the same direction.
3. Climate: Wherever the climate is congenial, the density of population will be high. In Assa even though there is abundant rainfall but the density of population is low because the climate is unhealthy. The malaria is always in an epidemic form.
4. Developed means of transporUition. With development of mans of transportation the business makes rapid progress and the density of population increases. The reason for high density of population in Ui., Biliar and West Bengal is the development of means of trahsportation.
5. Industrial development. At places whëre the faetones are located, thë density’ of population also increases. The reason is that people like to live in those areas where industrial development takes place. They can carry on tliei1 bushis mo easily in such areas, and they have better chances of earning more money. That iš why the density of population is high in Delhi, Mumbai and Kolkata.
SST Guide for Class 10 PSEB Population Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
What is the most important and valuable resource of a country?
Answer:
The healthy people of the country, mentally as well as physically, is the biggest natural resource of a country.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the development of human resources?
Answer:
The development of human resources is the framework for helping employees to develop their knowledge, skills and abilities, which improves an effectiveness of organisations. Because these are the people who with their abilities make a valuable material with the help of any natural resource. Human Resource Development is the vast field of training and development provided by organisations. HRD (Human Resource Development) can be formal like in classroom training, a college course etc.
Question 3.
What is the most important and pathetic mistake of the Indian Planning according to Dr. Amertya Sen?
Answer:
The most important and pathetic mistake of the Indian Planning according to Dr. Sen is the development of institution, on the basis of caste etc. In Delhi, he said, “several buildings do not have public toilets, which is important for every building. As compare to other such as China, Pakistan, Bangladesh have expanded education system and health care facilities. But this is a pathetic condition in India.
Question 4.
What problem is being faced by our country for not paying full attention to the development of Human Resources?
Answer:
The following problems are being faced by our country for not paying full attention to the development of Human Resource:
- In the Development of the country, Human Resources play an important role. So, not paying full attention to the development of Human Resources is a big mistake. With this our economic failures arise. Because of not paying full attention on social justice issues, economic decisions taken in independent India, not beneficial for women, poor people and vulnerable people. So problem of Economic issues arise.
- Recruitment, Retention and Motivation.
- Work force security issues is also a great problem.
- Human resources are the ultimate resource of nature because they uses technology and skills and add value to natural resources and if they ignored, ultimately our country faced several economic, social and political issues.
Question 5.
What were the causes of slow increase in population before independence?
Answer:
The causes of this slow growth were epidemics, wars and famines which increased death rate.
Question 6.
What was the population of India in the year 1901?
Answer:
The population of India was 23,83,96,327 (23.8 crore) in the year 1901.
Question 7.
Why the 1921 and 1951 years have been considered as population divider?
Answer:
Population increased rapidly after the years of 1921 and 1951. Therefore, these years are called demographic divide (population divider).
Question 8.
What was the population of India in the year 2011?
Answer:
The. population of India was 121 crores in the year 2011.
Question 9.
What is rank of India in the world from the population point of view?
Answer:
India ranks second in world (after China) in the view of population.
Question 10.
Write the name of the states with highest and lowest population.
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh has the highest population (19.9 crore) and Sikkim has the lowest population (6 lakh) in India.
Question 11.
How many states have the population of more than 5 crores?
Answer:
There are 10 states of India in which population is more than 5 crores.
Question 12.
What was the population of Punjab irr the year 2011 and what is the rank of Punjab from the population point of view?
Answer:
The population of Punjab was 2.77 crores in the year of 2011 and Punjab ranks 15th in the country in the view of population.
Question 13.
What percentage of population of India lives in Punjab?
Answer:
Almost 2.3 percent of total population of country lives in Punjab.
Question 14.
How many cities are there in India with a population of more than one lakh?
Answer:
There are 302 cities in India with the population of more than one lakh.
Question 15.
How much per cent of population of our country lives in plains?
Answer:
40% of population of the country lives in the plains.
Question 16.
How much percentage of population of the country lives in villages?
Answer:
69% of population of the country lives in the villages.
Question 17.
What is the average density of population in our country?
Answer:
The average density of population in India is 382 persons per square kilometre.
Question 18.
Name the states having highest and lowest density of population.
Answer:
Bihar is the state with largest density of population (1102) and Arunachal Pradesh is the state with lowest density of population (17) in India.
Question 19.
What is density of population of India?
Answer:
The density of population of India is 382 sq.km.
Question 20.
Which union territory has the highest density of population?
Answer:
National Capital Area Delhi has the largest density of population (11297).
Question 21.
Name the elements that determine the age structure.
Answer:
The factors which determine the age structure are:
- Fertility
- Mortality
- Migration.
Question 22.
What is percentage of population that falls in the 0-14 years age group in our country?
Answer:
37.2% of population is found in the country with the age group of 0-14 years.
Question 23.
What percentage of population falls in the 15-65 years age group in our country? ,
Answer:
58.4% of population is found in the country with the age group of 15-65 years.
Question 24.
What is the percentage of population that are voters?
Answer:
There is 60% of population as voters in the country.
Question 25.
What do you understand by sex ratio?
Or
What is meant by sex ratio?
Answer:
The number of women per thousand men is sex ratio.
Question 26.
What are the factors that are responsible for the decrease in rural and urban sex ratio?
Answer:
Following are the factors responsible for the decrease in rural and urban sex ratio:
- Social factors Indian society is patriarchal and male centric thoughts force. One family to have male child with old beliefs such as nomination process.
- Technological Factors. Ultrasoniography is the advent of science has made it possible for antenatal detection of sex.
- Economifcal factors. Social Evils such as dowry, etc. also considered economic burden for family. So people prefer male child.
- Lack of awareness. Because there is low contribution on female education, so they are not considered as important as males.
- Security issue. Also considered a major problem in the country.
Question 27.
What is the sex ratio among the Sikh segment of our country?
Answer:
Question 28.
Which people are called main workers of India?
Answer:
The main workers of India are those people who have done work for six months ih the last year (or 183 days) in any economic activity.
Question 29.
When was the concept of classifying the people as workers and non-workers introduced for the first time in India’s census?
Answer:
According to work, the population was divided into working Arid non-working population in the year 1961.
Question 30.
What percentage of labourers is there in rural areas?
Answer:
The percentage of labourers in the rural areas is 40%.
Question 31.
What is total urban population?
Answer:
The total urban population in India is 37.47%.
Question 32.
In which two categories can we divide population of India on economic basis.
Answer:
- Main workers, Marginal workers.
- Non-workers.
II. Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
What problems arise due to uneven distribution of population in states?
Answer:
There are 28 states in India. There is uneven distribution of population in these states. Many problems have been created as:
- Transport problem: It is a great problem to connect isolated rural settlement with towns by road.
- Basic needs: It is difficult to-provide basic facilities to rural areas.
- Other problems: Problems like Pollution, Transport, Settlement etc.


Question 2.
What are the factors that affect the distribution of population?
Answer:
Population in India is not evenly distributed. Many factors are responsible for this:
- Fertility of the soil. The states in which there is a large fertile area the density of population is high. U.P. and Bihar are such states.
- Amount of rainfall. The density of population is higher in regions of abundant rain. In northern India the amount of rainfall goes on decreasing from east to west. The density of population also goes on decreasing in the same direction.
- Climate. Wherever the climate is congenial the density of population will be high. In Assam even though there is abundant rainfall but the density of population is low because the climate is unhealthy. The malaria is always there is an epidemic form.
- Developed means of transportation. With development of means of transportation the business makes rapid progress and the density of population increases. The reason for high density of population in U.P., Bihar and West Bengal is the development of means of transportation.
- Industrial development. At places where the factories are located the density of population also increases. The reason is that people like to live in those areas where industrial development takes place. They can carry on their business more easily in such areas and they have better chances of earning more money. That is why the density of population is high in Delhi, Mumbai and Kolkata.
Question 3.
What is the importance of Economic Structure of Population?
Answer:
Importance of Economic Structure of Population:
- We come to know the percentage of people engaged in productive work.
- It shows the cultural composition of population which determines the stage of development of a country.
- It marks the backward areas of the country so that proper planning can be done.
Question 4.
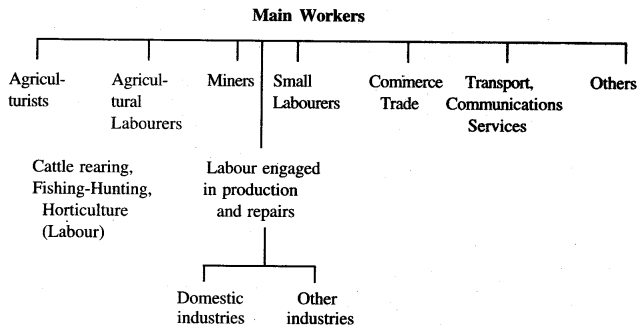
Into how many categories can we divide main workers? Name them.
Answer:
The table below shows the categories of main workers:
Question 5.
Why is there more percentage of male workers than female workers?
Answer:
The percentage of male workers is 37.50 in India (about 1/3rd of population)
- This is due to rapidly growing population. It increases the dependent population.
- Females are not allowed to go out for work,
- There is absence of female awareness and education.
Question 6.
Why is India known as a country of villages?
Answer:
There is no doubt that India is a country of villages.
- Most of the people live in villages.
- 3/4th of population lives in rural areas.
- There are more than 5 lakh and 50 thousand rural settlements, but 71% of urban population lives in 302 towns.
- About 40.1% of labourers live in rural areas and 30.2% of labourers live in urban areas.
Question 7.
Name the languages spoken in our country.
Answer:
There is a great diversity in languages spoken in India.
Assamese, Orriya, Urdu, Kannad, Kashmiri, Gujrati, Tamil, Telugu, Punjabi, Bangla, Malyalam, Sanskrit, Sindhi and Hindi are the main languages of India. These have a constitutional status. The languages of the South Tamil, Telugu, Kannad and Malyalam have their origin fthm Dravidian system. A large number of people ih India speak Hindi, understand Hiridiffe^bn if it is not their mother tongue. Hindi is the national language of India.
Question 8.
What are characteristic features of regional distribution of population?
Answer:
Characteristic features of regional distribution of population:
- The distribution of population is uneven in India. There is dense population in river valleys and coastal plains. There is sparse population in hilly areas, deserts and drought affected areas. 16% of the area of the country, in the Northern plains only 3% people of India live. 94% of population lives on an area of 18% in plains. Only 2% population lives on an area of 6% in Rajasthan.
- Most of the people live in villages. Only 31% people live in urban areas.
- A large part of minorities live in sensitive border area. Along the N.W. border of India; Sikhs in Punjab and Muslims in J & K, form a majority community. Along the borders of China and Burma, in the North-East, mostly Christians are found. It has created many political, economic and social problems.
- On the one hand, there is concentration of population in river valleys and coastal areas, but deserts, hilly areas are sparsely populated. It looks like a demographic divide.
Question 9.
Which are the states which have high density of population?
Answer:
There is dense population in Northern plain, western coastal plain, Eastern Coastal plain (Deltas). These areas have fertile soils and facilities of irrigation. So the population is dense. As we go westward, the rainfall goes on decreasing and the density of population also decreases. That is why the density of population in West Bengal is greater than that in Haryana and Punjab. Kerala has also high density because two or three crops can be grown due to high rainfall.
Question 10.
What are the causes of high density of population in plains?
Answer:
The density of population is high in plains. This is due to:
- The Northern plain is fertile.
- It has high rainfall.
- It has many big industrial centres.
- The means of transport are developed.
- Coastal plain has facilities of fishing and foreign trade.
Question 11.
What are the areas of low density of population?
Answer:
Arunachal Pradesh is the ara of low density of population followed by Andaman and Nicobar, Mizoram and Sikkim as per the census 2011.
Question 12.
Name the areas of low density of population. What are the causes of low density of population?
Answer:
Thar Desert, Eastern Himalayas and Chotta Nagpur plateau are sparsely populated areas.
- The soils are infertile or sandy or stony.
- The means of transport are not developed
- The climate is not healthy. It is either too hot or too cold. Himalayas get heavy rainfall.
- Industries are not developed in these areas except Chotta Nagpur plateau.
Question 13.
Why is it necessary to study the structure of population?
Answer:
It is necessary to study the structure of population of a country due to:
- We need different components of population such as age structure, sex ratio, occupational structure for the economic and social planning of a country.
- The different aspects of population have a close relationship with development on the one hand, These are affected by population and on the other hand these affect population and ’development. For example, if the percentage of children and old age people is high in age structure, a country has to spend more on education and health facilities. On the other hand, a high percentage of working age group encourages the economic development of a country.
Question 14.
Name the areas with small population.
Answer:
Sikkim, Lakshadweep are the areas with small population.
Question 15.
What is the importance of study of age structure?
Answer:
These are the advantages of study of age structure of population:
- By determining the 0-14 age group the govt, knows that there is need of expenditure on education, health and social services. So new schools, health centres and community centres are opened.
- We know the number of eligible voters in the country which is vital for a democracy. There should be 58% voters per age group, but actually there are 60% of voters in the country.
Question 16.
What are the causes of low sex ratio in India?
Answer:
The sex ratio of India is 940 per thousand males. There is a general declining trend in sex ratio. The ratio in 1901 was 972, It was declined to 934 in 1981. This decline has been due to social evils in our society.
In our society, female child is neglected. Male population dominates in our society. There is high death rate among females. Death rate is particularly high among married women. Women labour migrates to some mining and industrial centres. It also results in declining sex ratio.
Question 17.
What are the causes of increase in urban population in India?
Answer:
The rapid growth of population has posed many socio-economic problems in different countries. The main problems are :
- Food problem. Growth of population has led to shortage of foodgrains in many areas.
Agricultural production has increased due to new technology, yet many countries have to import agricultural products. - Housing problem. Housing conditions are poor in over-populated countries. People live in slum areas. Skyscrapers are being built in many Metropolitan towns.
- Unemployment. Rapid increase in population leads to unemployment. Migration of people from over-populated rural areas has added to Unemployment.
- Low standard of living. Per capita income is low in overcrowded areas so living conditions are poor. People do not afford to have basic necessities of life. Population explosion leads to poverty and a poor standard of living.
- Dependent population. A large percentage of young people become dependent on a small working population.
- Social problems. Many social problems arise due to overcrowding. Poor health and bad sanitary conditions lead to epidemics.
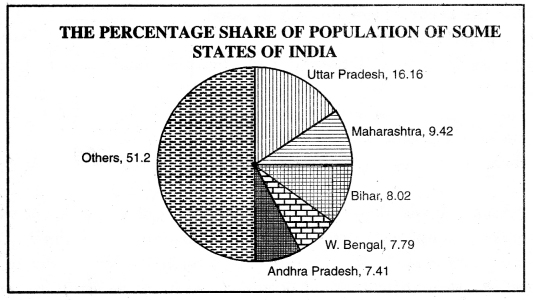
The percent share of population of some states of India’s total population
III. Answer the following questions subjectively:
Question 1.
Explain the regional structure of density of population in India.
Answer:
The distribution of population in India is unequal. According to 2011 census, the total population of India is 121 crore and the density of population is 382 persons per sq. kilometre. The density of population varies according to relief, climate and the agricultural productivity of the land. The density of population depends on the amount of rainfall.
The areas of sufficient rainfall can support a large number of people.
1. Densely populated areas. These areas have a density’of more than 400 persons per sq. kilometre. The high density areas make a girdle round the Deccan plateau. Right from Sutlej-Beas plain to Brahmputra valley, the density of population is very high.
(a) West Coastal Plain: Kerala has 859 persons per sq. kilometre density of population.
(b) East Coastal Plain: Tamil Nadu has a density of 555 persons per sq, kilometre.
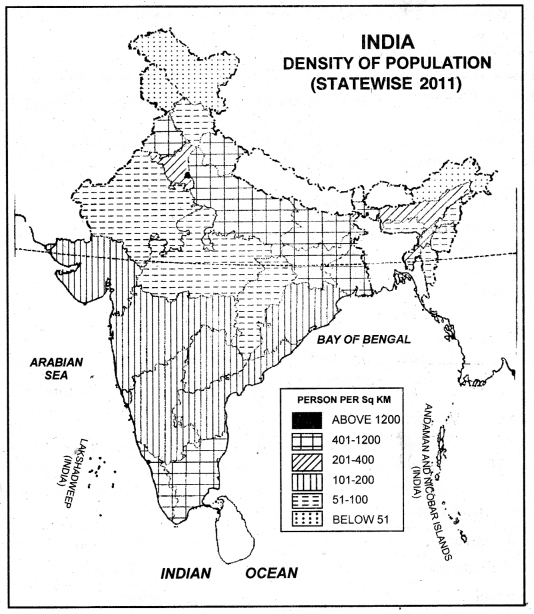
(c) The Northern Plain: It includes West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab.
Factors favouring high density:
- Sufficient rainfall
- Fertile river valleys and deltas.
- 2 to 3 crops of rice in a year.
- Irrigation facilities.
- Healthy climate.
- Rich in mineral and power resources.
2. Moderately populated areas. These include the areas with a density between 200 to 400 persons per sq. kilometre. These areas are surrounded by Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats. Haryana, Maharashtra, Andhra Pardesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Orissa, Goa, Assam have a moderate density.
Factors for moderate density:
- Agriculture is not developed due to thin and rocky soils.
- Rainfall is uncertain.
- Means of transportation are not developed.
- Some areas have high density of population due to irrigation, lava, soils and mineral resources.
3. Sparsely populated areas.
These areas have a density less than 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(a) North Eastern India. This region includes Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(b) Rajasthan Desert. Rajasthan has a density of 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(c) Western Himalayas. It includes Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. Factors for low density :
- The hilly nature of the land.
- Dense forests.
- Low rainfall
- Poor econoufic development.
- Absence of minerals.
- Lack of irrigation and agriculture.
- Cold climate.
Question 2.
Explain in detail the state-wise structure of sex ratio in India.
Answer:
Sex ratio means’the number of females per 1000 males. Now-a-days, women have equal rights with men. In developed countries, the number of women is equal to number of men. In some countries sex ratio is 1050. The average sex ratio in developing countries is 964. In India, in 2011, sex ratio was 940, and is one of the lowest in the world.
State-wise sex ratio. Sex ratio is not uniform in all states. Only one state, Kerala, has sex-ratio of 1084 and Puducherry (1036) (Above the average). In other states, sex ratio is less than average.
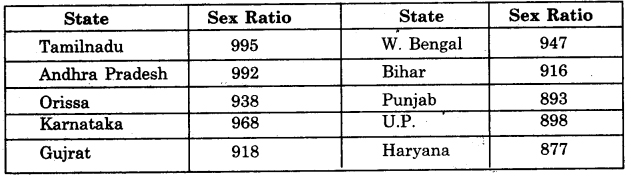
It is clear that Northern States have low sex ratio which is a matter of concern.
Question 3.
Explain the main characteristics of regional structure of distribution of population.
Answer:
The distribution of population in India is unequal. According to 2011 census, the total population of India is 121 crore and the density of population is 382 persons per sq. kilometre. The density of population varies according to relief, climate and the agricultural productivity of the land. The density of population depends on the amount of rainfall.
The areas of sufficient rainfall can support a large number of people.
1. Densely populated areas. These areas have a density’of more than 400 persons per sq. kilometre. The high density areas make a girdle round the Deccan plateau. Right from Sutlej-Beas plain to Brahmputra valley, the density of population is very high.
(a) West Coastal Plain: Kerala has 859 persons per sq. kilometre density of population.
(b) East Coastal Plain: Tamil Nadu has a density of 555 persons per sq, kilometre.
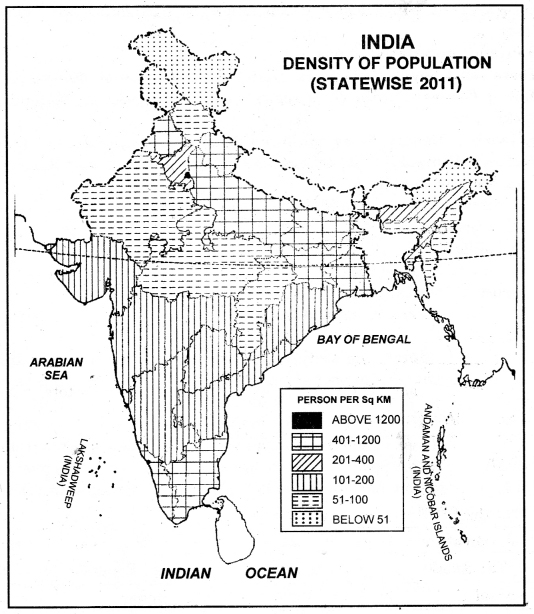
(c) The Northern Plain: It includes West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab.
Factors favouring high density:
- Sufficient rainfall
- Fertile river valleys and deltas.
- 2 to 3 crops of rice in a year.
- Irrigation facilities.
- Healthy climate.
- Rich in mineral and power resources.
2. Moderately populated areas. These include the areas with a density between 200 to 400 persons per sq. kilometre. These areas are surrounded by Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats. Haryana, Maharashtra, Andhra Pardesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Orissa, Goa, Assam have a moderate density.
Factors for moderate density:
- Agriculture is not developed due to thin and rocky soils.
- Rainfall is uncertain.
- Means of transportation are not developed.
- Some areas have high density of population due to irrigation, lava, soils and mineral resources.
3. Sparsely populated areas.
These areas have a density less than 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(a) North Eastern India. This region includes Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(b) Rajasthan Desert. Rajasthan has a density of 200 persons per sq. kilometre.
(c) Western Himalayas. It includes Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. Factors for low density :
- The hilly nature of the land.
- Dense forests.
- Low rainfall
- Poor econoufic development.
- Absence of minerals.
- Lack of irrigation and agriculture.
- Cold climate.
Question 4.
What problems are arising due to increase in urban population in metro cities?
Answer:
The rapid growth of population has posed many socio-economic problems in different countries. The main problems are:
- Food problem. Growth of population has led to shortage of foodgrains in many areas.
Agricultural production has increased due to new technology, yet many countries have to import agricultural products. - Housing problem. Housing conditions are poor in over-populated countries. People live in slum areas. Skyscrapers are being built in many Metropolitan towns.
- Unemployment. Rapid increase in population leads to unemployment. Migration of people from over-populated rural areas has added to Unemployment.
- Low standard of living. Per capita income is low in overcrowded areas so living conditions are poor. People do not afford to have basic necessities of life. Population explosion leads to poverty and a poor standard of living.
- Dependent population. A large percentage of young people become dependent on a small working population.
- Social problems. Many social problems arise due to overcrowding. Poor health and bad sanitary conditions lead to epidemics.
Question 5.
Write a note on the cultural structures of population of India.
Answer:
1. Races. Ethnically, India consists of several races, the Dravidians, the Mongoloids, the Arayans and the Caucasians. In course of time these races have intermingled, losing many of original traits and acquiring new ones from others. And yet we notice a great diversity which is so characteristic of the Indian people. In fact, the richness and beauty of India culture lies in its diversity. Its spirit of tolerance, give-and- take assimilation makes it one of the distinctive cultures of the world.
2. Faiths. The Indian people follow different faiths. These do not follow regional, political and linguistic barriers. They speak different languages ^languages cut across race, religion, caste and often region. Notwithstanding these facial, religious linguistic arid regional diversities, we are all Indians first and Indians last. Ours is a plural society with a composite culture. It can be compared to a fine mosaic or to a garden with flowers of various colours and shades. This maintaining entity of each lends colour and beauty to the total cultural landscape of our country.
3. Religions. India is the home of Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Zorastrians and others. None of these people enjoy any special privileges on the ground of their religion. Nor do they suffer in economic, political or social life because of their faith in a .particular religion. All are equal before law and enjoy full freedom. All are bestowed with equal rights, .entailing corresponding responsibilities.
4. Languages. In India there are a large number of languages. Some of them are derived from Sanskrit while others are of Darvidian origin. The major Indian languages are Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Malyalam, Marathi, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu. Of these, four languages of southern India-Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malyalam are of Dravidian origin.
5. National Language. It would be a mistake to conclude that everybody speaking any of these languages is Dravidian by race. Similarly, not all who speak languages of Sanskrit origin are Aryans. Generally, the people who lived in a given area over a long period of time adopted the language of that region as their first language irrespective of ethnic or any other considerations. A great number of people speak Hindi. Similarly, a large number of people are able to understand this language even if it is not their mother tongue. This has led to the adoption of Hindi as the official language of the Union Government. For the convenience of the non-Hindi- speaking states English is also used officially.
6. Linguistic unity. Linguists are of the view that the Indian languages and their literatures have much more in common than their apparent or outward differences. All the Indian languages are phonetic in nature and have a more or less common structure and a surprisingly large common vocabulary. There is not much difference in the scripts of many of these languages.
Question 6.
Write an essay on problem of population increase in India and also enlighten the solution to this problem.
Answer:India’s population is growing rapidly, and creating some problems.
- Low standard of living. Indian people have low standard of living as compared that of Europeans. About 48% people live below poverty line. They do not have full meals. It results in low production capacity.
- Deforestation. The forests are cleared recklessly to meet the growing needs. It has resulted in problems of soil erosion, floods, pollution and loss of forest-wealth.
- Lack of pastures. India has only 4% land under pastimes. If this land is used for other purposes, it will result in shortage of fodder for cattle.
- Pressure on Land. Land is a limited source and cannot be increased. It is leading to pressure of population on land. It will decrease the productivity of the land.
- Lack of minerals. Industries are developed to meet the growing needs of people. So more minerals are used. These reserves will exhaust soon.
- Environment. Population growth has an adverse effect on environment. Clear water and air is a problem. Oxygen is also decreasing.
Solutions:
- Family planning should be adopted,
- People should be explained significance of small families by films, songs, plays,
- Illiteracy should be abolished so that people should understand harms of growing population,
- Female education should be increased, marriageable age of girls be increased.
Question 7.
Study critically the efforts being made Tor the expansion of Education in India.
Answer:
Education. One of the basic inputs in human resource development is education. Literacy and numeracy form the foundation on which superstructure of education is built.
1. At the time of independence only 14% of the people were literate. It meant that they could at least read and write names. By 2011 it has slowly risen to 65.58%. In absolute terms the number of the literates has grown to 550 million from 60 million. It is about 11 fold growth. But it is pertinent to note that the number of the illiterate persons has also increased.
2. Our constitution directed the Government to provide education for all children upto the age of fourteen. This was a big task because the bulk of the population was distributed over half a million villages. These villages are separated by considerable distance from one another. Priority was, therefore, given to set up schools in almost every village. As a result there are now half a million primary school in place of two lakhs in 1951. Similarly the middle schools also increased by as much as ten times. Earlier there was one middle school for every 15 primary schools. Now it stands for every four primary schools.
3. Although there has been a marked increase in the number of children getting into formal schools. One of the worries is that out of every 100 children in class I, only 40 manage to complete class V and 25 reach class VIII. Thus three fourths of the pupils drop out on their way.
4. We have also made progress in increasing the number of secondary schools, universities, industrial training as well as other institutions. Still educational facilities are not available to all because of fast growing population.
IV. Show the following on the map of India:
Question 1.
(i) Areas of high density of population.
(ii) Two States with high literacy rate.
(m) Two States of highest and lowest population.
(iv) Areas with high growth rate of population.
Answer:

Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here