WBBSE 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 1 Measurement
West Bengal Board 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 1 Measurement
WBBSE 9th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
Synopsis
- A physical quantity is one which is related to a material body or an event that can be measured directly or indirectly.
Example: mass, length, time, velocity, force etc. are examples of some physical quantities.
- Physical quantities are of two types- 1. scalar quantity and 2. vector quantity.
- The physical quantities which have only magnitude but no direction are called scalar quantities. Example: length, mass, time, temperature, density, volume, work, energy etc.
- The physical quantities which have both magnitude and direction are called vector quantities. Example: displacement, velocity acceleration, linear momentum, force, electric field etc.
- Electric current intensity have both magnitude and direction but it does not obey ‘vector rules’ and hence it is not a vector quantity.
- Units which are derived from one or more than one fundamental units are called derived units. Example: area, volume, speed, velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, etc. derived units.
TOPIC – A
Measurement and Units
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is a physical quantity? Give some examples.
Ans. Any natural event or phenomenon that can be measured directly or indirectly is called a physical quantity.
Example: Length, mass, temperature, work, acceleration, velocity, force, displacement etc. are physical quantities.
2. Can all natural phenomena be termed as physical quantities? Explain with examples.
Ans. We observe different natural phenomena in our day-to-day life and feel them. But all of them cannot be quantified by measurement.
Example: Anger, affection, charity etc. Since all these natural phenomena cannot be measured, they are not called physical quantities.
3. What is a scalar quantity? Give some examples of scalar quantities.
Ans. Those physical quantities which have only magnitude but no direction are called scalar quantities.
Example: Length, mass, work, temperature etc. are scalar quantities.
4. What is a vector quantity? Give some examples of vector quantities.
Ans. Those physical quantities which have both magnitude and direction and whose addition follow the rules of vector addition are called vector quantities.
Example: Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force etc. are vector quantities.
5. If any physical quantity has both magnitude and direction, can it be called a vector quantity?
Or, Electric current has both magnitude and direction. Then why is it called a scalar quantity?
Ans. Any physical quantity having magnitude and direction cannot necessarily be called a vector quantity. For example, electric current. Electric current has both magnitude and direction, but the addition of electric current does not follow the rules of vector addition. Hence, electric current is not a vector quantity but a scalar quantity.
6. What is unit?
Ans. While measuring any physical quantity, some convenient and definite quantity of it is taken as a standard and then the whole physical quantity is measured in terms of the standard. This standard is called one unit.
7. What is the necessity of unit?
Ans. In a scientific experiment, it is necessary to mention measurements accurately. So, unit is essential while measuring any physical quantity. Any physical quantity is expressed in terms of a numerical number and its unit. Measurement is not possible without unit. Unit is also necessary for establishing relationship among different physical quantities and to verify correctness of the equations involving physical quantities.
8. What is primary or fundamental or base unit? What are the primary units in SI?
Ans. Fundamental or primary unit is a set of units used in measurement of physical quantities from which other units can be derived. Primary units or base units are independent of each other.
In SI, length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, luminous intensity and amount of substance are represented by metre, kilogram, second, kelvin, ampere, candela and mole, respectively.
9. What is a derived unit? Explain with examples.
Ans. A unit of measurement that is formed by combining one or more fundamental units is called a derived unit.
Example: Units of velocity, acceleration, momentum, force, work etc. are derived units.
Therefore, unit of velocity is made up of unit of length and unit of time. So, it is a derived unit.
10. Distinguish the units of the following quantities into fundamental and derived units: area, volume, displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, work, energy, power, momentum, mass, weight, height, density, wavelength, time period.
Ans. Quantities with fundamental unit: Displacement, mass, height, wavelength, time period.
Quantities with derived unit: Area, volume, velocity, acceleration, force, work, energy, power, momentum, weight, density.
11. Give an example of a derived unit formed by two fundamental units.
Ans. Unit of speed is a derived unit formed by two fundamental units.
Unit of speed
∴ unit of speed is a derived unit formed by the two fundamental units of length and time.
12. Give example of a derived unit which is formed by three fundamental units.
Ans. Unit of force is a derived unit formed by three fundamental units.
∴ unit of force is a derived unit formed by three fundamental units of length, mass and time.
13. What is a system of units? What are the advantages of a system of units?
Ans. A system of units is a set of all the fundamental and derived units that constitute the units of all physical quantities.
Introduction of system of units has not only helped the scientific community but also removed the difficulties of maintenance of accounts in our daily lives. Saying that a table has a length approximately equal to four cubits does not signify its correct length. But if it is said that its length is 1.5 m, we get a correct idea about its length.
14. Why CGS system or SI is called metric system?
Ans. CGS system or Sl is called metric system because to convert any physical quantity from any definite unit to another smaller or larger unit in these systems, one has to only shift the decimal point. Example: 500 cm = 5m = 5000 mm = 0.005 km. No multiplication or division is necessary for this conversion.
15. What are the advantages of the metric system?
Ans. Advantages of the metric system are:
- The metric system is based on powers of 10. So, it is easier to convert units of any physical quantity simply by moving the decimal points.
- Once the meaning of the prefixes is remembered, one can easily convert mass, distance, volume measurements. No further conversion factors are to be memorised except the power of 10.
- There is a convenient relationship between mass and volume in this system. For example, mass of 1 cm³ of water is 1 g or mass of 1 L of water is 1 kg (at 4°C).
16. Define unit of time in SI.
Ans. Unit of time in SI is second (s). One second is the duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the atom. 133Cs
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Which of the following is the largest unit for measurement of length?
A. light year
B. parsec
C. kilometre
D. metre
Ans. B
2. Which of the following is not a physical quantity?
A. velocity
B. displacement
C. mass
D. anger
Ans. D
3. Which of the following is a physical quantity?
A. anger
B. affection
C. speed
D. frustration
Ans. C
4. Unit of which of the following quantities is different from the others?
A. pressure
B. stress
C. coefficient of elasticity
D. force
Ans. D
5. Which of the following is a scalar quantity?
A. momentum
B. weight
C. work
D. force
Ans. C
6. Unit of which of the following quantities is made up of two fundamental units?
A. force
B. acceleration
C. momentum
D. work
Ans. B
7. Unit of which of the following quantities is made up of three fundamental units?
A. velocity
B. speed
C. acceleration
D. momentum
Ans. D
8. Unit of which of the following quantities is made up of four fundamental units?
A. force
B. power
C. specific heat
D. heat capacity
Ans. D
9. The wavelength of a light ray is 6000 Å. What is the value of this wavelength in ‘m’ unit?
A. 6 × 10-7
B. 6 × 10-8
C. 6 × 10-6
D. 6 × 10-10
Ans. A
10. The distance from a point at which a length of 1 AU forms an angle of one second at that point is
A. 4.26 light year
B. 2.26 light year
C. 3.26 light year
D. 5.26 light year
Ans. C
11. Length, breadth and height of a water tank are 3m, 2m and 1 m, respectively and the tank is half-filled with water. What is the volume of water contained in the tank?
A. 6000 L
B. 30000 L
C. 3000 L
D. 60000 L
Ans. C
12 What is the temperature at which the density of water is maximum?
A. 0°C
B. 4°C
C. 8°C
D. 10°C
Ans. B
13. The density of iron is 7.8 g/cm³. What is the mass of 100 cm³ of iron?
A. 0.78 kg
B. 7.8 kg
C. 0.078 kg
D. 78 kg
Ans. A
14. Select one scalar quantity and one vector quantity from the following whose units are derived from three fundamental units
A. speed, velocity
B. work, acceleration
C. work, force
D. power, acceleration
Ans. C
15. Steradian is the unit of
A. angle
B. solid angle
C. arc of a circle
D. circumference
Ans. B
16. One ring is made up of 10 carat gold. What is the mass of gold in g unit?
A. 4
B. 2
C. 20
D. 0.2
Ans. B
Answer in brief
1. What are the types of physical quantities?
Ans. Physical quantities are of two types: 1. scalar and 2. vector.
2. State whether barn is a fundamental unit or a derived unit.
Ans. Barn is a derived unit.
3. What is barn?
Ans. 1 barn is equal to 10-28 m² and this unit is used to measure nuclear cross section.
4. What type of physical quantity is electric current?
Ans. Electric current is a scalar quantity.
5. What type of physical quantity is area?
Ans. Area is a vector quantity.
6. Give an example of the unit of a scalar quantity which is formed by two different fundamental units.
Ans. Unit of speed is a scalar quantity which is formed by two different fundamental units.
7. Give an example of the unit of a vector quantity which is formed by two different fundamental units.
Ans. Unit of velocity is a vector quantity which is formed by two different fundamental units.
8. What are the two present systems of unit?
Ans. Two present systems of unit are: 1. CGS system and 2. SI.
9. Give example of one scalar quantity and one vector quantity with the same unit.
Ans. Speed and velocity are the two physical quantities with the same unit, speed being a scalar quantity and velocity being a vector quantity.
10. What are the fundamental units in CGS system?
Ans. In CGS system, unit of length is centimetre (cm), unit of mass is gram (g) and unit of time is second (s).
11. In SI, how many basic units are there?
Ans. There are seven basic units in SI.
12. How much distance is meant by 1 AU?
Ans. 1 AU (astronomical unit) is the average distance between the sun and the earth.
13. Is light year a fundamental or a derived unit?
Ans. Light Year is a fundamental unit.
14. Which unit is used for measuring mass of molecules and atoms?
Ans. The unit u (unified atomic mass unit) is used for measuring the mass of molecules and atoms.
15. Which unit is used for measuring the mass of different precious stones?
Ans. Carat is used for measuring the mass of different precious stones. 1 carat = 0.200 g.
16. What is the relationship between Chandrasekhar limit (CSL) and the mass of the sun?
Ans. 1 Chandrasekhar limit = 1.39 × mass of the sun.
17. Which temperature is mentioned in the definition of litre?
Ans. 4°C or 277 K is mentioned in the definition of litre.
18. What is the temperature at which the density of water is maximum?
Ans. At 4°C or 277 K, the density of water is maximum.
19. What is the density of water at 4°C?
Ans. The density of water at 4°C is 1 g/cm³.
20. Which element is mentioned in the definition of second?
Ans. 133Cs is mentioned in the definition of second.
21. Which unit is used to measure interstellar distance?
Ans. AU (astronomical unit) is used to measure interstellar distance.
22. Is it possible to measure 0.4 mm by an ordinary scale?
Ans. With the help of an ordinary scale, measurement of 0.4 mm is not possible since the smallest constant in an ordinary scale is 1 mm.
23. 1 gallon = how many litre?
Ans. 1 gallon = 4.536 litre.
Fill in the blanks
1. Specific gravity is the ratio between two quantities having the same unit. So it has ……… unit.
Ans. no
2. At 4°C temperature, volume of 1 ………… of pure water is called ……….. litre.
Ans. kilogram, 1
3. Unit of area is a ………….. unit.
Ans. derived
4. Mass of unit ………….. of any material is known as the ……….. of that material.
Ans. volume, density
5. Number of fundamental units in SI is………….
Ans. 7
6. Number of fundamental units in CGS system is……………
Ans. 3
7. ……….. quantities have only magnitude but no direction.
Ans. scalar
8. ……….. quantities have both magnitude and direction.
Ans. vector
9. …………….. of water is minimum at 277 K.
Ans. volume
10. ………. is the unit of density in CGS system.
Ans. g/cm³
TOPIC – B
Dimension
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What do you mean by the dimension of a physical quantity? What is dimensional formula?
Ans. Dimension of a physical quantity is the power or index to which fundamental units like mass, length, time etc are raised to express that quantity.
Dimensional formula is the relationship between a physical quantity and the dimension of its fundamental units.
2. What is dimensional equation?
Ans. Dimensional equation is the equation by which any physical quantity is expressed in terms of dimensional formula.
3. How are the dimensional formulae of fundamental physical quantities expressed in SI?
Ans. There are seven fundamental units in Sl. These are length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, luminous intensity and quantity of matter, units of which are considered as fundamental units. These dimensional formulas are denoted as L, M, T, Θ, I, J and N, respectively.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Which of the following quantities has a unit but no dimension?
A. strain
B. atomic weight
C. angle
D. none of the above
Ans. C
2. Dimensional formula of force is
A. MLT-3
B. M2LT-2
C. ML-1T-2
D. MLT-2
Ans. D
3. Solid angle has
A. both dimension and unit
B. only dimension but no unit
C. only unit but no dimension
D. neither dimension nor unit
Ans. C
4. Strain has
A. both dimension and unit
B. only dimension but no unit
C. only unit but no dimension
D. neither dimension nor unit
Ans. D
5. Dimension of time in the dimensional formula of power is
A. -1
B. -2
C. -3
D. -4
Ans. C
6. Dimension of absolute humidity is ML-3. It is similar to the dimension of
A. mass
B. density
C. specific gravity
D. area
Ans. B
7. Which two physical quantities of the following have same dimensional formula?
A. velocity, speed
B. displacement, work done
C. force, momentum
D. velocity, acceleration
Ans. A
8. Dimensionless physical quantity is
A. mass
B. weight
C. specific heat
D. atomic weight
Ans. D
Answer in brief
1. Give example of two physical quantities which do not have any dimension or unit.
Ans. Atomic mass and specific gravity are two physical quantities which do not have any dimension or unit.
2. Give an example of a dimensionless physical quantity which has unit.
Ans. Angle is a physical quantity which is dimensionless but has unit (radian).
3. Write dimension of acceleration.
Ans. Acceleration has dimension 1 in length, 0 in mass and -2 in time.
4. Give an example of a physical quantity which have unit but no dimension.
Ans. Angle is such a physical quantity which have unit (radian) but no dimension.
5. Give example of two physical quantities which have no unit and dimension.
Ans. Atomic weight and specific density are two such physical quantities which have no unit and dimension.
6. Write dimensional formula of velocity.
Ans. Dimensional formula of velocity is LT-1.
7. Which physical quantity have dimensional formula ML-1T-2?
Ans. Pressure is a physical quantity which have dimensional formula ML-1T-2. (strain also have dimensional formula ML-1T-2).
8. A physical quantity have unit °F-1. Write dimensional formula of the physical quantity.
Ans. Dimensional formula of the physical quantity is K-1.
Fill in the blanks
1. ………… of two sides of a correct equation or relation is always same.
Ans. Dimension
2. Angle is a…………. physical quantity.
Ans. dimensionless
3. Nuclear density is a dimensionless quantity. Its dimensional formula is…………
Ans. M0L0T0
4. All the terms on the two sides of a physical equation must have the ………. dimension.
Ans. same
5. Dimension of atomic weight is …………
Ans. M0L0T0
State whether true or false
1. Dimensional formula is the relationship between a physical quantity and the dimension of its fundamental units.
Ans. True
2. Dimensional formula of kinetic energy is ML2T-2.
Ans. True
TOPIC – C
Measurement of Different Physical Quantities and Errors in Measurement
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is meant by parallax error? allax error?
Ans. While taking the readings of the two sides during measurement of length of a line by an ordinary scale, it is essential to look perpendicularly at the points of reading. Otherwise, the reading becomes erroneous. This error, which gives different readings due to different positions of the eyes, is called parallax error. In Fig., D is the correct position of the eye.
2. How do you measure the thickness of a page of a book with the help of an ordinary scale?
Ans. It is not possible to measure directly a thickness of less than 1 mm by an ordinary scale. As the thickness of a page is generally less than 1 mm, the thickness of a page is measured indirectly by an ordinary scale. Suppose there are n number of pages in a book. By compressing only the pages
(excluding the covers) such that the thickness of layers of air between the pages is excluded, the thickness of the book is measured several times [Fig.]. The mean of the readings is, say, b. Then, the thickness of each page is b/n.
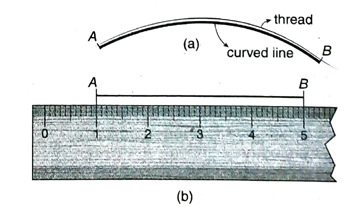
3. How do you measure the length of a curved line with the help of a thread and an ordinary scale?
Ans. Measurement of the length of a curved line with the help of a thread and a scale:
A long thread is taken and an ink mark is made at one end (A) of the thread. Marked end of the thread is placed at one end point of the curved line and the thread is positioned along the curve till it reaches the other end point [Fig. ]. Another ink mark is made on the thread at position B. Now, this thread is stretched over a scale and the length between the two marks on the thread is measured. This gives the length of the curved line by the thread and scale method.
4. How do you measure the diameter of a with the help of an ordinary scale?
Ans. It is not possible to directly measure a length less than 1 mm by scale. As the diameter of a thin wire is less than 1 mm, it is measured indirectly. The wire is wound several times on a cylinder of small radius so that there is no gap between the rounds [Fig. ]. Now with the help of a scale, total length of the wounds on the cylinder is measured. Several measurements are made to take an average measure. Suppose the mean length of the wire is b. If the number of coils made is n, then diameter of wire is b/n.

5. Why is an ordinary scale made up of wood instead of metal?
Ans. Metal is a good conductor of heat. If the temperature of a metal scale is increased or decreased, its length increases or decreases. As a result, the length between the two markings changes. Thus, a correct reading is obtained only at the temperature at which the scale was marked. If temperature increases, the correct reading is greater than the reading shown on the scale and if temperature decreases, the correct reading is smaller.
Wood is a bad conductor of heat. So, increase or decrease of the length of wood with changing temperature is ignored. As a result, the reading shown in the scale may be assumed to be correct. Hence, an ordinary scale is made of wood instead of metal.
6. Which instrument is used for the measurement of time? Describe a pendulum clock.
Ans. A clock is used for the measurement of time.
In a pendulum clock, a metal bob is attached to a metallic rod at one end and the other end is tied firmly with a fixed support and is suspended. This is a pendulum. The length from the point of suspension to the centre of gravity of the bob is known as the working length. The pendulum oscillates in a periodic motion. There are two hands in the clock, the bigger one indicates minutes and the smaller one indicates hours. The clock works with the help of a spring which stores potential energy when it is wound. This stored potential energy is the source of energy of a pendulum clock and is converted into kinetic energy. The clock needs to be wound at a regular interval as the clock stops working when the stored potential energy is exhausted.

7. What type of watch is used in swimming and running competitions? What is the problem of using an ordinary clock in these cases?
Ans. Stopwatch is used in swimming and running competitions.
Ordinary clock cannot be started and stopped at will. But stopwatch may be started and stopped according to our convenience [Fig. ]. Further, one can measure a minimum amount of one second by an ordinary clock whereas with the help of a modern digital stopwatch, a time interval of one-tenth of a second can be measured accurately.
8. Mention different types of clocks.
Ans. We measure time with the help of clocks. The oldest clock is sundial. With the progress of science and technology, different types of clocks have been invented over the time.
Example: Pendulum clock, table clock, wrist watch, electronic digital watch, chronometer, caesium atomic clock etc.
9. What is a metronome?
Ans. Metronome (electronic metronome) is a modern watch which measures time very accurately. This watch is used during launching of artificial satellites.
10. which instrument is used for measurement of the mass of a body? Elaborate the principle used in the measurement of mass by this instrument.
Ans. Common balance is used for measurement of the mass of a body.
While measuring the mass of a body by a common balance, the body is kept in the left pan while some known standard weights are put in the right pan. When the balance beam comes to a horizontal position, weight of the body in the left pan becomes equal to the standard weight placed in the right pan.
This is the principle of measurement of mass.
11. Why are the masses of of the standard weights in a weight box kept in the ratio of 5:2:2:1?
Ans. The masses of the standard weights in a weight box are kept in the ratio of 5:2:2:1 so that any mass between 10 mg and 211.11 g can be measured using them.
12. What are the qualities of a good common balance?
Ans. Qualities of a good common balance are:
- The common balance should be sensitive, that is, it should be able to measure the slightest difference in the mass of a body.
- The common balance must be strong.
- The common balance should be accurate, i.e., equal amount of masses put in the two pans should keep it horizontal.
- The common balance should be stable, i.e., its oscillation should be short-lived.
- The lengths of the arms and the masses of the two pans should be equal.
13. Why is a sensitive common balance not stable?
Ans. A common balance is considerably sensitive if the centre of gravity of the common balance is situated very near to the fulcrum. Again, the balance is stable if the centre of gravity is well below the fulcrum.
Now, it is not possible to have two opposite conditions in the same common balance simultaneously. This is the reason why a very sensitive common balance is not stable.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Smallest distance that can be measured by an ordinary scale is
A. 0.1 cm
B. 0.01 cm
C. 0.001 cm
D. 0.2 cm
Ans. A
2. The length which cannot be measured by an ordinary scale is
A. 4.2 cm
B. 2.13 cm
C. 7.7 cm
D. 9.5 cm
Ans. B
3. Lengths of the two arms of a common balance are equal but the two pans are of different masses. A body is found to be 20 g and 21 g when put in the left pan and the right pan, respectively. The actual mass of the body is
A. 20.2 g
B. 20.4 g
C. 20.5 g
D. 20.6 g
Ans. C
4. In the weight box of a common balance, the weights are taken in the ratio of
A. 5:3:2:1
B. 5:4:2:1
C. 5:2:2:1
D. 5:3:3:1
Ans. C
5. The physical quantity which is measured by a common balance is
A. volume
B. mass
C. weight
D. force
Ans. B
6. Which of the following instruments can be used to measure the volume of a wooden block of irregular shape?
A. common balance
B. measuring cylinder
C. metre scale
D. stopwatch
Ans. B
7. Which of the following is not a prerequisite for sensitivity of a common balance?
A. Beam of the balance should be long
B. The balance should be light
C. The pointer should be small in size
D. The centre of gravity should be very close to the fulcrum
Ans. C
8. Which of the following instruments does not function in a place where there is no gravity?
A. spring balance
B. common balance
C. ordinary scale
D. both A and B
Ans. D
9. Which of the following can be used to measure the area of a metallic strip with irregular shape?
A. ordinary scale
B. common balance
C. graph paper
D. string
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. What is the use of a chronometer watch?
Ans. Chronometer watch gives the correct time at Greenwich, London and this time has been adopted as a global standard time.
2. Name an instrument by which a length of 0.01 cm can be measured accurately.
Ans. A length of 0.01 cm can be measured accurately by using slide calipers.
3. Name an instrument by which a length of 0.001 cm can be measured accurately.
Ans. A length of 0.001 cm can be measured accurately by using a screw gauge.
4. What is the effective length of a pendulum clock?
Ans. The effective length of a pendulum clock is measured from the point of suspension to the centre of mass of its bob.
5. What type of energy is stored in the spring of a pendulum clock?
Ans. Potential energy is stored in the spring of a pendulum clock.
6. Which instrument is used to measure the mass of a body?
Ans. Common balance is used to measure the mass of a body.
7. What is the ratio in which the weights are kept in a weight box?
Ans. Weights are kept in the ratio of 5:2:2:1 in a weighing box.
8. What is least count?
Ans. The minimum measurement which can be performed by using an instrument in measuring a physical quantity, is called least count of this instrument.
9. What is the minimum length that can be measured by a metre scale correctly?
Ans. The minimum length that can be measured by a metre scale is 0.1 cm or 1 mm.
10. What is the maximum length that can be measured by a metre scale accurately?
Ans. 1 m or 100 cm is the maximum length that can be measured by a metre scale accurately.
11. What is the maximum time that can be measured by a wall clock?
Ans. The maximum time that can be measured by a wall clock is 12 hours.
12. What is the maximum mass that can be measured by a common balance using its weight box?
Ans. The maximum mass that can be measured by a common balance by using its weight box is 211.11 g.
13. What is the use of rider of a common balance?
Ans. Rider is used in a common balance To measure a mass of less than 10 mg.
14. What are the minimum and maximum measurement that can be measured by a measuring cylinder of volume 100 mL and 10 mL?
Ans. The minimum and maximum measurement of volume that can be measured by a measuring cylinder of 100 mL and 10 mL are 1 mL and 0.1 mL; 100 mL and 10 mL respectively.
15. What can be used to measure the length of a curve line?
Ans. The length of a curve line can be measured by using a thread and a meter scale.
16. What can be done to level the base of a common balance?
Ans. leveling screw can be used to balance the base of a common balance.
Fill in the blanks
1. ………….. cylinder and stopwatch can be used to measure the rate of flow of water from a tap.
Ans. Measuring
2. …………. time is the minimum possible time that can be measured by a wrist watch.
Ans. 1 s
3. ………… is the minimum mass that can be measured by a common balance.
Ans. 10 mg
4. Very small time intervals are measured by …………..
Ans. stopwatch
5. Number of hour hand in stop watch is ………….
Ans. zero
State whether true or false
1. Common balance is used for the measurement of the weight of an object.
Ans. False
2. Determination of area of a regular shaped sheet can not be done by using a graph paper.
Ans. False
3. Digital clock is used for accurate measurement of time.
Ans. True
4. Common balance can work even in the place where there is no gravity.
Ans. True
5. Volume of an irregular shaped body can be measured by a measuring cylinder.
Ans. True
6. Mass of a body can be measured by a spring balance even in a place where there is no gravity.
Ans. False