JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 5 Source of Energy
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 5 Source of Energy
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 5 Source of Energy
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Source of Energy Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ No activity is possible without energy.
◆ Renewable sources of energy are sun, water and wind etc.
◆ Substances having low ignition temperature are called inflammable substances.
◆ Substances burn at a moderate rate during slow combustion. Substances burn in a very short span of time during rapid combustion.
◆ During spontaneous combustion substances suddenly catch fire when their temperature is raised above ignition temperature.
◆ Gobar gas is produced by fermentation of cow-dung by anaerobic bacteria.
◆ Gobar gas or biogas is a fuel of high calorific value.
◆ Solar energy is the combination of visible infrared radiations and invi-sible (ultra-violet) energy radiated out by sun.
◆ Solar cooker, solar heaters, solar furnace and solar cells are devices using solar energy. Solar cells convert solar energy directly into electric energy. Solar cells are used to supply electric energy to watches, calculators and satellites.
◆ Excessive use of any source of energy disturbs the environment. We should try to use non-polluting (clean), economical and efficient sources of energy.
◆ Non-polluting sources of energy like solar and wind energy need to be promoted. It is neat and clean energy which is available free of cost.
IMPORTANT TERMS AND FACTS TO MEMORISE
⇒ Calorific value of fuel. It is the energy released when unit mass of fuel is burnt completely in excess of oxygen.
⇒ Fossil fuel. Petroleum and coal etc., produced inside the earth in millions of years 1 are called fossil fuel. Fossil fuel is non-renewal source of energy.
⇒ Solar energy is renewable and is free of cost.
⇒ Gobar gas is produced from waste of animals. Gobar gas has large calorific value and is non-polluting.
TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. What is a good source of energy?
Ans. Characteristics of a good source of energy. Characteristics of a good source of energy are :
(i) It should be sustainable and renewable source of energy.
(ii) It should provide great amount of energy per unit mass or volume.
(iii) It should be easily accessible and provide energy for a longer period of time.
(iv) It should not cause pollution.
(v) It should be economic to use.
(vi) It should be safe for the surrounding individuals.
Q. 2. What is a good fuel ?
Or
What are the characteristics of an Ideal fuel ?
Ans. Characteristics of a Good Fuel. A good fuel is that which:
(i) Has high calorific value when burnt it should produce large amount of heat per unit mass.
(ii) Should produce less smoke or preferably no smoke and should not leave any residue (ash).
(iii) Should be economical (low cost).
(iv) Should produce no pollution.
(v) Should have steady rate of combustion.
(vi) Should be easy to store and produce no hazard to transport and easy to handle.
Q. 3. If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why ?
Ans. For heating my food I would use fuel which fulfills the most of the characteristics of a good fuel such as:
(i) high calorific value,
(ii) pollution free,
(iii) easily available,
(iv) cheap. For this I would use L.P.G. if living in a city and wood/gobar gas if living in a remote village.
Q. 4. What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels ?
Or
Write down two disadvantages of fossil fuels.
Ans. Disadvantages of fossil fuels (Nonrenewable fuels):
(i) Burning of fossil fuels such like petrol, diesel, coal, natural gas etc. causes air pollution.
(ii) Burning of fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide (CO₂), a green house gas which causes global warming.
(iii) On burning fossil fuels, oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur are released. This leads to acid rain which affects our soil and water resources.
(iv) There are limited resources of fossil fuels since these were formed over millions of years and their continuous use would exhaust them and make them unavailable after some time.
Q. 5. Why are we looking at alternative sources of energy?
Ans. With the development of technology and swelled up population, the demand for energy has increased manifold which cannot be met with traditional non-renewable sources. We are, therefore, looking for alternative sources of energy because :
(i) Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum which are traditional sources of energy are nonrenewable and are not going to last long.
(ii) The traditional sources of energy are costly and cause pollution whereas alternative sources of energy like solar energy, wind energy and water energy do not cause pollution and are almost free of cost except for their installation cost.
Q. 6. How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience ?
Ans. Traditional use of wind energy was made to lift water from the well and run grinding machine to grind grams. The traditional use of wind energy has now been modified to generate electicity where turbines are made to rotate by the use of wind energy.
Likewise, the traditional use of water energy has been modified to generate electricity in hydropower plants. Water is collected in dams. It is then made to fall on turbines where potential energy of collected water is transformed into kinetic energy of running water which is made use of in running turbines and thus converting into electricity.
Q. 7. What kind of mirror-concave, convex or plane would be best suited for use in a solar cooker ? Why?
Ans. A concave mirror is the best for use in solar cooker for it focuses sun rays from large areas to a specific point. These concentrated heat rays produce large amount of heat at that point.
Q. 8. What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans ?
Ans. The energy obtained from oceans can be of the following kinds :
1. Tidal Energy. Due to attraction of the moon, there are high and low tides in the sea. Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing dam across a narrow opening in the sea and a turbine fixed at this opening converts tidal energy of waves into electricity.
The limitation of this kind of energy is there are only a few such locations available where dams can be constructed for production of energy. Therefore, this kind of energy will not be enough for commercial use.
2. Ocean Thermal Energy (O.T.E.) Due to sunlight, water at the surface of the ocean gets heated up while water in the deeper regions is relatively cold. This difference in temperature is exploited to get electric energy which is called ocean thermal energy. But the limitation of conversion efficiency is very low. These plants for generating electricity is that these plants work only when the temperature difference of water at the surface and at the depth upto 2 km is 20° C or more. Secondly, its operational cost is high and the efficiency is very low.
Q. 9. What is geothermal energy?
Ans. Geothermal Energy. Due to changes taking place within earth, molten rocks formed in the deeper hot regions of earth are pushed upward in the regions called ‘hot spots’. Steam is generated when underground water comes in contact with hot spots. The energy which is directly obtained from the heat inside the earth is called geothermal energy. Steam trapped in rocks is passed through a pipe to the turbine can generate electricity.
Q. 10. What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Ans. Advantages of Nuclear Energy.
1. A smaller space is required to get nuclear energy.
2. Nuclear energy is a non-conventional source of energy and produces large quantity of usable form of energy.
3. It costs less.
4. It is almost pollution free energy.
Q. 11. Can any source of energy be pollution free? Why or why not?
Or
Name two energy sources that you consider pollution free. Give reasons.
Ans. No source of energy can be perfectly pollution free e.g., bio-mass energy, hydro energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, solar energy is almost pollution free but the process involved in making these plants might have damaged the environment in some way.
Q. 12. Hydrogen has been used as a rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than C.N.G. ? Why or why not?
Ans. Hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than C.N.G. because the burning of hydrogen produes water which does not pollute the atmosphere. On the other hand, C.N.G. when burnt produces carbon dioxide and water. This carbon dioxide does produce greenhouse effect which ultimately leads to heating of environment. Hence, hydrogen is positively a cleaner fuel than C.N.G.
Q. 13. Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choice.
Ans. Two renewable sources of energy are :
(i) Hydro energy. It is the energy generated by using kinetic energy of running water to run dynamo. Hydro power is the main source of electricity now a days. Down from high altitude is utilized to trap energy for generating electricity and the unused water utlimately goes to oceans. Due to cyclic process (water → water vapours → clouds → rain → snow → running water at dams) again we get water. Water stored in reservoirs at dams is used for generating electricity. So hydro energy is a renewable source of energy.
(ii) Wind Energy. Wind energy is the kinetic energy due to motion of large mass of air. Wind energy can be used to sail boats, run windmills to produce electric power. Sun rays near the equator are stronger than in the polar region. As a result, air in the equitorial region becomes hot and rises up while cooler air in the polar region moves towards the equator. This causes the flow of air (wind). This process goes on in nature due to temperature differences, so wind energy is a renewable form of energy.
Q. 14. Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choice.
Ans. Coal and petroleum are two energy sources which are exhaustible. It takes millions of years for formation of petrol and coal inside the earth. Its reserves are limited. Coal if used at present rate will not last beyond two hundred years whereas petroleum products which are being used extensively are expected not to last more than 50 years. Therefore, these energy sources are exhaustible in nature.
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on a :
(a) sunny day
(b) cloudy day
(c) hot day
(d) windy day.
Ans. (b) cloudy day.
Q. 2. Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(a) wood
(b) gobar gas
(c) atomic energy
(d) coal.
Ans. (c) atomic energy.
Q. 3. Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) geothermal energy
(b) wind energy
(c) nuclear energy
(d) bio-mass.
Ans. (c), nuclear energy.
Q. 4. Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the sun as sources of energy.
Ans. Similarities.
1. Both are natural sources of energy.
2. Both are widely used sources of energy.
3. No technology is required to get energy by any of these sources.
Dissimilarities/Contrast.
1. Sun’s energy can be used only during day time but fossil fuel can be used to get energy at any time during day or during night.
2. Solar energy is almost free whereas fossil energy costs much.
3. Infinite amount of solar energy is available almost free of cost whereas there is a limited reserve of fossil fuel.
4. Solar energy is a renewable source of energy whereas it takes millions of year to produce fossil fuel.
5. Solar energy is totally pollution free whereas fossil fuel causes a lot of pollution on burning.
Q. 5. Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydroelectricity as a source of energy.
Ans. Similarities.
(i) Both bio-mass and hydro-electricity are natural sources of energy.
(ii) Working cost of both the sources of energy as low. However, initial installation cost of hydro-electricity sources is higher than bio-mass source.
(iii) Both are widely used sources of energy.
(iv) Hydroelectric plants can be erected only at specific points while biomass plant can be installed anywhere.
(v) The energy produced by hydro-electric plant is much more than produced by biomass plant, Dissimilarities.
| Biomass | Hydroelectricity |
|
|
Q. 6. What are the limitations of extracting energy from :
(a) the wind (b) waves (c) tides
Ans. (a) Limitations of Wind Energy.
(i) It is not available at all times and at all places since it depends upon the availability of wind.
(ii) The minimum wind speed required to run windmills should be 15 km h-1.
(iii) The initial cost of construction of windmill farm is very high.
(b) Limitations of wave energy.
(i) The wave is not available at all times for generating electricity.
(ii) The power from wave energy is expensive because the plant required to be set up for trapping energy from waves is very costly.
(iii) The output power obtained from waves is not constant.
(c) Limitations of tidal energy.
(i) There are a few locations for constructing dams for harnessing tidal energy.
(ii) The power generation by harnessing tidal waves is very high because the cost of construction of dams for this purpose is very costly.
Q. 7. On what basis would you classify energy sources as :
(a) renewable and non-renewable.
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible.
Are the options in (a) and (b) same ?
Ans. (a) Renewable Sources of Energy. Those sources of energy which after depletion (used up) can be replenished (brought back to its original form) are called renewable sources of energy. e.g., water, wind, tides and ocean.
Non-renewable sources. Those sources of energy which can not be replenished (regenerated) after when these are used up are called non-renewable sources of energy. e.g., fossil fuels, coal and petroleum.
(b) Exhaustible Sources of Energy. Those sources of energy which will get depleted some day are called exhaustible sources of energy. Exhaustible sources are non-renewable sources of energy.
Inexhaustible Sources of Energy. Those sources of energy which get replenished even after extraction of usable energy and are never depleted are called inexhaustible sources of energy. Inexhaustible sources of energy are renewable sources of energy.
Q. 8. What are qualities of an ideal source of energy?
Ans. Qualities (Characteristics) of an ideal source of energy. An ideal source of energy should have the following qualities :
1. It should give adequate amount of energy at steady rate.
2. It should be safe and convenient to use.
3. It should do large amount of work per unit volume or mass.
4. It should be economical.
5. It should be easy to store and transport.
Q. 9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker ? Are there places where solar cookers have limited utility ?
Ans. Advantages of using Solar Cooker.
1. It saves fuel.
2. The nutrients of food do not get destroyed during cooking.
3. If does not produce pollution.
4. Its maintenance cost is low.
5. It is easy to handle and there is no danger of any mishap.
Disadvantages of using Solar Cooker
1. Solar energy is not available in ample amount and uniformly all the time and at all places. It cannot be used at night and on cloudy days.
2. Direction of reflector of solar cooker has to be changed continuously towards the direction of sun rays.
3. It can not be used for cooking chapatis or for frying purpose.
4. It takes more time to cook food.
Yes, there are places where solar cookers have limited utility. At poles solar cooker has limited utility because here sun remains absent for six months. In hilly areas also the sun has limited utility because the sun shines for limited time and where inclined sun rays reach, the use of solar cooker becomes difficult.
Q. 10. What are environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption ?
Ans. The demand of energy is increasing day by day. Exploiting any source of energy may disturb the environment in one way or the other. For example, getting energy from fossil fuel may cause air pollution and getting energy by nuclear fission may create problem of disposal of nuclear waste.
Steps for reducing energy consumption should be such that we get maximum energy from least fuel.
For this :
1. Under the given situation the best possible technology should be utilised. For example, smokeless chullahs should be preferred to traditional chullahs.
2. Energy should be extracted by most economic method under the given situation. Whereas energy extraction by solar cell may be useless in big towns due to cost factor, it may be indispensable for artificial satellites.
3. Energy saved is energy produced. Therefore, wastage of energy should be strictly avoided.
4. Sources of energy should be such that it causes least damage to environment.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. How is hydroelectricity generated at hydroelectric power plant ? Give its advantages and disadvantages.
Ans. The basic principle of hydroelectric power is that the potential energy of the water stored in the dams is converted into kinetic energy by allowing the water to fall from a height on turbines placed at the bottom of dam. The falling water makes the blades of turbines to rotate which in turn rotates the coil of generator placed in a magnetic field. This results in the production of electricity.
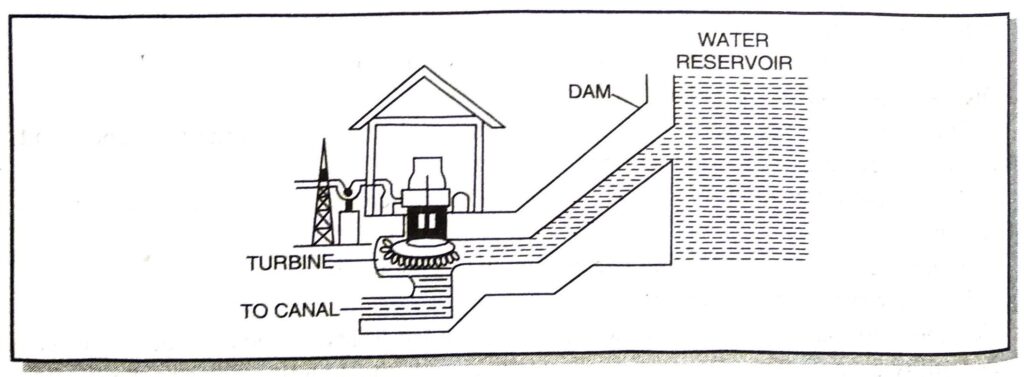
Fig. Outline of a hydroelectric power station.
Limitations of Water Energy. The flowing water is not available in plenty everywhere to turn the turbines to produce electricity. Therefore, useful work can be obtained from water energy only at limited places where the flow of water is more.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Generating Hydroelectricity
Advantages
(i) The use of water energy does not cause any pollution.
(ii) It is an economical and renewable source of energy which will never get exhausted.
Disadvantages
It causes a number of environmental problems. These are given below :
(i) The construction of dams on rivers results into a variety of ecological changes in the downstream area of the river. As a result a vast variety of flora and fauna (plants and animals) are destroyed and many people become homeless.
(ii) The soil in the downstream area may become barren because there were no annual floods to deposit nutrient rich silt on the banks of the river. Therefore, there may be ecological imbalance.
Therefore, while constructing the high-rise dams to generate hydroelectricity, special care should be taken to study its impact on the environment and social life.
Q. 2. Describe a wind mill. What are its functions ?
Ans. Wind mill. A wind-mill is a machine which works with the energy of wind and converts kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy or electricity. It consists of large fan like blades to catch the wind. When the wind strikes against these blades, the blades start rotating. This motion can then be passed onto connected crankshaft and is used to draw water from wells and to run flour mills for grinding grains. The picture below shows wind-mill drawing water from tube wells. [Fig.].
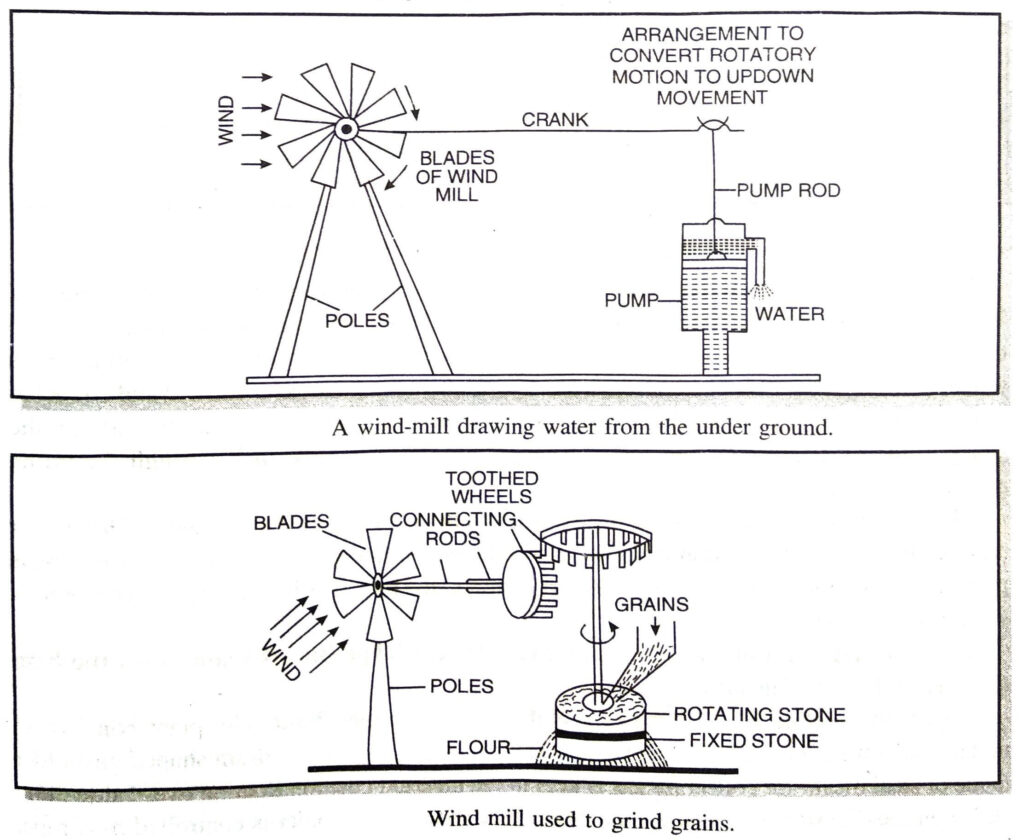
Wind mill for grinding grains. In fig. windmill is being used to grind grains by having suitable arrangement of toothed wheel and shaft.
Q. 3. Draw diagram of Fixed Dome Type Biogas plant and describe how biogas can be produced with this plant?
Ans. The plant consists of underground tank made of bricks called digester. The roof of the digester is dome-shaped made of cement and bricks. It acts as a storage tank for biogas, In the mixing tank, cattle dung is mixed with water to prepare slurry. This slurry is then fed into the inlet chamber for onward supply to digester through inlet ‘I’. At the bottom of digester and just opposite to the inlet there is outlet ‘O’ taking spent us slurry to the outlet chamber. There is a gas outlet ‘S’ at the top of dome for the supply of bio-gas.
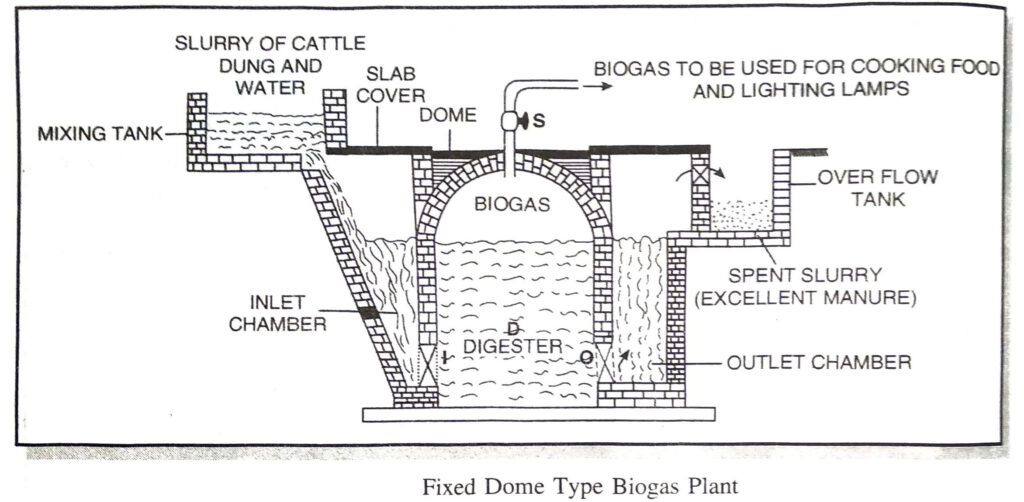
Working of Plant. Animal waste and water are mixed in equal proportions in the mixing tank to form a slurry. The slurry is fed into the digester tank through the inlet chamber. The tank is closed for about two months. During this period, the animal waste undergoes fermentation by anaerobic bacteria. As a result of fermentation, biogas is formed and collected in the dome. As more and more biogas gets collected in the dome, it exerts pressure on the slurry in the digestion tank and forces it to go into the over flow tank through the outlet chamber.
The spent slurry being rich in nitrogen and phosphorus can be used as a manure. Whenever required the biogas collected in the dome-can be taken out through a pipe ‘S’ Once the biogas plant starts functioning, more and more slurry may be fed into the digester to get a continuous supply of the biogas.
Q. 4. Explain the working of Floating Gas Holder Type Biogas Plants with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Ans. Construction of Floating Gas Holder Type Biogas Plant. The plant consists an underground well shaped tank made of bricks. It is called digester. A drum shaped gasholder made of steal meant for collecting gas is kept in the inverted position floating over cattle dung slurry on the digester tank. The up and down movement of gasholder is controlled by a pipe. At the top of the gasholder there is an outlet for gas. The digester tank is divided into two parts with a partition wall. On the left side of the digester tank there is an inlet pipe. The inlet pipe is connected to the mixing tank through which slurry is allowed to get into the digester. On the right side of the digester tank there is an outlet pipe which is connected to the overflow tank.
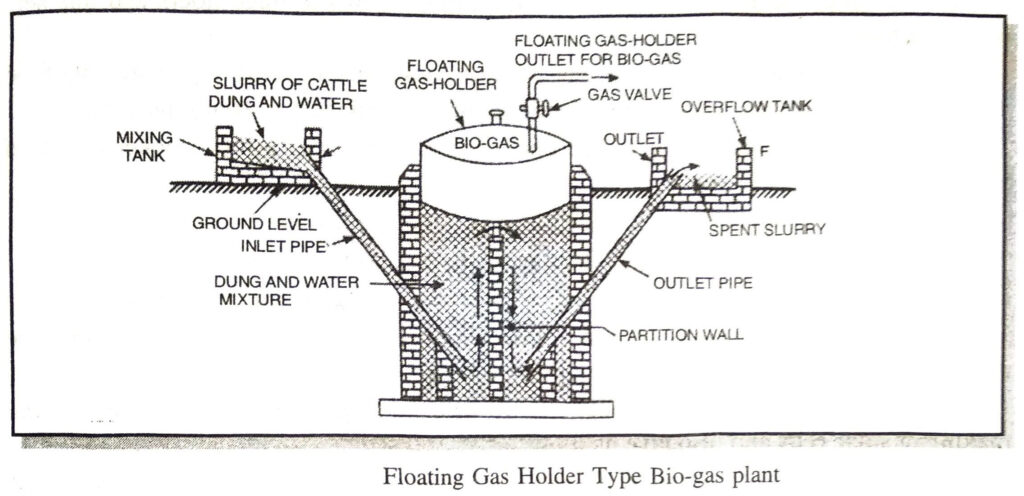
Working. Cattle dung and water are mixed in equal proportions in the mixing tank to make slurry. The slurry is then introduced into the digester tank through the inlet pipe. It is left for about 2 months during which dung undergoes anaerobic fermentation producing biogas. The biogas so produced starts collecting in the gas holder when more and more gas is produced. the gas holder starts rising. The spent up slurry left over is used as manure.
Q. 5. Draw a labelled diagram of a Box Type Solar Cooker. Also give its working and advantages.
Ans. A solar cooker consists of an insulated box (wooden or plastic) which is painted black from inside. A plane mirror reflector is attached to the box (fig.). The food to be cooked is placed in containers which are also painted black from outside. These containers are placed in the box and the box is covered with thick glass sheet. The cooker is kept in the sunlight and the position of the reflector is adjusted such that a strong beam of sunlight falls over the glass sheet. These rays pass through the transparent glass sheet cover and are absorbed by the cooker box and the containers and also heat radiations are not allowed to escape. The use of black surface of the box and containers is due to the fact that a blacksurface absorbs more heat than any other colour. Therefore, the box and the containers absorb maximum amount of infra-red radiations from the sunlight falling on it. As a result, the temperature inside the box rises to about 100°-140°℃ in two to three hours and this heat cooks the food.
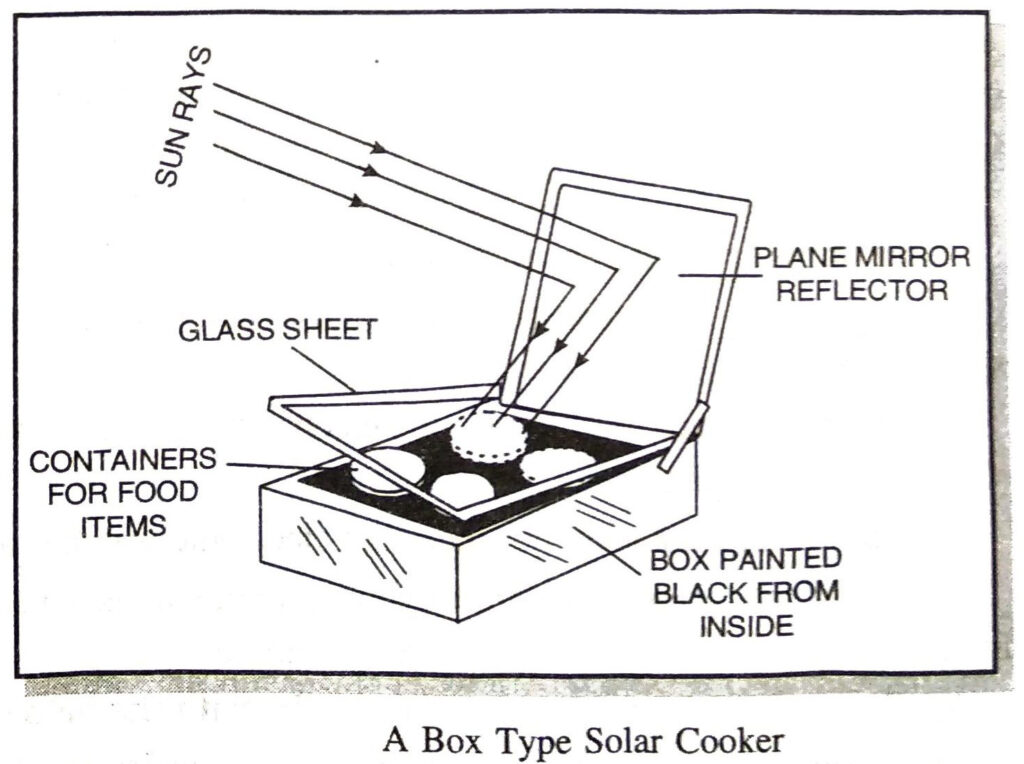
Limitation of Solar Cooker. This type of solar cooker can be used to prepare only food items which require slow heating and cannot be used for baking and frying purposes.
Advantages of a Solar Cooker. The important advantages of a solar cooker are given below:
(i) The use of solar cooker for cooking food materials saves fuel.
(ii) It is an economical method of cooking food since no fuel is used.
(iii) It does not cause any pollution because this does not give out any smoke.
(iv) In this method, food is cooked at comparatively lower temperature therefore, the nutrients of food do not get destroyed during cooking.
Q. 6. What is a Solar Cell ? What is its working principle ? Write short note on the making of solar cells and also give its uses.
Ans. Solar Cell. Solar cell is a device which converts solar energy directly into electricity.
Working Principle. Semi conductors (substances whose conductivity lies between metal and insulator) possess very low electrical conductivity. Silicon (Si), Gallium (Ga) and Germanium (Ge) are some examples of semi-conductors. In fact, semi-conductors are neither conductor nor insulator. However, it has been found that their conductivity increases when they are mixed with phosphorus or arsenic. Since the efficiency of such solar cells made of silicon and gallium was very low (10% to 15%) whereas the efficiency of modern cells is as high as 25%.
Making of Solar Cells. To make a solar cell thin wafers of semi-conducting materials containing impurities are arranged in such a way that when solar light falls on them, a potential difference develops between two areas of the semi-conductor. This potential difference results in producing current. A single solar cell produces an elective current of 60 mA (milli-amperes).
Uses of Solar Cells. The important uses of solar cells are given below :
(i) It is used for generating electricity for operating on board artificial sattelites and spaceprobes.
(ii) Solar cells are used to provide electricity to “light houses” situated in the sea and offshore oil drilling platform.
(iii) Solar cells are used for operating electronic watches and calculators.
(iv) Solar cells are used for street lighting, for operating water pumps and working of television in remote areas where electricity is not available.
Q. 7. What is solar cell panel ? Describe with the help of a suitable diagram.
Ans. Solar Cell Panel. A single solar cell consisting of thin wafer of silicon-arsenic or silicon-boron produces a very weak current. In order to get sufficiently high current so as to be capable of lifting water from deep well or to light a house, a large number of solar cells are joined together in a definite pattern to get solar cell panel.
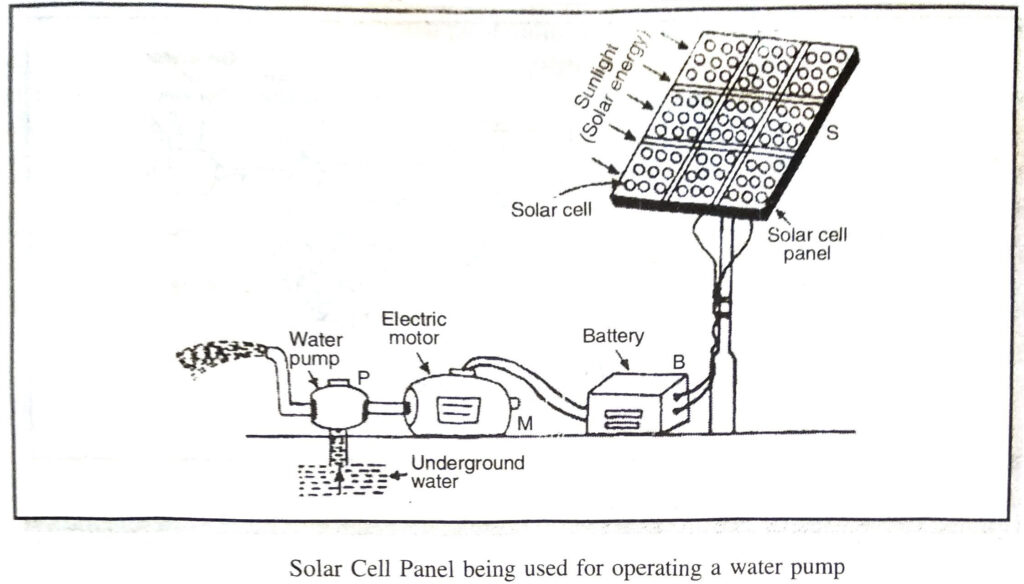
The figure above depicts a simple arrangement of a solar cell panel. In this solar cell panel hundreds of solar cells are joined together. The electric power produced by this solar cell panel is stored in battery B. This battery runs an electric motor M which drives water pump P to take out water from underground.
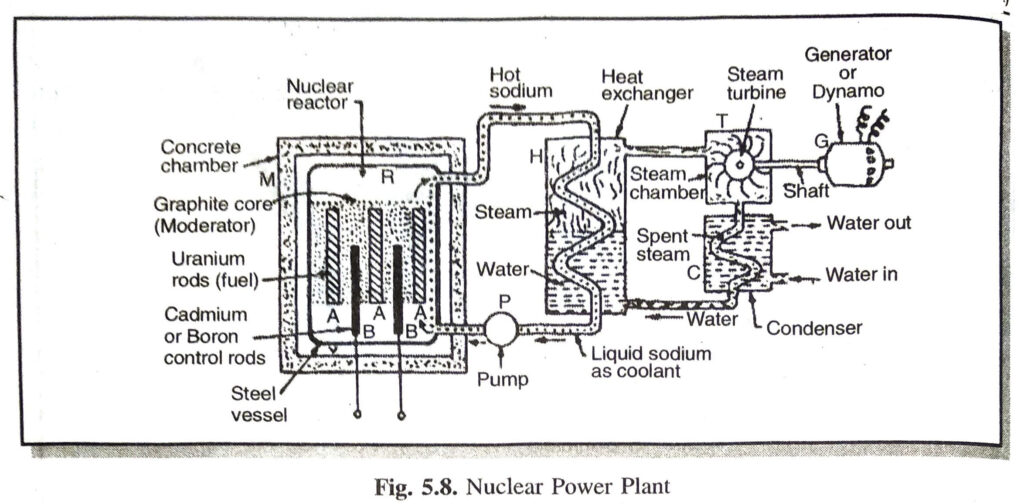
Q. 8. With the help of a labelled diagram, describe how electricity is generated in a nuclear power plant ?
Ans. Nuclear power plant consists the following parts :
(i) Nuclear Reactor ‘R’. It is a device in which energy is produced by a controlled nuclear fission of U-235. The reactor R is enclosed in a concrete chamber ‘M’ having thick walls to protect the outside world from nuclear radiations.
The nuclear reaction consists of steel vessel ‘V’ having graphite blocks which act as a moderator. The graphite core has number of enriched U-235 rods which act as a fuel. These are marked as ‘A’. In between the uranium rods are inserted cadmium or boron rods and which can be lowered or raised from outside. These rods will keep the fission under control.
(ii) Heat Exchanger ‘H’. The reactor ‘R’ is connected to a heat exchanger ‘H’ by pipes. The heat exchanger is a sort of bioler which contains water. The heat produced in the reactor is carried to water through coiled pipes.
(iii) Steam Turbine ‘T’. The heat exchanger is connected to a steam turbine ‘T’ and its shaft is connected to an electric generator ‘G’. The electricity produced by the generator is sent for transmission.
Working. After the uranium enriched rods are placed in position, the reactor is sealed. The cadmium or boron rods in the beginning are put inside so that they may absorb all neutrons emitted by U-235 and prevent fission all at once. The controlling rods of cadium or boron are withdrawn till they emit desirable number of neutrons. At this stage a controlled reaction takes place. The heat produced is withdrawn by circulating sodium. When sodium passes through the coil in the exchange it transfers heat to water. Now the water changes into steam which is passed into turbine chamber ‘T’. The turbine rotates the coil of the generator ‘G’ when electricity is generated.
Q. 9. What is Nuclear Fission ? Explain this phenomenon with the help of an example.
Ans. Nuclear Fission. The process in which an unstable nucleus of a heavy radioactive atom (like Uranium-235) splits up into two or more fragments of medium weight nuclei when bombarded by slow moving neutrons (possessing low energy) with the release of enormous amount of energy is called Nuclear fission.
In this process there is always a small loss of mass which appears as energy.
Example of Nuclear Fission. When uranium-235 (U-235) atoms are bombarded with slow moving neutrons, the heavy uranium atom breakes up producing two medium weight atoms Barium (Ba) and krypton-94 with the emission of three neutrons and release of a great amount of energy. The fission reaction can be represented in the form of following nuclear reaction :

In the fission of uranium some mass of uranium is lost which results in the production of large amount of energy. The energy can be made use of for generating electricity.
Q. 10. What is Nuclear Fusion ? Explain this phenomenon with the help of an example.
Or
Describe the process by which energy is released by the Sun.
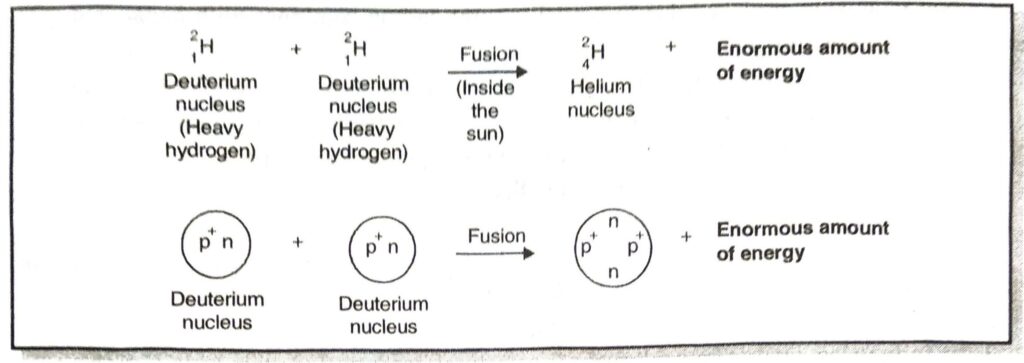
Ans. Nuclear Fusion. The process in which two nuclei of light atoms (hydrogen atom) combine to form a heavy and more stable atom (helium atom) with the liberation of a large amount of energy is called Nuclear Fusion.
This process is carried out by heating the light atoms to a very high temperature when some loss of mass occurs. This produces a large amount of energy. The energy produced in fusion reaction is much more than in a fission reaction.
Example of Nuclear Fusion. When Deuterium atoms (isotopes of heavy hydrogen atoms of mass number 2) are heated to an extremely high temperature, then two deuterium nuclei combine together to form a heavy nucleus of Helium and enormous energy is released. This nuclear reaction can be represented by the following equation:
4. Energy from salinity gradient in seas. The concentration of salts in the waters of different seas is different. The difference in salt concentrations in the water of two different seas is called salinity gradient. This difference in concentration of salt, where waters from two different seas meet, can be used to obtain energy in usable form.
5. Energy from sea vegetation or bio-mass. Sea vegetation or biomass is also an indirect source of energy. For example, the vast sea weed plantation may provide an endless supply of methane fuel in future.
6. Energy from the nuclear fusion of deuterium present in oceans. The oceans are also a source of deuterium (heavy hydrogen). Attempts are being made to produce energy by carrying out the controlled nuclear fusion of deuterium.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What are different types of combustion ?
Ans. Types of Combustion. There are mainly three types of combustion :
Slow Combustion is one which takes place at moderate rate. Burning of wood, candle, coke or coal etc., are examples of slow combustion.
Rapid Combustion is one in which the substance burns in a short span of time. In this type of combustion, the combustion of combustible substance is almost complete and a huge amount of heat and light is liberated.
Oxy-hydrogen flame used for welding purposes, L.P.G. in a gas burner, kerosene oil in a pressure stove are the examples of rapid combustion.
Spontaneous Combustion is one in which whole of the substance catches fire as soon as its temperature is brought to ignition temperature.
Gun powder exploding in a cracker is one example of spontaneous combustion.
Q. 2. What are hazards of incomplete combustion ?
Ans. Hazards of Incomplete Combustion. Fuels contain a good amount of carbon. When combustion is complete, most of carbon gets converted into carbon dioxide but when combustion is incomplete, the carbon does not burn properly resulting in ahead hazards:
1. Major portion of carbon gets converted into extremely poisonous carbon monoxide.
2. Sun emits a very large amount of ultraviolet rays which are very harmful to us. These radiations are stopped by layer of ozone gas (O3) at a height between 50 to 80 km above earth. Thus we are saved from harmful effects of ultraviolet rays.
Carbon monoxide produced due to partially burnt carbon combines with ozone and gets converted to carbon dioxide.
This damages ozone layer and hence exposes us to harmful effects of ultraviolet radiations.
3. During partial combustion some of the unburnt carbon passages into atmosphere in form of soot. There is not only sheer wastage of fuel but also pollutes atmosphere.
Q. 3. What is the role of fuel in everyday life?
Ans. Fuels play very important role in our everyday life.
1. For Domestic Use. Fuels like wood, coal, kerosene, domestic gas, cow-dung, charcoal etc., are used in our homes for cooking food and other domestic heating purposes.
2. For Transport. Coal, diesel and petrol are used to run the transport.
3. In Industries. Fuels like coal, fuel oil or natural gas are used in industries to heat up boilers.
4. To Generate Electricity. Fuels like coal or natural gas are used in thermal power plants to generate electricity.
5. As Rocket Fuel. Some special types of fuels such as hydrazine, liquid hydrogen, etc., are used in rockets.
Thus, fuels play a pivotal role in our lives by helping us in different areas.
Q. 4. Compare bio-mass and bio-gas as fuel.
Ans. Comparison between Bio-mass and Bio-gas as fuel.
| S.No. | Bio-mass (Wood/Cow dung cakes) | Bio-gas |
| 1. | It produces too much smoke. | It does not produce any smoke. |
| 2. | Its calorific value is very low. | Its calorific value is very high. |
| 3. | Ash is left as residue. | It does not leave any residue. |
| 4. | Organic manure gets burnt when cow dung cakes are burnt. | Organic matter gets enriched as spent slurry. |
| 5. | Using wood as a fuel requires cutting of tree. Deforestation leads to many problems. Again cow dung cakes when burnt destroys organic manure. Hence less manure is available to make land fertile. | Bio-gas uses waste bio-mass. It makes environment neat and clean. |
Q. 5. Hydrogen gas has high calorific value but it is not used as a domestic fuel. Why?
Ans. Though hydrogen has very high calorific value, yet it is not used as a domestic fuel because of the following reasons:
1. It is highly combustible gas and its combustion cannot be controlled.
2. Its transportation is difficult.
3. Its cost of production is high.
Q. 6. What is natural gas ? What are its advantages over other fuels ?
Ans. Natural gas is fossil fuel. It consists mainly of methane and small quantities of ethane and propane. Thus, methane is the principal constituent of natural gas (upto 97%). It occurs deep under the earth either alone or along with oil above of the petroleum deposits.
Q. 7. Write any two advantages of using bio-gas over cow-dung cakes.
Ans. Advantages of using bio-gas over cow-dung cakes are:
1. The calorific value of biogas is much higher than that of cow-dung cakes.
2. Bio-gas does not give out smoke like cow-dung cakes.
Q. 8. Which way of using cow-dung as fuel for domestic use is better : use of cow-dung cakes or use of cow-dung in a bio-gas plant? Give three reasons in support of your answer.
Ans. When cow-dung cakes burn, they produces a lot of smoke, which causes air pollution. However, the use of cow-dung in biogas plant is better because of the following reasons:
1. bio-gas burns without smoke.
2. bio-gas produces a large amount of heat.
3. the residue (slurry) left in the plant is rich in nitrogenous and phosphorus compounds and can be used as a useful manure.
Q. 9. What are fossil fuels ? What will happen if fossil fuels are used up at a fast rate? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans. Fossil Fuels. These are the energy-rich compounds of carbon which were originally made by the plants with the help of solar energy. Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas are formed under the earth over a long period of millions of years. So, if we continue to consume fossil fuels at this rapid rate, then all the fossil fuels will be exhausted one day. But the earth will not recreate fossil fuels so rapidly.
Q. 10. Why is biogas considered an ideal fuel for domestic use ?
Ans. Biogas is considered an ideal domestic fuel because of the following reasons:
(i) Biogas burns without smoke and hence does not cause air pollution.
(ii) Biogas has a high calorific value. That is, it produces a large amount of heat per unit mass.
(iii) Biogas is a very clean fuel and easy to use.
(iv) There is no storage problem for biogas as it is supplied by pipes directly from the gas plant.
Q. 11. What is Bio-energy?
Ans. Bio-energy. It is the energy generated by biomass. Energy may be in the form of fire, fuel, oil, biogas, animal dung, alcohol, charcoal or even human excreta. Biofuels are derived from biomass.
Bio fuel is an indirect source and renewable source of energy.
Q. 12. What are the constituents of biogas ? Write any two advantages of using biogas.
Ans. Composition of Biogas. Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide (CH4 + CO2 + H2 + H2S). The major constituent of bio-gas is methane, which is an excellent fuel. In fact, biogas contains about 65% methane gas.
Advantages of Biogas.
(i) Biogas has high calorific value, therefore, gives more energy per volume.
(ii) It is a clean fuel as it does not produce harmful gases.
Q. 13. What is meant by conventional sources of energy ? Write the names of two conventional sources of energy.
Ans. Conventional sources of energy are those which are being used from olden days. Getting heat energy by burning wood, petrol, diesel, coal are conventional sources of energy. They are non-renewable sources and cannot be reproduced easily.
Q. 14. You have wood, kerosene and L.P.G. Which one source of energy would you use for heating your food and why ? Give three reasons.
Ans. We prefer L.P.G. instead of wood and kerosene for heating food because :
(i) It has high calorific value.
(ii) It is easy to use.
Q. 15. Biogas is considered to be a boon to the farmers. Give reasons.
Ans. Biogas is considered as a boon to the farmers because :
(i) They can produce clean fuel from wastes.
(ii) They use spent up slurry as manure.
(iii) They can generate electricity from biogas.
Q. 16. Suggest two materials that can be used to produce biogas. Mention two uses of biogas and two advantages of biogas plant.
Ans. Biodegradable materials like agricultural waste, vegetable waste, sewage, human excreta and cow-dung, etc. can be used to produce biogas.
Advantages of Biogas:
(i) It is used for lighting.
(ii) It is also used as fuel for cooking.
(iii) It does not cause pollution as it burns without smoke and leaves no residue.
(iv) It has high calorific value.
Advantages of biogas plant:
(i) It manages agriculture waste of the village.
(ii) It produces biogas and manure.
Q. 17. Write the general principle involved in generating nuclear energy. Name one fuel used in a nuclear reactor.
Ans. Nuclear energy is generated by a process called nuclear fission.
In this process nucleus of a heavy atom is bombarded with slow moving neutrons to split and release a large amount of energy.
Nuclear Fuel. Uranium, plutonium, thorium are used as nuclear fuels.
Q. 18. Explain why :
(a) Solar cookers are covered with glass plate.
(b) The solar cooker is painted black from inside.
Ans. (a) To attain the high temperature the solar cookers are covered with glass plate. This plate focuses the sun rays to a point and temperature inside the box is increased.
(b) The black surface of the solar cooker absorbs more heat as compared to white surface.
Q. 19. Why is it not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs? State at least three reasons to support your answer.
Ans. Solar cells do not meet all our energy needs due to :
(i) High cost of installation.
(ii) Limited availability of special grade silicon to make solar cells.
(iii) Unavailability of efficient system to store electrical energy generated by solar panels.
Q. 20. Name two semiconductors used in solar cell. What is solar cell panel ? State two main advantages of solar panel.
Ans. Two semiconductors used in solar cells are: Silicon (Si), Galium (Ga).
Solar Cell Panel. A large number of solar cells are combined in an arrangement, called solar panel.
Advantages of solar panel :
(i) Its maintenance is easy.
(ii) No moving parts are present in it.
(iii) It works quite satisfactorily without the necessity of any focusing the device time and again.
(iv) It can be set up in remote and inaccessible hamlets.
Q. 21. Write three points to distinguish between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Ans. Differences between Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion :
| Fission | Fusion |
| 1. In a fission reaction, a heavy nucleus breaks up to form two lighter nuclei. | 1. In a fusion reaction two light nuclei combine to form a heavy nucleus. |
| 2. Nuclear fission is a chain reaction. | 2. Nuclear fusion is not a chain reaction. |
| 3. Fission reactions are carried out by bombarding the heavy nuclei with neutrons. | 3. Fusion reactions are carried out by heating the light atoms to an extremely high temperature. |
| 4. Nuclear fission reactions can be controlled to generate electricity. | 4. Nuclear fusion reactions have not been controlled so far. |
| 5. Nuclear fission produces a large amount of energy. | 5. The energy produced in a nuclear fusion reaction is much more than that produced during fission. |
Q. 22. State the advantages of the nuclear fusion reactions over nuclear fission. reactions. Also state one disadvantage.
Ans. Advantages of Nuclear Fusion over Nuclear Fission.
(i) The amount of energy liberated in a fusion reaction is much more than that in a fission reaction.
(ii) The products of a fusion reaction are not radioactive. They are harmless and hence can be disposed off easily. On the other hand, the products and by-products of fission reactions are radioactive and hence harmful. So the problem of their disposal arises.
Disadvantage. It has not been possible to have a controlled fusion reaction so far.
Q. 23. What should be done to minimise the pollution caused by energy sources ?
Ans. (i) We should promote the maximum use of non-polluting renewable sources of energy like solar energy and the energy from bio-mass wastes.
(ii) We should avoid the wasteful use of energy resources like wood, coal and kerosene. (iii) We should promote and undertake research and development programmes to find out economical and safe guarding the bio-sphere from fuel wastes.
Q. 24. What is a Wind Mill ?
Ans. A wind-mill is a machine which works with the energy of wind and converts kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy or electricity. It consists of large fan like blades to catch the wind. When the wind strikes against these blades, the blades start rotating. This motion is then passed onto connected crankshaft and is used to draw water from wells and to run flour mills for grinding grains.
Q. 25. What is a Solar Cooker ?
Ans. Solar Cooker. Solar cooker is a device which collects solar energy directly in the form of heat since solar energy (infrared rays) falling on the earth is very much diffused and scattered, so it is concentrated and then collected. To increase its efficiency it utilises :
(i) Reflector (plane mirror or concave mirror).
(ii) Glass sheet which allows visible and infrared rays to pass through to produce heating effect.
(iii) Black painted surface to absorb maximum amount of heat.
Q. 26. Write down the uses of coal.
Ans. Uses of coal.
1. Coal is used in production of electricity thermal power generation.
2. It is cheapest source of energy used in different industries such as production of steel and cement.
3. It is used as domestic fuel.
4. It is used for gasefication and liquefaction.
Q. 27. Write down uses of petroleum.
Ans. The main uses of Petroleum are:
1. Transportation.
2. Industrial power.
3. Heating and lighting. Heavier oils are used in central heating of shops, offices and homes as well.
4. Lubricants.
5. Petrochemical industry.
6. Use of by-products. Faecal stocks for making chemicals, plastics and synthetic
Q. 28. Write down the uses of wind energy.
Ans. 1. To generate wind power. The must important use of wind energy is to generate electricity with wind mills.
2. Wind energy is used in transportation.
3. For Wind Sports. This uses a mast and a soil for wind surfing, small vehicles having wheels for land sailing.
4. For pumping water through the use of a wind pump.
Q. 29. What are the advantages of hydel power plant over thermal power plant ?
Ans. Hydel power plant is fuelled by water for the generation of electricity. Therefore, it does not consume water and even does not cause any pollution. On the other hand thermal power plants use fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas and therefore cause pollution.
Since water in the dams will get filled by itself due to rain, it is renewable and efficient source of energy without being reliant on international fuel sources unlike in thermal power plant.
The construction of dams help in controlling floods and providing irrigation facility and water supply, while it is not so in case of thermal power plant where water is consumed.
The operational cost of hydel power plant is very low while it is recurring and very high in thermal power plant.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What are constituents of coal gas ?
Ans. Coal gas is a mixture of 55% hydrogen, 30% of methane, 10% of carbon monoxide and 5% of ethylene.
Q. 2. What is added to L.P.G. to detect leakage ?
Ans. Mercaptan (C2H5SH) which possess strong foul smell, is added to L.P.G. to detect gas leakage.
Q. 3. Name the secondary fuel.
Ans. Charcoal and biogas are secondary fuels.
Q. 4. What is cracking ?
Ans. Cracking. The process of breaking bigger hydrocarbon into smaller hydrocarbons by heating is called cracking.
Q. 5. Mention two advantages of liquid and gaseous fuels over solid fuels.
Ans. (i) Calorific value of liquid and gaseous fuels are more than solid fuel.
(ii) Combustion in solid fuel is seldom complete whereas it is almost complete in liquid and gaseous fuel.
Q. 6. Write two examples of fossil fuels.
Ans. Fossil fuels are those which are present inside earth’s crust as remains of animals and plants. Coal, petroleum, natural gas etc., form fossil fuels.
Q. 7. What is the range of temperature which can be attained in a box type solar cooker in two to three hours exposure to sun ?
Ans. 100°C to 140°C.
Q. 8. Name the device which directly converts solar energy into electrical energy.
Ans. Solar cell.
Q. 9. What is the basis of harnessing geothermal energy?
Ans. The deeper regions of earth’s crust are very hot. These are called hot spots, which are the source of geothermal energy.
Q. 10. What is hot spot springs ?
Ans. The deeper hot regions in the earth’s crust from where hot water comes out are called hot-springs.
Q. 11. Name the energy which is harnessed by boiling water by utilizing the heat inside the earth.
Ans. Geothermal energy.
Q. 12. What is biogas ?
Ans. Biogas. It is a mixture of gases such as methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) produced by the decay of biomass in the absence of air.
Q. 13. Name the main constituent of biogas.
Ans. The main constituent of biogas is methane.
Q. 14. Which type of micro-organisms are able to carry the process of decomposition in biogas plants?
Ans. Anaerobic micro-organisms.
Q. 15. What is meant by the term anaerobic?
Ans. A condition in which air is absent.
Q. 16. Name two main combustible components of biogas.
Ans. Methane (CH4) and hydrogen.
Q. 17. List two nutrients in which the slurry left behind in the digester is rich ?
Ans. It is rich in nitrogenous and phosphorus compounds.
Q. 18. What type of energy is possessed by huge wäves near the seashore ?
Ans. Kinetic energy.
Q. 19. What is tidal energy?
Ans. Tidal Energy. The energy possessed by the rising and falling water in tides caused by attraction of moon is called Tidal energy.
Q. 20. When do high tides occur ?
Ans. On every new moon day and full moon day.
Q. 21. What is bio-mass energy?
Ans. Biomass Energy. It is the energy produced from biomass. Energy may be in the form of fire produced by wood, fuel and animal dung.
Q. 22. Define solar energy. Which material is best used in solar cels?
Ans. Solar Energy. Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics. It is an important source of renewable energy. Silicon is used in making solar cells.
Q. 23. What is wind energy?
Ans. Wind Energy. Wind energy describes the process by which wind is used to generate electricity. It is readily available renewable energy.
Q. 24. Name four types of energy that we get from oceans.
Ans. 1. Ocean Thermal Energy (OTE)
2. Sea wave energy.
3. Tidal Energy
4. Energy from salinity gradient in seas.
Q. 25. Define nuclear energy.
Ans. Nuclear Energy. The energy produced due to nuclear fission (bombardment by slow moving neutron) of atoms of heavy metals is called nuclear energy).
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Which gas cannot be used as a fuel ?
(A) C.N.G.
(B) L.P.G.
(C) Oxygen
(D) Hydrogen.
Ans. (C) Oxygen
2. Bio-gas is produced from bio-matter by :
(A) anaerobic fermentation
(B) destructive distillation
(C) fractional distillation
(D) mixing petrol in biomatter.
Ans. (A) anaerobic fermentation
3. Natural gas is mostly :
(A) Methane
(B) Ethane
(C) Propane
(D) Pentane.
Ans. (D) Pentane.
4. Solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on :
(A) sunny day
(B) cloudy day
(C) hot day
(D) windy day.
Ans. (A) sunny day
5. Which of the following causes maximum pollution on burning ?
(A) Gobar cakes
(B) Petrol
(C) C.N.G.
(D) L.P.G.
Ans. (A) Gobar cakes
6. Ideal fuel should :
(A) have high calorific value necessarily
(B) have low calorific value
(C) leave no residue and have high calorific value
(D) have low calorific value and burn at once.
Ans. (C) leave no residue and have high calorific value
7. Which one of the following energies are freely available?
(A) Bio gas
(B) Sunlight
(C) Water gas
(D) Hydrogen.
Ans. (B) Sunlight
8. Which of the following is needed for formation of biogas from cow dung ?
(A) Water
(B) Oxygen
(C) Carbon dioxide
(D) Hydrogen.
Ans. (B) Oxygen
9. Which of the following sources is not derived from the sun ?
(A) Biomass
(B) Wind
(C) Hydroelectricity
(D) Geothermal energy.
Ans. (D) Geothermal energy.
10. Agent which decomposes animal dung into biogas is :
(A) Anaerobic bacteria
(B) Nitrifying bacteria
(C) Aerobic bacteria
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Anaerobic bacteria
11. Non-renewable source of energy other than fossil fuel is :
(A) Uranium
(B) Petroleum
(C) Coal
(D) All of them.
Ans. (A) Uranium
12. A solar heater cannot be used to get hot water on a :
(A) sunny day
(B) cloudy day
(C) hot day
(D) windy day.
Ans. (B) cloudy day
13. Which gas cannot be used as a fuel ?
(A) C.N.G.
(B) L.P.G.
(C) Oxygen
(D) Hydrogen.
Ans. (C) Oxygen
14. Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source?
(A) Wood
(B) Biogas
(C) Atomic energy
(D) Cow-dung.
Ans. (C) Atomic energy
15. Non-conventional source of energy is :
(A) Coal
(B) Biogas
(C) Atomic energy
(D) Cow dung.
Ans. (C) Atomic energy
16. Main constituent of biogas is :
(A) methane
(B) carbon dioxide
(C) hydrogen
(D) hydrogen sulphide.
Ans. (A) methane
17. Non-renewable source of energy is :
(A) energy of flowing water
(B) solar energy
(C) natural gas
(D) wind energy.
Ans. (C) natural gas
18. In a hydroelectric power plant, energy of …………. is used.
(A) flowing water
(B) blowing wind
(C) burning fossil fuels
(D) all the above.
Ans. (A) flowing water
19. A hydropower plant causes :
(A) destruction of agricultural land and human habitation
(B) submerged large ecosystems
(C) production of methane gas by rotting of submerged vegetation
(D) All the above.
Ans. (D) All the above.
20. The gas that is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide is :
(A) natural gas
(B) biogas
(C) coal gas
(D) L.P.G.
Ans. (B) biogas
21. Solar energy is converted into thermal energy by a solar :
(A) water heater
(B) furnace
(C) cooker
(D) all the above.
Ans. (D) all the above.
22. Solar energy is converted into electrical energy by a solar:
(A) water heater
(B) cell
(C) cooker
(D) all the above.
Ans. (B) cell
23. Which statement is correct about glass sheet used in solar heating devices ?
(A) sun rays can pass through it but rays emitted by inside black surface are not allowed to pass
(B) sun rays and light rays emitted both are allowed to pass through it
(C) sun rays and light rays emitted both are not allowed to pass through it
(D) sun rays are not allowed to pass through it, but light rays emitted by black surface are allowed to pass.
Ans. (A) sun rays can pass through it but rays emitted by inside black surface are not allowed to pass
24. The elements used as semiconductors to construct a solar cell, are :
(A) silicon and lithium
(B) silicon and aluminium
(C) silicon and gallium
(D) lithium and germanium.
Ans. (C) silicon and gallium
25. The component of sunlight causing heating effect is :
(A) visible-light
(B) infrared radiation
(C) ultraviolet radiation
(D) all the above.
Ans. (B) infrared radiation
26. Fossil fuels are formed by the process of:
(A) fractional distillation
(B) destructive distillation
(C) carbonization
(D) all the above.
Ans. (C) carbonization
27. Charcoal and coke are formed by the process of :
(A) fractional distillation
(B) destructive distillation
(C) carbonization
(D) all the above.
Ans. (B) destructive distillation
28. The ultimate source of energy is:
(A) air
(B) water
(C) sun
(D) fossil fuels.
Ans. (C) sun
29. Nuclear fusion is the :
(A) Fusion of molecules
(B) Fusion of atoms with high molecular mass
(C) Fusion of the nucleus of atoms
(D) None of the above.
Ans. (C) Fusion of the nucleus of atoms
30. Which of the following elements is used to generate Nuclear Energy?
(A) Silicon
(B) Plutonium
(C) Lead
(D) Oxygen.
Ans. (B) Plutonium
31. Thorium can generate :
(A) Wind Energy
(B) Solar Energy
(C) Nuclear Energy
(D) Biomass Energy.
Ans. (C) Nuclear Energy
32. Uranium is used to obtain :
(A) Tidal Energy
(B) Geothermal Energy
(C) Wave Energy
(D) Nuclear Energy.
Ans. (D) Nuclear Energy.
33. Wave energy is a type of :
(A) Geothermal energy
(B) Nuclear energy
(C) Conventional source of energy
(D) Non-conventional energy.
Ans. (C) Conventional source of energy
34. Conventional source of energy cause :
(A) Air pollution
(B) Certain diseases
(C) Greenhouse effect
(D) All of these.
Ans. (B) Certain diseases
35. Which of the following radiations of sun are responsible for heat?
(A) Ultra-violet
(B) Infra-red
(C) X-rays
(D) a-rays.
Ans. (B) Infra-red
36. Which of the following is an example of biomass energy?
(A) Nuclear energy
(B) Tidal energy
(C) Solar energy
(D) Gobar gas.
Ans. (D) Gobar gas.
37. Nuclear fusion occurs in :
(A) Hydrogen bomb
(B) Atom bomb
(C) Neutron bomb
(D) Co-Ni bomb.
Ans. (B) Atom bomb
38. Which of the following sources of energy we shall conserve ?
(A) Renewable source
(B) Non-renewable source
(C) Exhaustible source
(D) Both (B) and (C).
Ans. (D) Both (B) and (C).
39. Which of the following is not an example of biomass energy?
(A) Wood
(B) Gobar Gas
(C) Nuclear energy
(D) Coal.
Ans. (C) Nuclear energy
40. Best suited mirror in a solar cooker is:
(A) Concave mirror
(B) Convex mirror
(C) Plane mirror
(D) All of these.
Ans. (A) Concave mirror
41. Which source of energy can be considered best for use?
(A) Renewable source
(B) Non-renewable source
(C) Exhaustible source
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Renewable source
42. Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy?
(A) Wood
(B) Gobar Gas
(C) Solar energy
(D) Wave energy.
Ans. (C) Solar energy
43. The semi conductor material used for making solar cells is :
(A) Silver
(B) Germanium
(C) Silicon
(D) Silicon and Germanium.
Ans. (D) Silicon and Germanium.
44. The main source of energy on earth is :
(A) Coal
(B) Sun
(C) Petroleum
(D) Naural Gas.
Ans. (B) Sun
45. The source of energy in a hydropower station plant is :
(A) Water
(B) Petrol
(C) Coal
(D) Sunlight
Ans. (A) Water
46. The semi-conductor material used for making solar cells is :
(A) Silver
(B) Silicon
(C) Germanium
(D) Silicon and gallium
Ans. (D) Silicon and gallium
47. Which of the following countries is called country of winds where it is harnessed for electricity ?
(A) Germany
(B) Denmark
(C) India
(D) Japan
Ans. (B) Denmark
48. Porcelain is an example of :
(A) Insulator
(B) Conductor
(C) Semi-conductor
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Insulator
49. ‘CNG’ means :
(A) Common natural gas
(B) Combustion natural gas
(C) Compressed natural gas
(D) None of these.
Ans. (C) Compressed natural gas
50. A solar cell is made of :
(A) An insulating material
(B) A conducting material
(C) A semi-conducting material
(D) An alloy.
Ans. (C) A semi-conducting material
51. The percentage of carbon in Anthracite is :
(A) 60
(B) 30
(C) 65-70
(D) 94-98
Ans. (D) 94-98
52. The colour of Lignite is:
(A) Bright
(B) Black
(C) Brown
(D) None of these.
Ans. (D) None of these.
53. The main source of energy on the earth is :
(A) Coal
(B) Nuclear energy
(C) Sun
(D) Biogas.
Ans. (C) Sun
54. Gobar gas is :
(A) Mathane gas
(B) Ethane gas
(C) L.P.G.
(D) Nitrogen.
Ans. (A) Mathane gas
55. Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source?
(A) Wood
(B) Gobar gas
(C) Nuclear energy
(D) Coal.
Ans. (C) Nuclear energy
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here