JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions And Equations
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions And Equations
JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions And Equations
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Science Solutions
J&K class 10th Science Chemical Reactions And Equations Textbook Questions and Answers
BASIS AND BASICS
◆ Chemical reaction. It is a chemical change in which new substances are produced from the interaction between the substances.
Or
It is a process in which the old bonds in the reactants break and new bonds are formed giving rise to products.
◆ A complete chemical equation represents reactants, products and their physical states with the help of symbols.
◆ Reactants. In a chemical reaction, the substances which react are called reactants.
◆ Products. In a chemical reaction, new substances which are produced as a result of chemical reaction are called products.
◆ Chemical equation. A chemical equation represents symbolically, the reactants, products, their physical states and conditions under which a reaction occurs. It is balanced in terms of mass and charge.
◆ Balanced chemical equation. It is a chemical equation in which number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides of the equation.
◆ Law of conservation of mass. In a chemical reaction the total mass of the products must be equal to the total mass of the reactants.
◆ Skeletal or Skeleton chemical equation. It is an equation which simply represents the symbols and formulae of reactants and products. It may or may not be balanced.
◆ Balancing of chemical equations is based upon law of conservation of mass. ❖
◆ Molecular equation. The balanced chemical equation in which all the substances taking part in the reaction are present in their molecular forms.
◆ Ionic equation. It is an equation which shows only atoms and ions which actually take part in a chemical reaction.
◆ Simple reactions. It can be classified as combination, decomposition, displacement and double displacement reactions.
◆ Combination reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
◆ Decomposition reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down to produce two or more simpler substances.
◆ Displacement reaction. In this reaction, a more active element displaces or removes other element from a compound in solution.
◆ Double displacement reaction. In this reaction, two different atoms or groups of atoms are displaced by other atoms/groups of atoms.
◆ Oxidation. It is a chemical reaction which involves the addition of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
◆ Reduction. It is a chemical reaction which involves the loss of oxygen or addition of hydrogen.
◆ Oxidising agent. It is a substance which oxidises other substances and itself gets reduced.
◆ Reducing agent. It is a substance which reduces other substances and itself gets oxidised.
◆ Redox reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously.
◆ Non-redox reaction. It is a reaction in which neither oxidation nor reduction takes place.
◆ Combination and decomposition. These reactions represents opposite processes.
◆ Exothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is given out.
◆ Endothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed.
◆ Precipitation reaction. A chemical reaction in which insoluble salts are produced is called precipitation reaction.
◆ Neutralisation. The interaction of an acid with a base to form salt and water is called neutralisation.
◆ Corrosion. It is the slow eating up of metals by the action of air and moisture on their surfaces. (J&K Board 2011)
◆ Rusting. It is a special case of corrosion of iron. Chemically rust is hydrated ferric oxide (Fe₂O3.xH₂O).
◆ Rancidity. When fats and oils or food containing oils and fats are exposed to air or oxygen, they get oxidised due to which their smell and colour change. This process is called rancidity.
◆ Rancidity of fatty foods. It can be prevented by flushing the containers with nitrogen gas or by adding antioxidants to them.
◆ Roasting. It is the process of heating an ore strongly in the presence of free supply of air or oxygen.
◆ The symbols s, l, g, aq, ↑ and ↓ in a chemical equation represent solid, liquid, gas aqueous solution, evolution of a gas and formation of a precipitate respectively.
IMPORTANT TERMS AND FACTS TO MEMORISE
⇒ The chemical reaction can be studied with the help of following observations :
(a) Change in colour.
(b) Change in state.
(c) Evolution of a gas.
(d) Change of temperature.
(e) Formation of a precipitate.
⇒ The chemical reactions are mainly of four types :
(a) Combination reactions.
(b) Decomposition reactions.
(c) Displacement reactions.
(d) Double displacement reactions.
⇒ In case of exothermic reactions, + Q cal or + Q kJ is written along with products.
⇒ In case of endothermic reactions, – Q kcal or – Q kJ is written along with products.
⇒ Rust has the chemical formula, Fe₂O3. xH₂O (Hydrated ferric oxide).
TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Ans. Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from its surface.
Q. 2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(a) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(b) Barium chloride + Aluminium Sulphate → Barium Sulphate + Aluminium Chloride
(c) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Ans. (a) H₂ + Cl₂→ 2HCl
(b) BaCl2 + (NH4)2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NH4Cl
(c) 2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
Q. 3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
(a) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(b) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride and water.
Ans. (a) BaCl₂ + Na₂SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
(b) NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H₂O (l)
Q. 4. A solution of substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
(a) Name the substance ‘X’and write its formula.
(b) Write the reaction of the substance X named in (a) above with water.
Ans. (a) X is calcium oxide (quick lime) and its formula is CaO.
(b) CaO(s) + H₂O (l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
Q. 5. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other ? Name this gas. is
Ans. When electric current is passed through acidulated water, the reaction taking place is
Therefore hydrogen and oxygen produced are in the ratio 2 : 1 by volume. Hence volume of gas collected in one test tube is double the volume of gas collected in another tube. This gas is hydrogen.
Q. 5. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change, when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans. This is because iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution producing ferrous sulphate and copper.
Therefore, the concentration of copper sulphate solution decreases and blue colour of solution gradually fades away.
Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
(Blue) (Green)
Q. 6. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in the activity 6. 10 given in textbook
Ans. NaCl (aq) + AgNO3(aq) → NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) ↓
Q. 7. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions :
(a) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(b) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Ans.
| Reaction | Substance oxidised | Substance reduced |
| (i) | Na (s) | O 2(g) |
| (ii) | H2(g) | CuO (s) |
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES (SOLVED)
Q. 1. Which of the statements about the reactions below are incorrect? 2PbO (s) + C (s) → 2Pb (s) + CO₂ (g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced.
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d) Lead oxide is being reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all.
Ans. (i).
Q. 2. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction.
(b) double displacement reaction.
(c) decomposition reaction.
(d) displacement reaction.
Ans. (d)
Q. 3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings? Tick the correct answer.
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
Ans. (a).
Q. 4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced ?
Ans. Balanced chemical equation. It is a chemical equation in which number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides of the equation.
The chemical equation should be balanced because law of conservation of mass holds good i.e., the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products.
Q. 5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them :
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans. (a) 3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g) +2SO2
(b) 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2H2O(l) + 2SO2(g)
(c) 3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3 → 2 AlCl3(aq) + 3BaSO4(s) ↓
(d) 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
Q. 6. Balance the following chemical equations :
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO2 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Ans. (a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Q. 7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions :
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water.
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver.
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper.
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium Sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride.
Ans. (a) Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO3 + H₂O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) 2Al+ 3CuCl₂ → 2AlCl3 + 3 Cu
(d) BaCl₂ + K₂SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
Q. 8. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reaction and identify the type of reaction in each case.
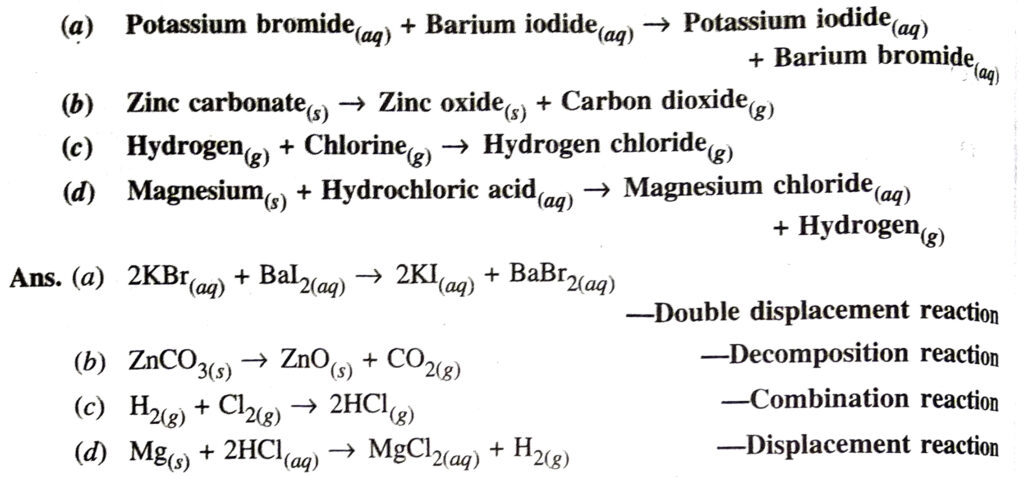
Q. 9. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions ? Give examples.
Ans. Exothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is given out.
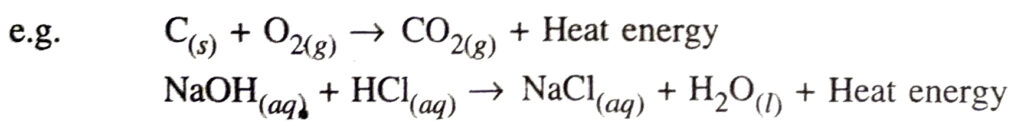
Endothermic reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed.
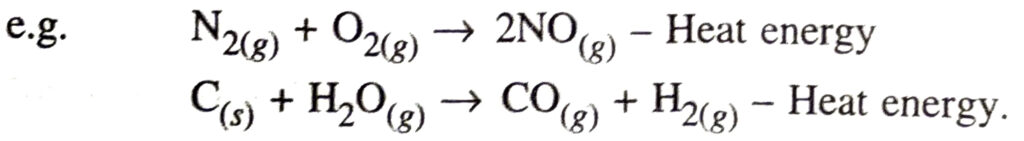
Q. 10. Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction ? Explain.
Ans. During respiration oxidation of glucose occurs which produces heat energy.
Q. 11. Why are decomposition reactions called opposite of combination reactions ? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans. During decomposition a single substance breaks down into two or more substances which is just the reverse of combination reaction.
Examples for decomposition reactions are :
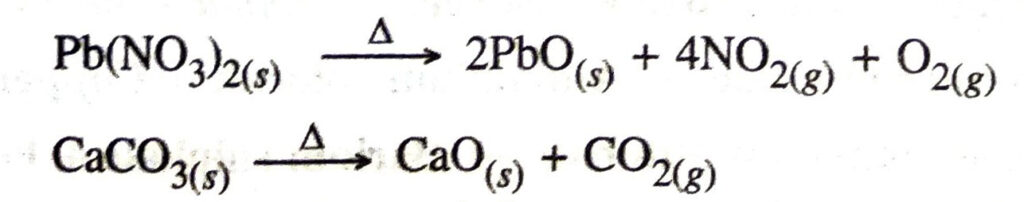
Q. 12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Ans. In the reaction
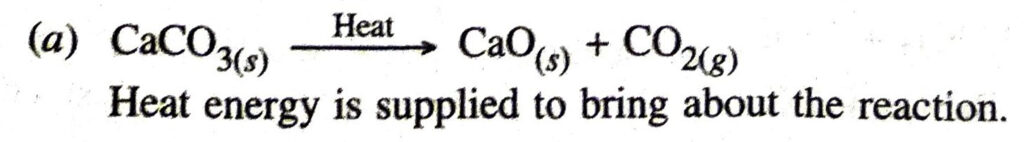
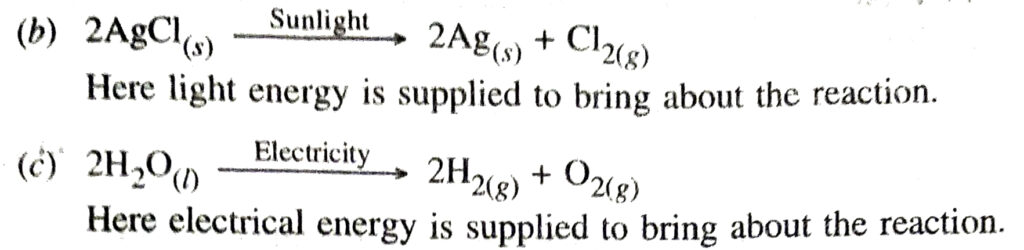
Q. 13. What is the difference between the displacement and double displacement reactions ? Write equations for these reactions.
Or
Describe briefly any two types of chemical reactions with one example in each case.
Ans. Displacement reaction. In this reaction a more active element displaces less active element from solution of its compound. Examples
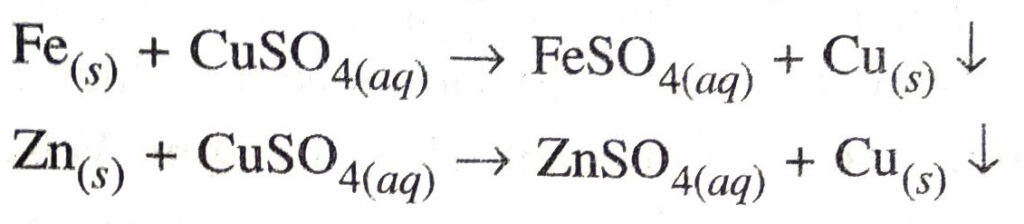
Double displacement reaction. The reaction in which there is an exchange of ions between two reactants is called a double displacement reaction.
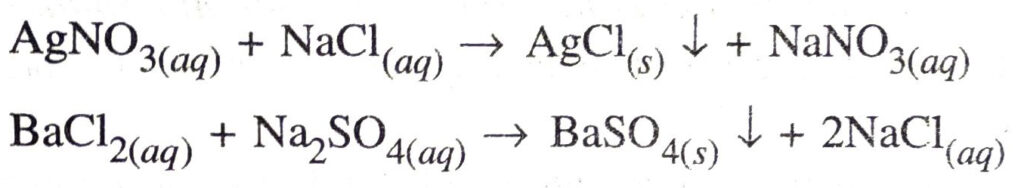
Q. 14. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans. Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag ↓
Q. 15. What do you mean by precipitation reaction ? Explain by giving examples.
Ans. Precipitation reaction. A reaction in which an insoluble product or precipitate is produced is called precipitation reaction
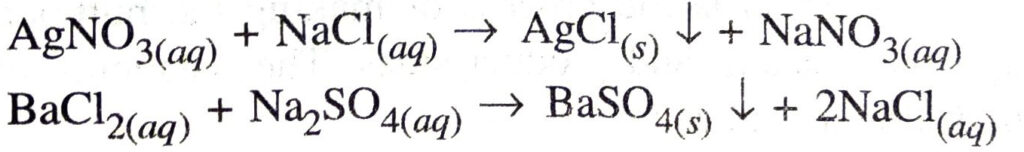
Q. 16. Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each: (a) Oxidation (b) Reduction.
Or
Explain oxidation and reduction with two examples in each case.
Ans. (a) Oxidation. A chemical reaction in which a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen is called oxidation.
Example
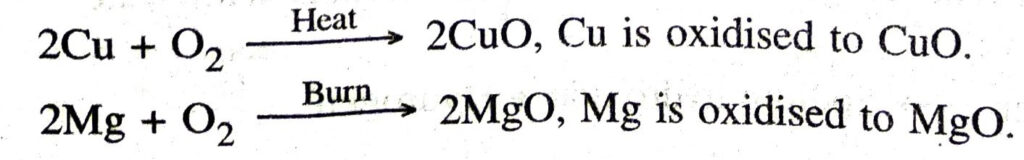
(b) Reduction. A chemical reaction in which a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen is called reduction.
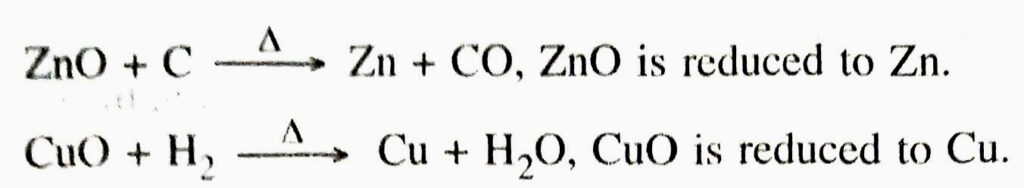
Q. 17. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans. The element X is copper.
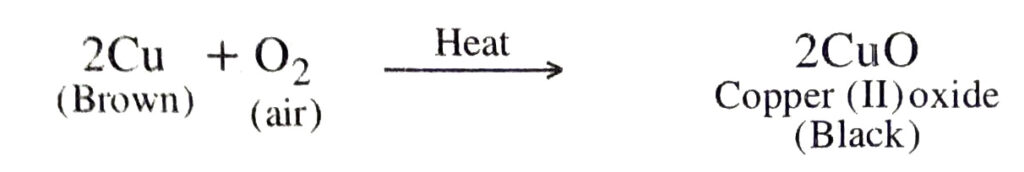
Therefore the black coloured compound formed is copper (II) oxide (CuO).
Q. 18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles ?
Ans. The iron articles can be protected from rusting by applying paint on them so that the iron surface does not come in contact with air (or oxygen) and moisture which cause rusting.
Q. 19. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans. This is because food items are prevented from oxidation by oxygen of air.
Q. 20. Explain the following terms with one example each :
(a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity.
Ans. (a) Corrosion. The slow eating up of metals by the action of air and moisture on their surfaces is called corrosion.
(b) Rancidity. When fats and oils or food containing oils and fats get oxidised with air or oxygen, their smells and tastes change. This process is called rancidity.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. How is a chemical equation balanced? Discuss with the help of an example.
Ans. Balancing of chemical equation is the process of making the number of different types of atoms equal on both the reactant and product sides. The balancing of a chemical equation is completed in the following steps:
- Write the symbols and formulae of the various reactants and products without making them equal. This is called a skeleton equation.
- Select the biggest formula which contains the largest number of atoms. Balance its atoms on the sides of the arrow.
- Balance the remaining atoms on the both sides of the arrow.
- Make the equation molecular. The gases like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine etc. are first written in the atomic form and then they are written in molecular form.
Example. Let us consider a reaction in which sodium metal reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen :
Sodium+ Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
The steps for balancing the above equation are as follows:
1. The skeleton equation for the chemical reaction is :
Na + H₂O → NaOH + H
2. The number of Na atoms on both sides of the arrow are equal. Similarly, the number of oxygen and hydrogen atoms on both sides of the equation are also equal.
3: This means that the equation is balanced but it is not molecular because hydrogen is in atomic form.
4. To make hydrogen molecular or to write it as H₂ multiply the entire equation by 2. The equation may be re-written as :
2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
This is the balanced equation.
Q. 2. What are the types of combination reactions? Give examples of each type.
Ans. Combination reactions are of three types. These are discussed as follows:
1. Combination between two elements. In these reactions, two elements combine under suitable conditions to form a compound. A few examples of this type of combination reactions are :
(a) Carbon element burns in oxygen to form carbon dioxide.

(b) Iron and sulphur elements when heated form iron sulphide.
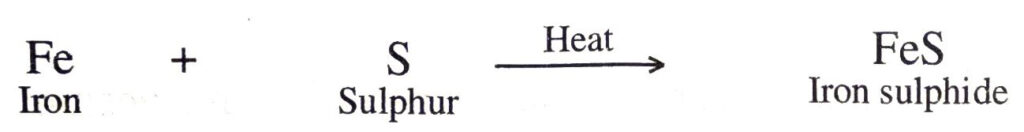
2. Combination between an element and a compound. In these reactions, one of the combining substances is an element whereas the other is a compound. A few example of this type of combination reactions are :
(a) Carbon monoxide combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide
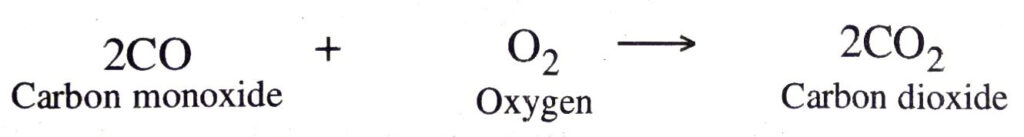
(b) Sulphur dioxide combines with oxygen upon heating to form sulphur trioxide.
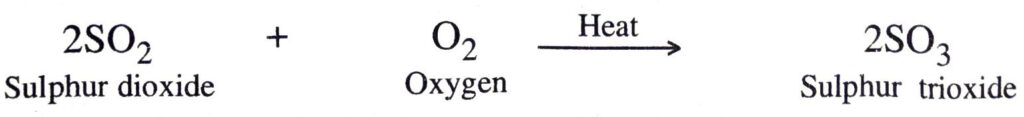
3. Combination between two compounds. In these combination reactions, two compounds take part to form a new compound. For example,
(a) Ammonia reacts with hydrogen chloride to form ammonium chloride.

(b) Carbon dioxide combines with calcium oxide (quick-lime) to form calcium carbonate.
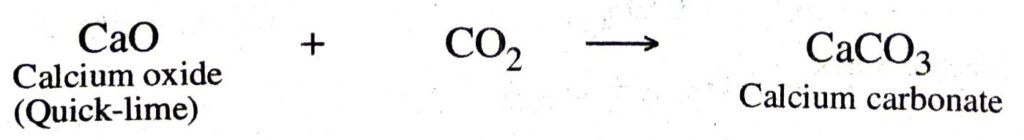
Q. 3. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case :
(a) Barium chloride (aq) + Aluminium sulphate (aq) → Barium sulphate (s) + Aluminium chloride (aq)
(b) Zinc carbonate (s) → Zinc oxide (s) + carbon dioxide (g)
(c) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) → Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g).
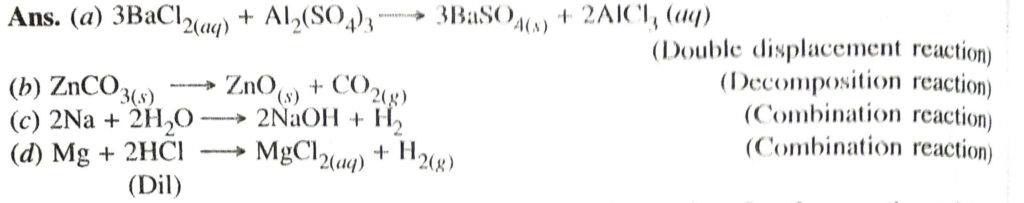
Q. 4. Write word equations and then write balanced equations for the reaction taking place when :
(a) dil H2SO4 reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dil HCI reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dil H2SO4 reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dil H2SO4 reacts with iron filings.
Ans. (a) Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to give zinc sulphate and hydrogen.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
(Dil)
(b) Magnesium ribbon reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to give magnesium chloride and hydrogen.
Mg + 2HCI → MgCl2 + H2
(Dil)
(c) Aluminium powder reacts with dil. sulphuric acid to give aluminium sulphate and hydrogen.
2Al + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
(Dil)
(d) Iron filings react with dilute sulphuric acid to give ferrous sulphate and hydrogen.
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4+H2.
(Dil)
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. With the help of an example define decomposition reaction.
Ans. Decomposition reaction. It is a chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down to produce two or more still simpler substances.
Examples:
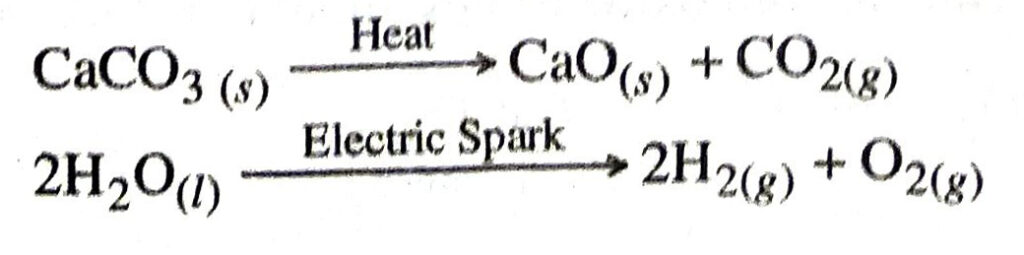
Q. 2. What are the informations conveyed by a chemical equation ?
Ans. 1. It indicates the names of reactants and products.
2. It indicates the relative number of molecules of reactants and products.
3. It indicates the relative number of moles of reactants and products.
4. It indicates the relative masses of the reactants and products.
5. It indicates the relative volumes of gaseous reactants and products.
Q. 3. What are oxidising and reducing agents according to electronic concept?
Ans. According to electronic concept, an oxidising agent may be defined as a substance which oxidises other substances by gaining one or more electrons. For example,
Cl2 + 2e– → 2Cl– (Cl2 is an oxidising agent)
According to electronic concept, a reducing agent may be defined as a substance which reduces other substances by giving one or more electrons. For example,
Na → Na+ + e– (Na is a reducing agent)
Q. 4. What is redox reaction according to electronic concept ?
Or
Explain redox reactions. Give two examples.
Ans. According to electronic concept, a redox reaction may be defined as a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously. This is because while one substance loses electrons, the other substance gains electrons.
For example, consider the reaction

Here, Na is oxidised to Na+ ions and Cl₂ is reduced to Cl– ions. Therefore, it is a redox reaction.
(ii) H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl.
Q. 5. What is corrosion? How is it prevented ?
Or
What is corrosion ? Give two ways to prevent corrosion of metals.
Ans. Corrosion of metals. The process of deterioration of a metal as a result of its reaction with air (or oxygen) and moisture (present in environment) surrounding it is called corrosion.
Corrosion of metals can be prevented :
1. By coating the metal surface with paint varnish, grease etc.
2. By coating the metal with a thin coating of more reactive metal.
3. By forming alloys.
Q. 6. Discuss rancidity.
Ans. Rancidity. When fats and oils or food containing oils and fats are exposed to air or oxygen, they get oxidised due to which the smell and colour change. This process is called rancidity.
Rancidity of fatty foods can be prevented by flushing the containers with nitrogen gas by adding antioxidants to them.
Q. 7. Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
(a) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder
(b) Steam is passed over ions.
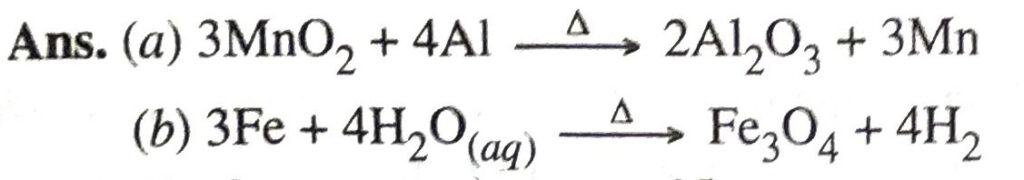
Q. 8. Explain the effect of oxidation reactions in your daily life.
Ans. 1. These are involved in the combustion of substances.
2. These are involved in the release of energy from food.
3. Oxidation causes rancidity of food and rusting of iron.
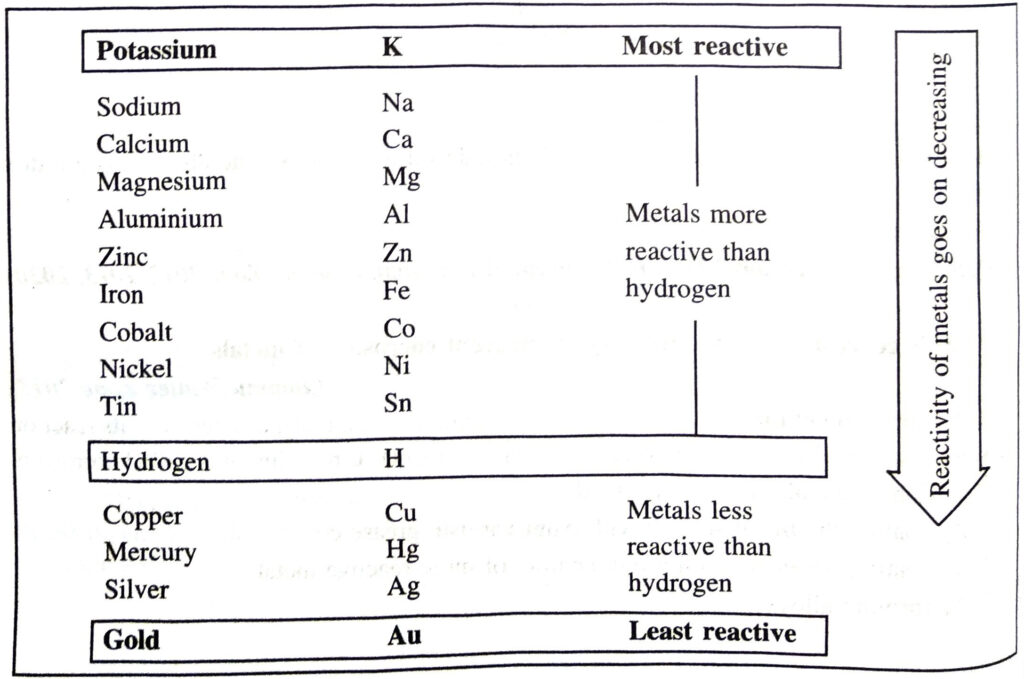
Q. 9. What do you understand by the reactivity series of metals ? Arrange the important metals in order of their decreasing reactivity.
Ans. Reactivity series of metals. It may be defined as a series which is obtained by arranging the metals in decreasing order of their reactivity or activity.
The arrangement of some metals in decreasing order of reactivity is as follows:
Q. 10. Give four points of similarities between rusting and burning.
Ans. 1. Both require oxygen.
2. Both produce oxides.
3. Both produce heat energy.
4. Both involve a chemical change.
Q. 11. Give important points of distinction between rusting and burning.
Ans.
| S. No. | Rusting | Burning |
| 1. | It is a slow process. | 1. It is a fast process. |
| 2. | It occurs only in case of iron. | 2. It occurs in a variety of substances. |
| 3. | Heat is evolved at very very slow rate. | 3. Heat is evolved rapidly. |
| 4. | Air (or O₂) and moisture are required. | 4. Only oxygen is required. |
| 5. | There is a slow rise in temperature. | 5. There is a sudden rise in temperature. |
Q. 12. Mention five ways by which rusting can be prevented.
Or
How can corrosion of metals prevented ?
Ans. 1. By painting metal surfaces with enamel paints.
2. By applying oils and greases on surfaces.
3. By plastic coating on the surfaces.
4. By galvanisation.
5. By forming alloys.
Q. 13. Mention two ways by which rancidity of fatty foods can be prevented.
Ans. (a) By adding antioxidants to the fatty foods.
(b) By flushing the food containers with nitrogen to prevent food from oxidation.
Q. 14. What is Balanced Chemical Equation ? Why should the chemical equation be balanced?
Ans. The equation in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on two sides of an equation is called a balanced chemical equation. This is based upon law of conservation of mass i.e., total mass of the products must be equal to the total mass of the reactants.
Q. 15. Balance the following chemical equations :
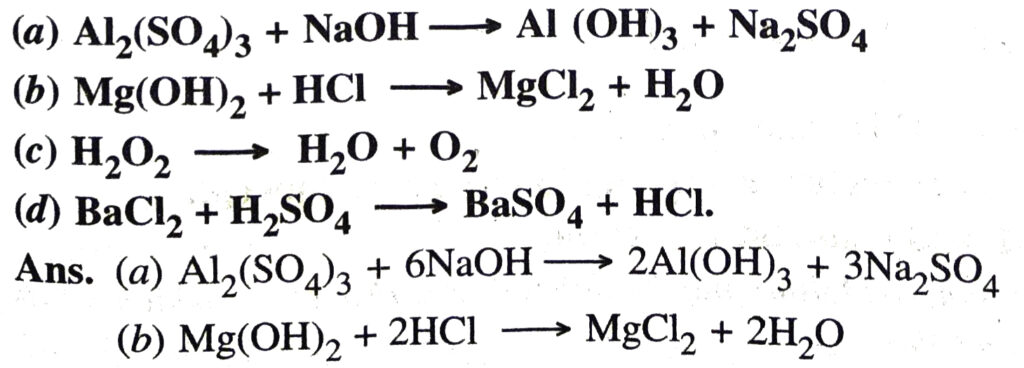
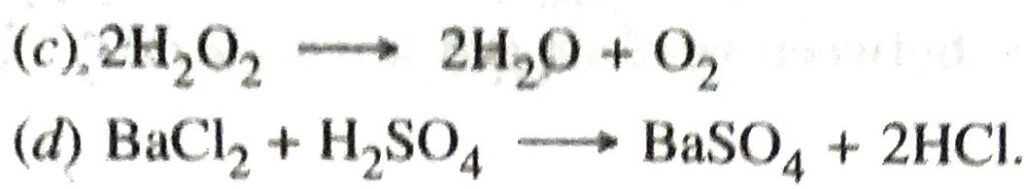
Q. 16. Define corrosion of iron. Give necessary conditions for corrosion of iron. State two ways to prevent the corrosion of iron.
Or
Define corrosion. How is it prevented ?
Ans. Corrosion of iron. When iron objects are exposed to moist air for a long time, their surface is covered with a brown substance called rust. This is called corrosion or rusting of iron.
Chemically rust is Fe2O3. xH2O
The two conditions necessary for corrosion of iron are:
1. Presence of air or oxygen.
2. Presence of moisture.
Two ways to prevent the corrosion of iron are:
1. By painting the iron articles with enamel paints.
2. By greasing the iron articles.
Q. 17. Explain the oxidation and reduction reactions in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
Or
Explain oxidation and reduction reactions with the example for each.
Ans. Oxidation. It is defined as a process which involve again of oxygen.
Reduction. It is defined as a process which involves loss of oxygen.
Examples
1. When copper oxide is heated with hydrogen, water and copper are formed.
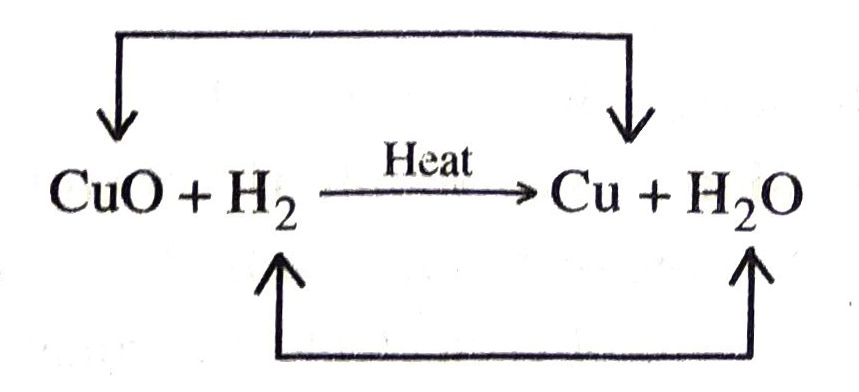
Here CuO is reduced to Cu and H₂ is oxidized to H2O.
2. When zinc oxide is heated with carbon, then zinc metal and carbon monoxide are formed.
Here ZnO is reduced to Zn and C is oxidized to CO.
Q. 18. Discuss oxidation and reduction according to electronic concept.
Ans. Electronic concept of oxidation and reduction.
According to electronic concept, oxidation may be defined as a process in which an atom or an ion loses one or more electrons.
For example,
Na → Na+ + e–
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–
According to electronic concept, reduction may be defined as a process in which an atom or an ion gains one or more electrons.
For example,
2H+ + 2e– → H₂
Cl₂ + 2e– → 2Cl–
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. What is a chemical equation ?
Ans. The symbolic representation of an actual chemical reaction is called a chemical equation.
Q. 2. Give the significance of →, ↑ and ↓ in a chemical equation.
Ans. → indicates to produce,
↓ indicates the precipitation of a product and
↑ indicates evolution of a gas.
Q. 3. What is the significance of  in a chemical equation ?
in a chemical equation ?
Ans. It represents that the reaction is reversible in nature.
Q. 4. How are the following information indicated in a chemical equation ?
1. Formation of a precipitate
2. Evolution of a gas
3. A solution made in water
4. Evolution of heat.
Ans. 1. Formation of precipitate is indicated by arrow pointing downwards (↓).
2. Evolution of gas is indicated by an arrow pointing upwards (↑).
3. A solution made in water is indicated by symbol ‘aq’ or aqueous.
4. Evolution of heat is indicated as + Heat.
Q. 5. Give the reaction of aluminium oxide with
(i) HCI (ii) NaOH.
Ans. (i) Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
(ii) Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O.
Q. 6. Convey the following information in the form of chemical equation :
“An aqueous solution of ferrous sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form a precipitate of ferrous hydroxide and sodium sulphate remains in solution.”
Ans.
Q. 7. When potassium nitrate is heated, it decomposes into potassium nitrite and oxygen. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and add the symbols wherever necessary.
Ans.
Q. 8. In the reaction PbS (s)+ 4H2O2 (aq) → PbSO4 (s) + 4H2O (l) which is oxidising agent and which is reducing agent ?
Ans. H₂O₂ is oxidising agent and PbS is reducing agent.
Q. 9. What are non-redox reactions ? Explain with the help of examples.
Ans. The reaction in which neither oxidation nor reduction takes place are called non-redox reactions. e.g.
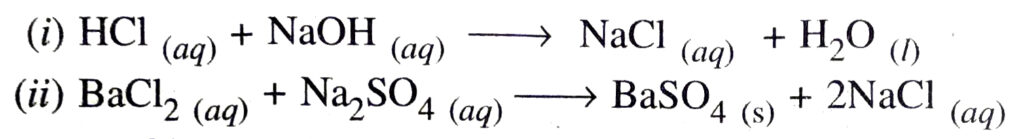
Q. 10. Give the example in which oxidation and reduction reaction is also displacement reaction.
Ans. Zinc + Copper sulphate → Zinc sulphate + Copper
Q. 11. Give two examples from everyday life situations where redox reactions are taking place ?
Ans. (i) Photosynthesis of carbohydrates
(ii) Combustion reactions.
Q. 12. Predict whether the combustion of glucose is an exothermic or endothermic reaction.
Ans. Exothermic reaction.
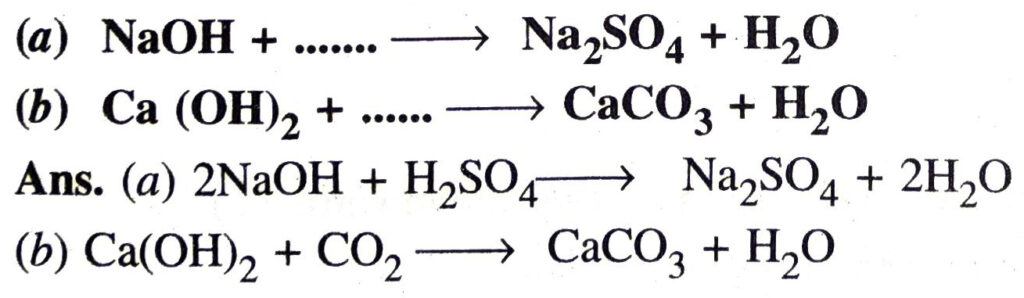
Q. 13. Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct answer out of the four alternatives :
1. Formation of CuO from copper and oxgen denotes :
(A) Reduction
(B) Oxidation
(C) Redox reaction
(D) None of these.
Ans. (A) Reduction
2. Which of the following is not a chemical reaction ?
(A) Souring of milk
(B) Dissolution of sugar in water
(C) Rusting of iron
(D) Digestion of food.
Ans. (B) Dissolution of sugar in water
3. Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
(A) Applying grease
(B) Applying paint
(C) Applying coating of Zinc
(D) All of these.
Ans. (C) Applying coating of Zinc
4. The correct formula of rust is :
(A) Fe2O3
(B) Fe3O4
(C) Fe2O3.xH2O
(D) Fe3O4.xH2O.
Ans. (C) Fe2O3.xH2O
5. Rancidity occurs when oils and fats are:
(A) Oxidised
(B) Reduced
(C) Decomposed
(D) None.
Ans. (A) Oxidised
6. When lime stone is heated, the chemical reaction that takes place :
(A) Decomposition
(B) Combination
(C) Electrolysis
(D) Displacement.
Ans. (A) Decomposition
7. CaCO3  CaO + CO2 is an example of:
CaO + CO2 is an example of:
(A) Decomposition reaction
(B) Combination reaction
(C) Displacement reaction
(D) Double displacement reaction.
Ans. (A) Decomposition reaction
8. Rusting is :
(A) Reducing reaction
(B) Decomposition reaction
(C) Oxidation reaction
(D) Redox reaction.
Ans. (D) Redox reaction.
9. The reaction in which heat energy is given out is called :
(A) Endothermic reaction
(B) Exothermic reaction
(C) Isomerisation reaction
(D) None.
Ans. (B) Exothermic reaction
10. Consider the reaction KBr + AgNO3 → KNO3 + AgBr.
(A) Decomposition reaction
(B) Double decomposition reaction
(C) Combination reaction
(D) Displacement reaction.
Ans. (B) Double decomposition reaction
11. Which is correctly balanced equation ?
(A) 3Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
(B) Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
(C) Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(D) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
Ans. (D) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
12. ZnO + C→ Zn + CO The above given reaction is an example of :
(A) Oxidation
(B) Reduction
(C) Redox reaction
(D) Combination reaction.
Ans. (C) Redox reaction
13. Which of the following shows no corrosion ?
(A) Iron
(B) Copper
(C) Gold
(D) None of the above.
Ans. (C) Gold
14. When magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen it gets converted into :
(A) Magnesium hydroxide
(B) Magnesium oxide
(C) Magnesium chloride
(D) None of these.
Ans. (B) Magnesium oxide
15. When quick lime is added to water which of the following does not happen?
(A) Heat is evolved
(B) Missing sound
(C) A chemical reaction occurs
(D) CO2 is produced.
Ans. (D) CO2 is produced.
16. MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + H2O + Cl2 is:
(A) Oxidation reaction
(B) Redox reaction
(C) Reduction reaction
(D) Displacement reaction.
Ans. (B) Redox reaction
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here