JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 10 Acids, Bases And Salts
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 10 Acids, Bases And Salts
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 10 Acids, Bases And Salts
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Acids, Bases And Salts Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ Acid. It is a substance which when dissolved in water produce H+ (aq.) or hydronium ions (H2O+) as the only positively charged ions e.g. HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 etc. They turn blue litmus solution red.
◆ Base. It is a metallic oxide or metallic hydroxide or aqueous ammonia which reacts with an acid to form salt and water e.g. CuO, Mg(OH)2, NaOH etc. They turn red litmus solution blue.
◆ Alkali. It is a basic hydroxide which when dissolved in water produce hydroxyl ions (OH-) as the only negatively charged ions e.g. NaOH, KOH etc. The water soluble bases are called alkalies.
◆ All alkalies are bases but all bases are not alkalies.
◆ pH value of a solution is given as pH = -log [H+ (aq)] or pH or pH = -log [H3O+] [H+] = Molar concentration of H+ ions in solution.
◆ pH scale is a measure of acidic or basic strength of an aqueous solution.
For acid solution pH lies between 0 to 7
For basic solution pH lies between 7 to 14
For neutral aqueous solution or pure water, pH = 7.
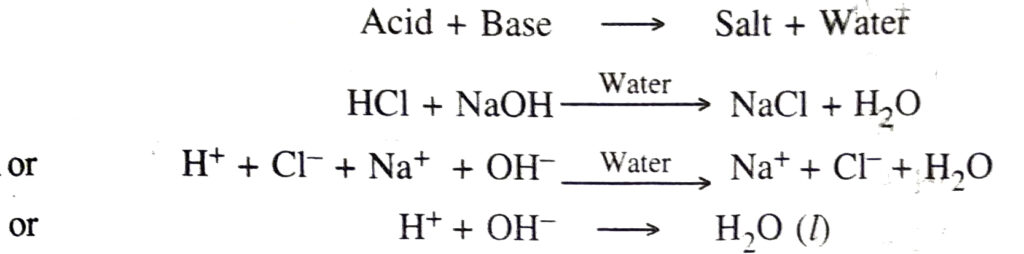
◆ Neutralisation. It is the interaction of an acid with a base to form salt and water.
◆ Strength of acid/base depends upon its degree of ionisation. The more the degree of ionisation, the stronger the acid or base will be.
◆ Acid-base indicators are the dyes or mixtures which are used to indicate acidic, basic or neutral nature of a solution.
◆ The commonly used acid-base indicators are litmus solution, phenolphthalein, methyl orange and methyl red.
◆ The acidic and basic solutions in water conduct electricity because they produce hydrogen ons (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH–) respectively in solutions.
◆ When an acid reacts with a metal, hydrogen gas is evolved and a corresponding salt of acid is produced.
◆ When a base reacts with metal, hydrogen gas is evolved and a salt is formed which contains a negative ion composed of metal and oxygen.
◆ When an acid reacts with metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate, it gives the corresponding salt, carbon dioxide and water.
◆ The mixing of concentrated acids or bases with water is high exothermic reaction.
◆ All living beings carry out their metabolic activities within an optimal pH range.
◆ Salts have various uses in daily life and in chemical industries.
◆ Water of crystallisation is the definite number of molecules of water chemically attached to each formula unit of a salt in its crystalline form. e.g. in CuSO4. 5H2O, five molecules of water are attached to one formula unit of CuSO4.
◆ Salt hydrolysis. The interaction of a salt with water to give an acid and base is called salt hydrolysis.
◆ The solution obtained as a result of hydrolysis of a salt may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the nature of salt.
◆ Washing soda is hydrated sodium carbonate, Na2CO3.10H2O. Washing soda is manufactured by Solvay’s process by using common salt, lime stone and process.
◆ Baking soda (NaHCO3) is a primary product obtained during the manufacture of washing soda by Solvay’s process.
◆ Baking soda (NaHCO3) is used as a constituent of baking powder.
◆ Plaster of paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate, CaSO4.1/2H2O or 2 CaSO4.H2O.
◆ Bleaching powder is calcium oxychloride, CaOCl2.
TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube ?
Ans. Dip a strip of red litmus paper in solution taken in each test tube.
(a) The tube in which the red litmus paper turns purple contains distilled water.
(b) The tube in which red litmus paper turns blue contains basic solution.
(c) The tube in which red litmus paper remains red contains acidic solution.
Q. 2. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels ?
Ans. Curds and other sour substances contain acids which react with the metal surface of brass and copper vessels to produce toxic compounds which are unfit for consumption.
Q. 3. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal ? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Ans. When an acid reacts with metal, generally hydrogen is produced.
e.g. Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
(Dil.)
Pass this gas (H2) through soap solution. The soap bubbles filled with the gas will rise up. If a burning splinter is brought near the gas, the bubble will burn with a ‘pop’ sound.
Q. 4. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Ans. CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂ ↑
(A) (Dil.)
CO2 extinguishes a burning candle.
Q. 5. Why do HCl, HNO3 etc. show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character ?
Ans. HCl, HNO3 etc undergo dissociation in water to given Hydrogen ions, H+ (aq.) ions and show acidic characteristics. These are compounds like alcohol and glucose don’t dissociate in water to give hydrogen ions, H+ (aq.) ions. Hence, they don’t show acidic properties.
Q. 6. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity ?
Ans. The aqueous solution of an acid contains ions such as hydrogen ions, H+ (aq.) and other anions. Hence, it conducts electricity.
Q. 7. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour on the dry litmus paper ?
Ans. This is because dry HCP gas is a covalent compound and it does not undergo dissociation to give hydrogen ions, H+ (aq.) and hence no change in colour of dry litmus paper.
Q. 8. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid ?
Ans. The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is an exothemic process. This is because if water is added to concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating.
Q. 9. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted ?
Ans. The concentration of hydronium ions, decreases when a solution of an acid is diluted.
Q. 10. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH–] affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide ?
Ans. When excess of base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide, concentration of OH– ions increases.
Q. 11. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration ? Which of these is acidic and which one is basic ?
Ans.
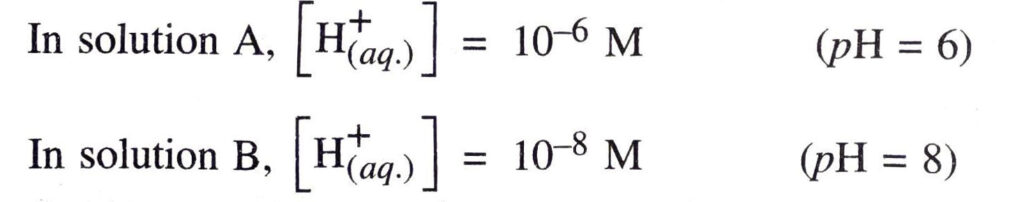
∴ The solution A has more hydrogen ion concentration.
Solution A is acidic (pH <7)
Solution B, is basic (pH > 7).
Q. 12. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution ?
Ans. 1. If [H+] <10–7 M, it is basic solution.
2. If [H+] >10–7 M, it is an acidic solution.
3. If [H+] =10–7 M, it is a neutral aqueous solution.
Q. 13. Do basic solutions also have H+ (aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic ?
Ans. Basic solutions also contain H+ (aq) ions. But in basic solutions :
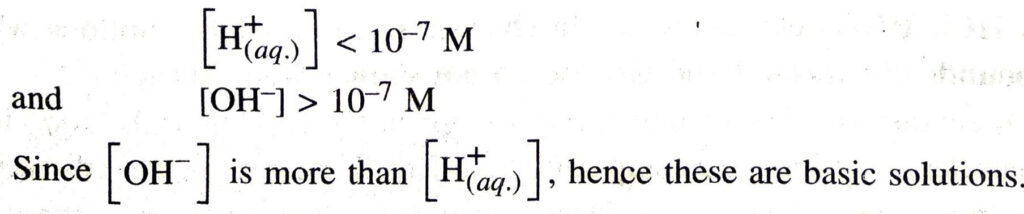
Q. 14. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) ?
Ans. If the pH of the soil is less than 7, i.e. it is acidiq, the farmer will treat the soil with quick lime, slaked lime, chalk.
Q. 15. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl₂ ?
Ans. Bleaching powder.
Q. 16. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Ans. Dry slaked lime. Scar
Q. 17. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Ans. Washing soda.
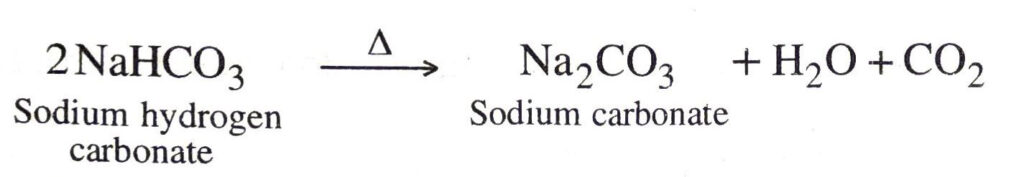
Q. 18. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated ? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Ans. It decomposes to give sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas (which is colourless, odourless and turns lime water milky).
Q. 19. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Ans. CaSO4. 1/2 H2O + 3/2 H2O → CaSO4. 2H2O
Gypsum
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be :
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10.
Ans. (d).
Q. 2. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains :
(a) NaCl
(b) HCI
(c) LICI
(d) KCI.
Ans. (b).
Q. 3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount HCI solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be:
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL.
Ans. (d). base ob
Q. 4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion ?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic.
Ans. (c).
Q. 5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when :
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
(d) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with iron filings.
Ans.

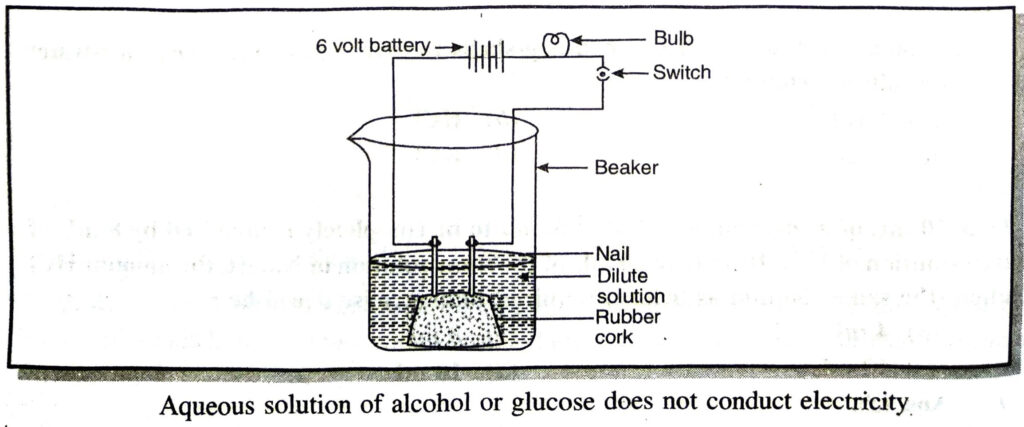
Q. 6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Ans. Fix two nails on a cork and place it in a 100 ml beaker. Connect these nails to a 6 volt battery through a bulb and switch as shown in the figure.
Pour some aqueous solution of alcohol or aqueous solution of glucose in the beaker so that nails dip in it. Switch on the current. The bulb does not glow, indicating that alcohol and glucose don’t dissociate in aqueous solution and hence does not produce H+(aq) ions although they contain hydrogen
Q. 7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does ?
Ans. Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it contains no ions. Rain water contains ions due to dissolved salts, hence it conducts electric current.
Q. 8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water ?
Ans. This is because in the absence of water, acids do not dissociate to give hydrogen ions, (H+(aq)).
Q. 9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is :
(a) neutral ?
(b) strongly alkaline ?
(c) strongly acidic ?
(d) weakly acidic ?
(e) weakly alkaline ?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
Ans.
| Solution | pH | Nature of Solution |
| A | 4 | Weakly acidic |
| B | 1 | Strongly acidic |
| C | 11 | Strongly alkaline |
| D | 7 | Neutral |
| E | 9 | Weakly alkaline |
The increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration is :
11 <9<7 < 4 < 1 (pH values)
Q. 10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCI) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Ans. Fizzing occurs more vigorous in test tube A as compared to in test tube B. This is because concentration of hydrogen ion, [H+(aq)] is more in test tube A than in test tube B, as hydrochloric acid a strong acid and acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid.
Q. 11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd ? Explain your answer.
Ans. Its pH will decrease due to the production of lactic acid which is acidic in nature.
Q. 12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline ?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd ?
Ans. (a) So that the milk is not spoiled readily and medium remains basic.
(b) Because the lactic acid produced during curding reacts with baking soda.
Q. 13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why ?
Or
Write down the reaction of plaster of Paris with water.
Ans. This is because in the presence of moisture, plaster of paris sets to give a hard mass.
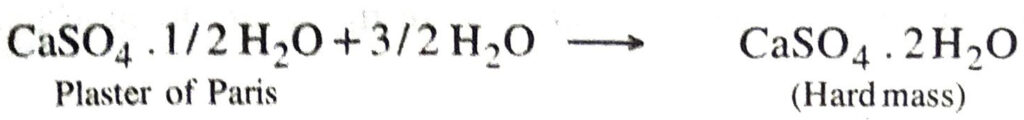
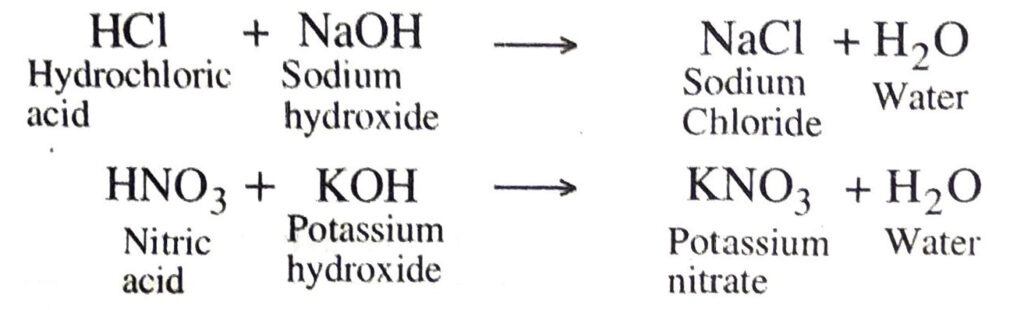
Q. 14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Ans. The interaction of an acid with a base to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction.
Examples:
Q. 15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Ans. (a) Uses of Washing soda
(i) It is used in the manufacture of glass and soap.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of borax.
(b) Uses of baking soda
(i) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher.
(ii) It is used for making baking powder.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Give important properties of acids.
Or
Give four properties of acids.
Ans. PROPERTIES OF ACIDS
1. Taste. Acids have a sour taste.
2. Physical State. Some acids are solids while others are liquids at room temperature.
Examples:
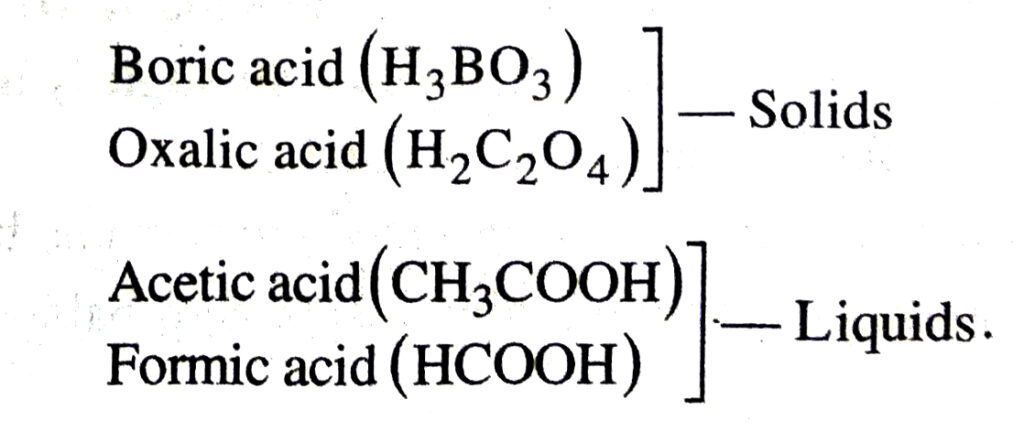
3. They can change the colours of indicators (complex acids or bases) e.g,
(a) They turn blue litmus solution red.
(b) They change the colour of methyl orange from yellow to pink.
(c) They turn pink colour of phenolphthalein in alkalies to colourless.
4. They act as electrolytes. They can conduct electricity in aqueous solutions.
5. Action with active metals. Both, dilute HCl and dilute H2SO4 react vigorously with active metals like potassium, sodium and calcium, producing metallic salts and hydrogen.
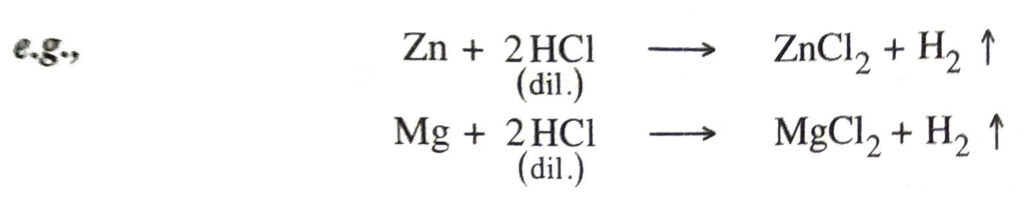
6. Action with bases (neutralisation). They neutralise bases such as metallic oxides and hydroxides to produce salt and water only.
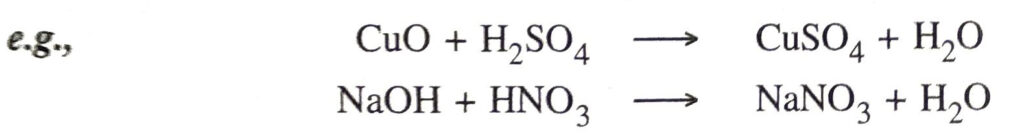
7. Action with carbonates and bicarbonates. They liberate carbon dioxide from metallic carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates on bicarbonates.
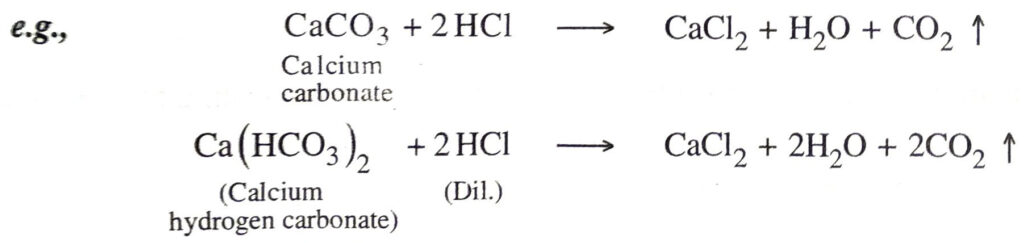
8. Action with sulphides. They react with metal sulphides to produce hydrogen sulphide.

Q. 2. Give the important properties of bases (alkalies).
Or
Explain four general characteristic properties of bases.
Ans. Properties of Bases (Alkalies)
1. Bases are soapy to touch and have bitter taste.
2. They change the colour of indicators.
| Indicator | Colour change |
|
Litmus
Phenolphthalein
Methyl orange
|
From red to blue
From colourless to pink
From orange to yellow
|
3. They act as electrolytes.
4. They have a corrosive action on the skin.
5. Action with ammonium salts. When they are warmed with an ammonium salt, ammonia gas is produced.

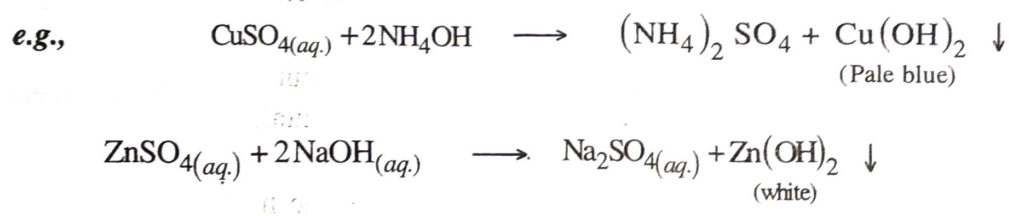
8. Precipitation reactions. When added to the solutions of the salts of the heavy metals viz. copper, iron, zinc, etc., the bases produce insoluble metal hydroxides as precipitates.
9. Action of heat. All bases except NaOH and KOH decompose on heating to give oxides.
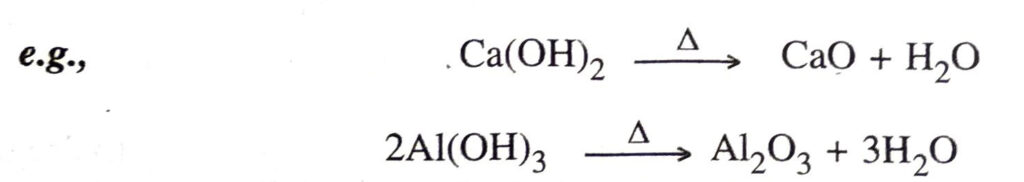
10. Amphoteric nature. The hydroxides of zinc, aluminium and lead are amphoteric, i.e. they can act as weak bases as well as weak acids.
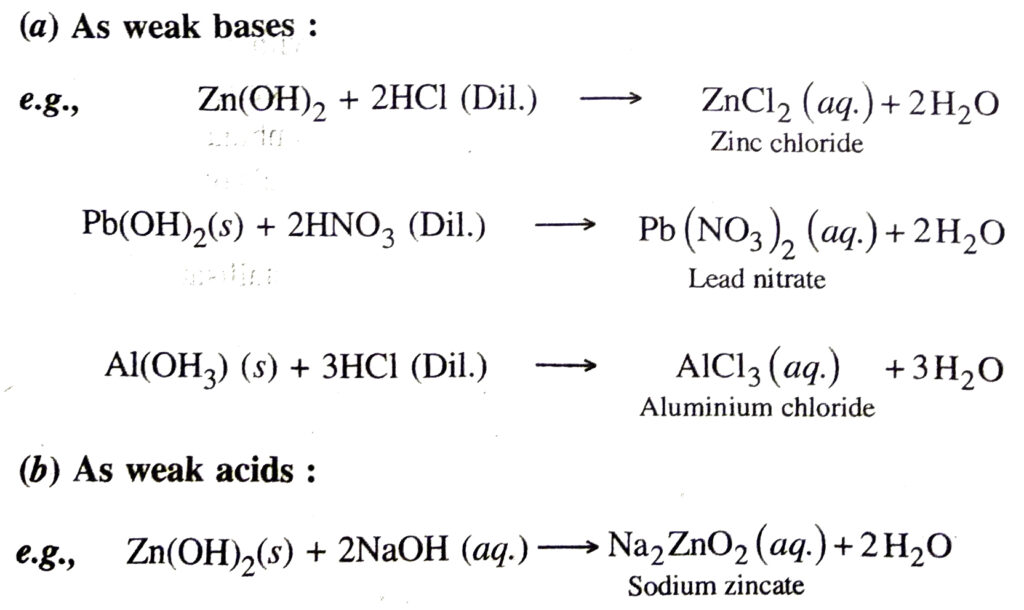
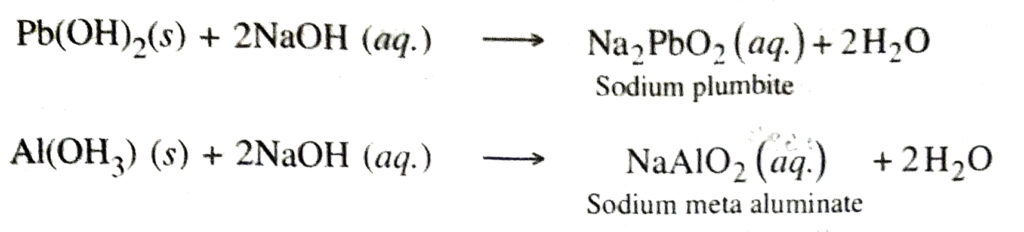
Q. 3. Define neutralisation. Give practical applications of neutralisation. Ans. Neutralisation. It is the interaction of an acid with a base to form salt and water.
Practical Applications of Neutralisation
1. The acidity of soil is removed by adding slaked lime.
2. Antacid tablets containing magnesium hydroxide are given to the persons suffering from acidity.
3. The sting of yellow wasps contains alkalies which are neutralised by rubbing acetic acid (vinegar) on the affected area. The sting of ants and bees contain formic acid which can be neutralised by rubbing with soap of some other alkali.
4. Astronauts in space ships use the alkali, to neutralise the harmful levels of carbon dioxide in exhaust.
Q. 7. (a) What are hydrated salts and water of crystallization ?
(b) Give experiment to show that blue vitriol crystals contain water of crystallization.
Or
Give an activity to show that hydrated copper sulphate contains water of crystallization.
Ans. (a) Hydrated Salts – Water of Crystallization
Some salts crystallise out from their saturated aqueous solutions with a definite number of molecules of water called Water of crystallisation. Such salts are called hydrated salts. These molecules of water of crystallisation are in loose chemical combination with the salt. This water of crystallisation is given out by heating the powdered crystals of these salts above 100°C.
On heating these hydrated crystalline salts, they lose water of crystallisation and
(i) become amorphous.
(ii) lose their colour, if coloured and become white.
Examples:
CuSO4. 5H2O — Copper sulphate pentahydrate.
Na2CO3. 10H2O — Sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Na2SO4. 10H2O — Sodium sulphate decahydrate.
(b) Experiment to show that blue vitriol crystals contain water of crystallisation :
Take some powdered copper sulphate crystals in a clean and dry test tube and heat the crystals with slightly tilting it downwards. Drops of colourless liquid will condense on the cooler parts. Collect it in a dish.
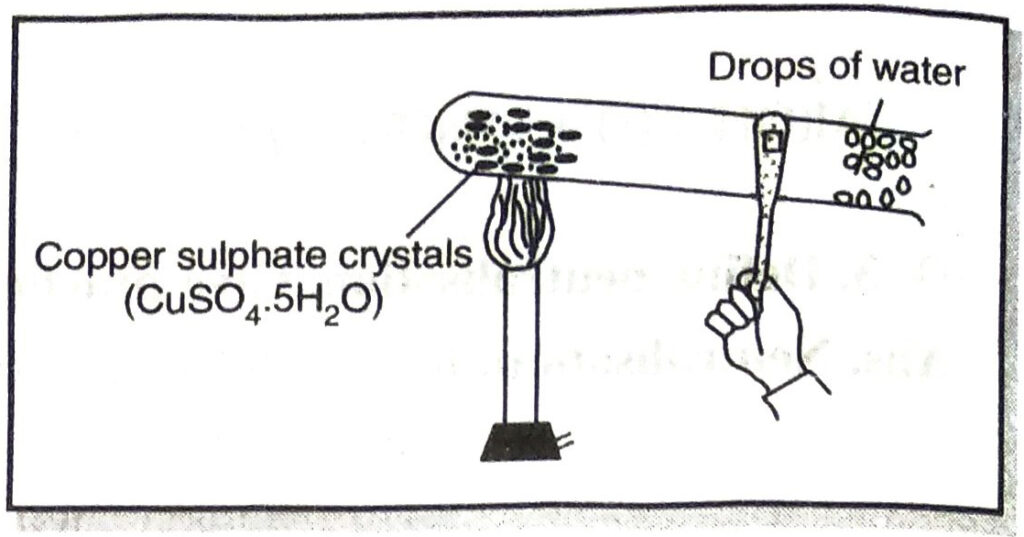
Anhydrous white copper sulphate is left behind in the test tube. This liquid turns anhydrous copper sulphate blue indicating that this liquid is water.
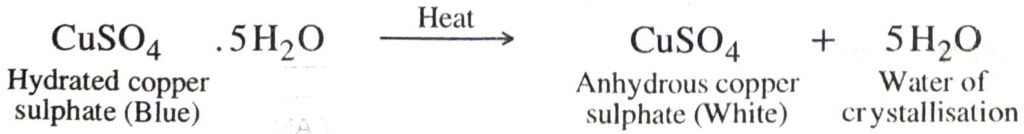
Q. 5. Baking soda is used in small amounts in making bread and cake. It helps to make these soft and spongy. An aqueous solution of baking soda turns red litmus blue. It is also used in soda acid fire extinguisher.
Use this information to answer the following questions :
(a) How does Baking Soda help to make cakes and bread soft and spongy ?
(b) How does it help in extinguishing fire ?
(c) Is the pH value of baking soda solution lesser than or greater than 7 ?
Ans. (a) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. When baking powder is heated or mixed with water, CO₂ is produced.
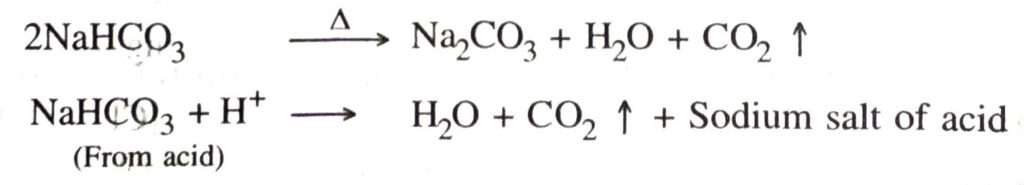
CO₂ so produced causes bread and cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
(b) In fire extinguishers, baking soda reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to produce CO₂ which extinguishes fire.
(c) Greater than 7.
Q. 6. Discuss the manufacture of sodium carbonate by Solvay’s process.
Ans. Principle. When carbon dioxide gas is passed through a brine solution (about 28% NaCl), saturated with ammonia, it gives sodium bicarbonate.
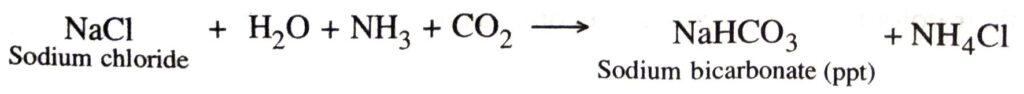
The precipitated sodium bicarbonate is filtered and dried. It is ignited to give sodium carbonate.

The raw materials for the process are :
(a) Sodium chloride (NaCl).
(b) Limestone (CaCO3) for carbon dioxide.
(c) Ammonia gas (NH3).
The manufacture of Na2CO3 involves the following steps :
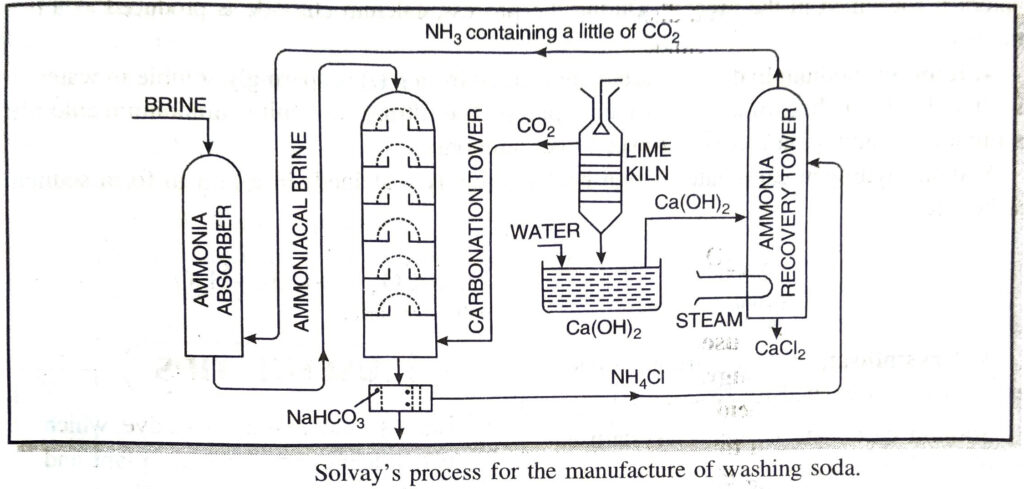
1. Carbonation tower. Cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride (called brine) is saturated with ammonia. This ammoniacal brine solution is fed from the top of a tower known as carbonation tower. This tower is packed with a number of horizontal perforated plates. Carbon dioxide is introduced from the base of the tower. As the ammoniacal brine solution slowly trickles down the tower, it meets the upcoming carbon dioxide and forms sodium hydrogen carbonate (or sodium bicarbonate) by the following reaction :
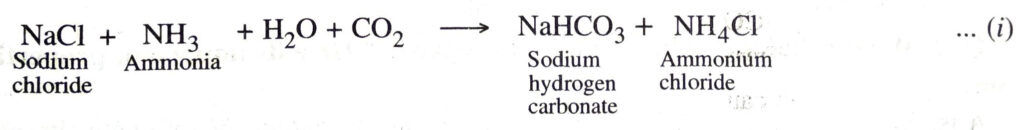
2. Lime kiln. The carbon dioxide used in reaction (i) is obtained by heating limestone (CaCO3) to about 1300 K in a lime kiln.
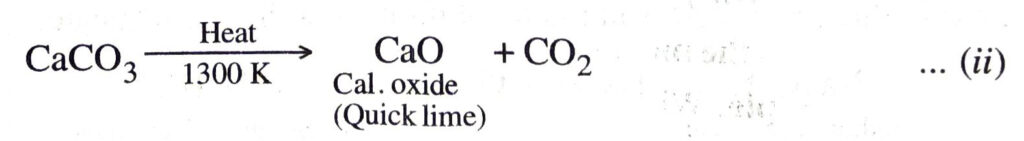
Quicklime (CaO) obtained in the above reaction is dissolved in water to form calcium hydroxide (slaked lime).
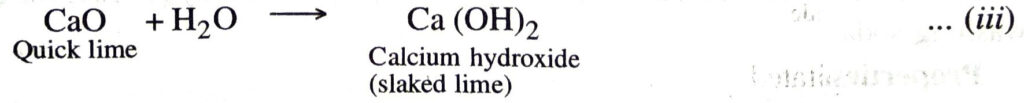
3. Ammonia recovery tower. The slaked lime is then boiled with ammonium chloride to liberate ammonia in a tower known as ammonia recovery tower.
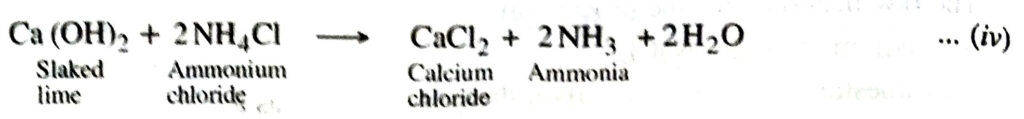
Ammonia is recycled for further use in reaction (i).
Thus, most of the ammonia can be recovered. Sodium chloride and limestone are the only materials consumed in the process. During the process, calcium chloride is produced as a byproduct.
4. Ignition. Sodium hydrogen carbonate formed in step (i) is sparingly soluble in water. It is filtered with the help of a rotary vacuum pump. The filtrate containing ammonium chloride is pumped to ammonia recovery tower to get ammonia.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is then heated strongly (calcined) in a kiln to form sodium carbonate.
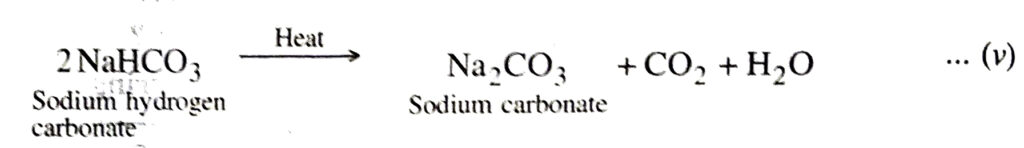
5. Crystallisation. The carbon dioxide evolved is recirculated for reaction (i).
Sodium carbonate is then recrystallised by dissolving in water to get washing soda.
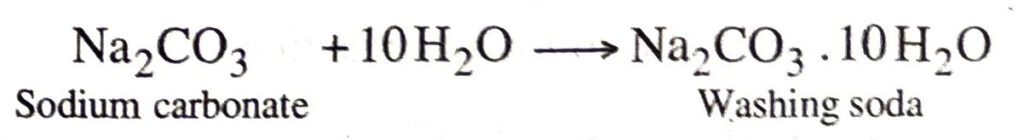
Q. 7. What is baking soda ? How is it prepared ? Give its important properties and uses.
Ans. Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate. Its chemical formula is NaHCO3.
Preparation. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is prepared in the laboratory by passing carbon dioxide through a cold saturated solution of sodium carbonate.
Because of its low solubility, it separates out as white crystals. It is also manufactured as a primary product in the Solvay process for the manufacture of washing soda.
Properties,
1. Sodium bicarbonate is white crystalline solid.
2. It is soluble in water and its aqueous solution is alkaline in nature.
3. On heating, sodium bicarbonate gets converted into sodium carbonate with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
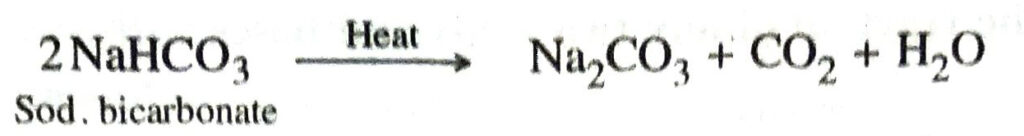
Since carbon dioxide is given off on heating, it is used as a constituent of baking powder to aerate the dough.
Uses of Baking Soda
1. It is mainly used in the preparation of baking powder. Baking powder contains sodium hydrogen carbonate and an acid like tartaric acid or citric acid.
2. It is used in medicines to remove acidity of the stomach. Therefore, it is an important constituent of antacids.
3. It is used in the manufacture of aerated water (soda water).
4. Sodium bicarbonate is also used in fire extinguishers.
Q. 12. (a) Which gas is produced in figure (a) given below :
(b) What will happen to moist litmus paper in figure (b) ?
(c) Write down the balanced equation for reaction occurring in figure (a) ?
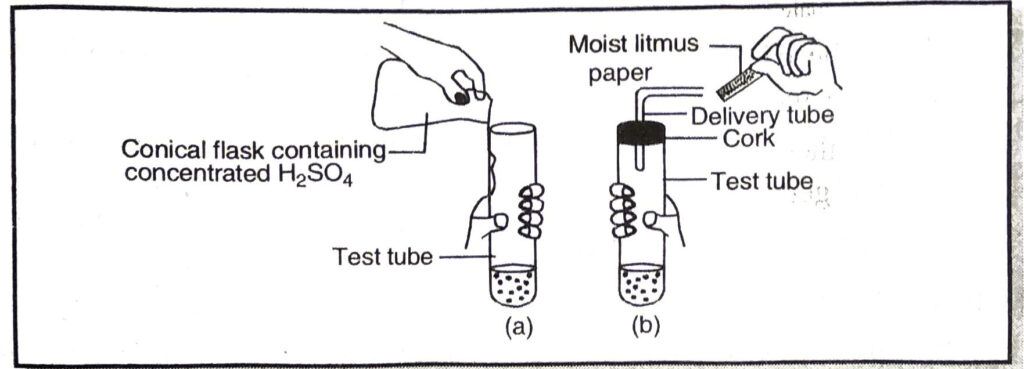
Ans. (a) Hydrochloric acid gas
(b) It turns red.
(c) NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
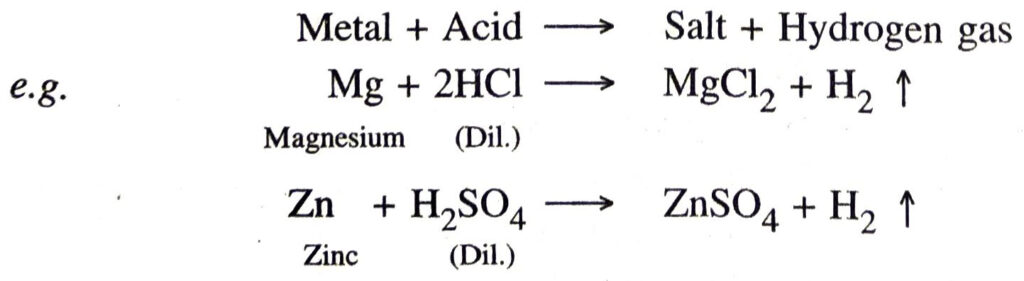
Q. 1. What happens when an metal reacts with dil. HCl or dil. H2SO4 ? Give two examples.
Ans. The metals displace hydrogen from acid give salt and hydrogen.
Q. 2. Give the names and formula of two strong acids and two weak acids.
Ans. Strong acids : Hydrochloric acid, HCl, Sulphuric acid, H2SO4
Strong Bases: Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, Potassium hydroxide KOH
Q. 3. Explain the reaction of any two acids and bases with water.
Ans. Reaction of acids with water:
(i) SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
(ii) CO2 + H2O → H2SO3
Reaction of basis with water:
(i) CaO + H2O → Ca (OH)2
(ii) Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
Q. 4. Explain why for diluting an acid, concentrated acid is added to water and not water to concentrated acid ?
Ans. This is because the process of dissolution of an acid in water is highly exothermic process. For dilution of concentrated acid, the acid must be added slowly to water with constant stirring. If water is added to acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating.
Q. 5. Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas hydrochloric acid does. Give one reason.
Ans. This is dry HCl is a polar covalent compound and there is no H+ ions but in aqueous HCl there are H+ (aq.) ions.
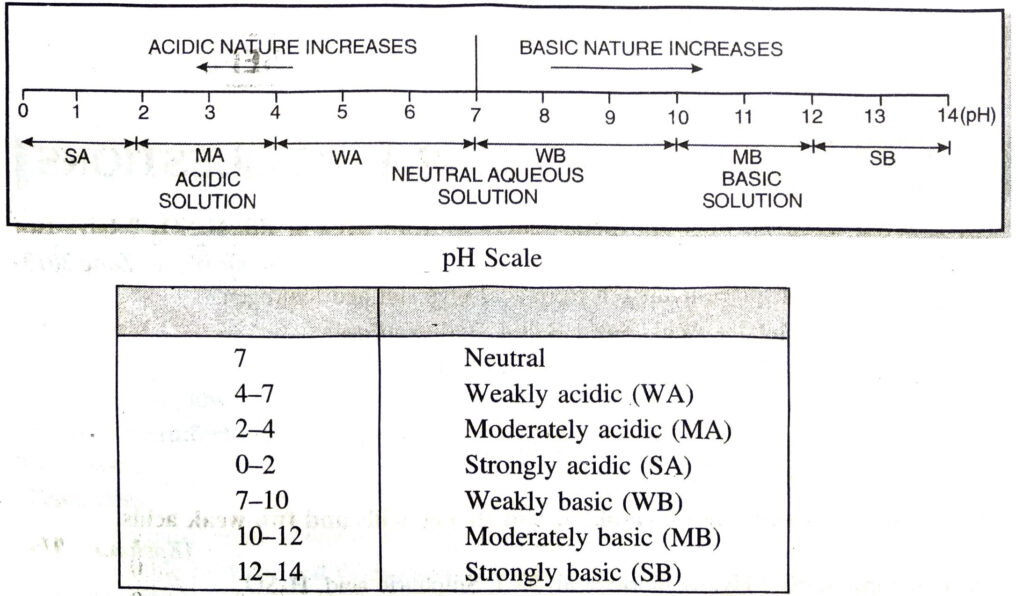
Q. 6. Write a note on pH scale.
Ans. pH scale is that scale which indicates whether the given solution is acidic, basic or neutral. On this scale, pH values of various solutions lie between 0 to 14.
Q. 7. Name two metals which will d displace hydrogen from dil. acids and two metals which will not ?
Ans. Zinc and Magnesium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids. Copper and silver can’t displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Q. 8. What is common name of the compound CaOCl₂? Name substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Ans. CaOCl2 is bleaching powder.
CaSO4. 1/2H2O + 3/2H2O → CaSO4. 2H2O
Q. 9. What happens when an acid reacts with a metal carbonate ? Explain with the help of an example. Write chemical equation of reaction involved.
Ans. When an acid reacts with metal carbonate, carbon dioxide is produced
MgCO3 + Dil 2HCI → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2
Q. 10. Calculate the pH of 0.5 M HCl.
Ans.

Q. 11. How is sodium hydroxide obtained from common salt ? Name the other byroducts obtained.
Ans. Sodium hydroxide is obtained from conc. NaCl solution in water by electrolysis Electrolysis
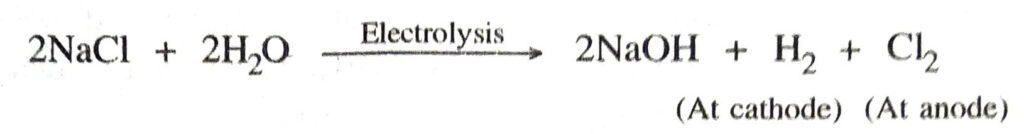
Byproducts. Hydrogen,
Q. 12. What is the biological importance of pH ?
Ans. Biological importance.
(a) Our body works within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8.
(b) Living organisms can supplies in a narrow pH range.
(c) When the pH of rain water becomes less than 5.6, it is called acid rain. When this water flows into the rivers, the survival of aquatic life becomes difficult due to decrease in pH.
Q. 13. How can pH change cause the tooth decay?
Ans. Bacteria present in the mouth produce free acids by the degradation of sugar and food particles present in the mouth after food. Due to this, pH in the mouth falls below 5.5 which causes the corrosion of tooth enamel made up of calcium phosphate.
Q. 14. How can tooth decay be prevented ?
Ans. 1. By cleaning the mouth after eating food.
2. Using toothpastes, s, which are generally basic because they can neutralise the excess of acid and prevent tooth decay.
Q. 15. Give four uses of bleaching powder.
Ans. 1. It is used for bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry.
2. It is used for bleaching wood pulp in paper factories.
3. It is used for disinfecting drinking water.
4. It is used as an oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
Q. 16. What is bleaching powder ? Give equations for its reactions with : 1. HCI 2. CO2 3. H2SO4?
Ans. Bleaching powder is CaOCl2. (Calcium Oxychloride)
Reactions of bleaching powder with :

Q. 17. How is Plaster of Paris prepared ? Why is temperature control necessary during its preparation ? How does it react with water?
Ans. It is prepared by heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) at 373 K in a kiln.
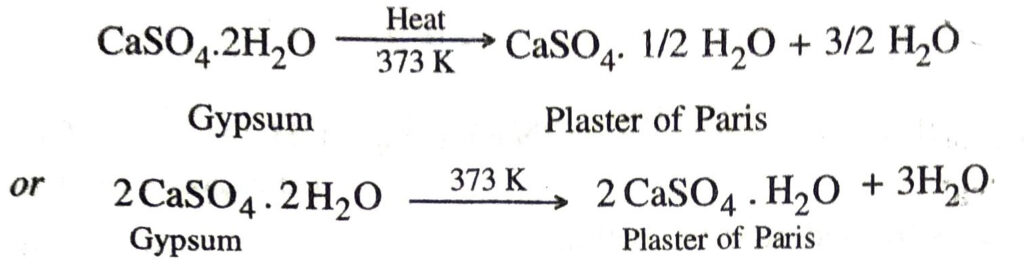
It may be noted that the temperature should be controlled carefully. It should not be allowed to rise above 425 K, because the whole of water is lost and anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4) is produced. It is called dead burnt plaster. It has no such property as that of Plaster of Paris.
When mixed with water, it forms a paste which sets into a hard mass. This is called setting of Plaster of Paris. The setting of Plaster of Paris is due to its hydration into gypsum.
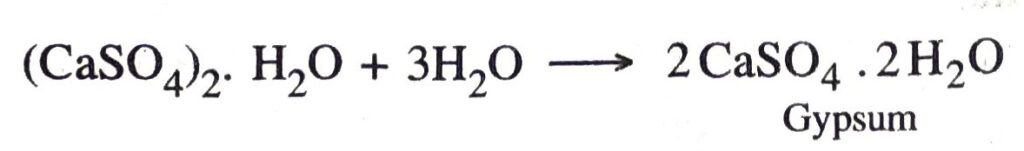
Q. 18. Give important uses of Plaster of Paris.
Ans. 1. Plaster of Paris is used for producing moulds for toys, pottery, ceramics, etc.
2. It is used for making statues, models and other decorative materials.
3. It is used in medical applications known as plasters for setting broken and fractured bones in the right position and also in dentistry.
4. It is used for making smooth surfaces and ornate designs on walls and ceilings.
5. It is used as a fire proofing material.
6. It is used in the laboratories for sealing the air gaps in an apparatus to make it air tight.
Q. 19. What is bleaching powder ? What is meant by available chlorine ?
Ans. Bleaching powder is CaOCl2.
Available chlorine. The amount of chlorine evolved on treatment of bleaching powder with excess of a dilute acid is known as available chlorine. It is expressed as percentage of the total weight of the bleaching powder. A good quality bleaching powder contains 35 to 38% of available chlorine. However, available chlorine has decreased due to auto-oxidation in the course of time.
Q. 20. Write the chemical formula of washing soda. What happens when crystals of washing soda are exposed to air ?
Ans. The chemical formula of washing soda is Na2CO3.10H2O.
When crystals of washing soda are exposed to air, they lose nine molecules of water of crystallisation and form a monohydrate. This process is known efflorescence.
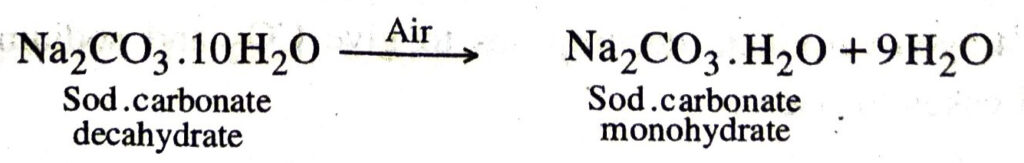
Q. 21. How is sodium hydroxide prepared ?
Ans. When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), sodium hydroxide is produced. Hydrogen and chlorine are produced as by-products. This process is called chlor-alkali process.
The reaction taking place is
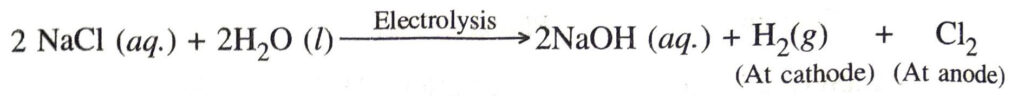
Sodium hydroxide solution is formed near the cathode.
It is concentrated by evaporation to get solid sodium hydroxide.
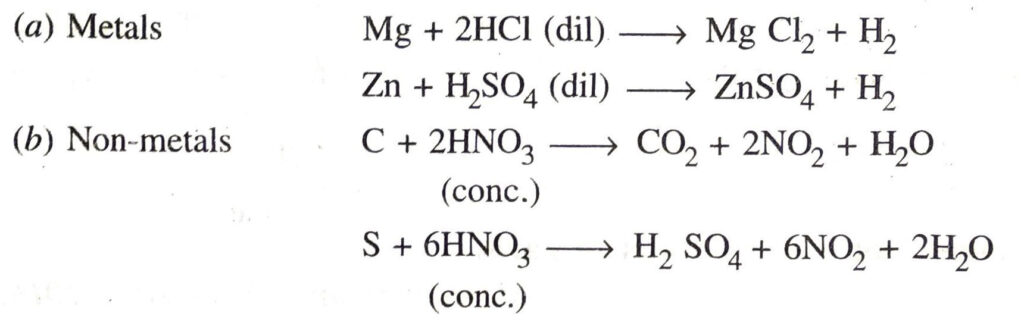
Q. 22. How do acids and bases react with metals? Give equation for each.
Ans.
Q. 23. Give a brief account of the chemicals obtained from common salt.
Ans. Sodium Hydroxide, Baking soda, H2, Cl2, HCI.
Q. 24. Write the constituents of baking powder. How does it cause the cake to rise and become fluffy ?
Ans. Baking powder is a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and tartaric acid or citric acid. When baking powder is heated, sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes to give carbon dioxide and sodium carbonate. Carbon dioxide causes bread and cakes to rise and make it light. Tartaric acid or citric acid present in the bak powder neutralises sodium carbonate. It may be noted that if tartaric acid or citric acid is not present in baking powder, it will taste bitter due to the presence of sodium carbonate.
Q. 25. State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based :
1. as an antacid
2. as a constituent of baking powder.
Ans. 1. It is alkaline and neutralizes excess acid in the stomach. Therefore, it is used as an antacid.
2. Baking powder contains baking soda and tartaric acid. When baking powder is heated, sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes to give CO2 and sodium carbonate, CO2 causes breads and cakes to rise.
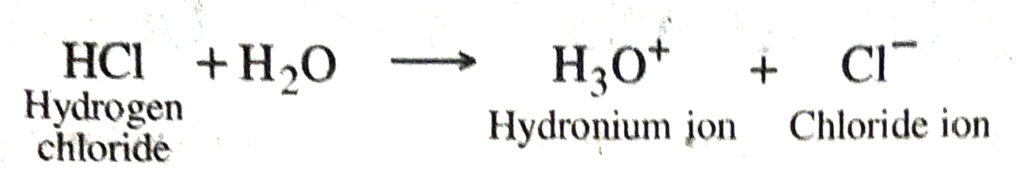
Q. 26. Anhydrous hydrogen chloride is not an acid but its aqueous solution is a strong acid. Explain.
Ans. Anhydrous hydrogen chloride is covalent compound, therefore it is not an acid but in aqueous solution it ionises to give hydronium ions. Hence it behaves as a strong acid.
Q. 27. Answer the following:
(a) Why is Plaster of Paris written as CaSO4. ½H2O ? How is it possible to have half a water molecule attached to CaSO4?
(b) Why is Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate an essential ingredient in antacids ? (c) When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, three products are obtained. Why is the process called chlor-alkali ?
Ans. (a) In plaster of paris, one molecule of H2O is bonded to two CaSO4 molecules.
(b) This is because it is weakly alkaline and increases pH.
(c) This is because chlorine and sodium hydroxide (alkali) are produced.
Q. 28. Explain the differences between acids and bases.
Ans.
| S. No. | Properties | Acids | Bases |
| 1. | Action with methyl orange | They turn methyl orange red. | They turn methyl orange yellow. |
| 2. | Action with phenolphthalein | No action. | They turn phenolphthalein pink. |
| 3. | Action with litmus paper | They turn blue litmus paper red. | They turn red litmus paper blue. |
| 4. | Action with carbonates or bicarbonates | They decompose carbonates or bicarbonates to liberate carbon dioxide gas. | No action |
| 5. | By touching | Just like water. | Soapy to touch |
Q. 29. Fill in the blanks which suitable words: An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the only 1………… ions. A base is a compound which if soluble in water contains 2. ……… ions. A base react with an acid to form a 3……………. and water only. This type of reaction is known as 4…………
Ans. 1. positive, 2. hydroxyl, 3. salt, 4. neutralisation.
Q. 30. Give three uses of caustic soda (NaOH).
Ans. 1. It is used in manufacture of soaps and detergents.
2. It is used in paper industry.
3. It is used in the manufacture of artifical fibres.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. Name a substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Ans. Dry slaked lime, Ca(OH)2.
Q. 2. What is the lime water commonly used in laboratories?
Ans. A solution of calcium hydroxide in water.
Q. 3. Which element is common to all acids ?
Ans. Hydrogen.
Q. 4. What is the maximum value of pH of a solution ?
Ans. 14.
Q. 5. Write the chemical formula of two substances which contain water of crystallisation.
Ans. Hydrated copper sulphate, CuSO4.5H2O. Hydrated magnesium sulphate, MgSO4.7H2O.
Q. 6. What is litmus solution ?
Ans. It is a purple dye which is extracted from lichen, a plant.
Q. 7. What is denatured alcohol ?
Ans. Ethyl alcohol mixed with some CH3OH so that it is unfit for drinking purposes is called denatured alcohol.
Q. 8. Give one example of a weak base.
Ans. Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
Q. 9. What is an alkali ?
Ans. It is a metal oxide or hydroxide which is soluble in water and contains hydroxide (OH–) ions.
Q. 10. What is pH range of our body in which it works?
Ans. 7.0 to 7.8
Q. 11. What is the pH of milk of magnesia ?
Ans. 10.
Q. 12. What is the pH of acid rain ?
Ans. Less than 5.6.
Q. 13. In addition of sodium bicarbonate, baking powder contains a substance ‘X’. Name, ‘X’. les
Ans. ‘X’ is tartaric acid or citric acid.
Q. 14. During summer season, a milkman usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. G to fresh milk. Give one reason.
Ans. To preserve milk and to avoid to fermentation and to increase the pH from 6 to slightly alkaline.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Choose the correct/most appropriate answer from the four alternatives given below against each question and write it in your answer-book :
Zinc, reacts with H2SO4 to give :
(A) N2
(B) O2
(C) H2
(D) Cl2
Ans. (C) H2
2. CaSO4. 1/2 H2O is the formula of :
(A) Bleaching powder
(B) Plaster of Paris
(C) Gypsum
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Plaster of Paris
3. Which turns phenolphthalein pink?
(A) Salt solution
(B) Base
(C) Acid
(D) Lime water.
Ans. (B) Base
4. pH of base solution is :
(A) 7
(B) >7
(C) <7
(D) 1.
Ans. (B) >7
5. When bases are dissolved in water they give :
(A) H+ ions
(B) H2O+ ions
(C) OH– ions
(D) OH+ ions.
Ans. (C) OH– ions
6. Salts are mostly :
(A) Liquids
(B) Gases
(C) Ionic Compounds
(D) None.
Ans. (C) Ionic Compounds
7. The formula of Plaster of Paris is :
(A) CaSO4
(B) CaSO4.2H2O
(C) CaSO2.1/2 H2O
(D) CaSO4.H2O.
Ans. (B) CaSO4.2H2O
8. Which of the following phenomena occur when a small amount of acid is added to water?
(A) Ionisation
(B) Dilution
(C) Neutralisation
(D) Salt formation.
Ans. (A) Ionisation
9. Which turns red litmus blue?
(A) Lemon juice
(B) Orange juice
(C) Tamarind juice
(D) Cucumber.
Ans. (D) Cucumber.
10. Base + Acid → ?
(A) Salt + water
(B) Salt + H2
(C) Salt + CO2+ H2O
(D) Salt + CO2
Ans. (A) Salt + water
11. What is the pH of Blood ?
(A) 7
(B) 1
(C) 7.3
(D) 0.0.
Ans. (C) 7.3
12. Sting of Nettle plant contains :
(A) Methanoic acid
(B) Citric acid
(C) Oxalic acid
(D) Tartaric acid.
Ans. (A) Methanoic acid
13. The chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate is :
(A) CuSO4.10H2O
(B) CuSO4.5H2O
(C) CuSO4
(D) CuSO4.2H2O.
Ans. (A) CuSO4.10H2O
14. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be :
(A) 1
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 10.
Ans. (B) 4
15. A solution turns red litmus solution blue, its pH is likely to be :
(A) 1
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 10.
Ans. (B) 4
16. Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel, its nature is :
(A) basic
(B) acidic
(C) neutral
(D) amphoteric.
Ans. (A) basic
17. Common salt is :
(A) Acidic
(B) Basic
(C) Slightly alkaline
(D) Neutral.
Ans. (D) Neutral.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here