JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 6 Manufacturing Industries
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 6 Manufacturing Industries
JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions chapter – 6 Manufacturing Industries
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Social Science Solutions
INTRODUCTION TO THE CHAPTER
- In the process of manufacturing goods, primary products are made more useful, i.e., value is added.
- Value addition is thus the chief characteristic of secondary activity. It is this value addition that not only changes the form and utility of goods but also increases national wealth.
- Agriculture is the backbone of an economy. It not only feeds a nation but also provide raw materials to the manufacturing sector. The development of the manufacturing sector is considered the basis of economic development.
- Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into valuable products. The economic strength of a nation can be measured by the development of manufacturing industries.
- In order to benefit the liberation process, the New Industrial Policy (1991) was proposed to make industrial licensing more flexible, to remove many unnecessary controls, as well as to enforce a greater degree of responsibility on the private sector.
- The distribution of industries within a geographical region is known as spatial distribution, and greatly influences both the quality and price of the product.
- Manufactured goods are more useful and valuable then the raw materials. The location of manufacturing industries depends on two main factors-physical and socio-economic.
- The physical factors affecting the location of an industry are availability and nearness to the source of raw material, power resources and climate is essential for certain industries.
- Industrial location is directly related to urbanisation. Industries are influenced by availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market.
- Industries can be broadly divided into five types on the basis of labour size, their role, ownership, raw material used and source of raw material.
- On the basis of source of raw material used, industries can be classified as Agrobased industries and mineral based industries.
- Basic industries or key industries are those industries which supply raw materials for manufactures of other goods.
- Consumer industries are those industries which produce goods for the direct use of consumers.
- Large industries are those industries which employ a large labour force and invest a large amount of capital in plant and machinery.
- Heavy industries are those industries which use raw materials in bulk. Light industries are those industries which use light raw materials and also produce light finished goods.
- On the basis of ownership. Industries are classified as private sector industries, public sector industries, joint sector industries and co-operative sector industries.
- Textile industry in India is the oldest and occupies a unique position in the Indian economy.
- The first cotton textile mill was set up at Fort Gloster, Calcutta (now Kolkata) in 1818.
- The first cotton mill, combining spinning, weaving and finishing, was established in 1854 in Bombay (now Mumbai).
- The first fertiliser plant was set up in India in 1906 at Ranipet (Tamil Nadu) and the first cement factory was set up at Madras (now Chennai) in 1904.
- India ranks 3rd in the world in steel production.
- Bengaluru is the electronic capital of India.
- Apart from contributing significantly to industrial and economic growth, industries also causes land, water, air and noise pollution, which results in the degradation of the environment.
IMPORTANT TERMS
- Agro-based Industries. Industries which use raw materials obtained from agriculture.
- Basic Industries. Industries which promote other industries, for example, iron and steel or chemicals like sulphuric acid are required by other industries.
- Industry. Production of goods from raw materials. The production activities generate profits and involve producing a particular commodity.
- Integrated Steel Plants. A large steel plant which handles everything under one roof, from sorting out raw materials to processing and steel making. In an integrated steel plant everything is done in a chain.
- Manufacturing. The process of converting raw materials into useful goods.
- Smelting. The process by which mineral is melted to remove impurities.
- Sponge Iron. Porous iron reduced from an oxide at a temperature below the melting point.
- Steel. It is pure metal and is also alloyed with carbon and other elements to make various grades of steel.
- Synthetic Fibres. Fibres made from wood, coal and petroleum through chemical processes.
- Wrought Iron. It is obtained from pig iron. Heating is done with ferric oxide.
J&K class 10th Social Science Manufacturing Industries Textbook Questions and Answers
Q. 1. Multiple Choice Questions
(i) Which one of the following industries uses limestone as a raw material ?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Sugar
(d) Jute.
Ans. (b) Cement.
(ii) Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the public sector plants ?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC.
Ans. (b) SAIL.
(iii) Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material ?
(a) Aluminium Smelting
(b) Cement
(c) Jute
(d) Steel.
Ans. (a) Aluminium Smelting.
(iv) Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computer, etc. ?
(a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c) Aluminium
(d) Information Technology.
Ans. (d) Information Technology.
Q. 2. Answer the following briefly in not more than 30 words.
(i) What is manufacturing ?
Ans. Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into finished products. It is called the utility of raw materials.
(ii) Name any three physical factors for the location of the industry.
Ans. (a) Raw materials; (b) Power; (c) Climate.
(iii) Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
Ans. (a) Capital; (b) Government policies; (c) Market.
(iv) What are basic Industries ? Give an example.
Ans. Basic industries are those industries which provide raw materials to other industries, such as iron and steel industry.
(v) Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement.
Ans.. Limestone, coal, gypsum, silica and alumina.
Q. 3. Write the answers of the following questions in 120 words.
(i) How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants ? What problems does the industry face?
Or
What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity ?
Ans. An integrated steel plant is a large unit. It handles everything in one complex. These collect raw materials to make steel, by rolling and shaping.
Mini steel plants are smaller units. These have electric furnaces. These use steel scrap and sponge iron. These have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. These produce mica and alloy steel.
| Integrated Steel Plants | Mini Steel Plants |
|
(a) An integrated steel plant is a large unit.
(b) It handles everything in one complex.
(c) These collect raw materials to make steel, by rolling and shaping.
|
(a) Mini steel plants are smaller units.
(b) These have electric furnaces.
(c) These use steel scrap and sponge iron. These have re-rollers that use stee! ingots as well. These produce mica and alloy steel.
|
Problems faced by these Industries :
(a) High cost of production.
(b) Limited availability of coking coal.
(c) Lower productivity of labour.
(d) Irregular supply of energy.
(e) Poor infrastructure.
Recent Developments: Some developments have increased the production capacity of this industry such as:
(a) Liberalisation
(b) Foreign direct investment
(c) Private ownership
(d) Resources for research and development have been increased
(ii) How do industries pollute the environment ?
Or
Industries pollute the environment. List one instance of it.
Ans. Environmental pollution is becoming a serious problem for mankind. Industries have caused air, water, land and noise pollution. Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide gases cause air pollution. Smoke from chemical industries and burning of fossil fuels cause hazards. Bhopal Gas Tragedy is an example. Industrial wastes dumped into lakes and seas cause water pollution. Wastes from Nuclear plants cause cancer. Industrial processes also cause noise pollution.
(iii) Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
Ans. The National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC), a major Government of India undertaking, has adopted an aggressive approach for the task of preserving and protecting our natural environment. In all its operations, it has taken some of the following measures for rejuvenating the environment:
- Optimise equipment utilisation and upgrade the existing facilities.
- Minimising waste generation and maximising the use of wastes, like ash from power plants by supplying the same to the bricklaying industries free of cost. It has also adopted some innovative techniques and passed on the technology to small bricklayers.
- To reduce pollution of all types, techniques such as-waste management, recycling of resources, etc., are being adopted on a regular basis.
- It has also embarked on public awareness measures, to prevent industries from degrading the environment.
J&K class 10th Social Science Manufacturing Industries InText Questions and Answers
Q. 1. Classify the following into two groups on the basis of bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods.
(i) Oil
(ii) Knitting needles
(iii) Brassware
(iv) Fuse wires
(v) Watches
(vi) Sewing machines
(vii) Shipbuilding
(viii) Electric Bulbs
(ix) Paint Brushes
(x) Automobiles
Ans. (i) On the basis of raw-material: Oil, Brassware, Shipbuilding and Automobiles.
(ii) On the basis of finished goods: Knitting Needles, Fuse Wire, Watches, Sewing Machine, Electric Bulb and Paint Brush.
Q. 2. Why did Mahatma Gandhi lay emphasis on spinning yarn and weaving khadi ?
Ans. Mahatma Gandhi laid emphasis on the spinning of yarn and weaving khadi because he thought that by promoting these industries, more employment opportunities should be generated. By doing so, he also wanted to spread the use of homemade clothes.
Q. 3. Why is it important for our country to keep the mill sector loomage lower than power loom and handloom ?
Ans. Mill sector loomage provides much less employment than the power loom and handloom. The power loom and handloom are established in rural and semi-urbanised areas, hence they develop the surrounding areas, whereas the mill sector loomage are located in urban areas and do not contribute to increasing the standard of living of the rural people.
Q. 4. Why is it important for us to improve our weaving sector instead of exporting yarn in large quantities ?
Ans. It is important for us to improve the weaving sector instead of exporting yarn in large quantities because of the following reasons:
(i) It would lead to earning of more foreign exchange.
(ii) It would generate more income.
(iii) It would add more value to the yarn sector.
Q. 5. Make a list of all such goods made of steel that you can think of.
Ans. Try it yourself.
Q. 6. Why is the per capita consumption of steel low in India ?
Ans. The per capita consumption of steel is low in India because of the following reasons:
(i) The quality of infrastructure is very poor.
(ii) Most of the Indian population live in villages, which require a very small quantity of steel.
(iii) Low development in tribal areas.
Q. 7. Collect information about steel plants located in your own State and show them on the map of India.
Ans. Try it yourself.
Q. 8. Have you read about the Kalinganagar controversy ? Collect information from different sources and discuss.
Ans. Try it yourself.
Q. 9. A factory produces aluminium saucepans with plastic handles. It obtains aluminium from a smelter and a plastic component from another factory. All the manufactured saucepans are sent to a warehouse :
(i) (a) Which raw material is likely to be most expensive to transport and why ?
(b) Which raw material is likely to be the cheapest to transport and why?
(ii) Do you think the cost of transporting the finished products after packaging is likely to be cheaper or more expensive than the cost of transporting aluminium and plastic? Why?
Ans. (i) (a) Aluminium is likely to be the most expensive because it is very bulky and a heavy raw material. It is not easy to transport it from far away areas.
(b) Plastic is likely to be the cheapest to transport because it is a very light material and is easily available in the nearby areas.
(ii) The transporting of finished goods is likely to be more costly because these goods are carefully packed and handeled than the raw-materials.
Q. 10. Where would it be economically viable to set up the cement manufacturing units ?
Ans. It would be economically viable to set up the cement manufacturing industries near the sources of raw materials.
Q. 11. Find out where the plants are located in other States of India. Find their names.
Ans. Try it yourself.
J&K class 10th Social Science Manufacturing Industries Important Questions and Answers
Objective Type Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
1. The first cotton textile mill was established at Mumbai in :
(A) 1834
(B) 1844
(C) 1854
(D) 1864.
Ans. (C) 1854.
2. Manufacturing is an activity of which type :
(A) Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Quarternary.
Ans. (B) Secondary.
3. TISCO is an industry of which sector :
(A) Public
(B) Private
(C) Joint
(D) Multinational.
Ans. (B) Private.
4. ……….. is the chief centre of cotton textiles.
(A) Patna
(B) Ahmedabad
(C) Bhopal
(D) Kanpur.
Ans. (B) Ahmedabad.
5. Where was the first fertilizer plant setup?
(A) Ranipet
(B) Raipur
(C) Ahmedabad
(D) Kirtpur.
Ans. (A) Ranipet.
6. Heavy industries are:
(A) Capital intensive
(B) labour intensive
(C) Land intensive
(D) All of the above.
Ans. (D) All of the above.
7. Jute mills are located in:
(A) Mahanadi Basin
(B) Damodar Valley
(C) Hougli Basin
(D) Kosi Basin.
Ans. (C) Hougli Basin.
8. Which is the oldest centre of cotton textile industry in India ?
(A) Kolkata
(B) Mumbai
(C) Jamshedpur
(D) Kerala.
Ans. (B) Mumbai.
9. Which town is the electronic capital of India ?
(A) Mumbai
(B) Kolkata
(C) Bangalore
(D) Pune.
Ans. (C) Bangalore.
10. Where does India rank in world production of steel?
(A) 9th
(B) 10th
(C) First
(D) Second.
Ans. (A) 9th.
Fill in the blanks :
1. TISCO was set up in …………… .
Ans.1907
2. …………… is an agro based industry.
Ans. Sugar
3. Jamshedpur is in ……………. state.
Ans. Jharkhand
4. …………… is the electronic capital of India.
Ans. Bangalore
5. …………….. industry is the basis of modern industrialization.
Ans. Iron and Steel
6. The first modern cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in the year …………. .
Ans. 1854
7. Capital and ……………… are among the requirements for the location of an industry.
Ans. power resources.
True/False :
1. Bhadravati steel plant is in Karnataka.
Ans. True
2. Mohali (Punjab) is called electronic city in Punjab.
Ans. True
3. SAIL is steel authority in India.
Ans. False
4. Khetri in Jharkhand a copper smelting plant in India.
Ans. False
5. TISCO is a steel plant in Private sector.
Ans. True
6. Bhopal gas tragedy which occurred in Madhya Pradesh.
Ans. True
7. TISCO is a public sector industry.
Ans. False
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. What is manufacturing ?
Ans. Manufacturing refers to the production of goods in large quantities, after being processed from raw materials to more valuable products.
Q. 2. Define the concept of ‘Industry’.
Ans. Production of goods from raw material in factories and the activities involved in producing a particular service to the society.
Q. 3. What are agro-based industries ?
Ans. Agro-based industries are those industries which use raw materials supplied by the agricultural sector.
Examples – Cotton textiles and sugar industries.
Q. 4. What do you know about mineral based industries ?
Ans. Mineral based industries are those industries which get their raw materials from minerals, for manufacturing their product.
Q. 5. Define basic industries.
Ans. Those industries which supply raw materials for the manufacture of other goods are known as basic or key industries. Examples are iron and steel.
Q. 6. What do you know about consumer industries ?
Ans. Consumer industries produce goods for the direct use of consumers. Examples are sugar, toothpaste, sewing machines, etc.
Q. 7. Classify industries on the basis of their ownership.
Ans. On the basis of ownership, industries are classified as:
(i) Private sector industries
(ii) Public sector industries
(iii) Joint sector industries
(iv) Cooperative sector industries.
Q. 8. On the basis of bulk and weight of raw material used, how are industries classified ?
Ans. On the basis of bulk and weight of raw material used, industries are classified as:
(i) Heavy Industries
(ii) Light Industries.
Q. 9. What are heavy industries ?
Ans. Heavy industries are those industries which used raw material in bulk. Iron and steel industries is an example of heavy industries.
Q. 10. What do you know about light industries ?
Ans. Light industries are those industries which uses light raw material and also produced light finished goods.
Q. 11. List two physical factors which affect the location of an industry.
Ans. The two factors which influence the location of industries:
(i) Availability of raw materials.
(ii) Nearness to the source of raw material.
Q. 12. What are large scale and small scale industries? Give one example of each.
Ans. Large scale industries employ a large number of labourers. Cotton textile industries are large scale industries. Small scale industries employ a small number of labourers. Gur and Khandsari are small scale industry.
Q. 13. Name the four important cotton textile centres of Maharashtra.
Ans. Mumbai, Pune, Sholapur and Wardha.
Q. 14. ‘The cotton textile industry is the largest industry’. Give two points to support the statement.
Ans. (i) It provides employment to 15 lakh people.
(ii) 20% of industrial labour is employed.
Q. 15. State the three main factors which led to the concentration of cotton textile industries at Mumbai.
Ans. (i) Large amount of capital.
(ii) Facilities of Mumbai as a port.
(iii) Humid climate and cheap power.
Q. 16. Name four varieties of silk.
Ans. (i) Mulberry; (ii) Tussar; (iii) Eri; (iv) Muga.
Q. 17. Name the four important centres of silk industry.
Ans. Bengaluru, Mysore, Murshidabad and Srinagar.
Q. 18. State three mineral based industries.
Ans. Iron and Steel, Oil Refinery and Smelting Units.
Q. 19. Where was the first modern steel plant established ?
Ans. The first modern steel plant was set up at Jamshedpur in 1907.
Q. 20. Name the ‘cottonopolis of India’.
Ans. Mumbai is known as the cottonopolis of India.
Q. 21. Which Indian city is known as ‘Manchester of India’ and why?
Ans. Ahmadabad is the largest producer of cotton textile in India and hence is known as the ‘Manchester of India’.
Q. 22. Where are the four main iron plants set up in India with the help of foreign collaboration ?
Ans. These iron plants are set up at:
(i) Bhilai
(ii) Rourkela
(iii) Durgapur
(iv) Bokaro
Q. 23. Name two gases causing air pollution.
Ans. Sulphur dioxide and Carbon-monoxide.
Q. 24 Name a gas tragedy which took place in Madhya Pradesh.
Ans. Bhopal Gas Tragedy.
Q. 25. Name two industries causing water pollution.
Ans. Tanneries and Textiles Industries.
Q. 26. Where is the chief centre of cotton textile industry ?
Ans. Ahmedabad is the chief centre of cotton textile industry.
Q. 27. Why is Salem famous ? Name the state where is it located ?
Ans. Salem is in Tamil Nadu. It is famous for steel plants which were established along with two other mini-steel plants.
Q. 28. How is steel marketed in India ?
Ans. Steel is marketed in India through TISCO and SAIL.
Q. 29. Where and when in India was the first fertiliser plant set up ?
Ans. The first fertiliser plant was set up in India at Panipet (Tamil Nadu) in 1906.
Q. 30. What is a Cottage Industry?
Ans. Cottage Industry is a small business in which people work in their own houses, often using their own equipments.
Q. 31. What is the full form of SAIL?
Ans. Steel Authority of India Limited.
Q. 32. What is the full form of OIL ?
Ans. Oil India Limited.
Q. 33. What is the full form of EMS ?
Ans. Emergency Medical Services,
Short Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. In what ways are the industries classified ?
Ans. The industries can be classified on the following basis :
1. On the basis of size of the industries, the industries can be classified into two categories :
(i) Large scale industries.
(ii) Small scale industries.
2. On the basis of development of the industries, the industries are of two types :
(i) Cottage industries.
(ii) Mill industries.
3. On the basis of ownership, the industries fall into three groups:
(i) Public sector
(ii) Private sector
(iii) Co-operative sector.
4. On the basis of raw materials, industries mainly are of two types :
(i) Agro-based industries.
(ii) Mineral-based industries.
5. On the basis of manufactured goods, the industries are of two types :
(i) Heavy industries.
(ii) Light industries.
6. Similarly different types of industries are grouped as handicrafts, village industries, household industries, key industries and consumer industries.
Q. 2. Why is iron and steel industry called a basic industry?
Ans. Iron and steel industry is the basis of modern industrialization. Iron and steel industry supplies the basic raw material for a large number of assembly industries such as engineering, automobiles, locomotive, ship building, machine tools etc. It is the foundation of modern machines, tools and transportation. It has great strength, toughness and low cost of production. Therefore, iron and steel industry is known as basic industry or key industry. It lays the foundation of industrial development in this age of steel.
Q. 3. What are the problems being faced by the Indian Cotton Industry ?
Ans. Problems of cotton textiles industry
- There is a shortage of long staple cotton. So long staple cotton is imported.
- Most of the cotton mills are not of economic size.
- Most of the machinery in mills is old, obsolete and inefficient.
- Productivity is low and cost of production is high.
- India has lost many foreign markets due to strong competition.
Q. 4. List the factors which favour the location of steel plant at Jamshedpur.
Ans. Jamshedpur is ideally situated with respect to raw materials and market for the location of iron and steel industry. The plant has the following favourable facilities :
Geographical factors for location
- Availability of iron ore from Singhbhum region.
- Coking coal from Jharia and Raniganj.
- Limestone, Manganese and Quartz are available nearby.
- Damodar, Subarnrekha, Kharkai rivers provide water and sand.
- Cheap labour from densely populated state of Bihar and West Bengal.
- Facilities of ch transport and port of Kolkata.
- Water power is available from D.V.C.
Q. 5. Why is iron and steel industry located in Peninsular India only?
Ans. Iron and Steel is a heavy industry using very bulky raw materials. Therefore, its location is governed by close proximity to raw materials and go transport system. The north eastern and southern parts of Peninsular India are mineral rich suitable for location of Iron and Steel industry.
Q. 6. ‘The sugar mills are shifting towards southern and western states of India.’ Support the statement by giving four reasons.
Ans. The sugar mills are shifting towards southern and western state of India on account of the following reasons:
- The yield per hectare of sugarcane is high in the southern and western Indian states.
- The sucrose content of the sugarcane is very high, as compared to the north Indian states.
- Climatic conditions are suitable for the growth of sugarcane in the southern and western parts of India.
- The cooperative movement is very active in these states, which is helping to install new sugar mills in these area.
Q. 7. How does the textile industry occupy a unique position in the Indian economy? Examine by giving three reasons.
Ans. The textile industry occupies a unique position in the Indian economy because :
- It contributes nearly 14% in the industrial production.
- It provides employment to nearly 35 million people.
- Export of textile goods earns valuable foreign exchange. It contributes 4% toward GDP.
Q. 8. Classify industries on the basis of the sources of raw material.
Ans. On the basis of sources of raw-material, industries can be classified as:
(i) Agro-based industries. These industries chiefly use raw materials supplied by the agricultural sector.
Examples are, cotton, textile, sugar, silk, jute, etc.
(ii) Mineral-based Industries. Minerals like iron, mica, bauxite and cement from the basic raw material for the manufacture of goods. Iron and steel industry and aluminium industries are examples of mineral based industries.
Q. 9. “Manufacturing industries are considered the backbone of economic development of India.” Give three reasons.
Or
“Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of economic development of a country. “Support the statement with examples.
Or
Analyse the role of the manufacturing sector in the economic development of India.
Ans. The following statements support the statement that ‘manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of economic development of a country’:
- It provides employment to a large number by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- It helps in the export of goods and brings in valuable foreign exchange.
- It helps in making a country prosperous as the industries transform raw materials into a wide variety of furnished goods.
Q. 10. ‘Agriculture and industries are complementary to each other.’ Support the statement by giving three examples.
Or
‘Agriculture and industries move hand in hand.’ Analise the statement with three examples.
Ans. Agriculture not only feeds a nation, but also provides raw materials to the manufacturing sector. Agriculture and industries are complementary to each other on account of the following reasons:
- Manufacturing sector provides machines, tools and even fertilisers for undertaking any agricultural activity. Automation and mechanisation reduces the drudgery of doing everything manually and boosts output.
- Mechanisation enhances the income of the farmers and provides employment to the skilled and unskilled workers.
- Industrial development is also a prerequisite for the removal of unemployment and poverty from our country. In the absence of industries, agriculture by itself cannot absorb the huge work force.
Q. 11. How do industries pollute air and water ? Explain with examples.
Ans. Industries are responsible for causing air and water pollution in the following ways.
- Air pollution is caused by the emission of gases from the industrial complexes and power generation units. Air pollution adversely affects all life forms and endangers the health of humans, animals, plants and fish. It also affects buildings and our environment as a whole. Toxic gases released from the industries also cause air pollution and many other diseases.
- Water pollution is caused by the flow of organic and inorganic industrial wastes on land, rivers and lakes. The major culprits are the paper, pulp, chemical, textile, dyeing, tanning, refining and electroplating industries. Many hazardous hospital wastes are also allowed to flow into the water bodies. The water is thus, contaminated with dangerous chemicals like lead and mercury. Pesticides, fertilisers, solid wastes such as fly ash, phosphorus, gypsum and iron slag also contaminate the water.
Q. 12. In what ways are industries classified ?
Ans. Industries can be classified on the following basis:
(i) On the basis of size, the industries can be classified into two categories:
(a) Large-scale industries
(b) Small-scale industries
(ii) On the basis of development of the industries, the industries are of two types:
(a) Cottage industries
(b) Mill industries
(iii) On the basis ownership, the industries fall into three groups:
(a) Public sector
(b) Private sector
(c) Co-operative sector.
(iv) On the basis of raw materials, industries mainly are of two types:
(a) Agro-based industries
(b) Mineral-based industries
(v) On the basis of the bulk and weight of raw material used, industries are of two types:
(a) Heavy industries
(b) Light industries
(vi) Similarly, different types of industries are grouped such as handicrafts, village industries, household industries, key industries and consumer industries.
Q. 13. What are agro-based industries in India ? Describe their significance in the Indian economy.
Ans. Agro-based industries are those industries which are based on agricultural products. Textiles, sugar, vegetable oil and plantation industries are called agro-based industries. Agrobased industries form the backbone of the Indian economy. After agriculture, these industries provide employment to the largest number of people in India. The textile industry alone provides employment to 15 lakh people. These industries produce a variety of things to meet our daily needs. India earns a lot of foreign exchange by exporting products like textiles, jute, sugar, tea, coffee, footwear, etc.
Q. 14. Why Iron and Steel industry is called a ‘basic industry’? Explain three reasons.
Ans.
- Iron and steel industry is the basis of modern industrialisation. Iron and steel industry supplies the basic raw material for a large number of assembly industries such as, engineering, automobiles, locomotive, shipbuilding, machine tools, etc.
- It is the foundation of modern machines, tools and transportation. It has great strength, toughness and a low cost of production.
- Therefore, iron and steel industry is known as the basic industry or key industry. It lays the foundation of industrial development in this age of steel.
Q. 15. Classify industries on the basis source of raw material. How are they different from each other?
Ans. On the basis of the raw material, Industries can be classified as :
(1) Agro-based industries (2) Mineral-based industries
| Agro Based Industry | Mineral-Based Industry |
|
1. These industries are based on products of primary occupation, like agriculture.
2. Agricultural products are transformed into useful products like textile from cotton, sugar from sugarcane.
3. These are labour intensive industries.
|
1. These industries get their raw materials from mineral products like iron, mica, bauxite, cement, etc.
2. Iron & steel industry and aluminium industries are examples.
3. These are located near the source of the raw materials.
|
Q. 16. Distinguish between private and public sector.
Ans.
| Private Sector | Public Sector |
|
1. The industries owned and managed by an individual or a group of individuals are private sector units.
2. Many industries run by capitalists, like Birla and Tata industries, are under the private sector.
3. Private sector runs under strong competition as in Japan and U.S.A.
|
1. The industries owned collectively by a community or the government are refered to as public sector industries.
2. Schools, public buildings and nationalised industries are under the public sector, such as Bhilai steel plant.
3. Public sector runs on a socialistic pattern as in India.
|
Q. 17. Distinguish between agro industries and heavy industries.
Ans.
| Agro Industries | Heavy Industries |
|
1. Agro industries are based on products of primary occupations, such as agriculture.
2. Agricultural products are transformed into useful products, such as, textiles from cotton, sugar from sugarcane, etc.
3. These are labour-intensive industries.
4. These cover small-scale and medium-scale industries.
|
1. Heavy industries are based on manufactured goods involving the use of machines.
2. A number of complex products are manufactured from semi-finished goods, as iron is used in the making of machinery.
3. These are capital-intensive industries.
4. These cover large-scale industries.
|
Q. 18. What is manufacturing ? Why is manufacturing sector considered as the backbone of economic development of the country ? Explain three reasons.
Ans. Manufacturing. It is the process of transforming raw materials into finished goods or products. Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of economic development of the country because:
- It provides employment to a large number of people just as in cotton textile and steel industry.
- It helps in the export of goods and earns a valuable foreign exchange.
- It also makes a country economically sound.
Q. 19. Why have the textile industries moved from Mumbai towards Ahmedabad? Explain with the help of suitable examples.
Ans. The first modern cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854. Location of the Gujarat port, humid coastal climate, development of chemical industry, availability of capital and easy import of machinery were some of the advantages. Raw cotton was imported from other states. Later, the dispersal of cotton textile industry started, as a result of which cotton mills were established at Ahmedabad, in the heart of the cotton growing belt. At Ahmedabad, the level land as well as capital was available. Ahmedabad had no problems of strikes and high wages and therefore, it came to be referred to as the ‘Manchester of India’ (the largest textile centre of India).
Q. 20. Why are we not able to perform to our full potential in the production of iron and steel in India ? Explain any three reasons.
Ans. We are not able to perform to our full potential in the production of iron and steel in India because of the following reasons.
- High costs and limited availability of coking coal
- Lower productivity of labour
- Irregular supply of energy
- Poor infrastructure (any three).
Long Answer Type Questions
Q. 1. Explain the locational factors of industries with the help of suitable examples.
Or
Name the three physical factors for the location of an Industry.
Ans. Manufacturing. Manufacturing is a secondary process of transforming raw materials into finished products. The manufactured goods are more useful and valuable than the raw materials. The location of manufacturing industries depends on a number of physical and socio-economic factors.
- Nearness to sources of raw material. Large quantities of raw materials are needed for industries. Therefore, industries are located near the sources of raw materials. It saves the cost of transportation. Steel centres are developed where coal and iron are easily available. Jute mills in West Bengal and Cotton Textile mills in Maharashtra are located due to the availability of the raw materials.
- Power resources. Coal, oil and water-power are the main sources of power. Most of the industries are located around coalfields. Aluminium industries and Paper industry are located near hydro-electric stations.
- Means of Transportation. Modern industries need cheap, developed and quick means of transportation. Cheap means of transportation are required for the movement of workers, raw materials and machinery to the factories.
- Climate. Stimulating climate increases the efficiency of the labourers. Cotton textile industry requires humid climate. Film industry needs good weather with clear blue skies. Aircraft industry needs clear weather.
- Skilled labour. Cheap and skilled labour is essential for the location of the industries. Glass industry at Firozabad, sports goods industry in Jalandhar are located due to the availability of skilled labour.
Q. 2. Write about major steel plants of India.
Ans. A modest beginning of the industry was made at Kulti (West Bengal) in 1870. The first modern steel plant was established in 1907 at Sakchi (Jamshedpur) in Jharkhand by Jamshedji Tata.
Centres of Production :
- Damodar Valley. This region has TISCO (Tata Iron and Steel Company) steel plant at Jamshedpur and IISCO (Indian Iron and Steel Company) steel plant at Kulti-Burnpur. Chhota Nagpur plateau (including West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa and M.P.) is the natural core of this industry.
- Viswesvaraya Iron and Steel Limited. This steel plant is located at Bhadravati (Karnataka). It was started in 1923. It produces alloy and special steel. Iron ore is obtained from Babaudan Hills, charcoal from Kadur forests; water power from Jog falls; limestone from Bhandigudda mines.
- Steel Centres in Public Sector. Four steel plants have been developed in the public sector under HSL (Hindustan Steel Limited) with the Collaboration of some foreign countries.
- Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) With the help of Russia.
- Rourkela (Orissa) By German firm Kruppe-Demag.
- Durgapur (W. Bengal) With British aid.
- Bokaro (Jharkhand) With the help of Russia.
- New Steel Plants. The government has set up new steel plants at :
- Vishakhapatnam (Andhra Pradesh),
- Salem (Tamil Nadu),
- Vijaynagar (near Hospet, Karnataka).
The capacity of the different steel plants is being expanded. The production of pig iron and steel is being increased by setting up new mini plants based on scrap iron. At present there are 169 mini steel plants in India. India exports about 10 lakh tonnes of steel every year. In 1973 SAIL (Steel Authority of India Limited) has been established for the better management of these steel plants.
Q. 3. Describe the location and development of Cotton Textile Industry in India.
Ans. Cotton Textile Industry. India has a glorious past of cotton textile industry. The modern cotton mill was set up at Fort Gloster (Kolkata) in 1818. The real first cotton mill was established in 1854 in Mumbai. A large home market, manufacturing of textile machinery and abundant supply of cotton have led to the growth of this indusry in India. There are about 1719 textile mills scattered over 80 towns and the annual production of cloth is about 37.4 billion metres. India is the second largest producer of cotton textile in the world. The number of composite units is 282 while the number of spinning mills are 770. The per capita availability of cloth is 30 metres.
Distribution of Cotton Textile Industry
- Maharashtra. Mumbai is the oldest centre of cotton textile industry in India. Mumbai is known as ‘Cotton polis of India’. Nagpur, Pune, Sholapur, Amravati are other centres.
- Gujarat. Ahmedabad is the largest producer of cotton textiles in India. It is known as the “Manchester of India”. Ahmedabad is situaged in the heart of cotton growing area. Cheap land is also available.
- Tamil Nadu. The development of hydro-electricity in the south and cultivation of long staple cotton led to the location of this industry in Southern India. Madurai, Coimbatore, Salem and Chennai are main centres.
- West Bengal. Most of the mills are located at Kolkata in the Hooghly basin.
- Uttar Pradesh. Kanpur is the main centre and is called the “Manchester of Northern India”.
- The dispersal of this industry has led to the growth of the new centres like Bhopal, Gwalior, Bangalore, Phagwara, Bhiwani, Delhi and Kota.
Importance
- (i) Cotton textiles is the oldest and the biggest industry in India.
- About 64 million workers are engaged in this industry.
- It has the largest amount of capital (₹ 1300 crores) invested.
- It earns about a sum of ₹ 2000 crores as foreign exchange by export of manufactured goods.
- Many industries such as dyes, chemicals depend on cotton products.
Q. 4. How does industrial pollution degrade environment ?
Ans. The industries emit smoke and discharge liquids including polluted water. The smoke contains many undesirable gases such as carbon mono-oxide and sulphur dioxide. Air borne particles are in solid, liquid and gaseous form. The pollutants in atmosphere have tendency to form their own sinks and layers in atmosphere. The chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which come from aerosol sprays, nuclear weapons, refrigerators etc. have caused a hole in the ozone layer of atmosphere. This hole is allowing increased amount of ultraviolet rediations reaching the earth.
Similarly, industrial sources of water pollution are numerous. Industrial effluents contain many harmful chemicals. Even though industries are now banned from discharging effluents into rivers and other water bodies, these are still washed away into water bodies during rainfall, dust storms or floods. This principal, factories, producing effluents of various kinds are textiles, petroleum, leather, tanning, refining and electroplating.
Unwanted loud noise from transport vehicles including aircraft factories and hundreds of other sources is causing pollution and degradation of environment.
Q. 5. Describe the location and development of Electronic Industry in India.
Ans. Electronic Industry:
- Products. Electronic industry covers a wide range of products, ranging from transistor sets to television sets. It also produces telephone exchanges, cellular telecoms, pagers, computers and various other equipments used in post and telegraph offices. This industry also looks after the needs of defence equipments, railways, airways space flights and meterological departments.
- Importance. These industries have revolutionised the life of the masses and changed the country’s economy and the quality to human life. Television industry grew as a hardware in the nineties. Besides hardware, the country has earned high reputation in the development of software. It is fast growing sector of Indian economy. The production of audio system registered a phenomenal growth in recent years. The Indian electronic industry is contributing a lot to the space technology as well.
- Centres. Bangalore has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other major electronic goods producing centres are Hyderabad, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kanpur, Pune, Lucknow and Coimbatore. Software Technology Parks have been developed at 18 centres in the country.
- Production. These centres provide single window service and high data communication facility to the software experts. India produces electronic goods worth of ` 68,450 crore. Contribution of electronic goods to the total export trade of Indian is 2.4 per cent.
Q. 6. ‘The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns’. Support the statement by giving four measures that can be taken by industries to protect the environment.
Ans. Specific measures taken in this field, for controlling (protecting) the environment are :
- Water resources can be conserved in a number of ways, depending on uses of water. The industrial water waste can be treated at the source, in any one of the three scientific ways and can be reused. The three scientific ways of treatment are:
- Primary. The primary treatment aims at the physical removal of floatable and sedimentary wastes. It passes through many stages of filtration before being reused.
- Secondary. The secondary treatment involves the biological processes of removal of dissolved salts and other solids.
- Tertiary. The tertiary treatment focuses on the removal of excess nitrogen, phosphorus and other nutrients through biological, chemical and physical processes and may also involve recycling.
In all the above methods, sludge produced can also be treated and used in agriculture for plant growth.
- Rainwater harvesting and conservation of ground water resources to meet water scarcity.
- For mineral conservation, some important steps including raising efficiency in mining and recycling can be taken.
- Clear air is also essential for plant and animal life and we need to adhere to certain norms and acts.
- Steps can also be taken to reduce smoke released by vehicles and industries. 1
Q. 7. What are the problems being faced by the Indian Cotton Industry ? Suggest ways to solve them.
Ans. Problems of the cotton industry:
- There is a shortage of long staple cotton, therefore it is imported.
- Most of the cotton mills are not of economic size.
- Most of the machinery in mills is old, obsolete and inefficient.
- Productivity is low and the cost of production is high.
- India has lost many foreign markets due to strong competition.
Solution to the problem:
- Area under the long staple cotton should be increased.
- The old machines should be replaced by automatic looms.
- Sick mills should be abandoned.
- Efficient labour should be employed.
Q. 8. Describe the problems of the jute industry in India.
Ans. The problems faced by the Jute industry in India are as follows:
- There is a shortage of good quality raw jute.
- There is a strong competition from other countries in the international markets.
- The use of substitutes like paper, cloth and synthetic material is increasing. It has led to the decline in the demand of jute goods.
- The machinery is old and obsolete; therefore the cost of production is high.
- Sales promotion of jute carpets and packing material has not been done properly.
Q. 9. Why is the sugar industry located in Uttar Pradesh ? Give reasons.
Ans. Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of sugar in India. It has about 50% of the 460 sugar mills in the country and produces about 30 lakh tonnes of sugar. This is due to:
- Uttar Pradesh, with fertile soils, is the largest producer of sugarcane in India. So, sugarcane is easily available.
- Cheap labour is available from densely populated areas.
- There is a large market due to local demand.
- Coal is available from Jharia (Jharkhand).
- Cheap transport is available.
- Electricity is easily available to run the mills.
Q. 10. Give an account for the concentration of cotton textiles at Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
Ans. The first cotton textile mill in India was established in 1854 in Mumbai. A large home market, manufacturing of textile machinery and abundant supply of raw cotton has favoured the growth of this industry in India. There are 1,050 mills scattered over 80 towns of India. India is the world’s largest cotton textile producer. Mumbai is the oldest centre of cotton textile industry in India. Mumbai is known as the ‘Cottonopolis of India’.
The following factors have led to the concentration of this industry at Mumbai:
- Early start.
- Warm and humid climate.
- Nearness to the cotton producing areas of Maharashtra.
- Easy import of machinery, chemicals and long staple cotton from the port of Mumbai.
- Cheap skilled labour.
- Water power from Tata Hydro Electric Works.
- Large ready market.
- Facilities of trade, banking and transport.
Ahmedabad (Gujarat) is the largest producer of cotton textiles in India and is therefore known as the Manchester of India. Ahmedabad is situated in the heart of the cotton growing areas of Gujarat. Cheap land, water, power and skilled labour are also available. The combination of these factors have led to the growth of the cotton textile industry in Ahmedabad.
Q. 11. Why are jute industries mainly located in the Hooghly basin ?
Or
Explain any five factors that are responsible for the location of the ‘jute mills’ mainly along the banks of the ‘Hugli River’.
Ans. The jute industry is one of the oldest in the country. The first jute mill was established in Rishra, near Calcutta. (Kolkata) in 1859. Jute industry is major foreign exchange earner, accounting for about 30% of the world’s export of jute goods. The jute industry is concentrated in the Hooghly basin due to many favourable factors such as:
Locational Factors :
- Raw jute is available from West Bengal (about 70% of India’s jute production).
- Coal is available from the nearby Raniganj coal fields.
- Clear soft water is available, for washing jute, from Hooghly and other rivers.
- Cheap skilled labour is available from the densely populated adjoining states.
- Easy water transport is available through rivers and canals.
- Warm humid climate is favourable.
- Early start.
- Facilities of import and export through the Kolkata port.
Q. 12. Describe the importance, factor responsible for growth distribution and problem faced by sugar industry in India.
Ans. Sugar is an important article of food and has universal demand. Sugar is one of the major agro-based industries of India. India is regarded as the birth place of sugarcane and sugar.
Importance of sugar industry:
- India is the largest producer of sugar in the world.
- It is the second largest industry of India with the capital of ₹1,000 crore.
- About 3 lakh workers are engaged in this industry.
- About two crore farmers depend upon this industry.
- India exports about 5 lakh tonnes of sugar every year.
- Many industries, such as, alcohol, paper, wax, fertilisers, cattle-feed are based on its by-products.
India is one of the oldest producers of sugarcane in the world. The home industry was granted protection in 1932. Since then, the industry has rapidly developed. There are about 460 sugar mills in the country, 50% of them are in Uttar Pradesh. The total production of sugar in 2005-06 was about 200 lakh tonnes. North India (U.P. and Bihar) produces about 60% of sugar in India.
Factors of growth :
- Availability of sugarcane in Northern India
- Cheap and skilled labour
- Large demand
- Availability of coal
- Cheap transport.
Main centres :
- Uttar Pradesh. Saharanapur, Muzaffarnagar, Meerut, Gorakhpur, Sitapur and Bareilly.
- Bihar. Champaran and Patna.
- Maharashtra. Ahmednagar and Sholapur.
- Andhra Pradesh. Hyderabad.
- Punjab. Amritsar, Bhogpur, Phagwara, Batala and Saheed Bhagat Singh Nagar (Nawanshahar).
- Ratlam (Madhya Pradesh), Rohtak (Haryana) and Madurai (Tamil Nadu).
Problems. Sugar industry is facing some problems such as:
- Yield of sugarcane is low.
- Sugar content is low.
- It is a seasonal industry.
- There is absence of industries consuming the by-products of sugarcane.
- Cost of sugar is high.
Q. 13. How are industries responsible for polluting fresh water ? Suggest any three measures to reduce the water pollution.
Or
Suggest any five measures to control industrial pollution in India.
Ans. Environmental pollution is becoming a serious problem for mankind. Industries have caused air, water, land and noise pollution. Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide gases cause air pollution. Smoke from chemical industries and burning of fossil fuels cause hazards. Bhopal Gas Tragedy is an example. Industrial wastes dumped into lakes and seas cause water pollution. Wastes from Nuclear plants cause cancer. Industrial processes also cause noise pollution.
The National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC), a major Government of India undertaking, has adopted an aggressive approach for the task of preserving and protecting our natural environment.
- Optimise equipment utilisation and upgrade the existing facilities.
- Minimising waste generation and maximising the use of wastes, like ash from power plants by supplying the same to the bricklaying industries free of cost.
- It has also adopted some innovative techniques and passed on the technology to small bricklayers.
- To reduce pollution of all types, techniques such as-waste management, recycling of resources, etc., are being adopted on a regular basis.
- It has also embarked on public awareness measures, to prevent industries from degrading the environment.
MAP SKILLS
Q. 1. On the outline map of India, locate and label the following:
1. A town called the ‘Manchester of India’; 2. Coimbatore; 3. A woollen textile centre in Punjab; 4. Kanpur; 5. A silk textile centre in Karnataka; 6. A steel plant in Chhattisgarh; 7. Salem; 8. A Software park in Rajasthan; 9. Noida.
Ans.
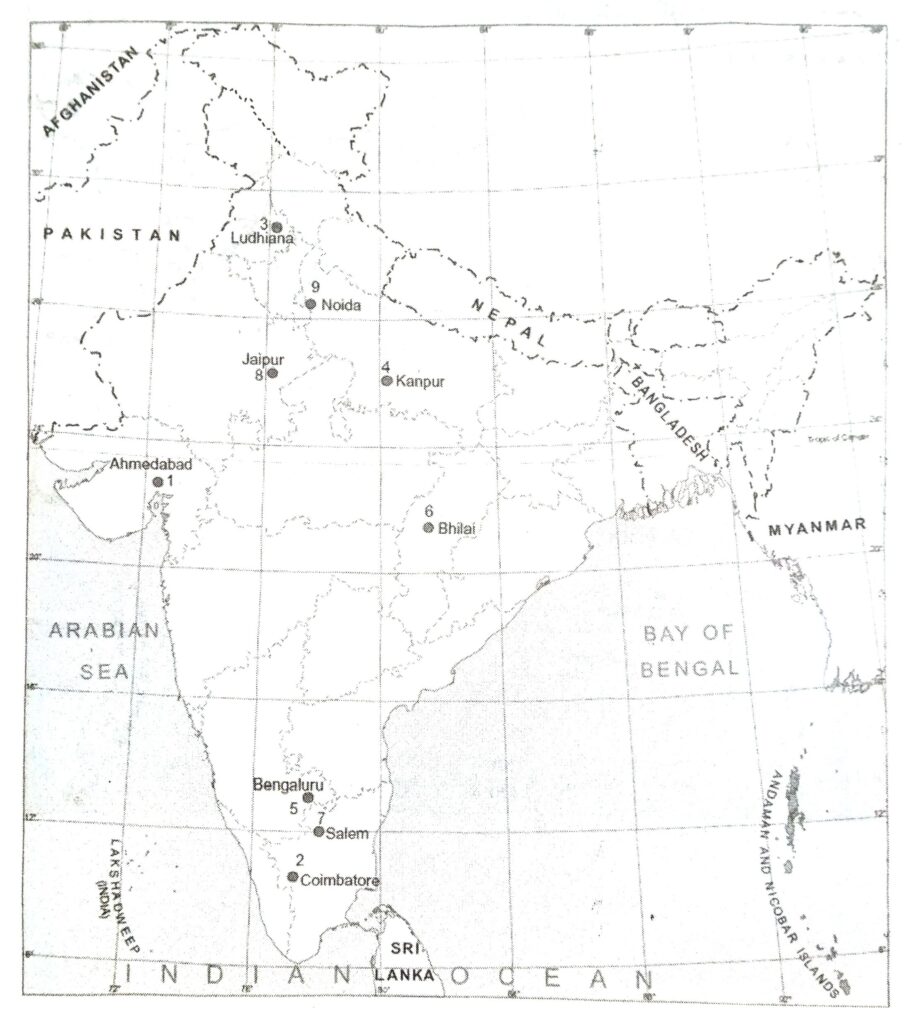
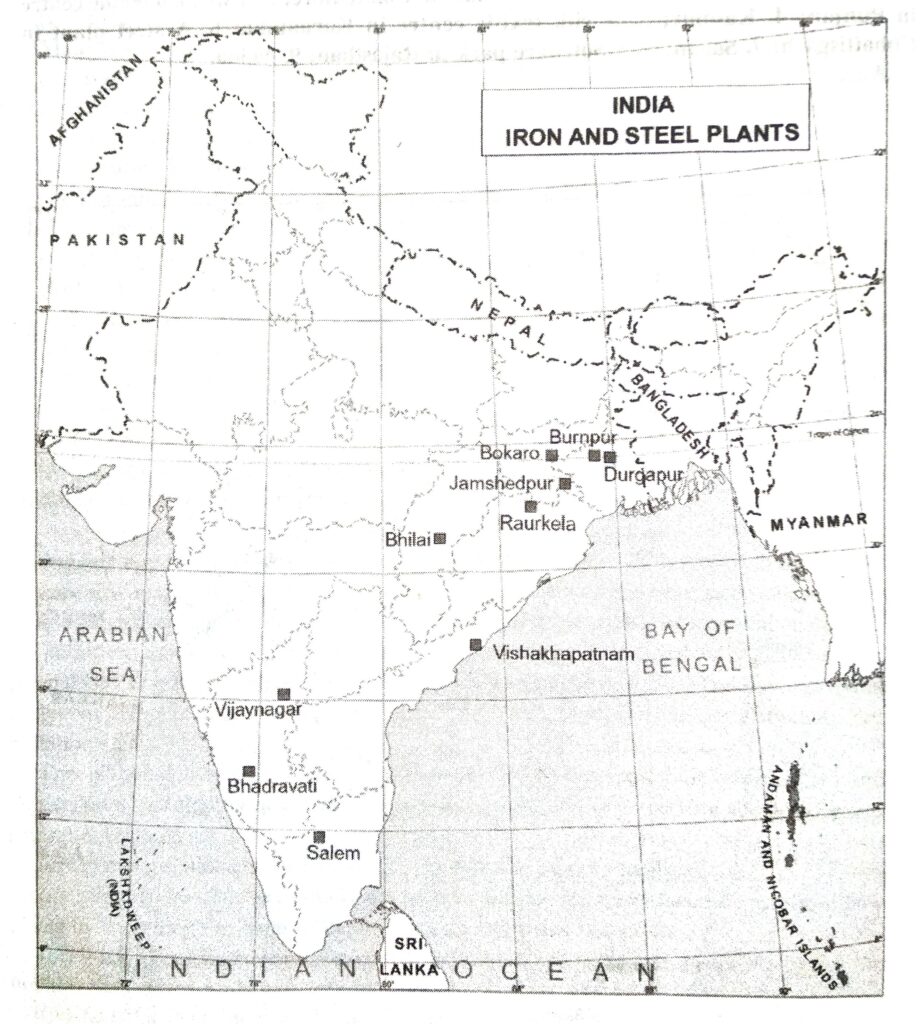
Q. 2. On the political map of India, locate and mark the iron and Steel plants.
Ans.
Q. 3. On the political map of India, locate and mark the major textile industries of India.
Ans.

Q. 4. On the political map of India, locate and mark the major software technological and software electronic centres.
Ans.

Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here