PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
PSEB 9th Class Science Solutions Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
→ There are about 10 million living organisms present on earth and only 1/3rd of these organisms have been identified.
→ All organisms differ from each other in their structure.
→ The classification of organisms is arranging organisms into groups or sets on the basis of similarities and differences which also exhibit their relationships.
→ Each organism is different from all others to a lesser or greater extent.
→ The science of classification is called taxonomy.
→ Bacteria are microscopic of a few micrometres in size whereas blue whale and red Wood trees of California are of size 30 metres and 100 metres respectively.
→ Present-day diversity in living beings is the product of 3.5 billion years of organic evolution.
→ Carolus Linnaeus is the Father of Taxonomy.
→ Classification makes the study of a wide variety of organisms easy.
→ Classification helps us explore the diversity of life forms.
→ Linnaeus classified organisms on the basis of similarities and differences.
→ Binomial nomenclature was given by Linnaeus. Each organism is assigned two names, generic name, name of the genus, and specific name, of species.
→ In two-kingdom systems of classification, kingdom Plantae and kingdom Animalia were classified.
→ Plants are autotrophic, prepare their own food and plant cells have cell walls made up of cellulose. Divided into two groups crypto game and phanerogamae.
→ Animals lack chlorophyll and are heterotrophic in nutrition.
→ R. H. Whittaker (1969) proposed five kingdom systems of classification.
→ The five kingdoms are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
→ Monerans lack well-defined nuclei and membrane-bound cell organelles.
→ This group includes bacteria, blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), and Mycoplasma.
→ Protists include unicellular eukaryotic organisms. Some may have specialized structures for moving such as cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia.
→ Agar, diatoms, and protozoans are examples.
→ Plantae and Animalia are further divided into subdivisions on the basis of increasing complexity.
→ Charles Darwin (1959) described the idea of evolution in his book, ‘The Origin of Species’.
→ ‘Primitive’ or ‘lower’ organisms have ancient body designs.
→ Advanced or higher organisms acquired their particular designs relatively recently.
→ Complexity in design increases over evolutionary time.
→ Biodiversity refers to a variety of life forms found in a particular region.
→ The warm and humid tropical regions of the earth are rich in diversity of plant and animal life. The region is called the region of megadiversity.
→ Ernst Haeckel (1894), Robert Whittaker (1959), and Carl Woese (1977) have tried to classify all living organisms into broad categories, called Kingdoms.
→ Aristotle classified animals according to their habitat (land or water).
→ Basis of classification
- Nature of cell Prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.
- The number of cells Single-cell or multicellular.
- Method of preparing food
- Plants carry out photosynthesis thus autotrophs.
- Fungi absorb food, thus absorptive.
- Animals have an ingestive (holozoic) modes of feeding.
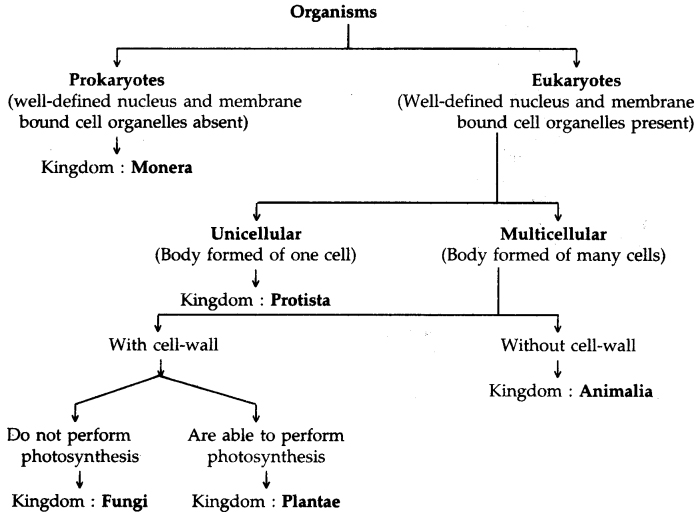
Classification of Kingdom Animalia:
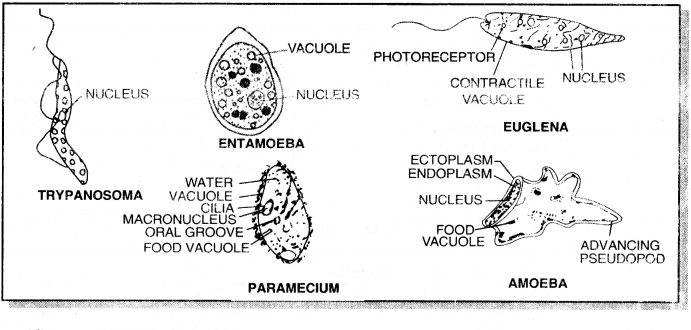
→ Protozoa are included in Protista, include single-celled, aquatic, free-living or parasitic organisms.
Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena.
→ Phylum Porifera era includes pore-bearing organisms called sponges which are the simplest multicellular animals.
→ Sponges are vase-like, rounded, sac-like, or branched. Euplectella, Sycon, Spongilla, Bath sponge are examples.
→ Phylum Cnidaria is a diploblastic radially symmetrical animal with two-layered body walls.
Examples: Hydra, Jellyfish, Sea anemone, and Corals.
→ In Phylum Platyhelminthes, flatworms have been included which are mostly parasitic.
Examples: Dugesia, Liver fluke, Tapeworm.
→ Round or threadworms are included in Phylum Aschelminthes which are triploblastic, unsegmented, and of bilateral symmetry. Example: Ascaris.
→ Annelids are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrically elongated with segmented bodies.
Examples: Earthworm, Leech, Nereis.
→ Animals with jointed legs have been placed in Phylum Arthropoda. These animals’ body is covered with chitinous cuticle.
Examples: It is the largest phylum and includes prawns, insects, spiders, scorpions, etc.
→ In Phylum Mollusca, the body is divided into three regions i.e. head, a dorsal visceral mass, and ventral foot. These are soft-bodied animals.
Examples: Pila, Unio.
→ Phylum Echinodermata includes starfishes, brittle stars, and sea urchins. These are spiny-skinned.
Examples: Starfish, Sea lily
→ In Phylum Hemichordata, the body is divided into three parts i.e. proboscis, collar, and trunk.
Examples: Balanoglossus.
→ Phylum Chordata represents the most advanced group of kingdom Animalia.
→ Protochordate group includes Herdmania and Amphioxus.
→ Chordates bear
- a solid rod-like structure called the notochord, on the dorsal side above the gut
- dorsal hollow nervous system
- pharynx, perforated by gill slits
→ Systematics: It is the study of the diversity of organisms and all their comparative and evolutionary relationship.
→ Taxonomy: It deals with the identification, nomenclature, and classification of different types of organisms.
→ Species: A group of living organisms of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes and interbreeding. The species is ranked below a genus.
Example: Homo sapiens.
→ Fertilization: Fusion of male gamete and female gamete is called fertilization.
→ Classification: It is the arrangement of organisms into groups on the basis of similarities and differences.
→ Binomial Nomenclature: Every organism is given a scientific name that has two parts, the first is the name of the genus (generic name) and the second is the name of the species (specific name).
→ Dicotyledonous: Plant having seeds with two cotyledons.
→ Ovule: A structure in the ovary of a seed plant that develops into a seed following fertilization.
→ Gametophyte: The haploid generation producing gametes in plants.
→ Annuals: A plant that completes its life cycle in one growing season.
→ Mycelium: A mass of filament or hyphae, composing the vegetative part of many fungi.
→ Hyphae: One of the filaments composing mycelium.
→ Saprophyte: A plant that lives on decaying organic matter.
→ Notochord: An elongated dorsal cord which is the primitive axial skeleton of chordates.
→ Aerobe: An organism that can grow and live in the presence of oxygen.
→ Nocturnal: Active during night e.g. cockroach.
→ Polygamy: When one male lives in the company of many females e.g. Struthio.
→ Producers: The first trophic level in a food chain. Producers are those organisms that can prepare food from inorganic materials i.e. green plants.
PSEB 9th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Give a broad outline classification of kingdom plantae.
Answer:
Classification of kingdom Plantae:
- Kingdom Plantae is divided into five subdivisions i.e. Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
- Thallophyta includes Algae.
- Algae are found in water and moist places.
- Fungi are non-green, heterotrophic (parasitic and saprophytic) thallophytes.
- In Bryophytes, plant body is thallus-like (thalloid) or leaf-like (foliose). Body differentiated to form stem and leaf-like structure. Riccia, Marchantia and Funaria are examples.
- In pteridophytes plant body is differentiated into root, stem and leaves. There is specialised tissue for conduction of water and other materials. This group includes Marselia, Ferns, and horse tails.
- In Gymnosperms, seeds are not covered with fruit wall or pericarp. Cycas, Pine, and deodar are examples.
- In Angiosperms, seeds are covered with fruit wall or pericarp to form fruits.
Question 2.
What are phanerogams? Write characters of gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Answer:
Phanerogamae. These are seed-bearing plants. Vascular tissue is present. They are found on land. This division is composed of two main sub-divisions i.e. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Characters of gymnosperms:
- They are flowering plants and seeds develop inside fruit.
- Cotyledons are the plant embryos present inside the seed.
- Plant body is divided into root system and shoot system. Examples: Mango, Rose, Wheat, Grasses.
Question 3.
Give an outline classification of animal kingdom with two characters of each phylum with example.
Answer:
Classification of kingdom Animalia:
| Name of phylum | Characters | Examples |
| 1. Porifera | Pore bearing body, spongocoel present. | Leucosolenia, Sycon, Spongilla |
| 2. Coelenterata | Diploblastic, radial symmetry, nematocysts present. | Hydra, Obelia, Physalia, Aurelia |
| 3. Platyhelminthes | Triploblastic, flat body, acoelomate | Fasciola, Taenia, Turbellaria |
| 4. Nematehelminthes | Pseudocoelomate, cylindrical body | Ascaris, Dracunculus |
| 5. Annelida | coelomate, segmented body, setae or suckers or parapodia present. | Pheretima, Nereis, Leech |
| 6. Arthropoda | Jointed appendages, chitinous exoskeleton, haemocoel present | Crab, prawn, centipede, spider, cockroach |
| 7. Mollusca | soft-bodied, shell present | Pila, Unio, Chiton, Dentalium |
| 8. Echinodermata | spiny skin, water vascular system | Sea Lily, Seastar, Sea urchin, Sea cucumber |
| 9. Hemichordata | Notochord in proboscis, Tomaria larva | Balanoglossus |
| 10. Chordata | Notochord present, dorsal hollow nerve tube, pharynx perforated by gill slits | Fishes, Frog, Toad, Snakes, Lizard, Birds, Mammals |
Question 4.
Write characters of phylum protozoa and phylum porifera.
Answer:
Characters of Phylum Protozoa:
1. Very minute, one-celled microscopic organisms. Cell itself is an organism therefore, they are also called acellular organisms.
2. Structure is very simple. The body consists merely of a mass of protoplasm. There is no tissue or organ formation.
3. Generally, there is no skeleton. However, locomotory and feeding organelles such as pseudopodia, flagella or cilia may be present.
Example. Amoeba, Entamoeba, Paramecium, Trypanosoma.
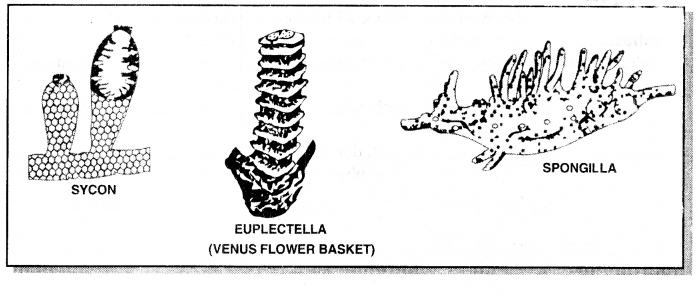
Characters of Phylum Porifera:
1. They are primitive, sessile animals with specialized cells but no tissues or organs.
2. Pores ali over the body, no digestive tract.
3. Collar cells filter out food particles from water current flowing through canal system.
4. Mostly marine.
5. They are called sponges.
Examples: Euplectella, Sycon, Spongilla.
Question 5.
Give a brief account of Whittaker’s five kingdoms of life.
Answer:
Whittaker’s Five Kingdoms are: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
- Kingdom Monera: Monerans are prokaryotes. Examples: Bacteria, Blue-green algae.
- Kingdom Protista: Protists are unicellular eukaryotes having widely diverse lifestyles. Protists form tine precursors from which higher forms-Plantae, Fungi and Animalia-arose on photosynthetic, assimilative and ingestive lines. Examples: Mastigophores, Ciliates, Sarcodines, Sporozoans, Slime moulds, Diatoms.
- Kingdom Fungi: Fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms with assimilative nutrition. Examples: Rhizopus, Agarieus,
- Kingdom Plantae: Plantae includes eukaryotic, multicellular, photosynthetic organisms. It includes green multicellular plants.
- Kingdom Animalia: Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular consumer characterised by ingestive nutrition. It includes non-chordates and chordates.
Question 6.
Differentiate between plants and animals.
Answer:
Differences between plants and animals:
| Characters | Plants | Animals |
| 1. Mode of nutrition | Autotrophs, prepare food from inorganic substances. | Heterotrophs, feed on complex organic compounds. |
| 2. Photosynthesis | Photosynthesize. | Do not photosynthesize. |
| 3. Chlorophyll | Possess chlorophyll. | Have no chlorophyll. |
| 4. Locomotion | Are fixed but move parts of the body. | Move the whole body. |
| 5. Branching | Branching body. | Compact body. |
| 6. Response | Are less sensitive and respond slowly. | Are highly sensitive and respond quickly. |
| 7. Cell wall | Cellulose cell walls usually present. | Have no cellulose cell walls. |
Question 7.
Enlist the peculiar features of phylum Arthropoda.
Answer:
- These have organ-system organization and bilateral symmetry.
- These are triploblastic and haemocoelomates (have hemocoel-a body cavity with blood).
- Their body is externally covered by a sclerotized chitinous exoskeleton formed of plates, called sclerites, and are formed of chitin.
- Body is divided into 2 (cephalothorax and abdomen) or 3 parts (head, thorax and abdomen).
- Mouth is surrounded by mouthparts which are of different types in different arthropods.
- These have jointed appendages which are of different types to perform different functions.
- These have complete and coiled gut.
- Respiration occurs by gills or book lungs or tracheae (air tubes).
- Blood is colourless and is called hemolymph.
- Excretion occurs by green glands or coxal glands or malpighian tubules.
- Examples: Insects Periplaneta (cockroach), Butterfly, Dragonfly, Housefly, Crustaceans, Crab, Centipede, Palaemon (Prawn), Millipede and Scorpion (Arachnid).
Question 8.
Write distinct features of phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
- Spiny skin of these animals contain dermal calcareous plates. Spines may be movable (c.g. sea urchin).
- Pentaradial symmetry in adult but larva is bilaterally symmetrical.
- Head absent. But divisible into central disc and arms.
- Water vascular system (Ambulacra! system) is present. It consists of an array of radiating and tube-like appendages called tube feet. Locomotory organs are tubular tube feet or podia and also aid in capturing prey.
- Body has oral surface bearing mouth and aboral surface bears anus.
- Tube feel, and dermal branchiae aid in gaseous exchange.
- All are marine, mostly gregarious and free living, creep slowly on the sea bottom.
Examples: Star fish, Sea urchin. Sea cake, Sea lily and Sea cucumber.
Question 9.
Give diagnostic characters of phylum chordata.
Answer:
Diagnostic characters of Phylum Chordata:
- Presence of notochord, at any stage of life history. Notochord is stiff rod-like structure which is retained throughout life in lower chordates. It is replaced by vertebral column in higher chordates.
- Presence of dorsal, hollow nervous system.
- Pharynx is perforated by gill slits at any stage of life history.
- Tail is present at any stage of life history.
- Respiratory pigment haemoglobin is present in the R.B.C.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Briefly describe diversity of life.
Answer:
Diversity of life (also called biological diversity or biodiversity) is the variety of living systems. It may refer to extinct organisms, but also to their diversity in the past. It usually covers multiple levels of biological diversity. About 2 million species have been described upto date. About 17000 – 19000 new species are added every year to the list. Exact number of species present on earth is unknown, current estimates favouring figures in the range of 8-12 million.
Thus biological diversity includes all forms of life including micro-organisms, plants and animals. Biological diversity is constantly changing.
Question 2.
Differentiate taxonomy and systematics.
Answer:
Difference between Taxonomy and Systematics:
| Taxonomy | Systematics |
| 1. It is the science of identification, nomenclature and classification.
2. It deals with rules and principles of classification. |
1. Systematics is the science of identification, nomenclature, description and classification.
2. It brings out unique properties at every level of classification |
Question 3.
Describe the importance of classification.
Answer:
Importance of classification:
- Recognition: Classification of living beings recognises the basic taxonomic units or species.
- Description: Classification of organisms is responsible for description of species.
- Relationship: It tells a possible way for grouping these units on the basis of their resemblances and relationships.
- Phylogeny: It gives us most of the information permitting a reconstruction of phylogeny of life. It helps in understanding the evolution of organisms.
- Applied biology: It has great role in applied biology (agriculture, public health, environmental biology) also.
- The introduction of harmful plants and animals can be checked. Exact identification of harmful pests, a disease vector, a pathogen and their control is made possible with knowledge of applied biology.
- Human health: Exact identification of insects helps in controlling the epidemic diseases like malaria, filaria, dengue fever, kala-azar etc.
- Horticulture: Several ornamentals have been introduced due to proper identification and nomenclature.
Question 4.
Why are local names not sufficient to recognize the organisms? What are the advantages of keeping scientific names?
Answer:
Local names are not understood elsewhere. The common name of a species often varies with language and region of world. In Biology, we deal with a very large number of species. It would not be possible to refer to them unless each one of them had a separate name for itself.
Advantages of scientific names:
- The scientific names are same all over the world.
- They are uniformly binomial.
- They are definite and accepted universally.
- They are descriptive.
- They indicate general relationship.
Question 5.
Write different categories of classification.
Answer:
- Species: It is defined as a dynamic group of organisms, which:
- resemble each other in all essential respects, i.c. structure and function.
- Interbreed among themselves to produce fertile young ones of their own kind.
- Genus: It forms the taxonomic higher category than species. It is a group of closely related species.
- Family: A number of genera having several common characters constitute a family.
- Order: A number of families having many common characters are placed in an order.
- Class: The class is the basic category. Similar orders are grouped together in the common class. A class is generally a subdivision of a phylum.
- Phylum: A number of classes having common features constitute a phylum.
- Division: In the case of plants, many classes constitute a division which corresponds to the phylum of animal kingdom.
- Kingdom: All the animals are included in Kingdom Animalia, while all plants are included in the Kingdom Plantae. It is the highest taxonomic category.
Question 6.
Classify tiger and mango.
Answer:
| Category | Tiger | Mango |
| Kingdom | Animalia | Plantae |
| Phylum/Division | Chordata | Tracheophyta |
| Sub-Phylum | Vertebrata | — |
| Class | Mammalia | Mangoliopsida |
| Order | Carnivora | Spindales |
| Genus | Panther a | Mangifera |
| Species | Tigris | Indica |
Question 7.
List differences between monocot plants and dicot plants.
Answer:
Apart below:
| Monocot plants | Dicot plants |
| 1. Roots are generally adventitious. | 1. They usually possess tap root. |
| 2. Venation in leaves is parallel. | 2. Venation is reticulate. |
| 3. Flowers of monocots are trimerous i.e. floral leaves in each whorl are either three or a multiple of three. | 3. Flowers in dicots are either tetramerous or pentamerous. |
| 4. The calyx and corolla are not differentiated and the outer two whorls are exactly alike to form perianth. | 4. The flower has distinct calyx and corolla. |
| 5. Vascular bundles in stem are scattered and closed. | 5. The vascular bundles in dicot stem arranged in-ring and are open. |
Question 8.
What are the basis of Whittaker’s system of classification?
Answer:
Whittaker based his classification on the following three criteria:
- The prokaryotic versus eukaryotic structure of cell.
- The unicellular versus multicellular organization.
- The three different modes of nutrition i.e. autotrophic, absorptive and holozoic (ingestive).
Question 9.
What are the advantages of five-kingdom system of classification?
Answer:
Advantages of five-kingdom system:
- The subdivisions of two kingdoms have been redistributed among additional kingdoms. Such an arrangement reflects the phylogeny evolutionary history of different life styles in a better way.
- This system allows us to visualize the increase of complexity with evolutionary time.
- Five kingdom arrangement allows us to visualize the divergence of their modes of nutrition in the multicellular organisms.
- An added advantage of Whittaker’s system lies in the coherence and definable characters of a kingdom as a unit of classification.
Question 10.
Name the five kingdoms as proposed by R.H. Whittaker. Give at least one example in each case.
Answer:
Robert H. Whittaker of Cornell University organised the living organisms into five kingdoms as follows:
- Kingdom Monera (Bacteria, Blue-green algae)
- Kingdom Protista (Amoeba, Euglena)
- Kingdom Fungi (Mushroom)
- Kingdom Plantae (Green Plants)
- Kingdom Animalia (Animals)
Question 11.
Give general characters of kingdom Monera.
Answer:
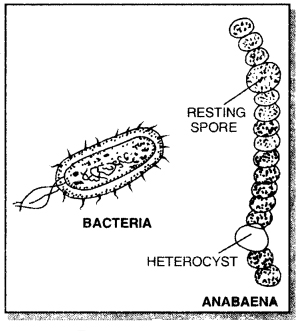
Characters of Kingdom Monera:
- Body is formed of single-cell but the cells lack nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts etc.
- They may be motile or non-motile. Flagella, if present, have a solid core and formed of flagellin protein.
- Monerans have various forms of nutrition: some are autotrophs capable of photosynthesis, others are capable of deriving energy from inorganic chemical reaction (chemosynthetic).
- Most species absorb organic nutrients from their environment.
- Reproduction is asexual.
- Some organisms may have cell wall.
- Monerans are the important decomposers in the biosphere. Examples are Bacteria, Blue-Green algae (Cyanobacteria) and Mycoplasma.
Question 12.
What kinds of organisms are grouped under Protista?
Answer:
Characters of Kingdom Protista:
- This kingdom includes diverse kinds of mostly unicellular and primarily aquatic eukaryotes.
- They are eukaryotic organisms having typical eukaryotic cell organelles such as nucleus, mitochondria, ER, Golgi bodies, plastids etc.
- Mode of nutrition may be absorptive, ingestive or photo-autotrophic.
- Mostly bear eukaryotic flagella or cilia composed of 9 + 2 internal microtubular structure.
- Reproduction asexual as well as sexual. Examples: Protozoan (Amoeba), Euglena, Diatoms.
Question 13.
Write the general characters of kingdom Fungi.
Answer:
Tire kingdom of multicellular decomposers is Fungi. This kingdom includes diverse kinds of eukaryotic, predominantly multicellular, heterotrophic organisms.
Characters of Kingdom Fungi:
1. Body organization mycelial or secondarily unicellular, composed of hyphae, coenocytic or septate.
2. They are non-green as chlorophyll is absent.
3. They are heterotrophic in nutrition and obtain food from dead and decaying organic matter by absorption.
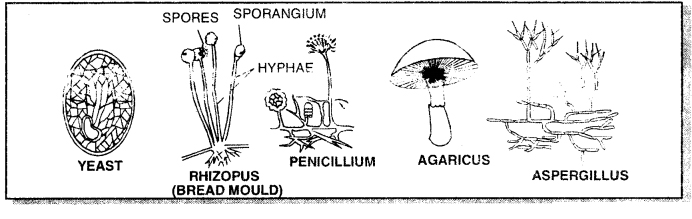
4. Cell wall is chitinous cellulose
5. Asexual reproduction by spore formation.
6. Sexual reproduction also occurs.
Examples: Bread moulds, mushrooms, puff balls and bracket fungi, Penicillium, yeast and certain parasitic fungi.
Question 14.
Make a list of characteristics of kingdom Plantae.
Answer:
Kingdom Plantae. This kingdom includes multicellular producers. The characteristics are:
- Complex multicellular plants adapted for photosynthesis.
- The plant cells are rigid because of cellulose cell wall.
- Mostly the cells are rigid and cannot contract and relax like animal cells do. Plants are immobile and do not exhibit the phenomenon of locomotion.
- Plant synthesize all organic constituents from water, C02 and inorganic forms of essential elements using light energy trapped by chlorophyll and accessory pigments.
- They have unlimited growth.
Question 15.
List the general characters of kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
Characters of Kingdom Animalia:
- Members of the group are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue differentiation.
- Nutrition hetero trophic, ingestive mode of intake of food.
- Muscle cells well developed which provide mobility.
- Nervous system well developed.
- Ecologically animals are consumers.
- Sexual reproduction occurs. Examples: Sponges, insects, molluscs, fishes, birds, reptiles and mammals.
Question 16.
What is binomial nomenclature? Illustrate with an example.
Answer:
In binomial nomenclature, name of every organism is composed of two components-first one is genus (generic) and second species name (specific).
Example: Scientific name of human is Homo sapiens where Homo is generic name and sapiens is specific name.
Question 17.
Give some examples of binomial nomenclature.
Answer:
- Scientific name of potato is Solanum tuberosum Linn. Where Solanum is genus, tuberosum is species and Linn is the scientist.
- Man is scientifically called as Homo sapiens Mill. Here Homo is a generic name and sapiens is specific name.
- Mill is the scientist. Sometimes specific names can be given after a country or locality e.g. Rosa indica, Rumcx nepalensis.
Question 18.
Write some advantages of binomial nomenclature.
Answer:
(a) The biological names are same all over the world.
(b) They are uniformly binomial.
(c) They are definite and accepted universally.
(d) They are descriptive.
(e) They indicate general relationship.
(f) All newly discovered plants and animals can be named and described easily.
Question 19.
Write distinguishing features of division Thallophyta.
Answer:
Characters of Division Thallophyta:
(a) Plants belonging to this group are the simplest and primitive.
(b) The plants are made up of single cell or group of cells.
(c) The plant body is thallus i.e. it is not differentiated into stem, root and leaves. id) The reproductive organs are unicellular and thus unjacketed.
(e) The zygote formed after fertilization, gives rise to either plant body directly or produces spores.
(f) Vascular tissue absent.
Question 20.
Write three characters of Algae. Give examples.
Answer:
Characters of Algae
(a) Green in colour due to chlorophyll.
(b) They are photoautotrophs.
(c) Reserve food material is starch.
Example: Chlamydomonas, Volvox, Ulothrix, Spirogyra.
Question 21.
Sketch Aspergillus, Penicillium and Agaricus.
Answer:
Question 22.
What are lichens?
Answer:
Lichens: They are organisms formed of intimate combination of an alga and fungus found in all types of habitat. It is an example of mutualism. Mycobiont is the fungal component and phycobiont an algal partner.
Example: Graphis, Parmelia and Usnea.
Question 23.
Write important characters of division Bryophyta.
Answer:
Characters of Division Bryophyta
(a) The plant body is not differentiated into root, stem and leaves (thalloid).
(b) Absorbing and anchoring organs are rhizoids.
(c) Vascular tissue and mechanical tissue absent.
(d) Vegetative reproduction is very common.
(e) Sexual reproduction is by gamete formation.
(f) Sex organs are multicellular and jacketed.
(g) Formation of sporogonium takes place.
Examples: Riccia, Porella, Punaria (Moss), Marchantia (Liverwort) and Anthoceros.
Question 24.
List four important features of Pteridophytes.
Answer:
Important features of Pteridophytes:
- The dominant plant body in ferns is sporophyte. It is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- The leaves are large (megaphyllous), variously-shaped and look like the branches. They are called as fronds.
- The stem may be an underground rhizome or a trunk as in tree ferns while the roots are adventitious.
- Ferns bear special spore-bearing leaves called the sporophylls. The spores are produced in sporangia.
- Spores in ferns, germinate each forming an independent, small gametophyte, the prothallus. The latter bear the sex organs, antheridia (male) and archegonia (female).
Question 25.
Make a few diagrams of common pteridophytes.
Answer:

Question 26.
What are the two main divisions of angiosperms on the basis of number of cotyledons.
Answer:
Classification according to cotyledons
The number of cotyledons in seed of a flowering plant is either one or two. The angiosperms are divided into two groups-1. Monocotyledons and 2. Dicotyledons.
1. Monocotyledons are the plants in which the seed contains a single cotyledon; e.g. Wheat, Rice, Maize, Sugarcane, Grasses. There are about 50,000 species of them.
2. Dicotyledons are those flowering plants in which the seed contains two cotyledons.
e.g. Solarium sp, Mango, Beans, Castor, Gram, Sunflower.
Question 27.
Write two differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Answer:
Differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms:
| Gymnosperms | Angiosperms |
| 1. The seeds are naked.
2. These are cone-bearing plants. |
1. The seeds are present within fruits.
2. They bear flowers. |
Question 28.
What characters of seed plants make them specially adapted to life on land?
Answer:
Characters of seed plants which make them specially adapted to life on land are:
- Presence of vascular tissue.
- The development of seed habit removed the liquid medium as an essential feature for fertilization.
- Presence of cuticle in the leaves.
Question 29.
Write three features of kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
Features of Kingdom Animalia:
- Eukaryotic cells lack cell wall.
- They do not perform photosynthesis instead take readymade food, thus heterotrophs.
- They have power of locomotion.
Question 30.
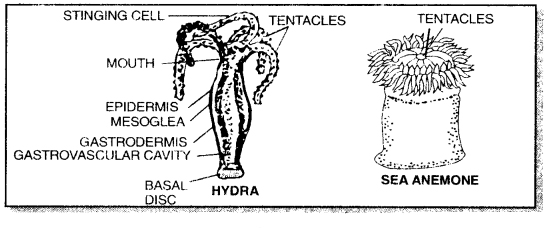
Write unique features of Coelenterates (cnidarians).
Answer:
Unique Features of Coelenterates (cnidarians)
- Tissue level of organisation of the body.
- Special stinging cells, the cnidoblasts, for defence and offence.
- Incomplete digestive tract bounded by gastrodermis of body wall.
- Simple gonads without gonoducts.
- Show polymorphism.
Examples: Hydra, Jellyfish and Sea Anemone.
Question 31.
Write characters of flatworms. Give example.
Answer:
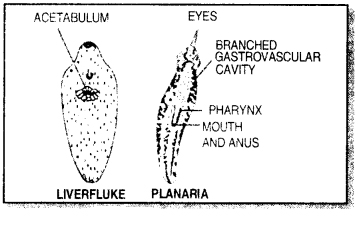
Characters of Flatworms:
- Dorsoventrally flattened triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical animals.
- They are acoelomate.
- Mostly parasite, a few are free living.
- Incomplete branched or unbranched alimentary canal.
- Bisexual or hermaphrodite. Life history is complicated. Examples: Planaria, Fasciola and Taenia.
Question 32.
Write features of roundworms.
Answer:
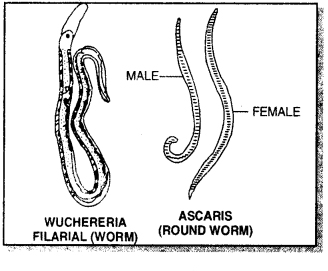
Features of Roundworms:
- Unsegmented, bilaterally symmetrical cylindrical worms also called as roundworms.
- They are triploblastic and pseudo- coelomatic.
- Mostly free living.
- Complete alimentary canal present.
- Sexes are separate and show sexual dimorphism. Fertilized egg has a thick wall and survive adverse conditions. Examples: Ascaris (Roundworm), Ancylostoma (Hookworm), Dracunculus (Guinea worm), Rhabditis.
Question 33.
List unique features of phylum Annelida. Give examples.
Answer:
Unique Features of Phylum Annelida:
1. Metameric segmentation i.e. body divided externally by grooves into metameres or segments and internally bv septa into compartments.
2. Nephridia for excretion and osmoregulation.
3. Closed circulatory system with respiratory pigment dissolved in the plasma. Examples : Nereis, Pheretima (Earthworm), Ilirudinaria (Leech), Aphrodite (Sea-mouse).
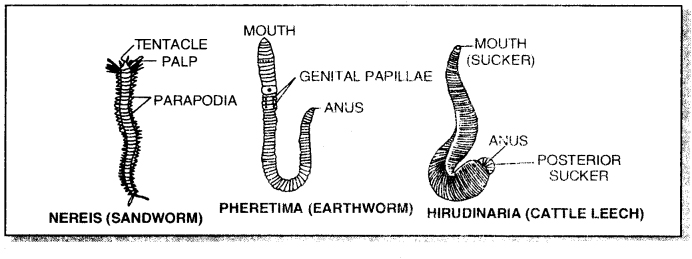
Question 34.
List three important distinguishing characters of phylum Arthropoda.
Answer:
Distinguishing Characters of Phylum Arthropoda
1. Body covered with chitinous exoskeleton.
2. Body bears jointed appendages.
3. One or two pairs of jointed antennae present.
4. There is an open circulatory system, and so the blood does not flow in well defined blood vessels.
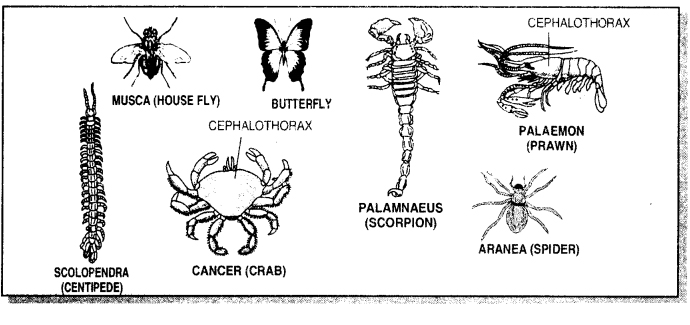
Question 35.
Write unique features of phylum Mollusca. Give three examples.
Answer:
Unique Features of Phylum Mollusca:
1. Three body regions head, visceral mass and foot.
2. A glandular fold, the mantle, over the body.
3. Mantle cavity with anal, excretory and genital apertures in it.
4. Calcareous shell around the body in most cases.
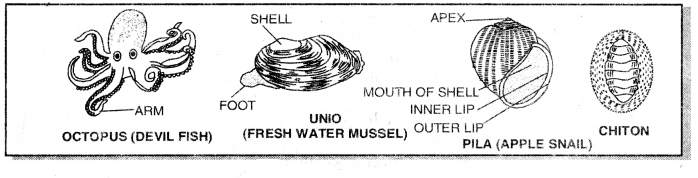
5. A rasping organ, the radula in the buccal cavity.
Examples: Pila, Sepia, Octopus.
Question 36.
What are Echinoderms?
Answer:
1. Phylum Echinodennata includes starfish, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, sea lilies etc.
2. The animals show pentaradial symmetry.
3. There is an exoskeleton of calcareous plates and spines.
4. Locomotion is by tube feet.
5. There occurs a peculiar water vascular system. Echinoderms are confined to sea.
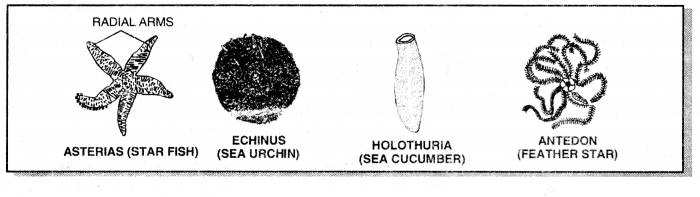
Question 37.
Write five examples of echinoderms.
Answer:
Examples of echinoderms
- Asterias (Star fish)
- Sea urchin
- Antedon (Sea lily)
- Sea Cucumber
- Sea cake
Question 38.
List three characters of phylum Hemichordata. Give one example.
Answer:
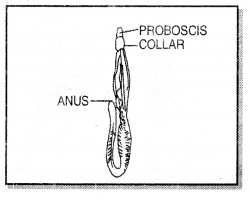
Characters of Phylum Hemichordata
- Body divided into proboscis, collar and trunk.
- Respiration through gills.
- Bilateral symmetry.
- Example: Balanoglossus (Tongue worm).
Question 39.
Give the general characteristics of the vertebrates.
Answer:
General Characters of Vertebrates:
- The body is divided into three regions – a head with an internal cranium, trunk and postanal tail.
- The notochord is replaced by vertebral column during life history.
- Body contains cartilaginous or bony endoskeleton.
- The post-anal part called tail is usually present.
- There is a complex brain with special sense organs.
- There is well developed ventral heart with two, three or four chambers.
- Two pairs of lateral appendages, fins or limbs present.
- The excretory organs are kidneys.
- Respiration occurs through gills or lungs.
- The sexes are separate.
Question 40.
Differentiate exoskeleton and endoskeleton.
Answer:
Differences between exoskeleton and endoskeleton:
| Exoskeleton | Endoskeleton |
| 1. It is present outside the body.
2. Examples: chitinuous cuticle of insects, calcareous shell of mollusc, hard plates of echinoderm, scales, feathers, hair, nails, horns of vertebrates. |
1. It is present inside the body.
2. Bones and cartilages constitute the endoskeleton. |
Question 41.
Write characters of class Pisces.
Answer:
Characters of Class Pisces:
- All fish varieties belong to this class which are exclusivusingely water living animals.
- Their skin is covered with scales/plates.
- They obtain oxygen dissolved in water by gills.
- The body is streamlined and a muscular tail is used for movement.
- They are cold-blooded and their hearts have only two chambers.
- Some fish varieties have their skeletons made entirely of cartilage, such as Sharks and some with a skeleton made of both bone and cartilage, such as Tuna or Rohu.
Question 42.
List distinguishing characters of cartilaginous fishes.
Answer:
Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous fishes):
1. Skeleton cartilaginous
2. Mouth and nares ventral
3. Gill slits uncovered
4. Tail fin asymmetrical
5. No swim bladder
6. Intestine with scroll valve
7. Males with claspers
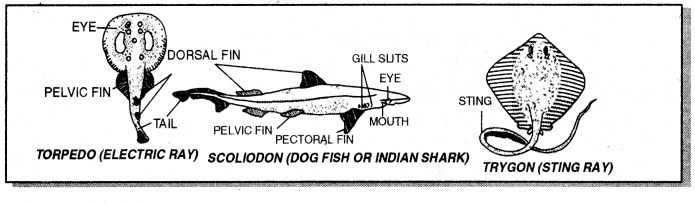
Examples: Scoliodon, Narcine, Torpedo, Trygon, Angler fish, Lionfish
Question 43.
List distinguishing features of bony fishes.
Answer:
Osteichthyes (Bony fishes):
1. Skeleton bony
2. Mouth anterior
3. Gill slits covered by opercula
4. Tail symmetrical
5. Swim bladder present
6. Intestine without scroll valve
7. Copulatory organs claspurs absent.
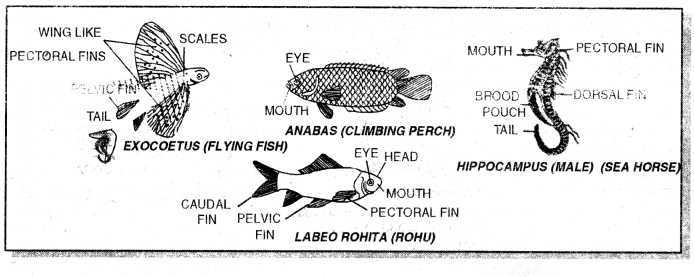
Examples: Labeo, Rita, Exocoetus, Hippocampus, Solea, Muraena, Lophius, Anabas, Protopterus.
Question 44.
Give a few features of class Amphibia.
Answer:
Features of Class Amphibia:
Amphibia (amphibians): First land vertebrates, evolved from lobe-finned bony fishes, skin naked and moist for respiration, have four limbs, digits without claws, sac-like lungs, 3-chambered heart, eggs laid in water, tailed, gill-breathing larva undergoes metamorphosis, embryonic membranes not formed.
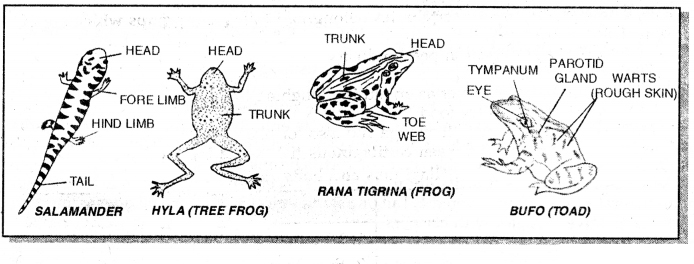
Examples: Ichthyophis, Ram (Frog), Bufo (Toad), Salamander.
Question 45.
Write distinguishing features of class Reptilia.
Answer:
Distinguishing characters of Class Reptilia
1. Dry homy scale-covered skin present.
2. Body divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail,
3. Heart divisible into incomplete four-chambered heart.
Question 46.
Write distinct features of class Aves.
Answer:
Features of Class Aves:
- Body covered with feathers.
- Forelimbs modified into wings.
- jaws absent, beak present.
- Lungs with air sacs.
Question 47.
Write distinguishing features of class Mammalia.
Answer:
Distinguishing features of Class Mammalia:
- Body is covered with hair.
- Presence of rnilk produced by mammary glands.
- Presence of pinnae or external ear.
- Presence of diaphragm.
- They give birth to young ones.
Question 48.
Name at least five invertebrates belonging to different groups which are of economic importance.
Answer:
- Pearl oyster helpful in pearl industry.
- Silkmoth spins silk.
- Earthworm helps the farmer as an aid in ploughing.
- Palaemon is consumed as food.
- Bath sponge is used as bath sponge and also for making cushions.
Question 49.
Write differences between cartilaginous fishes and bony fishes.
Answer:
Differences between cartilaginous and bony fishes:
| Cartilaginous Fish | Bony Fish |
| 1. Alwavs marine. | 1. May be marine or fresh water. |
| 2. Skin covered by small placoid scales. | 2. Scales are large either cycloid or ganoid. |
| 3. Mouth is subterminal or ventral. | 3. Mouth terminal. |
| 4. Gill slits not covered by operculum. | 4. Gills covered by operculum. |
| 5. Swim bladder absent. | 5. Presence of swim bladder. |
| 6. Endoskeleton entirely cartilaginous. | 6. Endoskeleton bony. |
| 7. Tail fin asymmetrical. | 7. Tail fin symmetrical. |
| 8. Usually viviparous. | 8. Oviparous. |
| Examples-Sharks, Rays, Sea horse. | Examples-Labeo, Catfish, Flat fish. |
Question 50.
Draw a few examples of common birds.
Answer:
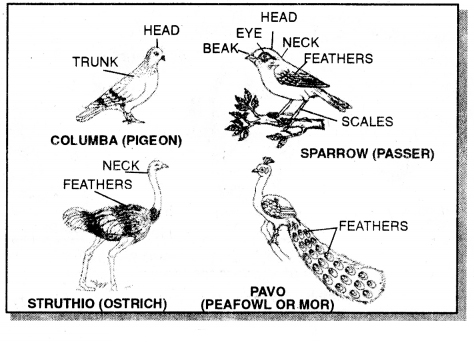
Question 51.
Make a flow chart of classification of Kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
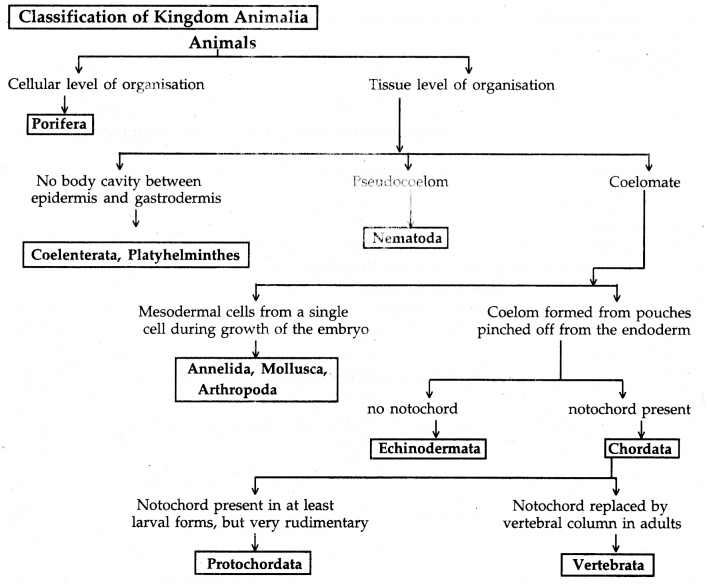
Question 52.
Write differences between chardates and non-chardates.
Answer:
Differences between chordates and non-chordates:
| Chordates | Non-Chordates |
| 1. Notochord is present in some stage of the life cycle.
2. Tail is present at some stage. 3. A living endoskeleton is present. 4. Pharyngeal gill slits are present at some stages of life. 5. Digestive tract is complete. 6. Heart is ventral. |
1. The notochord is absent in non- chordates.
2. Tail is absent in most cases. 3. Endoskeleton if present, is non-living. 4. Pharyngeal gill slits are absent. 5. Digestive tract may be complete, incomplete or absent. 6. Heart is absent, if present, then on dorsal or lateral side. |
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is Classification?
Answer:
The method of placing organisms into groups and such groups depending upon similarities and differences.
Question 2.
Who is the father of taxonomy?
Answer:
Carl Linnaeus.
Question 3.
Define species.
Answer:
Species. It is defined as a dynamic group of organisms, which:
1. resemble each other in all essential respects, i.e. structure and function.
2. interbreed freely under natural conditions to produce fertile young ones of their own kind.
Question 4.
Name the two groups according to old system of classification.
Answer:
1. Plant kingdom
2. Animal kingdom.
Question 5.
Who devised binomial nomenclature?
Answer:
Carolus Linnaeus.
Question 6.
Write two sub-groups of plant kingdom.
Answer:
1. Cryptogamae
2. Phanerogamae.
Question 7.
Why are algae green in colour?
Answer:
Green colour of algae is due to the presence of chlorophyll pigment in their cells.
Question 8.
How do fungi obtain their food?
Answer:
Fungi obtain their food from dead decaying matter by absorption.
Question 9.
Name two kinds of angiospermic plants.
Answer:
1. Monocotyledonous plants
2. Dicotyledonous plants.
Question 10.
Name the respiratory organ of fishes.
Answer:
Gills.
Question 11.
How many chambers are present in the heart of fishes?
Answer:
Two chambers.
Question 12.
Give examples of bony fishes.
Answer:
Labeo (Rahu), Anabas, Exocoetus, Hippocampus (Sea horse).
Question 13.
Write examples of phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
Starfish, Sea cucumber, Sea Lily, Sea urchin, Antedon (Feather star).
Question 14.
Write examples of phylum Urochordata.
Answer:
Herdmania, Doliolum, Pyrosoma.
Question 15.
Give one example of cartilaginous fish.
Answer:
Scoliodon.
Question 16.
Name the excretory structures of flatworms.
Answer:
Flame cells
Question 17.
Name the body cavity of Nematodes.
Answer:
Pseudocoel.
Question 18.
Give the habitat of Ascaris.
Answer:
An endoparasite of intestine of man, especially children.
Question 19.
Name any two mammals.
Answer:
1. Elephant
2. Monkey
Question 20.
What are the different forms with respect to size in which life occurs on earth?
Answer:
Microscopic bacteria a few micrometres in size, the ~30 metre long blue whale and -100 metre tall redwood trees of California.
Question 21.
Name the plant having life span of more than thousand years.
Answer:
Pine trees.
Question 22.
Which division of biology helps us in exploring the diversity of life forms?
Answer:
Taxonomy.
Question 23.
Who made the first attempt to classify animals?
Answer:
Aristotle.
Question 24.
Name any five marine animals.
Answer:
Whale, Octopus, Star fish, Shark, Sea horse.
Question 25.
Name the organisms which carry out photosynthesis.
Answer:
Green plants.
Question 26.
What do you mean by characteristics?
Answer:
Characteristic is a particular form or function of a living organism.
Question 27.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell. A cell without clearly demarcated nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Question 28.
Give examples of prokaryotes.
Answer:
Prokaryotes (monerans) includes bacteria, blue-green algae.
Question 29.
What is evolution?
Answer:
Descent with modification.
Question 30.
Who wrote the book ‘Origin of species’?
Answer:
Charles Darwin (1859).
Question 31.
What are primitive animals?
Answer:
The group of animals which have ancient body divisions and have not changed very much. They are also called lower organisms.
Question 32.
Define advanced organisms.
Answer:
The group of organisms that have acquired their particular body design relatively recently, also called ‘higher’ organisms.
Question 33.
Name five kingdoms as proposed by R.H. Whittaker.
Answer:
Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia.
Question 34.
What are basis of five kingdom classification as proposed by Whittaker?
Answer:
1. Nature of cells
2. Number of cells
3. Mode of nutrition
Question 35.
Name the two divisions as proposed by Karl Woose.
Answer:
1. Archaebacteria
2. Eubacteria
Question 36.
Name the various taxonomic categories.
Answer:
Species, genus family, order, class, phylum and kingdom.
Question 37.
Name the tnree aspects of systematics.
Answer:
Identification, nomenclature and classification.
Question 38.
What is highest taxonomic category?
Answer:
Kingdom.
Question 39.
What is the nature of cells of monerans?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell.
Question 40.
Name the kind of mode of nutrition in kingdom Monera,
Answer:
Autotrophic and Saprotrophic.
Question 41.
Give examples of kingdom Monera.
Answer:
Bacteria, Cyanobacteria and Mycoplasma.
Question 42.
Write locomotory structures of kingdom Protista.
Answer:
1. Cilia
2. Flagella
Question 43.
Write examples of Protista.
Answer:
Single-celled algae, Protozoa (Fuglena, Amoeba) and Diatoms.
Question 44.
Give examples of Fungi.
Answer:
Yeast, Mushroom, Mucor, Rhizopus.
Question 45.
What is the mode of nutrition of Fungi?
Answer:
Fungi obtain their food from dead decaying organic matter.
Question 46.
What is symbiosis?
Answer:
An inter-relationship between two different species e.g. Lichens.
Question 47.
Write few characters of kingdom Animalia.
Answer:
1. Eukaryotic
2. Multicellular
3. Heterotrophic mode of nutrition
Question 48.
What is thallus-like plant body?
Answer:
When there is no differentiation of the plant body into root, stem and leaves.
Question 49.
Give few examples of Bryophytes.
Answer:
Riccia, Mardmntia, Funaria (Moss).
Question 50.
Name the division which is called ‘amphibians of plant kingdom’.
Answer:
Bryophyta.
Question 51.
What is hypha?
Answer:
In fungi, thallus is made up of colourless filamentous structure called hypha.
Question 52.
What is the mode of nutrition in Fungi?
Answer:
Absorptive-saprophytic, Heterotrophic.
Question 53.
Name the group in which seeds are naked.
Answer:
Gymnosperms.
Question 54.
Name the group in which reproductive organs are flowers.
Answer:
Angiosperms.
Question 55.
Name the class of angiosperms in which reticulate venation is present.
Answer:
Dicots.
Question 56.
Name the class of organisms in which leaves show parallel venation.
Answer:
Monocots.
Question 57.
Name the reproductive organ of Angiosperms.
Answer:
Flower.
Question 58.
What are cryptogams?
Answer:
Cryptogams are flowerless, seedless, lower plants.
Question 59.
What are phanerogams?
Answer:
Phanerogams are seed bearing plants.
Question 60.
What are Algae?
Answer:
These are green, autotrophic thallophytes.
Question 61.
Write examples of dicot plants.
Answer:
Pea, Gram, Rose.
Question 62.
How do oviparous and viviparous animals differ from each other?
Answer:
Oviparous animals lay eggs e.g. birds, while viviparous animals give birth to young ones e.g. most of mammals.
Question 63.
What are hermaphrodite animals?
Answer:
Animals which have both male and female reproductive organs e.g. earthworm, leech, etc.
Question 64.
Name the skeletal elements of sponges.
Answer:
Spicules (needles) or spongin fibres or both.
Question 65.
What are cnidoblasts? Give their function.
Answer:
These are stinging cells present on the tentacles of coelenterates like Hydra. These inject the hypnotoxin and paralyze the prey.
Question 66.
Name the cavity present in the body of Coelenterates.
Answer:
Coelenteron.
Question 67.
Mention two characters of sponges.
Answer:
Presence of two types of pores (dermal ostia and osculum) and collar cells.
Question 68.
Which characters appeared for the first time in the flatworms?
Answer:
Triploblastic, bilateral symmetry and organ-system organisation.
Question 69.
Write two examples of phylum Annelida.
Answer:
Earthworm, Leech.
Question 70.
Write two examples of phylum Coelenterata.
Answer:
Hydra, Obelia.
Question 71.
Name five animals belonging to kingdom Arthropoda.
Answer:
Prawn, Butter fly, Housefly, Spider, Crab, Body Louse.
Question 72.
Write two examples of phylum Mollusca.
Answer:
Pila, Unio, Cuttlefish.
Question 73.
Give two examples of phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
Star Fish, Sea lily.
Question 74.
What is primary unit of classification?
Answer:
Species.
Question 75.
What were the two most outstanding contributions of Linnaeus to the modem science of taxonomy?
Answer:
The outstanding contributions of Linnaeus were his method of grouping species in a hierarchy and his binomial method of nomenclature.
Question 76.
What is a genus?
Answer:
Group of related species.
Question 77.
Why do species included in a genus resemble in many features?
Answer:
Because they have originated from a common ancestor.
Science Guide for Class 9 PSEB Diversity in Living Organisms InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why do we classify organisms?
Answer:
Classification helps in the study of broad group of organisms with a wide variety in a simple way.
Question 2.
Give three examples of the range of variations that you see in life forms around you.
Answer:
Different forms in which life occurs on earth
- Size. Microscopic bacteria a few micrometres in size at one end of the size-scale and ~ 30 metre long blue whale and ~ 100 metre tall red wood trees of California.
- Life Span. Pine trees live for thousands of years while insects such as mosquitoes die within few days.
- Colour. Colourless or transparent worms to brightly coloured birds and flowers.
Question 3.
Which do you think is more basic characteristic for classifying organism and why;
(a) the place where they live?
(b) the kind of cells they are made of?
Answer:
The kind of cells is more basic characteristic for classification of organisms. The cells may be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. The presence or absence of nucleus, or membrane bound organelles would reflect on every aspect of cell design and capacity to make a multicellular body.
Question 4.
What is the primary characteristic on which the first division of organism is made?
Answer:
Nature of Cell. Prokaryotic cell or eukaryotic cell.
Question 5.
On what bases plants and animals put into different categories?
Answer:
- Mode of nutrition. Plants prepare their own food by photosynthesis due to the presence of chlorophyll in chloroplasts and animals acquire ready made food.
- Plants are fixed whereas animals are motile.
- Plants show limited growth whereas animals stop growing after attaining a certain size.
- Plant cells are surrounded by cell wall and animal cells lack cell wall.
Question 6.
Which organisms are called primitive and how are they different from the so called advanced organisms?
Answer:
- Primitive organisms: The organisms which have ancient body designs that have not changed very much. They are also called ‘lower’ organisms.
- Advanced organisms: The group of organisms that have acquired their particular body design relatively recently. They are also called ‘higher’ organisms.
Question 7.
Will advanced organisms be the same as complex organisms? Why?
Answer:
Yes, complexity in design will increase over evolutionary time, hence older (primitive) organisms are simple while younger organisms are more complex.
Question 8.
What is the criterion for classification of organisms as belonging to kingdom monera or protista?
Answer:
The criterion for classification of monera and protista Nature and number of cell. Prokaryotes belong to kingdom monera and single celled eukaryotes belong to kingdom protista.
Question 9.
In which kingdom will you place an organism which is single celled eukaryotic and photosynthetic?
Answer:
Protista.
Question 10.
In the hierarchy of classification, which grouping will have the smallest number of organisms with a maximum of characteristics in common and which will have the largest number of organisms?
Answer:
- Species will have smallest number of organisms.
- Kingdom will have largest number.
Question 11.
Which division among plants has simplest organisms?
Answer:
Algae (Thallophytes).
Question 12.
How are pteridophytes different from phanerogams?
Answer:
- Phanerogams produce seeds while pteridophytes do not.
- Reproductive organs are hidden in pteridophytes but well developed in phanerogams.
- Pteridophytes have specialised tissue for the conduction of water whereas proper vascular tissues are present in phanerogams.
Question 13.
How do gymnosperms and angiosperms differ from each other?
Answer:
Differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms:
| Gymnosperms | Angiosperms |
| 1. Seeds are naked. | 1. Seeds are enclosed in fruits. |
| 2. Reproductive organs sporophylls form cones. | 2. Reproductive organs are flowers. |
| 3. Ovules not enclosed in ovary. | 3. Ovules are enclosed in ovary. |
| 4. Xylern lack vessels. | 4. Xylem contain vessels. |
| 5. Companion cells are absent in phloem. | 5. Companion cells are present. |
Question 14.
How do poriferans animals differ from coelenterate animals?
Answer:
Differences between poriferans and coelenterates:
| Poriferans | Coelenterates |
| 1. Numerous minute pores ostia for entry of water and single osculum for exit of water present. | 1. The body bears a single pore. |
| 2. Appendages absent. | 2. Tentacles as appendages present. |
| 3. Intercellular digestion. | 3. Digestion is intracellular as well as intercellular. |
| 4 Spicules or spongin fibres present. | 4. Stinging cells called cnidoblasts present. |
Question 15.
How do annelid animals differ from arthropods?
Answer:
Differences between annelids and arthropods
| Annelids | Arthropods |
| 1. Jointed appendages absent.
2. Body covered with cuticle. 3. True coelom as body cavity present. 4. Closed type of circulatory system present. |
1. Body bears jointed appendages.
2. Body covered with chitinous cuticle forming exoskeleton. 3. Haemocoel present. 4. Open type of circulatory system present |
Question 16.
What are the differences between amphibia and reptilia?
Answer:
Differences between amphibia and reptilia:
| Amphibia | Reptilia |
| 1. Body wall not covered with any kind of exoskeleton. | 1. Scales or dermal plates present. |
| 2. Body divided into head and trunk. | 2. Body divided into head, neck, trunk and tail. |
| 3. Fertilization is external. | 3. Fertilization is internal. |
Question 17.
What are the differences between animals belonging to the aves group and those in the mammalia group?
Answer:
Differences between aves and mammals:
| Aves | Mammals |
| 1. Body covered with feathers. | 1. Body covered with hair. |
| 2. Wings present. | 2. Wings absent. |
| 3. Pinna absent. | 3. Pinna present. |
| 4. Diaphragm absent. | 4. Diaphragm present. |
PSEB 9th Class Science Guide Diversity in Living Organisms Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the advantages of classifying organisms?
Answer:
Advantages of classification
- Classification makes the study of wide variety of organisms easy.
- Classification of organisms is responsible for description of species.
- It helps in understanding the interrelation among different groups of organisms.
- Classification of living beings recognises the basic taxonomic units of species.
- It helps in understanding the evolution of organisms.
- Exact identification of insects helps in controlling epidemic diseases like malaria, filaria, dengue fever, kala azar etc.
Question 2.
How would you choose between two characteristics to be used for developing a hierarchy in classification?
Answer:
Characteristic is a particular form or function. Many inter-related characteristics are used in order to classify all living organisms.
- Nature of cell is basic characteristic of classification.
- Number of cells.
Question 3.
Explain the basis for grouping organisms into five kingdoms.
Answer:
- Nature of cell. Prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
- Number of cells. Unicellular or multicellular.
- Mode of nutrition. Absorptive, autotrophic or holozoic.
Question 4.
What are the major divisions in kingdom Plantae? What are the basis for these divisions?
Answer:
Major divisions of Kingdom Plantae.
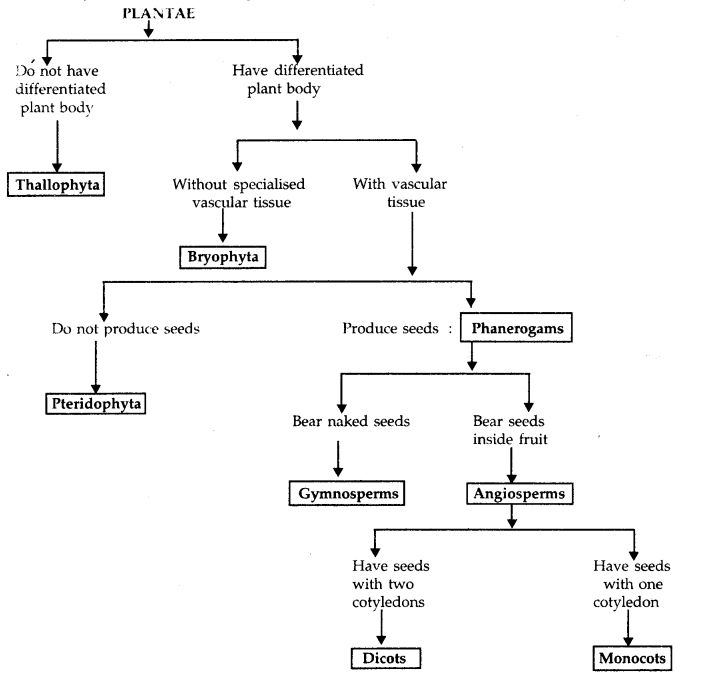
Question 5.
How are the criteria for deciding divisions in plants different from the criteria for deciding the subgroups among animals?
Answer:
Criteria for dividing plants: The eukaryotic multicellular organisms with cell wall and those which carry out photosynthesis are placed under kingdom plantae.
The first level of classification among plants depends on whether the plant body has well-differentiated, distinct components. The next level of classification is based on whether the differentiated plant body has special tissues for the transport of water and other substances within it. Further classification looks at tire ability to bear seeds and whether the seeds are enclosed within fruits.
Criteria for dividing animals into sub-groups: The eukaryotic multicellular heterotrophic and those which lack cell wall are placed in animal kingdom. They are further classified on the basis of extent and type of body design and differentiation presence.
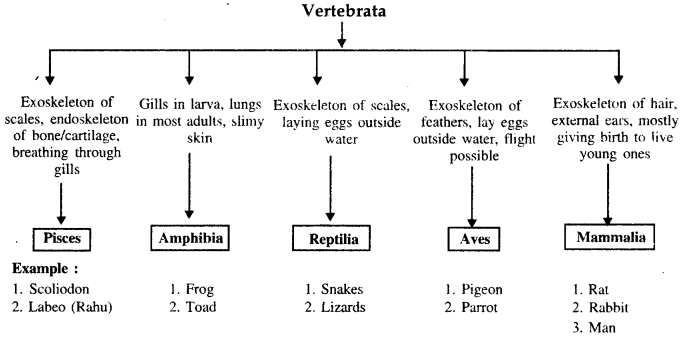
Question 6.
Explain how animals in vertebrata are classified into further sub-groups.
Answer:
Classification of vertebrata
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here