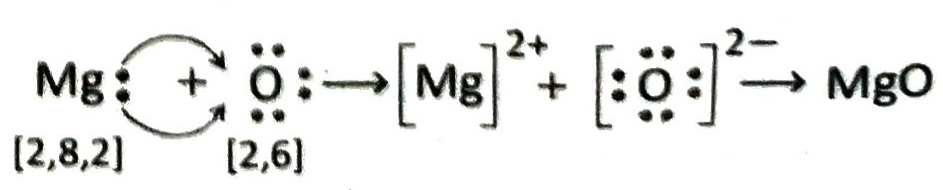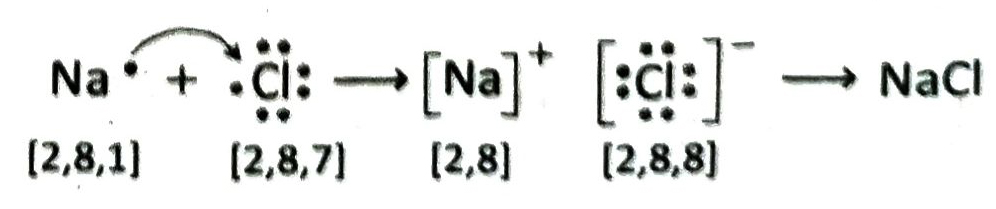WBBSE 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.2 Ionic and Covalent Bonds
West Bengal Board 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.2 Ionic and Covalent Bonds
WBBSE 10th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
8.2 Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Synopsis
Electronic Concept of Valency, Ionic Bonding and Properties of Ionic Compounds
- The force of attraction which holds two or more constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in different chemical species is known as chemical bond. It is formed either by losing or gaining electrons or by sharing pairs of electron.
- Octet rule: To attain chemical stability, an atom tends to acquire stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas, i.e., tends to attain 8 electrons in its outermost shell either by gaining or losing electrons or by sharing pairs of electron. This tendency to acquire 8 electrons in the outermost shell of the atoms is called octet rule. There are many compounds where the constituent atoms do not follow octet rule.
- Duplet rule: The elements near helium (H, Li, Be) in the periodic table try to attain the stable electronic configuration of. He by gaining, losing or sharing electrons in their outermost shells. This tendency to acquire 2 electrons in the outermost shell of atoms is called duplet rule.
- Electrovalency: To achieve stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas, some atomis completely give up one or more electrons from their outermost shell to form stable cations while some other atoms gain these electrons to form stable anions. These two oppositely charged ions then combine together through electrostatic force of Ca for attraction to form chemical compounds. The capacity of the elements for such chemical combination is known as electrovalency or ionic valency. The bond formed between the atoms due to electrovalency is called electrovalent bond or ionic bond and the compound formed in this way is called electrovalent or ionic compound.
- Characteristics of ionic compounds: lonic compounds do not exist as discrete molecules. They solid crystalline substances with high melting and boiling points. They do not conduct electricity in solid state but are good conductors in molten state or in aqueous solution. lonic compounds are soluble in polar solvents and react very fast in solution.
- The term ‘molecular mass’ is not applicable for ionic compounds as they do not exist in molecular form. Instead, formula mass of these compounds is determined. For covalent compounds, both molecular and formula mass are the same.
- In NaCl crystal, a large number of Na+ and CI– ions remain closely packed by strong electrostatic force of attraction. This leads to the formation of stable three dimensional crystal lattices.
TOPIC – A
Electronic Concept of Valency, Ionic Bonding and Properties of Ionic Compounds
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Why do atoms of different elements react with each other?
Ans. The electronic configuration of the noble gases are very stable. To attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gases, atoms of different elements react with each other.
Q.2 Define chemical bond.
Ans. The force of attraction which holds two or more constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in different chemical species is called chemical bond. It is formed either by losing or gaining electrons or by sharing pairs of electrons by atoms.
Q.3 What is octet rule?
Ans. To attain chemical stability, an atom tends to acquire stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas either by gaining or losing electrons or by sharing pairs of electrons of its outermost shell. This tendency to acquire 8 electrons in the outermost shell of an atom is called octet rule.
Q.4 State the limitations of octet rule.
Ans. Octet rule has certain limitations. These are –
- In some compounds, the central atom has more or less than 8 electrons, yet the molecules are highly stable. Octet rule fails to explain this.
- Octet rule is based on the stability and inertness of noble gases. But some noble gases specifically Xe form compounds with oxygen and fluorine.
- This rule cannot explain the relative stability of different molecules.
Q.5 Octet rule is not always followed in case of ionic compounds. Give examples.
Ans. The stability of ionic compounds cannot be always explained by octet rule. In case of transition metals, it is observed that octet rule is not followed. For example, in FeCl2, Fe2+ ion has 14 electrons in its valence shell and in FeCl3, Fe3+ ion has 13 electrons in its valence shell. In both cases, octet rule is violated. Again, in LiH, both Li+ ion and H– ion have 2 electrons in their valence shells. Hence, octet rule is not valid for all ionic compounds.
Q.6 Show with an example that ionic compounds can be formed without fulfillment of octet of the corresponding ions.
Ans. The stability of all ionic compounds can not be explained with the concept of sharing 8 electrons in the valence shell of the constituting ions, or the octet rule, e.g., in LiH the constituting ions Li⊕ and HΘ both have 2 electrons in their valence shell. Moreover, in case of elements showing variable electrovalency, especially in transition metals octes rule is not obeyed in many instances. E.g., in FeCl2 or FeCl3, octet rule is not obeyed in Fe2+ and Fe3+.
Q.7 What is duplet rule?
Ans. To attain chemical stability an atom of an element nearer to He (H, Li, Be) tends to acquire stable electronic configuration like He either by gaining or losing electrons or by sharing electron pairs of its outermost shell. This tendency to acquire 2 electrons in the outermost shell of an atom is called duplet rule.
Q.8 Which type of chemical bond is formed by complete transfer of electron from one atom to another atom? Explain with an example.
Ans. Ionic bond or electrovalent bond is formed by complete transfer of electron from one atom to another atom.
Magnesium (electronic configuration: 2, 8, 2) loses 2 valence electrons to form Mg2+ ion and attains the stable electronic configuration of nearest inert gas. On the otherhand oxygen (electronic configuration: 2, 6) accepts these two electrons to form O2- ion and attains the stable electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas. Therefore when Mg and O atoms combine, the former transfers its valence electron to the latter resulting in the formation of Mg2+ and O2- respectively. The two ions are then held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction to form MgO.
Q.9 Define electrovalency.
Ans. To achieve the stable electronic configuration of nearest noble gas, some atoms give up one or more electrons from outermost shell completely to form stable cations while some other atoms gain these electrons to form stable anions. These two types of oppositely charged ions combine together through electrostatic force of attraction to form chemical compounds. The capacity of the elements for such chemical combination is known as electrovalency.
Q.10 How is electrovalency of an atom measured? Explain with example.
Ans. The number of electrons gained or released by an atom during the formation of ionic compound is measured as the electrovalency of that atom.
For example, during formation of NaCl, a Na– atom releases one electron to form Na+ ion while a Cl-atom accepts that electron and converts to Cl– ion. Hence, the electrovalency of both sodium and chlorine in NaCl is 1.
Q.11 lonic bonds are not real bonds-justify real bonds-just the statement.
Ans. In covalent compounds, two atoms share one or more pairs of electron with each other to form bonds having definite direction. But, in electrovalent compounds, the bond between two atoms is formed due to the strong electrostatic force of attraction between the cations and the anions. Here, no electron-pair is shared by the involved ions. That is why ionic bonds are not considered as real bond.
Q.12 State two important characteristics of wo important characteristics ionic bond.
Ans. An ionic bond shows the following characteristics – (1) An ionic bond is formed between atoms of an electropositive and an electronegative element. (2) lonic bond is in fact an electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions. So, sometimes, it is not considered, as a real bond.
Q.13 Write down some properties of ionic compound.
Ans.
- Ionic compounds form crystals of definite geometrical shape.
- The melting and boiling points of ionic compounds are generally very high.
- Ionic bond is non-directional in nature.
- Ionic compounds do not exhibit isomerism.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state, but in the molten state or in solution in a suitable solvent (like water) conduct electricity.
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve in polar solvents.
Q. 14 Why any ionic compound possesses high boiling point and melting point?
Ans. In ionic compounds, the oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. The mutual attraction between large number of oppositely charged ions results in the formation of large crystal lattices. Separation of ions from these crystal lattices require large amount of energy. Hence, ionic compounds possesses high melting and boiling points.
Q.15 Discuss the physical state of ionic compounds.
Ans. At normal temperature and pressure all ionic compounds are crystalline solids. This is because the oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction which results in the formation of regular three dimensional network called crystal lattice. Ionic compounds do not exist as discrete molecules.
Q.16 Why are ionic compounds hard in nature?
Ans. In ionic compounds, large number of oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction which results in the formation of large crystal lattices. The ions remain closely packed in the crystal and the intermolecular space between them is very small. Hardness of an ionic compound is due to the aggregation of large number of ions in a very small space.
Q.17 Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state or in aqueous solutions but are non-conductors in the solid state. Explain with reason.
Ans. In solid state, the cations and anions in an ionic compound are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. Hence, the ions are immobile and the compound fails to conduct electricity in solid state. However, when the compound is in molten state or is dissolved in water, the crystal lattice breaks and the ions are separated. Due to presence of such mobile ions, ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state or in aqueous solution.
Q.18 Discuss with example the solubility of ionic compounds.
Ans. Ionic compounds are generally soluble in polar solvents (such as water), but are insoluble in nonpolar solvents (such as CS2, CCl4, benzene etc). For example, NaCl is soluble in water but insoluble in benzene.
Q.19 Why does the reactions involving ionic compounds occur at a faster rate?
Ans. Reactions of ionic compounds generally take place in solutions. In solution, the ionic compounds dissociate to form ions which take part in the reaction. Due to participation of the ions, the reactions occur at a faster rate.
Q.20 Explain why ionic compounds are ories are soluble in polar solvents.
Ans. When an ionic compound is dissolved in a polar solvent, the negatively charged end of the polar solvent attracts the cations present in crystal lattice of the solid. Similarly the positive end of the solvent attracts the anions. This attraction by the solvent molecules decreases the force of attraction between cations and anions in the crystal lattice. Hence the dissociated ions are separated and are surrounded by solvent molecules in solution to get stabilised. This is why ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents.
Q.21 Why are ionic compounds insoluble in non-polar solvents?
Ans. The molecules of a non-polar solvent cannot attract the ions of an ionic compound effectively. Hence, ionic compounds do not generally dissociate in non-polar solvent. That is why ionic compounds are generally insoluble in non-polar solvents.
Q.22 A compound has high boiling and melting point. It does not conduct electricity in solid state but is a good conductor in solution. Which type of bond is present in the compound? What is the nature of the constituent particles of the compound?
Ans. The compound is an ionic or electrovalent compound. So, ionic bond is present in it.
The compound is composed of cations and anions.
Q. 23 Describe the formation of NaCl.
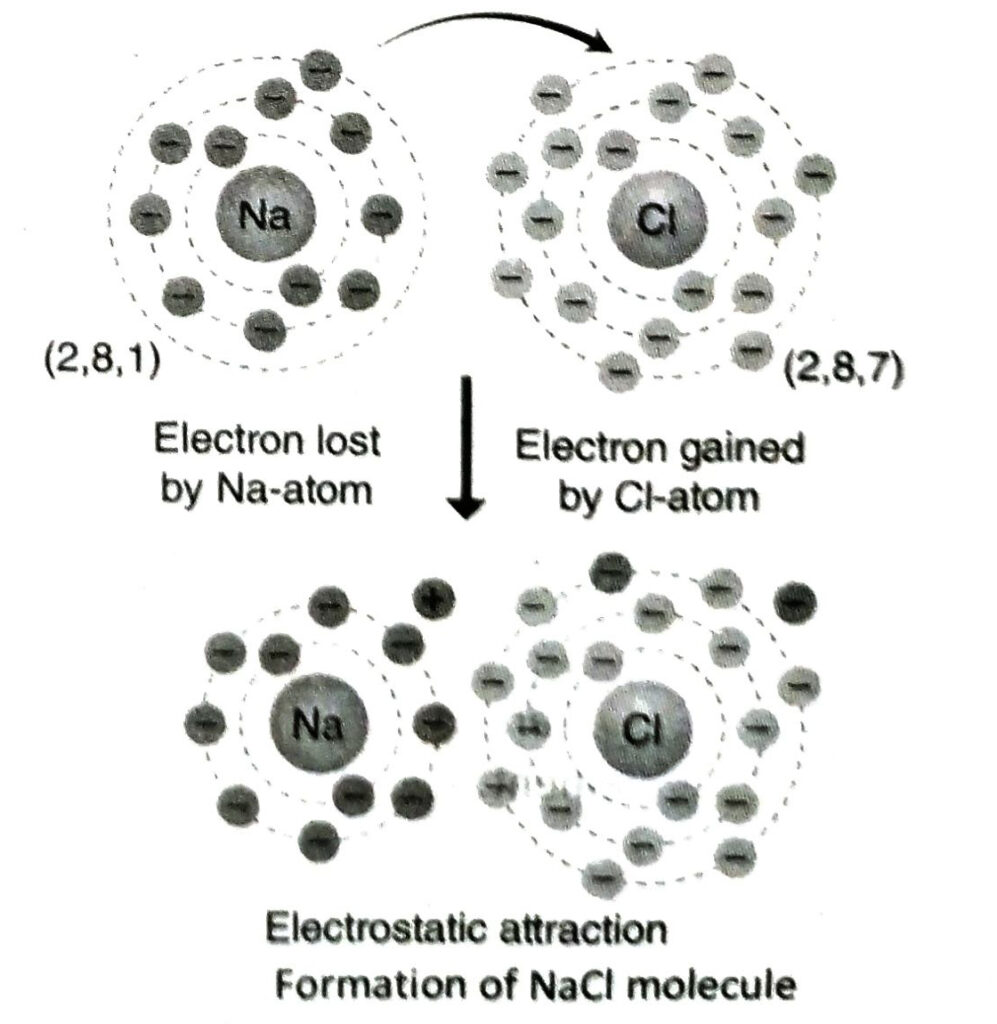
Ans. Electronic configuration of Na-atom is K = 2, L = 8, M = 1 and that of chlorine is K= 2, L = 8, M = 7. When sodium reacts with chlorine, 1 electron from the outermost shell of a sodium atom is transferred to a chlorine atom. As a result, Na+ and Cl– ions are formed. These ions combine by electrostatic force of attraction to form NaCl.
Q.24 Why the bond of sodium chloride can not be expressed as Na – Cl?
Ans. Na-atom loses its valence electron to form Na+ cation and Cl-atom accepts it to form Cl– anion. Na+ and Cl– ions are then held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction to form the electrovalent compound NaCl. Here no electron pair is formed and this force of attraction has no definite direction. So it can be said that the bond of sodium chloride can not be expressed as Na-Cl.
Q.25 Electronic configuration of two elements M and N are 2, 8, 1 and 2, 7 respectively. By which type of valency will the atoms combine to form compound? What will be the probable formula of the compound?
Ans. It is obvious from the electronic configurations that element M has a tendency to lose an electron from its valence shell to attain the stable electronic configuration and forms M+ cation. On the other hand element N has the tendency of accepting the electron in its valence shell to attain the stable electronic configuration and forms N– anion.
Therefore M+ and N– ions will held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction and form compound by electrovalency.
The probable formula of the compound will be MN.
Q.26 Sodium is a highly reactive metal which reacts with water violently. Chlorine is also a highly reactive non-metal having strong oxidising property. But the compound NaCl is safely used as common salt. Explain with reason.
Ans. Ions are generally more stable than free atoms. During chemical combination, Na-atom loses one electron to form Na+ ion while Cl-atom easily accepts that electron to form Cl– ion. Both Na+ and Cl– ions have stable electronic configurations of their nearest noble gases. In case of NaCl, a large number of Na+ and Cl– ions aggregate together to form crystals of NaCl. So, free atoms of sodium and chlorine are not present in NaCl and hence the compound is not as much reactive as free sodium and chlorine atoms. Hence, we can safely use NaCl as common salt.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. At normal temperature, ionic compounds exist as
A. solids
B. liquids
C. gases
D. crystalline solids
Ans. D
2. The solubility of ionic compounds are higher in
A. water
B. alcohol
C. benzene
D. ether
Ans. A
3. In aqueous solution, the crystals of ionic solid dissociates to release
A. molecules
B. atoms
C. cations
D. both cations and anions
Ans. D
4. Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
A. sugar
B. naphthalene
C. wax
D. NaCl
Ans. D
5. Which of the following, though ionic, is insoluble in water?
A. CuSO4
B. CH2COOH
C. NaNO3
D. CaCO3
Ans. D
6. An example of a polar solvent is
A. benzene
B. ether
C. chloroform
D. water
Ans. D
7. Which of the following is not a characteristic of an ionic compound?
A. high melting point
B. electrical conductivity in fused state
C. consist of oppositely charged ions
D. constituent ions form crystal lattice in fused state
Ans. D
8. The bond formed between the elements of group-1 (except H) and group-17 of the periodic table is
A. ionic
B. covalent
C. coordinate
D. polar covalent
Ans. A
9. The idea of ionic bond was given by
A. Dalton
B. Lewis
C. Kossel
D. Avogadro
Ans. C
10. The term ‘formula mass’ is applicable for
A. CH4
B. CaCl2
C. H2O
D. CH3COOH
Ans. B
11. In which of the following compounds, the metal ion has an incomplete octet?
A. LiH
B. NaCl
C. CaO
D. MgCl2
Ans. A
12. The electrovalency of Fe in ferrous compounds is
A. 3
B. 1
C. 2
D. 4
Ans. C
13. An element has 2 electrons in its outermost shell. Which of following statements is correct for the element?
A. the element will form cation
B. the element will form anion
C. the element is capable of forming both cation and anion
D. the element will not form ions
Ans. A
14. An element has 6 electrons in its outermost shell. The element will
A. form cation
B. form anion
C. form both cation and anion
D. not form ions
Ans. B
15. Between Na and Na+, which one has a filled octet?
A. Na
B. Na+
C. both Na and Na+
D. none of these
Ans. B
16. Which one among O, O– and O2–, is the most stable?
A. O
B. O–
C. O2–
D. all are of equal stability
Ans. C
17. The electronic configuration of Li+ resembles which of the following noble gas?
A. He
B. Ne
C. Ar
D. Kr
Ans. A
18. The electronic theory of valency was proposed by
A. Lewis and Kossel
B. Born and Haber
C. Proust
D. Avogadro
Ans. A
19. The nature of bond present in a compound consisting of molecules will be
A. ionic
B. electrovalent
C. covalent
D. metallic
Ans. C
20. In liquid state, a compound comprised of molecules
A. is ionic
B. is electrolytic
C. conducts electricity
D. does not conduct electricity
Ans. D
21. An ionic compound used in our daily life is
A. common salt
B. water
C. sugar
D. kerosene
Ans. A
22. The atomic number of elements A, B and C are respectively (Z-2), Zand (Z + 1). If B is a noble gas, the formula of compound formed by A and C will be
A. CA2
B. CA
C. C2A3
D. C2A
Ans. D
23. Which of the following electrovalent compounds is least soluble in water?
A. NaCl
B. AgCl
C. NaBr
D. Nal
Ans. B
24. The non-directional bond is
A. covalent bond
B. coordinate bond
C. electrovalent bond
D. all of these
Ans. C
25. Which one of the following does not conduct electricity?
A. molten NaOH
B. molten KOH
C. solid NaCl
D. molten NaCl
Ans. C
26. Which one is an ionic compound?
A. HCl
B. CH4
C. MgCl2
D. NH3
Ans. C
27. If the atomic number of two elements X and Y be 11 and 17 respectively, then the formula of the compound formed with them
A. XY
B. X2Y
C. XY2
D. X2Y3
Ans. A
28. In the compound LiH, both ‘Li’ and ‘H’ atom have attained the electronic configuration of the inert gas as in
A. Ar
В. He
C. Ne
D. Kr
Ans. B
29. The values of electronegativity of A and B are 1.2 and 3.5 respectively. What will be the nature of chemical bond formed between them?
A. covalent
B. coordinate
C. metallic bond
D. Ionic bond
Ans. C
30. Which of these does not exist in molecular form?
A. CO2
B. CH4
C. NaCl
D. SO2
Ans. C
31. Solid form of which compound is made up of ions?
A. sodium chloride
B. hydrogen chloride
C. naphthalene
D. glucose
Ans. A
Answer in brief
1. What happens when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of an ionic compound?
Ans. Electrolysis takes place when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of an ionic compound, resulting in the formation of new substances at the anode and cathode.
2. Mention the nature of force that operates between constituents of an ionic compound and water molecules in aqueous solution.
Ans. Electrostatic force of attraction operates between constituents of an ionic compound and water molecules in aqueous solution.
3. If an electron is transferred from one atom to another what will be the nature of valency?
Ans. Transfer of an electron from one atom to another results in electrovalency.
4. Between magnesium chloride and naphthalene, which one conducts electricity in molten state?
Ans. Magnesium chloride, being an ionic compound, conducts electricity in molten state.
5. In MgCl2, the electronic configuration of the constituent ions resemble which noble gases?
Ans. In MgCl2, electronic configuration of magnesium and chlorine ions resembles the electronic configuration of neon and argon respectively.
6. What are valence electrons?
Ans. The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom of an element takes part in bond formation. These electrons are known as valence electrons.
7. Who discovered noble gases?
Ans. Scientists Ralley and Ramsay discovered noble gases.
8. Find the formula mass of sodium chloride.
Ans. The formula mass of sodium chloride is (23 + 35.5) = 58.5
9. The atomic number of an element is 12. What type of bond will it form with chlorine?
Ans. It will form electrovalent bond with chlorine.
10. The atomic number of an element is 9. What type of bond will it form with sodium?
Ans. It will form ionic bond with sodium.
11. Name the atom with which the electronic configuration of hydride ion is identical.
Ans. The electronic configuration of hydride ion is identical with that of helium atom.
12. What is the similarity between O2– ion and Ne-atom?
Ans. Both O2– ion and Ne-atom contain 10 electrons and hence they have identical electronic configuration, i.e., they are isoelectronic species.
13. Name an electropositive element that forms both ionic as well as covalent compounds.
Ans. Hydrogen forms both ionic as well as covalent compounds.
14. Write the formula of the compound formed between elements X and Y placed in group-2 and group-17 respectively in periodic table.
Ans. The formula of the compound will be XY2.
15. What is electrovalent bond?
Ans. The bond formed between the atoms due to electrovalency is called electrovalent bond or ionic bond.
16. Name an ionic compound in which the electrovalency of both the anion and cation is 3.
Ans. Aluminium nitride (AIN)
17. A metallic element M forms an ionic oxide MO. How many electrons are present in the valence shell of the M-atom?
Ans. The valency of the metal M is 2. Hence it contains 2 electrons in its valence shell.
18. Give example of an ionic compound where the octet rule is not applicable.
Ans. Lithium hydride (LiH).
19. Give example of a stable cation in which octet is not fulfilled.
Ans. Li+.
20. Write down the number of valence electrons of alkali metals and halogens.
Ans. Number of valence electrons in alkali metals and halogens are 1 and 7 respectively.
21. in which type of compound molecule does not exist?
Ans. Ionic compound.
22. How manyelectrons are present in the valence shell of Ca?
Ans. 2 electrons.
23. Which type of chemical bond is present in CaO?
Ans. Ionic bond.
24. Which type of bond is present in CaCl2 ?
Ans. Ionic bond.
25. Atomic number of an element is 12. which type of compound will be formed by its reaction with chlorine?
Ans. Ionic compound will be formed.
26. Atomic number of an element is 9. Which type of compound will be formed by its reaction with sodium?
Ans. Ionic compound will be formed.
27. Which type of bond will be formed between A (2,8, 2) and B (2, 8, 7)?
Ans. Ionic bond will be formed between A and B.
Fill in the blanks
1. Ionic compounds are generally ………… and their crystals have a definite ………….. shape.
Ans. solid, geometrical
2. The crystals of ionic compounds are formed by a large number of …………. and ………….
Ans. cations, anions
3. Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in ………….. state.
Ans. solid
4. Ionic compounds conduct electricity in …………. state or in …………. solution.
Ans. fused, aqueous
5. Ionic compounds are soluble in ………… solvents such as …………
Ans. polar, water
6. Ionic compounds are generally …………. in organic solvents.
Ans. insoluble
7. An element which forms a cation to achieve the electronic configuration of neon is …………
Ans. sodium
8. In ………… bonds, the particles are held together by electrostatic force of attraction.
Ans. ionic
9. An atom gains …………. by either accepting or loosing electron(s).
Ans. stability
10. An ionic bond is formed between a ……….. and a ………… element.
Ans. metallic, non-metallic
11. Two elements form ionic bond with each other when the difference in electronegativity between the elements is ……….
Ans. high
12. An ionic compound is formed when a stable three dimensional ……….. is formed.
Ans. crystal
13. Electrovalency of Cu in cupric salts is …………
Ans. 2
14. Greater the magnitude of the ……….. energy of an ionic compound, greater will be the ………. of its crystal.
Ans. lattice, stability
15. In ionic compounds, the ionisation potential of the element forming cation should be ………..
Ans. low
16. In ionic compounds, the electronegativity of the element forming anion should be ………..
Ans. high
17. In CaO, the charge of calcium ion is ………..
Ans. 2+,
18. In LiH, the cation is …………. and the anion is ………….
Ans. Li+ , H–
19. ………… bond is not considered as a real bond.
Ans. Ionic
20. In 1894, Scientist …………… discovered the existence of Argon gas.
Ans. Lord Raley
TOPIC – B
Covalent Bonding and Properties of Covalent Compounds
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What is covalency?
Ans. In order to achieve the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas, equal number of electron(s) from the outermost shells of two atoms form one or more electron pairs which are evenly shared by the two atoms. The capacity of the elements for this type of chemical combination is called covalency.
Q.2 What are covalent bonds and covalent compounds?
Ans. The bond formed between the atoms by mutual sharing of electron pairs is called covalent bond and the compound containing covalent bonds is called covalent compound.
Q.3 Classify covalent molecules.
Ans. Covalent molecules are of two types. These are-
- Covalent elementary molecule: The atoms of the same element are covalently bonded with each other to form covalent elementary molecules. H2, O2, N2, F2 etc., are examples of this type.
- Covalent compound molecule: The atoms of different elements are covalently bonded with each other to form covalent compound molecules. NH3, CO2, HCl, CH4 etc., are examples of this type.
Q.4 How is covalency measured in covalent molecule?
Ans. During the formation of a covalent molecule, the number of electron pairs formed by an atom of an element is its covalency. For example, in methane (CH4) C-atom forms four electron pairs with 4 hydrogen atoms. Hence, covalency of carbon in methane is 4.
Q. 5 Glucose is a solid but methane is a gas though both are covalent compounds. Explain.
Ans. The force of attraction between the molecules of a covalent compound is very weak and the attractive force increases with an increase in molecular mass. The molecular mass of glucose is much higher than that of methane and hence the force of attraction between glucose molecules is stronger than that between methane molecules. Hence, glucose is solid at room temperature but methane is a gas.
Q.6 Explain why naphthalene is insoluble in water but readily dissolves in benzene.
Ans. Covalent molecules are generally insoluble in polar solvents and soluble in non-polar solvents. Water is a polar solvent while benzene is a nonpolar solvent. Thus, naphthalene being a covalent compound dissolves in benzene but is insoluble in water.
Q.7 Aqueous solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity, but aqueous solution of sugar or glucose does not conduct electricity. Explain why.
Ans. Sodium chloride (NaCl) being an ionic compound dissociates in aqueous solution to form Na+ and Cl– ions. These ions are responsible for conducting electricity and hence NaCl is a good conductor of electricity in aqueous solution. On the other hand, sugar or glucose being covalent compound does not dissociate in solution and hence they do not conduct electricity.
Q.8 Though HCl is a covalent compound, its aqueous solution conducts electricity. Why?
Ans. Electronegativity of chlorine is greater than that of hydrogen. As a result, the electron pair shared between H and Cl-atom in HCl molecule shifts more towards Cl-atom. Due to this, a partial positive charge develops on H-atom and a partial negative charge develops on Cl-atom. Water is also a polar molecule in which H-atom is partially positively charged and O-atom is partially negatively charged. Due to force of attraction between the opposite charges of HCl and water molecules, HCl ionises to form H3O+ and Cl– ions. As a result, of formation of these ions in solution, HCl conducts electricity.
Q.9 Why are the melting and boiling point of covalent compounds generally low?
Ans. The intermolecular force acting between the molecules of covalent compounds is very weak. Hence, less energy is required to separate the molecules. So, covalent compounds generally have low melting and boiling point.
Q.10 The reactions involving covalent molecules are slow. Explain with reason.
Ans. In covalent molecules, the atoms are bonded by strong covalent bonds. The cleavage of these bonds requires sufficient energy, time and sometimes catalysts. That is why, reactions involving covalent molecules take place slowly. For example- fermentation of glucose to ethanol takes almost 3 days to complete.
Q.11 Cl2 molecules are formed but Ne₂ molecules do not exist. Explain why.
Ans. Cl-atom has 7 electrons in its outermost shell. Two chlorine atoms contribute one electron each to form a common shared pair and in this way both of them complete their octets. The sharing of the electron pair results in the formation of Cl2 molecule.
On the other hand, Ne-atoms already have filled octet and hence do not show any tendency to combine with each other to form Ne2 molecule.
Q.12 Wh What is polar covalent bond?
Ans. When a covalent bond is formed between two atoms of different elements, due to difference electronegativity between the atoms the shared electron pair is attracted more towards the atom with greater electronegativity. As a result the more electronegative atom becomes partially negative charged. On the other hand, the less electronegative element develops a partial positive charge. This charge difference between the atoms causes polarity in the covalent bond. This type of bond is called polar covalent bond.
Q.13 Discuss about the electrical conductivity of covalent compound.
Ans. Covalent compounds do not possess cations or anions and so cannot usually conduct electricity in the fused or dissolved state. However, some covalent compounds when dissolved in a polar solvent form ions by reacting with the solvent molecules and conduct electricity. For example, hydrogen chloride dissolves in water and forms hydronium ions and chloride ions by reacting with water molecule. As a consequence aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride can conduct electricity.
Q.14 Describe the formation of H2O molecule with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
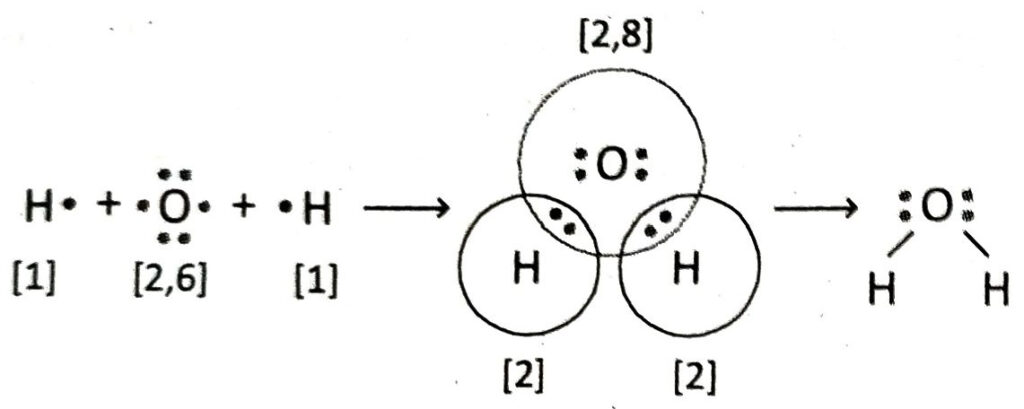
Ans. In H2O molecule, an O-atom is covalently bonded to two H-atoms. H-atom has 1 electron in its valence shell. On the other hand, O-atom has 6 electrons in its valence shell. During chemical combination, an oxygen atom shares its two valence electrons to separately pair with each electron of the two H-atoms. As a result, O-atom attains the stable electronic configuration of Ne and both the hydrogen atoms attain the electronic configuration of He. Thus, two single bonds are formed between O-atom and two H-atoms. The other two pairs of electrons in the valence shell of oxygen atom do not take part in bond formation and remain as lone pairs of electrons.
Q.15 Describe the formation of NH3 molecule with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
Ans. In NH3 molecule, N-atom is covalently bonded with three H-atoms. H-atom has 1 electron in its valence shell. On the other hand, N-atom has 5 electrons in its valence shell. During chemical combination, a nitrogen atom shares its three valence electrons to separately pair with each electron of the three H-atoms. As a result, N-atom attains the stable electronic configuration of Ne and all the three hydrogen atoms attain stable
electronic configuration of He. Thus, three single bonds are formed between N-atom and three H-atoms. One pair of electron in the valence shell of nitrogen does not take part in bond formation and remains as lone pair of electron.
Q.16 Describe the formation of CH4 molecule with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
Ans. In a CH4 molecule, a C-atom (2,4) is covalently bonded with four H-atoms. H-atom has 1 electron in its valence shell. On the other hand, C-atom has 4 electrons in its valence shell. During the chemical combination, a carbon atom shares its four valence electrons to separately pair with each electron of the four H-atoms. As a result, Catom attains the stable electronic configuration of Ne and all the four hydrogen atoms attain the electronic configuration of He and become stable. Thus, four single bonds are formed between Catom and four H-atoms. This results in the formation of CH4 molecule.
Q.17 Describe how a CO2 molecule is formed with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
Ans. During the formation of CO2 molecule, two electrons out of the 4 valence electrons of C-atom are shared with 2 valence electrons of an oxygen atom. As a result, a double bond is formed between C-atom and its O-atom. C-atoms uses its
remaining two valence electrons to form a double bond with another O-atom similarly. Thus, in a CO2 molecule the C-atom forms two double bonds with two oxygen atoms.
Q.18 Describe the formation of a C2H4 molecule with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
Ans. Ethylene molecule is formed by the combination of two C-atoms with four H-atoms. Each of the two C-atoms share two valence electron pairs with each other to form a double bond (C = C). Each of the C-atoms uses its two remaining valence electrons to form two single bonds with two hydrogen atoms. Thus, the molecule contains four C — H bonds apart from a C = C bond.
Q.19 Describe the formation of a N₂ molecule with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
Ans. During the formation of N2 molecule by the combination of two N-atoms (2,5), each N-atom shares its three valence electrons with three valence electrons of the other N-atom. Thus, three electron pairs are formed, which are equally shared by both N-atoms. Due to sharing of three electron pairs, a triple bond is formed between two N-atoms and N2 molecule is formed.
Q.20 Describe how a C2H2 molecule is formed with the help of Lewis-dot diagram.
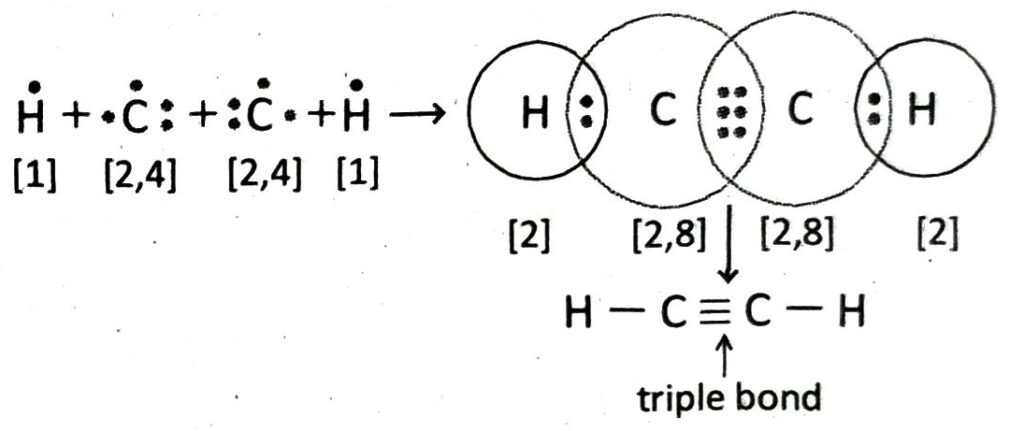
Ans. An acetylene molecule is formed by the combination of two C-atoms with two H-atoms. Each of the two C-atoms share three electron pairs with each other to form a triple covalent bond (C ≡ C). Each of the C-atoms uses its remaining valence electron to form single bond with a hydrogen atom. Thus, C2H2 molecule contains two C — H bonds apart from a C ≡ C bond.
Q.21 Draw the Lewis dot structure of CCl4.
Ans.
Q.22 Through what sort of chemical bonding does chloride combines with sodium and hydrogen to form sodium chloride and hydrogen chloride respectively? Draw corresponding electron dot structure in both cases.
Ans. Chlorine combines with sodium through ionic bonding or electrovalent bonding and with hydrogen through covalent bonding.
Electron dot structure of sodium chloride –
Electron dot structure of hydrogen chloride –
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. With respect to covalent compounds, the melting points of ionic compounds are generally
A. lower
B. higher
C. equal
D. lower or higher
Ans. B
2. Which of the following is insoluble in water?
A. MgCl2
B. Na2SO4
C. CHCl3
D. HCl
Ans. C
3. A covalent compound used in our daily life is
A. washing soda
B. alum
C. water
D. chalk
Ans. C
4. Both ionic and covalent bonds can not be formed by
A. H
B. O
C. Na
D. Cl
Ans. C
5. Which of the following compounds form both ionic and covalent bonds?
A. NH3
B. CCl4
C. CO2
D. CaCO3
Ans. D
6. Which of the following, though covalent, but possesses high melting point?
A. C6H6
B. SiO2
C. C4H10
D. CO2
Ans. B
7. The concept of covalent bonding was given by
A. Lewis
B. Arrhenius
C. Kelvin
D. Avogadro
Ans. A
8. The Lewis structure does not justify the experimental result for
A. N2
B. NH3
C. CH4
D. O2
Ans. D
9. A double bond is present in
A. H2O
B. NH3
C. CO2
D. CH4
Ans. C
10. A triple bond is present in
A. H2
B. O2
C. N2
D. F2
Ans. C
11. Elements forming covalent bonds are placed in periodic table at the
A. extreme left
B. extreme right
C. middle of the table
D. the bottom
Ans. B
12. Maximum number of covalent bonds that can be formed between two atoms is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Ans. C
13. In which of the following compounds, the central atom has an expanded octet?
A. CH4
B. PCl5
C. NH3
D. NCl3
Ans. B
14. In which of the following compounds, the central atom has an incomplete octet?
A. HCN
B. BF3
C. CO2
D. H2O
Ans. B
15. Covalent bond is not formed between
A. C & Cl
B. B & F
C. Cl & Cl
D. Na & F
Ans. D
16. A triple bond is absent in
A. C2H2
B. N2
C. HCN
D. C2H4
Ans. D
17. The nature of the bonds in HCl(g)
A. covalent
B. ionic
C. coordinate
D. ionic and covalent
Ans. A
18. In which of the following compounds ionic, covalent and coordinate-all the three types of bond are present?
A. KCl
B. H2O
C. NH2Cl
D. NaCN
Ans. C
19. Which of the following combines with hydrogen to form covalent compounds?
A. Ca
B. Na
C. C
D. Li
Ans. C
20. Which of the following is a covalent compound?
A. CaO
B. MgO
C. NaCl
D. CH4
Ans. D
21. Which of the following compound central atom contains lone pair of electron?
A. CH4
B. NH3
C. C2H2
D. C2H4
Ans. B
22. A compound with covalent triple bond is
A. H2O
B. CO2
C. C2H2
D. CH4
Ans. C
23. Compound containing covalent double bond is
A. OF2
B. N2
C. C2H4
D. C2H2
Ans. C
24. Which one of the following does not conduct electricity in molten state or in solution?
A. NaCl
B. NaF
C. CCl4
D. KCl
Ans. C
25. True bond can be found in
A. ionic bond
B. covalent bond
C. nuclear bond
D. none of these
Ans. B
26. Number of covalent bonds in nitrogen molecule is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Ans. C
27. In which of the following compound covalent bonds are present?
A. hydrogen chloride
B. sodium chloride
C. lithium hydroxide
D. calcium oxide
Ans. A
Answer in brief
1. Name a non-polar solvent.
Ans. Benzene is a non-polar solvent.
2. Between water and benzene, which one dissolves kerosene?
Ans. Kerosene, a covalent organic substance, dissolves in a non-polar solvent like benzene.
3. Name a crystalline substance that contains covalent bonds.
Ans. Diamond is a crystalline solid in which C-C covalent bonds are present.
4. Name a covalent solid whose hardness is more than any ionic compound.
Ans. Diamond, a covalent compound, is the hardest substance. Its hardness is more than any ionic compound.
5. Define crystal lattice.
Ans. A crystal lattice is defined as a regular three dimensional network of constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) of the crystal.
6. The atomic number of an element is 6. What type of bond will it form with the element having atomic number 17?
Ans. Both the elements are non-metals. So, they will form covalent bond.
7. Name an electronegative element that forms both ionic and covalent compounds.
Ans. Chlorine forms both ionic and covalent compounds.
8. What happens when crystals of sugar are heated?
Ans. When crystals of sugar are heated, it releases molecules of water and black particles of carbon are left behind as residue.
9. Name a non-volatile covalent compound.
Ans. Sugar or cane sugar (C12H22O11) is a nonvolatile covalent compound.
10. Give example of a solid and a liquid covalent compound.
Ans. A solid covalent compound is glucose (C6H12O6) and a liquid covalent compound is water (H2O).
11. Between water and ethanol, which one is more volatile?
Ans. Ethanol is more volatile than water.
12. Is it possible to differentiate between solid naphthalene and solid common salt on the basis of their electrical conductivity?
Ans. In solid state, both naphthalene and common salt are bad conductors of electricity. Hence, it is not possible to differentiate between them on the basis of their electrical conductivity.
13. How many covalent bonds can be formed between two atoms?
Ans. Two atoms can form a maximum of 3 covalent bonds between them.
14. Show the structure of C2H2 by dash formula.
Ans. H—C≡C—H.
15. Give an example of a single bonded covalent molecule which is liquid at normal temperature.
Ans. Water is a single bonded covalent molecule which is liquid at normal temperature.
16. Name a gaseous hydrocarbon that contains only single bonds.
Ans. Methane (CH4) is a gaseous hydrocarbon that contains only single bonds.
17. Name a gaseous hydrocarbon that contains double bond.
Ans. Ethylene (C2H4) is a gaseous hydrocarbon that contains a double bond.
18. Give an example of a molecule which contains an atom having a lone pair of electrons.
Ans. In ammonia (NH3) molecule, the nitrogen atom contains a lone pair of electrons.
19. The electronic configuration of N-atom is 2(K), 5(L). How many electrons in the valence shell of nitrogen do not take part in the formation of N2 molecule?
Ans. 2 electrons from each N-atom do not take part in the formation of N2 molecule.
20. Name a gaseous covalent compound which ionises in aqueous solution and conducts electricity.
Ans. Hydrogen chloride (HCI) is a gaseous covalent compound which ionises in aqueous solution and conducts electricity.
21. What is Lewis-dot diagram?
Ans. Lewis-dot diagram is a simple representation of a covalent molecule. Here, each electron is represented by a dot and each bond is represented by a pair of dots in between two atoms involved in bond formation.
22. What is the linear formula of covalent compounds?
Ans. Linear formula of a covalent compound is a simple representation in which each covalent bond is represented by a line or dash between the atoms involved in bond formation.
23. How many types of covalent bonding are there?
Ans. There are three types of covalent bondsingle bond, double bond and triple bond.
24. Isomerism can be found in which type of compound?
Ans. Covalent compound.
25. Give example of a solid covalent which is good conductor of electricity.
Ans. Graphite.
26. Give example of a single bonded covalent compound which is liquid at room temperature.
Ans. Water.
27. Give example of two covalent compounds whose boiling and melting points are very high.
Ans. Boron carbide (B4C) and Silica (SiO2).
28. Which one between ionic or covalent compounds are generally electrolytes?
Ans. Ionic compounds are generally electrolytes.
29. Which type of chemical bond is present in hydrogen chloride molecule?
Ans. Covalent bonds are present in pure hydrogen chloride molecule.
30. Which type of bond is present in HF?
Ans. Covalent bonding is present in HF.
31. By which type of bonding do carbon and hydrogen atoms combine to form methane?
Ans. Covalent single bond.
Fill in the blanks
1. An example of a solid covalent crystalline compound is ………..
Ans. sugar
2. The total number of valence electrons in the atoms of the molecule of HCN is ………..
Ans. 10
3. Ethanol is ……….. in water.
Ans. soluble
4. Chloroform and water are ……….. with each other.
Ans. immiscible
5. Aqueous solution of glucose is a ………… of electricity.
Ans. non-conductor
6. …………. a is covalent substance that conducts electricity in solid state.
Ans. Graphite
7. Only …………… electrons are shown in Lewis dot diagram.
Ans. bonded
8. …………… is an example of a covalent compound which is widely used as a solvent.
Ans. Water
9. Sugar does not ………….. in aqueous solution.
Ans. ionise
10. Covalent bonds are formed due to the formation of ………..
Ans. electron-pairs
11. The covalent bond in HCl is …………. in nature.
Ans. polar
12. The number of lone pairs of electrons in O- atom of H2O molecule is ………..
Ans. 2
13. ………….. is a covalent compound in which all the 4 bonds are identical.
Ans. Methane
14. The number of bond pairs of electrons in CO2 is ………….
Ans. 4
15. Among CH4, C2H4 and C2H2, triple bond is present in ………..
Ans. C2H2
16. Covalent bond has a definite …………
Ans. direction
17. In NH3 molecule, N-atom has …………. lone pair of electrons.
Ans. 1
18. The structure of covalent compounds are represented by ……….. diagram.
Ans. Lewis-dot
19. The number of single bonds present in C2H4 is ………….
Ans. 4
20. Number of covalent bonds present in nitrogen molecule is ……….
Ans. three
State whether true or false
1. Lewis-dot diagram cannot explain the experimental observation regarding the structure of O2.
Ans. True
2. Boiling and melting point of covalent compounds are high due to strong force of attraction between the covalent molecules.
Ans. False
3. van der Waal’s force of attraction between two covalent molecules increases as the molecular mass increases.
Ans. True
4. Coordinate bond can be found in H3O+ ion.
Ans. True
5. Covalent compounds can exist as discrete molecules.
Ans. True
6. Covalent compounds can be soft solid at normal temperature.
Ans. True
7. Some transition metal elements can form four bonds between two atoms.
Ans. True
8. Formula mass and molecular mass are not the same for covalent compounds.
Ans. False
9. NaH is a covalent compound.
Ans. False
10. Aqueous solution glucose can conduct electricity.
Ans. False
11. Carbon tetrachloride is a polar solvent.
Ans. False
12. Maximum two covalent bonds can be formed between two atoms.
Ans. False
13. There are 5 covalent bonds present in ethyne molecule.
Ans. True