JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
J&K 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions
INTRODUCTION
In class IX, we have learnt about linear equations in one variable and two variables.
The general form of a linear equation in two variables is
ax + by + c = 0
or ax + by = c where a, b, c are real number and a 0, b ≠ 0.
Any pair of values of x and y which satisfies the equation
ax + by + c = 0
or ax + by = c is called its solution. The graph of a linear equation in one variable is a straight line parallel to x-axis or y-axis according as the equation is of the form ay = b or ax = b where a ≠ 0
The graph of a linear equation in two variables is also a straight line.
Every solution of linear equation determine on the line represented by it.
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables.
Two linear equations which are in the same two variables x and y simultaneously are called a pair of linear equations in two variables.
The general form for a pair of linear equations in two variables x and y is
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0
and a2x + b2y + C2 = 0
where a1, b1, C1, a2, b2, c2 are all real numbers and 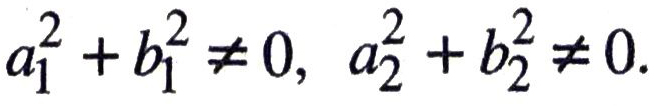
Solution Set: Solution set is collection of all those values of variables x and y satisfying each one of the equations in a given system of pair of linear equations in two variables.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.1
Q. 1. Aftab tells his daughter, “Seven years ago, I was seven times as old as you were then. Also, three years from now, I shall be three times as old as you will be” (Isn’t this interesting ?) Represent this situation algebraically and graphically.
Solution. Let Aftab’s present age = x years and Aftab’s daughter’s present age = y years
Algebraical-Situation
According to 1st condition,
x – 7 = 7 (y – 7)
or x – 7 = 7y – 49
or x – 7y + 42 = 0
According to 2nd condition,
x + 3 = 3 (y + 3)
or x + 3 = 3y + 9
or x – 3y – 6 = 0
∴ Pair of Linear Equation in two variables are
x – 7y + 42 = 0
and x – 3y – 6 = 0 Ans.
Graphical-Situation
x – 7y + 42 = 0
x – 3y – 6 = 0
x = 7y – 42 …….(1)
x = 3y + 6 …….(2)
Putting y = 5 in (1), we get
x = 7 x 5 – 42
= 35 – 42 = -7
Putting y=6 in (1), we get :
x = 7 x 6 – 42
= 42 – 42 = 0
Putting y=7 in (1), we get :
x = 7 x 7 – 42
= 49 – 42 = 7
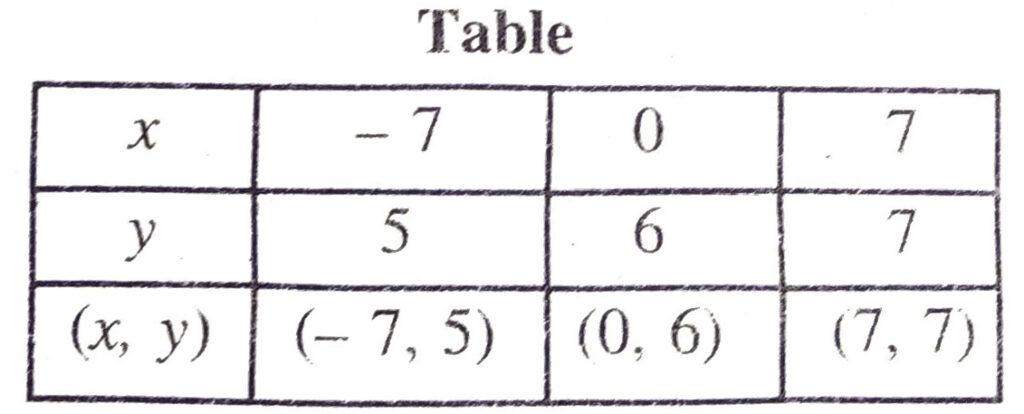
Plotting the points A (-7, 5), B (0, 6), C (7, 7) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation x – 7y + 420 = 0
Putting y = 0 in (2), we get
x = 3 × 0 + 6
= 0+6=6
Putting y = 3 in (2), we get :
x = 3 × 3 + 6
= 9+ 6 = 15
Putting y = – 2 in (2), we get :
x = 3 x – 2 + 6
= – 6 + 6 = 0
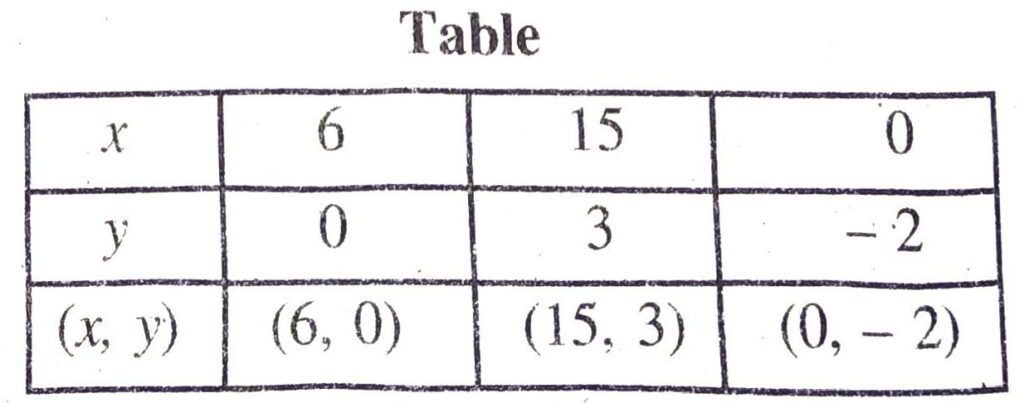
Plotting the points D (6, 0), E (15, 3), F (0, -2) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation x – 3y – 6 = 0
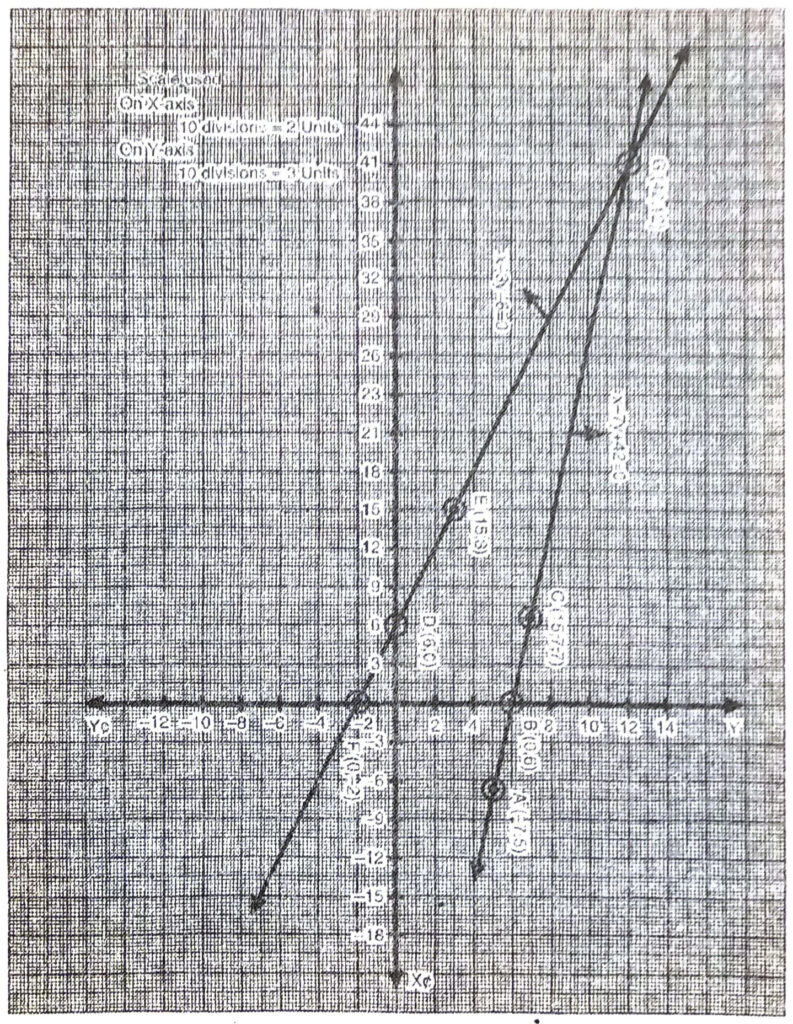
From the graph it is clear that the two lines intersect at G (42. 12).
Hence, x = 42 and y = 12 is the solution of given pair of linear equations. Ans.
Q. 2. The coach of a cricket team buys 3 bats and 6 balls for ₹ 3900. Later, she buys another bat and 3 more balls of the same kind for ₹ 1300. Represent this situation algebraically and geometrically.
Solution. Let cost of one bat = ₹ x
Cost of one ball = ₹ y
Algebraical-situation
According to 1st condition,
3x + 6y = 3900
According to 2nd condition,
1x + 3y = 1300
∴ Pair of linear equations in two variables are :
3x + 6y = 3900
and x + 3y = 1300 Ans.
Graphical-situation
3x + 6y = 3900
x + 2y = 1300
x = 1300 – 2y ………(1)
Putting y = 0 in (1), we get
x = 1300 – 2 x 0 = 1300
Putting y = 500 in (1), we get:
x = – 1300 – 2 x 500
= 1300 – 1000 = 300
Putting y = 650 in (1), we get :
x = 1300 – 2 x 650
= 1300 – 1300 = 0

Plotting the points A (1300, 0), B (300, 500) and C (0, 650) drawing a line joining them we get the graph of the equation 3x + 6y = 3900

Plotting the points A (1300, 0), E (- 200, 500), F (400, 300) and drawing a line joining them we get the graph of the equation x + 3y = 1300

From the graph it is clear that the two lines intersect at A (1300, 0).
Hence x = 1300 and y = 0 is the solution of given pair of linear equations. Ans.
Q. 3. The cost of 2 kg of apples and 1 kg of grapes on a day was found to be ₹ 160. After a month, the cost of 4 kg of apples and 2 kg of grapes is ₹ 300. Represent the situation algebraically and geometrically.
Solution. Let cost of 1 kg apples = ₹ x Cost of 1 kg grapes = ₹ y
Algebraical-situation
According to 1st condition,
2x + 1y = 160
According to 2nd condition,
4x + 2y = 300
∴ Pair of linear equations in two variables are
2x + y = 160
and 4x + 2y = 300 Ans.

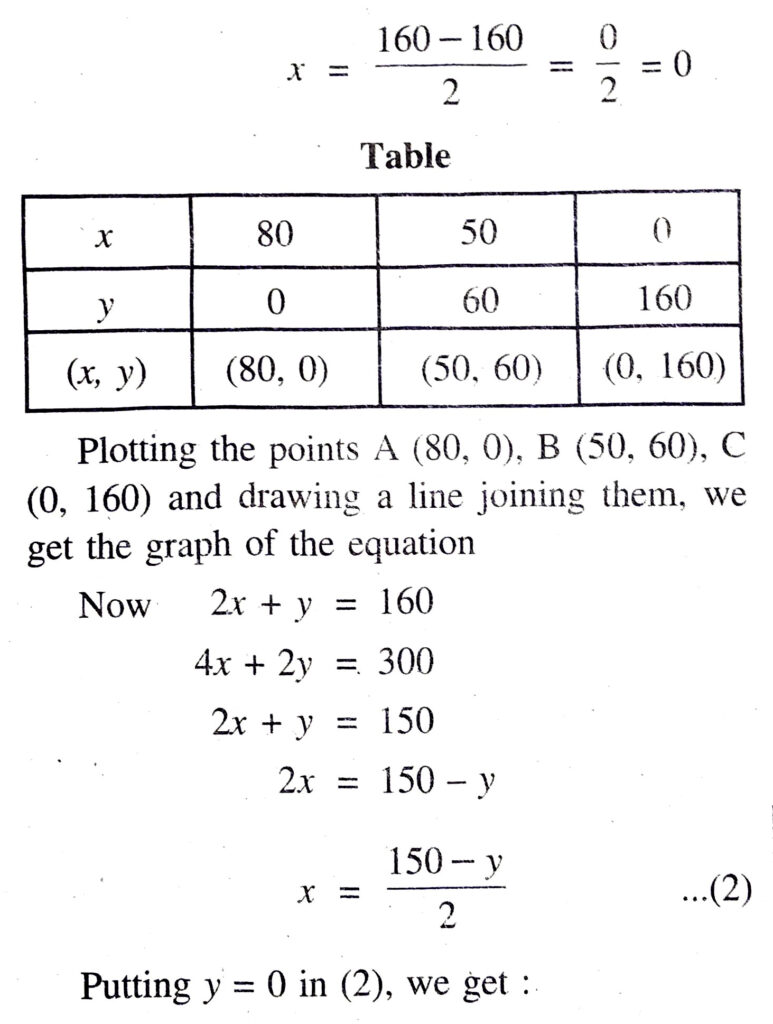
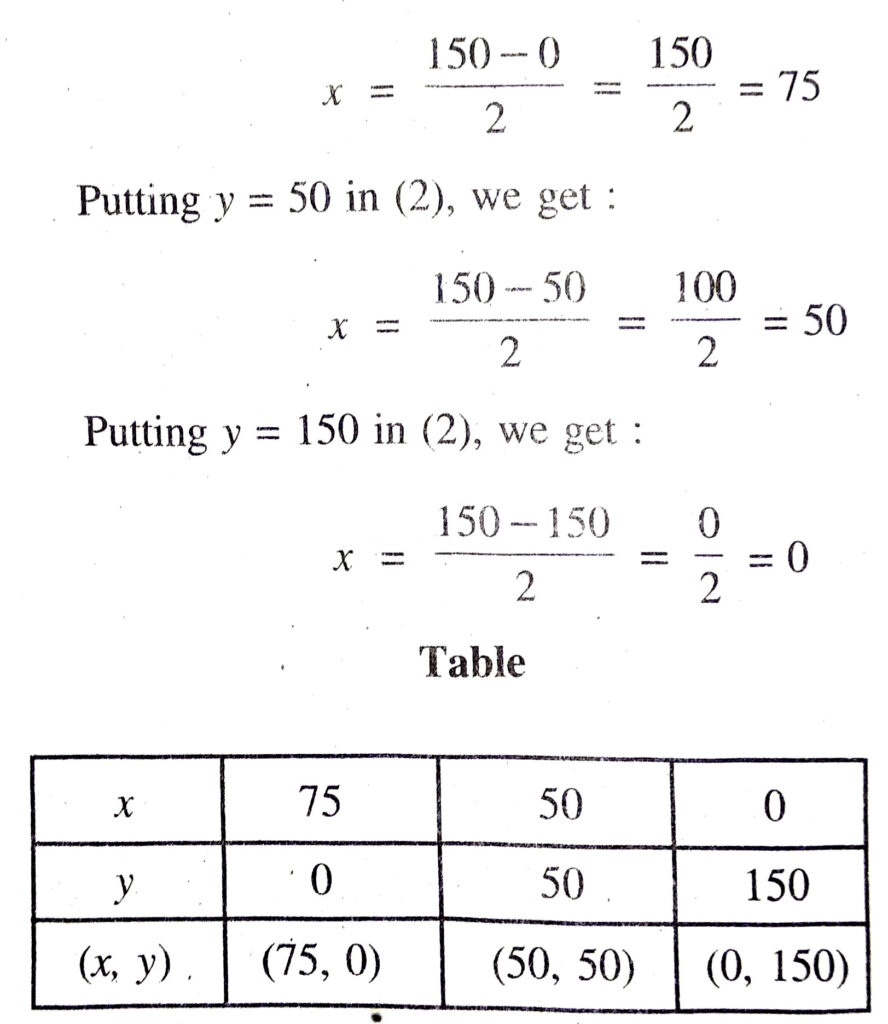
Plotting the points D (75, 0), E (50, 50), F (0, 150) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of equation 4x + 2y = 300
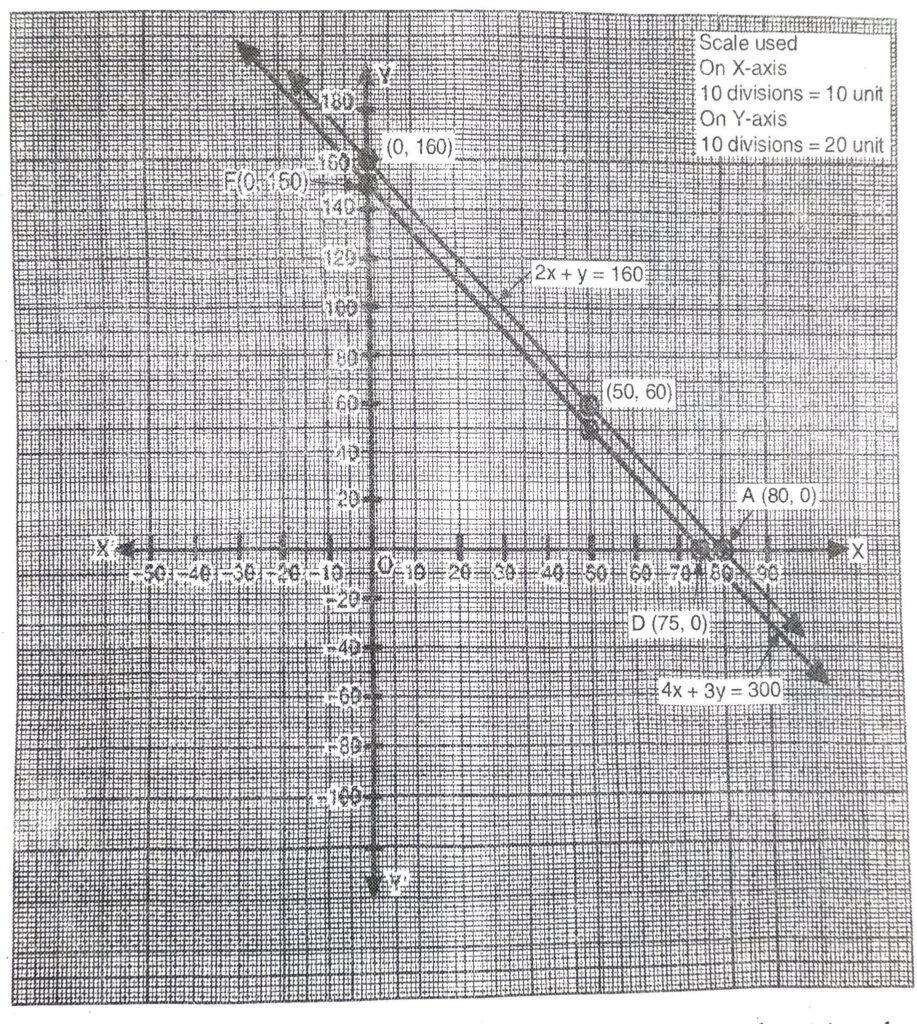
From the graph, it is clear that the two lines do not intersect anywhere i.e. they are parallel.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.2
Q. 1. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems, and find their solutions graphically.
(i) 10 students of Class X took part in a Mathematics quiz. If the number of girls is 4 more than the number of boys, find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
(ii) 5 pencils and 7 pens together cost ₹ 50, whereas 7 pencils and 5 pens together cost ₹ 46. Find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Solution. (i) Let the number of boys in the Quiz = x
and the number of girls in the Quiz = y
Total number of students took part in Quiz = 10
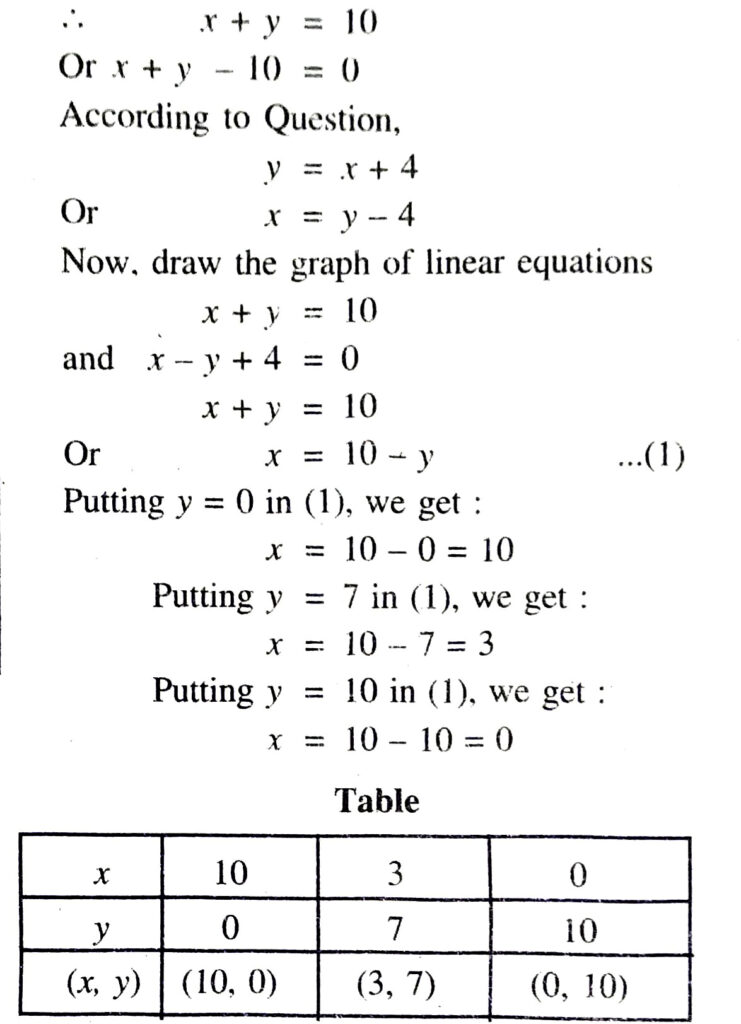
Plotting the points A (10, 0), B (3, 7), C (0, 10) and drawing a line joining them we get the graph of the equation x + y = 10
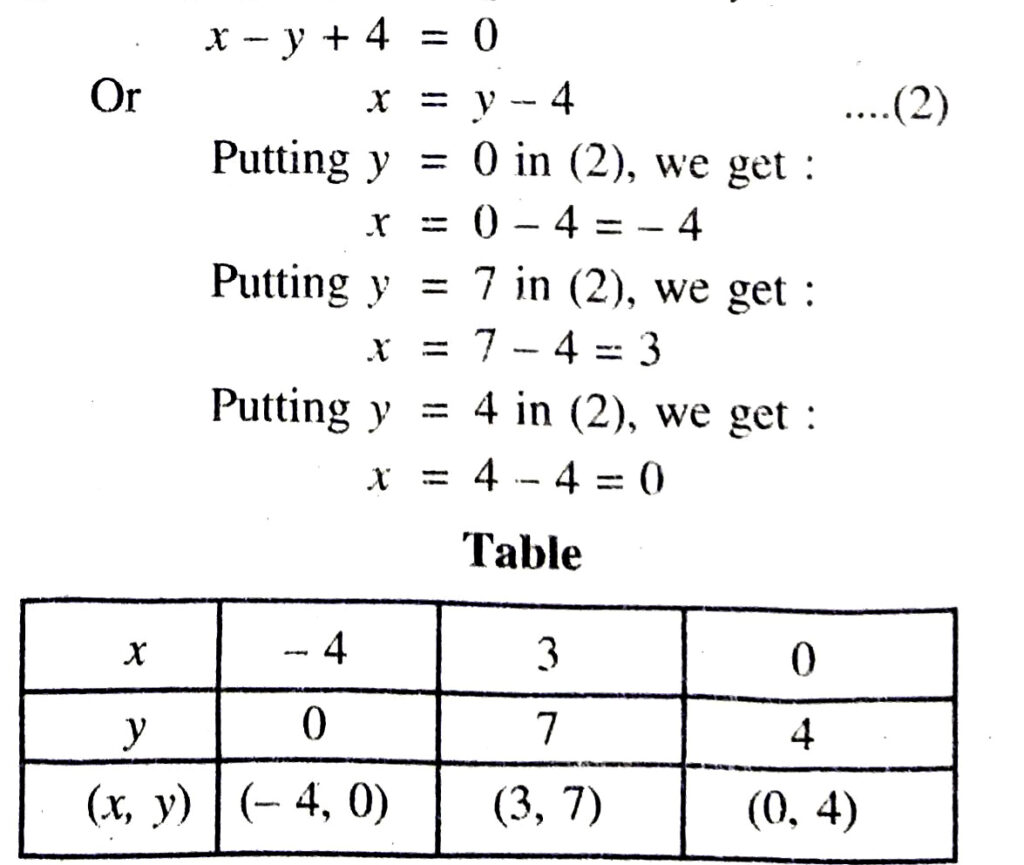
Plotting the points D (-4, 0), B (3, 7), E (0, 4) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation x – y + 4 = 0
From the graph it is clear that both the linear equations meets at a point B (3, 7).
∴ Point B (3, 7) is the graphic solution.
Hence, number of boys in the Quiz = 3
Number of girls in the Quiz = 7 Ans.
(ii) Let cost of one pencil = ₹ x
and cost of one pen = ₹ y
According to 1st condition,
5x + 7y = 50
According to 2nd condition,
7x + 5y = 46
∴ Pairs of linear equation is
5x + 7y = 50
7x + 5y = 46
Now, draw the graph of these linear equation.
5x + 7y = 50
or 5x = 50 – 7y
or x = 50-7y/5
Putting y = 0 in (1), we get : …(1)
Putting y = 0 in (1), we get :
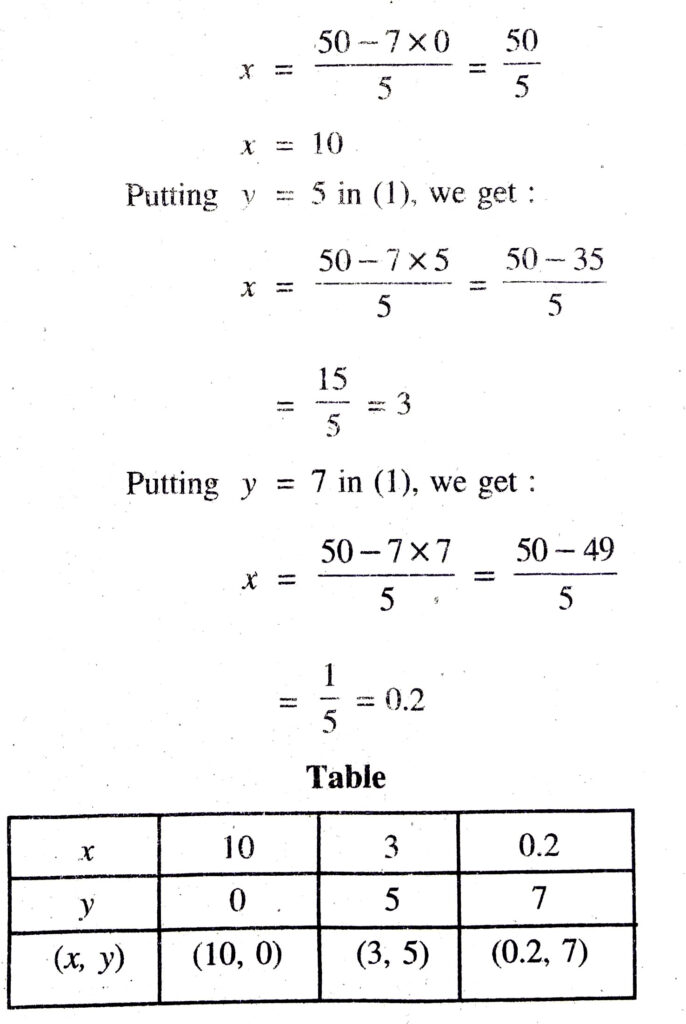
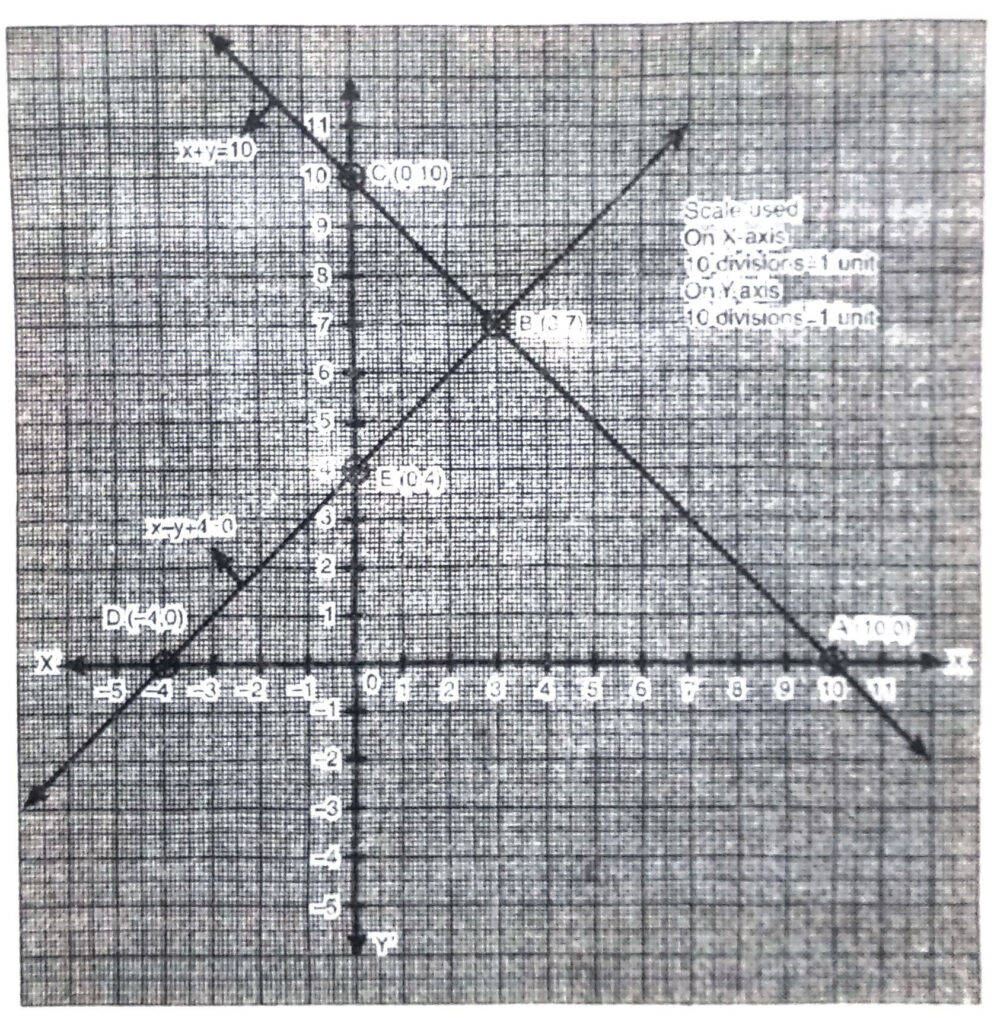
Plotting the points A (10, 0), B (3, 5), C (0.2, 7) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation
5x + 7y = 50

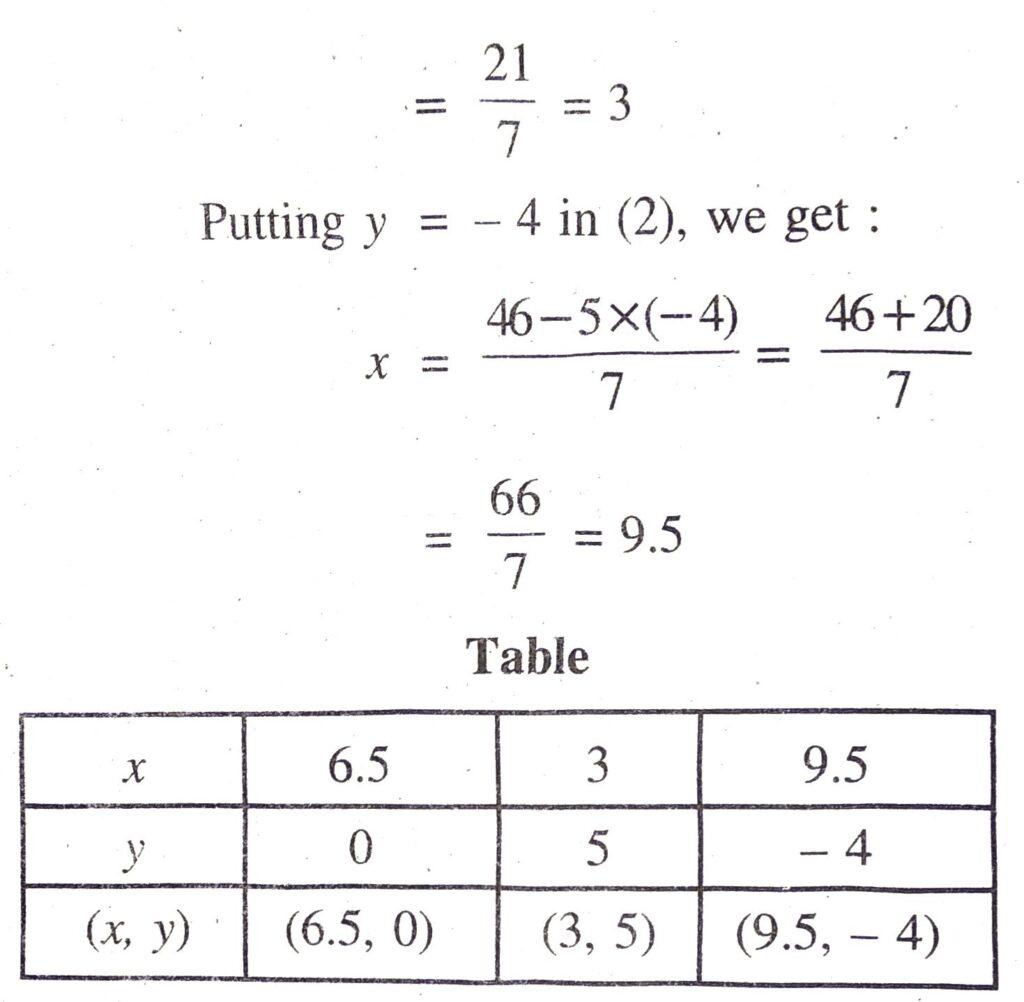
Plotting the points E (6.5, 0), B (3, 5), F (9.5, 4) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation.
7x + 5y = 46
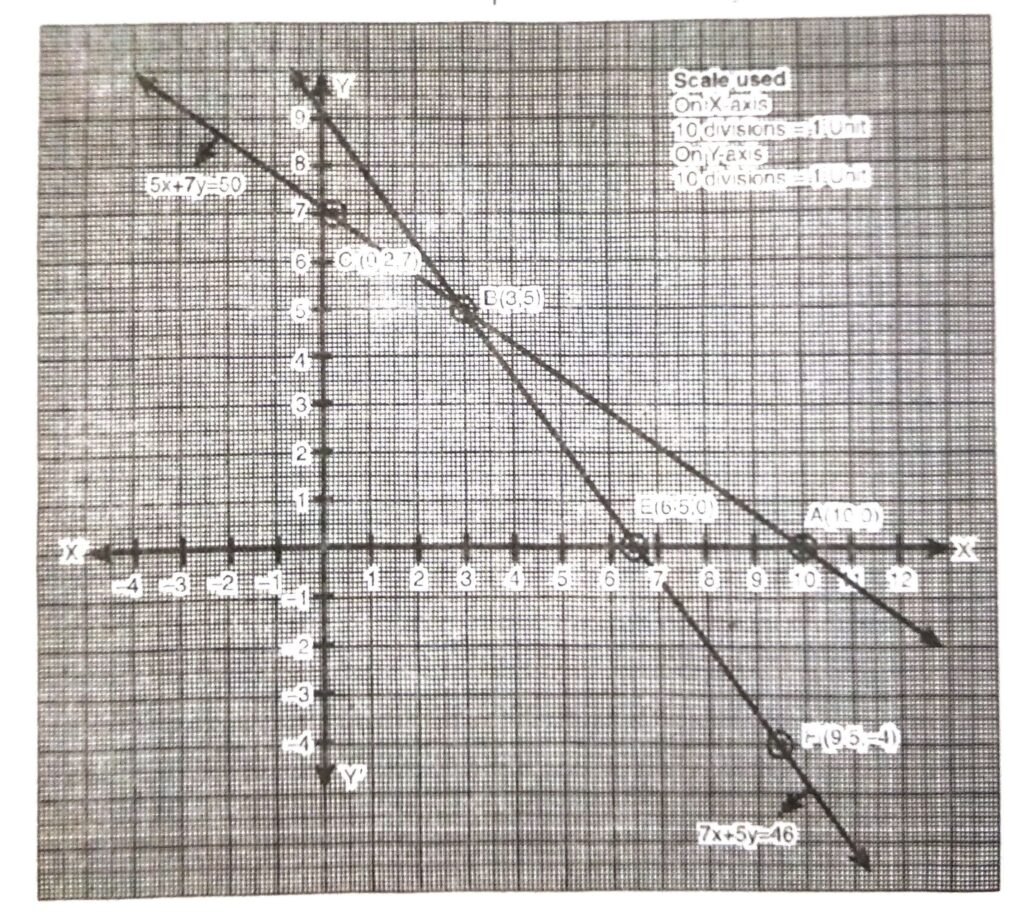
From the graph, it is clear that both the linear equations meets at a point B (3, 5).
∴ point B (3, 5) is the graphic solution.
Hence, cost of one pencil = ₹ 3
Cost of one pen = ₹ 5 Ans.
Q. 2. On comparing the ratios  find out whether the lines representing the following pairs of linear equations intersect at point, are parallel or coincident :
find out whether the lines representing the following pairs of linear equations intersect at point, are parallel or coincident :
(i) 5x – 4y + 8 = 0
7x + 6y – 9 = 0
(ii) 9x + 3y + 12 = 0
18x + 6y + 24 = 0
(iii) 6x – 3y + 10 = 0
2xy + 9 = 0
Solution. (i) Given pairs of linear equation is

Hence, given pairs of linear equation intersect at a point. Ans.


Hence, given pairs of linear equation are coincident. Ans.
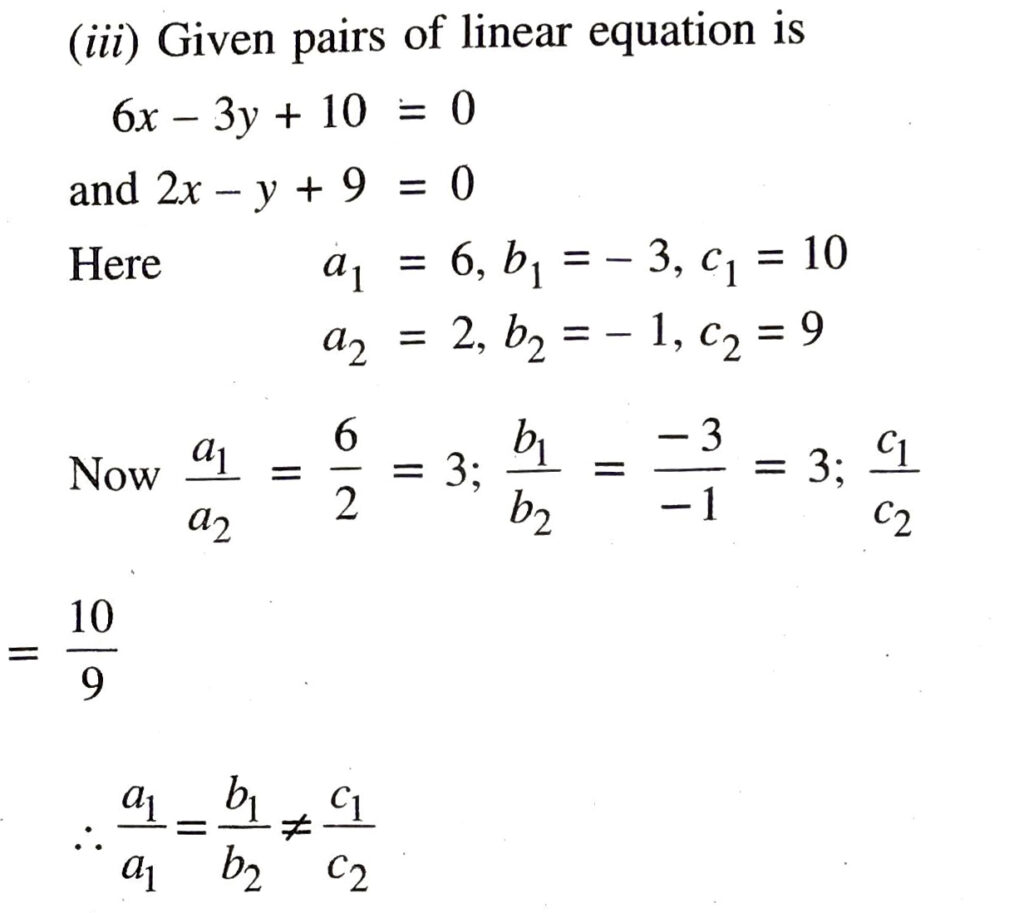
Hence, given pairs of linear equations are parallel to each other. Ans
Q. 3. On comparing the ratios  and find out whether the following pair of linear equations are consistent, or inconsistent.
and find out whether the following pair of linear equations are consistent, or inconsistent.

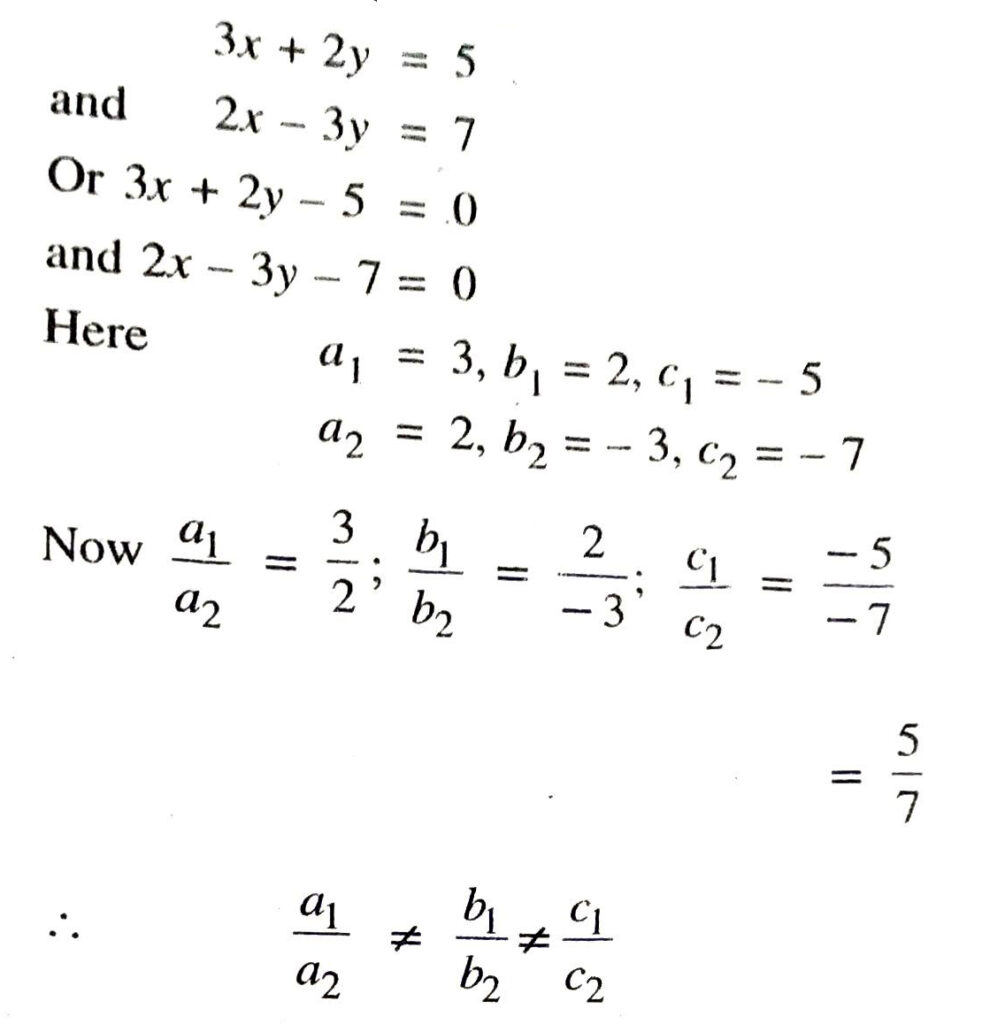
Hence, given pair of linear equation are consistent. Ans.
(ii) Given pair of linear equation is
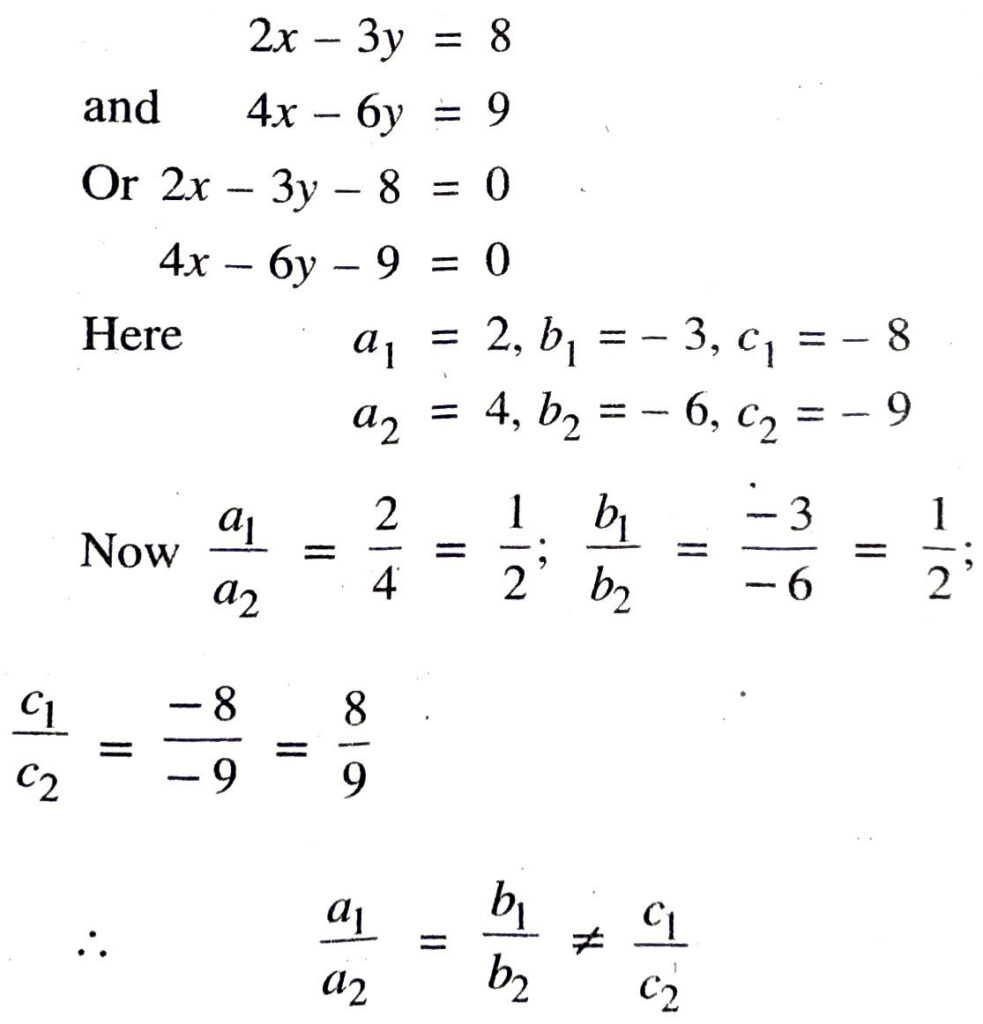
Hence, given pair of linear equation are inconsistent. Ans.
(iii) Given pair of linear equation is :

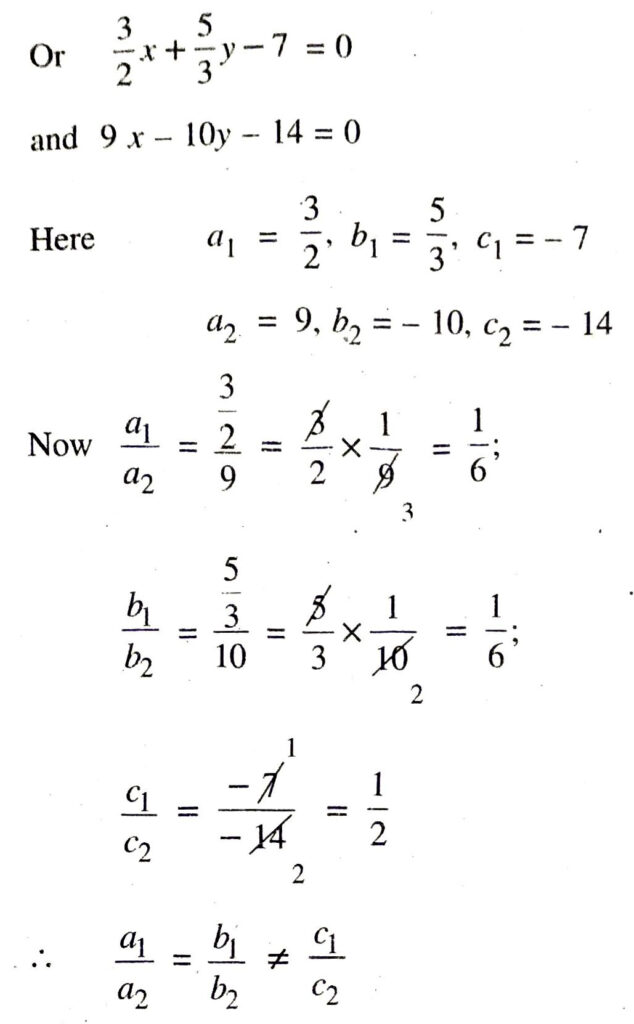
Hence, given pair of linear equation are inconsistent. Ans.
(iv) Given pair of linear equation is

Hence given pair of linear equation are consistent. Ans
(v) Given pair of linear equation is

Hence, given pair of linear equation are consistent. Ans.
Q. 4. Which of the following pairs of linear equations are consistent/inconsistent ? If consistent, obtain the solution graphically.
(i) x + y = 5, 2x + 2y = 10
(ii) x – y = 8, 3x – 3y = 16
(iii) 2x + y − 6 = 0, 4x – 2y – 4 = 0
(iv) 2x – 2y – 2 = 0, 4x – 4y – 5 = 0
Solution. (i) Given pair of linear equation is
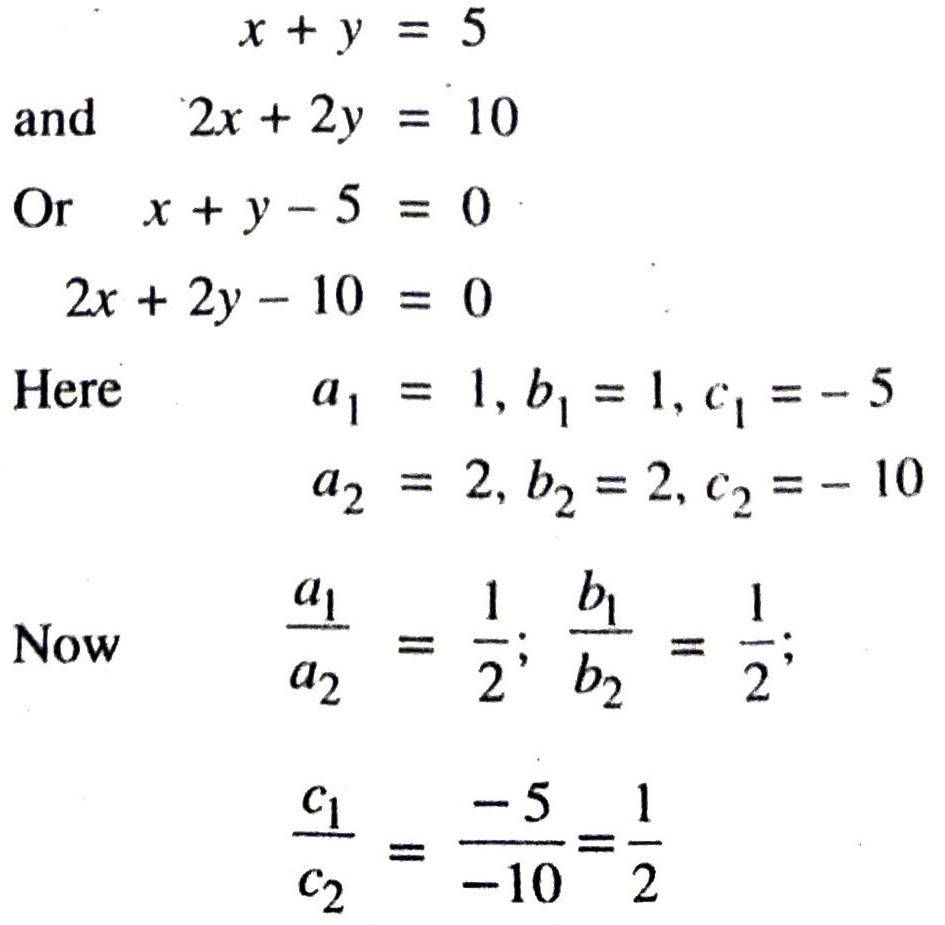

∴ Given pair of linear equation are consistent. Draw the graph of these equations
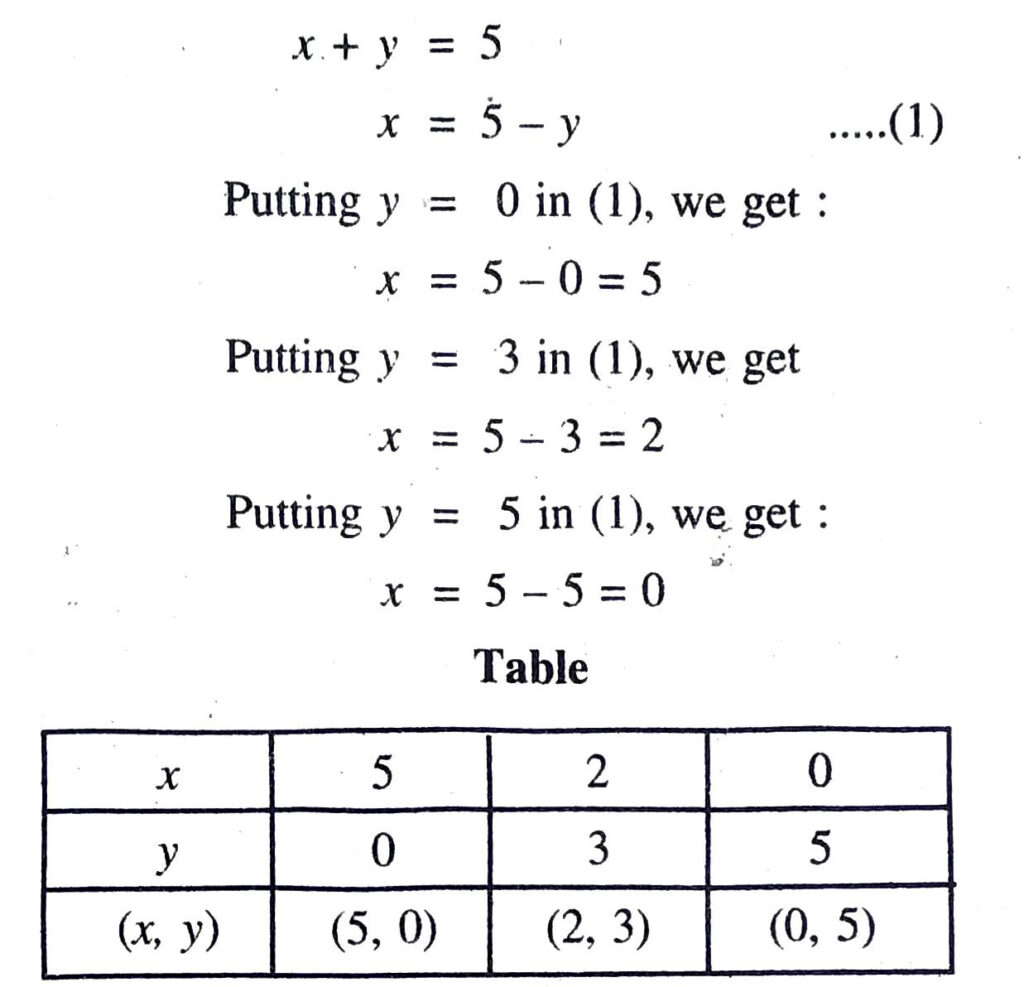
Plotting the points A (5, 0), B (2, 3), C (0,5) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation x + y = 5
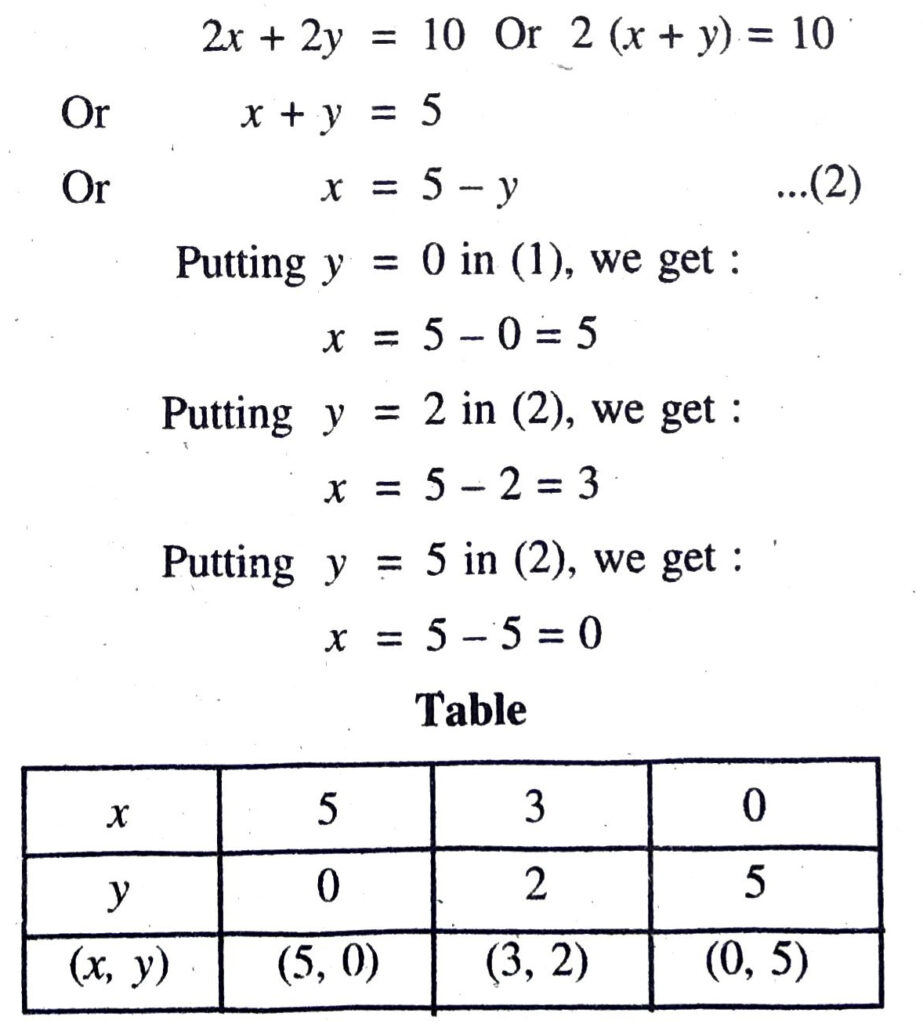
Plotting the points A (5, 0), D (3, 2), € (0, 5) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation 2x + 2y = 10
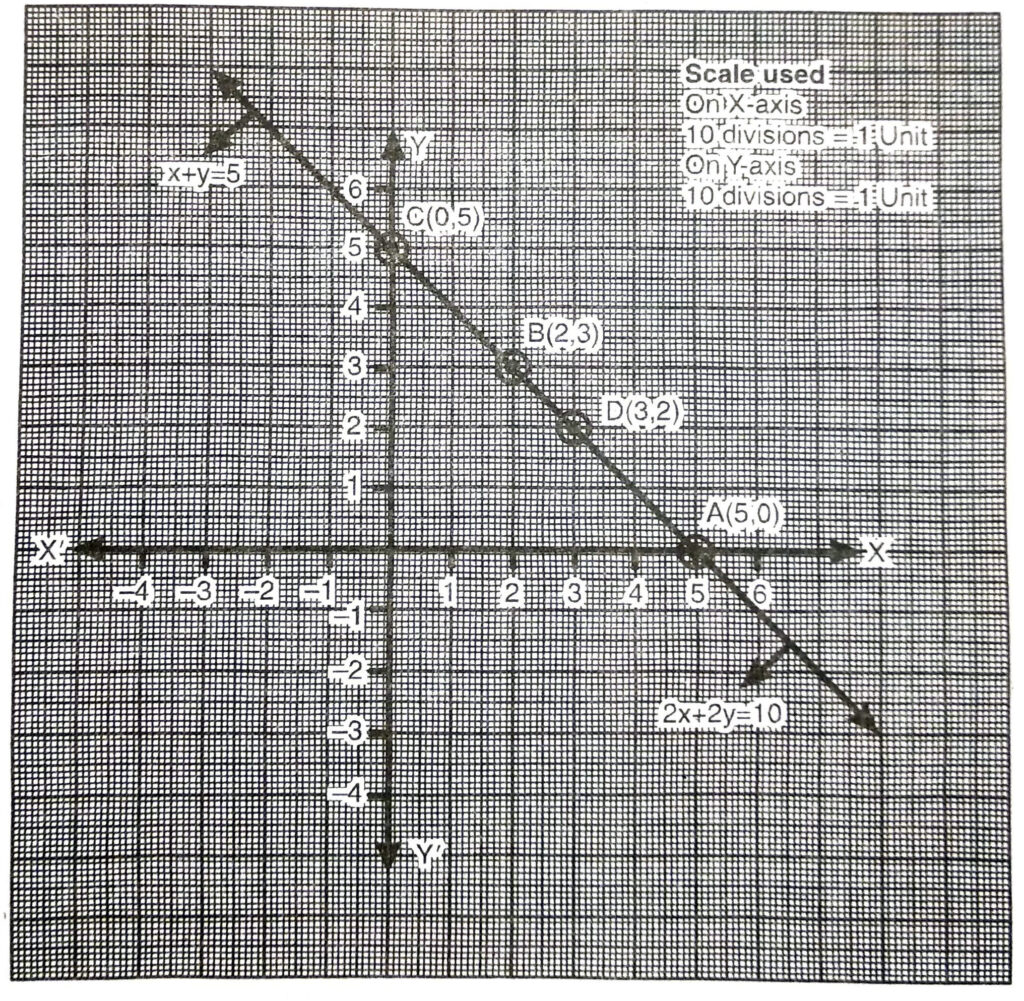
From the graph, it is clear that given pair of linear equation are parallel lines OR an infinite number of solutions. Ans.
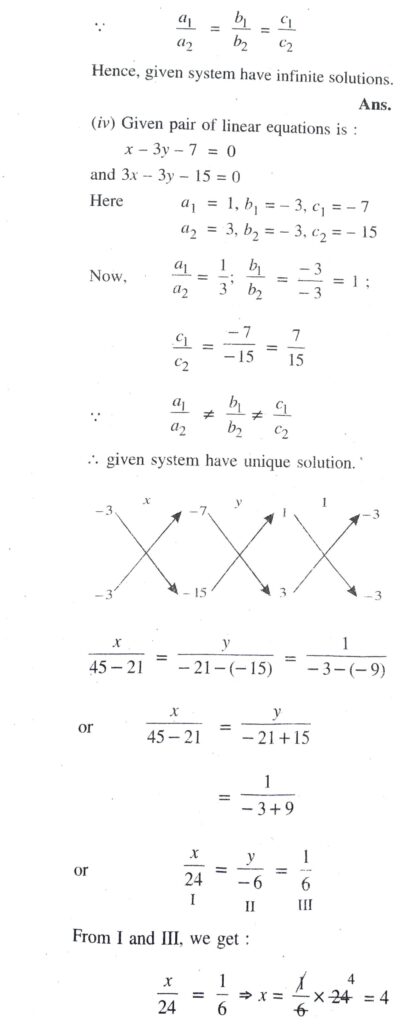
(ii) Given pair of linear equation is :
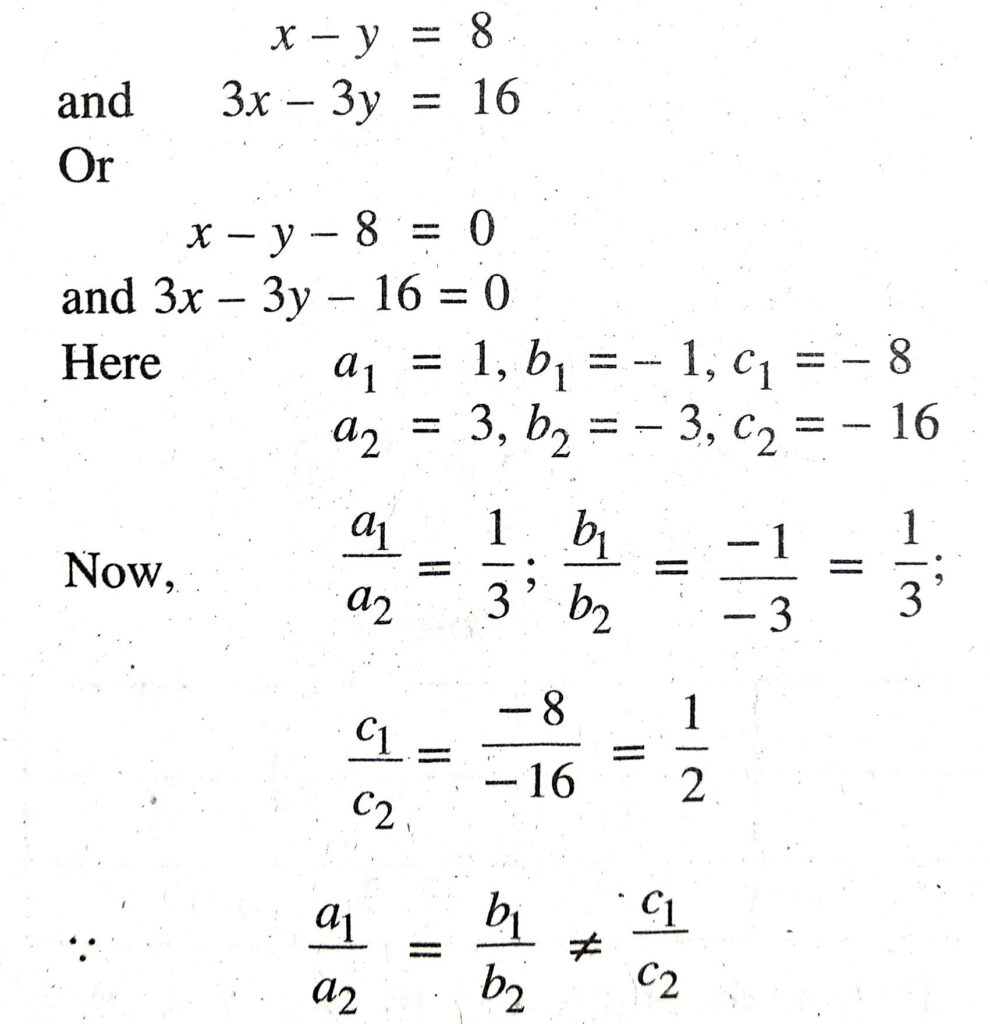
Hence, gives pair of system have inconsistent solution. Ans.
(iii) Given pair of linear equation is :

∴ given pair of system are consistent. Draw the graph of these linear equations


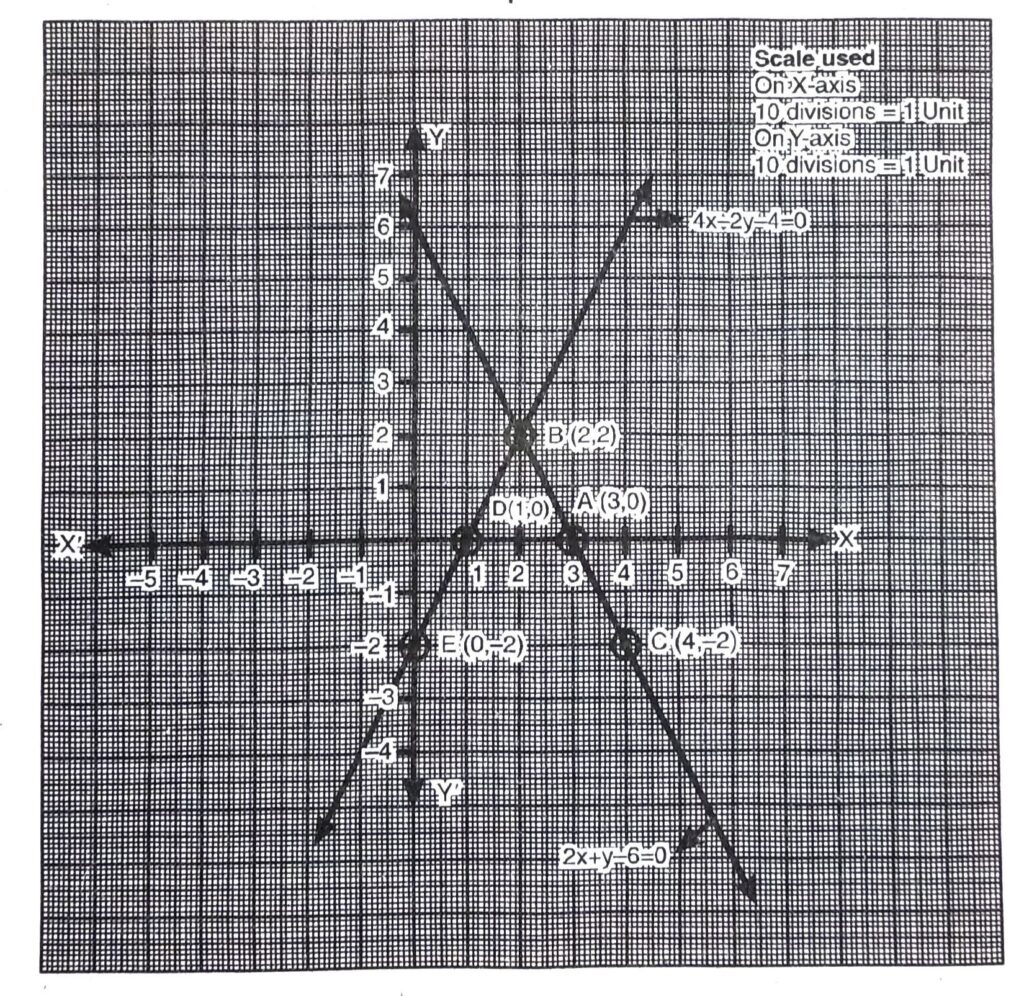
From the graph, it is clear that given system of equations meets at a point B (2, 2).
Hence, given pair of linear equation have unique solution. Ans.
(iv) Given pair of linear equation is :

Hence, given pair of system have consistent solution. Ans.
Q. 5. Half the perimeter of a rectangular garden,, whose length is 4 m more than its width is 36 m. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Solution. Let length of Width of garden = y m
Perimeter of garden = 2 [x + y] m
Half perimeter of garden = (x + y) m
According to 1st condition
x = y + 4
According to 2nd condition
x + y = 36
∴ Pair of linear equation is
x = y + 4
and x + y = 36
x = y + 4 …(1)
Putting y = 0 in (1), we get :
x = 0 + 4 = 4
Putting y = – 4 in (1), we get:
x = – 4 + 4 = 0
Putting y = 16 in (1), we get :
x = 16 + 4 = 20
Table
| x | 4 | 0 | 20 |
| y | 0 | – 4 | 6 |
| (x, y) | (4, 0) | (0, – 4) | (20, 16) |
Plotting the points A (4, 0), B (0, – 4), C (20, 16) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation.
x = y + 4
x + y = 36
x = 36 – y ….(2)
Putting y = 12 in (2), we get :
x = 36 – 12 = 24
Putting y = 24 in (2), we get :
x = 36 – 24 = 12
Putting y = 16 in (2), we get :
x = 36 – 16 = 20 –
Table
| x | 24 | 12 | 20 |
| y | 12 | 24 | 16 |
| (x, y) | (24, 12) | (12, 24) | 20, 16) |
Plotting the points D (24, 12), E (12, 24), C (20, 16) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation.
x + y = 36

From the graph, it is clear that pair of linear equations meet at a point C (20, 16).
∴ C (20, 16) i.e. x = 20 and y = 16 is the solution of linear equations.

Another Method
Let width of garden = x m
Lengh of garden = (x + 4) m
Perimeter of garden = 2 [Length + Width]
= 2 [x + x + 4] m
= 2 [2x + 4] m
∴ Half perimeter of garden = (2x + 4) m
According to Question,

Q. 6. Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0, write another linear equation in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is:
(i) intersecting lines
(ii) parallel lines
(iii) coincident lines
Solution.
Case I. For Intersecting Lines
Given linear equation is :
2x + 3y – 8 = 0 ….(1)
There are many another linear equation in two variables which satisfies the condition of

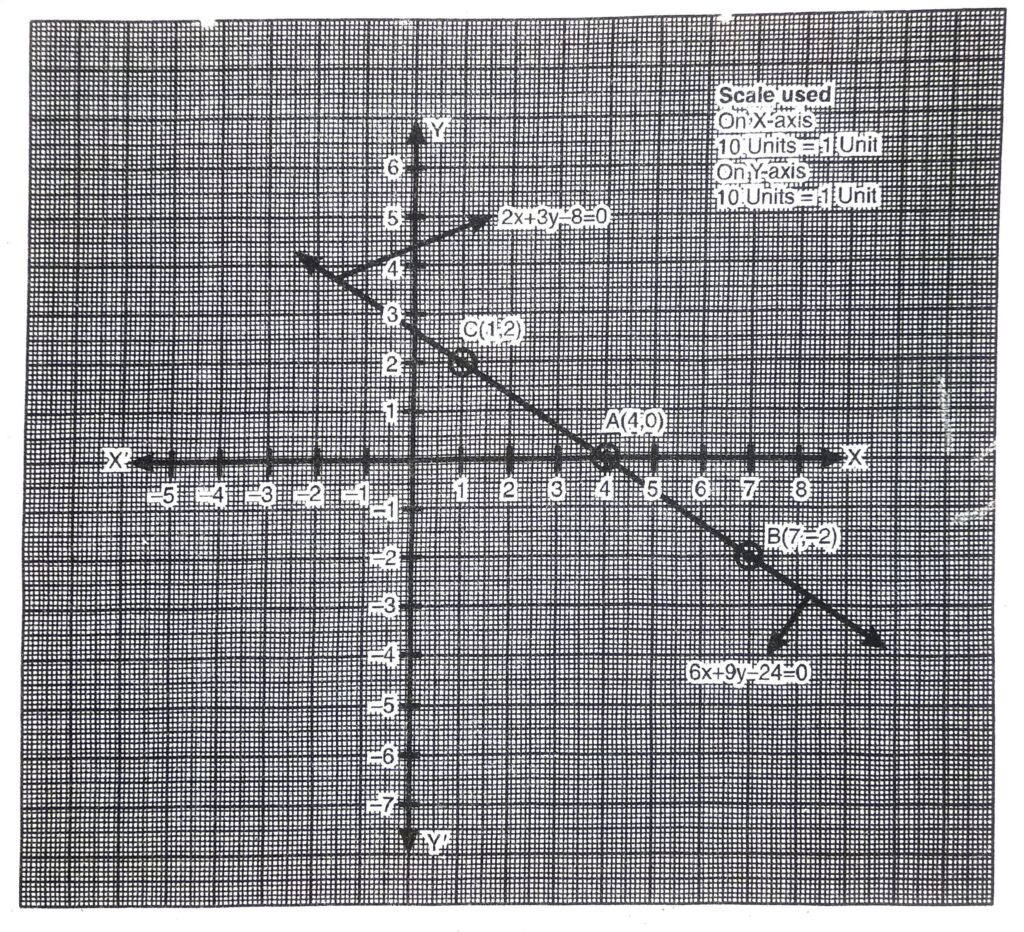
Plotting the points A (4, 0), B (7, – 2), C (1, 2) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation

Plotting the points D (2, 0), E (0, -3), F (4, 3) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation
3x – 2y – 6 =0
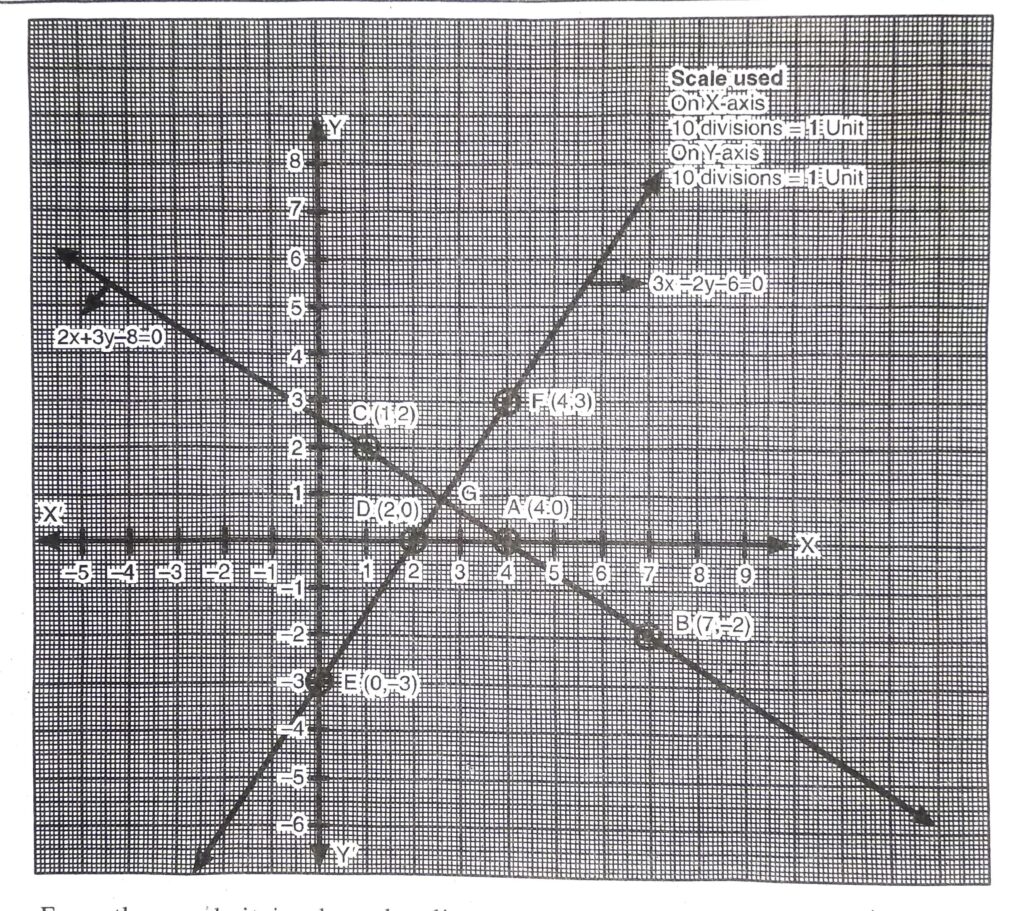
From the graph it is clear that linear equations intersect at a point G.
Case II. For Parallel Lines
Given linear equation is
2x + 3y – 8 = 0 …(1)
There are many other linear equation in two variables which satisfies the condition of parallel
Table for linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0 is follow :

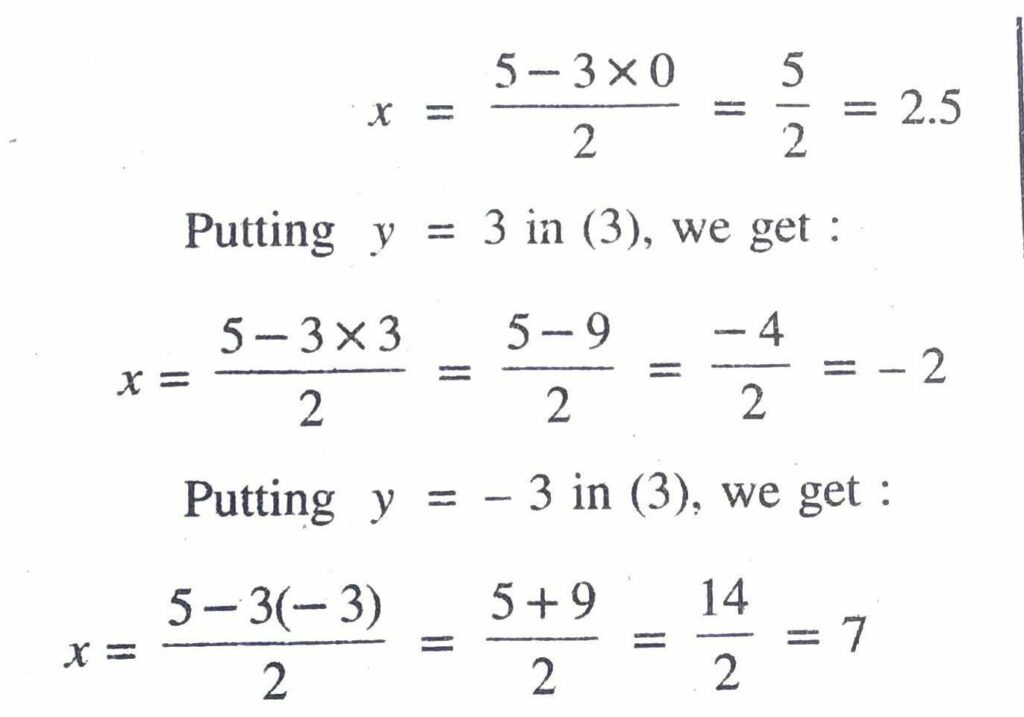

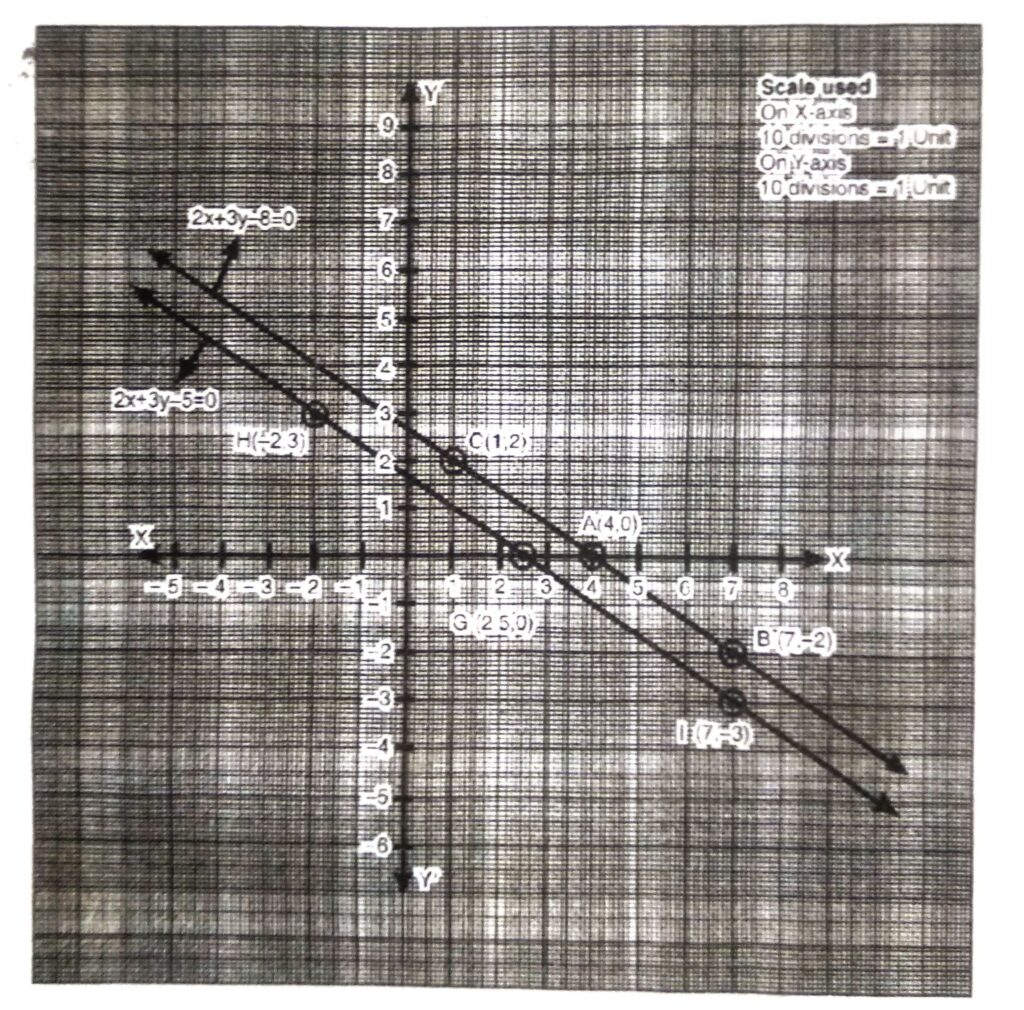
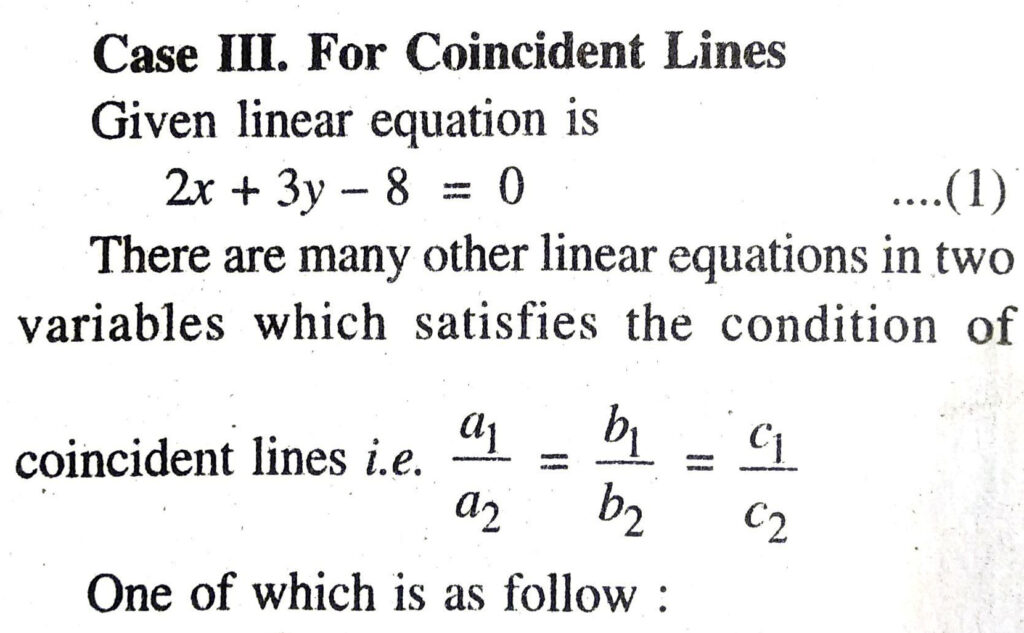
6x + 9y – 24 = 0 ….(4)
Now, draw the graph of linear equations (1) and (4).
Consider linear equation (4)
6x + 9y – 24 = 0
Or 3 [2x + 3y – 8] = 0
Or 2x + 3y – 8 = 0
∴ The points of both are same and line of both equations are same.
Q. 7. Draw the graphs of the equations x – y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the x-axis and shade the triangular region.
Solution. Consider the pair of linear equation
x – y + = 0
and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0
x – y + 1 = 0
Or x = y – 1 …(1)
Putting y = 0 in (1), we get :
x = 0 – 1 = – 1
Putting y = 3 in (1), we get:
x = 3 – 1 = 2
Putting y = 1 in (1), we get :
x = 1 – 1 = 0
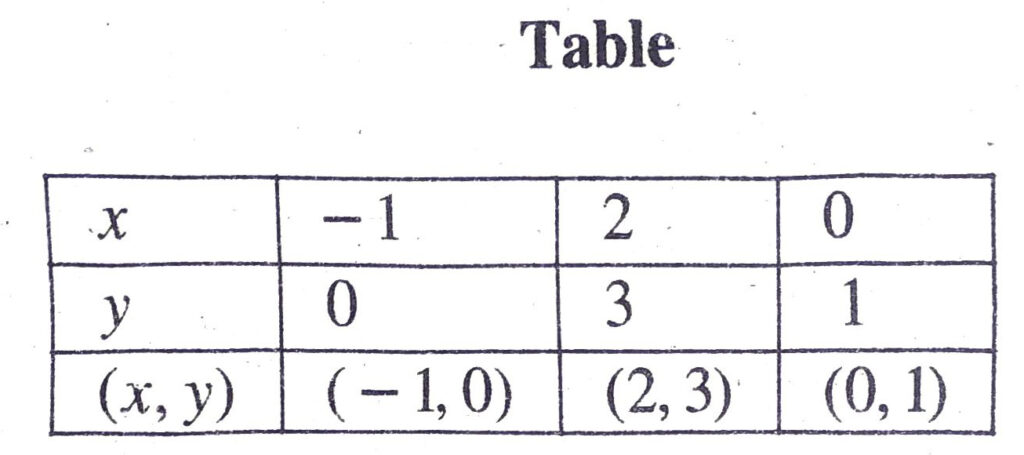
Plotting the points A (-1,0), B (2, 3), C (0, 1) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation x-y+1=0
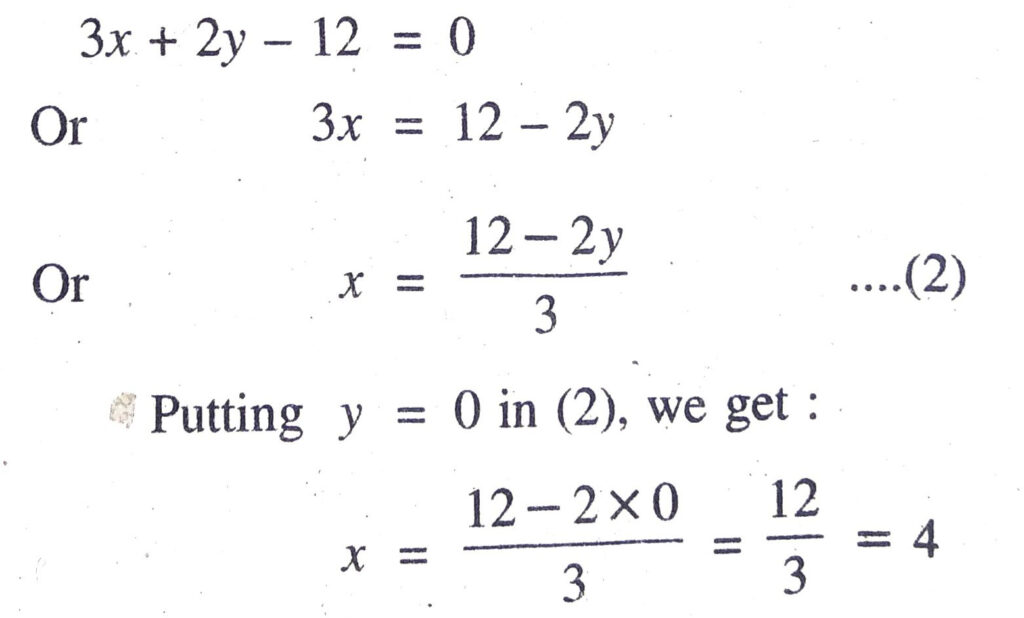
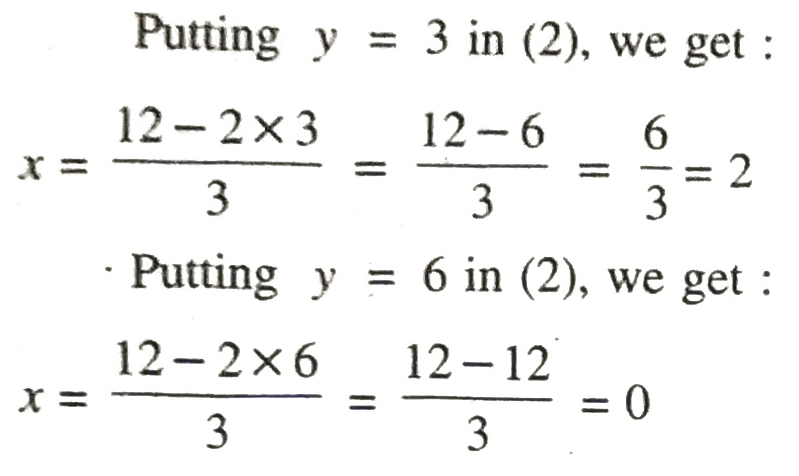

Plotting the points D (4, 0), B (2, 3), E (0, 6) and drawing a line joining them, we get the graph of the equation 3x + 2y – 12 = 0

The vertices of the triangle formed by pair of linear equations and the x-axis are shaded in the graph. The triangle so formed is ΔABD.
Coordinates of the vertices of ΔABD are A (– 1, 0), B (2, 3) and D (4, 0).
Now, length of Base AD = AO + OD
= 1 + 4 = 5 units
Length of perpendicular BF = 3 units
∴ Area of ΔABD = 1/2 x Base x altitude
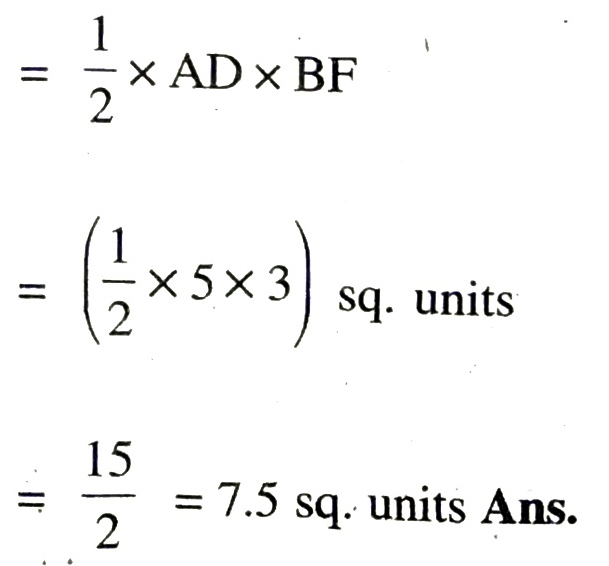
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.3
Q. 1. Solve the following pair of linear equations by the substitution method :
(i) x + y = 14
x-y = 4


This statement is true for all values of x.
However, we do not get a specific value of x as a solution. Therefore we cannot obtain a specific value of y. This situation has arises because both the given equations are same.
Therefore, equations (1) and (2) have infinitely many solutions. Ans.
(iv) Given pair of linear equation is



Hence, x = 2 and y = 3 Ans.
Q. 2. Solve 2x + 3y = 11 and 2x – 4y = – 24 and hence find the value of ‘m’ for which y = mx + 3.
Solution. Given pair of linear equations is :

Substitute the value of x = – 2, y = 5, we get:
5 = m (- 2) + 3
or 5 – 3 = – 2m
or 2 = – 2m
or – 2m = 2
or m = – 1
Hance, x = – 2, y = 5 and m
= – 1 Ans.
Q. 3. Form the pair of linear equations for the following problems and find their solution by substitution method.
(i) The difference between two numbers is 26 and one number is three times the other. Find them.
(ii) The larger of two supplementary angles exceeds the smaller by 18 degrees. Find them.
(iii) The coach of a cricket team buys 7 bats and 6 balls for ₹ 3800. Later, she buys 3 bats and 5 balls for ₹ 1750. Find the cost of each bat and each ball.
(iv) The taxi charges in a city consist of a fixed charge together with the charge for the distance covered. For a distance of 10 km, the charge paid is ₹ 105 and for a journey of 15 km, the charge paid is ₹ 155. What are the fixed charges and the charge per kilometre? How much does a person have to pay for travelling a distance of 25 km ?
(v) A fraction becomes 9/11 if 2 is added to both the numerator and the denominator. If 3 is added to both the numerator and the denominator it becomes 5/6. Find the fraction.
(vi) Five years hence, the age of Jacob will be three times that of his son. Five years ago, Jacob’s age was seven times that of his son. What are their present ages ?
Solution. (i) Let two numbers be x and y.




or – 4y = – 30 – 10
or – 4y = – 40
or y = 10
Substitute this value of y in (1), we get:
x = 3 (10) + 10
= 30 + 10 = 40
Hence, Jacob and his son’s ages are 40 years and 10 years respectively. Ans
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.4
Q. 1. Solve the following pair of equations by the elimination method and the substitution method.
(i) x + y = 5 and 2x – 3y = 4
(ii) 3x + 4y = 10 and 2x – 2y = 2
(iii) 3x – 5y – 4 = 0 and 9x = 2y + 7
(iv) x/2 + 2y/3 = – 1 and x – y/3 = 3
Solution. (i) Given pair of linear equations is :






Q. 2. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems, and find their solutions (if they exist) by the elimination method :
(i) If we add 1 to the numerator and subtract 1 from the denominator, a fraction reduces to 1. It becomes 1/2 if we only add 1 to the denominator. What is the fraction ?
(ii) Five years ago, Nuri was thrice as old as Sonu. Ten years later, Nuri will be twice as old as Sonu. How old are Nuri and Sonu ?
(iii) The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 9. Also, nine times this number is twice the number obtained by reversing the order of the number. Find the number.
(iv) Meena went to a bank to withdraw ₹ 2000. She asked the cashier to give her ₹ 50 and ₹ 100 notes only. Meena got 25 notes in all. Find how many notes of ₹ 50 and v 100 she received.
(v) A lending library has a fixed charge for the first three days and an additional charge for each day thereafter. Saritha paid ₹ 27 for a book kept for seven days, while Susy paid ₹ 21 for the book she kept for five days. Find the fixed charge and the charge for each extra day.
Solution. (i) Let numerator of fraction = x Denominator of fraction = y




TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.5
Q. 1. Which of the following pairs of linear equations has unique solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. In case there is a unique solution, find it by using cross multiplication method.



Q. 2. (i) For which values of a and b does the following pair of linear equations have an infinite number of solutions ?
2x + 3y = 7
(a – b) x + (a + b) y = 3a + b – 2
(ii) For which value of k will the following pair of linear equations have no solution ?
3x + y = 1
(2k-1) x + (k − 1) y = 2k + 1
Solution. (i) Given pair of linear equations is

or a = 9b – 4 ………(1)
From II and III, we get :
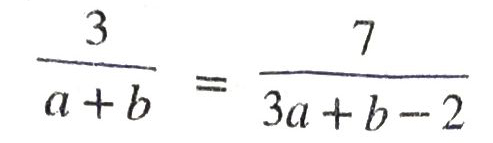
or 9a + 3b – 6 = 7a + 7b
or 2a – 4b – 6 = 0
or a – 2b – 3 = 0
Substitute the value of a from (1) in above, we get :
9b – 4 – 2b – 3 = 0
or 7b – 7 = 0
or 7b = 7
or b = 1
Substitute this value of b in (1), we get
a = 9 x 1 – 4 = 9 – 4
a = 5
Hence a = 5 and b = 1 Ans.
(ii) Given pair of linear equations is
3x + y = 1
and (2k-1) x + (k − 1) y = 2k + 1
or 3x + y − 1 = 0
and (2k − 1) x + (k − 1) y – (2k + 1) = 0
Here a1 = 3, b1 = 1, c1 = – 1
a2 = (2k-1), b2 = k − 1, c2 = − (2k + 1)
∴ system of equations have no solution

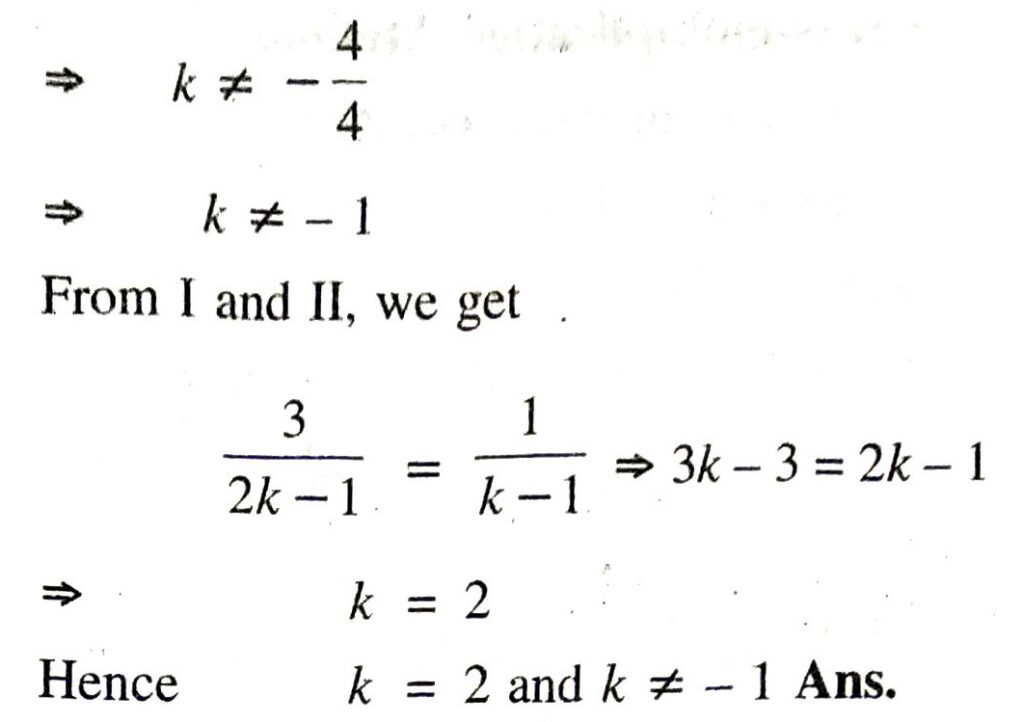
Q. 3. Solve the following pair of linear equations by the substitution and crossmultiplication methods:
8x + 5y = 9
3x + 2y = 4
Solution. Given pair of linear equation is :
8x + 5y = 9
3x + 2y = 4
Substitution Method

Cross-multiplication Method
Given pair of linear equation is :

Q.4. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems and find their solutions (if they exist) by any algebraic method.
(i) A part of monthly hostel charges is fixed and the remaining depends on the number of days one has taken food in the mess. When a student A takes food for 20 days she has to pay 1000 as hostel charges whereas a student B, who takes food for 26 days, pays 1180 as hostel charges. Find the fixed charges and the cost of food per day.
(ii) A fraction becomes 1/3 when 1 is subtracted from the numerator and it becomes 1/4 when 8 is added to its denominator. Find the fraction.
(iii) Yash scored 40 marks in a test, getting 3 marks for each right answer and losing 1 mark for each wrong answer. Had 4 marks been awarded for each correct answer and 2 marks been deducted for each incorrect answer, then Yash would have scored 50 marks. How many questions were there in the test ?
(iv)Places A and B are 100 km apart on a highway. One car starts from A and another from B at the same time. If the cars travel in the same direction at different speeds they meet in 5 hours. If they travel towards each other, they meet in 1 hour. What are the speeds of the two cars?
(v) The area of a rectangle gets reduced by 9 square units if its length is reduced by 5 units and breadth is increased by 3 units. If we increase the length by 3 units and the breadth by 2 units, the area increases by 67 units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
Solution. (i) Let monthly fixed hostel charges = ₹ x
and cost of food per day = ₹ y
According to 1st condition
x + 20y = 1000 …….(1)
According to 2nd condition
x + 26y = 1180 …….(2)
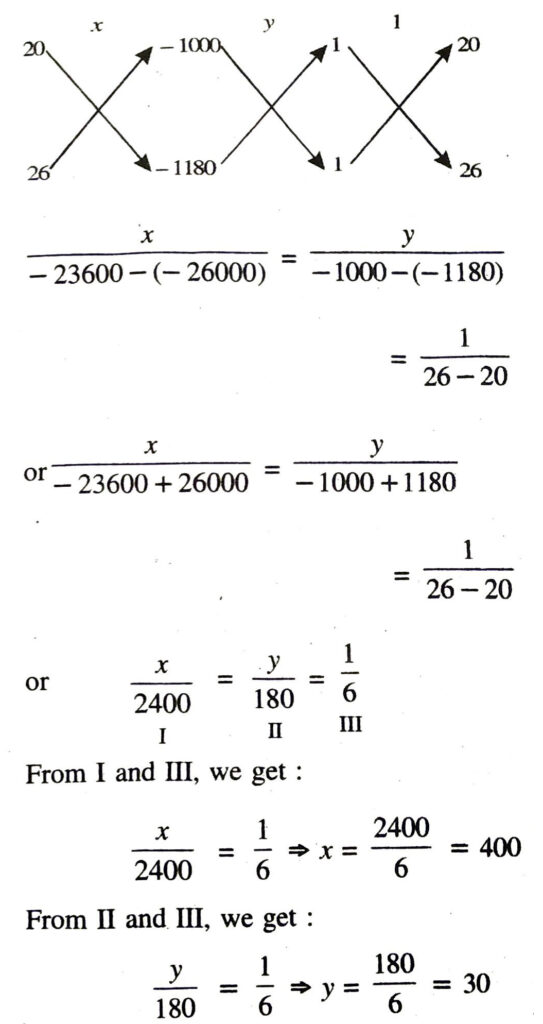
Hence, monthly fixed hostel charges and cost of food per day are ₹ 400 and ₹ 30 respectively. Ans.
(ii) Let numerator of fraction = x
Denominator of fraction = y
∴ required fraction = x/y
According to 1st condition,
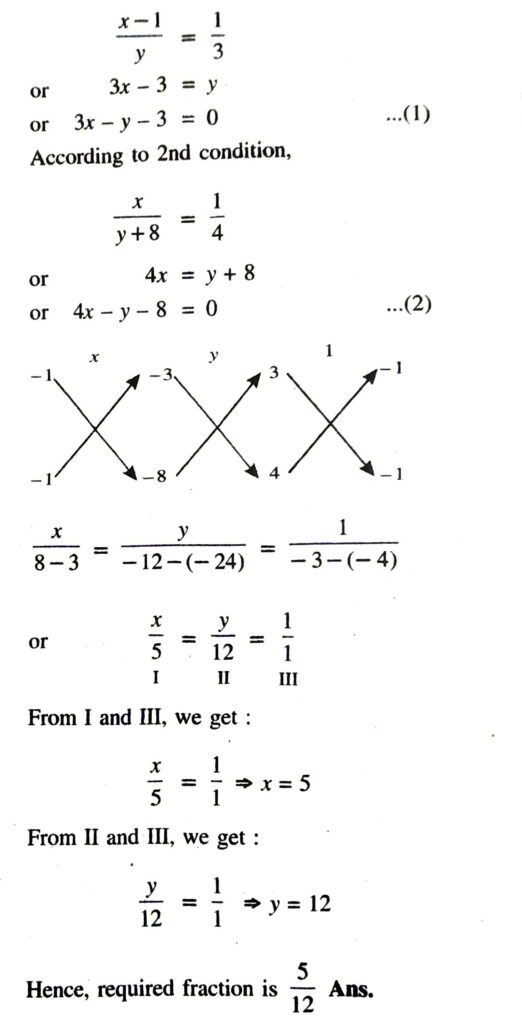
(iii) Let, number of right questions attempted by Yash = x
and Number of wrong questions attempted by Yash = y
According to 1st condition,
3x – y = 40
or 3x – y – 40 = 0 …(1)
According to 2nd condition,

(iv) Let speed of car at place A = x km/hour and speed of car at place B = y km/hour Distance between places A and B = 100 km
In case of 5 hours
Distance covered by car A = 5x km
[ ∵ Distance = Speed x Time]
Distance covered by car B = 5y km
According to 1st condition,
5x – 5y = 100

Hence, speeds of two cars at places A and B are 60 km/hour and 40 km/hour. Ans.
(v) Let length of rectangle = x units
and breadth of rectangle = y units
∴ Area of rectangle = xy sq. units
According to 1st condition,
(x – 5) (y + 3) = xy – 9
or xy + 3x – 5y – 15 = xy – 9
or 3x – 5y – 6 = 0 ……(1)
According to 2nd condition,
(x + 3) (y + 2) = xy + 67
or xy + 2x + 3y + 6 = xy + 67
or 2x + 3y – 61 = 0 …(2)
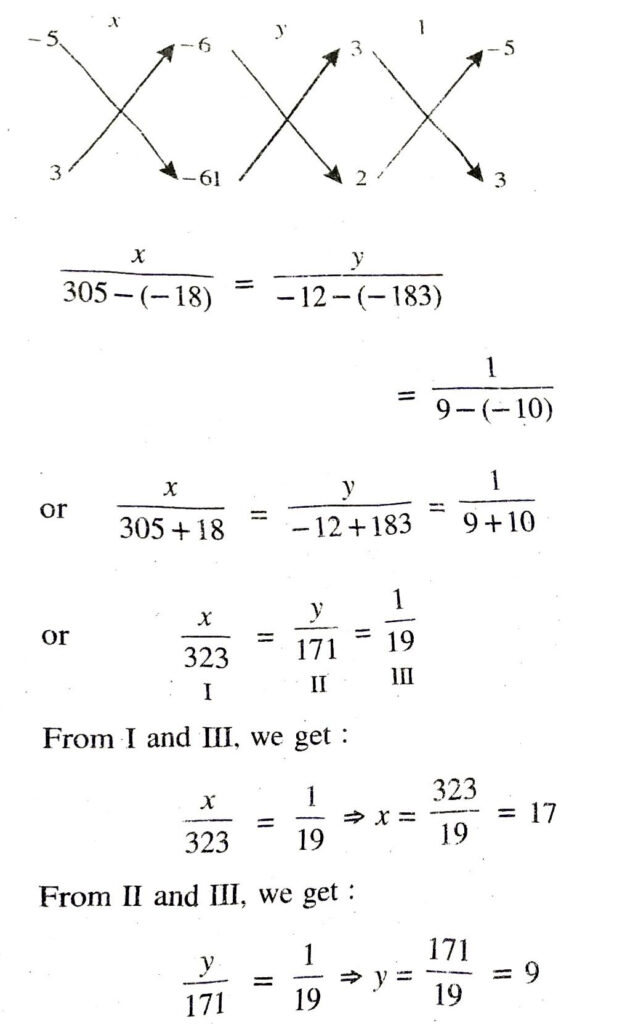
Hence, length and breadth of rectangle are 17 units and 9 units respectively. Ans.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 3.6
Q. 1. Solve the following pairs of equations by reducing them to a pair of linear equations :
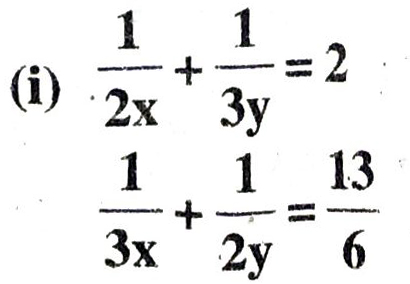
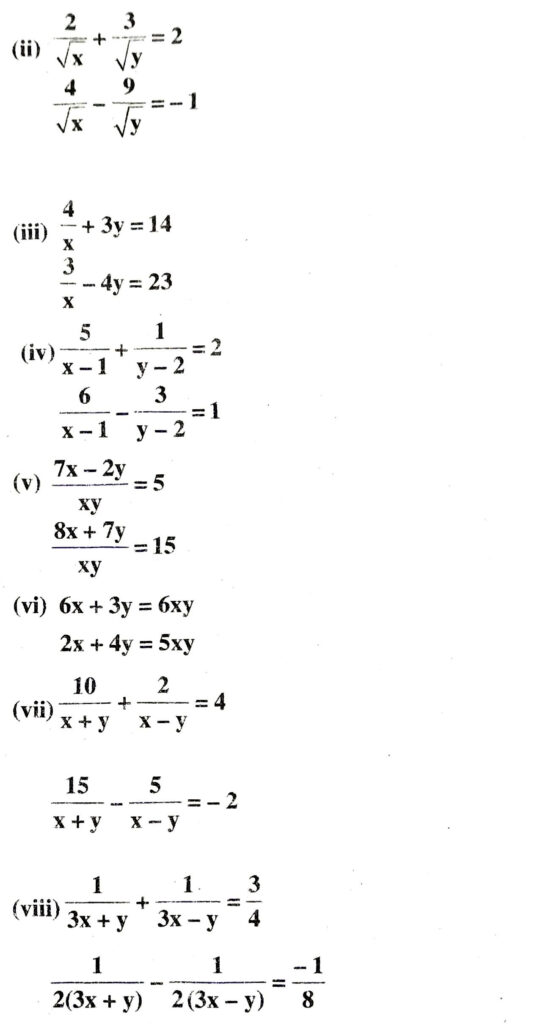
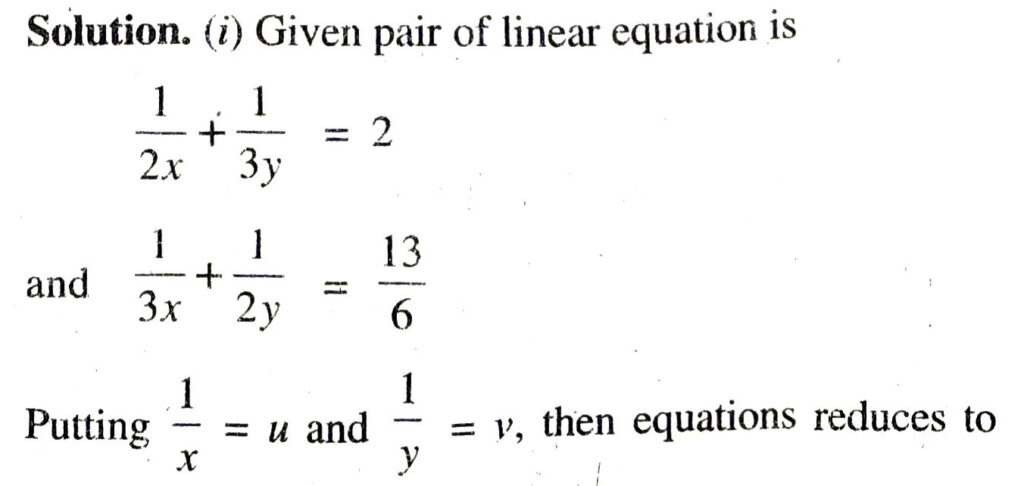





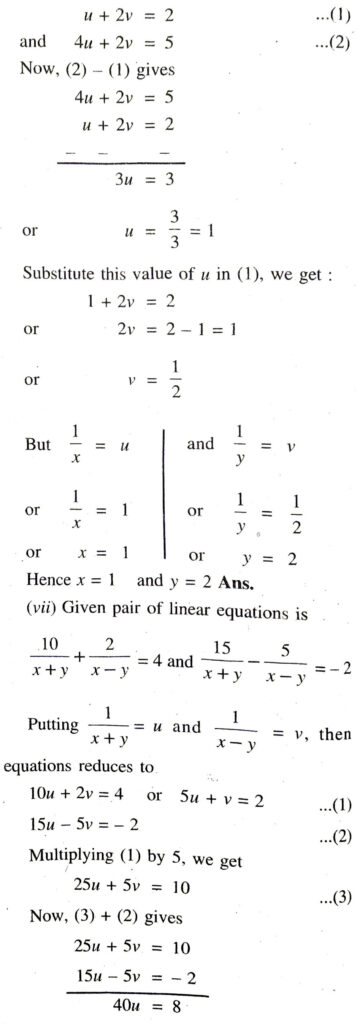


Q. 2. Formulate the following problems as a pair of equations, and hence find their solutions.
(i) Ritu can row downstream 20 km in 2 hours, and upstream 4 km in 2 hours. Find her speed of rowing in still water and the speed of the current.
(ii) 2 women and 5 men can together finish an embroidery work in 4 days, while 3 women and 6 men can finish it in 3 days. Find the time taken by 1 woman alone to finish the work, and also that taken by 1 man alone.
(iii) Roohi travels 300 km to her home parly by train and partly by bus. She takes 4 hours if she travels 60 km by train and the remaining by bus. If she travels 100 km by train and the remaining by bus, she takes 10 minutes longer. Find the speed of the train and the bus separately.
Solution. (i) Let the speed of Ritu in still water = x km/hour
and the speed of current = y km/hour
∴ speed in upstream = (x – y) km/hour
and speed in downstream = (x + y) km/hour
Distance covered by Ritu in downstream in 2 hours
= Speed x Time
= (x + y) x 2 km
According to 1st condition
2 (x + y) = 20
x + y = 10 …(1)
Distance covered by Ritu in upstream in 2 hours
= Speed x Time
= 2 (x – y) km
According to 2nd condition,

Substitute this value of x in (1), we get :
6 + y = 10
y = 10 – 6 = 4
Hence, Ritu’s speed in still water 6 km/hour
and speed of current = 4 km/hour Ans.
(ii) Let one woman can finish the work = x days
One man can finish the work = y days


Hence, one woman and one man alone can finish work in 18 days and 36 days respectively. Ans.
(iii) Let speed of train = x km/hour
and speed of bus = y km/hour
Total distance = 300 km
Case I
Time taken by train to cover 60 km

Case II
Time taken by train to cover 100 km = 100/x hours
Time taken by bus to cover 200 km (= 300 – 100) = 200/y hours


Hence, speed of train and bus are 60 km/hour and 80 km/hour respectively. Ans.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES 3.7
(OPTIONAL)
Q. 1. The ages of two friends Ani and Biju differ by 3 years. Ani’s father Dharam is twice as old as Ani and Biju is twice as old as his sister Cathy. The ages of Cathy and Dharam differ by 30 years. Find the ages of Ani and Biju.
Solution. Let Ani’s age = x years
and Biju’s age = 4 years
Dharam’s age = 2x years
Cathy’s age = 1/2 y years
According to 1st condition,
(Ani’s age) – (Biju’s age) = 3)
x – y = 3 …..(1)
According to 2nd condition,
(Dharam’ age) – (Cathy’s age) = 30
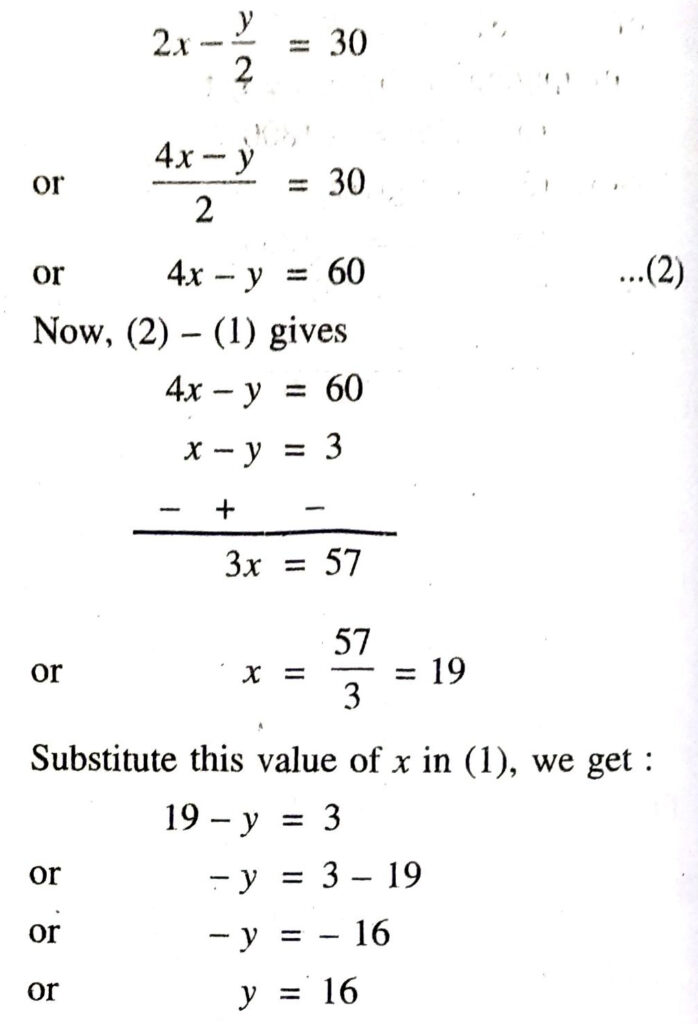
Hence, Ani’s age = 19 years
Biju’s age = 16 years. Ans.
Q. 2. One says, “Give me a hundred, friend! I shall then become twice as rich as you”. The other replies, “If you give me ten, I shall be six times as rich as you.” Tell me what is the amount of their (respective) capital?
[From the Bijaganita of Bhaskara II]
[Hint : x + 100 = 2 (y – 100),
y + 10 = 6 (x – 10)].
Solution. Let Capital of one friend = ₹ x and capital of 2nd friend = ₹ y
According to 1st condition
x + 100 = 2 (y – 100)
or x + 100 = 2y – 200
or x – 2y = – 200 – 100
or x – 2y = – 300 …..(1)
According to 2nd condition
y + 10 = 6 (x – 10)
y + 10 = 6x – 60
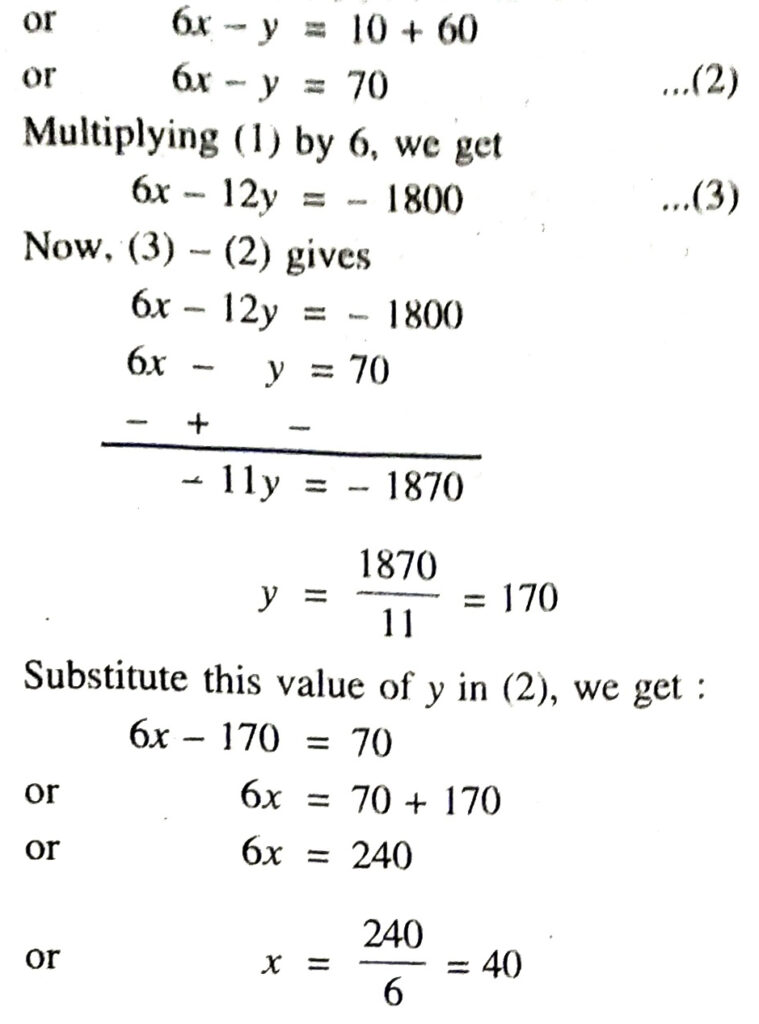
Hence, amount of their capital are ₹ 40. and ₹ 170 respectively. Ans.
Q. 3. A train covered a certain distance at a uniform speed. If the train would have been 10 km/h faster, it would have taken 2 hours less than the scheduled time. And, if the train were slower by 10 km/h; it would have taken 3 hours more than the scheduled time. Find the distance covered by the train.
Solution. Let speed of train = x km/hour
and time taken by train = y hour
∴ Distance covered by train
= (Speed) (Time)
= (xy) km
According to 1st condition,
(x + 10) (y − 2) = xy
or xy – 2x + 10y – 20 = xy
or – 2x + 10y – 20 = 0
or x – 5y + 10 = 0 ……….(1)
According to 2nd condition,
(x – 10) (y + 3) = xy
or xy + 3x – 10y – 30 = xy
or 3x – 10y – 30 =0 ……(2)
Multiplying (1) by 3, we get :
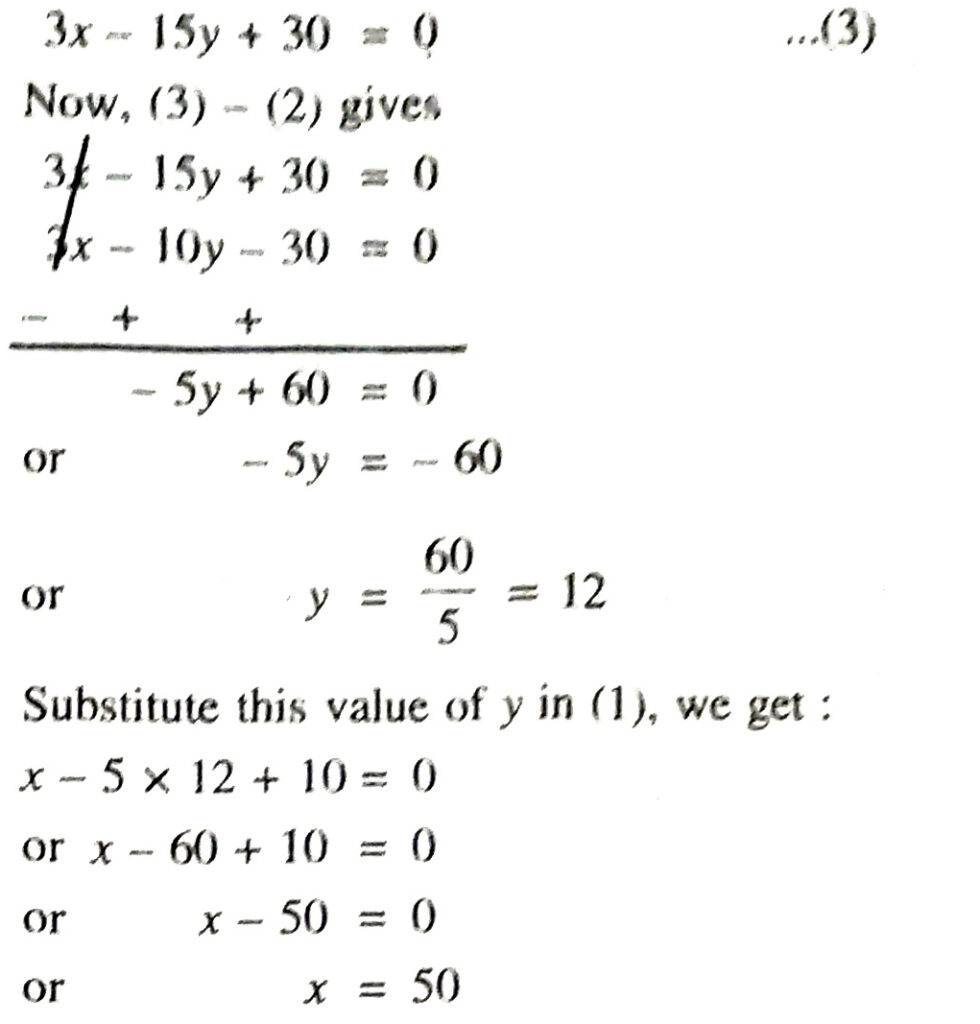
∴ Speed of train = 50 km/hour
Time taken by train = 12 hour
Hence, distance covered by train
= (50 × 12) km
= 600 km Ans.
Q. 4. The students of a class are made to stand in rows. If 3 students are extra in a row, there would be 1 row less. If 3 students are less in a row, there would be 2 rows more. Find the number of students in the class.
Solution. Let number of students in each row = x
and number of rows = y
Total number of students in the class = xy
According to 1st condition,
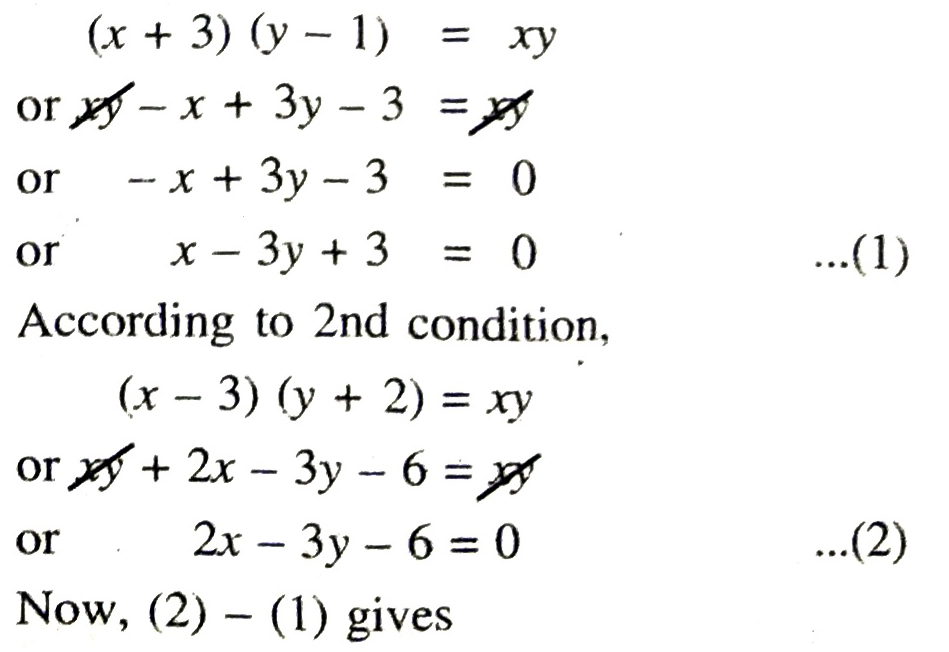
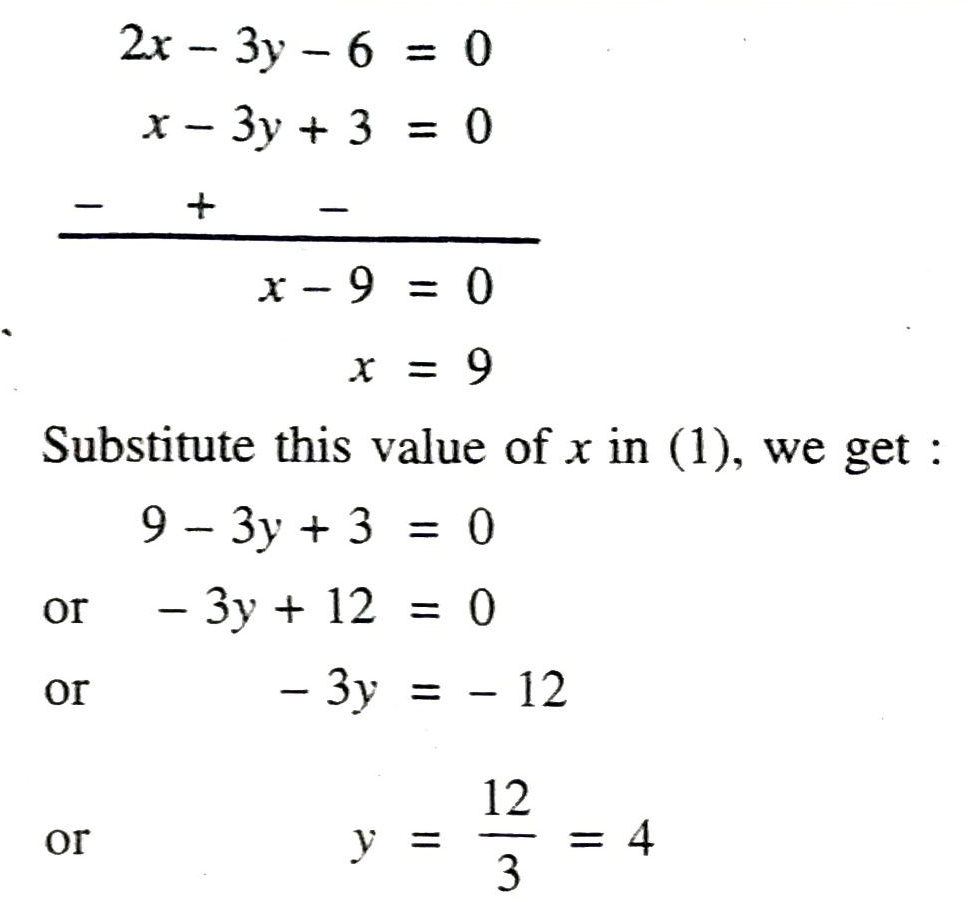
∴ Number of students in each row = 9
and number of rows = 4
Hence, total number of students in the class = 9 × 4 = 36 Ans.
Q. 5. In a ΔABC, ∠C = 3 ∠B = 2 (∠A + ∠B) find the three angles.
Solution. In ΔABC,
Given that, ∠C = 3∠B = 2 (∠A + ∠B)
I II III
From II and III, we get :
3∠B = 2 (∠A + ∠B)
or 3∠B = 2∠A + 2∠B
or 3∠B – 2∠B = 2∠A
or ∠B = 2∠A ……(1)
From I and II, we get :
∠C = 3∠B
or ∠C = 3(2∠A) [using (1)]
or ∠C = 6∠A ……(2)
Sum of three angles of a triangle is 180°
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
or ∠A + 2∠A + 6∠A = 180°
or 9∠A = 180°
or ∠A = 180°/9 = 20°
Hence, ∠A = 20°; ∠B = 2 x 20° = 40°
∠C = 6 x 20° = 120°. Ans.
Q. 6. Draw the graphs of the equations 5x – y = 5 and 3x – y = 3. Determine the co-ordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the y-axis.
Solution. Given pair of linear equation are 5x – y = 5 and 3x – y = :3
Consider,
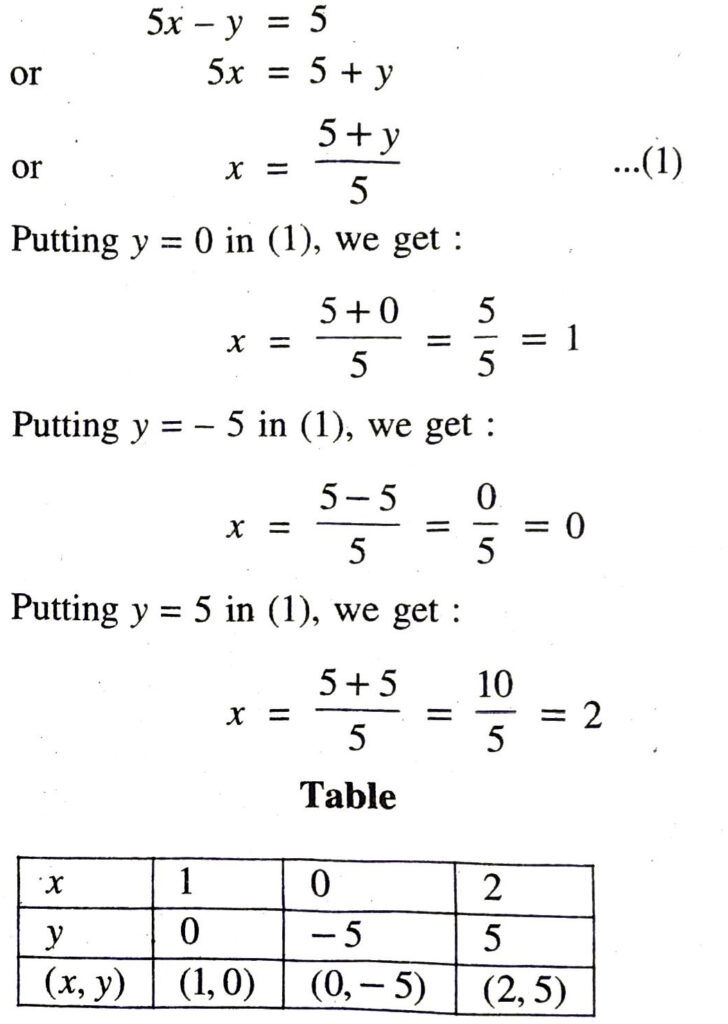
Plotting A (1, 0); B (0, – 5); C (2, 5) on the graph, we get the equation of line 5x – y = 5


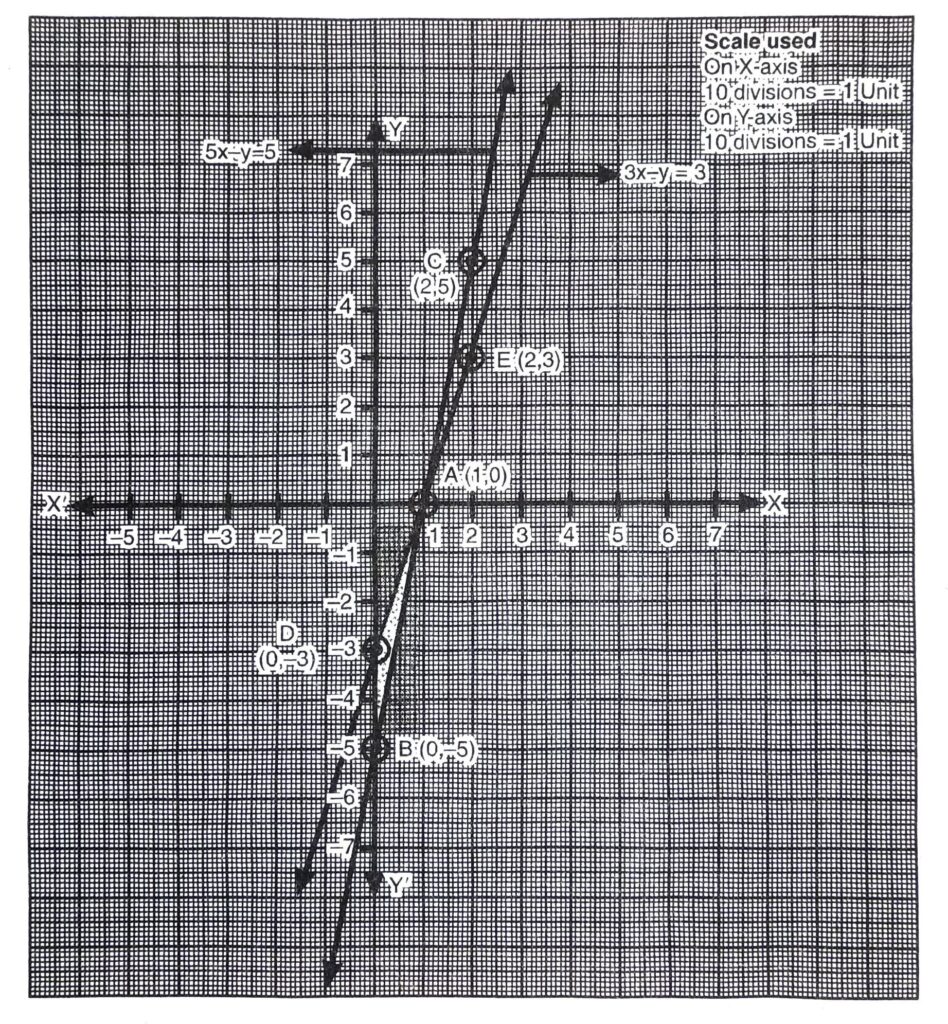
Plotting A (1, 0); D (0, – 3); E (2, 3) on the graph, we get the equation of line 3x – y = 3
From the graph, it is clear that given lines intersect at A (1, 0). Triangle formed by these lines and y axis are shaded in the graph i.e. ΔABD. Coordinates of the vertices of ΔABD are A (1, 0); B (0, – 5) and D (0, -3) Ans.
Q.7. Solve the following pair of linear equations :
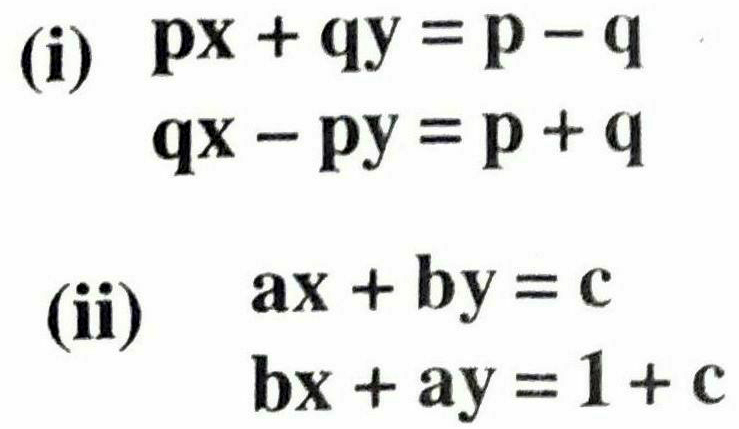


Solution. (i) Given pair of linear equation are




Hence, x = 2 and y = 1 Ans.
Q. 8. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral (see Fig.) Find the angles of the cyclic quadrilateral.

Solution. In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD,
∠A = (4y + 20); ∠B = 3y – 5;
∠C = 4x and ∠D = 7x + 5
Sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are of measure 180°.
∠A + ∠C = 180°
or 4y + 20 + (4x) = 180°
or 4x + 4y = 180° – 20
or 4x + 4y = 160
or x + y = 40
or y = 40 – x …..(1)
and ∠B + ∠D = 180°
or 3y – 5 + (7x + 5) = 180°
or 3y – 5 + 7x + 5 = 180°
or 7x + 3y = 180° ……(2)
Substitute the value of y from (1) in (2), we get:
7x + 3 (40 – x) = 180°
or 7x + 120 – 3x = 180°
or 4x = 180 – 120
or 4x = 60
or 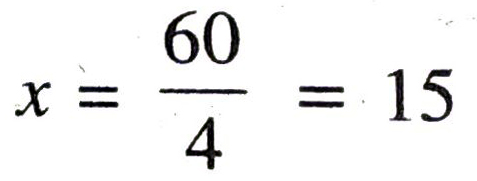
Substitute this value of x in (1), we get :
y = 40 – 15 = 25
∴ ∠A = 4y + 20 = 4 x 25 + 20 = 120°
∠B = 3y – 5 = 3 x 25 – 5 = 70°
∠C = 4x = 4 x 15 = 60°
∠D = 7x + 5 = 7 x 15 + 5 = 110°
Hence, ∠A = 120°, ∠B = 70°; ∠C = 60°
and ∠D = 110° Ans.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here