Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
GSEB Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1. Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Answer:
(a) Cu cannot displace Na → No reaction
(b) Al cannot displace Mg → No reaction
(c) Ag cannot displace Fe → No reaction
(d) Cu can displace Ag → Reaction takes place
Question 2. Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
Question 3. An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. This element is likely to be –
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer:
(a) Calcium.
Question 4. Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because –
(a) zinc is costlier than tin.
(b) zinc has higher melting point than tin.
(c) zinc is more reactive than tin
(d) zinc is less reactive than tin.
Answer:
(c) Zinc is more reactive than tin.
Question 5. You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non – metals.
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non – metals.
Answer:
(a) To distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals one can use hammer to beat the given material into sheets, if it breaks it is a non-metal but if it is beaten into thin sheets it is a metal.
One can also use battery, wires, bulb and switch to make a circuit and use the given material to complete the circuit one by one, if the electric current flows and the bulb glows then it is a metal and if not then it is a non-metal.
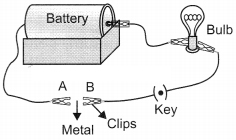
(b) Though these tests gives us rough ideas in distinguishing between metals and non¬metals but they are not reliable because both in metals & non-metals there are exceptions. For example, Na metal is brittle and graphite can show conductivity.
Question 6. What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer:
The oxides which behave as acid as well as base are called amphoteric oxides example: Al2O13 and ZnO are amphoteric oxides, they both react with acid as well as base to give salt and water.
Question 7. Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not.
Answer:
Metals which lie above hydrogen in the activity series i.e. Zn, Al, Mg can displace hydrogen from dilute acids, because they are more reactive than H2. Metals which lie below hydrogen in the activity series i.e. Cu, Ag, Au cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids, because they are less reactive than hydrogen.
Question 8. In the electrolytic refining of M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer:
For electrolytic refining of M:
Impure metal M → will be anode
Pure sample of M → will be cathode
Electrolyte → Acidified, soluble salt of metal M
Question 9. Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it as shown in figure below:
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper?
(ii) moist litmus paper?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Answer:
(a) (i) There will be no effect of gas on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Moist blue litmus paper turns red.

(b) (i) S + O2 SO2
(ii) ![]()
Question 10. State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
- Rusting can be prevented by painting iron articles so that iron surface does not come in contact with air and moisture required for rusting.
- By coating iron articles with a protective layer of zinc metal i.e., by galvanization which prevents the rusting of iron.
Question 11. What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Answer:
When non-metals combine with oxygen they form acidic oxides.
Example: SO2 , CO2, NO2.
[In some cases it also form neutral oxide example H2O, CO]
Question 12. Give reasons:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer:
(a) Au, Ag and Pt are highly lustrous, malleable, ductile and among least reactive metals, so they are used in making jewellery.
(b) Na, K and Li are highly reactive metals, they react with oxygen present in air at room temperature and catches fire in presence of moisture. They don’t react with oil (kerosene), hence stored in oil.
(c) Aluminium form a protective layer of Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) on its surface which protects it from corrosion (or reaction with any food item).
(d) Reduction of metal oxides to metal is cheaper and easier than the reduction of carbonate and sulphide ores. So carbonate and sulphide ores are first converted to metal oxide and then further reduced to form metals.
Question 13. You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels?
Answer:
Copper metal corrodes to form copper carbonate and get tarnished. On cleaning with lemon or tamarind juice, the acid present in them dissolves the copper carbonate, thereby cleaning the vessel.
Question 14. Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
Answer:
Metal:
- Metals lose electrons to form positive ions.
- Metals form basic oxides.
- Metals can displace hydrogen from acids.
- All metals do not combine with hydrogen to form hydrides (except reactive metals like Na, K, Ca).
Non – metal:
- Non – metals gain electrons to form negative ions.
- Non – metals form acidic oxides. Non – metals cannot displace hydrogen from acids.
- All non – metals combine with hydrogen to form hydrides.
Question 15. A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Answer:
The solution is aqua regia (1 part of cone. HNO3 acid and 3 part of cone. HCl acid) is used by the goldsmith, which dissolves gold.
Question 16. Give reason why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
Answer:
Copper does not react with any form of water, not even with steam. It is cheap, easily available and a good conductor of heat which makes it useful to make hot water tanks as compared to steel.
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define metals.
Answer:
Elements which lose electrons to form positive ions are called metals.
Question 2. Name a metal which can be cut with knife.
Answer:
Sodium
Question 3. Name two metals which do not react with oxygen.
Answer:
Gold and silver
Question 4. What type of oxides are formed when metals combine with oxygen?
Answer:
Basic oxides
Question 5. Name two metals which are best conductors of heat.
Answer:
Silver and copper
Question 6. Name two metals which are poor conductors of heat.
Answer:
Lead and mercury
Question 7. Name a non-metal which is in liquid state and a metal which is found in liquid state.
Answer:
Non – metal – Bromine
Metal – Mercury
Question 8. Non-metals are non-lustrous, except one. Name the non-metal that is lustrous.
Answer:
Iodine is a lustrous non-metal.
Question 9. What are such metals called, which are soft, can be cut with knife, low densities and low melting point?
Answer:
Alkali metals, e.g., lithium, sodium and potassium.
Question 10. Name two metals with very low melting point.
Answer:
Gallium and caesium.
Question 11. Name two allotropes of carbon.
Answer:
Diamond and graphite.
Question 12. Name two metal oxides which are soluble in water.
Answer:
Sodium oxide and potassium oxide.
Question 13. Name two metals which are stored by keeping them immersed in kerosene.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium.
Question 14. Why is sodium/potassium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Answer:
Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals, they catche fire when kept in open. So they are kept immersed in kerosene oil.
Question 15. Why is it that sodium when react with water form sodium hydroxide whereas aluminium forms only aluminium oxide?
Answer:
Sodium metal reacts with water to form sodium oxide which further dissolves in water to form sodium hydroxide whereas aluminium oxide does not dissolve in water to form aluminium hydroxide.
Question 16. Magnesium when reacts with hot water starts floating. Explain.
Answer:
Magnesium reacts with hot water to form magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas is evolved. It is due to this hydrogen gas it starts floating. Hydrogen bubbles stick to the surface of magnesium and when hydrogen gas rises it lifts magnesium also.
Question 17. What are ionic bonds?
Answer:
Bonds formed between a metal and a non-metal by the transfer of electrons are known as ionic bonds.
Example:
Na+ + Cl– → NaCl
Question 18. Name two metals which are ductile and malleable.
Answer:
Gold and silver
Question 19. Which ores are converted into metal oxides by calcination?
Answer:
Carbonate ores
Question 20. Name the ores of mercury.
Answer:
Cinnabar, HgS.
Question 21. Name three common types of ores where metal exists in nature.
Answer:
Oxide, carbonate and sulphide ores.
Question 22. What is gangue?
Answer:
The impurities present in ore such as soil, sand, etc. is called gangue.
Question 23. What is concentration of ore?
Answer:
The removal of impurities from the ore is called concentration of ore.
Question 24. What are two types of reducing agents used to reduce metal oxide?
Answer:
Carbon and highly reactive metals such as sodium, calcium, aluminium are used as reducing agents to reduce metal oxide into metal.
Question 25. During electrolytic refining of a metal, what type of electrolyte should one take?
Answer:
During electrolysis of impure metals the electrolyte should be the solution of impure i metal only.
Question 26. What is anode mud?
Answer:
The impurities collected down the anode during electrolytic refining of metals is called anode mud.
Question 27. What is rust?
Answer:
The red-brown flaky substance obtained when iron is exposed to air and moisture is called rust.
Question 28. Give one use of anhydrous calcium chloride.
Answer:
It is used as drying agent because it absorbs moisture from the air.
Question 29. What makes silver turn black and copper turn green when kept exposed for few days?
Answer:
Silver when left exposed in air turns black due to the coating of silver sulphide, copper turns green due to the coating of copper carbonate.
Question 30. What is amalgam?
Answer:
While making an alloy of metals, if one of the metals is mercury then it is called amalgam.
Example:
Ag + Hg → silver amalgam.
Question 31. What is solder?
Answer:
Solder is an alloy of lead and tin.
Question 32. Name two alloys of copper.
Answer:
Brass (Cu + Zn) and bronze (Cu + Sn) are the alloys of copper.
Question 33. Name two alloys of iron.
Answer:
Iron alloys – Steel (Fe + C)
Stainless steel (Fe + Cr + Ni + C)
Question 34. Name two heavy metals.
Answer:
Lead and Chromium
Question 35. Name two sources of heavy metal pollution.
Answer:
Discarded mercury thermometer, lead acid batteries or battery cells thrown in the garbage.
Question 36. Name the solution used to dissolve gold in it.
Answer:
The aqua regia is the solution used to dissolve gold in it.
Question 37. What is aqua-regia?
Answer:
Aqua-regia is a freshly prepared mixture of 1 part of concentrated nitric acid and 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid. It can dissolve all metals.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Give electron dot structure of chlorine and oxygen.
Answer:

Question 2. Explain why the surface of some metals acquire dull appearance when exposed to air for long time?
Answer:
Metals combine with different gases present in air to form a compound due to which the metals acquire dull appearance when left exposed in air for long time. Example: Silver forms silver sulphide black surface.
Question 3. What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer:
Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which shows both acidic and basic behaviour. They react with acids as well as bases to form salts, e.g., Al2O3, ZnO.
Example: Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Question 4. Define alloy. Give two advantages of making alloys.
Answer:
Alloys are the homogeneous mixture of metals or metals and non-metals. Alloys are made to get the desired properties of metals e.g., for low melting point, solder is made, stainless steel is rust-free and lustrous.
Question 5. Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Answer:
Ionic compounds when in molten state allow electricity to flow through it because it ionises to form positive and negative ions.
Question 6. Why do covalent compounds have low melting point?
Answer:
Covalent compounds are made up of covalent bonds which are not strong enough and needs less heat energy to melt.
Question 7. Why jewellery made of 24 carat gold is not preferred?
Answer:
Gold is highly ductile and malleable in the purest form i.e., 24 carat. Jewellery made out of this gold do not retain their shape for long and hence an alloy of gold and copper is used to make jewellery so that it retains the shape or design.
Question 8. State five points of differences between ionic compound and covalent compound.
Answer:
Ionic compound:
- Ionic compounds contain ionic bond made up of ions.
- Loss and gain of electrons takes place.
- Can conduct electricity.
- Has high melting point.
- Are soluble in water.
Covalent compound:
- Covalent compounds contain covalent bond made up of atoms and not ions.
- Sharing of electrons takes place.
- Cannot conduct electricity.
- Has low melting point.
- Are insoluble in water.
Question 9. What is thermite reaction? Give its one use.
Answer:
A reaction in which more reactive metal acts as a reducing agent and reduces the metal oxide, the reaction is highly exothermic hence called thermite reaction. The metal produced in such reactions is in the molten form which is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
Example:
![]()
Question 10. How can you obtain pure metal from ores of metals of high reactivity?
Answer:
To obtain pure metal from an ore of high reactivity following steps are involved:
- Concentration of ore → removal of impurities
- Electrolysis of molten ore → Metal is obtained at cathode of the electrolytic cell. This metal obtained is pure metal, Example: Na, K, Mg, Ca.
Question 11. Metals when react with nitric acid does not release hydrogen gas. Explain.
Answer:
Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. When metals react with other acids they release hydrogen gas, but in case of nitric acid the hydrogen gets oxidised to form water.
[But there are two exceptional cases i.e., Mg and Mn that release H2 gas from HNO3]
Question 12. Show the following reactions with balanced equations:
(a) Calcium + Water
(b) Aluminium + Water
Answer:
(a) Calcium + Water → Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
(b) Aluminium + Water → Aluminium oxide + Hydrogen
2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3S(S) + 3H2(g)
Question 13. Name the property of metal used in the following cases:
(a) Aluminium foil
(b) Metal jewellery.
(c) Cable wires
(d) Bells
Answer:
(a) Aluminium foil → malleability
(b) Metal jewellery → lustrous, malleability and ductility
(c) Cable wire → good conductors of electricity, ductility
(d) Bells → sonorous
Question 14. Why are metals good conductors of electricity?
Answer:
Metals are good conductors of electricity because they contain free electrons which can move easily through the metal and conduct electric current. The metals offer very low resistance to the flow of electric current.
Question 15. Why is aluminium extracted from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolytic reduction and not by reducing with carbon?
Answer:
The bond between aluminium and oxygen is much stronger for carbon to reduce oxygen from it. Hence carbon cannot be used as reducing agent. To reduce alumina (Al2O3) so as to obtain aluminium, electrolytic reduction is done, with the help of electricity, aluminium and oxygen are separated and aluminium is obtained at cathode.
Question 16. Ionic salts do not conduct electricity in solid state but conducts electricity in molten state.
Answer:
Ionic salts in solid state contain ions which are held tightly and cannot move freely. When the ionic compounds dissolve in water or melt the ionic compound then the ions become free to move and conduct electricity.
Question 17. The use of iron metal is causing lot of economical loss. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Iron metal when used in commercial areas like building construction or railways, bridges etc. the metals undergo rusting and can become weak and shatter the structures. The metal has high strength and cannot be replaced with other metals as it is cheap and easily available but its rusting causes lot of loss and damage.
Question 18. Give three points of difference between metals and non-metals based on physical properties.
Answer:
Metals:
- Metals occur in solid state except
- Metals have high melting point.
- Metals are ductile and malleable.
Non-metals:
- Non-metals occur in solid, liquid or gaseous state.
- Non-metals have low melting point.
- Non-metals are non-ductile and non-malleable.
Question 19. Give reasons:
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide.
- Non-metals do not conduct electricity.
- Metals displace hydrogen gas from acids.
Answer:
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide because it shows the properties of both acidic and basic oxide. It reacts with both acids and bases to form salt and water
- Non-metals do not have free ions which can allow the flow of electricity. Hence they do not conduct electricity.
- Metals when react with acids, donate electrons to hydrogen ions present in acid so that they become hydrogen atoms and these atoms further form hydrogen gas.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Show that for rusting of iron both air and moisture are required.
Answer:
Take three test tubes A, B, and C as shown in the figure. In test tube A – put 2 iron nails, water and close it with cork.
In test tube B-put 2 iron nails, boiled distilled water and 1 mL of oil and close the mouth of test tube with cork. In test tube C – put 2 iron nails and anhydrous calcium chloride (drying agent) to absorb moisture present in the test tube and close its mouth with cork.
It is observed that the nails in test tube A only undergo rusting because only in test tube A, the nails were directly exposed to air and water.
In test tube B, layer of oil prevents the contact of nails with air, hence it does not rust. In test tube C, anhydrous CaCl2 prevents contact of nails with both air and water. Hence, it does not rust.

Question 2. (a) What is activity series of metals? Arrange the given metals in activity series: Fe, Au, Zn, Al, Cu.
(b) State two points of difference between calcination and roasting with an example of each.
Answer:
(a) The arrangement of metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity is called the activity series of metals.
Arrangement of given metals in activity series.
Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Au
(b) 
Question 3. (a) Explain why copper is used to make taps, hot water tanks and not any other metal?
(b) What will happen if iron nails are kept in a solution containing copper sulphate?
(c) Write the chemical equations for the following and balance it.
(i) Ca + H2O →
(ii) Al + HCl →
(iii) Fe + H2O →
Answer:
(a) Copper does not react with any form of water, not even with steam. It is cheap, easily available, hence it is used to make taps and hot water tanks.
(b) On keeping iron nails in a copper sulphate solution, the blue colour of the copper sulphate fades due to displacement of copper by iron. Few deposits of red-brown metal i.e. copper is collected near the surface of iron metal.
(c) (i) Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2(g)
(ii) Al + HCl → 2AlC3 + 3H2(g)
(iii) Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2(g)
Question 4. What is meant by ‘refining of metals’? Describe the electrolytic refining of copper with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
Refining of Metals: Removing impurities from a metal and purifying it is called refining of metals.

Electrolytic refining of copper: Arrange the set up as shown in the figure:
Anode – impure metal – Cu Cathode – Pure metal – Cu
Electrolyte – Acidified copper sulphate
Allow the electric current to pass through it. The impurities get collected below the anode called anode mud. The pure metal is collected at the cathode.
Question 5. How can you prove that zinc is more reactive than copper?
Answer:
Take strips of zinc and copper and two test tubes with copper sulphate and zinc sulphate solution. Add zinc in copper sulphate solution and copper metal in zinc sulphate solution.
Observation: The test tube with zinc in copper sulphate will show the reaction which is shown by the fading away of the blue colour of copper sulphate. The other test tube will not show any change. This proves that zinc is more reactive than copper and can displace it.

Practical Based Questions (Solved)
Question 1. Three metals looks similar in the lab and they are zinc, magnesium and aluminium. A student wants to confirm the identity of each metal. How can he use the reactivity test to do so?
Answer:
The student can take three test tubes containing zinc sulphate and add a small piece of each metal in it. The test tube in which no reaction takes place has zinc metal. To identify the aluminium metal, take two test tubes and add aluminium sulphate in it. Now add magnesium in one and aluminium in the other test tube. The one in which there is no reaction, the aluminium metal was added in it.
Question 2. The lab attendant made three solutions of zinc sulphate, magnesium sulphate and aluminium sulphate. He forgot to label the reagent bottles. Explain how you can label these bottles by using the metal reactivity studies.
Answer:
Take three test tubes and add little amount of each solution from the reagent bottle separately. Drop a small piece of magnesium in it. The test tube in which there is no reaction the reagent is magnesium sulphate. Similarly, to identify the other two solutions, take these two solutions in two different test tubes and add a small piece of aluminium metal to them. The test tube in which there is no reaction contains
aluminium sulphate and the other one is zinc sulphate.
Question 3. While performing an experiment, a student kept the spatula in the test tube containing copper sulphate. Record his observation next day.
Answer:
The student will observe that the blue colour copper sulphate solution has changed its colour to green and the iron spatula has got the coating of brown colour metal on it only on that surface which is kept immersed in the solution.
Question 4. Name any three metal salts which are white in colour.
Answer:
The white coloured metal salts are magnesium sulphate, aluminium sulphate and zinc sulphate.
Question 5. How will you identify the copper sulphate, iron sulphate and barium sulphate salts in the lab?
Answer:
The color of iron sulphate is generally green (ferrous sulphate) and brown if it is ferric sulphate. The colour of the copper sulphate is blue and the white colour salt is barium sulphate.
Question 6. State the safety precautions for handling metals like sodium or potassium in the lab.
Answer:
Highly reactive metals like sodium and potassium should be handled very carefully. Do not touch them with bare hands. Do not randomly pour any water on it this may catch fire and explosion. If any contact with sodium or potassium causes burning immediately allow some water to run over the affected skin surface till the irritation stops and subject to first aid thereafter.
Question 7. Give three safety measures one should take while performing the reactivity series experiment in the lab.
Answer:
- The metals or any chemical should not come in contact with your skin.
- Do not inhale any fumes or gas released during the experiment.
- Do not taste any chemical or material and always use clean apparatus with no contamination of other chemical in it.
- Wear safety goggles, hand gloves and lab coat before handling the chemicals.
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals InText Questions and Answers
Question 1. Give an example of a metal which
- Is a liquid at room temperature
- Can be easily cut with knife.
- Is the best conductor of heat
- Is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
- Mercury (Hg)
- Sodium and potassium
- Silver
- Lead
Question 2. Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
- Malleable : A metal is said to be malleable if it can be beaten into thin sheets, example silver and gold are the best malleable metals.
- Ductile : A metal is said to be ductile when it can be drawn into thin wires, example silver and gold are the best ductile metals.
Question 3. Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive metal. It reacts with oxygen in air at room temperature, the reaction is highly exothermic. To prevent this, sodium is kept preserved under kerosene. Sodium does not react with kerosene.
Question 4. Write equations for the reactions of
- Iron with steam
- calcium and potassium with water
Answer:
1. Iron with steam
![]()
2. Calcium and potassium with water

Question 5. Samples of four metals A,B, C and D were taken and added to the following solutions one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.

Use the table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
- Which is the most reactive metal?
- What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
- Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
- B is most reactive.
- Blue colour of copper sulphate solution disappears and reddish brown copper metal is deposited on the metal B.
- B > A > C > D is the order of reactivity.
Question 6. Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
When a reactive metal reacts with hydrochloric acid hydrogen gas is produced. A reactive metal displaces the hydrogen from acid and release hydrogen gas.
Fe(s) + dil. H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H4(g)
Question 7. What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than iron, hence when added to iron (II) sulphate, it can displace iron metal and the colour of solution fades from green to colourless due to formation of zinc sulphate. The greyish black iron metal gets deposited.
![]()
Question 8.
(i) Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na20 and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are the ions present in these compounds?
Answer:
(i)

(ii)

(iii) Ions in Na2O are Na+ and O2-
Ions in MgO are Mg2+ and O2-
Question 9. Name two metals which are found in nature in free state.
Answer:
Gold, platinum and silver.
Question 10. What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Answer:
To obtain metals from its oxides for metals of medium reactivity one can use carbon as reducing agent and the chemical process is called reduction. Also, displacement reaction is used in which highly reactive metal acts as reducing agent. But for the metals of high reactivity the method of electrolytic reduction in used.
Example:
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(S) + heat
Question 11. Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals.

In which cases will you find displacement reactions take place?
Answer:

Question 12. Which metals do not corrode easily?
Answer:
Metals which are less reactive and lie at the bottom of reactivity series i.e., silver, gold, platinum do not react with atmospheric gases and hence do not corrode easily.
Question 13. What are alloys?
Answer:
Alloys are homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or metal and non-metal.
Example:
Brass – Cu + Zn metal + metal
Bronze – Cu + Sn metal + metal
Steel – Fe + Ni + Cr + C metals + non-metal
In-Text Activities Solved
Activity 3.1
Answer:
Take samples of iron, copper, aluminium and magnesium. The metal surface looks dull. On rubbing it with sand paper it shows the shining surface. This is called lustre.
Activity 3.2
Answer:
Among small pieces of iron, copper, aluminium, magnesium and sodium, we can cut only sodium and magnesium metal with knife. Rest all the other metals are hard.
Activity 3.3
Answer:
Take iron, zinc, lead and copper and hammer it. The metals change their shape, they are beaten into thin sheets. This property of metals is called malleability.
Activity 3.4
Answer:
Metals → Iron, copper, aluminium, lead. Metals show the property called ductility i.e., metals can be drawn into wires.
Activity 3.5
Answer:
1. Take wire of aluminium or copper. Fix it on the clamp stand as shown in the figure. Fix a pin to the free end of the wire using wax.
2. Heat the wire with burner at other end. After some time the pin drops.
3. This shows that the metals conduct heat.

Activity 3.6
Answer:
Set up an electric circuit as shown in the figure. Place the metal to be tested in the circuit between terminals A and B as shown in the figure.
Yes, the bulb glows; the metal is a good conductor of electricity.

Activity 3.7
Answer:
Samples of carbon (coal or graphite), sulphur and iodine

Activity 3.8
Answer:
1. Take Mg ribbon, rub it and burn it. The white ashes obtained is dissolved in water. The resultant solution turns red litmus paper into blue but do not show any colour
change of blue litmus paper. This shows that magnesium on burning forms magnesium oxide, which is basic in nature.
2. Take sulphur powder, burn it in test tube and collect the fumes produced in another test tube, add some water to the test tube and shake it. The resultant solution turns blue litmus red but does not change the colour of red litmus paper.
3. This shows that sulphur on heating produces sulphur dioxide, which is acidic in nature.
Conclusion → Metal oxides are basic in nature and non-metal oxides are acidic in nature.
Activity 3.9
Burn metals with the help of pair of tongs to record the following observations:
Answer:

Conclusion: Na reacts vigorously with oxygen. It even catches fire if left open in air. Mg and Ca reacts less quickly with oxygen.
Fe, Al and Zn reacts slowly with oxygen. Cu did not burn but formed a black coating of CuO.
Activity 3.10
Answer:
Put samples of small pieces of metals in beakers half-filled with cold water.
- Metals that reacted with cold water → Na, K and Ca.
- Metals that produced fire → Na and K.
- Metals that started floating after some time → Ca and Mg.
- Metals that reacted with hot water → Mg.
- Metals that reacted with steam → Al, Zn and Fe.
- Metals that did not react with steam also → Pb, Cu, Ag and Au.
- Reactivity of Metals.
- K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au
Activity 3.11
Answer:

Activity 3.12
Answer:

In the given set up (A) and (B) reactivity of metals is observed.
Test tube (A) → Iron nail dipped in CuSO4 solution
Reaction → Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + cu
Colour change → Blue colour → Green colour Reddish brown deposit of Cu on iron metal.
Name of the reaction → Displacement reaction.
Test tube (B) → Copper wire B dipped in FeSO4 solution
Reaction → NO reaction
Conclusion → Iron is more reactive than copper, therefore it displaces copper from its salt solution.
Activity 3.13
Answer:
Take samples of sodium chloride, potassium iodide and barium chloride and record the following observations:

Activity 3.14
Answer:
The given set up of 3 test tubes A, B and C is shown below.

The iron nails in test tube A rusts.
The iron nails in test tube B and C does not rust.
Reason : Nails in test tube A → exposed to air and water.
Nails in test tube B → does not get exposed to air due to layer of oil.
Nails in test tube C → does not get both air and water.
Conclusion : Both air and water and required for iron nails to rust.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here