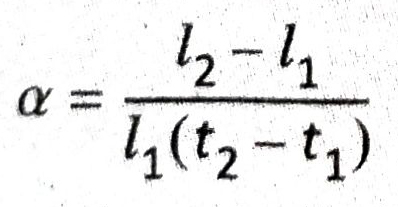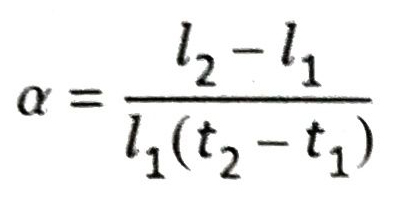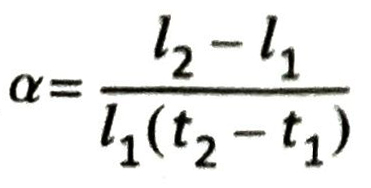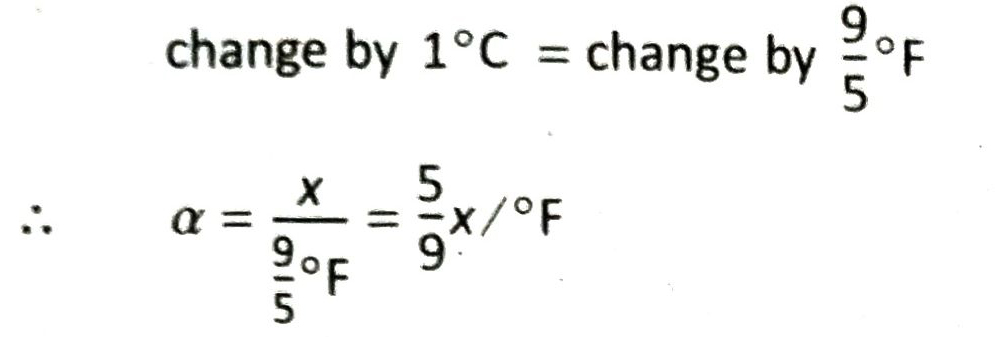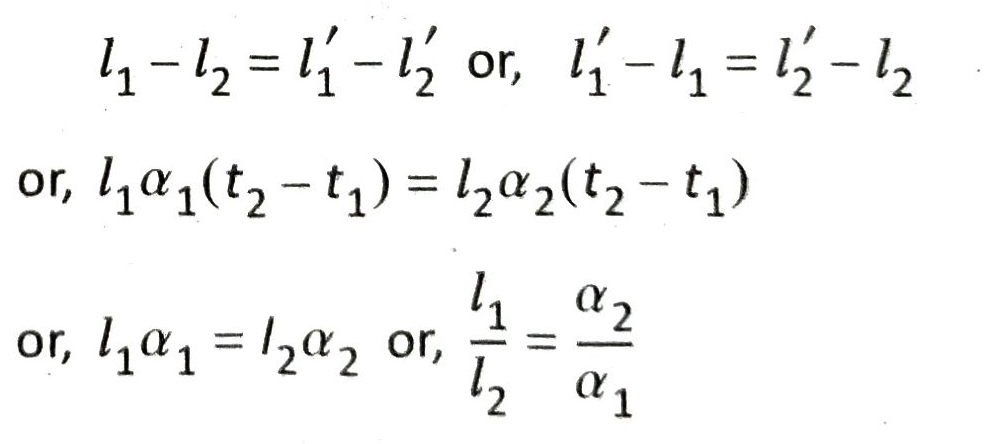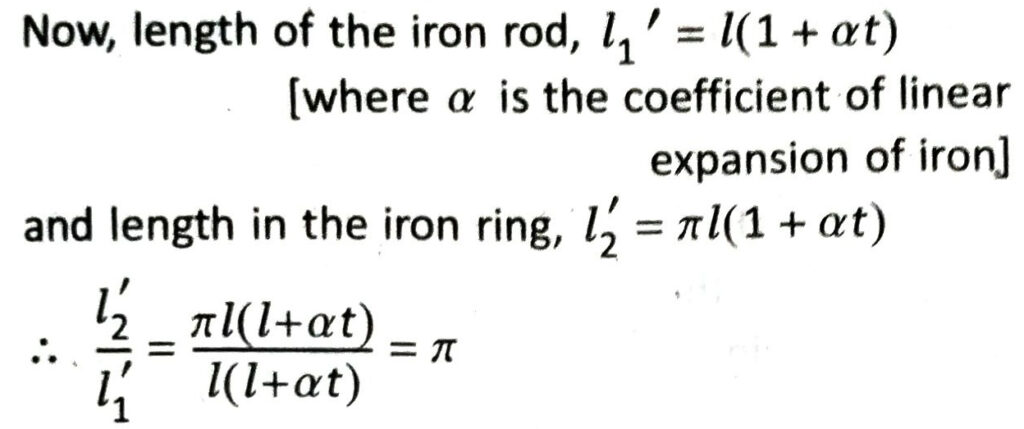WBBSE 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 4 Phenomena of Heat
West Bengal Board 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 4 Phenomena of Heat
WBBSE 10th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
Synopsis
Thermal Expansion of Solid, Liquid and Gas
- If the temperature of a solid substance is increased, its area and volume also expand. This phenomenon is called thermal expansion of a solid substance.
- Thermal expansion of a solid is of three types: (1) Expansion of length (2) Expansion of area (3) Expansion of volume.
- The coefficient of linear expansion of a solid is the fractional increase in its length per degree rise in temperature. It is generally denoted by a. If l1 and l2 are the lengths of a solid substance (say a metallic rod) at temperatures t1 and t2 respectively, then
- Unit of coefficient of linear expansion α
Therefore, unit of a is independent of unit of length and it depends on the unit of temperature. So, CGS unit of α is °C-1, in Sl it is K-1 and in FPS system it’s unit is °F-1.
- The change in temperature by 1°F = 5/9°C change in temperature
∴ value of α in Fahrenheit scale
(αF) = 5/9 × value of α in Celsius scale (αC)
TOPIC – A
Thermal Expansion of Solid, Liquid and Gas
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What is thermal expansion of a solid substance? There are two scales for measurement of length (distance). One is made of invar and the other of iron. Which one of these two is more suitable for measuring accurately the distance between two definite places in different times of the year, Give reason of your answer.
Ans. If the temperature of a solid substance is increased, the volume of the substance expand. This expansion due to the increase of temperature is called thermal expansion of a solid substance.
The temperature of a place is different during different seasons of the year. The distance between two places does not depend on the temperature. But if the measuring scale is made of a metal, the length of scale changes according to the temperature. As a result, different readings are found for the same length at different times of the year with this scale. Invar has a coefficient of linear expansion (1.2 × 10-6K-1 at 20°C) which is much lower than the coefficient of linear expansion of iron (11.8 × 10-6K-1 at 20°C). This means that the change in length of a scale made of invar is insignificant compared to the change in length of an equal scale made of iron. For this reason, a scale made of invar is more suitable for the measurement of distance.
Q.2 Write the expression for the coefficient of linear expansion of a solid. What do you mean by the statement that the coefficient of linear expansion of iron is 12 x 10-6/°C?
Ans. Suppose l1 is the length of a solid substance at temperature t1 and the length becomes l2 when the temperature is raised to t1.
If α is the coefficient of linear expansion of the solid substance, then according to definition,
The above statement means that if the temperature of an iron rod is increased by 1°C, 12 x 10-6 part of its original length increases.
Q.3 There are several rods of same length and made of the same substance. What is the change in their lengths for different increase in their temperatures? Show that the unit of coefficient of linear expansion does not depend on the unit of length but depends only on the unit of temperature. the unit of temperature.
Ans. The change in lengths of the rods made of the same substance and having same length is directly proportional to the change in temperature. Therefore more the temperature is increased, more is the change in length of the rod. The ratio between change in temperature and change in this length is constant.
Mathematically,
change in length ∝ change in temperature
or, (l2 – l1) ∝ (t2– t1)
Suppose, l1 is the length of a rod at temperature t1. It is heated to a higher temperature t2 when its length becomes l2.
Hence, coefficient of linear expansion,

is the ratio of two quantities having the 4₁ same dimension. So it has no unit. Therefore, coefficient of linear expansion depends only on the unit of (
t2–
t1), i.e., on the unit of temperature.
Q. 4 There are several rods of different lengths and made of the same substance. If the temperature of the rods is increased by the same amount, what is the change in their lengths? A stopper made of steel gets stuck firmly in the mouth of a bottle made of brass. How can you open it?
Ans. The change in length of the rods made of the same substance and of different lengths is directly proportional to the lengths of the rods for the same increase of temperature. In other words, more the initial length of the rod, more is the change of length of the rod. The ratio between the initial length and the change in length is a constant.
Mathematically, change in length x initial length
or, (l2 – l1) ∝ l1
The coefficient of linear expansion for brass is greater than that for steel. If the system is heated, expansion of brass is more than that of steel. As a result, the stopper is stuck all the more. But if the system is cooled, contraction of brass is more than that of iron. Hence, the stopper loosens and comes out.
Q.5 How does the length of a rod depend on the initial length of the expanding rod (l1) and on difference of temperature (Δt)? Establish a relationship between the coefficients of linear expansion in Celcius and Fahrenheit scales.
Ans. Expansion of length (Δl) is directly proportional to the initial length of the rod and increase in temperature (Δt), i.e.
Δl ∝ l1 (when At remains the same]
and Δl ∝ Δt [when l1 is constant]
∴ Δl ∝ l1 Δt [when both l1 and Δt change]
Let us assume that the coefficient of linear expansion of a solid substance, α = x/°C.
Again, we know that,
Hence, if the coefficients of linear expansion are αC and αF respectively, then
Q.6 Explain what happens when a bimetallic strip made of brass and iron is heated.
Ans. For the same increase in temperature, different solid substances of the same length have different amount of expansion. The coefficient of linear expansion of brass is more than that of iron. The lengths of brass and iron are the same in the bimetallic strip. As the linear expansion of brass is more than that of iron for the same rise in temperature, the bi-metallic strip bends with brass remaining outside.
Q.7 There is one rod of iron, one iron scale and one invar scale in a room. The temperature of the room changes every hour. By which scale, the length of the rod is to be measured so that no change of length is observed? Establish the condition to maintain a constant difference in the lengths of two rods at all temperatures.
Ans. For the same change in temperature, change in length of invar is negligible compared to the change in length of iron which is much more. As the rod is made of iron, its change in length per unit length is equal to the change in length per unit length of the scale, with the same change in temperature. As a result, no change in length of the rod is noticed if the length of rod is measured with the iron scale.
Let us assume that at temperature t1 , lengths of the two rods are l1 and l2 (l1 > l2). After the temperature increases to t2 , the lengths of these two rods become l’1 and l’2 respectively. Let the coefficients of linear expansion of these rods be α1 and α2 respectively.
According to the given condition,
This is the required condition.
Q.8 An iron rod is fixed along the diameter of a circular iron ring. If the system is heated uniformly, does the ring remain circular? Explain.
Ans. Suppose, the length of the iron rod, l1 = l
Let the length of the iron ring be l2.
So, diameter of the circle = l and length of the iron ring, l2 = πl
Suppose, increase in temperature of the system = t
As the ratio of the circumference of the circle and diameter remain the same in both the cases, the ring remains circular.
Q.9 Write the expression for the coefficient of surface expansion for solid. Show that the unit of coefficient of area expansion does not depend on the unit of area but only on the unit of temperature.
Ans. Let the coefficient of surface expansion be denoted by β.
If S1 and S2 are the surface areas of a solid at temperatures t1 and t2 respectively, then increase in surface area is (S2 – S₁) with a rise in temperature of (t₂ – t₁).
Here

is a ratio of two similar quantities and thus does not have any unit. Therefore, the unit of coefficient of surface expansion depends only on the unit of (t
₂ – t
₁) i.e., on the unit of temperature.
Q.10 On which factors and how does the surface expansion of a solid depend? Why is some gap left between two iron plates in a joint of a bridge?
Ans. Suppose, the surface area of a solid is S1 at temperature t1 . If the temperature is increased to t2 , area becomes S2.
Thus, expansion of area = (S2 – S1) and increase of temperature = (t₂ – t₁)
Therefore, expansion of area is directly proportional to the initial area of the solid and also on the increase in temperature.
∴ (S2 – S1) ∝ S1 [when (t₂ – t₁) remains the same]
and (S2 – S1) ∝ (t₂ – t₁) [when S1 is constant]
i.e., S2 – S1 ∝ t₂ – t₁ [when both S1 and (t₂ – t₁) are changing]
A solid gets expansion due to increase of temperature. The iron plates of the joints of a bridge are heated by the sun rays and require sufficient space for expansion. For this reason, some gap is left between the two plates. Without this gap, one iron plate puts pressure on another due to thermal expansion. As a result, the bridge may get damaged.
Q.11 Write down the expression for the coefficient of volume expansion of solid. Show that the unit of coefficient of volume expansion does not depend on the unit of volume but depends only on the unit of temperature.
Ans. Let the expression be denoted by γ.
Hence, unit of coefficient of volume expansion depends only on the unit of temperature.
Q.12 What do you mean by the statement that the coefficient of volume expansion of iron is 36 × 10-6/°C? A roof casting generally needs rods of iron but not of any other metal-explain why?
Ans. The coefficient of volume expansion of iron is 36 × 10-6/°C means that with a rise of temperature of 1°C, the volume increases by 36 x 10-6 of its initial volume.
Alternative answer: The coefficient of volume expansion of iron is 36 × 10-6/°C. Thus, if the temperature of 1 cm³ or 1 m³ of iron is increased by 1°C, the volume of iron increases by 36 × 10-6cm³ or 36 × 10-6m³.
During casting, iron rods are entered into concrete. In summer, temperature is high and so both concrete and rod undergo thermal expansion. On the other hand, temperature is low in winter and both of them contract. It has been found that the coefficient of expansion for both are almost equal. That is why only iron rods are used during casting. Expansion or compression of any other metal does not match with that of concrete and as a result, cracks develop in the casting.
Q.13 Two identical sheets, one of copper and the other of iron, are riveted together. What happens if this system is heated? What happens if the temperature of this system is decreased?
Ans. The coefficient of linear expansion of copper is greater than that of iron. So, with the same increase in temperature, linear expansion of copper is more than that of iron. As the two sheets are riveted together, this pair of sheets bend. Expansion of copper being more, it remains outside [Fig. 3].
With the decrease in temperature, this pair of sheets bend. Contraction of copper being more, it remains inside [Fig. 4].
Q.14 Establish the relation between apparent and real expansions of a liquid with the help of a simple experiment.
Ans. Experiment: At first, a glass flask fitted with a stopper is taken. A thin glass tube is entered through the stopper and a scale is fixed with the tube. A portion of the tube and the entire glass flask are filled with a coloured liquid. Let the initial level of liquid in the tube be A. Now this flask is immersed in a vessel filled with hot water. It can be observed that the level of liquid comes down from A to B. Then the level of liquid goes up slowly to C.
Conclusion: When the flask is immersed in hot water, glass gathers heat from water and expands itself. This is the reason why the level of liquid in tube comes down from A to B. Then heat is transmitted to liquid through glass and liquid expands so that its level in the tube goes up. From this experiment, it is clearly understood that the volume of the liquid in the glass tube between points A and B is the measure of expansion of the vessel and the volume of the liquid in the glass tube between points B and C is the measure of real expansion of the liquid. If we ignore the expansion of the vessel, the expansion of the liquid is called apparent expansion. Therefore, the volume of the liquid in the glass tube between points A and C represents the apparent expansion of liquid.
Here, BC = AB + AC
Hence, real expansion of the liquid = expansion of volume of the vessel + apparent expansion of the liquid.
Q.15 What is the coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid? What are the factors on which the apparent expansion of a liquid depends?
Ans. The coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid is the ratio of apparent expansion in volume to its original volume for each degree rise in temperature.
The apparent expansion of a liquid depends on the following factors: (1) Initial volume of the liquid (2) Increase of temperature (3) Nature of the liquid Substance of the vessel.
Q.16 Write the expression for the coefficient of real expansion of a liquid. What is the unit of this physical quantity?
Ans. Suppose, the volume of a definite mass of liquid is V₁ at temperature t₁ and if the temperature is increased to t₂, its real volume is V₂.
Therefore, coefficient of real expansion of the liquid,
Unit of the coefficient of real expansion of a liquid is °C-1 or °F-1 or K-1 .
Q.17 What is the coefficient of real expansion of a liquid? What are the factors on which the real expansion of a liquid depends?
Ans. The coefficient of real expansion of a liquid is the ratio of actual expansion in volume to its original volume for each degree rise in temperature.
The real expansion of a liquid depends on the following factors: (1) Initial volume of the liquid (2) Increase in temperature (3) Nature of the liquid.
Q.18 Between the coefficients of apparent and real expansions, which does measure the inherent property of a liquid?
Ans. To measure the coefficient of thermal expansion of a liquid, it must be kept in a vessel. The coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid depends on the coefficient of volume expansion of the vessel. For different vessels made of different substances, coefficients of apparent expansion are different; but the coefficient of real expansion remains unchanged. Therefore, between the coefficients of apparent and real expansions, coefficient of real expansion measures the inherent property of a liquid.
Q.19 What do you mean by apparent expansion and real expansion of liquid? A liquid has coefficient of apparent expansion but in case of a gas, why is the coefficient of apparent expansion not taken into consideration?
Ans. Apparent expansion of liquid: In case of a liquid kept in a vessel, if the expansion of the vessel is neglected, the expansion of the liquid that is obtained is called the apparent expansion of the liquid.
Real expansion of liquid: In case of a liquid kept in a vessel, if the expansion of the vessel is taken into consideration along with the apparent expansion of the liquid, the expansion of the liquid is called the real expansion of the liquid.
Both liquid and gaseous substances have to be kept inside a vessel and then heated. As a result, expansion of the vessel also takes place along with the expansion of liquid or gas. Expansion of solid is less than the expansion of liquid but, it cannot be neglected. But in case of a gas, expansion of the vessel is not considered as the expansion of solid is 1/100th part of the expansion of a gas taken in it. For this reason, coefficient of apparent expansion of gas is not taken into 100 account.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Unit of coefficient of surface expansion depends
A. only on the unit of area
B. only on the unit of temperature
C. on the units of area and temperature
D. on the units of temperature and time
Ans. B
2. Initial temperature at the time of expansion of gas is taken as
A. any temperature
B. 0K
C. 0°C
D. 4°C
Ans. C
3. Which of the following liquids displays anomalous expansion?
A. mercury
B. kerosene
C. glycerine
D. water
Ans. D
4. Expansion of the length of a solid depends on
A. initial length
B. increase in temperature
C. the material
D. all of the above
Ans. D
5. Which of the following has practically no expansion in spite of increase in temperature?
A. iron
B. nickel
C. steel
D. invar (nickel-iron alloy)
Ans. D
6. If the temperature of a metallic rod of length 4 m is increased by 2°C, its length increases by 88 × 10-6m. a of this rod is
A. 9 × 10-6°C-1
B. 10 × 10-6°C-1
C. 11 × 10-6°C-1
D. 12 × 10-6°C-1
Ans. C
7. The temperatures of two iron rods of lengths 1 m and 2 m are increased to the same extent. What is the ratio of expansion of their lengths?
A. 1:2
B. 1:4
C. 1:8
D. 2:1
Ans. A
8. If any solid substance is heated, which parameter is extended?
A. only length
B. only area
C. only volume
D. all the three
Ans. D
9. There are two rods made of the same substance, each of length 1. But their radii are r and 2r, respectively. If the temperatures of both the rods are increased by the same amount, then
A. the length of the first rod increases more
B. the length of the second rod increases more
C. both increase by the same length
D. it is not possible to predict their expansion
Ans. C
10. There is a hole in the middle of a metal sheet. What happens if the temperature is increased?
A. radius of the hole decreases
B. radius of the hole increases
C. radius of the hole remains unchanged
D. it is not possible to say whether the radius of the hole will increase or decrease
Ans. B
11. There are two spheres made of the same substance and having the same radii, one is solid but the other is hollow. If the temperature of both the spheres is increased by the same amount, then
A. expansion of the hollow sphere is more
B. expansion of the solid sphere is more
C. both have the same expansion
D. it is not possible to say which sphere will have more expansion
Ans. C
12. A metallic rod is attached along the diameter of a circular metal plate. Both are made of the same element. If the system is heated, ratio of the circumference and the diameter of the circle is
A. π
B. π/2
C. π/4
D. π/6
Ans. A
13. The dimension of the coefficient of surface expansion of a solid is
A. 1 in length, 2 in mass, 1 in temperature
B. 1 in length, 2 in time, 1 in temperature
C. –1 in temperature
D. 2 in temperature
Ans. C
14. The dimension of the coefficient of volume expansion of a solid is
A. 2 in length, 1 in temperature
B. 2 in mass, 1 in temperature
C. 1 in length, 1 in temperature
D. –1 in temperature
Ans. D
15. Volume expansion of a solid depends
A. only on the initial volume
B. only on the rise of temperature
C. only on the coefficient of volume expansion
D. on all the above
Ans. D
16. Surface expansion of a solid depends
A. only on the initial surface area
B. only on the rise of temperature
C. only on the coefficient of surface expansion
D. on all the above
Ans. D
Answer in brief
1. The container has no role in the expansion of which-solid or liquid?
Ans. The container has no role in the expansion of solid.
2. There are two spheres made of the same substance and also have equal radii. One of them is solid and the other is hollow. If the same amount of heat is given to both the spheres, which one expands more?
Ans. The hollow sphere expands more.
3. What is the unit of coefficient of linear expansion of solid?
Ans. The unit of coefficient of linear expansion of solid is °C-1 or °F-1 or K-1.
4. Write one use of bimetallic strip.
Ans. Bimetallic strip is used as thermostat.
5. A bimetallic strip is made up of two metals A and B. The coefficient of linear expansion of A is more than that of If the bimetallic strip is heated, it bends. Which metal remains inside the curvature?
Ans. Metal B remains in the inside portion of the curvature.
6. A bimetallic strip is made up of two metals A and B. The coefficient of linear expansion of A is more than that of B. If the bimetallic strip is cooled, it bends. Which metal remains inside the curvature?
Ans. Metal A remains in the inside portion of the curvature.
7. What is the coefficient of linear expansion of a solid?
Ans. The coefficient of linear expansion of a solid is the fractional increase in length per degree rise in temperature.
8. Does the unit of coefficient of linear expansion of a solid depend on the unit of length?
Ans. No, it does not depend on the unit of length.
9. What is the coefficient of surface expansion of a solid?
Ans. The coefficient of surface expansion of a solid is the fractional increase in area per degree rise in temperature.
10. Does the unit of coefficient of surface expansion of a solid depend on the unit of area?
Ans. No, it does not depend on the unit of area.
11. Define the coefficient of volume expansion of a solid substance.
Ans. The coefficient of volume expansion of a solid is the fractional increase in volume per degree rise in temperature.
12. Does the unit of coefficient of volume expansion of a solid depend on the unit of volume?
Ans. No, it does not depend on the unit of volume.
13. A scale made of brass is graduated at 0°C. What error may arise in the measurement of a certain distance with this scale at 30°C?
Ans. If a distance is measured by the given scale at 30°C, the reading obtained is less than the actual length.
14. A scale made of brass is graduated at 0°C. What error may arise in the measurement of a certain distance with this scale at 10°C?
Ans. If a length is measured by the given scale at 10°C, the reading obtained is more than the actual length.
15. Why can a platinum wire be easily sealed with glass by application of heat?
Ans. As the coefficient of linear expansion of glass and platinum are nearly equal, a platinum wire can be easily sealed with glass by application of heat.
16. Why cannot a copper wire be sealed with glass by application of heat?
Ans. As the coefficient of linear expansion of copper is greater than that of glass, a copper wire cannot be sealed with glass by application of heat.
17. Name an alloy whose coefficient of thermal expansion is much less than the same of its constituents.
Ans. Invar, an alloy with 36% nickel and 64% iron, has very low coefficient of thermal expansion compared to that of its constituent elements.
18. A liquid is kept in a vessel whose coefficient of volume expansion is 5 × 10-6°C-1. If the real coefficient of expansion of the liquid is 20 × 10-5°C-1, then what is the value of apparent coefficient of expansion?
Ans. Coefficient of apparent expansion of the liquid = coefficient of real expansion of the liquid-coefficient of volume expansion of the substance of the vessel
= (20 × 10-5– 5 × 10-6)°C-1
= 19.5 × 10-5°C-1
19. A liquid is kept in two vessels A and B separately and then both are heated. The coefficient of volume expansion of the substance A is greater than that of B. The coefficient of apparent expansion of the liquid is greater in which vessel?
Ans. The coefficient of apparent expansion of the liquid is greater in the vessel B.
20. A spherical metallic ball is heated. Among the radius, surface area and volume, which has the highest percentage increase?
Ans. The volume of the sphere has the highest percentage increase.
21. A spherical metallic ball is heated. Among the radius, surface area and volume, which has the lowest percentage increase?
Ans. The radius of the sphere has the lowest percentage increase.
22. Which coefficient of expansion of a liquid does not depend on the expansion of the container?
Ans. The coefficient of real expansion of a liquid does not depend on the expansion of the container.
23. Which coefficient of expansion of a liquid depends on the expansion of the container?
Ans. The coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid depends on the expansion of the container.
24 What is the nature of the coefficient of volume expansion of a substance whose volume decreases with increase temperature?
Ans. The coefficient of volume expansion of a substance, whose volume decreases with increase in temperature, is negative.
25. The coefficient of volume expansion of water is negative in the temperature range 0°C-4°C. Does the volume of water increase or decrease with increase in temperature, in the given temperature range?
Ans. The volume of water decreases with increase in temperature, in the given temperature range.
26. Name one whose liquid substance coefficient of volume expansion is negative in a definite temperature range.
Ans. The value of coefficient of volume expansion of water is negative in the temperature range of 0°C-4°C.
27. Name one solid substance whose coefficient of volume expansion is negative in a definite temperature range.
Ans. The value of coefficient of volume expansion of pure silicon (a solid substance) is negative in the temperature range of -153°C to -255°C.
28. What is the dimensional formula of the coefficients of apparent and real expansion of a liquid?
Ans. The dimensional formula of the coefficients of apparent and real expansion of a liquid is Θ-1.
29. Define volume coefficient (γp) of a gas.
Ans. If the temperature of a gas is raised from 0°C to 1°C by keeping the pressure on a definite mass of gas constant, then the expansion in volume per unit volume of the gas is called the volume coefficient of that gas and it is expressed as γp .
30. What is the unit of volume coefficient of gas?
Ans. The unit of volume coefficient of gas is °C-1 or °F-1 or K-1 .
31 Mention a name of an electrical appliance in which thermostat is used.
Ans. Refrigerator.
32. Among solids, liquids and gases which expands less on application of heat?
Ans. Among solids, liquids and gases solids expand less on application of heat.
Fill in the blanks
1. The unit of coefficient of linear expansion of any solid substance depends only on the unit of ……….
Ans. temperature
2. If the coefficient of linear expansion of any solid substance in Celcius scale is 18 × 10-6/°C, then its value in Fahrenheit scale is ……………
Ans. 10 × 10-6/°F
3 Thermal expansion of solid is of ……….. types.
Ans. three
4. Increase of length of a solid substance = ………….. × coefficient of linear expansion × increase in temperature.
Ans. Initial length
5. If a stopper made of brass is stuck in a bottle made of steel, the bottle has to be ……… in order to open the stopper.
Ans. heated
6. The coefficient of ………. expansion of a liquid is its inherent property.
Ans. real
7. If the coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid is zero, then the level of liquid in a tube remains ……….
Ans. unchanged
8. For accurate measurement during expansion of a gas, volume at ………… is taken as the initial volume.
Ans. 0°C
9. While measuring the coefficient of volume expansion of a gas, pressure remains ………..
Ans. constant
10 Coefficient of real expansion of liquid = coefficient of real expansion of container + ………..
Ans. coefficient of apparent expansion of the liquid
11. …………. is the device which is used for automatic temperature control.
Ans. Thermostat
12. The coefficient of real expansion is an ………….. property of a liquid.
Ans. intrinsic
13. On heating a bimetallic strip, made by riveting together with a strip of iron and an equal strip of brass, bends so that, the ………….. is on the convex side of the curve.
Ans. brass
14. Density of liquids ………… with increase in temperature.
Ans. decrease
State whether true or false
1. The coefficient of volume expansion at constant pressure is the same for all ideal gases.
Ans. True
2. The unit of coefficient of apparent expansion of a liquid depends on the unit of temperature.
Ans. True
3. The unit of coefficient of real expansion of a liquid depends on the unit of volume.
Ans. False
4. Thermal expansion of invar is less than that of all other metals or alloys.
Ans. True
5. The thermal expansion of a liquid is generally greater than the thermal expansion of an equal volume of a solid for the same increase in temperature.
Ans. True
6. The thermal expansion of a liquid is generally greater than the thermal expansion of an equal volume of a gas for the same increase in temperature.
Ans. False
7. Coefficient of real expansion of water from 0°C to 4°C is positive.
Ans. False
TOPIC – B
Thermal Conductivity
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What is conduction? Write down the characteristics of transmission of heat in the process of conduction.
Ans. It is the method in which heat is transmitted from a warmer place of the substance to a colder place without any displacement of the molecules. In the conduction process-
- a solid medium is required for heat transmission.
- the medium becomes hot during heat transmission.
- there is no displacement of the molecules of the medium at the time of heat transmission.
- heat can be transmitted along any of a straight or a curved path.
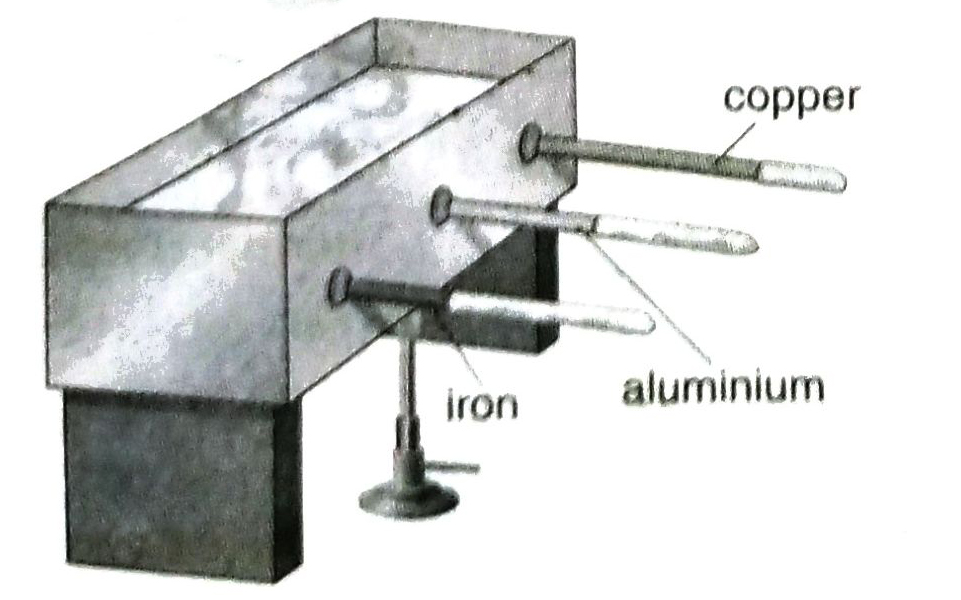
Q.2 What do you mean by pre-steady state condition in case of conduction of heat? Demonstrate with the help of an experiment that the capacity of heat conduction is different for different substances.
Ans. During transmission of heat through any object if both conduction and absorption go on simultaneously, it is called pre-steady state condition of heating.
Experiment: A rectangular, metallic vessel is taken. Three holes are made on its wall in the same height. Three different metal rods (say of copper, aluminium and iron) of same length and same cross sectional area are inserted through the holes. The portion of the rods outside the vessel are wax-coated.
Next, water is poured in the vessel and then it is heated uniformly by a bunsen burner. In this condition heat conducts along the lengths of the rods. After some time, it is seen that wax has melted in all the rods but up to different lengths. Conclusion: It is clearly understood from this experiment that the capacity of conducting heat is different for different substances. If wax melts up to I2 , I2 and I3 on copper, aluminium and iron rods respectively, it is observed that I2 > I2 > I3 .
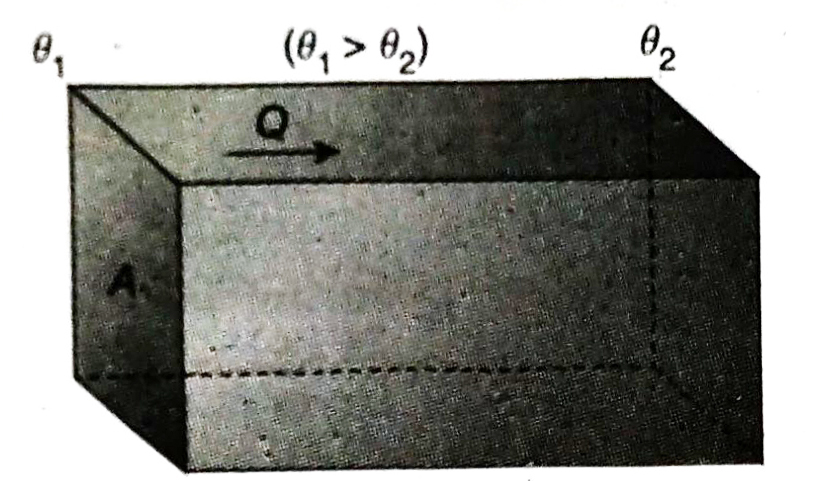
Q.3 What is thermal conductivity? Suppose the thickness of a rectangular plate is d, its cross sectional area is A and the temperature of its opposite sides are θ1 and θ2 respectively (where θ1 > θ2). At thermal steady state, if Q amount of heat is transmitted perpendicularly in time t from the hotter side to the colder side then how can you express thermal conductivity of the substance of the plate?
Ans. The thermal conductivity of a substance is defined as the heat conducted perpendicularly in one second across the opposite faces of a cuboid of unit cross sectional area and unit thickness, when the difference in temperature of its two opposite faces is unity.
where k is a constant, known as the thermal conductivity of the substance of the plate.
Q.4 Find out the unit of thermal conductivity. Establish a relationship between the units of thermal conductivity in CGS system and SI.
Ans. From definition, we have thermal conductivity,
Q.5 What do you mean by thermal resistance? What is the unit of thermal resistance?
Ans. From definition, we have thermal conductivity, Thermal resistance is defined as the property of a substance by which it resists the flow of heat through it.
Let the thickness of a body be d, its cross sectional area be A and the thermal conductivity of its substance be k.
Q.8 Define conductor and insulator of heat. Why is the handle of a kettle wrapped with cane?
Ans. Conductors of heat are those substances through which heat can be conducted easily. For example, iron.
Insulators of heat are those substances through which heat cannot be conducted easily. For example, wood.
Kettle is generally made of aluminium. Aluminium is a good conductor of heat. When water or any other liquid is heated in a kettle, the kettle also becomes hot along with the liquid inside it. In this condition, it is very difficult to touch the handle of the kettle. Cane is an insulator of heat. So, if cane is wrapped on the handle of the kettle, no heat is transmitted to the hand and the handle can be touched easily. For this reason, the handle of a kettle is wrapped with cane.
Q.9 If we touch two chairs, one of wood and the other of iron, both at the same temperature during winter, why does the iron chair feel colder than the other? In which condition they feel same in temperature?
Ans. Our body temperature generally remains higher than the temperature of a chair during winter. Wood is a bad conductor of heat but iron is a good conductor of heat. If we touch an iron chair, heat is transmitted very quickly from our body to the chair but when we touch a wooden chair, conduction of heat is very slow. This is why the iron chair feels colder.
As the temperature of the chair becomes equal with one’s body temperature, they feel same in temperature.
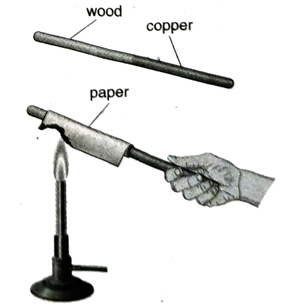
Q.10 Let us take a rod, half of which is made of wood and the other half is made of copper. The rod is wrapped with a thin paper. Now it is held directly over the flame of a burner. Explain what happens.
Ans. If the rod is held directly over the flame of a burner, it is seen that the paper surrounding the wooden portion is burnt immediately but the paper surrounding the copper side is not burnt. Copper being a good conductor of heat, heat is conducted evenly all over the rod and the temperature of the paper does not reach the ignition point. But in the case of wood which is
bad conductor of heat, heat is not conducted. As a result, temperature reaches the ignition point and the paper is burnt. But if held for a long time, paper on the copper part also gets burnt.
Q.11 why the birds fluff up their feathers during winter?
Ans. During winter the birds fluff up their feathers to keep themselves warm. When the birds fluff up their feathers, feathers trap air in them. As air being an insulator, does not allow heat from the body to escape. So the birds keep warm.
Q.12 Wearing of two relatively fiver clothes instead of a thick cloth is more comfortable. Why?
Ans. If we wear two relatively fiver clothes instead of a thick cloth, we feel warmer. This happens because the two clothes trap a layer of air between them. Air is a thermal insulator and so it prevents the heat from our body from escaping. So we feel warm and more comfortable.
Q.13 Why carpeted floor is more comfortable in winter?
Ans. During winters, walking bare feet on cemented floor makes us feel very cold. Because cemented floor is a good conductor of heat. So heat from our bodies gets conducted to the floor and spreads to the other parts rapidly and we feel cold. Carpeted floors feel warmer as carpets are insulators of heat. So the heat from our bodies is not conducted and spread through the carpet. That is why carpeted floor is more comfortable in winter.
Q.14 Why sawdust is used to prevent ice from melting?
Ans. Sawdust is used to cover ice to prevent it from melting. Sawdust is a bad conductor of heat and it also traps a lot of air it. Thus heat from outside cannot reach the ice block and this prevents it from melting.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Which of the following metals has the highest conductivity?
A. copper
B. aluminium
C. silver
D. gold
Ans. C
2. The value of thermal conductivity of an ideal conductor (in the unit of cal · cm-1.°C-1 · s-1) is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 100
D. ∞
Ans. D
3. The value of thermal conductivity of an ideal insulator (in the unit of cal · cm-1.°C-1 · s-1) is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 100
D. ∞
Ans. A
4. At steady state,
A. both conduction and absorption of heat take place
B. neither conduction nor absorption of heat takes place
C. only absorption of heat takes place, not conduction
D. only conduction of heat takes place, not absorption
Ans. D
5. What is the power of L in the dimensional formula of thermal conductivity?
A. 1
B. 2
C. –1
D. –2
Ans. A
6. Diamond is
A. good conductor of heat and electricity
B. bad conductor of heat and electricity
C. bad conductor of heat, good conductor of electricity
D. good conductor of heat, bad conductor of electricity
Ans. D
7. Which of the following is a good conductor of heat?
A. cork
B. air
C. wood
D. graphite
Ans. D
8. In which case the thermal conductivity increases from left to right?
A. Al, Cu, Ag
B. Ag, Cu, Al
C. Cu, Ag, Al
D. Al, Ag, Cu
Ans. A
9. For cooking food, which of the following type of utensil is most suitable?
A. high specific heat and high conductivity
B. low conductivity
C. low specific heat and low conductivity
D. low specific heat and high conductivity
Ans. D
10. Under steady state, the temperature of a body
A. increases with time
B. decreases with time
C. does not change with time and is same at all the points of the body
D. does not change with time but different at different points of the body
Ans. D
11. Two vessels of different materials are similar in size in every respect. The same quantity of ice filled in them gets melted in 20 minute and 30 minutes respectively. The ratio of their thermal conductivity will be
A. 3:2
B. 1:1
C. 2:3
D. 4:1
Ans. A
12. The coefficient of thermal conductivity depends upon
A. temperature difference of two surfaces
B. area of the plate
C. thickness of the plate
D. material of the plate
Ans. D
13. A piece of metal appears colder in winter morning than a piece of wood when touched because
A. metal has high specific heat
B. metal has high thermal conductivity
C. metal has low specific heat
D. metal has low thermal conductivity
Ans. B
14. On heating one end of a rod, the temperature of whole rod will be uniform when,
A. k = 1
B. k = 0
C. k = very small
D. k = infinity
Ans. D
15. Mud houses are cooler in summer and warmer in winter because
A. mud is a good conductor of heat
B. mud is a bad conductor of heat
C. thermal conductivity of mud is infinite
D. thermal conductivity of mud is 0
Ans. B
Answer in brief
1. Name one liquid which is a good conductor of heat.
Ans. Mercury is a liquid which is a good conductor of heat.
2. Name one substance whose electrical conductivity is very low but thermal conductivity is very high.
Ans. Diamond has very low electrical conductivity but very high thermal conductivity.
3. Name the substance with the highest thermal conductivity at room temperature.
Ans. According to the latest available information, monocrystalline synthetic diamond has the highest thermal conductivity at room temperature.
4. What is the thermal conductivity of monocrystalline synthetic diamond at room temperature?
Ans. The thermal conductivity of monocrystalline synthetic diamond at room temperature is 33.2 W · cm-¹. K-1 (approx.).
5. State whether diamond or copper has the higher value of thermal conductivity.
Ans. The thermal conductivity of diamond is approximately five times more than that of copper.
6. What is the unit of thermal conductivity in SI?
Ans. Unit of thermal conductivity in Sl is W · m-¹.k-1.
7. When is the value of the thermal resistance of a substance equal to the reciprocal of its thermal conductivity?
Ans. The value of the thermal resistance of a substance is equal to the reciprocal of its thermal conductivity when its thickness is equal to its cross sectional area.
8. By keeping the length (thickness) of a slab unchanged, if its area of cross section is halved, how many times does its thermal resistance increase?
Ans. By keeping the length (thickness) of a slab unchanged, if its area of cross section is halved, its thermal resistance increases two times.
9. By keeping the area of cross section of a slab unchanged, if the length (thickness) is halved, how many times does its thermal resistance increase?
Ans. By keeping the area of cross section of a slab unchanged, if its length (thickness) is halved, its thermal resistance is also halved.
10. When do we feel an iron chair and a wooden chair to be hot to the same extent, by touching?
Ans. We feel the two chairs to be hot to the same extent, when the body temperature and the temperatures of the two chairs become equal.
11. What are thermal conductors of heat?
Ans. Materials which can conduct heat easily are called thermal conductors of heat.
12. What are insulators or bad conductors of heat?
Ans. Materials which can not conduct heat easily are called insulators or bad conductors of heat.
13. If thickness and area of cross section of a metallic plate are unchanged then what will be the relation between thermal resistance and thermal conductivity?
Ans. If thickness and area of cross section of a rectangular slab are unchanged then thermal resistance (R) is inversely proportional to the thermal conductivity.
14. What is the value of thermal conductivity of vacuum?
Ans. The thermal conductivity of vacuum is zero.
15. What is the value of thermal conductivity of an ideal insulator of heat?
Ans. The value of thermal conductivity of an ideal insulator of heat is zero.
16. What is the value of thermal conductivity of an ideal conductor of heat?
Ans. The value of thermal conductivity of an ideal conductor is infinite.
17. In which state of conduction of heat through solids no heat is absorbed by any layer of the solid?
Ans. In steady state there is no absorption of heat by any layer of a solid.
18. In which state of conduction of heat through solids heat is absorbed by different layers of a solid?
Ans. In pre-steady state of conduction of heat through solids some amount of heat is absorbed by the different layer of the solid.
Fill in the blanks
1. There is ……….. displacement of the molecules of the medium during transmission of heat by conduction process.
Ans. no
2. Thermal conductance of wooden dust is ………… than that of wood.
Ans. less
3. Thermal conductivity of vacuum is ………….
Ans. zero
4. The value of thermal conductivity of diamond is …………. than that of gold.
Ans. more
5. If the value of thermal conductivity is more, thermal resistance is ………..
Ans. less
6. From ………… experiment it was proved that thermal conductivity of different materials are different.
Ans. Ingenhousz
7. SI unit of thermal resistance is ………..
Ans. K/watt
8. Flow of heat from one place to another is called …………. of heat.
Ans. transmission
9. Conduction usually takes place in …………..
Ans. solids
10. All gases are …………… conductors of heat.
Ans. bad
11. vacuum can not conduct heat and therefore it is an …………. insulator.
Ans. ideal
12. Rate of flow of heat is called ………….. current.
Ans. heat
13. The reciprocal of coefficient of thermal conductivity is …………. of the conductor.
Ans. thermal resistivity
14. Material medium is transmission of heat in necessary for the process of …………
Ans. conduction
15. In the process of …………… of heat, heat can travel along a straight or a curved path.
Ans. conduction
State whether true or false
1. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of a conductor does not depend on the substance of the conductor.
Ans. False
2. All metals are bad conductors of heat.
Ans. False
3. The rate of thermal conduction remains the same if the temperature difference between the two ends of a conducting rod is made twice the previous value.
Ans. False
4. Material medium is necessary for conduction of heat.
Ans. True
5. During conduction of heat through solids, molecules of the solid can move freely.
Ans. False
6. Vacuum is an ideal conductor of heat.
Ans. False
7. Thermal conductivity of diamond is less than that of silver.
Ans. False
8. Silver is the best metallic conductor of heat.
Ans. True
9. Thermal conductivity is the property of a material that indicates its ability to conduct heat.
Ans. True