JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
J&K 10th Class Maths Solutions chapter – 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Jammu & Kashmir State Board JKBOSE 10th Class Maths Solutions
Angle of Elevation and Angle of Depression
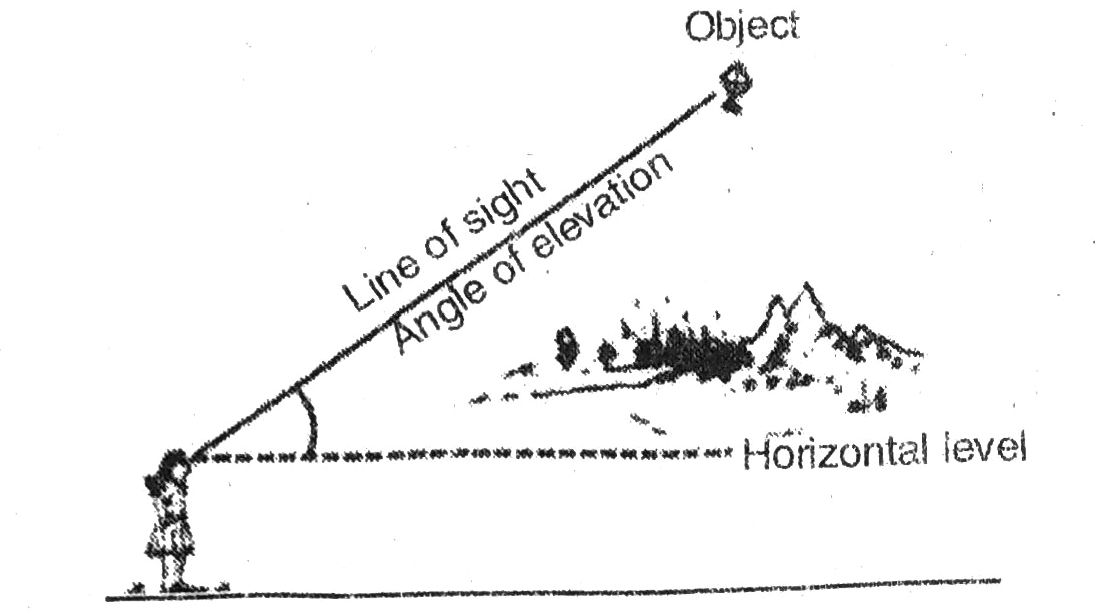
The line of sight is the line drawn from the eye of an observer to the point in the object viewed by the observer. The angle of elevation of the point viewed is the angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level, i.e., the case when we raise our head to look at the object (see fig.).
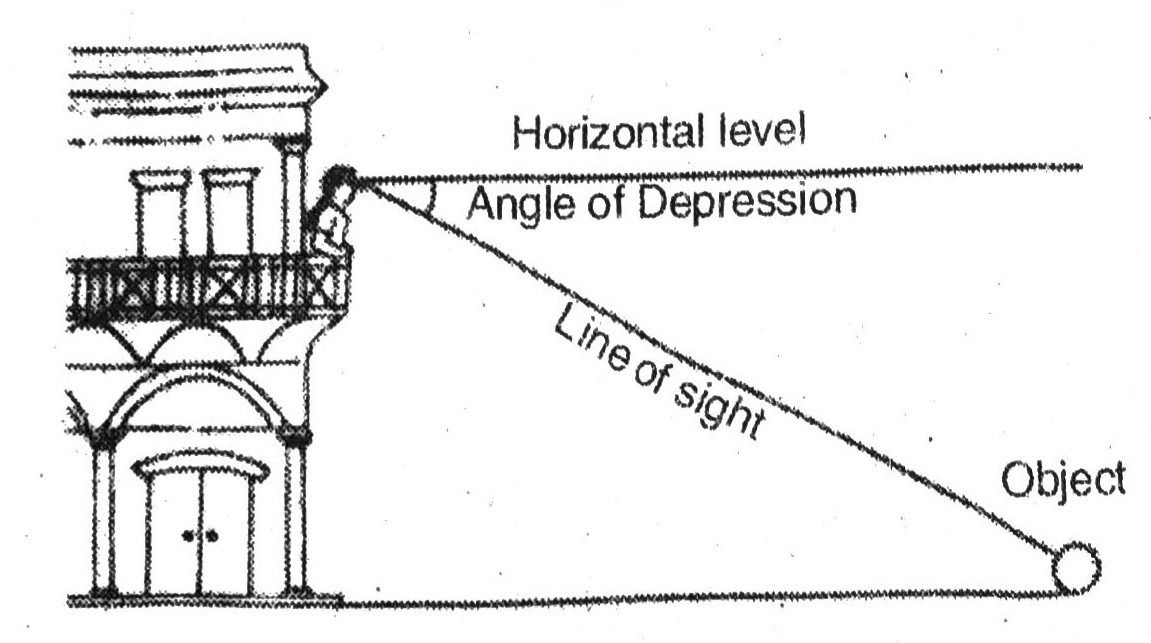
The angle of depression of a point on the object being viewed is the angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point is below the horizontal level, i.e., the case when we lower our head to look at the point being viewed (see fig.).
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE 9.1
Q. 1. A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is 30° (see fig.).
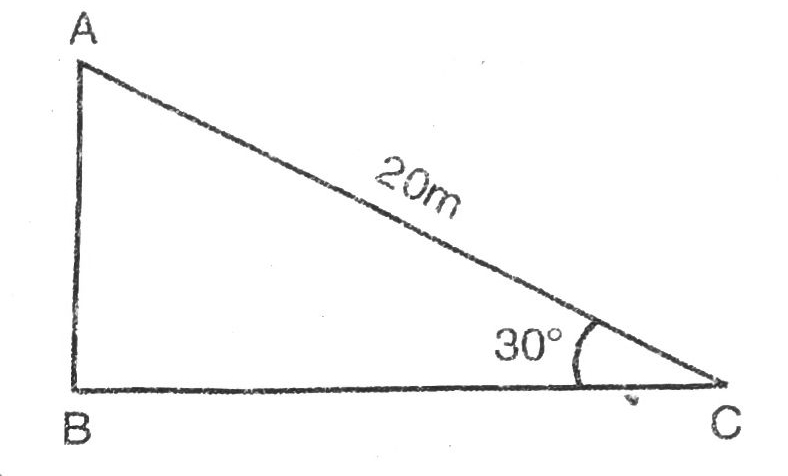
Solution. Let AB be the height of pole;
AC = 20 m be the length of rope.
The angle of elevation in this situation is 30°.
Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
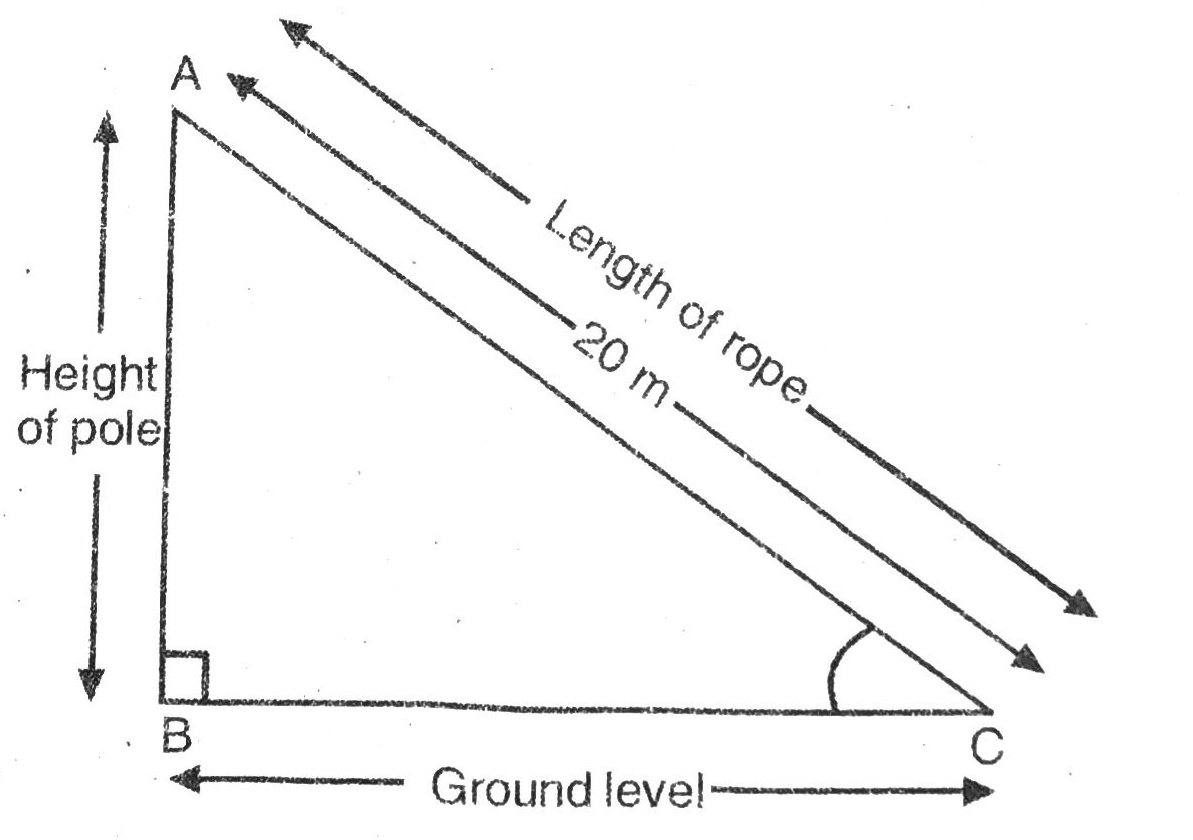
In right angled ΔABC,
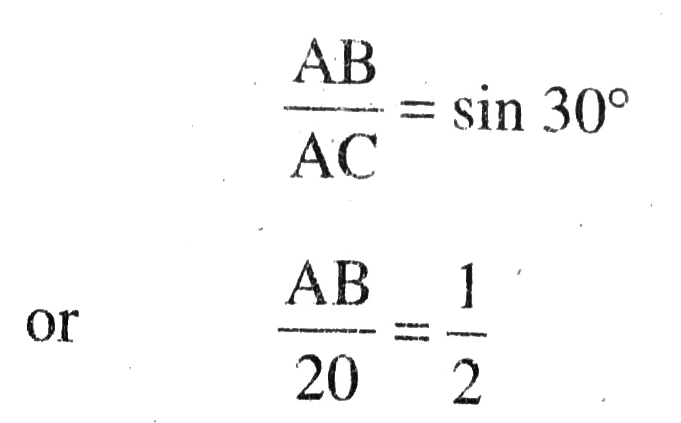
Hence, height of pole is 10 m. Ans.
Q. 2. A tree breaks due to storm and the broken part bends so that the top of the tree touches the ground making an angle 30° with it. The distance between the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is 8 m. Find the height of the tree.
Solution. Let BD be length of tree before storm. After storm AD = AC = length of broken part of tree. The angle of elevation in this situation is 30°. Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
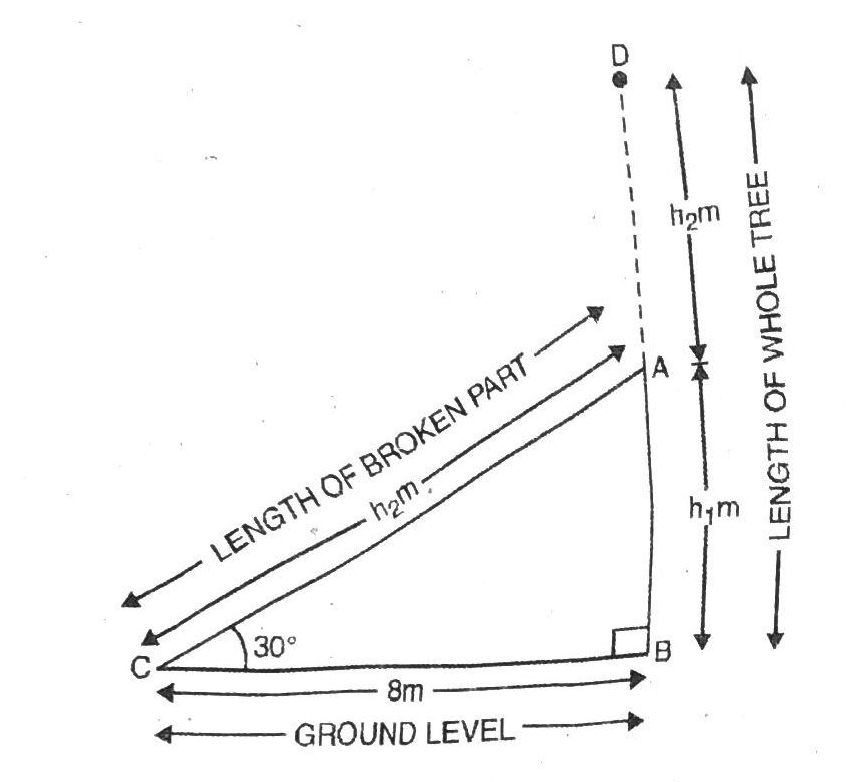
In right angled ΔABC,

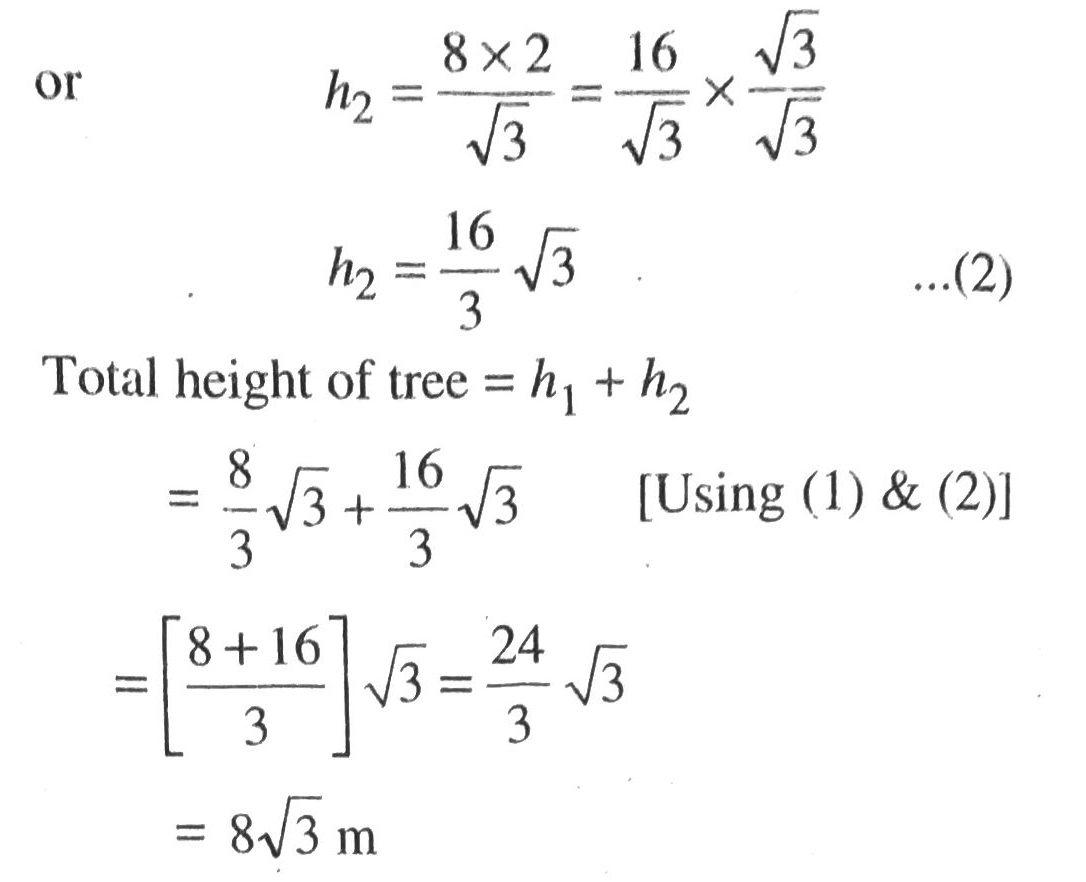
Hence, height of the tree is 8√3 m Ans.
Q. 3. A contractor plants to install two slides for the children to play in a park. For the children below the age of 5 years, she prefers to have a slide whose top is at a height of 1.5 m, and is inclined at an angle of 30° to the ground, whereas for elder children, she wants to have a steep slide at a height of 3 m, and inclined at an angle of 60° to the ground. What should be the length of the slide in each case ?
Solution.
Case I. For children below 5 years.
Let AC = 1₁m denote the length of slide and BC = 1 · 5 m be the height of slide. The angle of elevation is 30°.
Various arrangements are shown in figure.
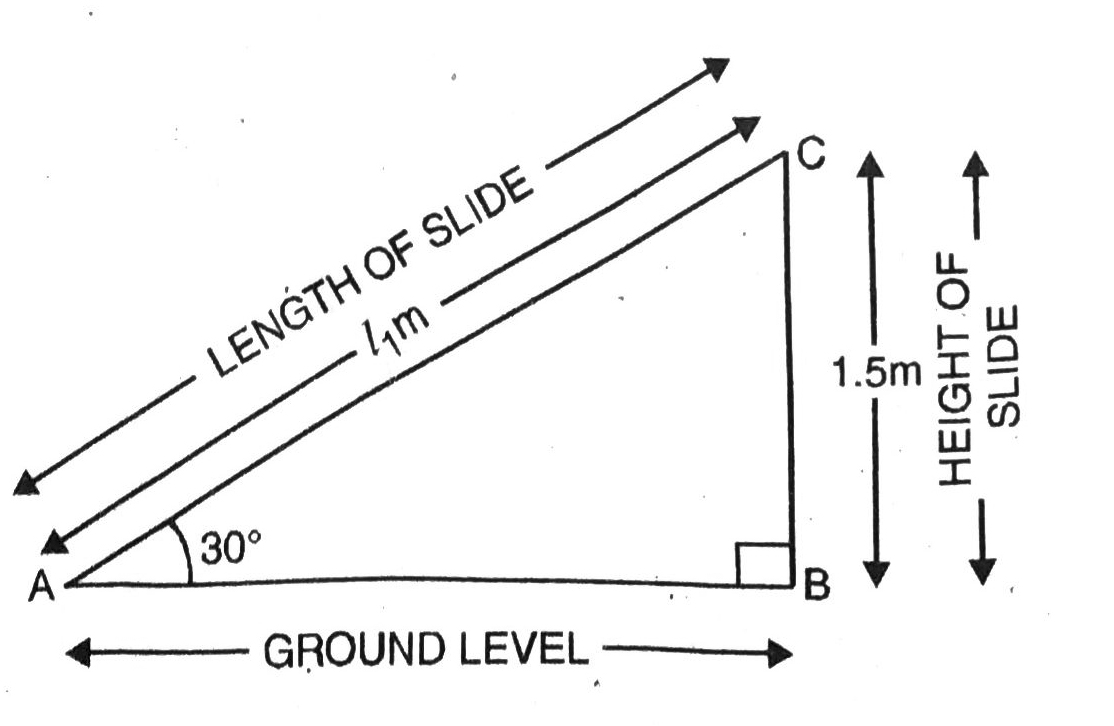
In right angled ΔABC,
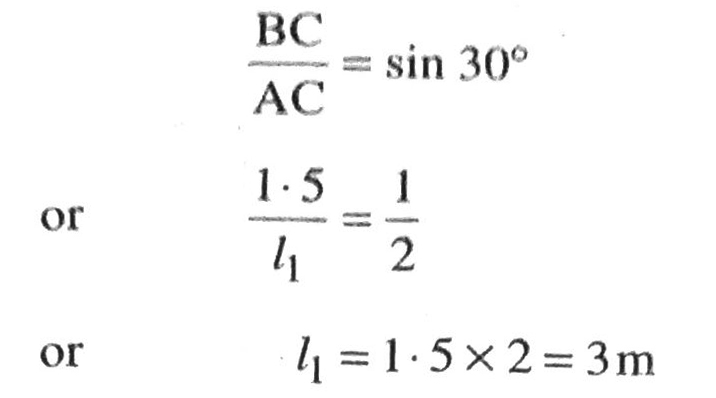
Case II. For Elder children
Let AC = 12m represent the length of slide and BC= 3 m be the height of slide. The angle of elevation is 60°. Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
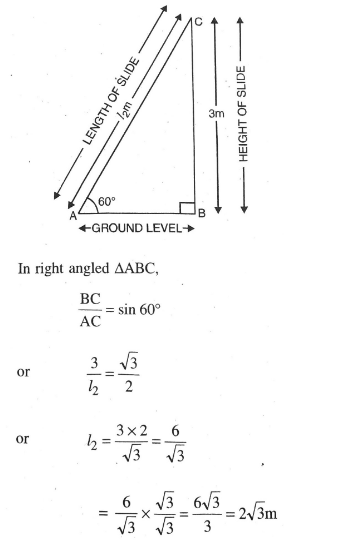
Hence, length of slides for children below 5 years and elder children are
3 m and 2√3 m Ans.
Q. 4. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of the tower, is 30°. Find the height of the tower.
Solution. Let BC = h m be the height of tower and AB = 30 m be the distance at ground level. Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
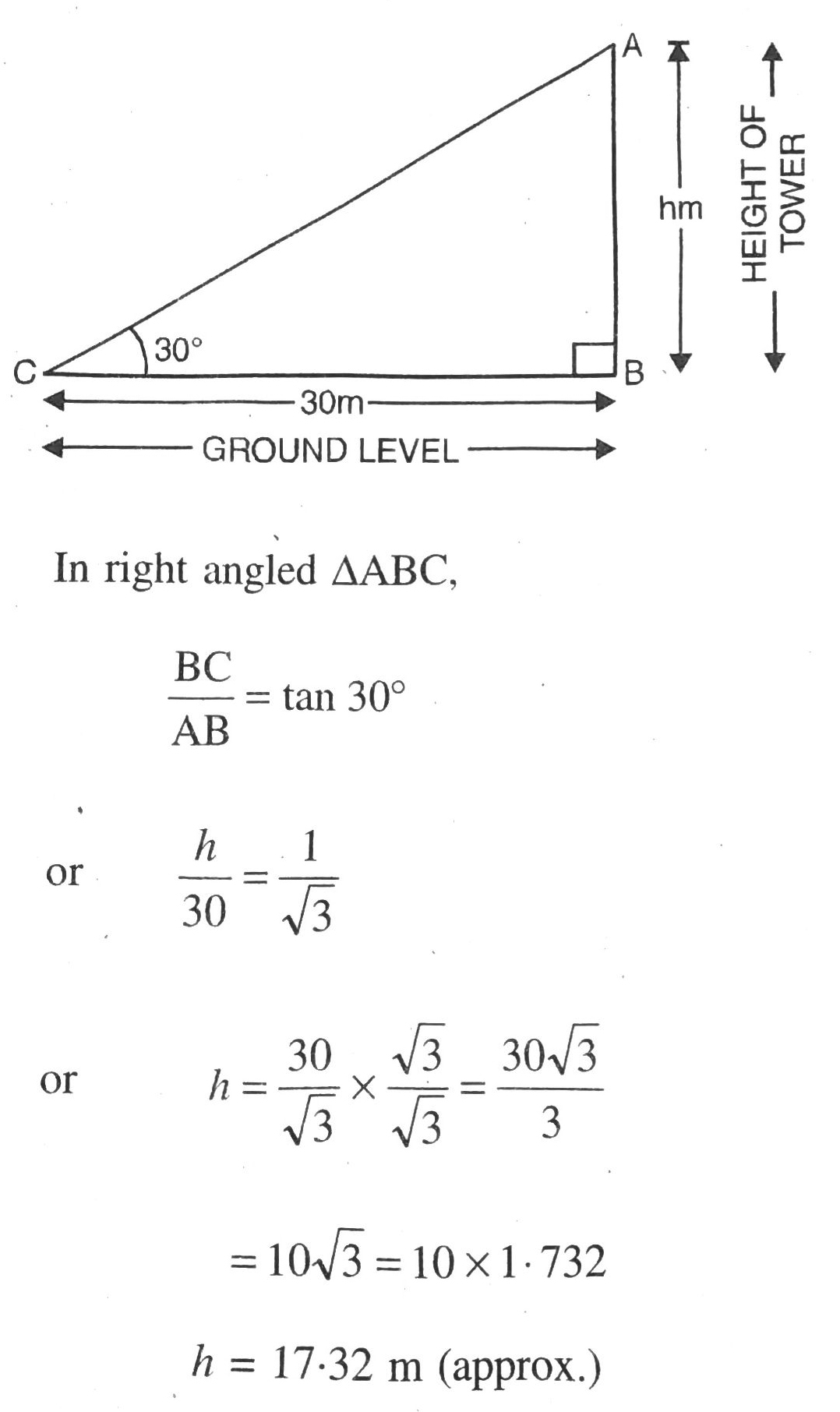
Hence, height of tower are 17·32 m. Ans.
Q. 5. A kite is flying at a height of 60 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
Solution. Let us suppose position of the kite is at point C. AC = l m be length of string with which kite is attached. The angle of elevation for this situation be 60°. Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
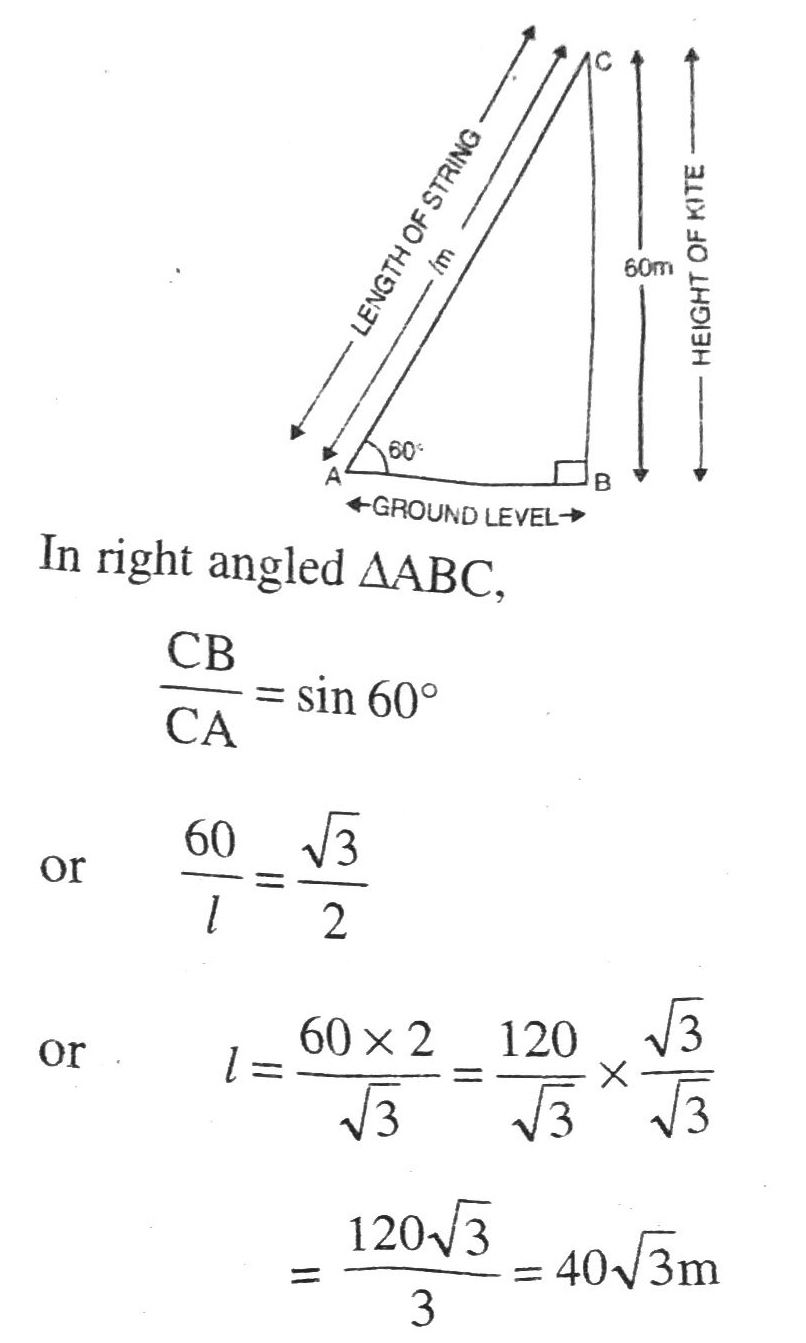
Hence, length of the string be 40√3 m Ans.
Q. 6. A 1.5 m tall boy is standing at some distance from a 30 m tall building. The angle of elevation from his eyes to the top of the building increases from 30° to 60° as he walks towards the building. Find the distance he walked towards the building.
Solution. Let ED = 30 m be the height of building and EC = 1.5 m be the height of boy. The angle of elevation at different situation are 30° and 60° respectively.
Various arrangements are as shown in figure. Now DC = ED – CE
= 30 m – 1.5 m
=28.5 m

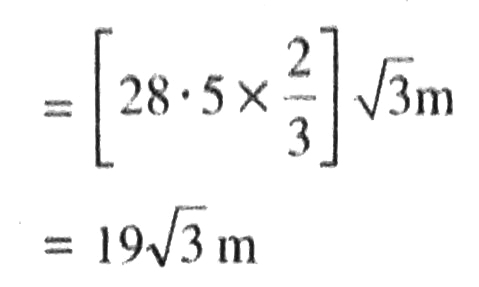
Hence, distance covered by boy towards the building is 19√3 m Ans.
Q. 7. From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a 20 m high building are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Solution. Let BC = 20 m be the height of building and DC = h m be the height of transmission tower. The angle of elevation of the bottom and top of a transmission tower are 45° and 60° respectively.
Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
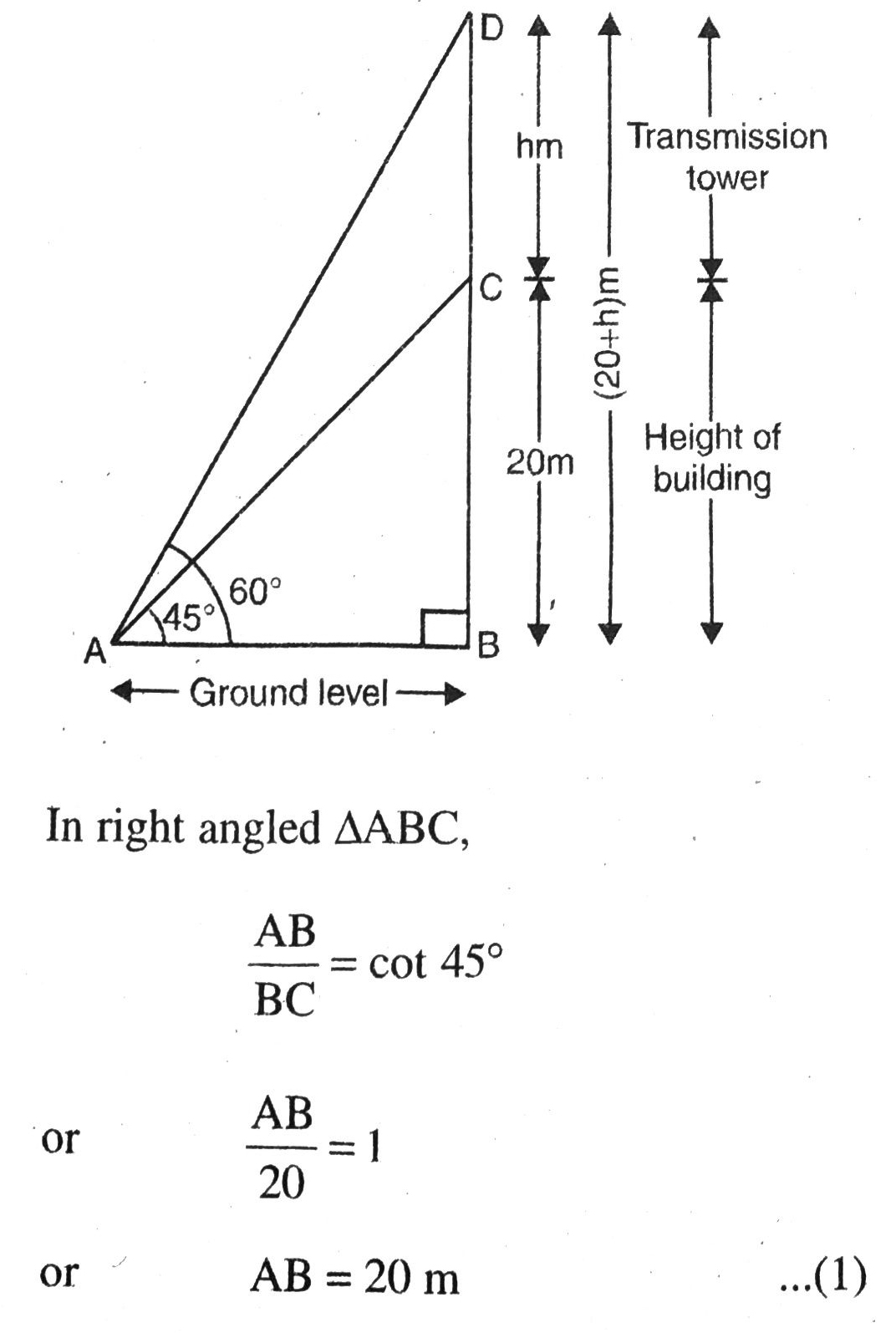

Hence, height of the tower is 14.64 m. Ans.
Q. 8. A statue 1.6 m tall stands on the top of a pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 45°. Find the height of the pedestal.
Solution. Let BC = h m be the height of Pedestal and CD = 1.6 m be the height of statue. The angle of elevation oftop of statu e and top pedestal are 60° and 45° respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
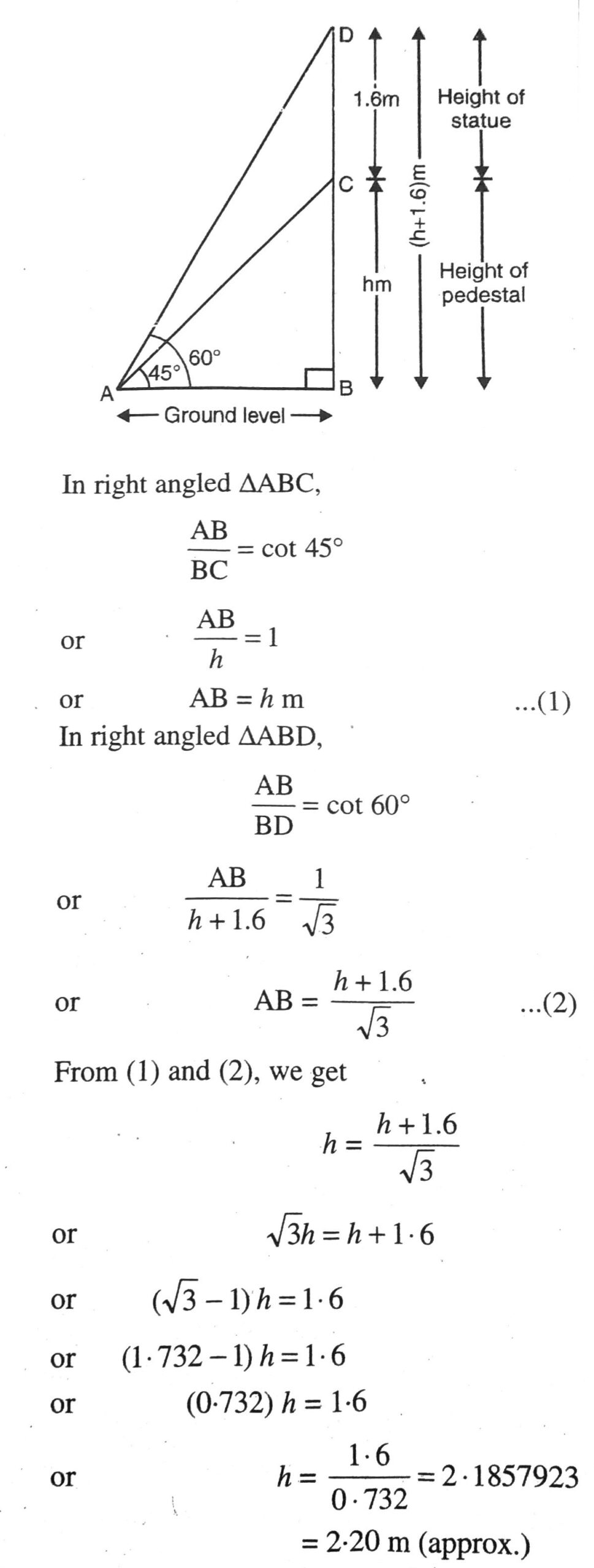
Hence, height of pedestal is 2·20 m. Ans.
Q. 9. The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the building.
Solution. Let BC = 50 m be height of tower and AD = h m be height of building. The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of tower and top of tower from foot of the building are 30° and 60° respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
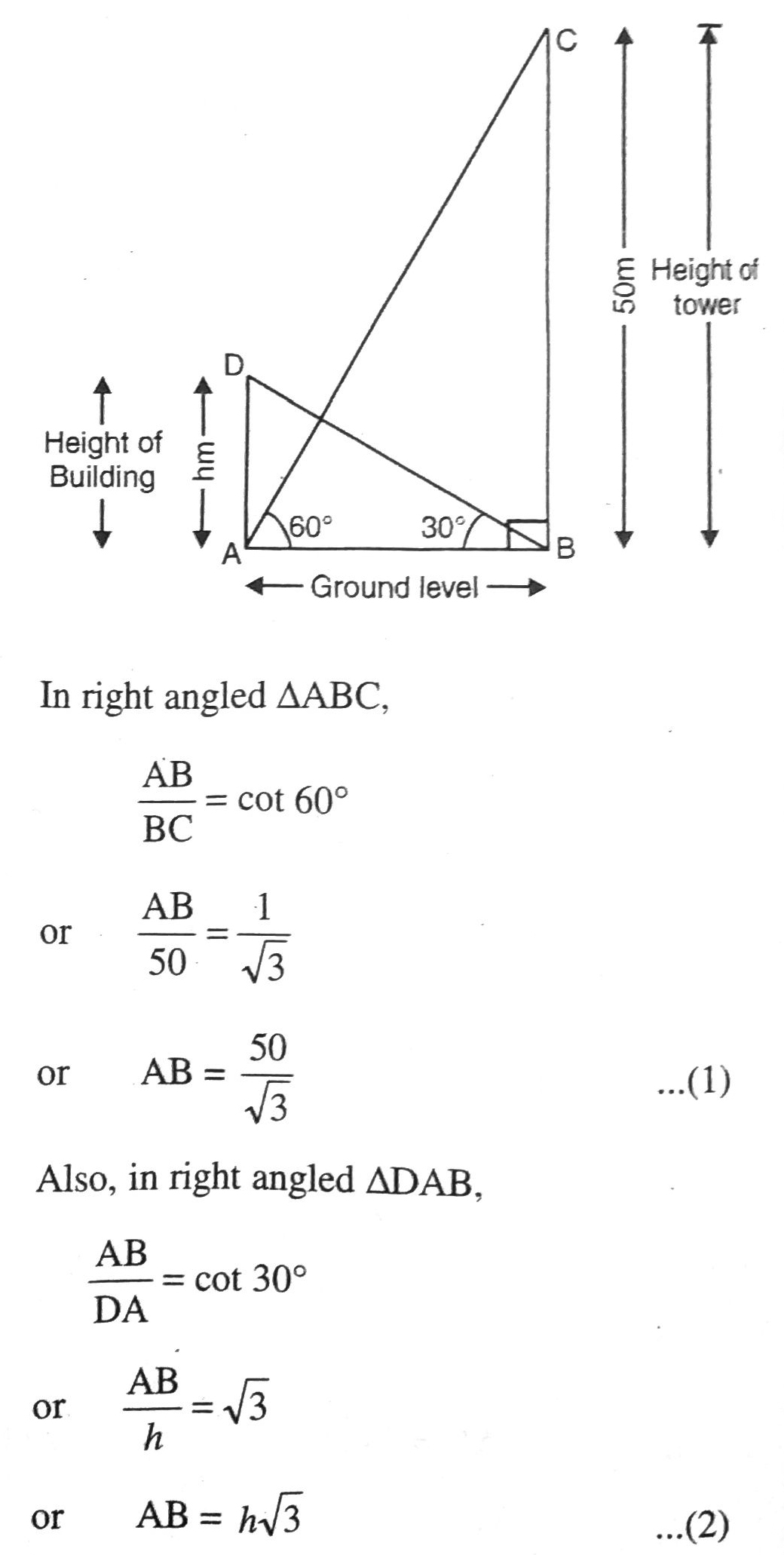
From (1) and (2), we get
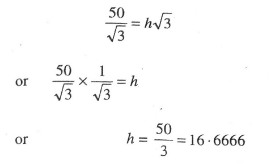
h = 16·70 m (approx.)
Hence, height of building is 16·70 m Ans.
Q. 10. Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30°, respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles.
Solution. Let BC = DE = h m be height of two equal poles and point A be the required position where the angle of elevations of top of two poles are 30° and 60° respectively. Various arrangement are as shown in the figure.
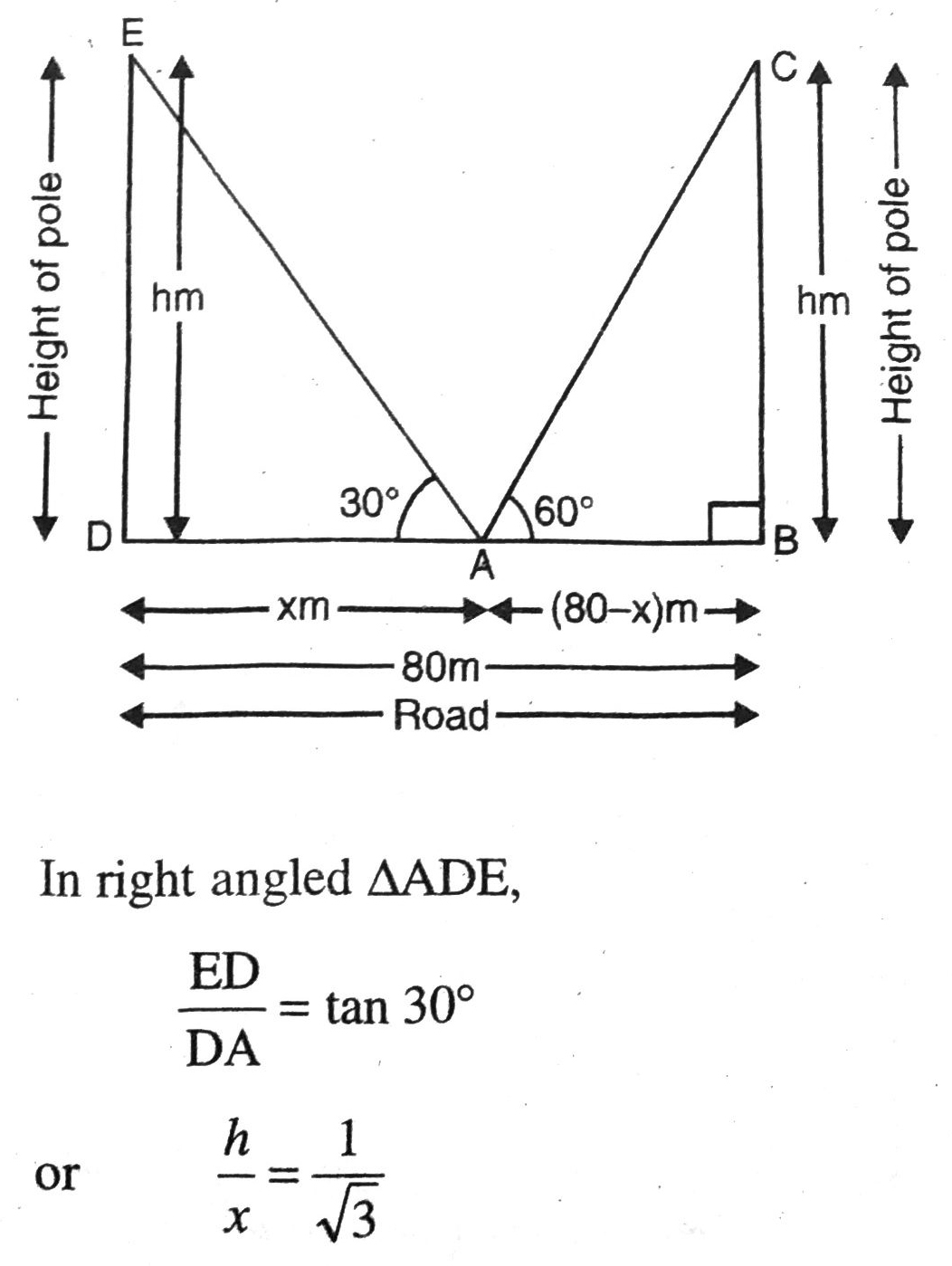

∴ DA = x = 60 m
and AB = 80 – x = (80-60) m = 20m.
Hence, heigth of the poles are 34·64 m and the distances of the point from the poles are 20 m and 60 m respectively. Ans.
Q. 11. A TV tower stands vertically on a bank of a canal. From a point on the other bank directly opposite the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 60°. From a point 20 m away from this point on the line joining this point of the foot of the tower the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30° (see fig.). Find the height of the tower and the width of the canal.
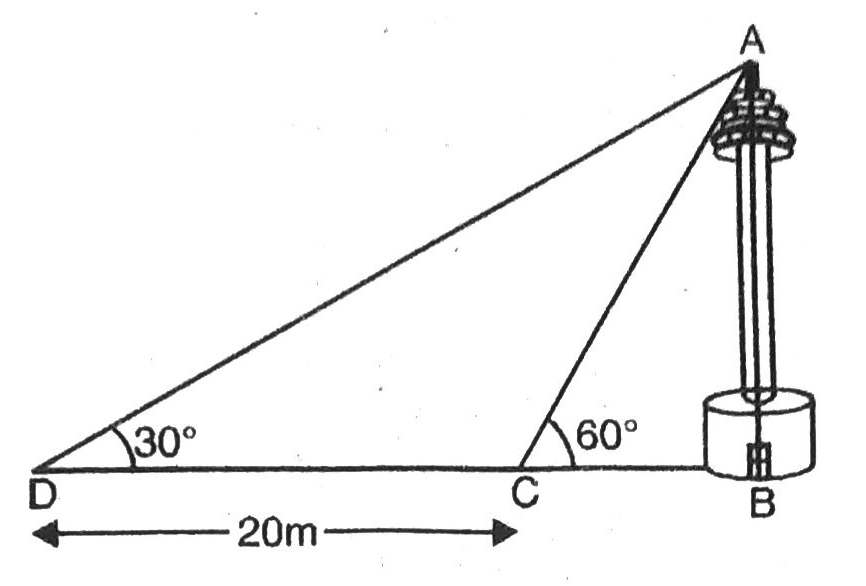
Solution. Let BC = x m be the width of canal and CD = h m be height of TV tower. The angles of elevation of top of tower at different position are 30° and 60° respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
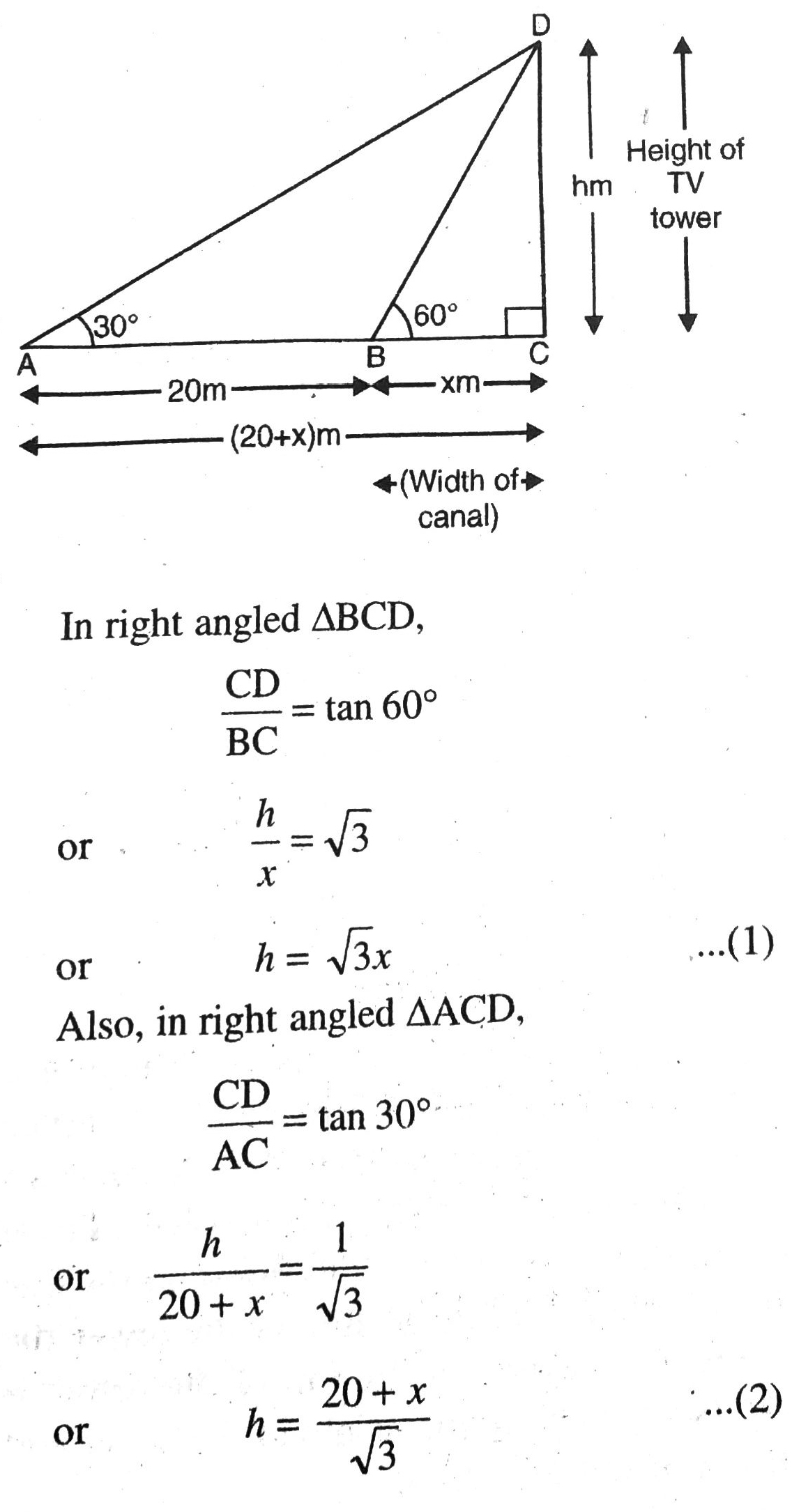
From (1) and (2), we get
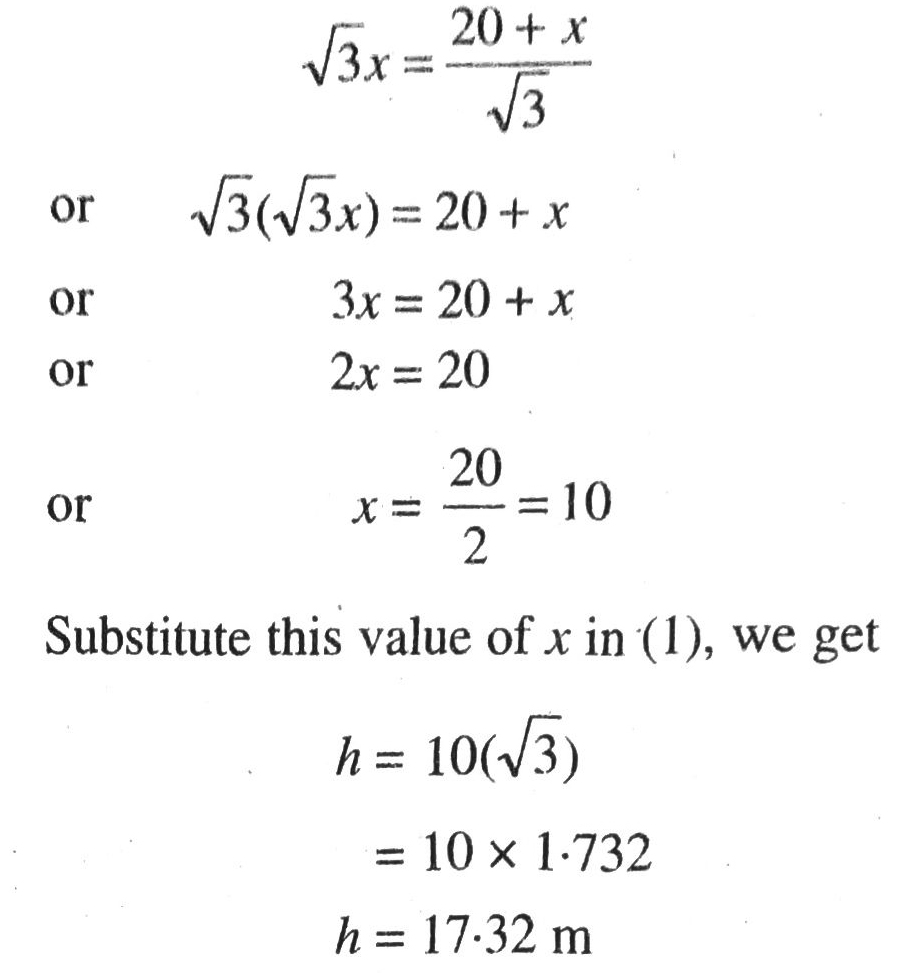
Hence, height of TV tower is 17·32 m and width of the canal is 10 m. Ans.
Q. 12. From the top of a 7 m high building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower is 60° and the angle of depression of its foot is 45°. Determine the height of the tower.
Solution. Let BD = h m be the height of cable tower and AE = 7 m be the height of building. The angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower and angle of depression of its foot from top of a building are 60° and 45° respectively.
Various arrangement are as shown in figure.
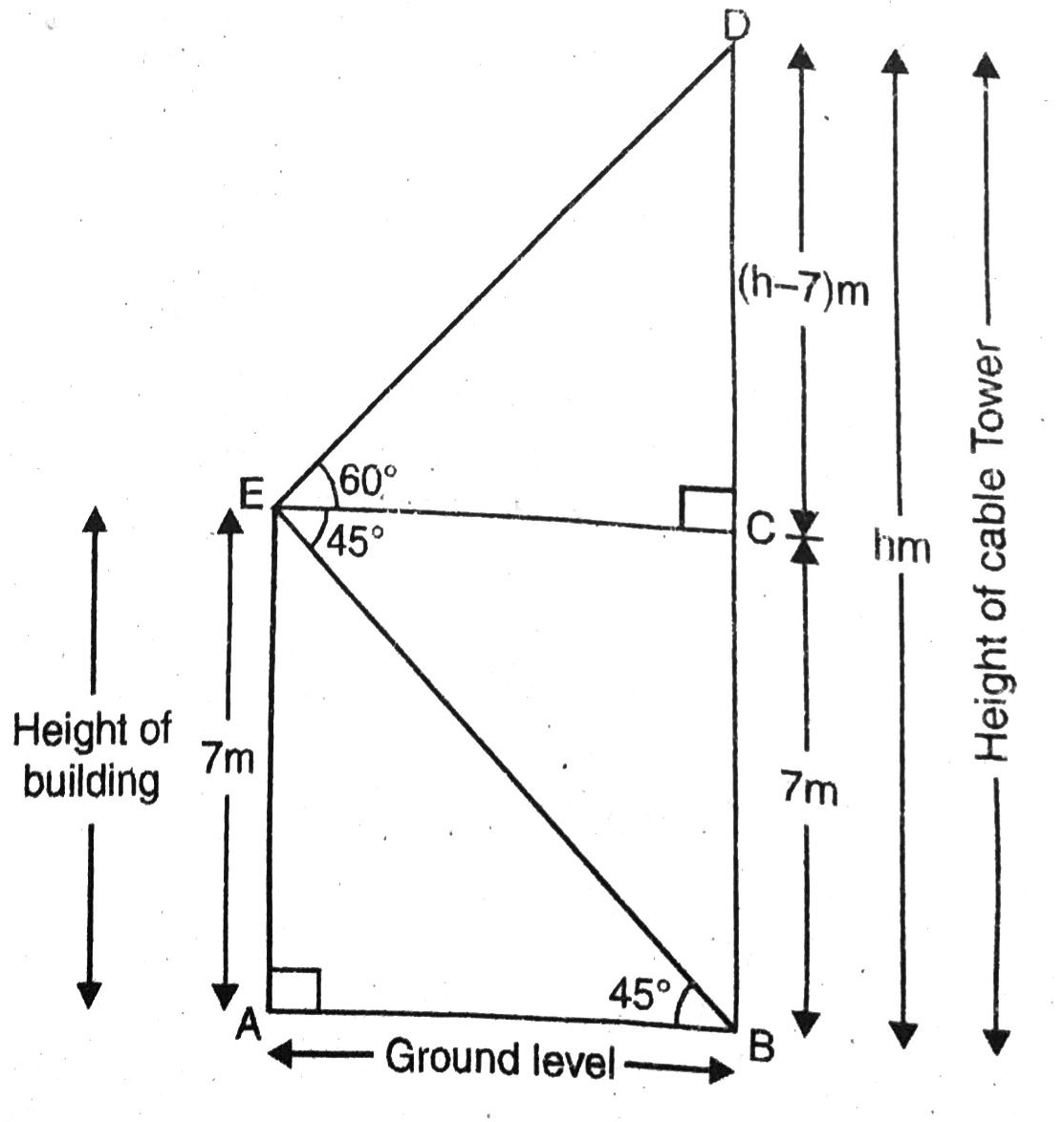

or h = 7(1·732 + 1) = 7(2·732)
or h = 19·124
or h = 19·20 m (approx.)
Hence, height of the tower is 19·20 m Ans.
Q. 13. As observed from the top of a 75 m high lighthouse from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the lighthouse, find the distance between the two ships.
Solution.
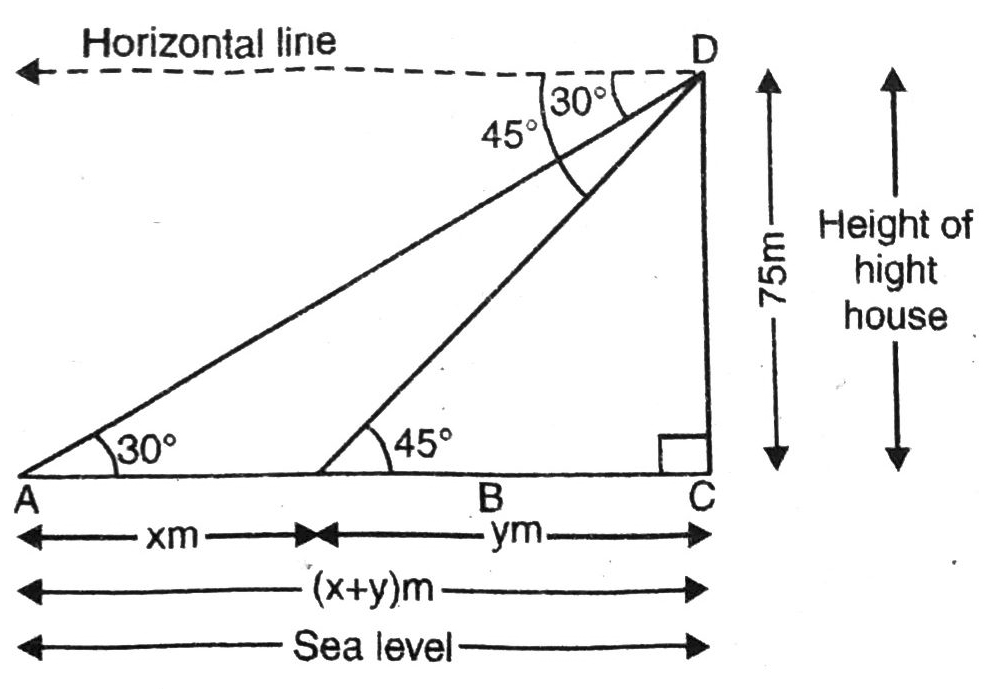
Let CD = 75 m be the height of light house and point D be top of light house from angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45° respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
In right angled ΔBCD,

Hence, distance between the two ships is 54·90 m. Ans.
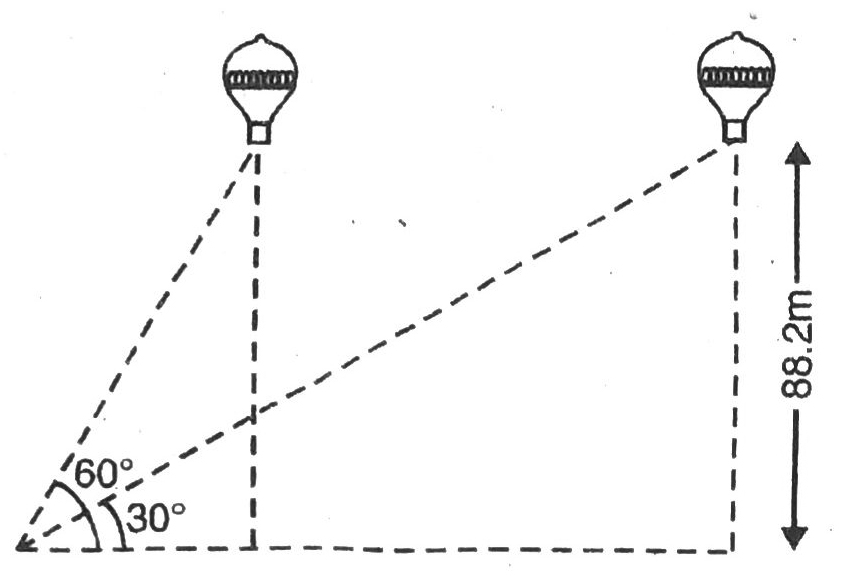
Q. 14. A 1.2 m tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of 88.2 m from the ground. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the eyes of the girl at any instant is 60°. After some time, the angle of elevation reduces to 30° (see fig.). Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval.
Solution.
Let ‘A’ be the position of 1.2 m tall girl, at the point of the angles of elevation of balloon at different distances are 30° and 60° respectively. Also, QE = RD = 88.2 m be height of balloon. Various arrangements are as shwon in the figure.
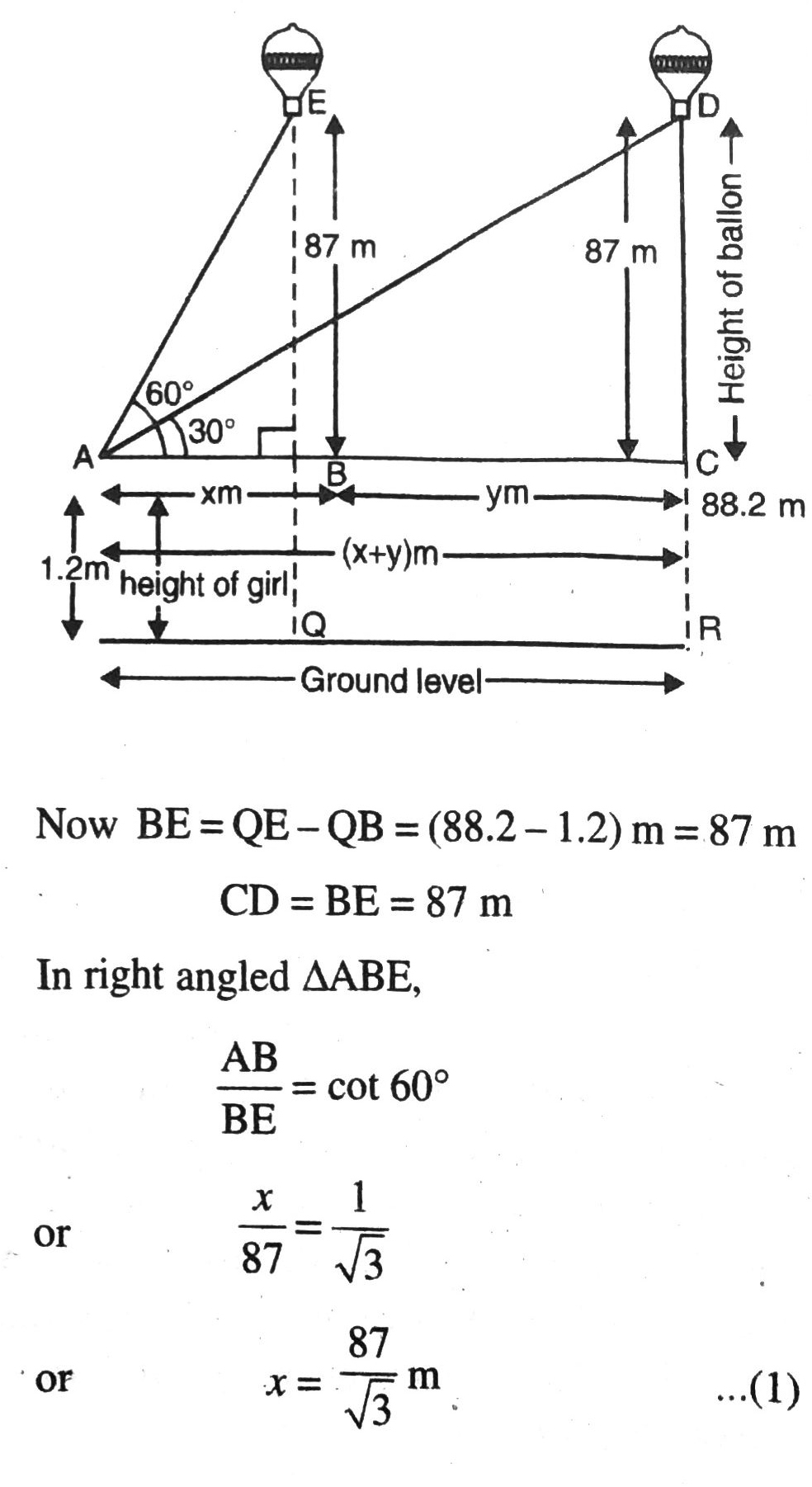
Also, in right angled ΔACD,
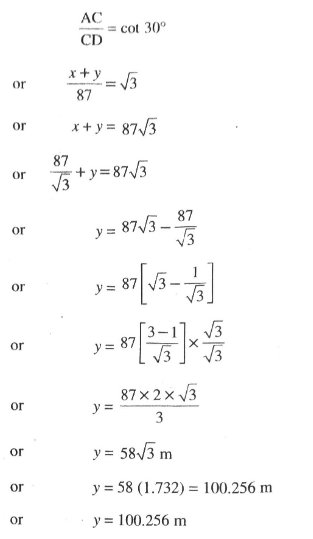
Hence, distance travelled by the balloon during the interval is 100.256 m. Ans.
Q. 15. A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing at the top of the tower observes a car at an angle of depression of 30°, which is approaching the foot of the tower with a uniform speed. Six seconds later, the angle of depression of the car is found to be 60°. Find the time taken by the car to reach the foot of the tower from this point.
Solution. Let CD be the tower of height h metres. Let A be initial position of the car and after six seconds the car be at B. The angles of depression at A and B are 30° and 60° respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in figure.
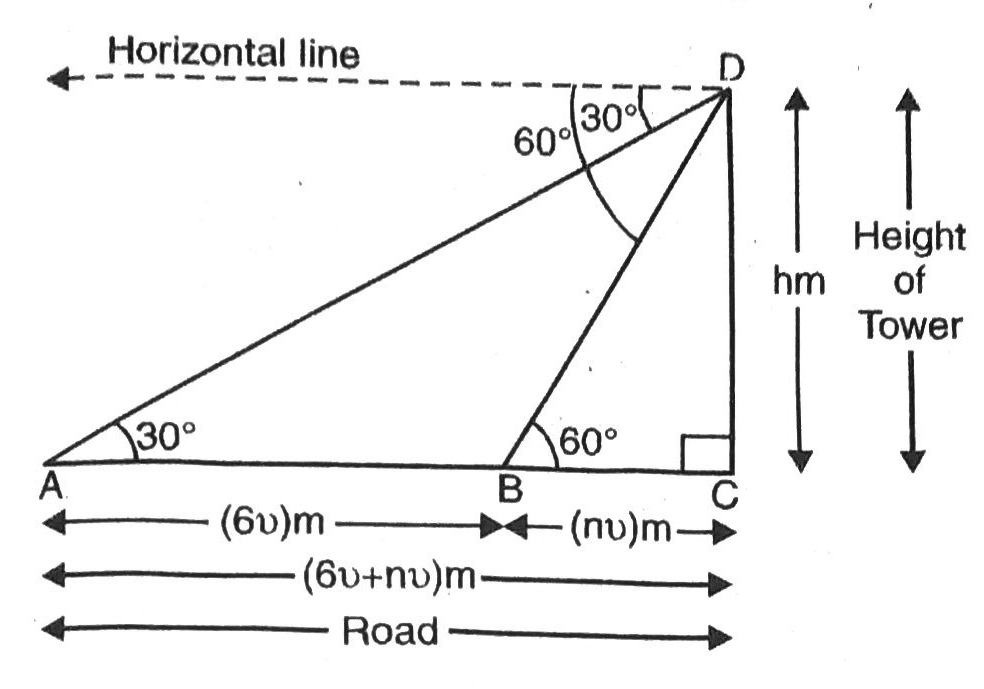
Let speed of the car be v metre per second using formula, Distance = Speed + Time
AB = Distance covered by car in 6 seconds
AB = 6υ metre
Also, time taken by car to reach the tower be ‘n’ seconds.
∴ BC = nυ metre
In right angled ΔACD,
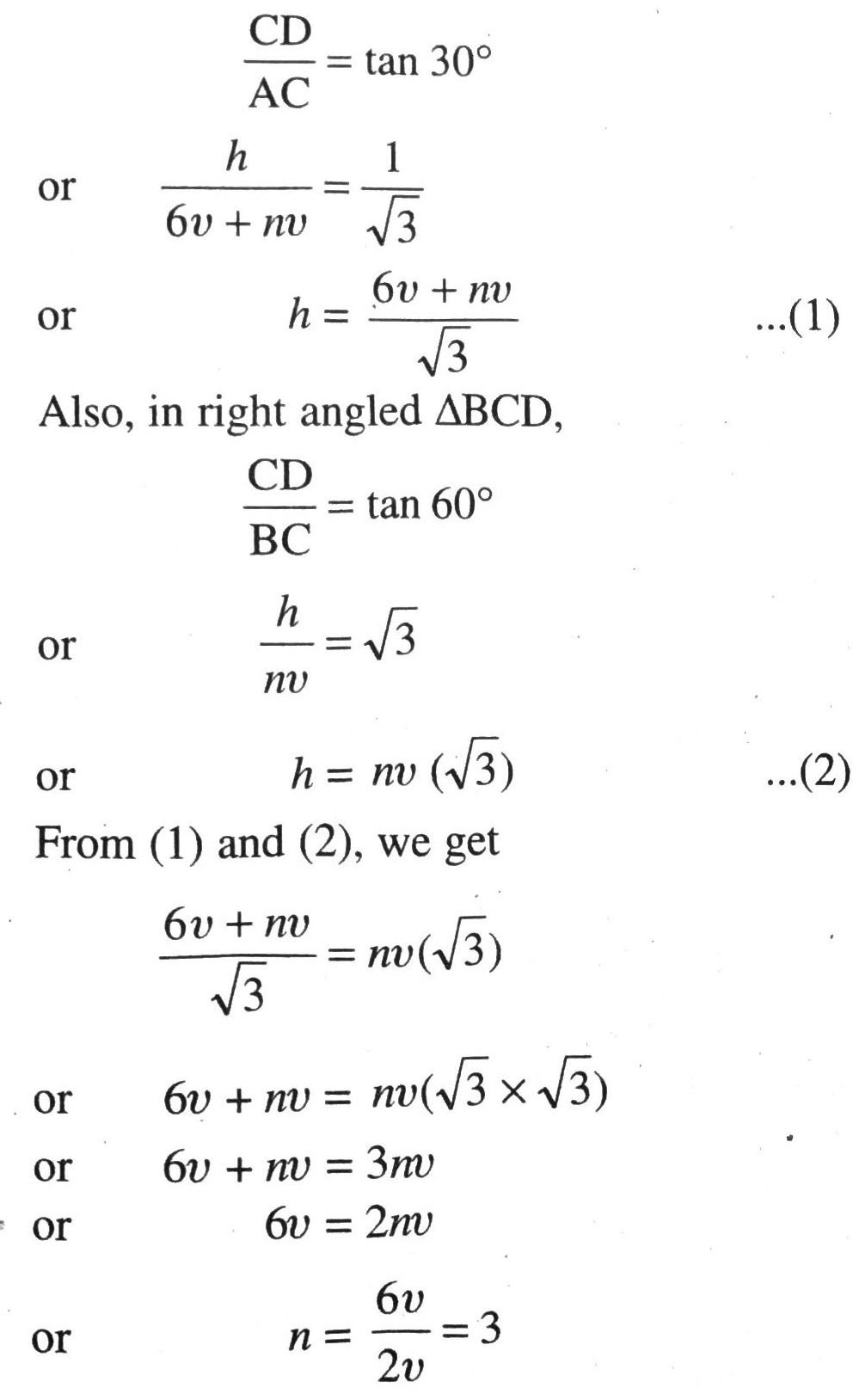
Hence, time taken by car to reach the foot of tower is 3 seconds.
Q. 16. The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is 6 m.
Solution. Let CD = h m be the height of tower and B; A be the required points which are at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the tower respectively. Various arrangements are as shown in the figure.
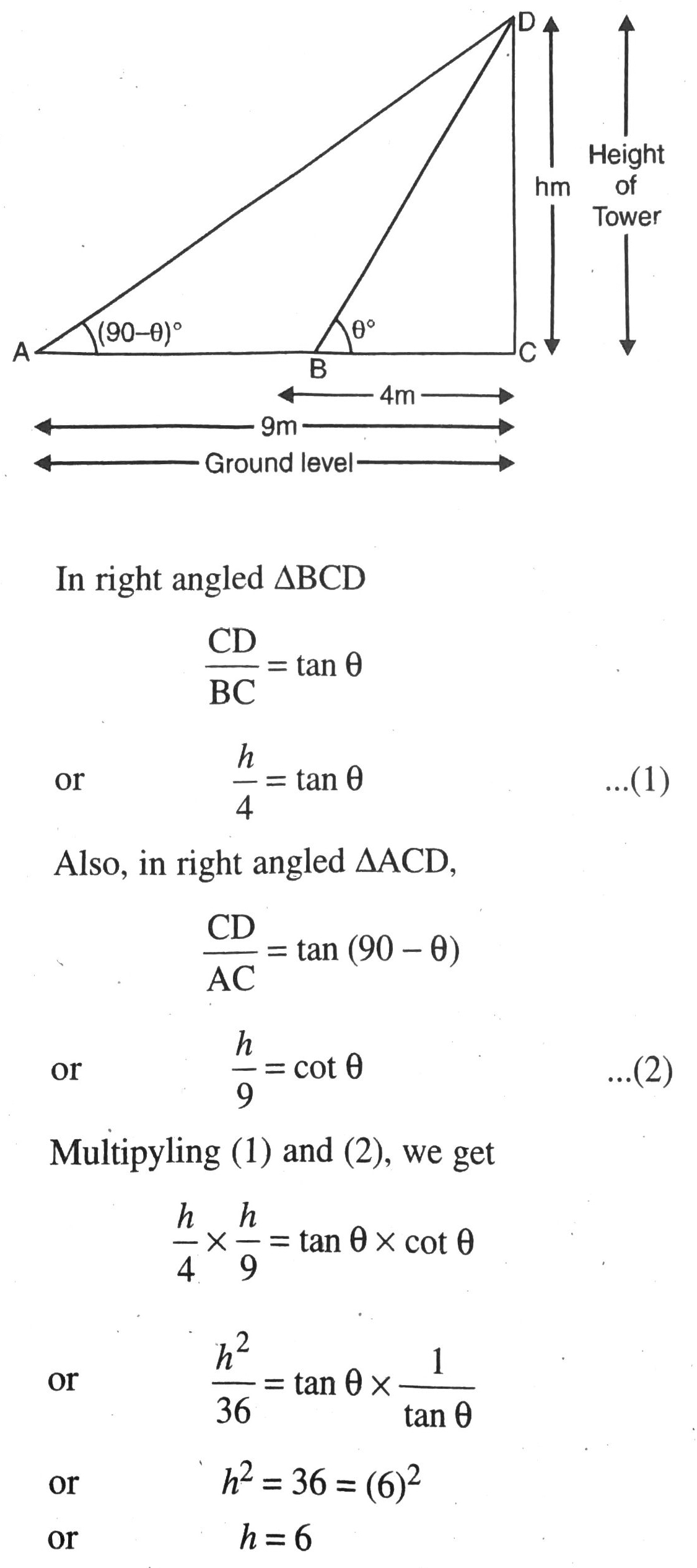
Hence, height of the tower is 6 m. Ans.
Follow on Facebook page – Click Here
Google News join in – Click Here
Read More Asia News – Click Here
Read More Sports News – Click Here
Read More Crypto News – Click Here