PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
PSEB 9th Class Science Solutions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
→ Matter: It is anything that occupies space, has mass, and can be judged by any one or more of the known five physical senses.
→ Early Indian philosophers classified matter into five basic elements called Panch Tatva. These are air, earth, fire, sky, and water.
→ Modern-day scientists have classified matter on the basis of its physical properties and chemical nature.
→ The matter is made up of extremely small particles and there are vacant spaces in them.
→ Particles of matter are always in motion and have kinetic energy.
→ The speed of particles increases with the increase in temperature.
→ The mixing up of particles of different substances is called diffusion.
→ All matter is made up of a large number of extremely small particles called molecules.
→ The material represents a particular kind of matter.
→ Material can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
→ Homogeneous material is a material that has a uniform composition throughout. It consists of a single phase.
→ Heterogeneous material is a material that does not have a uniform composition throughout. It consists of two or more phases.
→ The substance is a homogeneous material that is made up of only one kind of atom or material. (Substance always refers to pure substance).
→ Based upon its physical state, there are three states of matter, i.e. solid, liquid, and gas.
→ There are two new states of matter. These are plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate.
→ Solid: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass, volume, and shape.
→ Liquid: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass and volume but has no definite shape.
→ Gas: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass but has neither definite shape nor definite volume.
→ The forces of attraction between the particles are maximum in solids, intermediate in liquids, and maximum in gases.
→ The vacant spaces between the constituent particles and kinetic energy of particles are minimum in the case of solids, intermediate in liquids, and maximum in gases.
→ The arrangement of constituent particles is most ordered in the case of solids, in the case of liquids the layers can slip over each other while in the case of gases, there is no order, particles can move randomly.
→ The different states of matter are interconverted by changing temperature or pressure or both.
→ Melting point is the temperature at which solid changes into a liquid state.
→ The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid changes into vapour under atmospheric pressure. At boiling point, vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to atmospheric pressure.
→ Boiling is a bulk phenomenon as it involves the whole of the liquid.
→ The rate of evaporation depends upon the surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
→ The slow passing out of molecules of a liquid into a gaseous state at a temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
→ Evaporation causes cooling. It is a surface phenomenon.
→ Boiling is a fast process whereas evaporation is a slow process.
→ Sublimation is the process due to which a solid directly changes into the gaseous state on heating and a gaseous state directly changes into a solid-state on cooling without changing into the liquid state.
→ Vapour is a substance that exists in the gaseous state at a temperature lower than the boiling point of its liquid state.
→ Temperature on Kelvin scale = 273 + Temperature on centigrade scale. (T K = 273 + t°C) Water freezes at 0°C or 273 K.
→ Water boils at 100°C or 373 K.
→ Units of Latent heat of fusion are kJ/kg or kcal/kg
→ Units of Latent heat of vaporisation are kJ/kg or kcal/kg
→ F−32/9=C/5
F = Temperature on Fahrenhiet scale.
C = Temperature on Centigrade scale.
Some measurable quantities and their units are:
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol |
| Temperature | kelvin | K |
| Length | metre | m |
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Weight | newton | N |
| Volume | cubic metre | m3 |
| Density | kilogram per cubic metre | Kg m-3 |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa |
→ Matter: It is anything that occupies space, has mass, and can be judged by any one or more of the known five physical senses.
→ Panch Tatva: Indian philosophers classified matter into our basic elements called Panch Tatva. These are air, earth, fire, sky, and water.
→ Diffusion: It is the property of the mixing of particles of two or more substances.
→ Solid: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass, volume, and shape.
→ Liquid: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass and volume but has no definite shape.
→ Gas: It is that state of matter which has a definite mass but has neither definite shape nor definite volume.
→ Density: It is the mass per unit volume of a substance.
→ Melting point: It is the temperature at which solid changes into the liquid state.
→ Fusion: It is the process of conversion of a solid into a liquid.
→ Solidification or freezing: It is the process of conversion of a liquid into a solid.
→ Sublimation: It is the process due to which a solid directly changes into the gaseous state on heating and a gaseous state directly changes into the solid state on cooling without changing into a liquid state.
→ Latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at its melting point.
→ Latent heat of vaporisation is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure and at its boiling point.
→ Boiling is a bulk phenomenon as it involves the whole of the liquid.
→ Boiling point: It is the temperature at which a liquid changes into vapour under atmospheric pressure.
→ Evaporation: The slow passing out of molecules of a liquid into a gaseous state at a temperature below its boiling point.
→ Dry Ice: Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice.
→ Freezing point: It is the temperature at which a liquid substance changes into a solid substance.
→ Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG): When butane is subjected to the action of high pressure, it is liquid to give LPG which is used as a fuel.
→ Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): When natural gas is subjected to the action of high pressure it gets liquified to give CNG which is used as a fuel for automobiles.
→ Vapour: It is a substance that exists in the gaseous state at a temperature lower than the boiling point of its liquid state.
PSEB 9th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Give important characteristics of solid state.
Answer:
Characteristics of solid state:
- The solids have definite mass, volume and shape.
- The particles in a solid state are closely packed and the empty spaces in them are negligible.
- The solids are rigid.
- A solid does not undergo a change in shape easily.
- The solids can have any number of free surfaces.
- There are large attractive forces between the molecules in a solid.
- Solids have high densities.
- A solid always tends to resist any change in its structure.
- The solids don’t show the property of diffusion.
Question 2.
Give important characteristics of the liquid state.
Answer:
Characteristics of the liquid state:
- A liquid has a definite mass and volume but no definite shape.
- A liquid can take the shape of a container.
- Liquids have only one free surface.
- The vacant spaces between the molecules of liquid are more as compared to solids.
- The attractive forces between the molecules in a liquid state are lesser than in the solids.
- The liquids have lower densities as compared to solids.
- The liquids show the property of diffusion.
- On heating a liquid, the molecules of it move apart, hence the liquids can expand on heating.
Question 3.
Give important characteristics of gas.
Answer:
Characteristics of a gas:
- A gas has definite mass but it has neither definite shape nor definite volume.
- The gases can occupy the whole space available to them.
- There are negligible attractive forces between the molecules of a gas.
- The gases have no free surface.
- There are large vacant spaces between the molecules of a gas.
- The gases show the property of diffusion.
- Gases have very low densities as compared to the solids and liquids.
- The molecules in a gas have high kinetic energies.
- There is no effect of gravity on the motion of the molecules of a gas.
- The gases exert equal pressure in all the directions on the walls of the container.
- The gases are highly compressible.
Question 4.
Give the main postulates of kinetic theory of matter.
Answer:
The main postulates of kinetic theory of matter are:
- All matter is made up of a large number of extremely small particles called molecules (sometimes atoms or ions).
- The molecules are always in a state of rapid random motion.
- The molecules possess kinetic energy.
- There are attractive forces between the molecules.
- The attractive forces between the molecules of same kind are called cohesive forces and the attractive forces between the molecules of different kinds are called adhesive forces.
- The kinetic energy of the molecules increases with the increase in temperature.
- As the distance between the molecules increases, the magnitude of attractive forces between the molecules decreases.
Question 5.
Distinguish between solids, liquids and gases.
Answer:
The main points of differences are:
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gss |
| 1. Packing of Particles | Most closely packed | Loosely packed | Large vacant spaces between the particles |
| 2. Energy | Particles have least energy | Particles have higher energies than in solids | Particles have high energies |
| 3. Shape | Definite | Take the shape of the container | Take the shape of container |
| 4. Volume | Definite | Definite | No definite volume |
| 5. Density | High | Low | Very low |
| 6. Compressibility | Not possible easily | More than in solids | High |
| 7. Number of free surfaces | Any number | One | No |
| 8. Rigidity | High | Low | Not rigid |
| 9. Fluidity | Don’t show | Show | Maximum fluidity |
| 10. Intermolecular spaces | Very small | Small | Large |
| 11. Thermal expansion | Very low | More than solids | Very large |
| 12. Interparticle attractive forces | Very large | More than in gases | Negligible |
Question 6.
How will you explain the three states of matter on the basis of Kinetic Model?
Answer:
Solid: In solids the constituent particles are closely packed and there are large attractive forces between them. Therefore, the particles have low kinetic energies and can’t move from one position to another but they have only vibratory motion. Hence solids have definite shapes and definite volumes.
Examples: Wood, rock, copper, iron, cement, stone etc.
Liquid: In liquids the molecules have higher kinetic energies, distances between the molecules are more and attractive forces between the molecules are small. Therefore, the molecules of a liquid can move from one position to another within the liquid. Hence the liquid can take the shape of the container. But the volume of the liquid remains fixed because the molecules can’t leave the liquid.
Examples: Alcohol, milk, benzene, kerosene oil, petrol etc.
Gas: In gases, the molecules have high kinetic energies, there are large vacant spaces between the molecules and there are negligible attractive forces between the molecules. Therefore, in gases, molecules can move randomly and occupy the whole space available to them. Hence, they don’t have definite volumes and shapes.
Examples: Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur dioxide, carbon dioxide etc.
Question 7.
Define the terms given below and answer the questions associated with them.
(a) Sublimation: Which of the following substances sublime?
Ice, mercury, dry ice, iodine.
(b) Solid: Why do not solids diffuse in one another?
(c) Liquid: Why do liquids flow?
(d) Freezing point: What is the freezing point of water?
(e) Gas: Why are gases compressible and show diffusion?
Answer:
(a) Sublimation. It is the process in which a solid directly changes into vapour on heating and on cooling the gas directly changes into solid.
Dry ice and iodine sublime.
(b) Solid. It is that state of matter which has definite mass, volume and shape, e.g. sugar, rubber, table, stone etc.
The solids don’t diffuse because in the solid state the vacant spaces between the molecules are very small and molecules of a solid can’t move from one position to another.
(c) Liquid. A liquid is that state of matter which has definite mass and volume but has no definite shape, e.g. milk, petrol, kerosene oil, water etc. Liquids flow because the attractive forces between the molecules of a liquid are very small and the molecules can freely move within the liquid.
(4) Freezing point. It is the temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid state by giving out heat energy. For example, freezing point of water is 0°C.
(e) Gas. It is defined as that state of matter which has definite mass only but has neither definite shape nor definite volume. For example, carbon dioxide, oxygen, hydrogen, ammonia etc.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What are the necessary conditions for a substance to be a
1. Solid
2. Liquid and
3. Gas?
Answer:
1. Solid: The melting point of a substance is above room temperature at the atmospheric pressure.
2. Liquid: The melting point of the substance is below room temperature and boiling point is above room temperature under atmospheric pressure.
3. Gas: The boiling point of the substance is below room temperature under atmospheric pressure.
Question 2.
What are the two new states of matter in addition to solid, liquid and gases states?
Answer:
These are:
1. Plasma: It is produced in stars at very high temperature.
2. Bose-Einstein condensate: It is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density to super low temperature.
Question 3.
Heat, light, shadow, love, radio waves are not considered as matter, why?
Answer:
This is because these are massless and do not occupy space.
Question 4.
Solids have definite shapes and volumes, why?
Answer:
This is because:
- The vacant spaces between the constituent particles are very small.
- There are large attraction forces between the constituent particles.
Question 5.
List the factors which affect evaporation.
Answer:
These are:
- Exposed surface area
- Temperature
- Humidity in the air
- Wind speed.
Question 6.
Why is sponge solid although it can be compressed?
Answer:
This is because sponge has minute holes in which there is entraped air. When it is pressed, the air is expelled out.
Question 7.
Rubber band can change its shape, is it a solid?
Answer:
Rubber band is a solid because it changes its shape under force and return to its original state when the applied force is removed.
Question 8.
Indicate which of the following don’t constitute matter?
Car, truck, heat, light, sound, TV waves, radio waves, cement, love, hate, cotton cloth, rock.
Answer:
Heat, light, sound, TV waves, radio waves, love, hate.
Question 9.
What happens when the vacant spaces between the particles of a liquid decreases? How is this possible?
Answer:
The liquid will change into solid. This is carried out by decreasing the temperature or cooling the liquid.
Question 10.
Why do we observe water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice cold water?
Answer:
This is because water vapour present in air, on coming in contact with glass containing ice-cold water lose energy and get converted into liquid state which appear as water droplets.
Question 11.
Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
Answer:
This is because in summer, we perspire more and cotton being a good absorber of water, absorbs the sweat and exposes it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation.
Question 12.
Name the change of state during the following changes:
(a) Drying of wet clothes.
(b) Melting of wax when kept in sunshine.
(c) Melting of ice.
(d) Formation of clouds.
(e) Naphthalene balls become smaller when kept in air.
Answer:
(a) Liquid to gaseous state.
(b) Solid to liquid state.
(c) Solid to liquid state.
(d) Liquid to gaseous state.
(e) Solid to gaseous state.
Question 13.
State your observations in the following cases:
(a) Ammonium chloride is heated in a hard glass test tube.
(b) Carbon dioxide is compressed to 70 times the atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
(a) When ammonium chloride is heated in a hard glass test tube, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride fill the tube and deposit to give a white powder near the mouth of the tube (cooler parts).
(b) When carbon dioxide is compressed to 70 atmospheric pressure, it changes into solid state.
Question 14.
What is the difference between gas and vapour?
Answer:
- A gas is a substance which exists in the gaseous state even at room temperature. e.g. oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen etc.
- A vapour is a substance which can exist in the gaseous state at a temperature lower than that of its boiling point, e.g. water vapour, iodine vapour etc.
Question 15.
Why does a gas fill the container completely?
Answer:
The molecules in a gas are far apart and are in a state of rapid random motion in all possible directions with very high speeds. They move throughout the container in which they are put. Thus, a gas fills the container completely.
Question 16.
How is the liquid state different from the gaseous state?
Answer:
The liquid state is different from the gaseous state in terms of magnitude of attractive forces between the molecules.
Question 17.
Complete the following statements:
(a) The process of liquid changing into solid is called
(b) The process of gas changing into liquid is called
(c) The process of liquid changing into gas is called
(d) The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid is called
Answer:
(a) Solidification
(b) Condensation or Liquefaction.
(c) Evaporation
(d) Melting point.
Question 18.
What are the uses of interconversion of matter?
Answer:
The uses of interconversion of matter are:
- Water is converted into steam by heating. Steam is used to run turbines and to generate electricity.
- Metals are melted by heating and these molten metals can be converted into alloys and cast into machinery parts.
- Water can be changed into steam as well as ice. Therefore, in nature, ice (or snow), liquid water and water vapour are available.
Question 19.
Give the important properties on the basis of which the three states of matter can be distinguished.
Answer:
The three states of matter can be distinguished on the basis of shape, volume, compressibility, packing of molecules, number of free surfaces etc.
Question 20.
What is the importance of (a) melting point of solid and (b) boiling point of a liquid?
Answer:
(a) A pure solid has a sharp melting point. The impurities decrease the melting point of a solid. Therefore, melting point is used to check the purity of a solid compound.
(b) A pure liquid has a sharp boiling point. The impurities increase the boiling of liquid. Therefore, boiling point is used to check the purity of a liquid.
Question 21.
Give two differences between boiling and evaporation.
Answer:
| Boiling | Evaporation |
| 1. It takes place at a fixed temperature called boiling point of the liquid. | 1. It takes place at all temperatures. |
| 2. It is a fast process. | 2. It is a slow process. |
Question 22.
Name five substances which are solids, five substances which are liquids and five substances which are gaseous at room temperature.
Answer:
- Solids: Iron, copper, silver, glass and wood.
- Liquids: Water, milk, mercury, kerosene oil and petrol.
- Gases: Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium.
Question 23.
Represent interconversion of states by using a figure.
Answer:
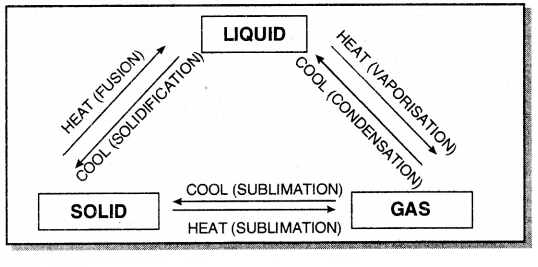
Question 24.
State what is observed when iodine is heated in a test tube as shown below.
Answer:
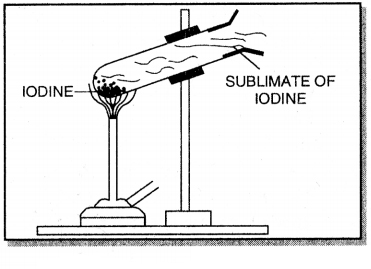
When some crystals of iodine are heated slowly in a test tube, the shiny grey iodine changes directly into vapour without melting. The vapour deposit as grey particles called sublimate on the upper cooler parts of the tube.
Question 25.
Why do gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume?
Answer:
In gases
(a) there are large spaces between the molecules of a gas.
(b) the molecules have high kinetic energies and
(c) there are negligible attractive forces between the molecules of a gas.
Hence the molecules in a gas have random motion. Therefore, gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
Question 26.
Give an experiment to prove that gases are more compressible as compared to liquids.
Answer:
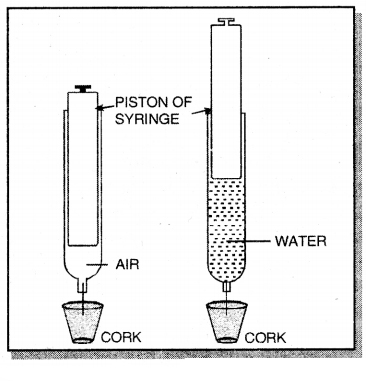
- Take a 100 ml syringe and close its nozzle by inserting it in a rubber cork or stopper. Remove the piston from the syringe so that whole of syringe is filled up with air.
- Apply a little vaseline to the piston and insert the piston. Compress piston and it moves downwards easily.
- Hence air is compressed to a very small volume.
- Now fill the syringe with water and repeat the above experiment. The piston moves hardly downwards, indicating that there is a negligible compression in volume.
- The above experiment indicates that gases are highly compressible as compared to liquids.
Question 27.
Which phenomenon occurs during the following changes:
- Size of naphthalene balls decreases
- Wax melts in the sun
- Drying of wet clothes
- Formation of clouds.
Answer:
- Sublimation
- Fusion
- Evaporation
- Condensation.
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Why do things around our surroundings look different?
Answer:
This is due to different shapes, sizes and textures.
Question 2.
Define matter.
Answer:
Everything in this universe is made up of material which occupies space, has mass and can be judged by any one or more of the known five physical senses is called matter.
Question 3.
Give five examples of matter.
Answer:
Air, food, stove, water, plants.
Question 4.
What are Panch Tatva?
Answer:
Early Indian philosophers classified matter in the form of five basic elements called Panch Tatva.
Question 5.
Name the Panch Tatva?
Answer:
Air, earth, fire, sky and water.
Question 6.
How many basic elements were there according to ancient greek philosophers?
Answer:
Four.
Question 7.
What are the basic elements according to greek philosophers?
Answer:
Earth, fire, air and water.
Question 8.
How do modem day scientists classify matter?
Answer:
Based upon their physical properties and chemical nature.
Question 9.
How is matter produced?
Answer:
It is composed of particles.
Question 10.
Why does a large volume of waier get coloured due to a few crystals of potassium permanganate?
Answer:
This is because a single crystal of pota .sium permanganate is made up of millions of tiny particles.
Question 11.
How small are particles of matter?
Answer:
The particles of matter are very very small beyond our imagination.
Question 12.
What is in between particles of matter?
Answer:
There are vacant spaces between particles of matter.
Question 13.
Why do common salt, sugar and dettol dissolve in water?
Answer:
This is because there are large vacant spaces between the particles of matter.
Question 14.
Why does the smell of lighted incence stick spreads out to a large space?
Answer:
This is because particles of a matter are in motion.
Question 15.
Why does common salt dissolve in water?
Answer:
This is because particles of common salt get into the vacant spaces between particles of water.
Question 16.
How will you check purity of honey?
Answer:
If honey falls into water in a stright line, it is a pure honey.
Question 17.
What is the effect of temperature on the particles?
Answer:
Increase in kinetic energy of particles.
Question 18.
Why are particles of a matter always in motion?
Answer:
This is due to kinetic energy.
Question 19.
Define diffusion.
Answer:
It is the mixing up of particles of two or more substances.
Question 20.
What is the effect of temperature on diffusion?
Answer:
Diffusion becomes faster.
Question 21.
What is the effect of pressure on particles of a matter?
Answer:
Pressure keeps particles of matter together.
Question 22.
What are the different stages of matter based upon physical states?
Answer:
Solid, liquid and gas.
Question 23.
Give three characteristics of solids.
Answer:
The solids have definite masses, volumes and shapes.
Question 24.
What is the effect of applied force on solids?
Answer:
The solids retain their shapes on applying force but they break when a large force is applied on them but they don’t change their shapes.
Question 25.
Rubber band can change its shape when stretched? Is it a solid?
Answer:
It is solid because it changes its shape under force and returns to its original shape when applied force is removed. It breaks when a very large force is applied to it.
Question 26.
Sugar, common salt etc. take the shape of containers although these are solids?
Answer:
This is because the shapes of their crystals do not change.
Question 27.
Why does a rubber can be compressed?
Answer:
This is due to the presence of air in the holes present in it and on compression air is expelled out.
Question 28.
What is liquid?
Answer:
A liquid has a definite mass and volume but has no definite shape.
Question 29.
Due to which property aquatic animals survive in water?
Answer:
This is due to the presence of oxygen dissolved in water.
Question 30.
Name the gas which gets dissolved in water and is necessary for plants.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 31.
Which form of matter can diffuse in liquids?
Answer:
Solids, liquids and gases.
Question 32.
Liquids show faster diffusion than solids. Why?
Answer:
This is because in liquids there are more vacant spaces and molecules can move freely.
Question 33.
Out of solids, liquids and gases which show maximum compressibility?
Answer:
Gases.
Question 34.
Which compressed gas is used in automobiles?
Answer:
Compressed natural gas (CNG).
Question 35.
Which gas is used as fuel in houses?
Answer:
Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG).
Question 36.
The smells of perfume and lighted incense stick spread rapidly, why?
Answer:
This is because there are large vacant spaces between the molecules and the molecules are in motion with very high speeds.
Question 37.
What are the different states of water?
Answer:
These are solid-ice, liquid-water and gas-water vapour.
Question 38.
Give characteristics of solids.
Answer:
The solids are generally hard. They cannot be compressed. They have definite shapes and definite volumes.
Question 39.
Give characteristics of liquids.
Answer:
They have definite volumes but have no definite shapes. They can be compressed slightly. They can flow.
Question 40.
Give characteristics of gases.
Answer:
The gases have neither definite shapes nor volumes. They are highly compressible.
Question 41.
Give four examples each of solids, liquids and gases.
Answer:
Solids: Wood, stove, sugar, common salt.
Liquids: Water, milk, oil, alcohol.
Gases: Oxygen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide.
Question 42.
What is the full form of CNG?
Answer:
Compressed Natural Gas.
Question 43.
Why do solids have definite shapes?
Answer:
This is because vacant spaces between molecules of a solid are very small and there are large attractive forces between them.
Question 44.
Why does a tyre can be inflated with large volume of air?
Answer:
This is because gases can bear high pressure.
Question 45.
Why don’t gases have definite shapes and volumes?
Answer:
This is because there are large vacant spaces between the molecules of a gas and these are in motion.
Question 46.
How many states of water are there?
Answer:
Three.
Question 47.
The temperature at which a solid melts is called?
Answer:
Melting point.
Question 48.
What is the SI unit of temperature?
Answer:
Kelvin.
Question 49.
0°C = ………. K.
Answer:
0°C = 273.16 K.
Question 50.
How is kelvin temperature changed to centigrade temperature?
Answer:
By substracting 273 from it.
Question 51.
How is centigrade temperature changed in kelvin temperature?
Answer:
By adding 273 to it.
Question 52.
Define fusion.
Answer:
The process of conversion of solid into liquid is called fusion.
Question 53.
What is the boiling point of water?
Answer:
373 K (100°C).
Question 54.
Define sublimation.
Answer:
It is the process of direct conversion of solid into gaseous state and back without changing into liquid state.
Question 55.
What is dry ice?
Answer:
Solid carbon dioxide.
Question 56.
What is the unit of pressure?
Answer:
Atmosphere (atm).
Question 57.
What is the SI unit of pressure?
Answer:
Pascal (Pa).
Question 58.
What is normal atmospheric pressure?
Answer:
The atmospheric pressure at sea level is called normal atmospheric pressure. It is taken as 1 atmosphere.
Question 59.
How does a liquid change into vapour without boiling?
Answer:
Due to evaporation.
Question 60.
Give one example of evaporation.
Answer:
Drying of wet clothes in sunlight.
Question 61.
Name the process of conversion of liquid into gaseous state without boiling.
Answer:
Evaporation.
Question 62.
Name the factors which increase rate of evaporation?
Answer:
These are increase in surface area, increase in temperature, decrease in humidity.
Question 63.
Why rate of evaporation increases with the increase in temperature.
Answer:
This is because kinetic energy of particles increases.
Question 64.
Why do clothes dry faster with the increase in speed of wind?
Answer:
This is because water vapour evaporates along with air and amount of water vapour decrease near the surface of clothes.
Question 65.
What is humidity?
Answer:
The amount of moisture present in the air is called humidity.
Question 66.
How is vaporisation related to humidity?
Answer:
With the increase in humidity in air, rate of evaporation decreases.
Question 67.
Why are clothes spread out for drying?
Answer:
This increases surface area and hence rate of evaporation increases.
Question 68.
How is cooling related to evaporation?
Answer:
With the increase in evaporation, cooling increases.
Question 69.
Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
Answer:
This is because in summer we perspire more and cotton being a good absorber of water, absorbs the sweat and exposes it to the atmosphere for evaporation which causes cooling.
Question 70.
How are particles present in plasma?
Answer:
In plasma, the particles have high energy and are excited. These particles are present in the form of ionised gas.
Question 71.
Wha is present in florescent tube and neon bulb?
Answer:
Plasma.
Question 72.
Why do sun and stars glow?
Answer:
Due to plasma.
Question 73.
Why is plasma produced in stars?
Answer:
Due to high temperature.
Question 74.
How is BEC produced?
Answer:
It is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density to super low temperature.
Question 75.
Who were awarded Noble Prize for Bose-Einstein Condensate state?
Answer:
Eric A. Cornell, Wolfgang Ketreley and Carl E. Wieman.
Question 76.
Which website is used to get information regarding fourth and fifth state of matter?
Answer:
www.chem4kids.com.
Question 77.
The phenomenon occuring during drying of wet clothes is
Answer:
Evaporation.
Question 78.
The intennolecular spaces are …………. in solids.
Answer:
Large or maximum.
Question 79.
A vapour on cooling changes into …………. and on further cooling changes into ………… .
Answer:
liquid, solid.
Question 80.
Matter changes from one state to another either by raising the or lowering the …………. .
Answer:
temperature, temperature.
Question 81.
A change in which a solid, on heating, directly changes into …………. state and the …………. on cooling again changes into ………… state is called …………… .
Answer:
gaseous, gas, solid, sublimation.
Question 82.
The intermolecular spaces are in …………… solids and ……………. in gaseous.
Answer:
minimum, maximum.
Science Guide for Class 9 PSEB Matter in Our Surroundings InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer:
Chair, air, almonds, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Question 2.
Give reasons for the following observations:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches us several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food we have to go close. This is because the rate of diffusion of a gas increases with the increase in temperature. In hot food, the rate of diffusion is large but in cold food, the rate of diffusion is slow.
Question 3.
A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool, which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer:
The diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool because in water the attractive forces between the molecules are small.
Question 4.
What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Answer:
The characteristics of the particles of matter are:
- The particles of matter have vacant spaces between them.
- The particles of matter are always in motion.
- There are attractive forces between the particles of matter.
Question 5.
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density, (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density – air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Answer:
The increasing order of density is
Exhaust from chimneys < air < cotton < chalk < honey < iron.
Question 6.
(a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following:
rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Answer:
(a) Differences in the characteristics of states of matter:
| Characteristics | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| 1. Vacant spaces | Very small | Small | Very large |
| 2. Attractive forces between particles | Very large | Small | Negligible |
| 3. Compressibility | Negligible | Low | High |
| 4. Rigidity | High | Low | Not rigid |
| 5. Density | High | Low | Very Low |
| 6. Energy | Small | Large as compared to solid | Very high |
(b) Rigidity: It is the property by virtue of which a substance can retain its shape when a force is applied to it. Solids possess the property of rigidity.
- Compressibility: The property by virtue of which the volume of a substance can be decreased by applying force or pressure on it. Gases have high compressibility because of large vacant spaces between the molecules of a gas.
- Fluidity: It is the property by virtue of which the molecules of one substance can flow from one point to another. Liquids and gases possess fluidity.
- Filling a gas container: A gas fills the container because there are negligible attractive forces between the molecules of a gas and the molecules of a gas move with very high velocities in all possible directions.
- Shape: It is the definite geometrical arrangement of constituent particles of a substance. Solids have definite shapes.
- Kinetic energy: It is the energy possessed by a particle due to its motion.
- Density: Density of a substance is the mass per unit volume. Its units are g/cc or kg/m3.
Question 7.
Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which if is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same in solid block of wood we need a Karate expert.
Answer:
(a) This is because in a gas the attractive forces between the molecules are negligible and molecules of a gas move with very high speeds in all possible directions.
(b) This is due to the hits or bombardments of the molecules of a gas against the walls of a container.
(c) This is because it has a definite mass, volume and shape.
(d) This is because in air, the attractive forces between the particles are negligible but in a solid block of wood, there are large attractive forces between the constituent particles.
Question 8.
Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer:
Ice floats over water because ice has lower density than liquid water. This is because in ice for a given mass volume is more as compared to in liquid water.
Question 9.
Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K?
Answer:
(a) 300 K = 300 – 273 = 27°C.
(b) 573 K = 573 – 273 = 300°C.
Question 10.
What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 250°C
(b) 100°C?
Answer:
(a) Gas
(b) Gas
Question 11.
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer:
This is because the heat supplied is used to overcome the attractive forces between the particles i.e., there is change in potential energy.
Question 12.
Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer:
The atmospheric gases can be liquefied by cooling under pressure.
Question 13.
Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer:
On a hot dry day due to increase in temperature and lesser humidity the evaporation of water will be faster.
Question 14.
How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Answer:
This is because the water comes out from the pores of earthen pot (matka) and it evaporates. Due to evaporation it causes cooling.
Question 15.
Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer:
This is because the particles of acetone or petrol or perfume gain energy from our palms and surroundings and evaporate causing cooling.
Question 16.
Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Answer:
Because a saucer provides more surface area than a cup for evaporation of liquid into vapour and it causes a more cooling effect.
Question 17.
What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Answer:
White cotton clothes.
PSEB 9th Class Science Guide Matter in Our Surroundings Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Convert the following temperature to the Celsius scale:
(a) 293 K
(b) 470 K.
Answer:
(a) 293 K = 293 – 273 = 20°C
(b) 470 K = 470 – 273 = 197°C
Question 2.
Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale:
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C.
Answer:
(a) 25°C – 25 + 273 = 298 K
(b) 373°C = 373 + 273 = 646 K
Question 3.
Give reason for the following observations:
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer:
(a) This is because naphthalene sublimes i.e. it directly changes into vapour without melting.
(b) This is because the molecules of perfume are moving with very high velocities (i.e. diffusion) in all the directions.
Question 4.
Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles-water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer:
The increasing order of intermolecular forces of attraction is Oxygen < Water < Sugar.
Question 5.
What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 25°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 100°C?
Answer:
(a) At 25° C, water is liquid.
(b) At 0° C, water is solid (Ice).
(c) At 100° C, water is gas (Steam).
Question 6.
Give two reasons to justify that:
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer:
(a) At room temperature water is liquid because the attractive forces between the molecules of water are small and can move from one point to another.
(b) An iron almirah is solid because the molecules are held together by strong intermolecular attractive forces and the molecules or particles are very close to each other.
Question 7.
Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature ?
Answer:
Ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at 273 K, this is because in ice, the molecules have lower energy as compared to the particles in the liquid water at the same temperature (273 K) and require latent heat of fusion for melting.
Question 8.
What produces more severe bums: boiling water or steam?
Answer:
Steam produces severe burns as compared to boiling water. This is because in steam the molecules have higher kinetic energy than in boiling water.
Question 9.
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing state change-
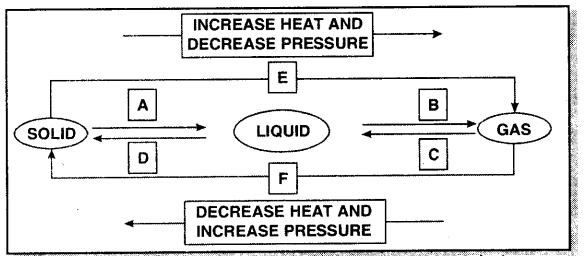
Answer:
A – Fusion
B – Vaporisation
C – Condensation
D – Solidification
E – Sublimation
F – Sublimation
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here