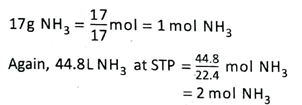WBBSE 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 4.2 Concept of Mole
West Bengal Board 9th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter – 4.2 Concept of Mole
WBBSE 9th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
Synopsis
TOPIC – A
Concept of Mole and Importance of Avogadro’s Number
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Define mole.
Ans. One mole of a substance is that amount of the substance (element or compound) which contains Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 1023) of fundamental particles (atoms, molecules or ions).
2. What is Avogadro’s number?
Ans. The number of molecules present in one grammole of a substance which may be either an element or a compound (solid, liquid or gas) is known as Avogadro’s number.
3. What is Avogadro’s constant? How is it different from Avogadro’s number?
Ans. The number of particles present per mole of a substance is called Avogadro’s constant. Thus, Avogadro’s constant is Avogadro’s number/mole. Its value is 6.022 × 1023 mol-1. It is a universal constant.
Avogadro’s number is a pure number. It has no unit but the unit of Avogadro’s constant is mol-1.
4. Why is it necessary to mention the corresponding fundamental particle while using the term ‘mole’?.
Ans. It is necessary to mention the corresponding fundamental particle while using the term ‘mole’. This is because the amount of a substance entirely depends on the nature of particles present in it. For example, the fundamental particle of oxygen can be atom as well as molecule. Thus, the term ‘1 mol oxygen’ does not clearly indicate the amount of oxygen present in that quantity, because 1 mol oxygen represents both 1 mol oxygen molecule and 1 mol oxygen atom. Now, 1 mol oxygen molecule contains twice the number of oxygen atoms present in 1 mol oxygen atom, although the number of particles in both the quantities are same.
5. Avogadro’s number creates a correlation between the macroscopic and microscopic world- explain.
Ans. Molecules or atoms are too small to be seen. So, it is extremely difficult to count the number of atoms or molecules in a given mass of substance. However, by using the mole concept, scientists have been able to successfully calculate the number of atoms, molecules or ions in a given mass of substance.
According to the definition of mole, 1 mol of a substance contains 6.022 × 1023 number of fundamental particles. This number (6.022 × 1023) is known as Avogadro’s number. We cannot see 1 molecule of water but, 1 mol of water (which is equal to 18 g water) is visible to us. Now, 1 mol of water (i.e., 18 g water) contains 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water.
Thus it can be concluded that, Avogadro’s number creates a correlation between the macroscopic and microscopic world.
6. Write down the importance of Avogadro’s number in biology. Or, Mention an use of Avogadro’s number in biology.
Ans. In biological science, Avogadro’s number can be used for quantitative calculations of solids, liquids and gases. Eg., chlorophyll contains 2.68% Mg. Using the concept of Avogadro’s number one can find the number of Mg atoms present in 1 g chlorophyll as 6.69 × 1020.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Which of the following correlates between the microscopic and macroscopic world?
A. Dalton’s number
B. Berzelius’ number
C. Avogadro’s number
D. Faraday’s number
Ans. C
2. The meaning of the Latin word ‘moles’ is
A. many
B. having large volume
C. having large mass
D. heap
Ans. D
3. The word ‘mole’ was first used by
A. Dalton
B. Ostwald
C. Avogadro
D. Millikan
Ans. B
4. The value of Avogadro’s number is
A. 6.024 × 1020
B. 0.6023 × 1022
C. 0.6022 × 1024
D. 0.623 × 1023
Ans. C
5. The amount of Avogadro’s number of fundamental particles (e.g., electron, proton, atom, molecule, ion) is known as
A. mole
B. gram-mole
C.. gram-atom
D. gram-ion
Ans. A
6. The element for which the number of gram-moles and number of gram-atoms will be equal for any quantity is
A. oxygen
B. helium
C. hydrogen
D. chlorine
Ans. B
7. Unit of Avogadro’s constant is
A. mole
B. per mole
C. (mole)²
D. dobson
Ans. B
8. Which of the following cannot be calculated using Avogadro’s number?
A. Boltzman constant
B. atomic radius of solid metals
C. velocity of light in vacuum
D. number of molecules in a definite volume of gas at STP
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. Who determined the value of Avogadro’s number?
Ans. Robert Millikan.
2. What is the unit of molar mass?
Ans. mol-1 or kg. mol-1.
3. What is the effect of temperature and pressure on Avogadro’s number?
Ans. Mass and number of molecules do not depend on either temperature or pressure. Hence, temperature or pressure has no effect on Avogadro’s number.
4. What is the SI unit of quantity of matter?
Ans. The Sl unit of quantity of matter is mole.
5. How many Fe-atoms does 1 gram-atom of iron indicate?
Ans. 6.022 × 1023 atoms of iron.
6. 2 balloons contain 1.8066 × 1023 number of hydrogen molecules and 2 mol hydrogen gas respectively. Which balloon contains higher number of molecules ?
Ans. The balloon having mol of hydrogen gas.
7. What is the total charge of 1 mol electron?
Ans. The charge of 1 mol electron is 1 Faraday.
Fill in the blanks
1. In physical science, the number 6.022 × 1023 is known as ………. number.
Ans. Avogadro’s
2. In 1 mol oxygen gas, the number of oxygen atoms is ………..
Ans. 2 × 6.022 × 1023
3. 1mol represents Avogadro’s number of ……….. particles.
Ans. fundamental
4. The unit of Avogadro’s constant is …………
Ans. mol-1
6. When the term ‘mole’ is used, it is necessary to mention the corresponding ……….. particle.
Ans. fundamental
7. 1 millimol = ………… mol.
Ans. 10-3
10. 1 mol nitrogen molecule = …………. g nitrogen.
Ans. 28
11. 1 millimol oxygen molecule indicates ………….. number of oxygen molecules.
Ans. 6.022 × 1020
12. Number of moles = mass of the substance ÷ mass of ………… of the substance.
Ans. 1 mol
State whether true or false
1. The value of Avogadro’s constant changes with the change in both temperature and pressure.
Ans. False
2. The given mass of any substance when divided by the number of moles gives the corresponding value of molar mass.
Ans. True
3. The value of Avogadro’s number was determined by Millikan.
Ans. True
4. The unit of Avogadro’s constant is mol-¹.
Ans. True
5. The number of atoms in 1 gram-atom of oxygen is 6.022 × 1023.
Ans. True
6. 1 mol N2 and 1 mol N signify the same amount.
Ans. False
7. 1 mol of CO2 contains 1 mol oxygen atom.
Ans. False
8. Avogadro’s number is not applicable for the microscopic substances.
Ans. False
9. Avogadro’s number is independent of the properties of matter, it only depends upon the volume, pressure and temperature.
Ans. False
TOPIC – B
Gram-Atom, Atomic Mass Unit, Gram-Mole, Molar Volume of Gases and Formula Mass
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Define relative atomic mass with respect to the hydrogen scale.
Ans. Considering the mass of one hydrogen atom as unity (1), the number of times an atom of an element is heavier than a hydrogen atom indicates the relative atomic mass of the given element. Thus, the relative atomic mass of an element is defined as the ratio of the mass of one atom of the element to the mass of one atom of hydrogen.
Relative atomic mass of an element
2. Define relative atomic mass with respect to the carbon (12C) scale.
Ans. The number of times an atom of an element is heavier than 1/12th part of the actual mass of an atom of 12C isotope indicates the relative atomic mass of the given element. Thus, the relative atomic mass of an element is defined as the ratio of mass of one atom of the element to 1/12th part of the mass of an atom of 12C isotope.
Relative atomic mass of an element
3. Why is Why is 12C and not hydrogen considered as the standard element to determine the relative atomic mass?
Ans. (1) Hydrogen is the lightest element. So, while calculating atomic mass with respect to hydrogen, a very small error in measurement causes a large deviation in the actual result. This does not happen when 12C is taken as the standard element.
(2) The atomic masses calculated with respect to hydrogen scale are found to be fractional for most of the elements. However, atomic masses of most of the elements are integers with respect to the 12C scale.
Due to these advantages, nowadays 12C is considered as the standard element in determination of relative atomic mass.
4. What is gram-atomic mass?
Ans. The gram-atomic mass of an element is defined as the atomic mass of the element expressed in gram. For example, atomic mass of oxygen is 16. Therefore, gram-atomic mass of oxygen is 16 g.
5. What is gram-atom?
Ans. 1 gram-atom of an element is defined as the amount of the element expressed in gram, which contains 6.022 × 1023 atoms of the element. For example, 1 gram-atom of nitrogen = 14 g nitrogen, because 14g nitrogen contains 6.022 × 1023 number of atoms.
6. Relative atomic mass of an element has mic mass of an element no unit. Explain
Ans. The relative atomic mass of an element
As relative atomic mass of an element is a ratio of the masses of two atoms, it has no unit.
7. What is atomic mass unit?
Ans. Atomic mass unit may be defined as the unit in which the actual mass of an atom is expressed and which is equal to 1/12th of the actual mass of an atom of 12C isotope.
1 atomic mass unit or 1u = 1.6605 × 10-24g
8. What is gram-molecule or gram-mole?
Ans. 1 gram-molecule or gram-mole of a substance (element or compound) is defined as the amount of the substance expressed in gram, which contains 6.022 × 1023 molecules of the substance. For example, 1 gram-mole of oxygen = 32 g oxygen, because, 32 g oxygen contains 6.022 × 1023 number of molecules.
9. What is meant by molar mass?
Ans. Molar mass is the mass of 1 mol of a substance. Alternatively, it is defined as the mass of Avogadro’s number of constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) of the substance. For example, gram-atomic mass of helium is 4g. Hence, molar mass of helium = 4g . mol-1. Again, gram-molecular mass of water is 18 g. Hence, molar mass of H2O = 18 g.mol-1.
10. What is gram-molar -molar mass?
Ans. The gram-molar mass of a substance (element or compound) is defined as the molar mass of that substance expressed in gram. For example, molar mass of carbon dioxide is 44 g . mol-1. Therefore, gram-molar mass of CO2 is 44 g.
11. What is molar volume?
Ans. At a given temperature and pressure, the volume occupied by 1 mol of any substance (element or compound) is known as its molar volume at that temperature and pressure. The molar volume of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 22.4 L.
12. What is formula mass?
Ans. Formula mass of an ionic compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in a formula unit of the compound. For example, formula mass of NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5.
13. What is gram-formula mass?
Ans. The gram-formula mass of an ionic compound is defined as that amount of the compound expressed in gram numerically equal to its formula mass. For example, formula mass of NaCl is 58.5. Therefore, gram-formula mass of NaCl is 58.5 g.
14. Use of formula mass instead of molecular mass is more appropriate in case of ionic compounds. Explain.
Ans. For an ionic compound, there is no existence of any discrete molecule. The formula of the compound represents the ratio of different ions in the compound. For example, although sodium chloride is expressed by the formula NaCl, yet there is no existence of individual sodium chloride molecule. Actually, the compound contains Na+ ions and Cl– ions in the ratio of 1:1 which is represented by the formula. In the crystalline form of sodium chloride, each Na+ ion is surrounded by 6 Cl– ions and each Cl– ion is further surrounded by 6 Na+ ions forming a network structure called crystal lattice. Thus, in the crystal lattice of sodium chloride, there is no presence of molecules. Hence, it is not appropriate to use the term molecular mass in case of ionic compounds rather, the term formula mass should be used.
15. Molecular mass and formula mass are always the same. Explain with examples.
Ans. Molecular mass of an element or a compound is calculated from the formula of the substance. So, molecular mass is numerically equal to the formula mass. However, the two terms are not always the same. The term molecular mass represents the relative mass of a molecule of a substance while formula mass represents the relative mass of 1 formula unit of the substance. For substances which exist as molecules, molecular mass and formula mass are the same. However, there are compounds which do not exist as molecules. For such compounds, the term molecular mass is not applicable.
For example, CO2 molecule actually exists. Hence, the term molecular mass is applicable for CO2 and both molecular mass and formula mass of CO2 is 44. However, NaCl molecule has no separate existence. Its formula mass is 58.5 but the term molecular mass is not applicable for NaCl because it constitutes of Na+ and Cl– ions.
16. What is the relation between grammolecular mass or gram-molecule and molar volume of a gas at STP?
Ans. From Avogadro’s law it can be proved that 1 mole of any gas at STP occupies 22.4 L. On the other hand, mass of 1 mol of molecules of any substance expressed in gram is called the grammolecular mass of that substance. Again, 1 grammolecule of a substance is the amount of the substance expressed in gram, which is numerically equal to its molecular mass.
Thus, it can be concluded from these three relations that, at STP, volume of 1 gram-molecule of any gaseous substance is 22.4 L. For example, 1 gram-molécule of oxygen = 32 g. Hence, it can be said that 32 g of oxygen at STP occupies 22.4 L. Similarly, gram-molecular mass of carbon dioxide is 44 g. Hence, the volume of 44 g of CO2 at STP is 22.4 L.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. 1 amu is equal to
A. 1.66 × 10-24 kg
B. 1.66 × 10-25 g
C. 0.166 × 10-23 g
D. 1.66 × 10-20 g
Ans. C
2. Molar volume of a gas at STP is
A. 1 L
B. 11.1 L
C. 22.4 L
D. 5.6 L
Ans. C
3. Molar mass of sulphuric acid is
A. 98 kg · mol-1
B. 98 g · mol-1
C. 49 u
D. 49 mg · mol-1
Ans. B
4. For which of the following gases, the mass of 22.4 L of the gas at STP is 44 g?
A. NH3
B. H2S
C. CO2
D. CH4
Ans. C
5. The formula mass of MgCl2 (Mg = 24) is
A. 95 u
B. 65 u
C. 85 u
D. 75 u
Ans. A
6. 117g NaCl is equal to how many gram-formula mass of NaCl?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Ans. B
7. The statement ‘molecular mass of sodium chloride is 58.5’ is wrong because
A. it is a radioactive substance
B. it is a solid
C. NaCl molecule has no separate existence
D. none of these
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. Which element is considered as the standard for determining the relative atomic mass of an element?
Ans. To determine the relative atomic mass of an 12. element, the 12C isotope of carbon (126C) is considered as the standard.
2. How many grams of H2O does 1 gram-mole of H2O indicate?
Ans. 1 gram-mole of H2O indicates 18 g of water.
3. 1u = how many grams?
Ans. 1u = 1.6605 × 10-24 g.
4. How are mass, molar mass and number of moles related?
Ans. Given mass (m) = number of moles (n) × molar mass (M)
5. What is the mass of one molecule of water (H2O) in amu?
Ans. 18 u.
6. For which compound between CaCl2 and H2O, the use of formula mass is appropriate?
Ans. The use of formula mass is appropriate for CaCl2 as it is an ionic compound.
7. What is the mass of a carbon atom in unified atomic mass unit?
Ans. 12 u.
8. Express the value of 1 amu in kg.
Ans. Value of 1 amu in kg is 1.6605 × 10-27 kg.
9. Name a gaseous substance whose atomic and molecular masses are equal to each other.
Ans. Helium (He).
10. In which case gram-atomic mass and grammolecular mass are of same meaning?
Ans. For monoatomic elements; e.g., noble gases.
11. If atomic mass of sodium is 23, what will be the mass of a sodium atom in ‘amu’?
Ans. 23 u or 23 amu.
12. Name two substances for which both molar mass and atomic mass are same.
Ans. Neon and potassium.
Fill in the blanks
1. The actual mass of one ammonia molecule is ……… u.
Ans. 17
2. The actual mass of an atom of an element = atomic mass of the element × ………. g.
Ans. 1.6605 × 10-24
State whether true or false
1. The relative atomic mass of an element can be defined with respect to hydrogen (1H) and carbon (12C) scales.
Ans. True
2. The actual mass of one molecule of CO2 is 7.31 × 10-23 g.
Ans. True
3. Formula mass is applicable for oxygen molecule.
Ans. False
4. The formula mass of NaCl is 58.5.
Ans. True
5. Atomic mass unit is denoted by ‘u’.
Ans. True
TOPIC – C
Chemical Calculations Using Molar Mass, Molar Volume and Formula Mass
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Explain whether 0.1 g of diamond will contain the same number of carbon atoms as present in 0.1 g of graphite.
Ans. Both graphite and diamond are the allotropes of carbon. Hence, equal amount (by mass) of both the substances will contain same number of carbon atoms. Thus, 0.1 g of diamond and 0.1 g of graphite contain equal number of carbon atoms.
2. How many gram-atoms and gram-moles of oxygen are present in 32 g oxygen?
Ans. Atomic mass of oxygen = 16.
∴ 16 g oxygen = 1 gram-atom oxygen.
∴ 32 g oxygen = 32/16 = 2 gram-atom oxygen.
Now, molecular mass of oxygen = 32.
∴ 32 g oxygen = 1 gram-mole oxygen.
3. Among equal volumes of Cl2 and O2 at STP, which one has more mass?
Ans. We know, the volume of 1 g-mole of any gaseous substance at STP is 22.4 L.
Now 1 g-mole Cl2 = 2 × 35.5 g = 71 g Cl2
1 g-mole O2 = 2 × 16 g = 32 g O2
∴ At STP, mass of 22.4 L of Cl2 gas = 71 g
and mass of 22.4 L of O2 gas = 32 g
∴ Cl2 gas will have more mass than O2 at given conditions.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Number of molecules in 36 g water is
A. 6.022 × 1023
B. 12.044 × 1023
C. 3.011 × 1023
D. 9.0345 × 1023
Ans. B
2. Which of the following contains maximum number of moles?
(i) 18 g water, (ii) 34 g ammonia, (iii) 71 g chlorine, (iv) 8 g hydrogen.
A. (i)
B. (ii)
C. (iii)
D. (iv)
Ans. D
3. Which of the following contains maximum number of atoms?
(i) 28 g N2, (ii) 18 g H2O, (iii) 17g NH3, (iv) 16 g CH4.
A. (i)
B. (ii)
C. (iii)
D. (iv)
Ans. D
4. Number of H-atoms in 2 mol water is
A. 1 mol
B. 2 mol
C. 3 mol
D. 4 mol
Ans. D
5. Number of moles of H+ ions obtained from 98 g H2SO4 is
A. 1 mol
B. 2 mol
C. 3 mol
D. 4 mol
Ans. B
6. Amount of Ca(OH)2 required to produce 1 mol of OH– ions is
A. 74 g
B. 148 g
C. 37 g
D. 60 g
Ans. C
7. Which of the following has a volume of 22.4 L at STP?
A. 36 g water
B. 64 g oxygen
C. 71 g chlorine
D. 4 g hydrogen
Ans. C
8. Which of the following contains maximum number of molecules?
A. 44 g CO2
B. 48 g O3
C. 8 g H2
D. 64 g SO2
Ans. C
9. At STP, the mass of 44.8 L of a gas is 88 g. The molecular formula of the gas is
A. N2
B. CO2
C. NH3
D. O2
Ans. B
10. How many grams of CO2 will contain the same number of molecules as that in 44.8 L of NH3 at STP?
A. 44 g
B. 66 g
C. 88 g
D. 132 g
Ans. C
11. If the mass of 6.022 × 1020 atoms of an element is 0.012 g, its atomic mass will be
A. 11
B. 12
C. 13
D. 24
Ans. B
12. The volume of 2 g-mol CO2 at STP is
A. 22.4 L
B. 44.8 L
C. 11.2 L
D. 2.24 L
Ans. B
13. Number of moles of oxygen atoms present in 6.022 × 1024 molecules of CO is
A. 10
B. 5
C. 1
D. 0.5
Ans. A
Answer in brief
1. Which of the given substances has maximum number of molecules- 28 g N2, 32 g O2, 18 g H2O and 100 g CaCO3 ?
Ans. 28g N2 = 1mol N2 ; 32g O2 = 1mol O2 ; 18g H2O = 1 mol H2O; 100 g CaCO3 = 1 mol CaCO3
As all the substances contain the same number of moles, the number of molecules in each of the substances will be equal i.e., 6.022 × 1023.
2. What is the mass of 112 mL hydrogen gas at NTP?
Ans. 0.01 g.
3. A gas jar contains 17g NH3 and another contains 44.8L NH3 at STP. Which gas jar contains more number of molecules?
Ans.
Hence, the second gas jar contains more number of molecules.
4. What is the volume of 7g of nitrogen at NTP?
Ans. At NTP, volume of 28 g of nitrogen = 22.4 L Hence, at NTP, volume of 7g of nitrogen = 22.4/28 × 7 L = 5.6 L.
5. Are the m asses of 1 mol sodium and 1 mol oxygen are same?
Ans. The masses of 1 mol sodium and 1 mol oxygen are not same.
6. What will be the volume of hydrogen gas at STP produced from the reaction of 23 g of Na with water?
Ans. 2Na+ 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 ↑
∴ Volume of hydrogen gas at STP = 11.2 L
7. What is the total number of electrons present in 1 mol of water?
Ans. Number of electrons in 1 mol of water
= 10 mol
= 10 × 6.022 × 1023
= 6.022 × 1024
8. What is the mass of 0.5 mol CO2 gas?
Ans. Mass of 0.5 mol of CO2 = 44 × 0.5 g = 22 g
Fill in the blanks
1. Number of CO2 molecules in 88g CO2 is ………….
Ans. 2 × 6.022 × 1023
2. 16mol protons will be obtained from …………. mol oxygen.
Ans. 1
3. Number of electrons present in 14 g nitrogen is …………
Ans. 7 × 6.022 × 1023
4. Number of protons in 18g water is …………
Ans. 10 × 6.022 × 1023
5. 1 mol of OH– ions is obtained from ………… g NaOH.
Ans. 40
6. At STP, the volume of ………… mol of any gas (elemental or compound) is 22.4 L.
Ans. 1
7. The number of H-atoms in 10 mol water is ………… mol.
Ans. 20
8. 98 g H2SO4 = …………. mol H2SO4.
Ans. 1
9. Total mass of 3.011 × 1023 number of oxygen atoms is ………… g.
Ans. 8
10. At STP, the volume of a gas (in L) = number of moles of the gas molecules × ………… L.
Ans. 22.4
State whether true or false
1. The molar volume of 256g of sulphur dioxide gas at STP is 89.6 L.
Ans. True
2. The percentage of calcium in CaCO3 is 60%.
Ans. False
3. 2 mol OH– ions can be obtained from 110 g KOH.
Ans. False
4. The number of atoms present in 3.2 g CH4 is 6.022 x 1023.
Ans. True
5. The number of chlorine atoms in 71 g HCl is 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023.
Ans. False
6. 6.022 × 1023 number of molecules are present in 36 g of water.
Ans. False
7. Volume of 32 g SO2 at STP is 11.2 L.
Ans. True
8. 4 mol CO2 = 88 g CO2.
Ans. False
9. Number of molecules present in 2 millimol of chlorine gas is 2 × 6.022 × 1020.
Ans. True
10. The volume of 64 g oxygen at STP is 10 L.
Ans. False