A computer network is a system in which multiple computers are connected to each other to share information and resources.
A network is the group of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources such as printers, files and other resources. It allows communication as well among different users within a network.
The computers in a network may be linked through any wired or wireless communication media, such as: cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites or infrared light beams. Network is capable of sharing Software and Hardware resources among users within a network.
Computer networks help users on the network to share the resources and in communication.
(i) To give Remote Access to computer or other terminals.
(ii) To ensured privacy among all the users of network.
(iii) To share hardware devices like printer, scanner, modem etc. with others
(iv) To share files across the network.
(v) To share of software or operating programs on remote systems with others.
(vi) To make information easier to access and maintain across the network users.
(vii) To allow multiple users to play games from different locations.
(viii) To allow multiple users to share the Internet connection.
(ix) To enable communication via email, video conferencing, instant messaging, etc.
(x) To access and backup of data among network users Securely
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NETWORK
Advantages of Network
Following are the advantages of computer network :
1. Sharing Files, Data and Information : Data, programs and different resources can be shared with other user easily. All the files are stored on server.
2. Sharing Hardware and Software Hardware and software can be shared within network easily.
3. Fast Communication: Computer Network provides a very fast communication media. For Example: E-mail.
4. File Integrity: Network helps in fast saving and sharing of files. So all the files remain integrated at all the time.
5. Cost Effective: We can share costly input and output devices like printer with network. Thus, it reduces the cost of system.
6. Reliability: Network ensures use of many resources to users. When hardware fails, information can be recovered from other computer with the help of network.
7. Flexibility: Computer network provides more flexibility for operations. There is a possibility of connecting devices of different organizations in it.
8. Backup: It is easy to take backup from server if we are linked with network.
9. Security Network provides security to users and devices. Network user can be restricted to access files or applications or devices.
10. Speed: Sharing and transferring files within networks is very fast. It saves time and money and energy of users.
Disadvantages of Network
Following are the disadvantages of network :
1. Network Failure : All the central facilities may fail due to network failure.
2. Management: For managing entire network, technical experts are required.
3. Security: There are security threats in a network. Data can be misused in network.
4. Expensive to Build : Building a network is costly affair. Cost of cables and other hardware equipment is very high. Many special hardware are also required for a network.
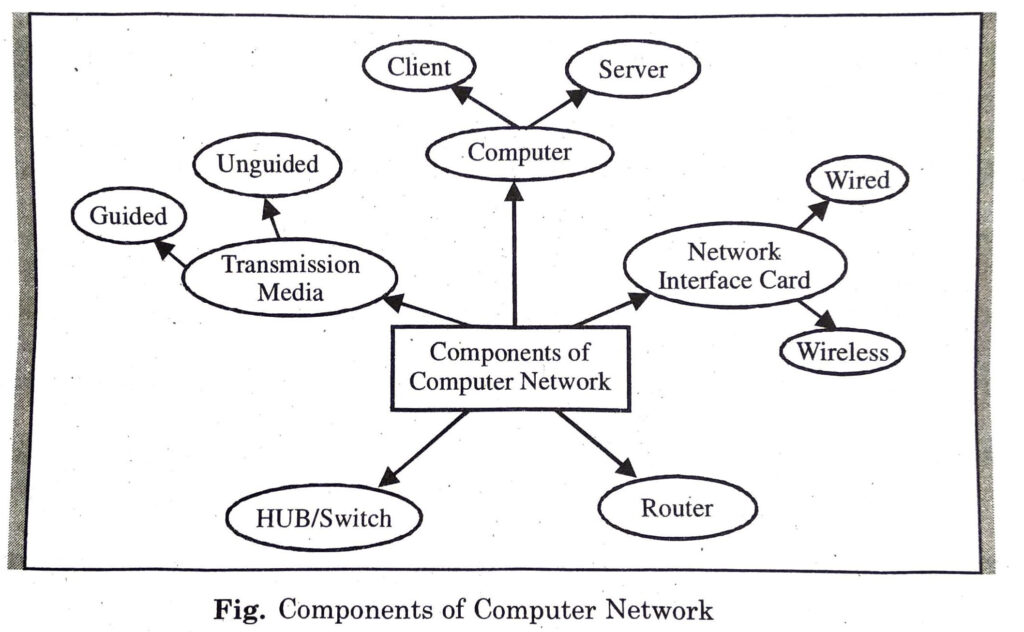
COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER NETWORK
A computer network consists of several components. Each of these components is very important for the proper functioning of a network. Computer networks components comprise both physical parts as well as the software required for installing computer networks, both at organizations and at home. The hardware components are the server, client, peer, transmission medium and connecting devices. The software components are operating system and protocols. Computer network components include the major parts that are required to install a network both at the office and home level.
1. Computer: The purpose of a network is to interconnect computers. The first step for setting up a network is to identify computers and users who want to participate in the network. There are two types of computers which are used for creating a network :
(i) Client: Client is a normal computer system. Clients are computers that request and receive service from the servers to access and use the network resources. These computers are connected to a network for sharing various types of resources.
(ii) Server Servers are high-configuration computers that manage the resources of the network. The network operating system is typically installed in the server and so they give user accesses to the network resources. Servers can be of various kinds: file servers, database servers, print servers etc.
2. Network Interface Card: A Network Interface Card(NIC) is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). It is installed on the motherboard inside a system-unit so that a computer can be connected to a network. It should be fitted in each client and server computer.
There are two types of network cards :
(i) Ethernet Card: The Ethernet NIC uses Ethernet cables and connectors as a medium to transfer data.
(ii) Wireless Card : In wireless card, the connection is made using such an antenna that employs radio wave technology.
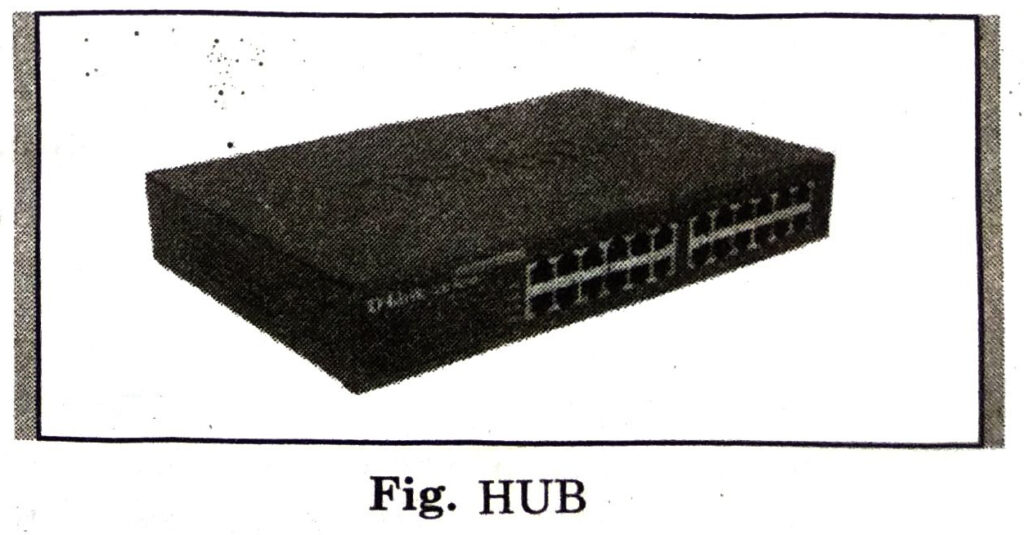
3. HUB/Switch : A Hub is a hardware device that divides the network connection among multiple devices. When computer requests for some information from a network, it first sends the request to the Hub through cable. Hub will broadcast this request to the entire network. All the devices will check whether the request belongs to them or not. If not, the request will be dropped.
Switch: A switch is a hardware device that connects multiple devices on a computer network. A Switch contains more advanced features than Hub. The Switch contains the updated table that decides where the data is transmitted or not. Switch delivers the message to the correct destination based on the physical address present in the incoming message.
4. Router: A router is a hardware device which is used to connect a LAN with an internet connection. It is used to receive, analyze and forward the incoming packets to another network.
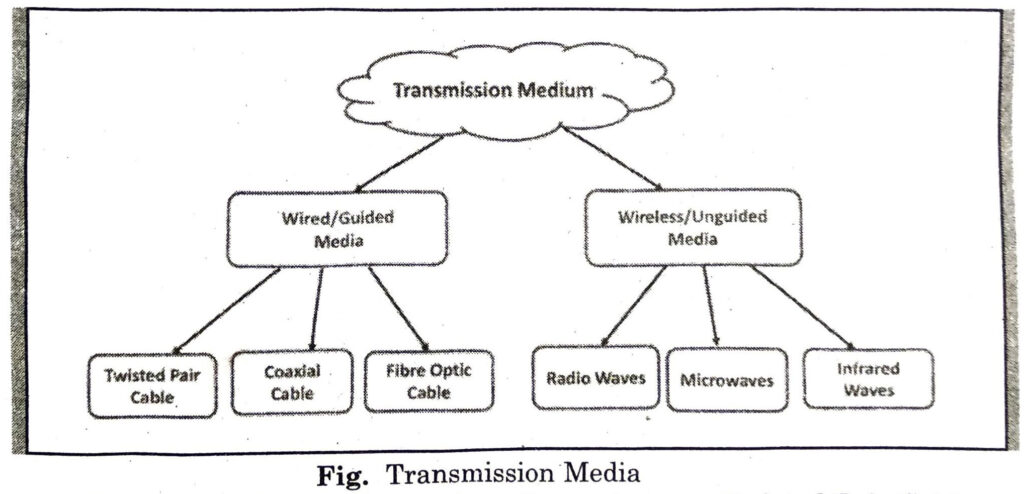
5. Transmission Media : In data communication terminology, a transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e. it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types :
(i) Guided Media: It is a wired media, such as Twisted Pair Cables, Coaxial Cables and Optical Fiber etc.
(ii) Unguided Media: It is a wireless media, such as Microwave signals,
TYPES OF NETWORK
There are several different types of computer networks. Computer networks can be characterized by their size as well as their purpose. The size of a network can be expressed by their geographical area and the number of computers that are connected to a network. Networks can cover anything from a handful of devices within a single room to millions of devices spread across the entire globe.
Networks may be small or large based on its size, complexity and Distribution area. On the basis of their size, Networks can be categorized as follows:
1. PAN (Personal Area Network)
2. LAN (Local Area Network)
3. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
4. WAN (Wide Area network)
Personal Area Network
Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters. Personal Area Network is used for connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network. A Personal Area Network is a computer network organized around an individual person within a single building. This could be inside a small office or residence. Personal area networks can be constructed with cables or it can be wireless. It refers to the interconnection of information technology devices or gadgets (include laptop computers, PDAs, cell phones, printers) within the environment of an individual user.
There are two types of Personal Area Network :
1. Wired Personal Area Network
2. Wireless Personal Area Network
Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is the most frequently used network. A LAN is a computer network that connects computers together through a common communication path, contained within a limited area, that is, locally. A LAN encompasses two or more computers connected over a server. The two important technologies involved in this network are Ethernet and Wi-fi. A LAN is a network that is used for communication among computer devices, usually within an office building or home. LAN’s enable sharing of resources such as files or hardware devices that may be needed by multiple users. It is limited in size, typically spanning a few hundred metres and no more than a mile. It is fast, with speeds from 10 Mbps to,10 Gbps. It requires little wiring, typically a single cable connecting to each device. Twisted pair, coaxial or fiber optic cable can be used in wired LAN’s. It is suitable to bus, ring or star topologies.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. This is the type of computer network that connects computers over a geographical distance through a shared communication path over a city, town or metropolitan area. This type of network is distributed in a city, college campus or large area just like a Cable TV network. A MAN might be owned and operated by a single organization, but it usually will be used by many individuals and organizations. Many LANs may be inter-connected in this type of network. A MAN often acts as a high-speed network to allow sharing of regional resources. A MAN typically covers an area of range between 5 to 50 km diameter. Examples of MAN :
1. Telephone company network that provides a high-speed DSL to customers and
2. Cable TV network.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over a large geographical distance through a shared communication path. It is not restrained to a single location but extends over many locations. WAN can also be defined as a group of local area networks that communicate with each other. WAN covers a large geographical area such as a country, continent or even the entire world. WAN can contain multiple smaller networks, such as LANs or MANs. In this network,various types of communication media such as – telephone lines, satellites, microwave signals etc. are used. These transmission media are linked with Router. The world’s most popular Wide Area Network is the Internet.
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
The term Topology refers to the way in which the various nodes or computers of a network are linked together.A Network Topology is the arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other. Topologies may define both physical and logical aspect of the network. Both logical and physical topologies could be same or different in a same network. Topology determines the data paths that may be used between any pair of devices of the network.Two or more nodes connect to a link; and two or more links form a topology.
The selection of a Network Topology depends on the choice of media and the access method used. The following factors are considered while selecting a topology:
(i) Cost
(ii) Reliability
(iii) Scalability
(iv) Bandwidth capacity
(v) Ease of installation
(vi) Ease of troubleshooting.
Types of Network Topologies
Following figure shows the different types of topologies are as follows:
1. Bus Topology
Bus Topology is the simplest type of network topology. All the nodes (Clients, Servers and Other Devices) are connected to the single cable with the help of T connectors in it. This central cable is the backbone of the network and is known as Bus. Every workstation communicates with other devices through this Bus. Both ends of the shared channel have line terminator. The data is sent in only one direction and as soon as it reaches the extreme end, the terminator removes the data from the line.
When a signal is broadcasted from the source, it is transmitted to all other nodes connected to the bus cable. Only the intended recipient, whose IP address matches, accepts it. If the IP address of machine doesn’t match with the intended address, machine discards the signal.
Advantages of Bus Topology
(i) Any new computer can be attached easily.
(ii) It is a cheaper topology.
(iii) If one computer fails, others are not affected.
(iv) Cable requirements are least as compared to other network topologies.
(v) It can be used in small networks. .
(vi) It is easy to understand the layout and connectivity
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
(i) Security is very low in this topology.
(ii) If the main central bus fails, the entire network breaks down.
(iii) The efficiency of network is reduced with the increase in number of computers
(iv) Cable length is limited.
(v) It is slower than some other topologies.
(vi) Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable.
(vii) It is difficult to identify the problem if the entire network breaks down.
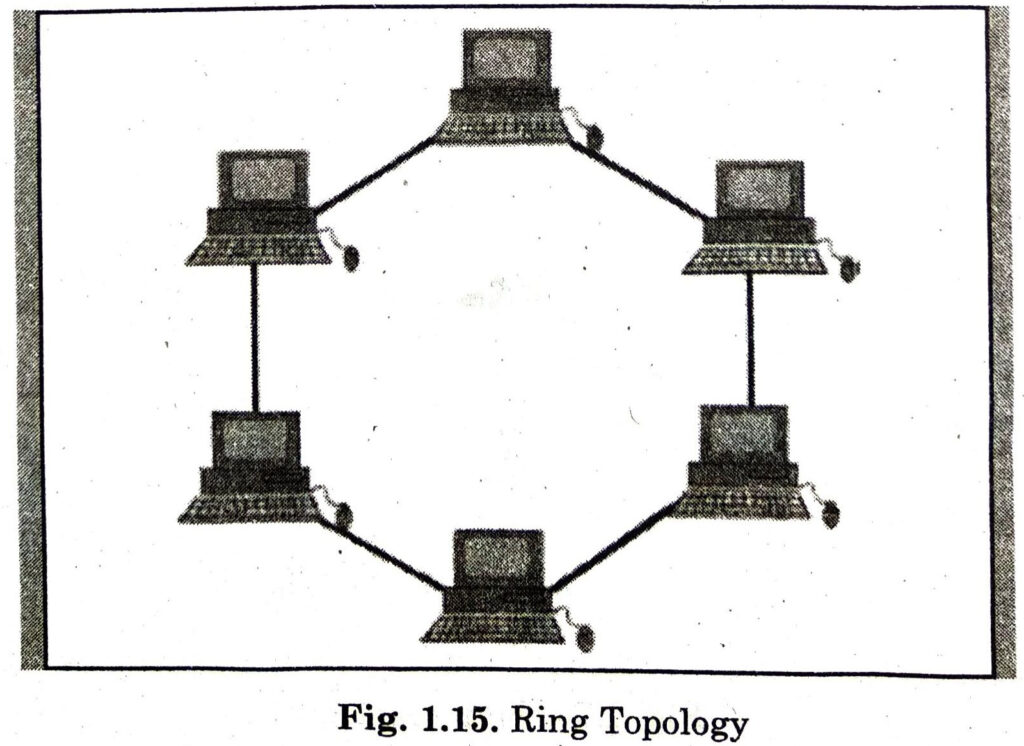
2. Ring Topology
Ring topology is like a bus topology, but with connected ends. All the computers are logically linked in the form of a ring. Each node is connected with two adjacent nodes. All traffic travels either clockwise or anticlockwise around the ring. At the time of accepting data, each node checks its address. If address matches with the node, it will accept it. Otherwise, data will be rejected by the node. There are two kinds of ring topologies :
1. Single Ring: In single ring network, a single cable connects all the devices and data travels only in one direction. Each device waits for its turn and then transmits data. When the data reaches at its destination, another device can transmit data.
2. Dual Ring: This topology uses two rings to send the data in both directions, i.e. clockwise and anti-clockwise. Thus, it allows more packets to be sent over the network.
Advantages of Ring Topology
(i) When no station is transmitting the data, then the token will circulate in the ring.
(ii) Very systematic network where every device has access to the data and the opportunity to transmit data.
(iii) Performs better than a bus topology under heavy network load.
(iv) The possibility of collision is minimum in this type of topology.
(v) Does not require a central node to manage the connectivity between the computers.
(vi) It is easier to locate the problems with device and cable i.e. fault isolation is simplified.
(vii) If one device does not receive a signal within a specified time, it can issue an alarm.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
(i) Failure of one computer can affect the entire network.
(ii) Difficult to troubleshoot.
(iii) Communication delay is directly proportional to the number of nodes.
(iv) Adding new devices increases the communication delay.
(v) Adding or removing Computers disrupts the network.
(vi) A ring network requires more cable than a bus network. (vii) It is not easy to setup and connect.
(viii) More Nodes can be connected easily.
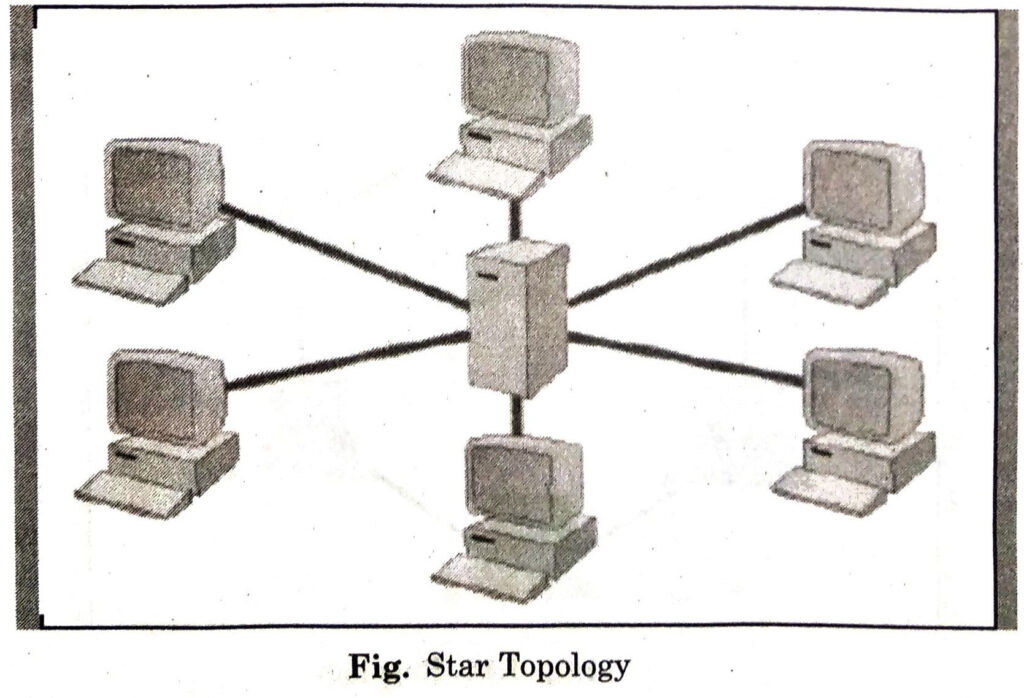
3. Star Topology
In star topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node. The hub can be passive in nature i.e., not an intelligent hub such as broadcasting devices, at the same time the hub can be intelligent known as an active hub. Active hubs have repeaters in them. Nodes in star topology cannot have a direct connection with each other. They have to be linked via hub.
Advantages of Star Topology
(i) If N devices are connected to each other in a star topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is N. So, it is easy to set up.
(ii) Failure of one computer does not affect the other.
(iii) Each device requires only 1 port i.e. to connect to the hub, therefore the total number of ports required is N.
(iv) More nodes can be connected easily in it.
(v) It is easier to find faults in network.
(vi) It is easy to troubleshoot.
(vii) It is easy to modify.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
(i) Failure of hub results in failure of entire network.
(ii) Cost of installation is high.
(iii) Performance is based on the single concentrator i.e. hub.
(iv) Cable requirements are more as compared to some other network topologies.
4. Mesh Topology
Mesh technology is an arrangement of the network in which computers are interconnected with each other through various redundant connections. There are multiple paths from one computer to another computer. In Mesh Topology, each node is directly connected to other nodes in the network. A mesh topology can be a fully or partially connected mesh topology.
(i) In a fully connected mesh topology, each computer in the network has a direct connection to all the other computers in that network.
(ii) In a partially connected mesh topology, at least two computers in the network have connections to other computers in that network.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
(i) Provides security and privacy.
(ii) Data can be transmitted from different devices simultaneously. This topology can withstand high traffic.
(iii) If any of the components fails, there is always an alternate route available. So, data transfer doesn’t get affected.
(iv) Expansion and modification in topology can be done without disrupting other nodes.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
(i) Installation and configuration process is difficult.
(ii) Cabling cost is more.
(iii) The cost of cables is high as bulk wiring is required, hence suitable for less number of devices.
5. Tree Topology
Tree topology combines the characteristics of bus topology and star topology. A tree topology is a type of structure in which all the computers are connected with each other in hierarchical fashion like the branches of a tree. Tree topology is known as a combination of a Bus and Start network topology. Tree network topology is the simplest topology in which only one route exists between any two nodes on the network. The pattern of connection resembles a tree in which all branches spring from one root, hence called Tree Topology.
Advantages of Tree Topology
(i) It is an extension of Star and Bus Topologies.
(ii) Expansion of Network is possible and easy.
(iii) We can divide the whole network into segments (star networks), which can be easily managed and maintained.
(iv) Error detection and correction is easy in it.
(v) If one segment is damaged, other segments are not affected.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
(i) Tree topology, relies heavily on the main bus cable, if it breaks whole network goes down.
(ii) The maintenance becomes difficult when more nodes are added.
(iii) Scalability of the network depends on the type of cable used.
(iv) It has higher cabling cost in setting up a tree structure.
6. Partial Mesh Topology
A partial-mesh topology is also a mesh topology similar to full-mesh topology. In partial-mesh topology, all the devices are not connected to each other as in full-mesh topology. In partial-mesh topology, some of the devices are connected to many devices together, but other devices are connected only to one or two devices. Partial-mesh topology is less complex than full-mesh topology, but less redundant than full-mesh topology. Implementation cost of partial-mesh topology is less than full-mesh topology.
Advantages of Partial Mesh Topology
(i) There is no traffic problem as there are dedicated point to point links for each computer.
(ii) It has multiple links, so if one route is blocked then other can be accessed for data communication.
(iii) It provides high privacy and security.
(iv) Fault identification is easy because of point-to-point connection.
Disadvantages of Partial Mesh Topology
(i) Mesh topology requires high number of cables and I/o ports for the communication.
(ii) Installation is very difficult in mesh topology, as each node is connected to every node.
(iii) Mesh topology is costly compared to the other network topologies i.e. star, bus, point to point topology.
7. Hybrid Topology
The combination of various different topologies is known as Hybrid topology. A hybrid topology is a type of network topology that uses two or more other network topologies, including bus topology, mesh topology, ring topology, star topology and tree topology. It is a mixture of any two or more topologies. In the following figure, Bus, Star and Tree topologies are connected to form a Hybrid Topology.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
(i) If a fault occurs in any part of the network will not affect the functioning of the rest of the network.
(ii) Size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices without affecting the functionality of the existing network.
(iii) This topology is very flexible as it can be designed according to the requirements of the organization.
(iv) Hybrid topology is very effective as it can be designed in such a way that the strength of the network is maximized and weakness of the network is minimized.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
(i) The major drawback of the Hybrid topology is the design of the Hybrid network. It is very difficult to design the architecture of the Hybrid network.
(ii) The Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are very expensive as these hubs are different from usual Hubs used in other topologies.
(iii) The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling, network devices, etc.
DATA COMMUNICATION
Data communications refers to the transmission of this digital data between two or more computers and a computer network or data network is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data. The device that transmits the data is known as sender/ source and the device that receives the transmitted data is known as receiver/destination. Data communication must fulfil following three conditions :
1. Delivery Network should deliver the data at intended destination.
2. Accuracy: Data communication should be free from fault.
3. Time limit : Data should reach at destination without any delay.
Components of Data Communication
There can be many varieties of components that may involve in Data communication. Some of the essential components of data communication are as follows:
1. Message: A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted from one person to another. It could be a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
2. Sender: It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or workstation, etc.
3. R ver: It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer, telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
4. Transmission Medium / Communication Channels : Communication channels are the medium that connect two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media.
5. Set of rules (Protocol): When someone sends the data (The sender), it should be understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is meaningless. For example, Sonali sends a message to Chetan. If Sonali writes in Hindi and Chetan cannot understand Hindi, it is a meaningless conversation.
Modes of Data Transmission
Modes of data transmission refer to the direction of flow of data between sender and receiver. Modes of data transmission are given below :
1. Simplex: In this mode of data transmission, communication is in one direction only. Only sender can broadcast information and receivers can only receive the broadcasted information. No receiver can send any type of information to anyone.
Example:
Television Communication.
Radio
Entering data using a keyboard, listing music using a speaker
2. Half Duplex: In this mode of data transmission, information can flow in directions but not at the same time. If information is sent by one node second can only receive it or vice versa as shown in the following figure.
Example :
Walky-talky system used by police and army.
3. Full Duplex: In this mode of data transmission, information can be transmitted in both directions at same time as shown in following figure. It provides fast communication between nodes.
Example:
Telephone System Mobile
Computer Guide for Class 9 PSEB Networking Textbook Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks :
1. ………………… is a group of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources such as printers, files and other resources.
(A) Network
(B) Internet
(C) Wireless
(D) Topology.
Ans. (A) Network
2. Which of the following is the smallest type of network ?
(A) MAN
(B) WAN
(C) LAN
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) LAN
3. ………………… is a device that allows you to connect multiple computers to a single network.
(A) HUB
(B) BUS
(C) Ring
(D) Star.
Ans. (A) HUB
4. In ………………. network topology, a single backbone cable is shared by all the devices.
(A) BUS
(B) TREE
(C) MESH
(D) STAR.
Ans. (A) BUS
5. ………….. prepares information and sends it.
(A) Protocol
(B) Receiver
(C) Sender
(D) Hub.
Ans. (C) Sender
Write True/False :
1. We cannot share hardware or software among network devices.
Ans. False
2. LAN covers a large geographic area.
Ans. False
3. In full duplex, information can be transmitted in both directions.
Ans. True
4. Protocols are set of rules by which data transmission takes place between nodes.
Ans. True
Write the Full Forms:
1. LAN : ……………………..
Ans. LAN Local Area network
2. MAN : ……………………..
Ans. MAN: Metropolitan Area Network
3. WAN : ……………………..
Ans. WAN : Wide Area Network
4. PAN : ……………………..
Ans. PAN : Personal Area network
5. NIC : ……………………..
Ans. NIC Network Interface Card
Short Answer Type Questions :
Q. 1. Write the names of any four Network Topologies.
Ans. The four type of network topologies are:
(i) Bus topology
(ii) Ring topology
(iii) Star topology
(iv) Tree topology
Q. 2. Define Network Interface Card (NIC).
Ans. A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). It is installed on the motherboard inside a system-unit so that a computer can be connected to a network. It should be fitted in each client and server computer.
Q. 3. Write the name of components of data communication.
Ans. The names of components of data communication are:
(i) Message
(ii) Sender
(iii) Receiver
(iv) Protocol
(v) Transmission media
Q 4. Write a short note on HUB.
Ans. A Hub is a hardware device that divides the network connection among multiple devices. When computer requests for some information from a network, it first sends the request to the Hub through cable.
Q. 5. What are the two types of ring topologies ?
Ans. The two types of ring topology are :
(i) Single ring topology
(ii) Double ring topology
Long Answer Type Questions :
Q. 1. What is Network ? Explain its advantages and disadvantages.
Ans. A network is the group of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources such as printers, files and other resources. It allows communication as well among different users within a network.
Advantages of Network :
Following are the advantages of computer network :
- Sharing Files, Data and Information : Data, programs and different resources can be shared with other user easily. All the files are stored on server.
- Sharing Hardware and Software Hardware and software can be shared within network easily.
- Fast Communication: Computer Network provides a very fast communication media. For Example: E-mail.
- File Integrity: Network helps in fast saving and sharing of files. So all the files remain integrated at all the time.
- Cost Effective: We can share costly input and output devices like printer with network. Thus, it reduces the cost of system.
- Reliability Network ensures use of many resources to users. When hardware fails, information can be recovered from other computer with the help of network.
- Flexibility: Computer network provides more flexibility for operations. There is a possibility of connecting devices of different organizations in it.
- Backup: It is easy to take backup from server if we are linked with network.
- Security Network provides security to users and devices. Network user can be restricted to access files or applications or devices.
- Speed: Sharing and transferring files within networks is very fast. It saves time and money and energy of users.
Disadvantages of Network :
Following are the disadvantages of network :
- Network Failure : All the central facilities may fail due to network failure.
- Management: For managing entire network, technical experts are required.
- Security: There are security threats in a network. Data can be misused in network.
- Expensive to Build : Building a network is costly affair. Cost of cables and other hardware equipment is very high. Many special hardware are also required for a network.
Q. 2. Explain the various components of computer network.
Ans. Following are components of Computer Network :
1. Computer: The purpose of a network is to interconnect computers. The first step for setting up a network is to identify computers and users who want to participate in the network. There are two types of computers which are used for creating a network :
- Client: Client is a normal computer system. Clients are computers that request and receive service from the servers to access and use the network resources. These computers are connected to a network for sharing various types of resources.
- Server Servers are high-configuration computers that manage the resources of the network. The network operating system is typically installed in the server and so they give user accesses to the network resources. Servers can be of various kinds: file servers, database servers, print servers etc. 20221
2. Network Interface Card: A Network Interface Card(NIC) is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). It is installed on the motherboard inside a system-unit so that a computer can be connected to a network. It should be fitted in each client and server computer.
There are two types of network cards :
- Ethernet Card: The Ethernet NIC uses Ethernet cables and connectors as a medium to transfer data.
- Wireless Card: In wireless card, the connection is made using such an antenna that employs radio wave technology.
3. HUB/Switch: A Hub is a hardware device that divides the network connection among multiple devices. When computer requests for some information from a network, it first sends the request to the Hub through cable. Hub will broadcast this request to the entire network. All the devices will check whether the request belongs to them or not. If not, the request will be dropped.
Switch A switch is a hardware device that connects multiple devices on a computer network. A Switch contains more advanced features than Hub. The Switch contains the updated table that decides where the data is transmitted or not. Switch delivers the message to the correct destination based on the physical address present in the incoming message.
4. Router: A router is a hardware device which is used to connect a LAN with an internet connection. It is used to receive, analyze and forward the incoming packets to another network.
5. Transmission Media : In data communication terminology, a transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e. it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types :
- Guided Media : It is a wired media, such Twisted Pair Cables, as Coaxial Cables and Optical Fiber etc.
- Unguided Media: It is a wireless media, such as Microwave signals, Satellites etc.
Q. 3. Write about different types of network.
Ans. On the basis of their size, Network can be categorized as follows:
1. Personal Area Network Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters. Personal Area Network is used for connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network. A Personal Area Network is a computer network organized around an individual person within a single building. This could be inside a small office or residence. Personal area networks can be constructed with cables or it can be wireless. It refers to the interconnection of information technology devices or gadgets (include laptop computers, PDAs, cell phones, printers) within the environment of an individual user.
2. Local Area Network (LAN): LAN is the most frequently used network. A LAN is a computer network that connects computers together through a common communication path, contained within a limited area, that is, locally. A LAN encompasses two or more computers connected over a server. The two important technologies involved in this network are Ethernet and Wi-fi. A LAN is a network that is used for communication among computer devices, usually within an office building or home. LAN’s enable sharing of resources such as files or hardware devices that may be needed by multiple users. It is limited in size, typically spanning a few hundred metres and no more than a mile. It is fast, with speeds from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps. It requires little wiring, typically a single cable connecting to each device. Twisted pair, coaxial or fiber optic cable can be used in wired LAN’s. It is suitable to bus, ring or star topologies.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. This is the type of computer network that connects computers over a geographical distance through a shared communication path over a city, town or metropolitan area. This type of network is distributed in a city, college campus or large area just like a Cable TV network. A MAN might be owned and operated by a single organization, but it usually will be used by many individuals and organizations. Many LANs may be interconnected in this type of network. A MAN often acts as a high-speed network to allow sharing of regional resources. A MAN typically covers an area of range between 5 to 50 km diameter. Examples of MAN :
4. Wide Area Network (WAN): WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over a large geographical distance through a shared communication path. It is not restrained to a single location but extends over many locations. WAN can also be defined as a group of local area networks that communicate with each other. WAN covers a large geographical area such as a country, continent or even the entire world. WAN can contain multiple smaller networks, such as LANS or MANs. In this network, various types of communication media such as – telephone lines, satellites, microwave signals etc. are used. These transmission media are linked with Router. The world’s most popular Wide Area Network is the Internet.
Q. 4. Explain the various modes of data transmission.
Ans. Modes of data transmission refer to the direction of flow of data between sender and receiver. Modes of data transmission are given below :
1. Simplex: In this mode of data transmission, communication is in one direction only. Only sender can broadcast information and receivers can only receive the broadcasted information. No receiver can send any type of information to anyone.
Example :
Television Communication.
Radio
Entering data using a keyboard, listing music using a speaker
2. Half Duplex: In this mode of data transmission, information can flow in both directions but not at the same time. If information is sent by one node then second can only receive it or vice versa as shown in the following figure.
Example:
Walky-talky system used by police and army.
3. Full Duplex: In this mode of data transmission, information can be transmitted in both directions at same time as shown in following figure. It provides fast communication between nodes.
Example:
Telephone System Mobile
PSEB 9th Class Computer Guide Networking Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the Blanks :
1. …………….. is a the group of two or more computers.
(A) Network
(B) Internet
(C) Wireless
(D) Topology.
Ans. (A) Network
2. …………….. is the normal computer system which is connected to network for sharing of resources.
(A) Server
(B) Client/Node
(C) LAN
(D) WAN.
Ans. (B) Client/Node
3. In ………………… network, a single cable is shared by all the devices and data travel only in one direction.
(A) Single Ring
(B) Dual ring
(C) MAN
(D) LAN.
Ans. (A) Single Ring
4. Process of error for data communication is called ……………….
(A) Delivery
(B) Accuracy
(C) Protection
(D) Protocol.
Ans. (B) Accuracy
5. …………………….. receive information.
(A) Sender
(B) Receiver
(C) Protocol
(D) Medium.
Ans. (B) Receiver
6. Graphical representation of Network devices is called.
(A) Topology
(B) Network
(C) Ring
(D) Cable.
Ans. (A) Topology
7. ……………… Topology uses common wire.
(A) Ring
(B) Star
(C) Bus
(D) Tree.
Ans. (C) Bus
Write True/False :
1. PAN covers a large geographic area.
Ans. False
2. In full duplex, information can move in both directions.
Ans. True
3. Protocol are rules under which data transmission takes place.
Ans. True
4. The efficiency of network is increased with increase of computers.
Ans. False
5. A node is a workstation which is connected to a computer.
Ans. True
6. MAN is a network which spreads in a city.
Ans. True
7. Data transfer rate is in Giga Bytes per second.
Ans. False
8. NIC connects server and workstations.
Ans. True
9. URL means Uniform resource locator in network.
Ans. True
10. 1 GBPS= 1,000,000,00
Ans. False
11. Air has unguided transmission medium.
Ans. True
12. A hub helps you to connect to a network.
Ans. True
13. Bandwidth is the capacity to transfer signals.
Ans. True
14. Available copy of a file can be used in computer network, in case of availability multiple copies.
Ans. True
Short Answer Type Questions :
Q. 1. Write a short note on Routers.
Ans. A Router is a network device that typically operates at the network layer of the OSI model. A Router performs the its job by examining the network Layer data packet (Ethernet Frame) and forwarding the packet to other devices based on IP Addresses. Both switches and bridges function using addressing system, also known as MAC addresses. Each port of a network switch is in a separate collision domain and therefore Switches are used to divide a big collision domain into multiple smaller collision domains.
Q. 2. Define Network.
Ans. A network is a set of devices connected by physical media links. A network is recursively is a connection of two or more nodes by a physical link or two or more networks connected by one or more nodes.
Q. 3. What is a LAN?
Ans. LAN is short for Local Area Network. It refers to the connection between computers and other network devices that are located within a small physical location.
Q. 4. What is a Node ?
Ans. A node refers to a point or joint where a connection takes place. It can be computer or device that is part of a network. Two or more nodes are needed in order to form a network connection.
Q. 5. Describe Network Topology.
Ans. Network Topology refers to the layout of a computer network. It shows how devices and cables are physically laid out, as well as how they connect to one another.
Q. 6. How does a network topology affect your decision in setting up a network ?
Ans. Network topology dictates what media you must use to interconnect devices. It also serves as basis on what materials, connector and terminations that is applicable for the setup.
Q. 7. What is WAN ?
Ans. WAN stands for Wide Area Network. It is an interconnection of computers and devices that are geographically dispersed. It connects networks that are located in different regions and countries.
Q. 8. Define star topology.
Ans. Star topology consists of a central hub that connects to nodes. This is one of the easiest to setup and maintain.
Q. 9. What advantages does fiber optics have over other media ?
Ans. One major advantage of fiber optics is that is it less susceptible to electrical interference. It also supports higher bandwidth, meaning more data can be transmitted and received. Signal degrading is also very minimal over long distances.
Q. 10. What is the difference between a hub and a switch?
Ans. A hub acts as a multiport repeater. However, as more and more devices connect to it, it would not be able to efficiently manage the volume of traffic that passes. through it. A switch provides a better alternative that can improve the performance especially when high traffic volume is expected across all ports.
Q. 11. Define networking.
Ans. Networking refers to the inter connection between computers and peripherals for data communication. Networking can be done using wired cabling or through wireless link.
Q. 12. What is mesh topology ?
Ans. Mesh topology is a setup wherein each device is connected directly to every other device on the network. Consequently, it requires that each device have at least two network connections.
Q. 13. What is the difference between logical and physical topology ?
Ans. Logical topology: The logical topology defines how the media is accessed by the hosts. It is used to describe the arrangement of devices on a network and how they communicate with one another. It is also referred to as Signal Topology.
Physical topology: The physical topology defines the actual layout of the wire i.e. media. It is concerned with the physical layout of the network; how the cables are arranged; and how the computers are connected. The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals.