JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 12 Areas Related to Circle
JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 12 Areas Related to Circle
J&K 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 12 Areas Related to Circle
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions
INTRODUCTION
Circle. Set of all those point which is at constant distance from a fixed point.
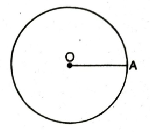
Radius. Fixed distance is know as radius of circle. It is denoted by R.
Centre. Fixed point is known as center (O).
Diameter. Longest chord passed through centre and whose end point lies on circle is known as diameter of circle.
Circumference of circle. The circumference of circle bears a constant ratio with the diameter of the circle i.e. Circumference/Diameter = π or circumference = 2лR or Distance covered in one complete round is called circumference or perimeter.
Concentric circle. Circles having same centre but different radii are known as concentric circle.
Area of Region Enclosed between two concentric circle. If ‘R’ is radius of outer circle and r is radius of smaller (inner) circle.
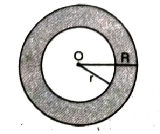
Area enclosed between two concentric circle
= πR² – πr²
= π [R² – r²] square unit.
Area of circle = лR²
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 12.1
Unless stated otherwise, use л = 22/7
Q. 1. The radii of two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles.
Solution.
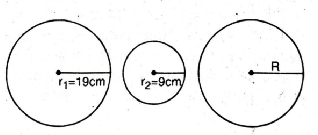
Radius of first circle (r1) = 19 cm
Radius of second circle (r2) = 9 cm
Let radius of third circle be R cm
According to condition
circumference of first circle
+ circumference of second circle
= circumference of third circle
2πr1 + 2πr2 = 2πR
2π [r1 + r2] = 2πR
19 + 9 = R
∴ R = 28
∴ Radius of third circle (R)
= 28 cm Ans.
Q. 2. The Radii of two circles are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find radius of circle which is having area equal to sum of the area of two circles.
Solution. Radius of first circle (r1) = 8 cm
Radius of second circle (r2) = 6 cm
Let radius of third circle be R cm
According to question
Area of third circle = Area of first circle
+ Area of second circle
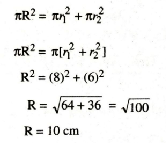
∴ Radius of required circle (R) = 10 cm. Ans.
Q. 3. Fig. depicts an archery target marked with its five scoring areas from the centre outwards as Gold, Red, Blue, Black and White. The diameter of the region representing Gold score is 21 cm and each of the other bands is 10.5 cm wide. Find the area of each of the five scoring regions.
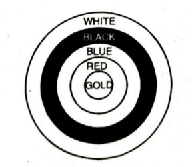
Solution. Diameter of Gold region = 21 cm
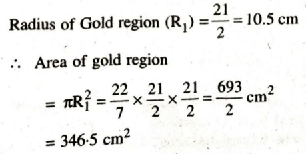
Width of each band = 10.5 cm
∴ Radius of Red and Gold region (R2)
= (10.5 + 10.5)
= 21 cm
Combined radius of Blue, Red and Gold region (R3)
= R2 + 10.5 cm
= 21 cm + 10.5 cm
= 31.5 cm
Combined radius of Black, Blue, Red and Gold (R4)
= R3 + 10.5
= 31.5 + 10.5
= 42 cm

Combined Radius of white, black, blue, red, gold region (R5)
= R4 + 10.5
R5 = 42 + 10.5 = 52.5 cm
Combined radius of black, blue, red and gold = (R4) = 42 cm.

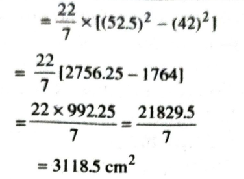
∴ Area of white scoring region = 3118.5 cm².
∴ Area of red region = Area of red region – Area of gold region
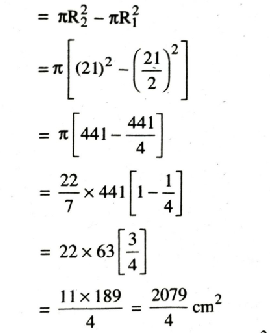
= 1039.5 cm²
∴ Area of Red region = 1039.5 cm²
Combined Radius of Gold, Red and Blue region R3 = (10.5 + 10.5 + 10.5) = 31.5 cm
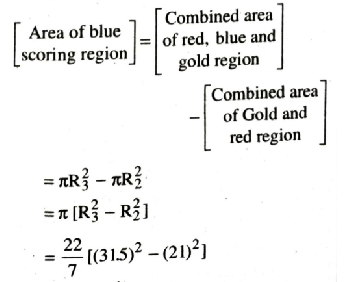
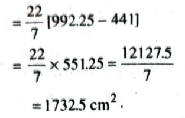
Hence, area of gold ring; red ring; blue ring; black ring; white ring are 346·5 cm²; 1039·5 cm²; 1732·5 cm²; 2425·5 cm²; 3118·5 cm² respectively. Ans.
Q. 4. The wheels of a car are of diameter 80 cm each. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is travelling at a speed of 66 km per hour?
Solution. Diameter of wheel = 80 cm
Radius of wheel (R) = 40 cm
= 4/100 = 0.04 m
Circumference of wheel = 2πr
= 2 × 22/7 × 0.04
= 22/7 ×0.08 m
Let us suppose wheel of car complete n revolutions of the wheel in 10 minutes
= n [0.08 × 22/7]
Speed of car = 66 km/hr.
Distance covered in 60 minutes
= 66 km = 66 × 1000 m
Distance covered in 10 minutes
= 66×1000/60 = 10
= 11000 m
According to question,
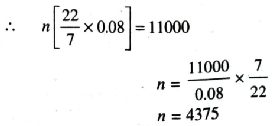
Hence, number of complete revolutions made by wheel in 10 minutes = 4375 Ans.
Q. 5. Tick the correct answer in the following and justify your choice: If the perimeter and area of a circle are numerically equal, then the radius of the circle is
(A) 2 units
(B) π units
(C) 4 units
(D) 7 units
Solution. Perimeter of circle = Area of circle
2πR = πR²
2R = R²
⇒ R = 2
∴ Correct option A is (R) = 2 unit. Ans.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 12.2
Unless stated otherwise, use π = 22/7
Q. 1. Find the area of sector of a circle with radius 6 cm, if angle of the sector is 60°.
Solution. Radius of sector of circle (R) = 6 cm
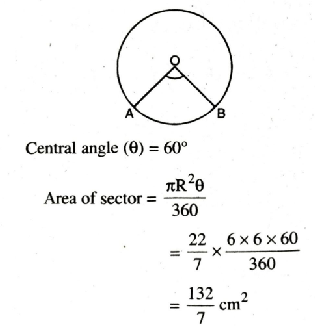
Area of sector = 18.86 cm2 Ans.
Q. 2. Find the area of a quadrant of a circle whose circumference is 22 cm.
Solution. Circumference of circle = 22 cm
2πR = 22

Area of quadrant = 9.625 cm² Ans.
Q. 3. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes.
Solution. Length of minute hand of clock = Radius of circle (R) = 14 cm

Hence, area swept by minute hand in 5 minutes is 51.33 cm².
Q. 4. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding : (i) minor segment (ii) major sector. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution. Radius of circle (R) = 10 cm
Central angle (0) = 90°

∴ Area of major sector = 235.5 cm2 Ans.
Q. 5. In a circle of radius 21 cm, an arc subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find :
(i) the length of the arc
(ii) area of the sector formed by the arc
(iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord
Solution. (i) Radius of circle (R) = 21 cm
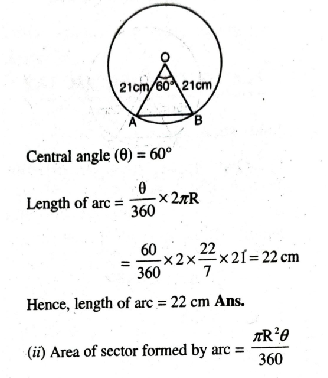

Area of segment = 40.26 cm² Ans.
Q. 6. A chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle.
(Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution. Radius of circle = (R) = 15 cm
Central angle (θ) = 60°
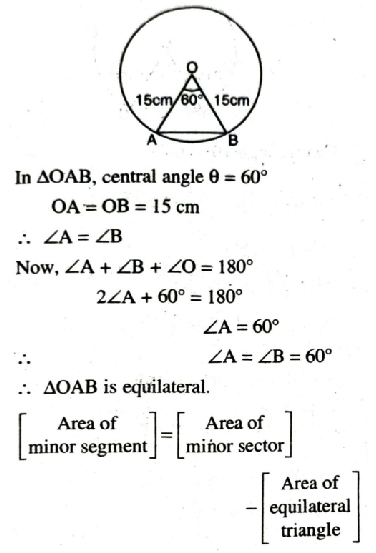
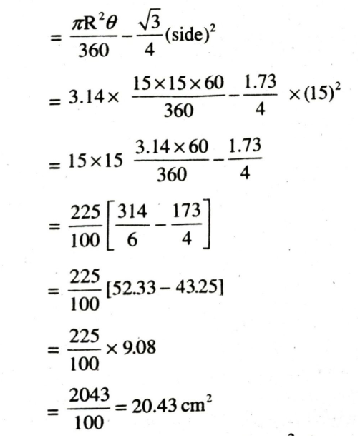
Area of minor segment = 20.43 cm². Ans.
Area of major segment
= Area of circle – Area of major segment.
= πR² – 20.43
= 3.14 × 15 × 15 – 20.43
= 706.5 – 20.43
= 686.07 cm²
Area of major segment = 686.07 cm² Ans.
Q. 7. A chord of a circle of radius 12 cm subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle.
(Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73).
Solution. Radius of circle (R) = 12 cm
Central angle (θ) = 120°
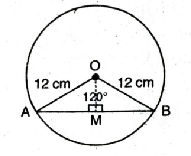
In ΔOAM, from O draw, angle bisector of ∠AOB as well as perpendicular bisector OM of AB.
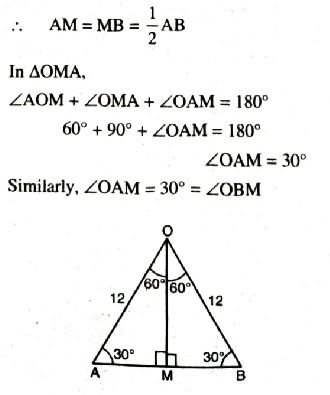

∴ Area of the segment = 88.44 cm² Ans.
Q. 8. A horse is tied to a peg at one corner of a square shaped grass field of side 15 m by means of a 5 m long rope (see fig.). Find :
(i) the area of that part of the field in which the horse can graze.
(ii) the increase in the grazing area of the rope were 10 m long instead of 5 m
(Use π = 3.14).
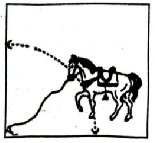
Solution. Side of square = 15 m
(i) Length of Peg = Radius of rope (R) = 5 m
Central angle (θ) = 90°
[Each angle of square]
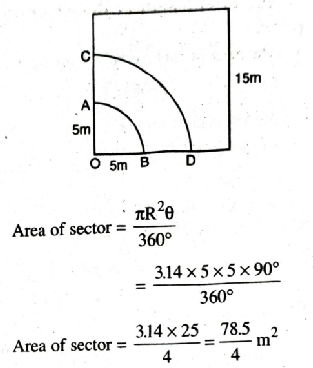
= 19.625 m² Ans.
(ii) When radius of sector increase to 10 m
Radius of sector OCD (R1) = 10 m
Central angle (θ) = 90°

∴ Increase in grazing area
= Area of sector OCD-Area of sector OAB
= 78.5 – 19.625
= 58.875 m²
Increase of grazing area = 58.875 m Ans.
Q. 9. A brooch is made with silver wire in the form of a circle with diameter 35 mm. The wire is also used in making 5 diameters which divide the circle into 10 equal sectors as shown in fig. Find :
(i) the total length of the silver wire required.
(ii) the area of each sector of the brooch.
Solution. Diameter of circle (D) = 35 mm
Radius of circle (R) = 35/2 mm
Number of diameter = 5
Number of equal sector = 10
(i) Wire used = Length of 5 diameters
+ circumference of circle (brooch)
= 5(35) + 2πR
= 175 + 2 × 22/7 × 35/2
= 175 + 110
= 285 mm Ans.
(ii) Sector angle of brooch

∴ Area of each brooch = 96.25 m² Ans.
Q. 10. An umbrella has 8 ribs which are equally spaced (see fig). Assuming umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella.
Solution. Radius of circle = 45 cm
Number of ribs = 8
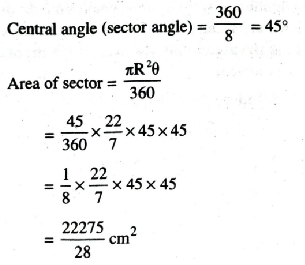
Area of sector = 795.53 cm²
∴ Area between two consecutive ribs of the umbrella = 795.53 cm² Ans.
Q. 11. A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 25 cm sweeping through an angle of 115°. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades.
Solution. Length of blade (R) = 25 cm
Sector angle (θ) = 115°
Wiper moves in form of sector.
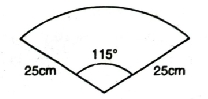
Area of sector = Area covered by one blade
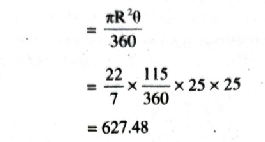
Area covered by two blades of wiper
= 2 Area of sector
= 2 × 627.48
= 1254-96 cm² Ans.
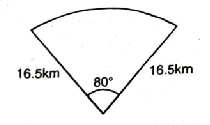
Q. 12. To warn ships for underwater rocks, a lighthouse spreads a red coloured light over a sector of angle 80° to a distance of 16.5 km. Find the area of the sea over which the ships are warned.
(Use π = 3.14)
Solution. Sector angle (θ) = 80°
Radius of sector (R) = 16.5 km
Area of sea over which the ships are warned
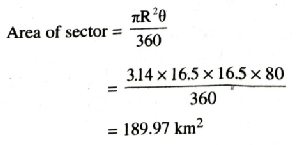
Area of sea over which the ships are warned
= 189.97 km² Ans.
Q. 13. A round table cover has six equal designs as shown in fig. If the radius of the cover is 28 cm, find the cost of making the designs at the rate of ₹ 3.50 per cm².
(Use √3 = 1.7)
Solution. Number of equal designs = 6
Radius of designs (R) = 28 cm
Each design is in the shape of sector central angle (θ) = 360/6 = 60°
Since central angle is 60° and OA = OB
∴ AOAB is equilateral triangle having side 28 cm.
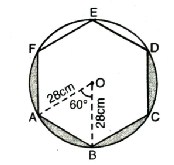
Area of one shaded designed portion = area of segment = Area of the sector OAB – area of ΔOAB
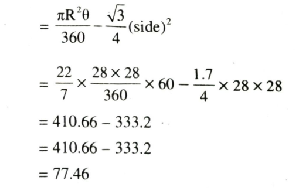
Area of one shaded designed portion
= 77.46
Area of six designed portions
= 6 [Area of one designed]
= 6 [77.46]
= 464.76 cm²
Cost of making 10 cm² = ₹ 3.50

= ₹ 162.68 Ans.
Q. 14. Tick the correct answer in the following:
Area of a sector of angle pᵒ of a circle with radius R is

∴ Correct option is (D). Ans.
Areas of Combinations of Plane figures
In our daily life, we saw various interesting designs like flower beds, drain covers, window designs etc. Some times, we want to find the areas of these designs then firstly we divide whole designs to known Plane figures whose area are previously known by us. Then, calculate the area of each part and by adding these areas, we get the area of required design. We illustrate the process of calculating areas of these types of figures through given problems.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 12.3
Unless stated otherwise, use π = 22/7
Q. 1. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., if PQ = 24 cm, PR = 7 cm and O is the centre of the circle.
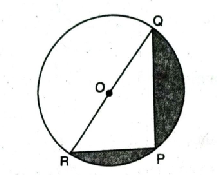
Solution. PQ = 24 cm
PR = 7 cm
RQ is diameter of circle
∠RPQ = 90° Angle in semi circle
In APQR,

∴ Area of shaded region = 161.53 cm² Ans.
Q. 2. Find the area of the shaded region in Fig., if radii of the two concentric circles with centre O are 7 cm and 14 cm respectively and ∠AOC = 40°.
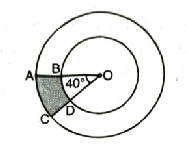
Solution. Radius of smaller circle (r)
= 7 cm
Radius of bigger circle (R) = 14 cm
Central angle ∠AOC (θ) = 40°
Area of shaded region
= Area of bigger sector OAC
– Area of smaller sector OBD
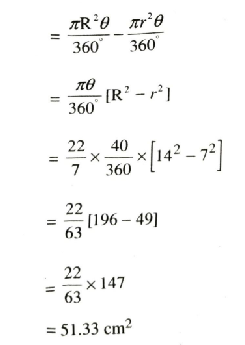
∴ Shaded Region = 51.33 cm².
Q. 3. Find the area of the shaded region in fig., if ABCD is a square of side 14 cm and APD and BPC are semicircles.
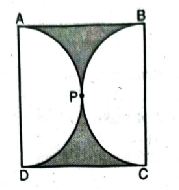
Solution. Side of square = 14 cm
Diameter of semicircle (AB = BC) = 14 cm
Radius of semi circle (R) = 7 cm
Area of square= (Side)²
= 14 × 14
= 196 cm²
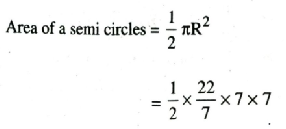
= 77 cm²
Area of two semi circle = 2(77)
= 154 cm²
Area of shaded region
= Area of square ABCD
– Area of two semi circle
= (196-154)
= 42 cm²
∴ Area of shaded region = 42 cm² Ans.
Q. 4. Find the area of the shaded region in fig., where a circular arc of radius 6 cm has been drawn with vertex O of an equilateral triangle OAB of side 12 cm as centre.
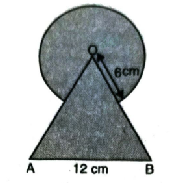
Solution. Radius of arc (R) = 6 cm
Side of equilateral triangle OAB = 12 cm
OA = OB = AB = 12 cm
Central angle of sector = 60°
[Each angle of equilateral angle are 60°]
Area of major sector of circle
= Area of circle – Area of sector

Shaded Area = Area of equilateral triangle
OAB + Area of major sector of circle
= 62.28 + 94.28
= 156.56
Shaded Area = 156.56 cm² Ans.
Q. 5. From each corner of a square of side 4 cm a quadrant of a circle of radius 1 cm is cut and also a circle of diamter 2 cm is cut as shown in fig. Find the area of the remaining portion of the square.
Solution. Side of square = 4 cm
Radius of each semi circle cut out (r)
= 1 cm
Diameter of circle (R) = 2 cm
∴ Radius of circle (R) = 1 cm
Area of square= (Side)²
= (4)² = 16 cm²
Area of 4 quadrants
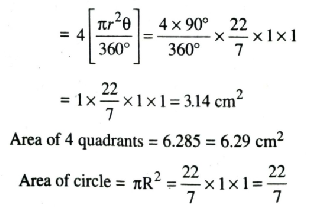
Area of circle = 3.14 cm²
Required area = Area of square
– Area of 4 quadrants – Area of circle
= (16-3.14-3.14) cm²
= 9.72 cm²
Required Area = 9.72 cm² Ans.
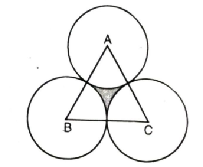
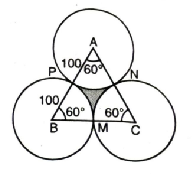
Q. 6. In a circular table cover of radius 32cm, a design is formed leaving an equilateral triangle ABC in the middle as shown in fig. Find the area of the design (shaded region).
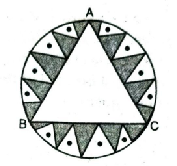
Solution. Radius of table cover (R) = 32 cm
OA = OB = OC = 32 cm
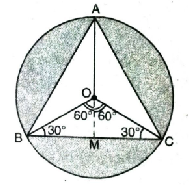
ΔABC is equilateral triangle with
AB = AC = BC = 32 cm
∠AOB = ∠BOC = ∠COA = 120°
Now, in ΔBOC,
From O draw, angle bisector of ∠BOC as well as perpendicular bisector OM of BC.
∴ BM = MC = ½ BC
Also, OB = OC [radii of the circle]
∴ ∠B = ∠C
∴ ∠O + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
120° + 2∠B = 180°
∠B = 30°
and ∠B = ∠C = 30°
Also, ∠BOM = ∠COM = 60°
ΔΟΜΒ ≅ ΔΟΜC [RHS cong.]
∴ In ΔOMB,
∠OBM = 30°
[∠O = 60° and ∠M = 90°]

= 3218.28 – 1328.64
= 1889.64 cm² Ans.
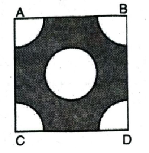
Q. 7. In fig., ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. With centres A, B, C and D, four circles are drawn such that each circle touch externally two of the remaining three circles. Find the area of the shaded region.
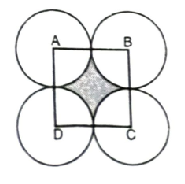
Solution. Side of square ABCD = 14 cm
Radius of circle (R) = 7 cm
Sector angle (θ)= 90°
[Each angle of square 90°]
Area of square = (side)²
= 14 × 14 = 196 cm²
Area of four quadrants
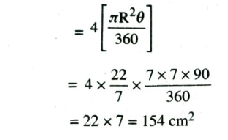
∴ Required shaded area
= Area of square – Area of 4 quadrants
= 196 – 154
= 42 cm² Ans.
Q. 8. Fig. depicts a racing track who left and right ends are semicircular.
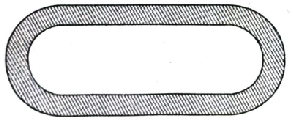
The distance between the two inner parallel line segments is 60 m and they are each 106 m long. If the track is 10 m wide, find
(i) the distance around the track along its inner edge.
(ii) the area of the track.
Solution.
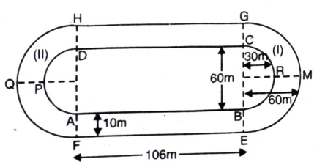
(i) Here AB = DC = 106 m
AF = BE = CG = HD = 10 m
Diameter of inner semicircle
(APD and BRC) = 60 m
∴ Radius of inner semicircle (APD) (r) = 30 m
Radius of outer semicircle (R) = r + 10 = 30 + 10 = 40 m
Distance around the track along inner edge
= AB + circumference of semi circle BRC
+ CD + circumference of semi circle DPA = 2AB + 2
[circumference of semi circle BRC]
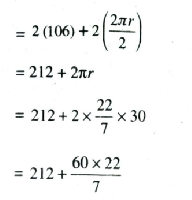
= 212 + 188.57
= 400.57 m Ans.
∴ Distance around the track along its inner edge = 400.57 m
(ii) Area of track
= Area of rectangle ABEF
+ Area of region BEMGCRB
+ Area of rectangle CGHD
+ area of region.
= 2 Area of rectangle ABCD
+ 2 Area of region (II)
= 2 (AB × AF) + 2
[Area of semi circle with Radius 60 cm – Area of semi circle with radius 30 cm]
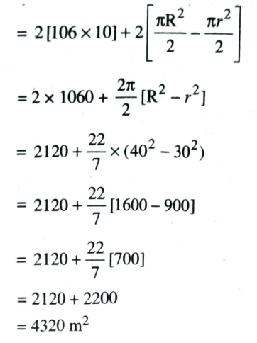
∴ Area of track = 4320 m² Ans.
Q. 9. In Fig., AB and CD are two diameters of a circle (with centre O) perpendicular to each other and OD is the diameter of the smaller circle. If OA = 7 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
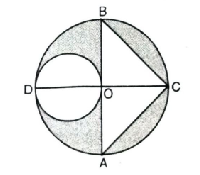
Solution. Diameter of circle = 14 cm
Radius of circle = 7 cm
Diameter of smaller circle = 7 cm
∴ Radius of smaller circle = 7/2 cm
Since AB and CD are two perpendicular diameters of a circle.
∴ AO ⊥ CD
Area of bigger circle = πR²
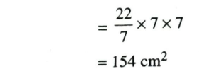
Area of smaller circle = πr²
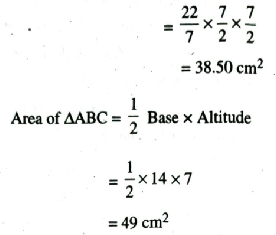
∴ Shaded Area = Area of bigger circle – Area of smaller circle – Area of triangle
= (154-38.5-49) cm²
= 66.5 cm² Ans.
Q. 10. The area of an equilateral triangle ABC is 17320.5 cm². With each vertex of the triangle as centre, a circle is drawn with radius equal to half of the length of the side of the triangle (see Fig.). Find the area of the shaded region.
(Use π = 3.14) and √3 = 1.73205)
Solution. Area of equilateral triangle ABC = 17320.5 cm²

∴ Required shaded Area
= Area of triangle – Area of three sectors
= 17320.5 – 15700 = 1620.5 cm²
∴ Hence, Required shaded Area
= 1620.5 cm² Ans.
Q. 11. On a square handkerchief, nine circular designs each of radius 7 cm are made (see Fig). Find the area of the remaining portion of the handkerchief.
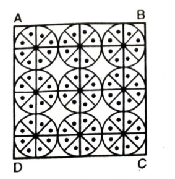
Solution. Radius of circle (R) = 7 cm
Diameter of circle = 2 × R
= 2 × 7
= 14 cm
Since there are three circles along a side of square
∴ side of squrae = 3 [14] = 42 cm
Total area of handkerchief
= Area of square= (side)²
= (42)² = 1764 cm².
Area of 9 circular designs = 9πR²
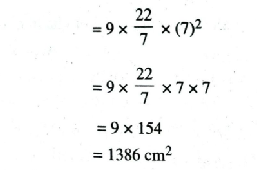
∴ Required area of remaining portion
= Area of square – Area of 9 circular designs
= 1764 – 1386 = 378 cm²
∴ Required area of remaning portion
= 378 cm² Ans.
Q. 12. In Fig., OACB is a quadrant of a cicle with centre O and radius 3.5 cm. If OD = 2 cm, find the area of the
(i) quadrant OACB,
(ii) shaded region.
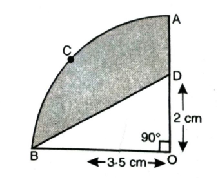
Solution. Radius of quadrant (R) = 3.5 cm

Hence, Shaded Area = 6.125 cm² Ans.
Q. 13. In fig., a square OABC is inscribed in a quadrant OPBQ. If OA = 20 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
(Use π = 3.14)
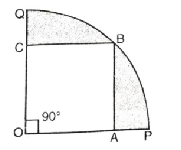
Solution. Side of square ABCO = 20 cm
∠AOC = 90°
AB = OA
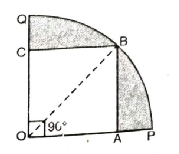
∴ In ΔOAB,

= 2 × 314 cm² = 628 cm²
∴ Required shaded Area
= Area of sector – Area of square
= (628-400) cm²
= 228 cm² Ans.
Q. 14. AB and CD are respectively arcs of two concentric circles of radii 21 cm and 7 cm and centre O. If ∠AOB = 30°, find the area of the shaded region.
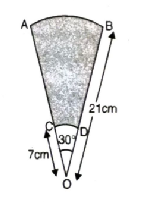
Solution. Radius of sector OBA (r) = 21 cm
Sector angle (θ) = 30°
Radius of sector ODC

Area of smaller sector (ODC)
= 12.83 cm²
Now, Shaded Area
= Area of bigger sector OAB
– Area of smaller sector OCD
= 115.5 – 12.83
= 102.66
Hence, Shaded Area = 102.66 cm² Ans.
Q. 15. In fig., ABC is a quadrant of a circle of radius 14 cm and a semicircle is drawn with BC as diameter. Find the area of the shaded region.
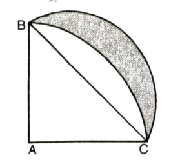
Solution. Radius of quadrant ACPB (r)
= 14 cm
Sector angle (θ) = 90°
AB = AC = 7 cm
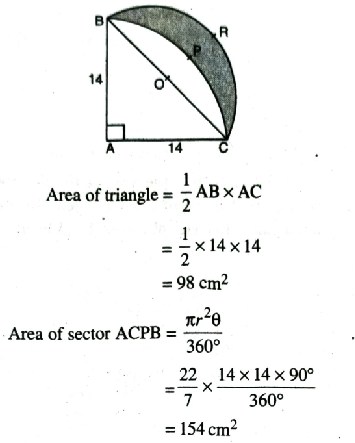
∴ Area of BOCPB
= Area of sector ABPC
– Area of ΔABC
= 154 cm² – 98 cm²
= 56 cm²
In ΔBAC, AB² + AC² = BC²
(14)² + (14)² = BC²

Required Area = Area of semicircle
– [Area of sector – Area of ABAC]
= 154 – [154 – 98]
= 154 – 56
= 98 cm²
Hence, Shaded Area = 98 cm² Ans.
Q. 16. Calculate the area of the designed region in fig. common between the two quadrants of circles of radius 8 cm each.
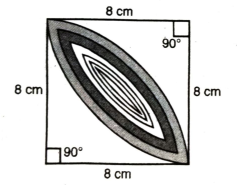
Solution. Side of square = 8 cm
Area of square= (8)² = 64 cm²
Line BD divides square ABCD into the equal parts
Area of ΔABD = ar of ΔBDC
Sector angle θ = 90°
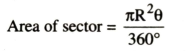

∴ Area of segment DMBPD
= Area of sector ABPD – Area of ΔABD
= 50.28 – 32
= 18.28 cm²
Hence, Shaded area
= 2 area of segment DMBPD
= 2 (18.28) = 36.56 cm² Ans.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here