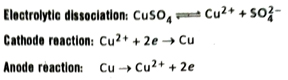WBBSE 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.3 Electric Current and Chemical Reactions
West Bengal Board 10th Class Science Solutions Physical Science & Environment Chapter 8.3 Electric Current and Chemical Reactions
WBBSE 10th Class Physical Science & Environment Solutions
8.3 Electric Current and Chemical Reactions
Synopsis
Electrolyte and Electrolysis
- Compounds, which in their molten state or in solution undergo chemical decomposition to yield their respective ions are called electrolytic substances or electrolytes. Acids such as, HCl, H2SO4 etc., bases such as KOH, NaOH etc., and aqueous solution of salts such as NaCl, KCl etc., are some examples of electrolytes.
On the other hand, compounds which do not conduct electricity in their molten state or in solution are called non-electrolytes. Sugar, wax, glucose, butter etc., are some examples of non-electrolytes.
- Electrolytes which dissociate almost completely into their constituent ions in molten state or in solution and thus have high electrical conductivity are called strong electrolytes. For example, HCl, NaOH, NaCl etc. are strong electrolytes. On the other hand, electrolytes that dissociate partially into their constituent ions in molten state or in solution and thus have low electrical conductivity are known as weak electrolytes. For example, CH3COOH, NH2OH etc., are weak electrolytes.
- Electrolytes dissociate spontaneously in solution to form cations and anions which are responsible for conduction of electricity. Undissociated molecules are non-conductors of electricity. In fact, electrons do not play any role in conduction of electricity through an electrolyte.
- The number of cations and anions produced due to the dissociation of an electrolyte in a solution may not be equal but the total positive charge of the cations at any moment during the conduction of electricity must be equal to the total negative charge of the anions.
- The fraction of total number of molecules of an electrolyte that ionise in molten or dissolved state under a particular condition is I called the degree of dissociation of that electrolyte. Obviously, the degree of dissociation of a strong electrolyte at any point is more (almost equal to one) than that that of a weak electrolyte (less than one). With the increase in the degree of dissociation, the conductance of the corresponding electrolyte also increases.
- In solid metallic conductors, free electrons conduct electricity, but in case of electrolytic solutions, the ions produced due to dissociation of the electrolyte conduct electricity. The metal atoms do not change their position while conducting electricity but the ions in the electrolytic solution change their positions while conducting electricity. Besides, the conductivity of a metallic conductor is almost 106 times than that of an electrolytic solution.
- The process by which an electrolyte in its molten state or in solution undergoes chemical decomposition to form new substances due to passage of electricity is known as electrolysis.
- The apparatus in which electrolysis is carried out is known as voltameter. The setup consists of a vessel (generally made of glass or fibre) in which the electrolytic solution (either molten or dissolved in a suitable solvent) is taken along with the corresponding electrodes. The two metallic rods or plates that are partially immersed in the electrolytic solution are known as electrodes. Generally the metals which are good conductors of electricity such as platinum, copper, iron etc., are taken as electrodes. Graphite, although being a non-metal is also used as an electrode because of its ability to conduct electricity. The electrode which is connected to the negative terminal of a battery is called the cathode while the other electrode which is connected to the positive terminal of the battery is known as the anode.
- Electrolysis takes place when direct current (DC) is passed through an electrolyte in its molten or dissolved state with the help of the electrodes. The cations move towards the cathode and are converted into neutral atoms or radicals by accepting electrons i.e., reduction occurs at the cathode. On the curs at the other hand, the anions move towards the anode and are converted into neutral atoms or radicals by releasing electrons i.e., oxidation occurs at the anode.
- Pure water is a non-conductor of electricity. However, in the presence of a trace amount of acid or base, water can conduct electricity. Electrolysis of water produces hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode.
- When an aqueous solution of CuSO4 is electrolysed using copper electrodes, copper atoms from the anode are oxidised to Cu2+ ions which passes into the solution whereas Cu2+ ions from the solution are reduced to Cu atoms by accepting electrons and get deposited at the cathode. Consequently, the anode gradually dissolves into the solution while the cathode becomes thicker.
Application of Electrolysis
- The process of electrolysis is used in extraction of metals, refining of metals and in electroplating.
- When a molten mixture of alumina, cryolite and fluorspar is electrolysed using graphite as anode and gas carbon as cathode, pure aluminium is deposited at the cathode.
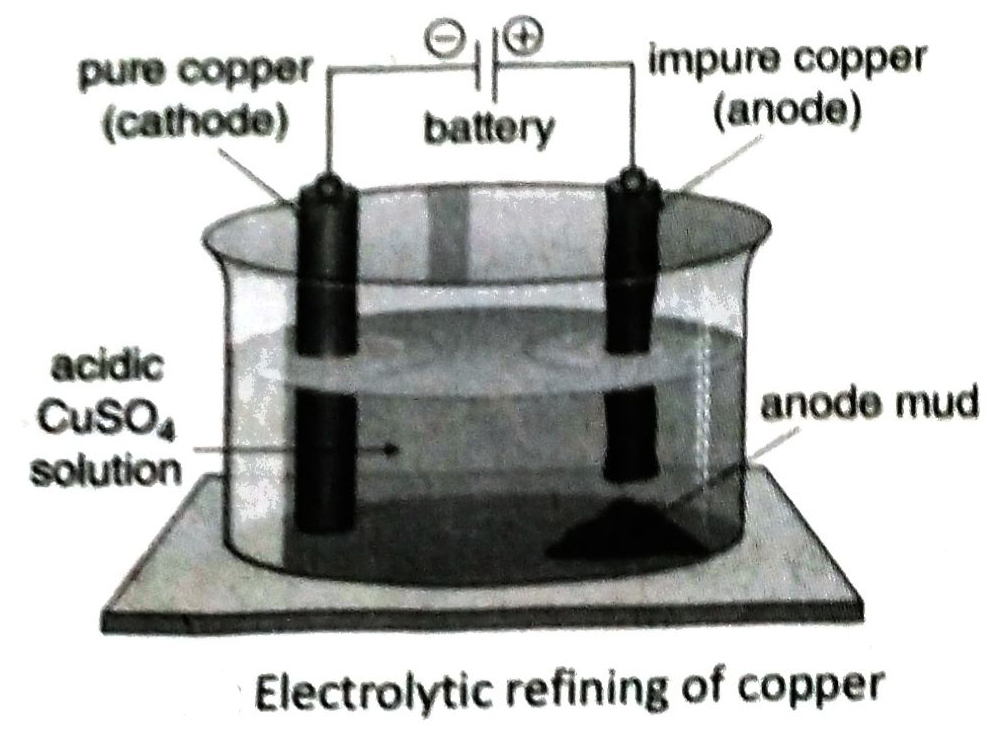
- Electrorefining of copper is carried out by taking an aqueous solution of CuSO4 containing small amount of H2SO4 as the electrolyte in a container coated with lead, the impure copper rod as anode and a thin plate of pure copper as cathode.
- During electroplating, the object on which electroplating is to be done is taken as the cathode, a plate of pure metal to be deposited on the object is taken as the anode and an aqueous solution of a salt of the metal to be deposited is taken as the electrolyte.
TOPIC – A
Electrolyte and Electrolysis
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What are electrolytes and non-electrolytes? Give example.
Ans. Electrolytes: An electrolyte is a compound which conducts electricity in molten state or in aqueous solution and thus dissociates to form ions in solution.
Example: Acid-HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, CH3COOH etc.
Base-NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 etc.
Salt-NaCl, AlCl3, CuSO4 etc.
Non-electrolytes: The compounds which do not conduct electricity in molten state or in solution are called non-electrolytes. Non-electrolytes do not form ions in molten state or in solution.
Example: pure water, benzene, alcohol, sugar, glucose, urea etc.
Q.2 Discuss the important characteristics of electrolytic substances.
Ans. (1) Electrolytes dissociate into ions in their molten state or in solution. The cations and anions produced due to ionization move randomly in the solution. (2) Due to presence of ions, the solution of an electrolyte can conduct electricity. (3) The conductivity of an electrolytic solution depends on the following factorsnature of electrolyte, concentration of solution and temperature.
Q.3 Classify the following substances as electrolytes and non electrolytes-sugar solution, fused sodium chloride, liquid HCl, mercury, kerosene, fused KCl, aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
Ans.
| Electrolytes |
Non-electrolytes |
| fused sodium chloride, fused KCl, aqueous solution of sodium chloride. |
sugar solution, mercury, liquid HCl, kerosene. |
Q.4 State the differences between electrolytes and non-electrolytes.
Ans. The differences are listed below-
| Electrolytes |
Non-electrolytes |
| Almost all ionic compounds and some polar covalent compounds act as electrolytes. |
Non-electrolytes are mainly covalent compounds. |
| Electrolytes are soluble in polar solvents. e.g. water. |
Non-electrolytes are generally soluble in non-polar solvents. Exception- glucose, sugar etc. |
| They produce ions in molten state or in solution. |
They do not produce ions either in molten state or in solution. |
| These substances conduct electricity in molten state or in solution. |
Solution of non-electrolytes are non-conductors of electricity. |
| These substances undergo chemical change during electrolysis. |
These are non-conductors, so do not undergo chemical change during electrolysis. |
Q.5 Describe the major differences in conduction of electricity by a metallic conductor and a solution of an electrolyte.
Ans. The major differences are-
| Metallic conductor |
Electrolyte |
| During conduction of electricity through a metallic conductor only physical changes take place in the conductor. |
During conduction of electricity, an electrolyte undergoes chemical change to produce new substances. |
| Free electrons conduct electricity. |
Cations and anions produced by the electrolyte conduct electricity. |
| Metallic conductors conduct electricity both in solid or liquid state e.g. mercury. |
Electrolytes conduct electricity only in molten state or in solution. |
| The atoms do not change their positions during conduction of electricity. |
Ions migrate towards the electrodes to conduct electricity. |
| With increasing temperature, resistance of metallic conductor increases and hence conductivity decreases. |
With increasing temperature the conductance of electrolytes increases. |
| The conductivity of metallic conductors are higher than that of electrolytes. |
Electrolytic solutions generally have low conductivity compared to metallic conductors. |
Q.6 Discuss the factors on which conductance of an electrolyte depends.
Ans. Conductance of electrolyte depends on-
- Nature of electrolyte: A strong electrolyte dissociates almost completely in solution and hence the solution contains large number of ions. So the conductance of strong electrolytes is generally higher. On the other hand, a weak electrolyte dissociates only partially and hence it produces less number of ions in solution. Therefore, the solution of a weak electrolyte conducts less electricity.
- Concentration of solution: Higher the concentration of a solution, more number of ions will be produced in the solution and hence the conductance will increase.
- Temperature: With increasing temperature kinetic energy of ions increases and hence cations and anions move quickly towards the electrodes. This increases the conductance of solution.
Q.7 What is degree of dissociation? How is conductance of an electrolyte related to its degree of dissociation?
Ans. The fraction of total number of moles of an electrolyte that dissociates in solution or in molten state is known as degree of dissociation of that electrolyte. Degree of dissociation of strong electrolytes is high and that of weak electrolytes is low.
With an increase in the degree of dissociation, the conductance of an electrolyte increases.
Q.8 Why do electrolytes conduct electricity only in solution or in molten state but not in solid state?
Ans. Electrolytic substances are generally crystalline solid at normal condition. In crystalline state, the cations and anions are strongly held together by electrostatic force of attraction. As the ions cannot move in solid state they cannot conduct electricity. In solution, the ions are separated and the force of attraction becomes weak. Hence the mobility of the ions increases. As a result, the solution conducts electricity.
Q.9 Among mercury and acidified water which one is an electrolyte and why?
Ans. Although mercury conducts electricity in liquid state, yet it is not termed as an electrolyte. Because mercury is an element and no chemical changes occurs during conduction of electricity through it. On the other hand during electrical conduction of acidified water it chemically decomposes and produces hydrogen and oxygen at cathode and anode respectively. That is why it is called an electrolyte.
Q.10 Hydrogen chloride can not conduct electricity in its liquid state where as sodium chloride can conduct electricity in its fused state-explain.
Ans. Being a covalent compound hydrogen chloride does not ionise in liquid state. it exists as a molecule and acts as a non-electrolyte. Hence liquid HCl can not conduct electricity.
On the other hand, sodium chloride is an ionic compound and ionises in fused state to form Na and Clions. Due to the presence of such ions, it is considered as an electrolyte and can conduct electricity.
Q.11 Explain why NaOH is a strong electrolyte but NH4OH is a weak electrolyte.
Ans. In molten state or in aqueous solution, NaOH dissociates almost completely to give Na+ and OH– ions. Due to the presence of greater number of ions in solution, the conductivity of NaOH solution is high. Hence, NaOH is a strong electrolyte.
NaOH → Na+ + OH–
On the other hand, NH4OH dissociates partially in solution and most of the molecules remain undissociated. As a result, the number of ions present in NH4OH solution is less. Hence, it is a weak electrolyte.
0.12 A metal undergoes physical changes during conduction of electricity-explain with example.
Ans. When electricity is passed through a metallic conductor, it becomes hot. This is known as heating effect of electricity. Sometimes the metal glows due to conduction of electricity. For example, if electricity is passed through a tungsten filament of an electric bulb, the filament gets illuminated and radiates light. When the flow of electricity is stopped, the filament comes back to its initial state. Thus, it is a physical change.
Q.13 What is electrode? What is cathode and anode?
Ans. Electrode: Two metallic (eg: Cu or Ag) or nonmetallic (eg: graphite, gas carbon) rods that are partially immersed in the electrolytic solution or fused electrolyte are known as electrode. When the electrodes are connected with battery electricity passes through the electrolytes.
Cathode: The electrode which is connected with the-ve end of a battery is called cathode. During electrolysis reduction occurs here.
Anode: The electrode which is connected with the +ve end of a battery is termed as anode. During electrolysis oxidation occurs here.
Q.14 Define electrolysis. Is electrolysis of fused wax possible?
Ans. The process by which an electrolyte in its molten state or in solution dissociates into its constituent ions on passing electricity through it, is known as electrolysis.
Electrolysis of fused wax is not possible as wax is not an electrolyte.
Q.15 Is electrolysis of an element possible? Justify.
Ans. During electrolysis, a substance is decomposed to produce new substances when electricity is passed through the molten state or solution of the substance in appropriate solvent. In solution, the process of electrolysis takes place due to presence of cations and anions formed by the dissociation of the electrolyte. Obviously, the electrolyte must produce oppositely charged ions in solution Elements does not dissociate into oppositely charged ions. Hence electrolysis of an element is not possible.
Q.16 Describe the ionic theory of electrolysis.
Ans. Electrolytes dissociate into ions in molten state or in solution. When electricity is passed through the solution, cations move towards the cathode and anions move towards the anode. At cathode, cations accept electrons and form neutral atoms or radicals. Similarly anions, at anode, give up electrons to form neutral atoms or radicals. For example, when molten NaCl is electrolysed using graphite anode and iron cathode, chlorine gas is produced at anode and metallic sodium is deposited at cathode.
NaCl → Na+ + Cl–
At cathode: Na+ + e → Na
At anode: Cl– → Cl + e ; Cl + Cl → Cl2
Q.17 During electrolysis, the solution of an electrolyte contains large number of cations and anions. Yet the solution remains neutral-explain.
Ans. Electrolytes dissociate into cations and anions in their molten state or in solution. The number of cations present in the solution at any moment may not be equal to the number of anions. But the total positive charge carried by the cations and total negative charge of the aníons are equal. For example, dissociation of one molecule of Na2SO4 gives two Na+ ions and one SO42– ion. Here, total positive charge = 2 × (+1) = +2 and total negative charge = 1 × (–2) = –2. Again, during electrolysis, the number of electrons accepted by the cations per second at cathode is equal to the number of electrons lost by the anions per second at anode. Thus, at any moment, total positive charge in the solution is equal to total negative charge and hence electrical neutrality of the solution is maintained.
Q.17 Electrolysis is basically a redox reaction-justify the statement.
Ans. According to the electronic theory of oxidation and reduction, oxidation is a process of loss of one or more electrons by an atom or ion and reduction is the gain of one or more electron(s) by an atom or ion.
When electricity is passed through the solution of an electrolyte, cations produced due to dissociation of the electrolyte move towards the cathode while anions move towards the anode. At cathode, cations accept electrons and form neutral atoms or radicals. So, we can say that the cations are reduced at cathode. Similarly anions, at anode, give up electrons to form neutral atoms or radicals. So, anions undergo oxidation at anode. Therefore, we can say that electrolysis is an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox reaction.
Q.18 Discuss the principle of electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrodes with equations.
Ans. Principle: Pure water is a non-conductor of electricity. But if a few drops of acid (H2SO4) is added to water, it becomes a good conductor. In this condition, water molecules ionize to produce H+ and OH– ions.
Electrolyte: Water containing trace amount of H2SO4.
Electrodes: Cathode and anode made of platinum. Cathode reaction: When electricity is passed through acidified water, H+ ions move towards the cathode. At cathode, an H+ ion accepts one electron and forms H-atom. H-atoms being unstable, combine with each other to form diatomic H2 molecules. As a result, hydrogen gas is liberated at cathode.
H+ + e → H, H + H → H2 ↑
Anode reaction: On passing electricity, OH– ions move towards the anode. At anode, each OH–
ion releases an electron to form OH radical. These OH radicals then combines together to form H2O and oxygen (O2). As a result oxygen gas is liberated at the anode.
OH– → OH + e, 4OH → 2H2O + O2 ↑
At a given temperature and pressure, the volume of hydrogen gas produced at the cathode is twice the volume of oxygen gas produced at the anode.
Q.19 How do you identify the gases formed by the electrolysis of water?
Ans. The gases formed at the cathode and anode can be identified in the following way-
- When a burning stick is introduced into the gas accumulated at the cathode, the fire in the stick extinguishes but the gas burns with a bluish flame. This indicates that the gas is hydrogen.
- When a burning stick thout flame is introduced into the gas accumulated at the anode, the stick catches fire and burns strongly with a flame but the gas itself does not burn. This indicates that the gas formed at anode is oxygen.
Q.20 During electroplating, DC of low intensity should be applied for longer period of time. Explain. What will happen if AC is applied instead of DC ?
Ans. During electroplating, DC current of low intensity is applied for longer period of time. Due to low supply of current, the solution does not become hot. At the same time, it helps in the formation of a uniform coating over the article.
If AC is applied instead of DC, the electrodes continuously change their nature. As a result, movement of ions in solution is restricted and electrolysis does not take place. Hence, alternating current is not suitable for electroplating.
Q.21 Does the concentration of the solution change during electrolysis of CuSO4 solution using Cu-electrodes?
Ans. During electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO4 using Cu-electrodes, at any moment the amount of copper deposited at cathode is equal to the amount of copper brought into solution from the anode. Hence, the concentration of Cu2+ ions in solution remains the same. So, the colour of the solution also does not change.
Cathode reaction: Cu2+ + 2e → Cu
Anode reaction: Cu → Cu2+ + 2e
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. Electrolytes conduct electricity in
A. solid state
B. molten state
C. aqueous solution
D. both C and B
Ans. D
2. An example of a strong electrolyte is
A. H2CO3
B. HNO3
C. NH4OH
D. HCOOH
Ans. B
3. An example of an inorganic salt which acts as a weak electrolyte is
A. KNO3
B. ZnCl2
C. CaCl2
D. Ca3(PO4)2
Ans. D
4. The aqueous solution of a weak electrolyte contains
A. only molecules
B. only ions
C. both ions and molecules
D. none of these
Ans. C
5. The solution of a non-electrolyte contains
A. only molecules
B. only ions
C. both ions and molecules
D. none of these
Ans. A
6. Which of the following is a non-electrolyte?
A. acetic acid
B. carbonic acid
C. chloroform
D. formic acid
Ans. C
7. With the rise in temperature, the conductance of a metallic conductor
A. increases
B. decreases
C. remains unchanged
D. may either increase or decrease
Ans. B
8. When an aqueous solution of an electrolyte is heated, the velocity of ions in the solution
A. decreases
B. increases
C. either decreases or increases
D. remains unchanged
Ans. B
9. The conductance of metallic conductors when compared to that of electrolytes is
A. low
B. high
C. either low or high
D. equal
Ans. B
10. During electrolysis, the temperature of the electrolyte
A. increases
B. decreases
C. shows no change
D. either increases or decreases
Ans. A
11. Which of the following compounds containing -OH group acts as an electrolyte?
A. phenol (C6H5OH)
B. methanol (CH3OH)
C. ethanol (C2H5OH)
D. 2-propanol (CH3CHOHCH3)
Ans. A
12. Which of the following compounds does not conduct electricity in its solid state?
A. NaCl
B. PbBr2
C. ice
D. all of these
Ans. D
13. Aqueous solution of which of the following compounds contains both ions and molecules of the compound?
A. NaCl
B. CH3COOH
C. CH3CH2OH
D. CHCl3
Ans. B
14. Which of the following compounds is not an electrolyte?
A. NaCl
B. H2SO4
C. KOH
D. glucose
Ans. D
15. Which of the following compounds is an electrolyte?
A. urea (H2NCONH2)
B. ethanol (C2H2OH)
C. acetic acid (CH3COOH)
D. distilled water
Ans. C
16. Which of the following pairs of bases acts as weak electrolytes?
A. Mg(OH)2, Fe(OH)2
B. KOH, NH4OH
C. NaOH, Mg(OH)2
D. NaOH, KOH
Ans. A
17. The ratio of the mass of hydrogen to oxygen produced during electrolysis of water, is
A. 1:8
B. 2:1
C. 2:3
D. 3:1
Ans. A
18. The ions discharged at the anode during the electrolysis of dilute and concentrated HCl are respectively
A. OH– & Cl–
B. Cl– & OH–
C. Cl– in both cases
D. OH– in both cases
Ans. A
19. The relative tendency of an ion to discharge at a particular electrode depends on the
A. position of the ion in the electrochemical series
B. concentration of the ion in the solution
C. nature of the electrode
D. all of these
Ans. D
20. During electrolysis of CuSO4 solution using Pt-electrode
A. the anode gradually dissolves into the solution while cathode becomes thicker
B. the anode becomes thicker while the cathode gradually dissolves into the solution
C. both cathode and anode become thicker
D. both cathode and anode remain unchanged
Ans. D
21. Which has the maximum tendency to get reduced at the cathode?
A. K+
B. Na+
C. H+
D. Ag+
Ans. D
22. Which of the following cations does not exist in free state in its aqueous solution?
A. H+
B. Na+
C. K+
D. Cu2+
Ans. A
23. The metal which can be extracted by electrolysis of its molten salt is
A. Fe
B. Al
C. Cu
D. Ag
Ans. B
24. Electrolysis of which of the following aqueous solutions will discharge the corresponding metal at the cathode?
A. NaCl
B. KCl
C. CuSO4
D. AlCl 3
Ans. C
25. When CuSO4 solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes, blue colour of solution
A. deepens
B. fades
C. remains unchanged
D. becomes colourless
Ans. C
26. When CuSO4 solution is electrolysed using Pt-electrodes, product obtained at anode is
A. Cu
B. Cu2+
C. O2
D. H2
Ans. C
27. When CuSO4 solution is electrolysed using either copper or Pt-electrodes, the product obtained at the cathode is
A. H2
B. Cu
C. O2
D. Cu2+
Ans. B
28. Aqueous solution of which one is an weak electrolyte?
A. CH3COOH
B. NaOH
C. H2SO4
D. NaCl
Ans. A
29. Which one of the following can conduct electricity?
A. fused NaCl
B. liquid HCl
C. solid NaCl
D. aqueous solution of glucose
Ans. A
30. Which of the following is an electrolyte?
A. mercury
B. aqueous solution of sugar
C. salt solution
D. bromine water
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. What do you mean by conductors of electricity?
Ans. Substances through which electricity can pass are called conductors of electricity. For example-different metals.
2. What do you mean by non-conductors of electricity or insulators?
Ans. Substances through which electricity cannot pass are called non-conductors of electricity or insulators. For example-wood, glass etc.
3. Name a non-metallic solid element which is a non-conductor of electricity.
Ans. Sulphur.
4. Between NaCl and HCl, which one is a nonelectrolyte in its pure state?
Ans. HCl.
5. Name an organic compound which can conduct electricity in its aqueous solution.
Or, Give example of a compound whose aqueous solution is an weak electrolyte.
Ans. Acetic acid (CH3COOH).
6. Name a liquid which can conduct electricity though it is not an electrolyte.
Ans. Mercury.
7. Name an inorganic non-electrolytic compound.
Ans. Silica (SiO2).
8. Name a liquid element which is a nonconductor of electricity.
Ans. Bromine.
9. Name a non-metallic substance which can conduct electricity but does not ionise.
Or, Give example of a non electrolytic conductor of electricity.
Ans. Graphite.
10. State whether an aqueous solution of sugar containing small amount of salt will conduct electricity or not.
Ans. An aqueous solution of sugar cannot conduct electricity but an aqueous solution of salt is an electrolyte. Hence, the aqueous solution of sugar containing a pinch of salt will conduct electricity.
11. Give an example of a non-metallic cation.
Ans. Ammonium ion (NH4+).
12. Give an example of a liquid non-electrolyte compound which is soluble in water.
Ans. Ethyl alcohol.
13. What are the constituents of the solution of a strong electrolyte?
Ans. The solution of a strong electrolyte contains cations and anions formed by the dissociation of the electrolyte. As a strong electrolyte dissociates completely, there is no undissociated molecules of the electrolyte in the solution.
14. What are the constituents of the solution of a weak electrolyte?
Ans. The solution of a weak electrolyte contains cations and anions formed by the dissociation of the electrolyte along with the undissociated molecules of the electrolyte.
15. Give an example of a weak electrolytic salt.
Ans. Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
16. Is the number of cations and anions formed due to the dissociation of an electrolyte always equal?
Ans. The number of cations in the solution of an electrolyte may or may not be equal to the number of anions. For example, in case of NaCl, it is same whereas for Na2SO4, it is not.
17. How the degree of dissociation of an weak electrolyte can be increased?
Ans. Degree of dissociation of an weak electrolyte can be increased up to a certain limit by diluting the solution of weak electrolyte.
18. Liquids like benzene, chloroform do not conduct electricity. Why?
Ans. Chloroform or benzene exists in liquid state, but they do not dissociate into cations and anions. Thus, they cannot conduct electricity.
19. What is a voltameter?
Ans. The apparatus in which electrolysis of an electrolyte is carried out is known as a voltameter. It consists of a vessel (generally made of glass or fibre) in which the electrolytic solution is taken along with the corresponding electrodes.
20. What is electrolytic dissociation?
Ans. Electrolytic substances dissociate spontaneously in molten state or in solution partially or completely to form their constituent ions. This phenomenon is known as electrolytic dissociation.
21. Which type of current is used in electrolysis?
Ans. Direct current or DC.
22. In which direction does the current flow through the electrolytic solution during electrolysis?
Ans. During electrolysis, electric current flows from the battery to the anode and again passes into the battery through the cathode.
23. State whether electrolysis will take place if alternating current (AC) is passed through an electrolytic solution?
Ans. No, electrolysis will not take place.
24. Which energy is responsible for chemical reaction occurring during electrolysis?
Ans. Electrical energy.
25. Which is responsible for conducting of electricity during electrolysis of electrolytes?
Ans. Corresponding cations and anions of the electrolyte.
26. Where do the cations migrate during electrolysis?
Ans. Towards the cathode.
27. Where do the anions migrate during electrolysis?
Ans. Towards the anode.
28. Mention the volumetric ratio of the gases produced at the cathode and anode during electrolysis of acidified water.
Ans. 2 : 1.
29. Which metal is used as cathode during electrolysis of water?
Ans. Platinum (Pt) metal.
30. Between Na+ and Na, which one is more stable?
Ans. Na+ ion.
31. Which substance is formed at anode during electrolysis of concentrated NaCl solution?
Ans. Chlorine gas.
Fill in the blanks
1. Electrolytic compounds are generally ………… in nature.
Ans. ionic
2. Generally ………… compounds are non – electrolytes.
Ans. covalent
3. The gas produced at ……….. during electrolysis of water burns with a bluish flame.
Ans. cathode
4. The conductivity of water increases on addition of small amount of ……….. or ………..
Ans. acid, base
5. ………… is a non-metal that can be used as electrode.
Ans. Graphite
6. At cathode, cations get …………… by accepting ………..
Ans. reduced, electron
7. At anode, anions get ………… by releasing …………
Ans. oxidised, electron
8. At the electrodes, ions lose their …………
Ans. charge
9. …………… is a covalent compound which acts as an electrolyte in its aqueous solution.
Ans. HCl
10. Strong electrolytes dissociate …………. to produce ions in aqueous solutions.
Ans. completely
11. In aqueous solution, very few molecules of a weak electrolyte undergo …………
Ans. dissociation
12. NaCl does not conduct electricity in ……………. state.
Ans. solid
13. Electrolytes dissociate into their corresponding ………… in polar solvents.
Ans. ions
14. …………. are responsible for conduction of electricity through metals.
Ans. Free electrons
15. ………….. are not transferred during conduction of electricity through metals.
Ans. atoms
16. The ions ………… from one part of the solution to another part during electrolysis.
Ans. move
17. The ………….. of the electrolyte is maintained at any instant during electrolysis.
Ans. electrical neutrality
18. The tendency of H+ ion to be discharged at the cathode is ………… than that of Na+.
Ans. greater
19. Electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of NaCl using mercury electrodes produces ………… at the cathode.
Ans. sodium-amalgam
20. In an electrolytic cell, ……………. energy is converted into ………….. energy.
Ans. chemical, electrical
TOPIC – B
Application of Electrolysis
SHORT AND LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Mention the practical uses of electrolysis.
Ans.
- Strong electro positive metals like Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al etc are extracted using electrolysis.
- Electrolysis is used in the purification process of some metals like Cu, Ag and Al.
- Electrolysis is used in the industrial preparation of several substances like oxygen, chlorine, sodium hydroxide etc.
- Electrolysis is used in the process of electroplating.
Q.2 What do you mean by the term extraction of metal’? Which type of metals can be extracted by electrolytic reduction and why?
Ans. Separation of a metal from its ores using a series of physical and chemical processes is known as extraction of metal. The processes are employed to obtain the pure metal by removing the impurities present in the ore of the metal.
Highly reactive metals like Na, K, Ca, Al, Mg etc., are extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction. The oxides of these metals are highly stable and hence carbon reduction process is not suitable for extraction of these metals. Thus, they are extracted by electrolysis of their molten chloride salts or sometimes their molten oxides (e.g. Al).
Q.3 Describe the process of extraction of aluminium from alumina by electrolytic method.
Ans. Electrolyte used: A molten mixture of pure alumina (Al2O3), cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) is used as the electrolytic solution.
Voltameter and electrodes: An iron tank is used as container in which the electrolyte is taken. The inner walls of the container are lined with gascarbon which acts as cathode. Some graphite rods are partially immersed into the solution. These rods act as anode.
Process: In the tank, a molten mixture of the electrolyte containing 60% cryolite (Na3AlF6), 20% pure alumina (Al2O3) and 20% fluorspar (CaF2) is taken. The melting point of pure alumina is 2050°C, but in the mixture the melting point decreases considerably to 900°C. The surface of the electrolytic mixture is covered with powdered coke to prevent the oxidation and resulting corrosion of the graphite anode. Aluminium is liberated at the cathode in molten state which deposits at the bottom of the vessel from where it is taken out through the outlet. At anode, oxygen is produced. The aluminium thus obtained is about 99.95% pure.
Q. 4 Why is cryolite and fluorspar added to alumina during extraction of aluminium by electrolytic method?
Ans. During electrolysis of aluminium by electrolytic method, cryolite and fluorspar are added to pure alumina because of the following-
- Alumina has a melting point of about 2050°C. At such a high temperature, most of the aluminium produced is wasted due to evaporation. Also, it requires a large amount of electricity to carry out the reaction. When cryolite and fluorspar are added to pure alumina the melting point of the mixture drops to 900°C. Hence, the cost of production decreases.
- Fluorspar decreases the viscosity of the solution. Therefore, ions can move freely in solution and the conductivity increases.
Q. 5 Electrolysis of acidified solution of CuSO4 deposits Cu at cathode. But, electrolysis of acidified solution of an Al-salt does not deposit Al at cathode. Explain with reasons.
Ans. Acidified solution of CuSO4 contains Cu2+ and H+ ions as cations. Tendency of Cu2+ ions to get discharged at cathode is more than that of H+ ions. Hence, Cu2+ ions migrate preferentially to cathode and accept electrons to form Cu-atoms. On the other hand, aqueous solution of an Al-salt contains Al3+ and H+ ions. But, the tendency of H+ ions to get discharged at cathode is more than that of Al3+ ions. So, H+ ions migrate preferentially towards cathode and are reduced to H-atom. Hence, Al-atoms are not discharged at cathode.
Q.6 What do you mean by electrorefining of metals? Discuss the principle of electrolytic refining.
Ans. The process of removal of impurities from a metal extracted from its ore and it’s conversion to pure metal by electrolysis is known as electro refining of metal.
In electrolytic refining, a block of impure metal is taken as anode and a plate or rod of pure metal is taken as cathode. An aqueous solution of a salt of that metal is taken as electrolyte. On electrolysis, metal atoms at anode are oxidized to ions and dissolve into solution. The cations of the metal are discharged at cathode and deposit on the cathode in pure state.
Q.7 Briefly describe the electrolytic refining of copper.
Ans. Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of copper sulphate (CuSO4) mixed with dilute H2SO4
Electrodes: A thin plate of pure copper is used as the cathode and a plate of impure copper is used as the anode.
Process: The electrolyte is taken in a container lined with lead and electricity is passed through the solution. At anode (impure Cu block), Cuatoms are oxidised to Cu2+ ions and dissolves into the solution. These Cu2+ ions move towards the cathode (pure Cu plate) and each accepts 2 electrons to form Cu-atom. The produced atoms are deposited at the cathode. The copper obtained in this method is almost 99.99% pure.
Q.8 What Is ‘anode mud’? Write its Importance.
Ans. During electrorefining of copper, the more electro positive metals (Fe, Ni, Zn etc.) present as impurities in impure copper anode, move into the solution and the less electropositive metals (Au, Ag, Pt etc.) deposit with other impurities below the anode as mud. This is known as anode mud.
Anode mud contains precious metals like gold, silver, platinum etc.
Q.9 What is electroplating? Describe the principles electroplating?
Ans. The process of formation of a uniform coating of a less reactive metal (such as iron, copper etc.) over a relatively more reactive metal (such as silver, gold, nickel etc.) by electrolytic method is known as electroplating.
The article which is to be electroplated is taken as cathode and a pure block of the metal which is to be used as coating is taken as anode. A solution of a water soluble salt of the metal which is used as coating is taken as electrolytic solution. For example, while a silver article is electroplated with gold, the silver article is taken as cathode, a block of pure gold is taken as anode and an aqueous solution of potassium aurocyanide is taken as the electrolytic solution.
Q.10 What are the purposes of electroplating?
Ans. (1) A reactive metal or its alloys are easily attacked by atmospheric oxygen, water vapour or CO2 and undergo corrosion. To prevent corrosion, the article is electroplated by a less reactive metal. (2) The physical appearance can be made more attractive by electroplating. For example, when silver jewellery are electroplated with gold, they become more attractive and beautiful. (3) Metal surface can be made more rigid and corrosion of metal due to friction can be avoided by electroplating.
Q.11 What precautions should be taken during electroplating?
Ans. (1) The concentration of metal ions in electrolytic solution should be high. (2) The solution should be of high conductivity. (3) The salt (electrolyte) should be stable, i.e., it should not react with air. (4) There should be considerable rate of dissolution at the anode so that concentration of the solution remains constant. (5) Direct current (DC) of low intensity should be applied to the solution for a longer period of time. (6) The metal surface on which the electroplating is to be done should be smooth and clean.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer
1. The process of electrolysis is applied in
A. electroplating
B. electrorefining
C. extraction of metals
D. all of these
Ans. D
2. During electroplating by nickel, the electrolyte used is
A. NiBr2 solution
B. NiSO4 · (NH4)2SO4 · 6H2O solution with small amount of H2SO4
C. molten nickel oxide (NiO)
D. NiCl2 solution
Ans. B
3. The objective of electroplating is to
A. protect metallic object from weathering
B. make the metallic object more attractive
C. increase the metallic mass of the object
D. both A and B
Ans. D
4. During electroplating of an object by silver, pure silver plate is used as the
A. cathode
B. anode
C. either anode or cathode
D. electrolyte
Ans. B
5. During electroplating, electrical conductivity of electrolytic solution used should be
A. high
B. low
C. moderate
D. of any value
Ans. A
6. During electroplating
A. the cathode is eroded
B. the anode is eroded
C. neither cathode nor anode is eroded
D. both the electrodes are eroded.
Ans. B
7. Which is not present in the anode mud deposited during electrorefining of copper?
A. Au
B. Ag
C. Pt
D. Fe
Ans. D
8. During electrorefining of copper, the electrolyte used is
A. pure CuSO4
B. aqueous solution of pure CuSO4
C. a mixture of aqueous solution of CuSO4 and small amount of H2SO4
D. none of these
Ans. C
9. Which of the following is used as cathode to electroplate iron substances with copper?
A. iron substance
B. copper plate
C. carbon substance
D. Nickel substance
Ans. A
10. Which of the following is used as cathode to electroplate on a substance with gold (gold plating)?
A. pure gold plate
B. the substance on which gold plating is to be done
C. platinum plate
D. copper plate
Ans. B
11. Which of the following is used as anode in the electrorefining of copper?
A. copper
B graphite
C. platinum
D. steel
Ans. A
12. Which one of the following is used as anode to electroplate a spoon of silver by gold?
A. Pt
B. Ag
C. Au
D. graphite
Ans. C
13. Which of the following metal is obtained from anode mud?
A. Au
B. Mg
C. Al
D. Na
Ans. A
14. Which of the following metal can not be extracted by electrolysis?
A. Na
B. Zn
A. Al
D. K
Ans. B
15. On which of the following metal can anodizing be done?
A. iron
B. aluminium
C. copper
D. zinc
Ans. B
16. Which of the following is used as anode to electroplate iron with nickel?
A. iron
B. nickel sulfate
C. nickel
D. NiSO4 + H2SO4
Ans. C
Answer in brief
1. Mention some important practical applications of electrolysis.
Ans. Some of the important practical applications of electrolysis are- (1) electroplating, (2) electrorefining and (3) metal extraction by electrolytic reduction.
2. Which compounds are used as cathode and anode during the extraction of aluminium from bauxite?
Ans. Graphite as anode and gas carbon as cathode.
3. Which substances are added to alumina during extraction of aluminium by electrolytic reduction?
Ans. Cryolite (AlF3 · 3NaF) and fluorspar (CaF2).
4. Name a metal which is extracted by electrolytic process.
Ans. Aluminium.
5. What is the melting point of the electrolytic mixture containing alumina, cryolite and fluorspar?
Ans. 900°C.
6. Name a metal other than aluminium which is extracted by electrolytic reduction.
Ans. Sodium.
7. How many electrons are exchanged between the cathode and anode during aluminium extraction?
Ans. 6 electrons are exchanged between the cathode and anode during aluminium extraction.
Cathode: 2Al3+ + 6e → 2Al
Anode: 3O2– → 3O + 6e
8. What are the products obtained during aluminium extraction form alumina?
Ans. Aluminium metal is obtained at cathode and oxygen gas is obtained at anode.
9. State the composition of the electrolytic mixture used in the extraction of aluminium by electrolytic method.
Ans. 20% alumina (Al2O3), 60% cryolite (Na3AlF6) and 20% fluorspar (CaF2).
10. Name the electrolyte used during electroplating of a metallic object by gold?.
Ans. Potassium aurocyanide, K[Au(CN)2] .
11. As which electrode the impure copper rod is taken during purification of copper in electrolytic method?
Ans. A thick slab of impure copper is taken as anode.
12. Name an element present in anode mud.
Ans. Gold (Au).
13. What should be used as the electrolyte to electroplate an iron spoon with chromium?
Ans. A mixture of chromic sulphate solution and a little amount of chromic acid i.e.,
Cr2(SO4)3 + H2CrO4.
14. Name the electrolyte used during electroplating of copper on any subject.
Ans. Aqueous copper sulphate solution along with a little amount of sulfuric acid.
15. What substance do you take as electrolyte to electroplate a silver spoon with gold?
Ans. Potassium aurocyanide (K[Au(Cn)2]).
16. What should be the electrolyte for electroplating of an iron spoon by nickel?
Ans. A mixture of nickel sulphate and a little amount of boric acid.
17. What can be taken as cathode while electroplating a copper spoon with silver?
Ans. The copper spoon.
Fill in the blanks
1. During electroplating, metal plate with which the electroplating is to be done is taken as the ………….
Ans. anode
2. During electroplating, the object on which the plating is to be done is taken as the …………
Ans. cathode
3. During electroplating, a …………. quantity of electric current should be passed through the solution for ……….. period of time.
Ans. small, long
4. Highly ………… metals are extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction method.
Ans. electropositive
5. Almost ……….. pure copper is obtained by electrorefining.
Ans. 99.9%
6. To reduce the melting point of the electrolyte in aluminium extraction ……….. and ……….. are mixed with alumina.
Ans. cryolite, fluorspar
7. The electrolyte used in Al-extraction melts at …………..
Ans. 900°C
8. …………. metal can be purified by electrolytic method.
Ans. Copper
9. By electroplating coating of ……….. reactive metal is done on ……….. reactive metal.
Ans. less, more
10. During silver plating rod of pure …………. is used as anode.
Ans. silver
State whether true or false
1. During extraction of aluminium from bauxite, graphite is used as anode and gas carbon is used as cathode.
Ans. True
2. During electroplating of an object by nickel, the electrolyte used is NiCl2 solution.
Ans. False
3. In case of electrorefining, a rod of impure metal is taken as anode while a rod of pure metal is taken as cathode.
Ans. True
4 Less reactive metals are generally extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction.
Ans. False
5. Ag, Au, Pt etc, metals can be found in anode mud.
Ans. True
6. Coating of more reactive metal is done on less reactive metal by electroplating.
Ans. False
7. The substance on which electroplating is to be done is used as cathode.
Ans. True
8. Gold plate is used as cathode for electroplating silver jewellery by gold.
Ans. False